Relationships among Sleep Time, Physical Activity Time, Screen Time, and Nutrition Literacy of Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study in Chongqing, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample
2.2. Outcome Variable: NL Score
2.3. Exposure Variable: Health Behavior
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Description
3.2. Association between Health Behavior and NL
3.3. Subgroup Analyses of the Association between Health Behavior and NL
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peng, J.; Yin, L.; Wang, K.; Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Luo, J. A Study on the Relationship between Adolescent Health Behavior, BMI, and Blood Physical and Chemical Properties. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 766101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, J.; Hill, C.M.; Harvey, N.C.; Crozier, S.; Robinson, S.M.; Godfrey, K.M.; Cooper, C.; Inskip, H. Duration of Sleep at 3 Years of Age Is Associated with Fat and Fat-Free Mass at 4 Years of Age: The Southampton Women’s Survey. J. Sleep Res. 2016, 25, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddle, S.J.H.; Bengoechea García, E.; Pedisic, Z.; Bennie, J.; Vergeer, I.; Wiesner, G. Screen Time, Other Sedentary Behaviours, and Obesity Risk in Adults: A Review of Reviews. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2017, 6, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.M.S.; Mendes, C.G.; Marques Miranda, D.; Romano-Silva, M.A. The Association between Screen Time and Attention in Children: A Systematic Review. Dev. Neuropsychol. 2022, 47, 175–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, J.M.; Iyer, P.; Chu, J.; Baker, F.C.; Pettee Gabriel, K.; Garber, A.K.; Murray, S.B.; Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Ganson, K.T. Contemporary Screen Time Modalities among Children 9–10 Years Old and Binge-Eating Disorder at One-Year Follow-Up: A Prospective Cohort Study. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 54, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartley, S.; Royant-Parola, S.; Zayoud, A.; Gremy, I.; Matulonga, B. Do Both Timing and Duration of Screen Use Affect Sleep Patterns in Adolescents? PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0276226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthold, R.; Stevens, G.A.; Riley, L.M.; Bull, F.C. Global Trends in Insufficient Physical Activity among Adolescents: A Pooled Analysis of 298 Population-Based Surveys with 1·6 Million Participants. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2020, 4, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Sluijs, E.M.F.; Ekelund, U.; Crochemore-Silva, I.; Guthold, R.; Ha, A.; Lubans, D.; Oyeyemi, A.L.; Ding, D.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Physical Activity Behaviours in Adolescence: Current Evidence and Opportunities for Intervention. Lancet 2021, 398, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfonsi, V.; Scarpelli, S.; D’Atri, A.; Stella, G.; De Gennaro, L. Later School Start Time: The Impact of Sleep on Academic Performance and Health in the Adolescent Population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.-H.; Yee, J.-Y.; Pyo, J.-S. Impact of Short Sleep Duration on the Incidence of Obesity and Overweight among Children and Adolescents. Medicina 2022, 58, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, L.; Beets, M.W.; Brazendale, K.; Moore, J.B.; Weaver, R.G. Exercise Dose and Weight Loss in Adolescents with Overweight–Obesity: A Meta-Regression. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauby-Secretan, B.; Scoccianti, C.; Loomis, D.; Grosse, Y.; Bianchini, F.; Straif, K. Body Fatness and Cancer—Viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendor, C.D.; Bardugo, A.; Pinhas-Hamiel, O.; Afek, A.; Twig, G. Cardiovascular Morbidity, Diabetes and Cancer Risk among Children and Adolescents with Severe Obesity. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2020, 19, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michou, M.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Costarelli, V. Low Health Literacy and Excess Body Weight: A Systematic Review. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2018, 26, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garad, R.; McPhee, C.; Chai, T.L.; Moran, L.; O’Reilly, S.; Lim, S. The Role of Health Literacy in Postpartum Weight, Diet, and Physical Activity. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, S.-F.; Liu, C.-H.; Liao, L.-L.; Osborne, R.H. Health Literacy and the Determinants of Obesity: A Population-Based Survey of Sixth Grade School Children in Taiwan. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doustmohammadian, A.; Omidvar, N.; Keshavarz-Mohammadi, N.; Abdollahi, M.; Amini, M.; Eini-Zinab, H. Developing and Validating a Scale to Measure Food and Nutrition Literacy (FNLIT) in Elementary School Children in Iran. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vettori, V.; Lorini, C.; Milani, C.; Bonaccorsi, G. Towards the Implementation of a Conceptual Framework of Food and Nutrition Literacy: Providing Healthy Eating for the Population. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleary, S.A.; Joseph, P.; Pappagianopoulos, J.E. Adolescent Health Literacy and Health Behaviors: A Systematic Review. J. Adolesc. 2018, 62, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, A.L.; Porter, K.J.; You, W.; Kirkpatrick, B.M.; Yuhas, M.; Vaught, S.S.; Zoellner, J.M. Low Health Literacy Is Associated with Energy-Balance-Related Behaviors, Quality of Life, and BMI Among Rural Appalachian Middle School Students: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Sch. Health 2021, 91, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koca, B.; Arkan, G. The Relationship between Adolescents’ Nutrition Literacy and Food Habits, and Affecting Factors. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambalis, K.D.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Psarra, G.; Sidossis, L.S. Screen Time and Its Effect on Dietary Habits and Lifestyle among Schoolchildren. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2020, 28, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.L.; Lumeng, J.C.; LeBourgeois, M.K. Sleep Patterns and Obesity in Childhood. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2015, 22, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Hou, M. Association between Food Preferences, Eating Behaviors and Socio-Demographic Factors, Physical Activity among Children and Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joulaei, H.; Keshani, P.; Kaveh, M.H. Nutrition Literacy as a Determinant for Diet Quality amongst Young Adolescents: A Cross Sectional Study. Prog. Nutr. 2018, 20, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Xian, J.; Xie, C.; Liu, Y.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, Y. The Evaluation Index System of Nutritional Literacy of Middle School Students in Chongqing Was Constructed Based on Delphi Method and Analytic Hierarchy Process. Health Med. Res. Pract. 2021, 18, 7–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zeng, M.; Xie, C.; Zhu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Sharma, M.; Zhao, Y. Development of Nutrition Literacy Scale for Middle School Students in Chongqing, China: A Cross-Sectional Study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 888137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Lancet. Social Media, Screen Time, and Young People’s Mental Health. Lancet 2019, 393, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Chinese Nutrition Society. The Chinese School-Age Children Dietary Guidelines (2016); People’s Medical Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, T.J. Establishing a Standard Definition for Child Overweight and Obesity Worldwide: International Survey. BMJ 2000, 320, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, B.; He, G.; Jia, Y. Association between Mobile Phone Addiction Index and Sugar-Sweetened Food Intake in Medical College Students Stratified by Sex from Shanghai, China. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, H.D.; Ellerbeck, E.F.; Befort, C.; Gajewski, B.; Kennett, A.R.; Yu, Q.; Christifano, D.; Sullivan, D.K. Measuring Nutrition Literacy in Breast Cancer Patients: Development of a Novel Instrument. J. Cancer Educ. 2016, 31, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalkan, I. The Impact of Nutrition Literacy on the Food Habits among Young Adults in Turkey. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2019, 13, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanpher, M.G.; Askew, S.; Bennett, G.G. Health Literacy and Weight Change in a Digital Health Intervention for Women: A Randomized Controlled Trial in Primary Care Practice. J. Health Commun. 2016, 21, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.-R.; Moser, D.K.; DeWalt, D.A.; Rayens, M.K.; Dracup, K. Health Literacy Mediates the Relationship between Age and Health Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2016, 9, e002250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michou, M.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Lionis, C.; Costarelli, V. Socioeconomic Inequalities in Relation to Health and Nutrition Literacy in Greece. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 70, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, E.W.; Austin, B.W.; French, B.F.; Cohen, M.A. The Effects of a Nutrition Media Literacy Intervention on Parents’ and Youths’ Communication about Food. J. Health Commun. 2018, 23, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Latif, M.M.M.; Saad, S.Y. Health Literacy among Saudi Population: A Cross-Sectional Study. Health Promot. Int. 2019, 34, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natour, N.; AL-Tell, M.; Ikhdour, O. Nutrition Literacy Is Associated with Income and Place of Residence but Not with Diet Behavior and Food Security in the Palestinian Society. BMC Nutr. 2021, 7, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, S.; Itani, L. Nutrition Literacy among Adolescents and Its Association with Eating Habits and BMI in Tripoli, Lebanon. Diseases 2021, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.K.; Sullivan, D.K.; Ellerbeck, E.F.; Gajewski, B.J.; Gibbs, H.D. Nutrition Literacy Predicts Adherence to Healthy/Unhealthy Diet Patterns in Adults with a Nutrition-Related Chronic Condition. Public Health Nutr. 2019, 22, 2157–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, B.; Mei, Y.; Ping, Z.; Zhang, Z. The Urban-Rural Disparity in the Status and Risk Factors of Health Literacy: A Cross-Sectional Survey in Central China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronto, R.; Ball, L.; Pendergast, D.; Harris, N. Adolescents’ Perspectives on Food Literacy and Its Impact on Their Dietary Behaviours. Appetite 2016, 107, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, R. Childhood Obesity in China: Does Grandparents’ Coresidence Matter? Econ. Hum. Biol. 2018, 29, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.; Seabrook, J.A.; Stranges, S.; Clark, A.F.; Haines, J.; O’Connor, C.; Doherty, S.; Gilliland, J.A. Examining the Correlates of Adolescent Food and Nutrition Knowledge. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Buhr, E.; Tannen, A. Parental Health Literacy and Health Knowledge, Behaviours and Outcomes in Children: A Cross-Sectional Survey. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferranti, R.; Marventano, S.; Castellano, S.; Giogianni, G.; Nolfo, F.; Rametta, S.; Matalone, M.; Mistretta, A. Sleep Quality and Duration Is Related with Diet and Obesity in Young Adolescent Living in Sicily, Southern Italy. Sleep Sci. 2016, 9, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barragán, R.; Zuraikat, F.M.; Tam, V.; Scaccia, S.; Cochran, J.; Li, S.; Cheng, B.; St-Onge, M.-P. Actigraphy-Derived Sleep Is Associated with Eating Behavior Characteristics. Nutrients 2021, 13, 852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcez, M.R.; de Castro, M.A.; César, C.L.G.; Goldbaum, M.; Fisberg, R.M. A Chrononutrition Perspective of Diet Quality and Eating Behaviors of Brazilian Adolescents in Associated with Sleep Duration. Chronobiol. Int. 2021, 38, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.-L.; Zhang, C.-G.; Cui, Z.-Y.; Wang, J.-Y.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.-W.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.-M. The Impact of Social Capital on Physical Activity and Nutrition in China: The Mediating Effect of Health Literacy. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egg, S.; Wakolbinger, M.; Reisser, A.; Schätzer, M.; Wild, B.; Rust, P. Relationship between Nutrition Knowledge, Education and Other Determinants of Food Intake and Lifestyle Habits among Adolescents from Urban and Rural Secondary Schools in Tyrol, Western Austria. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 3136–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz-Alkaya, S.; Kulakçı-Altıntaş, H. Nutrition-Exercise Behaviors, Health Literacy Level, and Related Factors in Adolescents in Turkey. J. Sch. Health 2021, 91, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rademakers, J.; Hahnraths, M.T.H.; van Schayck, O.C.P.; Heijmans, M. Children’s Health Literacy in Relation to Their BMI z-Score, Food Intake, and Physical Activity: A Cross-Sectional Study among 8–11-Year-Old Children in The Netherlands. Children 2022, 9, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayer, Ç.; Ergin, A. Status of Nutritional Literacy in Adolescents in the Semi-Rural Area in Turkey and Related Factors. Public Health Nutr. 2021, 24, 3870–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassi, T.; Bagordo, F.; Panico, A.; De Giorgi, M.; Idolo, A.; Serio, F.; Tumolo, M.R.; De Donno, A. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet of Children Living in Small Southern Italian Villages. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 71, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, K.; Mu, M.; Liu, K.; He, Y. Screen Time and Childhood Overweight/Obesity: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Child. Care Health Dev. 2019, 45, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godsell, S.; White, J. Adolescent Perceptions of Sleep and Influences on Sleep Behaviour: A Qualitative Study. J. Adolesc. 2019, 73, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moitra, P.; Madan, J.; Verma, P. Independent and Combined Influences of Physical Activity, Screen Time, and Sleep Quality on Adiposity Indicators in Indian Adolescents. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunderson, J.; McDaniel, K.; DiBlanda, A. Association between Insufficient Sleep, Depressive Symptoms, and Suicidality Among Florida High School Students. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2023, 20, 220403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delisle Nyström, C.; Carlander, A.; Cassel, S.; Rosell, M.; J-Son Höök, M.; Löf, M. Physical Activity and Screen Time in Swedish Children and Adolescents: The Generation Pep Study 2018–2021. Acta Paediatr. 2023, 112, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conger, S.A.; Toth, L.P.; Cretsinger, C.; Raustorp, A.; Mitáš, J.; Inoue, S.; Bassett, D.R. Time Trends in Physical Activity Using Wearable Devices: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Studies from 1995 to 2017. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2022, 54, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Bi, C.; Lin, H.; Ma, W.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Liu, J.-Z. Compared with Dietary Behavior and Physical Activity Risk, Sedentary Behavior Risk Is an Important Factor in Overweight and Obesity: Evidence from a Study of Children and Adolescents Aged 13–18 Years in Xinjiang, China. BMC Pediatr. 2022, 22, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friel, C.P.; Duran, A.T.; Shechter, A.; Diaz, K.M. U.S. Children Meeting Physical Activity, Screen Time, and Sleep Guidelines. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2020, 59, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Buman, M.P.; Cardon, G.; Carty, C.; Chaput, J.-P.; Chastin, S.; Chou, R.; et al. World Health Organization 2020 Guidelines on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Ma, S.X.; Chen, C.; Liu, S.J.; Zhang, C.F.; Cao, Z.B.; Jiang, F. Physical Activity Guidelines for Chinese Children and Adolescents. Chin. J. Evid. Based Pediatr. 2017, 12, 401–409. [Google Scholar]
- Notice of the General Office of the Ministry of Education on Further Strengthening the Sleep Management of Primary and Secondary School Students. General Office of the Ministry of Education PRC; 30 March 2021. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-04/02/content_5597443.htm (accessed on 7 April 2024).
- Guidelines for Preventing and Controlling Myopia in Children and Adolescents During Home Quarantine of infectious Disease Epidemic. National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. 28 July 2020. Available online: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/pqt/202008/8d379707d0ff4315912f0ac444c8b0bc.shtml (accessed on 7 April 2024).
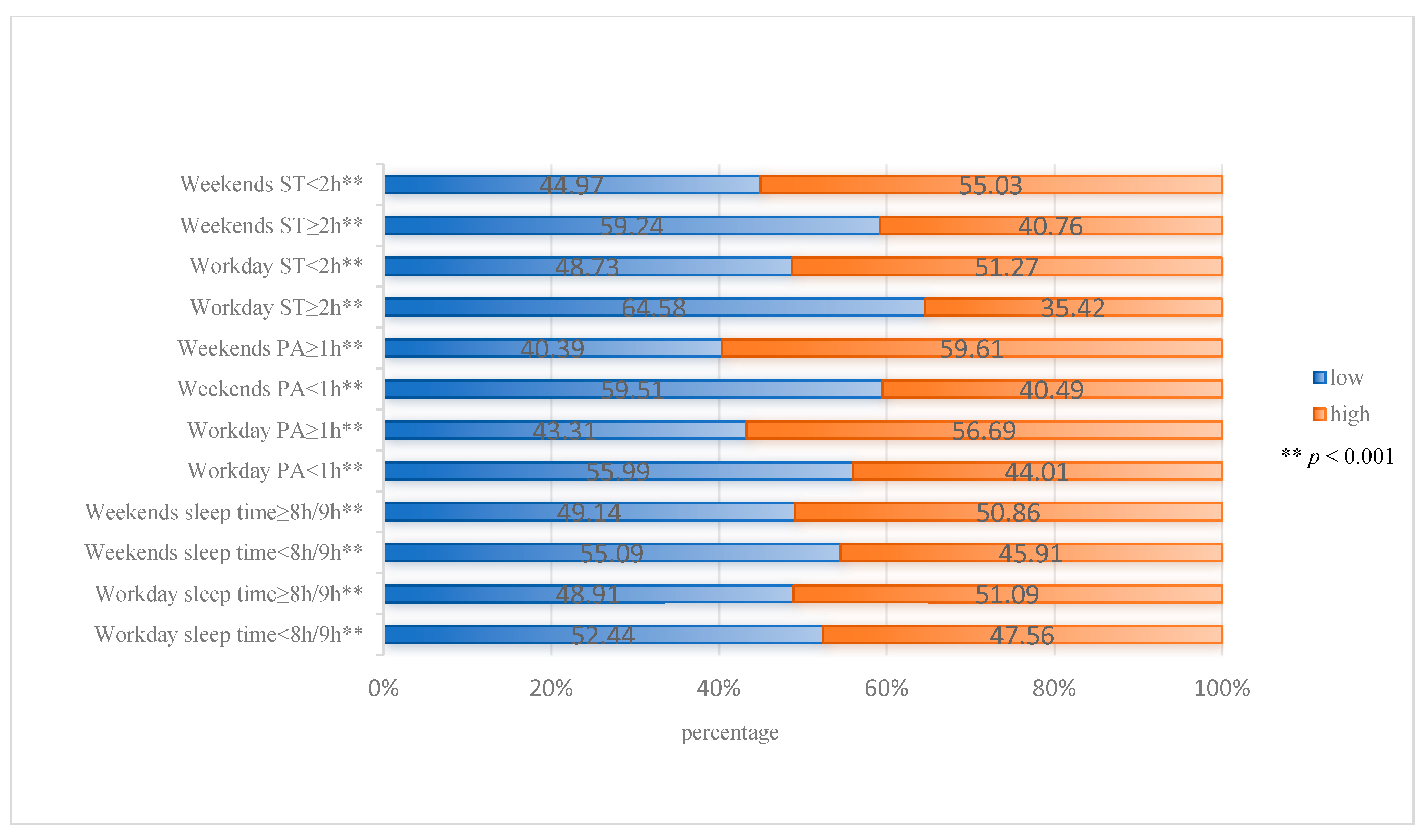
| Variables | All | NL | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | Low (n = 9688) | High (n = 8972) | ||
| Age (mean, SD) | 14.3 (1.8) | 14.6 (1.8) | 13.9(1.7) | <0.001 |
| Gender | 0.074 | |||
| Male | 9359 (50.16) | 4920 (52.57) | 4439 (47.43) | |
| Female | 9301 (49.84) | 4768 (51.26) | 4533 (48.74) | |
| Grade | <0.001 | |||
| Junior high school | 10,670 (57.18) | 4615 (43.25) | 6055 (56.75) | |
| High school | 7990 (42.82) | 5073 (63.49) | 2917 (36.51) | |
| Ethnicity | <0.001 | |||
| Han | 16,581 (88.86) | 8272 (49.89) | 8309 (50.11) | |
| Minority | 2079 (11.14) | 1416 (68.11) | 663 (31.89) | |
| BMI | <0.001 | |||
| Normal | 10,579 (56.69) | 5327 (55.35) | 5252 (49.65) | |
| Underweight | 2986 (16.00) | 1599 (53.55) | 1387 (46.45) | |
| Overweight-obesity | 5095 (27.31) | 2762 (54.21) | 2333 (45.79) | |
| Boarding school | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 12,183 (65.29) | 6886 (56.52) | 5297 (43.48) | |
| No | 6477 (34.71) | 2802 (43.26) | 3675 (56.74) | |
| Residence | <0.001 | |||
| Urban | 9062 (48.56) | 4219 (46.56) | 4843 (53.44) | |
| Rural | 9598 (51.44) | 5469 (56.98) | 4129 (43.02) | |
| Siblings | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 14,782 (79.22) | 7879 (53.30) | 6903 (46.70) | |
| No | 3878 (20.78) | 1809 (46.65) | 2069 (53.35) | |
| Caregiver model | <0.001 | |||
| Only parents | 13,313 (71.35) | 6766 (50.82) | 6547 (49.18) | |
| Others | 5347 (28.65) | 2922 (54.65) | 2425 (45.35) | |
| Father’s education | <0.001 | |||
| Primary school and below | 4176 (22.38) | 2519 (60.32) | 1657 (39.68) | |
| Junior high school | 9539 (51.12) | 4978 (52.19) | 4561 (47.81) | |
| High school a | 3264 (17.49) | 1479 (45.31) | 1785 (54.89) | |
| Bachelor’s degree or above | 1681 (9.01) | 712 (42.36) | 969 (57.64) | |
| Mother’s education | <0.001 | |||
| Primary school and below | 5852 (31.36) | 3566 (60.94) | 2286 (39.06) | |
| Junior high school | 8555 (45.85) | 4295 (50.20) | 4260 (49.80) | |
| High school a | 2865 (15.35) | 1267 (44.22) | 1598 (55.78) | |
| Bachelor’s degree or above | 1388 (7.4) | 560 (40.35) | 828 (59.65) | |
| Variables | Model 1 | Model 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Workday | Sleep time (≥8 h/9 h) | 1.15 (1.06, 1.25) * | 1.46 (1.34, 1.59) ** |
| PA time (≥1 h) | 1.67 (1.57, 1.77) ** | 1.69 (1.58, 1.80) ** | |
| ST (<2 h) | 1.92 (1.78, 2.07) ** | 1.56 (1.45, 1.69) ** | |
| Weekends | Sleep time (≥8 h/9 h) | 1.22 (1.15, 1.29) ** | 1.44 (1.35, 1.53) ** |
| PA time (≥1 h) | 2.17 (2.04, 2.30) ** | 2.10 (1.98, 2.24) ** | |
| ST (<2 h) | 1.78 (1.68, 1.88) ** | 1.66 (1.57, 1.77) ** | |
| Workdays | Weekends | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | Sleep Time (≥8 h/9 h) | p a | PA Time (≥1 h) | p a | ST (<2 h) | p a | Sleep Time (≥8 h/9 h) | p a | PA Time (≥1 h) | p a | ST (<2 h) | p a |
| Gender | 0.961 | 0.769 | 0.551 | 0.049 | 0.614 | 0.034 | ||||||
| Male | 1.48 (1.32–1.66) ** | 1.71 (1.56–1.87) ** | 1.53 (1.37–1.70) ** | 1.55 (1.42–1.69) ** | 2.09 (1.92–2.28) ** | 1.61 (1.48–1.75) ** | ||||||
| Female | 1.45 (1.28–1.65) ** | 1.67 (1.52–1.84) ** | 1.60 (1.43–1.79) ** | 1.35 (1.24–1.47) ** | 2.13 (1.95–2.33) ** | 1.74 (1.60–1.90 **) | ||||||
| Grade | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.908 | 0.430 | 0.000 | 0.000 | ||||||
| Junior high school | 1.73 (1.52–1.97) ** | 1.89 (1.74–2.06) ** | 1.55 (1.38–1.73) ** | 1.41 (1.30–1.53) ** | 2.37 (2.19–2.57) ** | 1.94 (1.79–2.09) ** | ||||||
| High school | 1.28 (1.14–1.44) ** | 1.43 (1.29–1.59) ** | 1.57 (1.41–1.74) ** | 1.48 (1.35–1.62) ** | 1.78 (1.61–1.96) ** | 1.36 (1.24–1.50) ** | ||||||
| BMI | 0.195 | 0.653 | 0.926 | 0.280 | 0.108 | 0.333 | ||||||
| Normal | 1.45 (1.30–1.63) ** | 1.67 (1.53–1.82) ** | 1.58 (1.43–1.76) ** | 1.39 (1.29–1.51) ** | 2.19 (2.01–2.37) ** | 1.64 (1.51–1.77) ** | ||||||
| Underweight | 1.31 (1.05–1.63) * | 1.77 (1.50–2.08) ** | 1.58 (1.30–1.91) ** | 1.43 (1.23–1.67) ** | 2.18 (1.87–2.55) ** | 1.81 (1.55–2.11) ** | ||||||
| Overweight | 1.58 (1.34–1.85) ** | 1.68 (149–1.91) ** | 1.51 (1.30–1.75) ** | 1.55 (1.37–1.74) ** | 1.91 (1.70–2.15) ** | 1.64 (1.46–1.84) ** | ||||||
| Ethnicity | 0.483 | 0.373 | 0.088 | 0.009 | 0.044 | 0.000 | ||||||
| Han | 1.45 (1.32–1.59) ** | 1.70 (1.59–1.82) ** | 1.60 (1.47–1.73) ** | 1.40 (1.32–1.50) ** | 2.15 (2.02–2.30) ** | 1.72 (1.61–1.83) ** | ||||||
| Minority | 1.51 (1.21–1.88) ** | 1.62 (1.33–1.97) ** | 1.32 (1.06–1.64) * | 1.79 (1.48–2.18) ** | 1.73 (1.42–2.10) ** | 1.28 (1.06–1.55) * | ||||||
| Boarding school | 0.006 | 0.009 | 0.006 | 0.452 | 0.000 | 0.009 | ||||||
| Yes | 1.37 (1.24–1.51) ** | 1.93 (1.72–2.16) ** | 1.46 (1.33–1.59) ** | 1.47 (1.36–1.59) ** | 1.93 (1.79–2.09) ** | 1.57 (1.46–1.70) ** | ||||||
| No | 1.81 (1.52–2.15) ** | 1.58 (1.46–1.71) ** | 1.84 (1.59–2.14) ** | 1.39 (1.25–1.54) ** | 2.47 (2.22–2.74) ** | 1.86 (1.68–2.05) ** | ||||||
| Residence | 0.161 | 0.667 | 0.167 | 0.802 | 0.493 | 0.007 | ||||||
| Urban | 1.56 (1.36–1.78) ** | 1.72 (1.56–1.89) ** | 1.66 (1.48–1.86) ** | 1.46 (1.34–1.59) ** | 2.18 (1.99–2.38) ** | 1.81 (1.66–1.97) ** | ||||||
| Rural | 1.42 (1.27–1.59) ** | 1.66 (1.52–1.81) ** | 1.46 (1.33–1.63) ** | 1.42 (1.31–1.55) ** | 2.04 (1.87–2.22) ** | 1.54 (1.41–1.67) ** | ||||||
| Siblings | 0.050 | 0.083 | 0.904 | 0.923 | 0.047 | 0.950 | ||||||
| Yes | 1.42 (1.29–1.55) ** | 1.65 (1.53–1.77) ** | 1.56 (1.43–1.70) ** | 1.44 (1.34–1.54) ** | 2.04 (1.90–2.19) ** | 1.66 (1.55–1.77) ** | ||||||
| No | 1.76 (1.42–2.18) ** | 1.86 (1.61–2.15) ** | 1.55 (1.30–1.86) ** | 1.44 (1.26–1.65) ** | 2.37 (2.06–2.73) ** | 1.67 (1.46–1.90) ** | ||||||
| Caregiver model | 0.282 | 0.995 | 0.793 | 0.015 | 0.663 | 0.042 | ||||||
| Only parents | 1.42 (1.28–1.58) ** | 1.69 (1.50–1.91) ** | 1.57 (1.43–1.72) ** | 1.52 (1.41–1.63) ** | 2.14 (1.98–2.30) ** | 1.61 (1.50–1.73) ** | ||||||
| Others | 1.56 (1.34–1.82) ** | 1.68 (1.56–1.82) ** | 1.55 (1.34–1.78) ** | 1.27 (1.13–1.42) ** | 2.04 (1.98–2.30) ** | 1.82 (1.62–2.03) ** | ||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Q.; Hu, Z.; Zeng, M.; Su, Y.; Jiang, K.; Li, S.; Li, Z.; Fu, L.; Shi, Z.; Sharma, M.; et al. Relationships among Sleep Time, Physical Activity Time, Screen Time, and Nutrition Literacy of Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study in Chongqing, China. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091314
Xu Q, Hu Z, Zeng M, Su Y, Jiang K, Li S, Li Z, Fu L, Shi Z, Sharma M, et al. Relationships among Sleep Time, Physical Activity Time, Screen Time, and Nutrition Literacy of Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study in Chongqing, China. Nutrients. 2024; 16(9):1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091314
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Qi, Zhichuan Hu, Mao Zeng, Yu Su, Ke Jiang, Shengping Li, Zhourong Li, Lin Fu, Zumin Shi, Manoj Sharma, and et al. 2024. "Relationships among Sleep Time, Physical Activity Time, Screen Time, and Nutrition Literacy of Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study in Chongqing, China" Nutrients 16, no. 9: 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091314
APA StyleXu, Q., Hu, Z., Zeng, M., Su, Y., Jiang, K., Li, S., Li, Z., Fu, L., Shi, Z., Sharma, M., & Zhao, Y. (2024). Relationships among Sleep Time, Physical Activity Time, Screen Time, and Nutrition Literacy of Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study in Chongqing, China. Nutrients, 16(9), 1314. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16091314








