The Relationship between Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratios with Nutritional Status, Risk of Nutritional Indices, Prognostic Nutritional Indices and Morbidity in Patients with Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
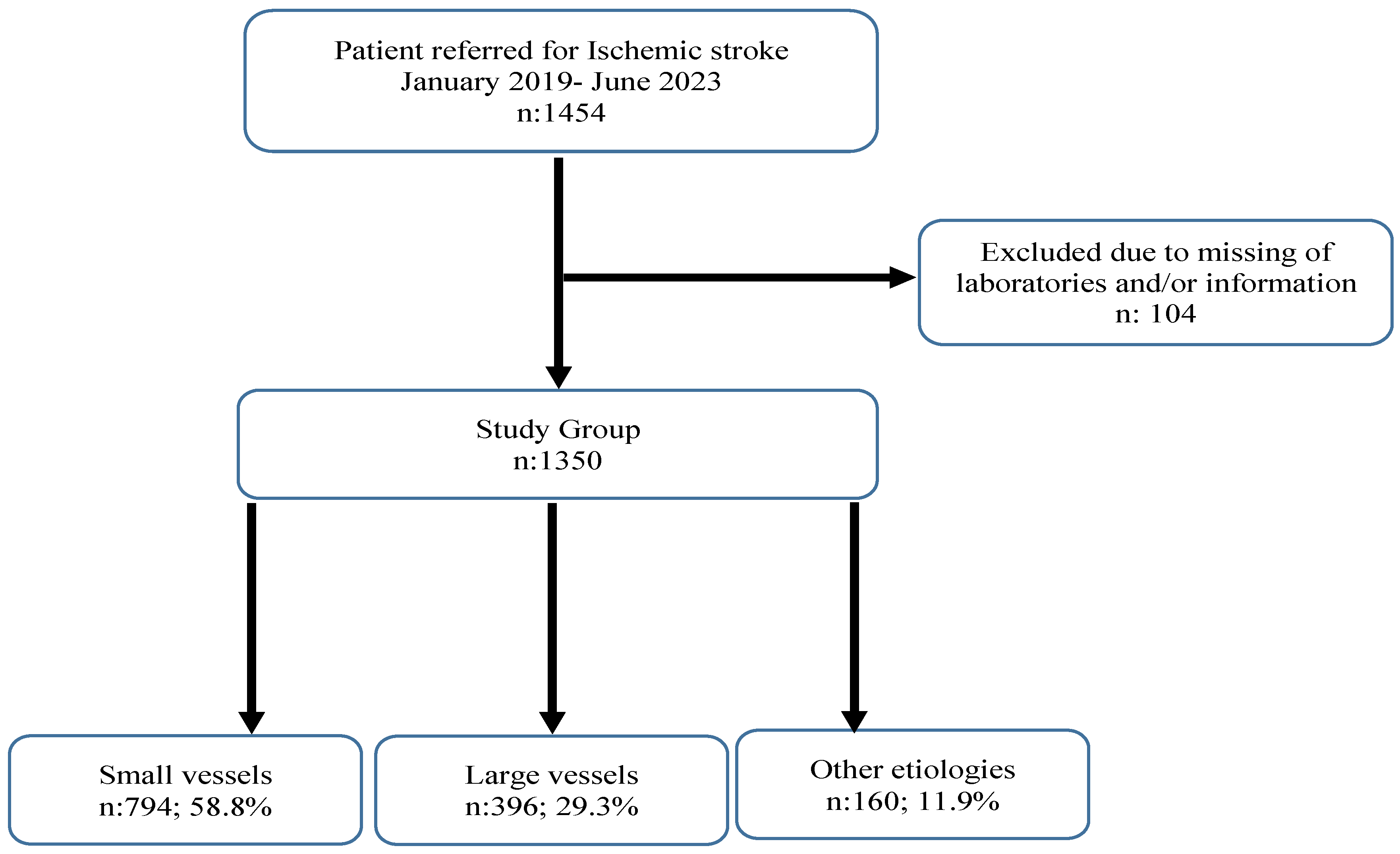
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
2.3. Exclusion Criteria
- Patients with arrest on presentation to the emergency department.
- Patients admitted after >24 h.
- Patients with hemorrhagic stroke.
- Patients with trauma-induced stroke.
- Patients with a history of intracranial mass.
- Patients with known hematologic disorders.
- Patients with a known history of thyroid disease.
- Patients with chronic renal failure, liver failure.
- Patients with concurrent acute coronary syndrome (ACS), pulmonary embolism (PE), or acute renal failure (AKF).
- Patients for whom adequate laboratory data are not available.
2.4. Laboratory Parameters
2.5. Nutritional Indices
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) Fact Sheets; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donnell, M.J.; Chin, S.L.; Rangarajan, S.; Xavier, D.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Rao-Melacini, P.; Zhang, X.; Pais, P.; Agapay, S.; et al. Global and regional effects of potentially modifiable risk factors associated with acute stroke in 32 countries (INTERSTROKE): A case-control study. Lancet 2016, 388, 761–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coupland, A.P.; Thapar, A.; Qureshi, M.I.; Jenkins, H.; Davies, A.H. The definition of stroke. J. R. Soc. Med. 2017, 110, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, E.J.; Virani, S.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Chiuve, S.E.; Cushman, M.; Delling, F.N.; Deo, R.; et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2018 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2018, 137, e67–e492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishioka, S.; Okamoto, T.; Takayama, M.; Urushihara, M.; Watanabe, M.; Kiriya, Y.; Shintani, K.; Nakagomi, H.; Kageyama, N. Malnutrition risk predicts recovery of full oral intake among older adult stroke undergoing enteral nutrition: Secondary analysis of a multicentre survey (the APPLE patients study). Clin. Nutr. 2016, 36, 1089–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzby, G.P.; Mullen, J.L.; Matthews, D.C.; Hobbs, C.L.; Rosato, E.F. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery. Am. J. Surg. 1980, 139, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignacio de Ulibarri, J.; González-Madroño, A.; de Villar, N.G.P.; González, P.; González, B.; Mancha, A.; Rodriguez, F.; Fernández, G. CONUT: A tool for controlling nutritional status. First validation in a hospital population. Nutr. Hosp. 2005, 20, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Vo, T.P.; Kristiansen, M.H.; Hasselbalch, H.C.; Wienecke, T. Elevated white blood cell counts in ischemic stroke patients are associated with increased mortality and new vascular events. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1232557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yue, X.; Jia, M.; Wang, J. Neuroinflammation and anti-inflammatory therapy for ischemic stroke. Heliyon 2023, 9, e17986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, J.; He, J.; Deng, Y.; Zhu, D.-S.; Guan, Y.-T. Circulating Leukocyte as an Inflammatory Biomarker: Association with Fibrinogen and Neuronal Damage in Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Inflamm. Res. 2023, 16, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, P.H.; Cuthbertson, B.H.; Croal, B.L.; Rae, D.; El-Shafei, H.; Gibson, G.; Jeffrey, R.R.; Buchan, K.G.; Hillis, G.S. Usefulness of neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio as predictor of new-onset atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass grafting. Am. J. Cardiol. 2010, 105, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahorec, R. Ratio of neutrophil to lymphocyte counts-rapid and simple parameter of systemic inflammation and stress in critically ill. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2001, 102, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Celikbilek, A.; Ismailogullari, S.; Zararsiz, G. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio predicts poor prognosis in ischemic cerebrovascular disease. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2014, 28, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhan, S.; Ozhasenekler, A.; Mansur Durgun, H.; Akil, E.; Ustundag, M.; Orak, M. Neutrophil lymphocyte ratios in stroke subtypes and transient ischemic attack. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tokgoz, S.; Keskin, S.; Kayrak, M.; Seyithanoglu, A.; Ogmegul, A. Is neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio predict to short-term mortality in acute cerebral infarct independently from infarct volume? J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. 2014, 23, 2163–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.P., Jr.; Bendixen, B.H.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biller, J.; Love, B.B.; Gordon, D.L.; Marsh, E.E., 3rd. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 1993, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.M.; Lee, Y.S.; Bae, H.J.; Kang, D.W. Homocysteine as a predictor of early neurological deterioration in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 2014, 45, 871–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Yang, X.R.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.F.; Sun, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.-M.; Qiu, S.-J.; Zhou, J.; et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index predicts prognosis of patients after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6212–6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onodera, T.; Goseki, N.; Kosaki, G. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery of malnourished cancer patients. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi 1984, 85, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa, H.; Yoh, K.; Enomoto, H.; Ishii, N.; Iwata, Y.; Takata, R.; Nishimura, T.; Aizawa, N.; Sakai, Y.; Ikeda, N.; et al. The Relationship between Controlling Nutritional (CONUT) Score and Clinical Markers among Adults with Hepatitis C Virus Related Liver Cirrhosis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseki, Y.; Shibutani, M.; Maeda, K.; Nagahara, H.; Ohtani, H.; Sugano, K.; Ikeya, T.; Muguruma, K.; Tanaka, H.; Toyokawa, T.; et al. Impact of the Preoperative Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score on the Survival after Curative Surgery for Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; You, J.; Cui, H.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, Q.; Yuan, L. The Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index Predicts Survival in Elderly Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients with Radiotherapy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najjar, Y.; Clark, A.L. Predicting Outcome in Patients With Left Ventricular Systolic Chronic Heart Failure Using a Nutritional Risk Index. Am. J. Cardiol. 2012, 109, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velez, L.; Toffel, S.; Trejo-Lopez, J.; Kresak, J.L.; Beal, S.G. Educational Case: Etiologies, Mechanisms, and Treatment of Stroke. Acad. Pathol. 2020, 7, 2374289520901817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank-Stein, N.; Mass, E. Macrophage and monocyte subsets in response to ischemic stroke. Eur. J. Immunol. 2023, 53, e2250233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestrini, I.; Tagzirt, M.; Gautier, S.; Dupont, A.; Mendyk, A.M.; Susen, S.; Tailleux, A.; Vallez, E.; Staels, B.; Cordonnier, C.; et al. Analysis of the association of MPO and MMP-9 with stroke severity and outcome: Cohort study. Neurology 2020, 95, e97–e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agard, T.A.; Hass, R.; Cavrak, M.E.; Foual, N.S.; Byrum, C.; Adcock, A.K.; Gehan, D.; Petrone, A.B. Neutrophil lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and systemic immune inflammatory index (SII) for the differential diagnosis of CT-negative mild acute ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack. Int. J. Neurosci. 2023, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Andjelkovic, A.V.; Zhu, L.; Yang, T.; Bennett, M.V.L.; Chen, J.; Keep, R.F.; Shi, Y. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction and recovery after ischemic stroke. Prog. Neurobiol. 2018, 163–164, 144–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraj, R.L.; Azimullah, S.; Beiram, R.; Jalal, F.Y.; Rosenberg, G.A. Neuroinflammation: Friend and foe for ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, K.; Zhu, S.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, P.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, W.; Sun, W.; et al. Association between malnutrition and long-term mortality in older adults with ischemic stroke. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 2535–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposeiras Roubín, S.; Abu Assi, E.; Cespón Fernandez, M.; Pardal, C.B.; Castro, A.L.; Parada, J.A.; Pérez, D.D.; Prieto, S.B.; Rossello, X.; Ibanez, B.; et al. Prevalence and Prognostic Significance of Malnutrition in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakmak, E.Ö.; Öcal, L.; Erdoğan, E.; Cerşit, S.; Efe, S.Ç.; Karagöz, A.; Yılmaz, F.; Fidan, S.; Alizade, E.; Zehir, R.; et al. Prognostic Value of 3 Nutritional Screening Tools to Predict 30-Day Outcome in Patients Undergoing Carotid Artery Stenting. Angiology 2022, 73, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Cai, J.; Li, Y.; Rong, X.; Li, Y.; He, L.; Li, H.; Liang, Y.; Huang, H.; Xu, Y.; et al. Baseline Objective Malnutritional Indices as Immune-Nutritional Predictors of Long-Term Recurrence in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Vincenzo, O.; Pagano, E.; Cervone, M.; Natale, R.; Morena, A.; Esposito, A.; Pasanisi, F.; Scalfi, L. High Nutritional Risk Is Associated with Poor Functional Status and Prognostic Biomarkers in Stroke Patients at Admission to a Rehabilitation Unit. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheri, C.F.; Scalfi, L.; Biffi, B.; Pancani, S.; Madiai, S.; Di Vincenzo, O.; Ghaderi, M.; Celoni, R.; Dalladonna, M.; Draghi, F.; et al. Relationship between Nutritional Risk, Clinical and Demographic Characteristics, and Pressure Ulcers in Patients with Severe Acquired Brain Injuries Attending a Rehabilitative Program. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| CONUT Score | Level of Malnutrition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Mild | Moderate | Severe | |
| Serum Albumin (g/dL) | ≥3.5 | 3–3.4 | 2.5–2.9 | <2.5 |
| Score | (0) | (2) | (4) | |
| Total Lymphocytes (×109/L) | ≥1600 | 1200–1599 | 800–1199 | <800 |
| Score | (0) | (1) | (2) | (3) |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | ≥180 | 140–179 | 100–139 | <100 |
| Score | (0) | (1) | (2) | (3) |
| Total Score | (0–1) | (2–4) | (5–8) | (9–12) |
| All Groups | Small Vessels (n: 794; 58.8%) | Large Vessels (n: 396; 29.3%) | Other Etiologies (n: 160; 11.9%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | n (%) | p Value |
| Male | 710 (52.60%) | 413 (52.00%) a | 155 (39.10%) b | 142 (88.80%) c | <0.001 |
| Female | 640 (47.40%) | 381 (48.00%) | 241 (60.90%) | 18 (11.30%) | |
| Hypertension | 1046 (77.50%) | 630 (79.30%) | 293 (74.00%) | 123 (76.90%) | 0.112 |
| Diabetes | 649 (48.10%) | 399 (50.30%) a | 168 (42.40%) b | 82 (51.30%) a,b | 0.027 |
| Dyslipidemia | 1101 (81.60%) | 667 (84.00%) a | 309 (78.00%) b | 125 (78.10%) a,b | 0.021 |
| Smoking | 784 (58.10%) | 457 (57.60%) a | 201 (50.80%) a | 126 (78.80%) b | <0.001 |
| Alcoholism | 353 (26.10%) | 202 (25.40%) a | 82 (20.70%) a | 69 (43.10%) b | <0.001 |
| Mortality | 431 (31.90%) | 157 (19.80%) a | 242 (61.10%) b | 32 (20.00%) a | <0.001 |
| All Groups | Small Vessels | Large Vessels | Other Etiologies | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean ± Std or Median (25p–75p) | Mean ± Std or Median (25p–75p) | Mean ± Std or Median (25p–75p) | Mean ± Std or Median (25p–75p) | p Value | |
| Age (years) | 64.38 ± 16.43 | 64.80 ± 16.59 | 64.30 ± 16.65 | 62.54 ± 14.96 | 0.280 |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) (kg/m2) | 28.30 ± 5.26 | 27.23 ± 4.97 b | 31.01 ± 4.33 a | 26.94 ± 6.24 b | <0.001 |
| Temperature (°C) | 36.99 ± 0.46 | 37.0 ± 0.46 | 36.99 ± 0.44 | 36.94 ± 0.45 | 0.397 |
| Systolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 153 (143–163) | 153 (141–157) a | 154 (144–164) b | 154 (144–163) a,b | 0.005 |
| Diastolic Blood Pressure (mmHg) | 85 (79–88) | 84 (79–88) a | 85 (80–89) b | 85 (79–88) a,b | 0.003 |
| NIHSS score | 7 (6–8) | 7 (5–8) | 7 (6–8) | 7 (6–8) | 0.160 |
| Lymphocytes (×109/L) | 1743.5 (1459–2074) | 1693.5 (1459–1973) a | 1667 (1348.5–1998) a | 4200 (2985–5370) b | <0.001 |
| Neutrophils (µL) | 7786 (6343–8212) | 7832.5 (7535–8194) a | 7871 (6330–8457) a | 4670 (3510–6900) b | <0.001 |
| Neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio (NLR) | 4.23 (2.96–5.16) | 4.46 (3.81–5.18) a | 4.63 (3.15–5.69) a | 1.27 (0.75–1.83) b | <0.001 |
| Systemic immune-inflammation index (SII) | 807.68 (506.32–1092.19) | 871.04 (650.62–1102.69) a | 898.17 (565.27–1165.79) a | 243.34 (142.97–367.66) b | <0.001 |
| White blood cell (103/µL) | 9.27 ± 2.03 | 9.29 ± 2.04 | 9.15 ± 1.99 | 9.53 ± 2.07 | 0.127 |
| Platelet (109/L) | 201.55 ± 47.81 | 201.38 ± 47.31 | 202.10 ± 49.05 | 201.05 ± 47.44 | 0.962 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 120 (102–145) | 120 (102–145) | 120 (100–145) | 120 (102–145) | 0.971 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 2.61 (2.55–2.7) | 2.62 (2.59–2.72) b | 2.6 (2.29–2.69) a | 2.61 (2.54–2.71) b | <0.001 |
| Prognostic nutritional index (PNI) | 37.71 ± 8.45 | 37.25 ± 7.23 a | 34.78 ± 8.16 b | 47.30 ± 8.06 c | <0.001 |
| Nutritional risk index (NRI) | 57.23 ± 9.53 | 55.33 ± 9.06 b | 62.02 ± 7.70 a | 54.78 ± 11.49 b | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | 159 (146–267) | 149 (140–156) a | 276 (194–527) b | 317.5 (278–395) a,b | <0.001 |
| C-reactive protein (CRP) mg/L | 66.42 (33.32–100.84) | 46.5 (18.97–82.84) a | 108.83 (66.42–247.63) b | 69.2 (42.09–99.83) c | <0.001 |
| CONUT | 5.23 ± 1.33 | 5.49 ± 1.20 a | 5.12 ± 1.46 b | 4.22 ± 1.11 c | <0.001 |
| Univariate | Backward (PNI Excluded) | Backward (CONUT Excluded) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p Value | OR (95% CI) | p Value | OR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Etiology (ref: Other etiology) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| Small Vessels | 0.986 (0.645–1.508) | 0.948 | 2.355 (1.428–3.885) | 0.001 | 3.664 (2.118–6.339) | <0.001 |
| Large vessels | 6.286 (4.061–9.73) | <0.001 | 24.076 (13.955–41.535) | <0.001 | 49.503 (26.526–92.383) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 1.159 (0.922–1.457) | 0.207 | 1.467 (1.120–1.921) | 0.005 | 1.517 (1.146–2.009) | 0.004 |
| Dyslipidemia | 1.643 (1.196–2.258) | 0.002 | 2.059 (1.414–2.996) | <0.001 | 1.753 (1.193–2.576) | 0.004 |
| Age (years) | 1.008 (1.001–1.015) | 0.024 | 1.010 (1.002–1.019) | 0.013 | 1.013 (1.004–1.021) | 0.004 |
| Diastolik Blood Preasure (mmHg) | 0.989 (0.976–1.002) | 0.088 | 0.980 (0.965–0.995) | 0.010 | 0.982 (0.966–0.998) | 0.024 |
| NIHSS score | 1.059 (0.985–1.138) | 0.121 | - | - | - | - |
| NLR | 0.846 (0.793–0.903) | <0.001 | 0.659 (0.602–0.722) | <0.001 | - | - |
| SII | 0.999 (0.999–1.000) | <0.001 | - | - | - | - |
| PNI | 1.057 (1.042–1.072) | <0.001 | - | - | 1.135 (1.110–1.160) | <0.001 |
| CONUT | 0.950 (0.872–1.035) | 0.244 | 1.170 (1.051–1.303) | 0.004 | - | - |
| All Group | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | SII | PNI | NRI | CONUT | |
| NLR | r | 0.826 * | −0.692 * | 0.034 * | 0.402 * |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.208 | <0.001 | |
| SII | r | −0.591 * | 0.039 * | 0.312 * | |
| p | <0.001 | 0.148 | <0.001 | ||
| PNI | r | −0.100 ¶ | −0.511 ¶ | ||
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| NRI | r | −0.022 ¶ | |||
| p | 0.418 | ||||
| Small Vessels | |||||
| SII | PNI | NRI | CONUT | ||
| NLR | r | 0.694 * | −0.653 * | −0.036 * | 0.335 * |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.311 | <0.001 | |
| SII | r | −0.455 * | −0.015 * | 0.164 * | |
| p | <0.001 | 0.674 | <0.001 | ||
| PNI | r | 0.023 ¶ | −0.376 ¶ | ||
| p | 0.523 | <0.001 | |||
| NRI | r | −0.027 ¶ | |||
| p | 0.454 | ||||
| Large Vessels | |||||
| SII | PNI | NRI | CONUT | ||
| NLR | r | 0.837 * | −0.577 * | 0.004 * | 0.389 * |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.937 | <0.001 | |
| SII | R | −0.504 * | 0.023 * | 0.321 * | |
| p | <0.001 | 0.650 | <0.001 | ||
| PNI | r | −0.039 ¶ | −0.646 ¶ | ||
| p | 0.444 | <0.001 | |||
| NRI | r | −0.009 ¶ | |||
| p | 0.853 | ||||
| Other Etiologies | |||||
| SII | PNI | NRI | CONUT | ||
| NLR | R | 0.919 * | −0.531 * | 0.107 * | 0.079 * |
| p | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.178 | 0.319 | |
| SII | r | −0.509 * | 0.090 * | 0.064 * | |
| p | <0.001 | 0.258 | 0.424 | ||
| PNI | r | −0.167 ¶ | −0.446 ¶ | ||
| p | 0.035 | <0.001 | |||
| NRI | r | 0.043 ¶ | |||
| p | 0.590 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Misirlioglu, N.F.; Uzun, N.; Ozen, G.D.; Çalik, M.; Altinbilek, E.; Sutasir, N.; Baykara Sayili, S.; Uzun, H. The Relationship between Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratios with Nutritional Status, Risk of Nutritional Indices, Prognostic Nutritional Indices and Morbidity in Patients with Ischemic Stroke. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081225
Misirlioglu NF, Uzun N, Ozen GD, Çalik M, Altinbilek E, Sutasir N, Baykara Sayili S, Uzun H. The Relationship between Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratios with Nutritional Status, Risk of Nutritional Indices, Prognostic Nutritional Indices and Morbidity in Patients with Ischemic Stroke. Nutrients. 2024; 16(8):1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081225
Chicago/Turabian StyleMisirlioglu, Naile Fevziye, Nedim Uzun, Gulenay Defne Ozen, Mustafa Çalik, Ertugrul Altinbilek, Necmettin Sutasir, Sena Baykara Sayili, and Hafize Uzun. 2024. "The Relationship between Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratios with Nutritional Status, Risk of Nutritional Indices, Prognostic Nutritional Indices and Morbidity in Patients with Ischemic Stroke" Nutrients 16, no. 8: 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081225
APA StyleMisirlioglu, N. F., Uzun, N., Ozen, G. D., Çalik, M., Altinbilek, E., Sutasir, N., Baykara Sayili, S., & Uzun, H. (2024). The Relationship between Neutrophil–Lymphocyte Ratios with Nutritional Status, Risk of Nutritional Indices, Prognostic Nutritional Indices and Morbidity in Patients with Ischemic Stroke. Nutrients, 16(8), 1225. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081225






