Analysis of the Association between Protein Intake and Disability-Adjusted Life Year Rates for Alzheimer’s Disease in Japanese Aged over 60
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.1.1. Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study Dataset
2.1.2. National Health and Nutrition Survey Dataset for Japan
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.2.1. Univariate Analysis
2.2.2. Evaluation Using Multiple Regression Models
2.2.3. Model-Based Simulation
2.2.4. Analysis Environment and Significance Threshold
3. Results
3.1. Univariate Analysis
3.2. Evaluation using Multiple Regression Models
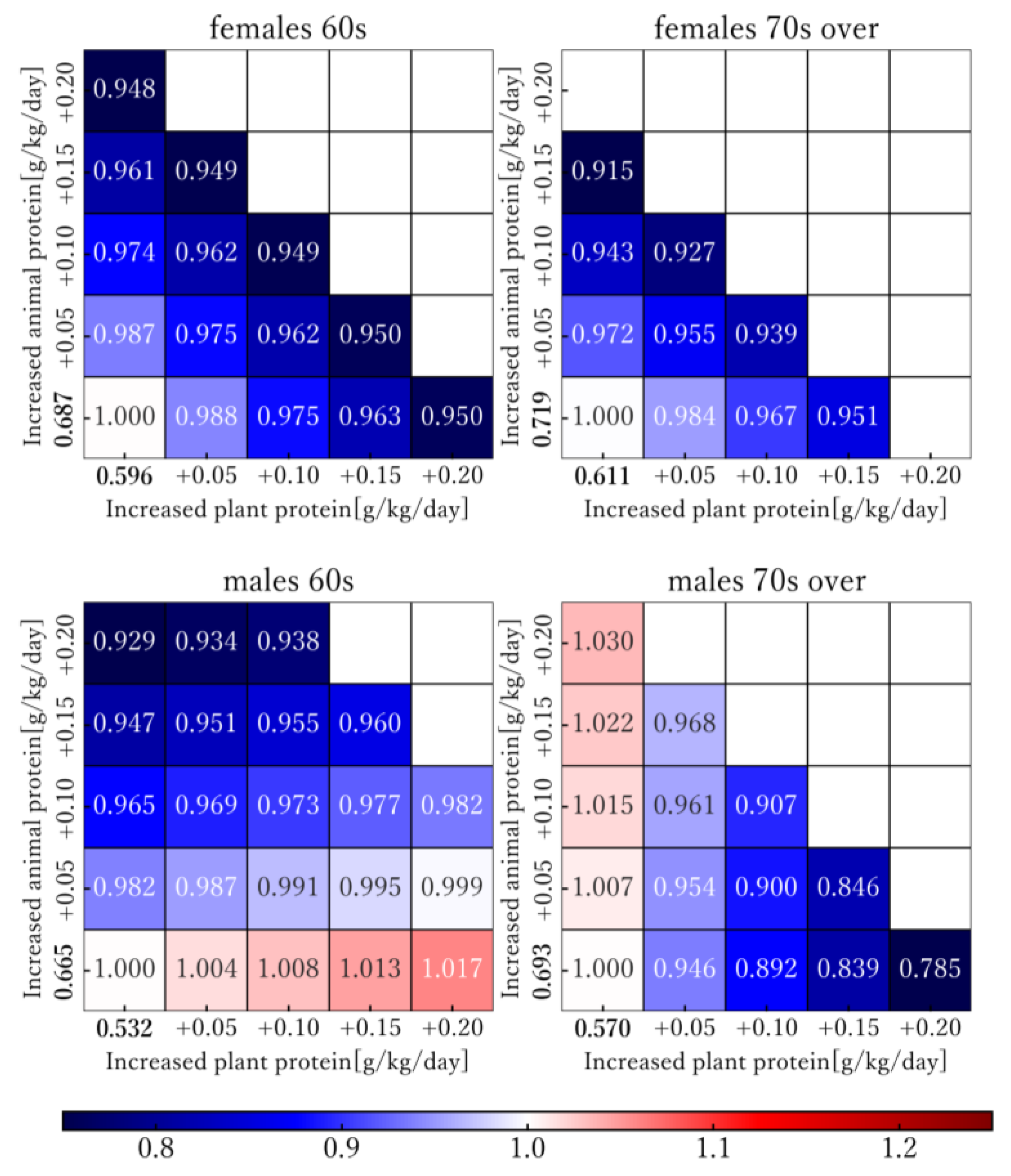
3.3. Model-Based Simulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Significant associations were found between higher protein intake and lower AD-DALY rates after excluding the effect of energy intake and socio-demographic factors in females.
- In the simulation, when protein intake was increased to 1.5 g/kg/day, AD-DALY rates decreased by 5–9 percent compared with 2019. However, the association between intake of animal and plant protein and AD-DALY rates were found to vary based on sex and age group.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wimo, A.; Jonsson, L.; Bond, J.; Prince, M.; Winblad, B.; International, A.D. The worldwide economic impact of dementia 2010. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2013, 9, 1–11.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan. Comprehensive Survey of Living Conditions. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/english/database/db-hss/cslc-index.html (accessed on 6 February 2024).
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2012 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2012, 8, 131–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, R.A.; Aisen, P.S.; Beckett, L.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Craft, S.; Fagan, A.M.; Iwatsubo, T.; Jack, C.R., Jr.; Kaye, J.; Montine, T.J. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2011, 7, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angeloni, C.; Businaro, R.; Vauzour, D. The role of diet in preventing and reducing cognitive decline. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2020, 33, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Risk Reduction of Cognitive Decline and Dementia: WHO Guidelines; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Luchsinger, J.A.; Tang, M.X.; Shea, S.; Mayeux, R. Caloric intake and the risk of Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.O.; Roberts, L.A.; Geda, Y.E.; Cha, R.H.; Pankratz, V.S.; O’Connor, H.M.; Knopman, D.S.; Petersen, R.C. Relative intake of macronutrients impacts risk of mild cognitive impairment or dementia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 32, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, T.-S.; Yuan, C.; Ascherio, A.; Rosner, B.A.; Blacker, D.; Willett, W.C. Long-term dietary protein intake and subjective cognitive decline in US men and women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Pan, S.; Bai, X.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Bao, M.; Zhang, K.; et al. Causal Relationships Between Relative Intake from the Macronutrients and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 87, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Guo, J.; Hu, L.; Veronese, N.; Smith, L.; Yang, L.; Cao, C. Association between Intake of Energy and Macronutrients and Memory Impairment Severity in US Older Adults, National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011–2014. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, A.D.; Murray, C.C. The global burden of disease, 1990–2020. Nat. Med. 1998, 4, 1241–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.-M.; Bisignano, C.; James, S.L.; Abady, G.G.; Abedi, A.; Abu-Gharbieh, E.; Alhassan, R.K.; Alipour, V.; Arabloo, J.; Asaad, M. Global, regional, and national burden of bone fractures in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Healthy Longev. 2021, 2, e580–e592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Pu, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, D.; He, S. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Protein–Energy Malnutrition: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Liu, S.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, H.; Pu, L.; Wang, L.; Han, L. Global Burden of Vitamin A Deficiency in 204 Countries and Territories from 1990–2019. Nutrients 2022, 14, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, S.; Yoneoka, D.; Tanaka, S.; Ishizuka, A.; Ueda, P.; Nakamura, K.; Uneyama, H.; Hayashi, N.; Shibuya, K. Forecasting disability-adjusted life years for chronic diseases: Reference and alternative scenarios of salt intake for 2017–2040 in Japan. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Yoneoka, D.; Ishizuka, A.; Ueda, P.; Nakamura, K.; Uneyama, H.; Hayashi, N.; Shibuya, K.; Nomura, S. Projections of disability-adjusted life years for major diseases due to a change in vegetable intake in 2017–2040 in Japan. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. The National Health and Nutrition Survey in Japan. 2019. Available online: https://www.nibiohn.go.jp/eiken/kenkounippon21/en/eiyouchousa/ (accessed on 6 February 2024).
- Christopher Frey, H.; Patil, S.R. Identification and review of sensitivity analysis methods. Risk Anal. 2002, 22, 553–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morley, J.E.; Argiles, J.M.; Evans, W.J.; Bhasin, S.; Cella, D.; Deutz, N.E.; Doehner, W.; Fearon, K.C.; Ferrucci, L.; Hellerstein, M.K. Nutritional recommendations for the management of sarcopenia. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2010, 11, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernando, W.; Rainey-Smith, S.R.; Gardener, S.L.; Villemagne, V.L.; Burnham, S.C.; Macaulay, S.L.; Brown, B.M.; Gupta, V.B.; Sohrabi, H.R.; Weinborn, M. Associations of dietary protein and fiber intake with brain and blood amyloid-β. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 61, 1589–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahni, S.; Mangano, K.M.; Hannan, M.T.; Kiel, D.P.; McLean, R.R. Higher Protein Intake Is Associated with Higher Lean Mass and Quadriceps Muscle Strength in Adult Men and Women. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, P.A.; Buchman, A.S.; Wilson, R.S.; Leurgans, S.E.; Bennett, D.A. Association of muscle strength with the risk of Alzheimer disease and the rate of cognitive decline in community-dwelling older persons. Arch. Neurol. 2009, 66, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenn, J.M.; Madero, E.N.; Bott, N.T. Dietary Protein and Amino Acid Intake: Links to the Maintenance of Cognitive Health. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, X.; Hill, E.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, J.; Ge, Z.; Wang, W.; He, M. Macronutrient Intake and Risk of Dementia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults: A Nine-Year Follow-Up Cohort Study. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 85, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Dietary Reference Intakes for Japanese. 2020. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/content/10904750/000586553.pdf (accessed on 6 February 2024).
- World Health Organization. Obesity Rates by Country. Available online: https://wisevoter.com/country-rankings/obesity-rates-by-country/ (accessed on 6 February 2024).
- Yamada, Y.; Yokoyama, K.; Noriyasu, R.; Osaki, T.; Adachi, T.; Itoi, A.; Naito, Y.; Morimoto, T.; Kimura, M.; Oda, S. Light-intensity activities are important for estimating physical activity energy expenditure using uniaxial and triaxial accelerometers. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 105, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.; Nishi, S.K.; Babio, N.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Castañer, O.; Martínez, J.A.; Alonso-Gómez, Á.M.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Vioque, J. Dairy Product Consumption and Changes in Cognitive Performance: Two-Year Analysis of the PREDIMED-Plus Cohort. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2022, 66, 2101058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Greenwood, D.C.; Risch, H.A.; Bunce, D.; Hardie, L.J.; Cade, J.E. Meat consumption and risk of incident dementia: Cohort study of 493,888 UK Biobank participants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 114, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare. Patient Survey. Available online: https://www.mhlw.go.jp/toukei/saikin/hw/kanja/20/index.html (accessed on 6 February 2024).
- Buchman, A.; Boyle, P.; Yu, L.; Shah, R.; Wilson, R.; Bennett, D. Total daily physical activity and the risk of AD and cognitive decline in older adults. Neurology 2012, 78, 1323–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luchsinger, J.A.; Tang, M.X.; Siddiqui, M.; Shea, S.; Mayeux, R. Alcohol intake and risk of dementia. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2004, 52, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, M.C.; Evans, D.A.; Bienias, J.L.; Tangney, C.C.; Bennett, D.A.; Aggarwal, N.; Schneider, J.; Wilson, R.S. Dietary fats and the risk of incident Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, A.; Jacques, P.F. Protein intake and human health: Implications of units of protein intake. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
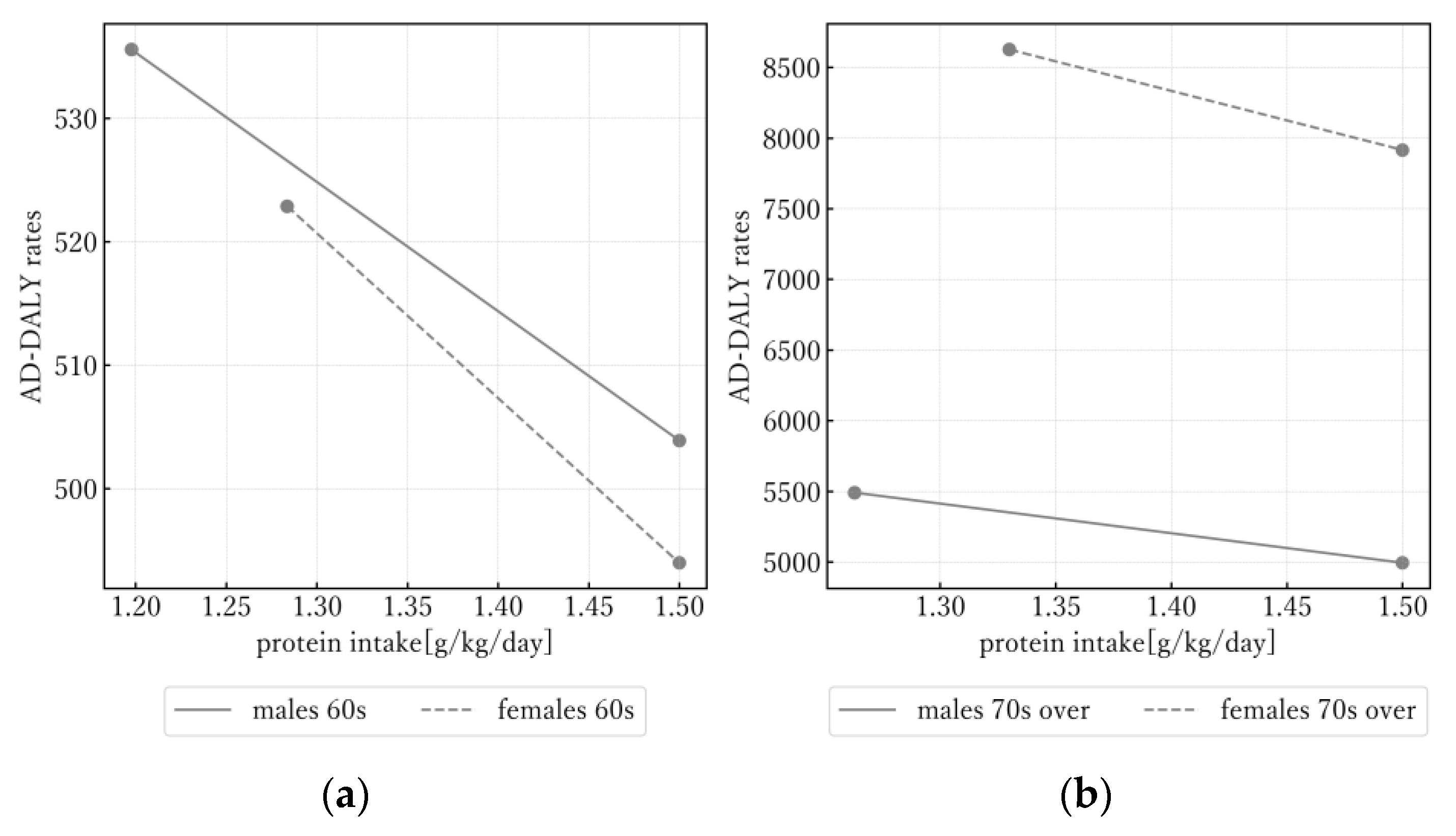
| Variable | Age | Sex | Mean ± SD | Correlation Coefficient (p-Value) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SDI | Energy (kcal/kg/Day) | Protein (g/kg/Day) | Animal Protein (g/kg/Day) | Plant Protein (g/kg/Day) | |||||||||
| AD-DALY rates (years/100,000 people) | 60s | Female | 510.120 ± 18.160 | 0.820 | (<0.001) | −0.825 | (<0.001) | −0.877 | (<0.001) | −0.801 | (<0.001) | −0.875 | (<0.001) |
| Male | 495.303 ± 29.845 | 0.913 | (<0.001) | −0.871 | (<0.001) | −0.863 | (<0.001) | −0.768 | (<0.001) | −0.891 | (<0.001) | ||
| 70+ | Female | 6625.386 ± 1387.956 | 0.979 | (<0.001) | −0.568 | (0.001) | −0.718 | (<0.001) | −0.473 | (0.008) | −0.847 | (<0.001) | |
| Male | 4295.484 ± 772.953 | 0.954 | (<0.001) | −0.756 | (<0.001) | −0.784 | (<0.001) | −0.632 | (<0.001) | −0.864 | (<0.001) | ||
| SDI | 60s | Female | 0.835 ± 0.022 | - | −0.850 | (<0.001) | −0.896 | (<0.001) | −0.727 | (<0.001) | −0.949 | (<0.001) | |
| Male | 0.835 ± 0.022 | - | −0.907 | (<0.001) | −0.854 | (<0.001) | −0.704 | (<0.001) | −0.925 | (<0.001) | |||
| 70+ | Female | 0.835 ± 0.022 | - | −0.590 | (<0.001) | −0.693 | (<0.001) | −0.423 | (0.002) | −0.845 | (<0.001) | ||
| Male | 0.835 ± 0.022 | - | −0.819 | (<0.001) | −0.790 | (<0.001) | −0.643 | (<0.001) | −0.865 | (<0.001) | |||
| energy (kcal/kg/day) | 60s | Female | 33.642 ± 1.532 | - | - | 0.876 | (<0.001) | 0.759 | (<0.001) | 0.899 | (<0.001) | ||
| Male | 34.850 ± 1.962 | - | - | 0.953 | (<0.001) | 0.869 | (<0.001) | 0.965 | (<0.001) | ||||
| 70+ | Female | 33.318 ± 1.714 | - | - | 0.884 | (<0.001) | 0.798 | (<0.001) | 0.863 | (<0.001) | |||
| Male | 33.532 ± 1.231 | - | - | 0.886 | (<0.001) | 0.816 | (<0.001) | 0.887 | (<0.001) | ||||
| protein (g/kg/day) | 60s | Female | 1.337 ± 0.081 | - | - | - | 0.943 | (<0.001) | 0.979 | (<0.001) | |||
| Male | 1.329 ± 0.126 | - | - | - | 0.960 | (<0.001) | 0.975 | (<0.001) | |||||
| 70+ | Female | 1.311 ± 0.091 | - | - | - | 0.931 | (<0.001) | 0.952 | (<0.001) | ||||
| Male | 1.282 ± 0.089 | - | - | - | 0.959 | (<0.001) | 0.969 | (<0.001) | |||||
| animal protein (g/kg/day) | 60s | Female | 0.688 ± 0.032 | - | - | - | - | 0.854 | (<0.001) | ||||
| Male | 0.700 ± 0.058 | - | - | - | - | 0.874 | (<0.001) | ||||||
| 70+ | Female | 0.667 ± 0.044 | - | - | - | - | 0.775 | (<0.001) | |||||
| Male | 0.662 ± 0.043 | - | - | - | - | 0.859 | (<0.001) | ||||||
| plant protein (g/kg/day) | 60s | Female | 0.650 ± 0.052 | - | - | - | - | - | |||||
| Male | 0.629 ± 0.072 | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||
| 70+ | Female | 0.645 ± 0.052 | - | - | - | - | - | ||||||
| Male | 0.621 ± 0.049 | - | - | - | - | - | |||||||
| Model | Age | Sex | Partial Regression Coefficient (p-Value) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein (g/kg/Day) | Animal | Plant | Energy (kcal/kg/Day) | SDI | |||||||||
| Protein (g/kg/Day) | Protein (g/kg/Day) | ||||||||||||
| Model I | 60s | Female | 0.785 | −13.352 | (0.017) | −2.545 | (0.288) | 84.462 | (0.637) | ||||
| Male | 0.862 | −10.472 | (0.078) | 3.045 | (0.506) | 973.778 | (<0.001) | ||||||
| 70+ | Female | 0.972 | −418.062 | (0.002) | 174.117 | (0.005) | 57802.130 | (<0.001) | |||||
| Male | 0.923 | −209.643 | (0.057) | 156.256 | (0.065) | 33935.859 | (<0.001) | ||||||
| Model II | 60s | Female | 0.785 | −13.579 | (0.262) | −12.990 | (0.470) | −2.562 | (0.319) | 89.210 | (0.757) | ||
| Male | 0.868 | −18.861 | (0.069) | 4.500 | (0.775) | 2.346 | (0.611) | 1214.526 | (0.001) | ||||
| 70+ | Female | 0.972 | −487.261 | (0.044) | −283.141 | (0.483) | 165.932 | (0.013) | 59557.907 | (<0.001) | |||
| Male | 0.929 | 83.305 | (0.703) | −605.898 | (0.038) | 152.262 | (0.066) | 29770.322 | (<0.001) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fujiwara, K.; Tanaka, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Nagao, K.; Ishikawa-Takata, K. Analysis of the Association between Protein Intake and Disability-Adjusted Life Year Rates for Alzheimer’s Disease in Japanese Aged over 60. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081221
Fujiwara K, Tanaka T, Kobayashi H, Nagao K, Ishikawa-Takata K. Analysis of the Association between Protein Intake and Disability-Adjusted Life Year Rates for Alzheimer’s Disease in Japanese Aged over 60. Nutrients. 2024; 16(8):1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081221
Chicago/Turabian StyleFujiwara, Kazuki, Takayuki Tanaka, Hisamine Kobayashi, Kenji Nagao, and Kazuko Ishikawa-Takata. 2024. "Analysis of the Association between Protein Intake and Disability-Adjusted Life Year Rates for Alzheimer’s Disease in Japanese Aged over 60" Nutrients 16, no. 8: 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081221
APA StyleFujiwara, K., Tanaka, T., Kobayashi, H., Nagao, K., & Ishikawa-Takata, K. (2024). Analysis of the Association between Protein Intake and Disability-Adjusted Life Year Rates for Alzheimer’s Disease in Japanese Aged over 60. Nutrients, 16(8), 1221. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081221







