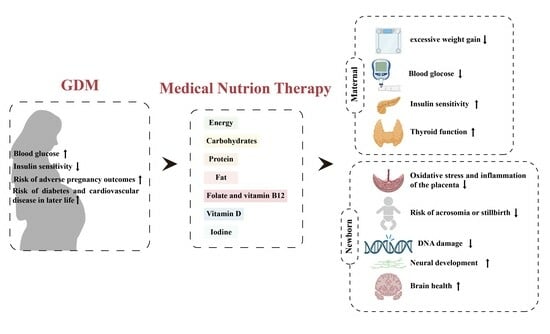
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: What Can Medical Nutrition Therapy Do?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Physiopathology of GDM
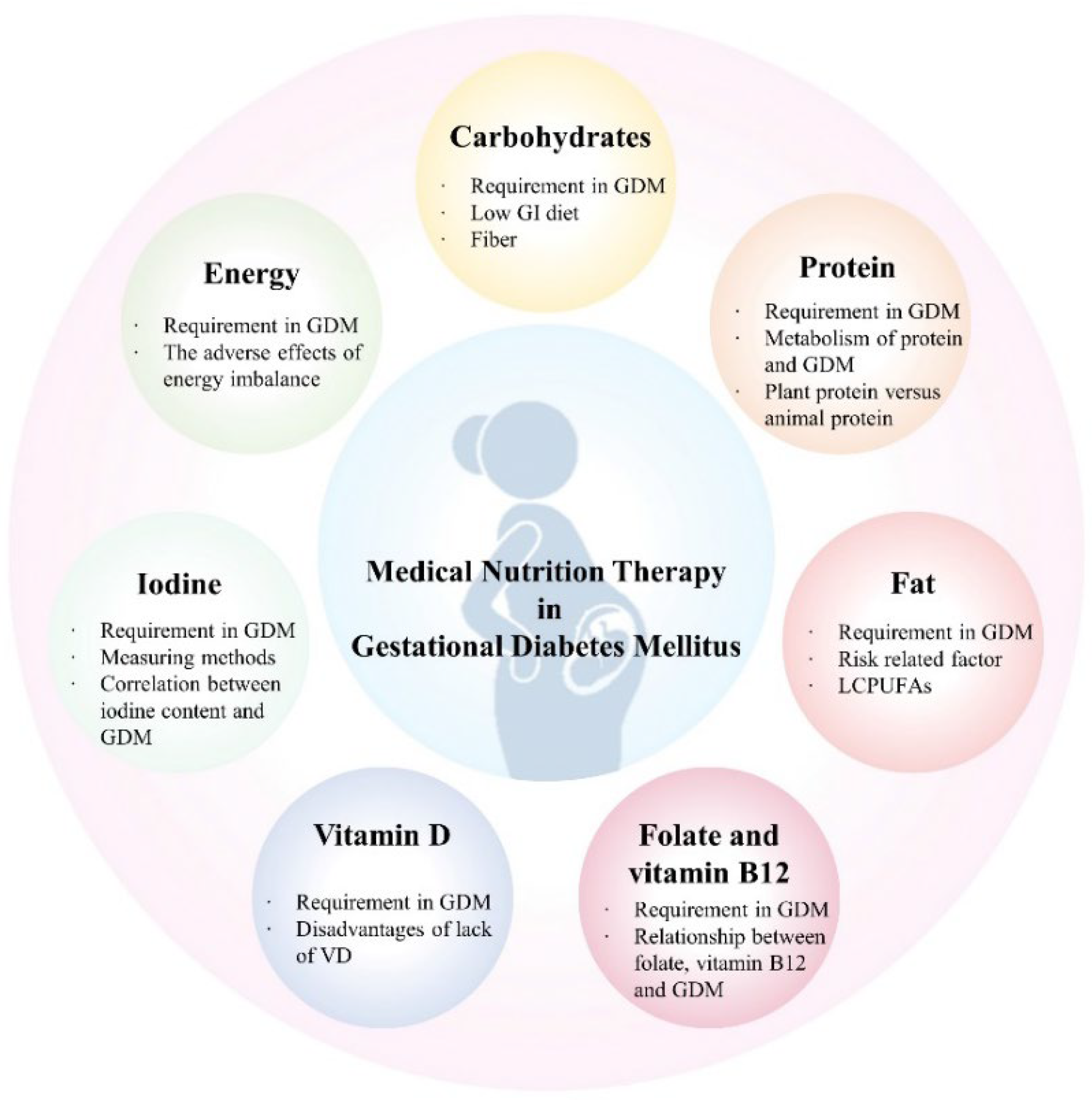
3. Application of Medical Nutrition Therapy in GDM
3.1. Restriction of Energy Intake
3.2. Low GI and High Quality of Carbohydrates
3.3. Good Dietary Protein
3.4. Dietary Fat
3.5. Vitamin and Mineral Supplements
3.5.1. Folate and Vitamin B12
3.5.2. Vitamin D
3.5.3. Iodine
4. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johns, E.C.; Denison, F.C.; Norman, J.E.; Reynolds, R.M. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms, Treatment, and Complications. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, H.D.; Catalano, P.; Zhang, C.; Desoye, G.; Mathiesen, E.R.; Damm, P. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2014, 37 (Suppl. S1), S81–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee on Practice Bulletins—Obstetrics. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 190: Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 131, e49–e64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coustan, D.R. Gestational diabetes mellitus. Clin. Chem. 2013, 59, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Yang, Y.; Cui, D.; Li, C.; Ma, R.C.W.; Li, J.; Yang, X. Effects of lifestyle intervention on long-term risk of diabetes in women with prior gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Li, N.; Chivese, T.; Werfalli, M.; Sun, H.; Yuen, L.; Hoegfeldt, C.A.; Elise Powe, C.; Immanuel, J.; Karuranga, S.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Estimation of Global and Regional Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Prevalence for 2021 by International Association of Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group’s Criteria. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Briggs Early, K.; Stanley, K. Position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: The Role of Medical Nutrition Therapy and Registered Dietitian Nutritionists in the Prevention and Treatment of Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, J.M.; Kellett, J.E.; Balsells, M.; García-Patterson, A.; Hadar, E.; Solà, I.; Gich, I.; van der Beek, E.M.; Castañeda-Gutiérrez, E.; Heinonen, S.; et al. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Diet: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Examining the Impact of Modified Dietary Interventions on Maternal Glucose Control and Neonatal Birth Weight. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 1346–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Estal, I.; Castorena-Torres, F. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Energy-Dense Diet: What Is the Role of the Insulin/IGF Axis? Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 916042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plows, J.; Stanley, J.; Baker, P.; Reynolds, C.; Vickers, M. The Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kampmann, U.; Knorr, S.; Fuglsang, J.; Ovesen, P. Determinants of Maternal Insulin Resistance during Pregnancy: An Updated Overview. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 5320156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalano, P.M. Trying to understand gestational diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2014, 31, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, T.A. Pancreatic B-cell defects in gestational diabetes: Implications for the pathogenesis and prevention of type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colletti, A.; Cravotto, G.; Citi, V.; Martelli, A.; Testai, L.; Cicero, A.F.G. Advances in Technologies for Highly Active Omega-3 Fatty Acids from Krill Oil: Clinical Applications. Mar. Drugs 2021, 19, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, K.; Melamed, N.; Vandenberghe, H.; Berger, H. The impact of adoption of the International Association of Diabetes in Pregnancy Study Group criteria for the screening and diagnosis of gestational diabetes. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 212, 224.e221–224.e229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasile, F.C.; Preda, A.; Ștefan, A.G.; Vladu, M.I.; Forțofoiu, M.-C.; Clenciu, D.; Gheorghe, I.O.; Forțofoiu, M.; Moța, M.; Schiattarella, A. An Update of Medical Nutrition Therapy in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. J. Diabetes Res. 2021, 2021, 5266919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, T.L.; Van Pelt, R.E.; Anderson, M.A.; Reece, M.S.; Reynolds, R.M.; de la Houssaye, B.A.; Heerwagen, M.; Donahoo, W.T.; Daniels, L.J.; Chartier-Logan, C.; et al. Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Randomized to a Higher-Complex Carbohydrate/Low-Fat Diet Manifest Lower Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, Glucose, and Free Fatty Acids: A Pilot Study. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oken, E.; Ning, Y.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Rich-Edwards, J.W.; Olsen, S.F.; Gillman, M.W. Diet During Pregnancy and Risk of Preeclampsia or Gestational Hypertension. Ann. Epidemiol. 2007, 17, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gubory, K.H. Mitochondria: Omega-3 in the route of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 1569–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landon, M.B.; Spong, C.Y.; Thom, E.; Carpenter, M.W.; Ramin, S.M.; Casey, B.; Wapner, R.J.; Varner, M.W.; Rouse, D.J.; Thorp, J.M.; et al. A Multicenter, Randomized Trial of Treatment for Mild Gestational Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, T.A.; Xiang, A.H.; Page, K.A. Gestational diabetes mellitus: Risks and management during and after pregnancy. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kintiraki, E.; Goulis, D.G. Gestational diabetes mellitus: Multi-disciplinary treatment approaches. Metabolism 2018, 86, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2000, 23 (Suppl. S1), S77–S79.
- Hod, M.; Kapur, A.; Sacks, D.A.; Hadar, E.; Agarwal, M.; Di Renzo, G.C.; Roura, L.C.; McIntyre, H.D.; Morris, J.L.; Divakar, H. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) Initiative on gestational diabetes mellitus: A pragmatic guide for diagnosis, management, and care. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2015, 131, S173–S211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopp, R.H.; Magee, M.S.; Raisys, V.; Benedetti, T.; Bonet, B. Hypocaloric diets and ketogenesis in the management of obese gestational diabetic women. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1991, 10, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelps, R.L.; Metzger, B.E. Caloric restriction in gestational diabetes mellitus: When and how much? J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1992, 11, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanovic-Peterson, L.; Peterson, C.M. Dietary manipulation as a primary treatment strategy for pregnancies complicated by diabetes. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1990, 9, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte-Gardea, M.O.; Gonzales-Pacheco, D.M.; Reader, D.M.; Thomas, A.M.; Wang, S.R.; Gregory, R.P.; Piemonte, T.A.; Thompson, K.L.; Moloney, L. Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Gestational Diabetes Evidence-Based Nutrition Practice Guideline. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 1719–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheard, N.F.; Clark, N.G.; Brand-Miller, J.C.; Franz, M.J.; Pi-Sunyer, F.X.; Mayer-Davis, E.; Kulkarni, K.; Geil, P. Dietary carbohydrate (amount and type) in the prevention and management of diabetes: A statement by the american diabetes association. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2266–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.J.; Wolever, T.M.; Taylor, R.H.; Barker, H.; Fielden, H.; Baldwin, J.M.; Bowling, A.C.; Newman, H.C.; Jenkins, A.L.; Goff, D.V. Glycemic index of foods: A physiological basis for carbohydrate exchange. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1981, 34, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand-Miller, J.; Hayne, S.; Petocz, P.; Colagiuri, S. Low-glycemic index diets in the management of diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 2261–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, M.I.; Mills, K.E.; Zheng, J.; Regmi, A.; Hu, S.Q.; Gou, L.; Chen, L.-L. Low-glycemic index diets as an intervention for diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 110, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergia, R.E.; Giacco, R.; Hjorth, T.; Biskup, I.; Zhu, W.; Costabile, G.; Vitale, M.; Campbell, W.W.; Landberg, R.; Riccardi, G. Differential Glycemic Effects of Low- versus High-Glycemic Index Mediterranean-Style Eating Patterns in Adults at Risk for Type 2 Diabetes: The MEDGI-Carb Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myette-Côté, É.; Durrer, C.; Neudorf, H.; Bammert, T.D.; Botezelli, J.D.; Johnson, J.D.; DeSouza, C.A.; Little, J.P. The effect of a short-term low-carbohydrate, high-fat diet with or without postmeal walks on glycemic control and inflammation in type 2 diabetes: A randomized trial. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2018, 315, R1210–R1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, F.M.; Carey, V.J.; Anderson, C.A.M.; Miller, E.R.; Copeland, T.; Charleston, J.; Harshfield, B.J.; Laranjo, N.; McCarron, P.; Swain, J.; et al. Effects of High vs Low Glycemic Index of Dietary Carbohydrate on Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors and Insulin Sensitivity. JAMA 2014, 312, 2531–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, J.M.; McGowan, C.A.; Mahony, R.; Foley, M.E.; McAuliffe, F.M. Low glycaemic index diet in pregnancy to prevent macrosomia (ROLO study): Randomised control trial. BMJ 2012, 345, e5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looman, M.; Schoenaker, D.A.J.M.; Soedamah-Muthu, S.S.; Geelen, A.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Mishra, G.D. Pre-pregnancy dietary carbohydrate quantity and quality, and risk of developing gestational diabetes: The Australian Longitudinal Study on Women’s Health. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 120, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.C.W.; Reynolds, A.N.; Akerman, A.P.; Mann, J. Dietary fibre and whole grains in diabetes management: Systematic review and meta-analyses. PLoS Med. 2020, 17, e1003053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filardi, T.; Panimolle, F.; Crescioli, C.; Lenzi, A.; Morano, S. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: The Impact of Carbohydrate Quality in Diet. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watford, M.; Wu, G. Protein. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 651–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 15. Management of Diabetes in Pregnancy: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, S232–S243. [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, F.; Lavigne, C.; Jacques, H.; Marette, A. Role of Dietary Proteins and Amino Acids in the Pathogenesis of Insulin Resistance. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2007, 27, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, D.; Zhao, D.; Quan, L.; Zhou, R.; Bao, W.; Cheng, G. Dietary Protein Intake, Meat Consumption, and Dairy Consumption in the Year Preceding Pregnancy and During Pregnancy and Their Associations with the Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Prospective Cohort Study in Southwest China. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, W.W.; Colega, M.; Cai, S.; Chan, Y.H.; Padmapriya, N.; Chen, L.-W.; Soh, S.-E.; Han, W.M.; Tan, K.H.; Lee, Y.S.; et al. Higher Maternal Dietary Protein Intake Is Associated with a Higher Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in a Multiethnic Asian Cohort. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Bowers, K.; Tobias, D.K.; Hu, F.B.; Zhang, C. Prepregnancy dietary protein intake, major dietary protein sources, and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A prospective cohort study. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 2001–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Tang, N.; Zeng, J.; Jing, J.; Cai, L. Dietary Protein Patterns during Pregnancy Are Associated with Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Pregnant Women. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boden, G.; Chen, X.; Ruiz, J.; White, J.V.; Rossetti, L. Mechanisms of fatty acid-induced inhibition of glucose uptake. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 2438–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, T.L. Carbohydrate Content in the GDM Diet: Two Views: View 1: Nutrition Therapy in Gestational Diabetes: The Case for Complex Carbohydrates. Diabetes Spectr. 2016, 29, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ryckman, K.K.; Spracklen, C.N.; Smith, C.J.; Robinson, J.G.; Saftlas, A.F. Maternal lipid levels during pregnancy and gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG 2015, 122, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, K.; Tobias, D.K.; Yeung, E.; Hu, F.B.; Zhang, C. A prospective study of prepregnancy dietary fat intake and risk of gestational diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Cui, C.-Y. Dietary Cholesterol Intake and Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2021, 41, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, D.Y.; Talukdar, S.; Bae, E.J.; Imamura, T.; Morinaga, H.; Fan, W.; Li, P.; Lu, W.J.; Watkins, S.M.; Olefsky, J.M. GPR120 Is an Omega-3 Fatty Acid Receptor Mediating Potent Anti-inflammatory and Insulin-Sensitizing Effects. Cell 2010, 142, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mierzyński, R.; Poniedziałek-Czajkowska, E.; Sotowski, M.; Szydełko-Gorzkowicz, M. Nutrition as Prevention Factor of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Gong, M.; Wei, W.; Jin, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Jin, Q. Antarctic Krill (Euphausia superba) Oil: A Comprehensive Review of Chemical Composition, Extraction Technologies, Health Benefits, and Current Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 514–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, X.; Meng, H.; Hao, W.; Yin, J.; Ma, F.; Guo, X.; Du, L.; Sun, L.; et al. Krill Oil Turns Off TGF-β1 Profibrotic Signaling in the Prevention of Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 9865–9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozaffarian, D.; Maki, K.C.; Bays, H.E.; Aguilera, F.; Gould, G.; Hegele, R.A.; Moriarty, P.M.; Robinson, J.G.; Shi, P.; Tur, J.F.; et al. Effectiveness of a Novel ω-3 Krill Oil Agent in Patients with Severe Hypertriglyceridemia. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2141898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Feng, R.; Cao, P.; Liu, Y. Effects of Antarctic krill oil on lipid and glucose metabolism in C57BL/6J mice fed with high fat diet. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarshi, P.P.; Grant, R.W.; Ikonte, C.J.; Hazels Mitmesser, S. Maternal Omega-3 Nutrition, Placental Transfer and Fetal Brain Development in Gestational Diabetes and Preeclampsia. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobbe, S.; Van Der Straeten, D. Folate biofortification in food crops. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 44, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, S.; Storozhenko, S.; Mehrshahi, P.; Bennett, M.J.; Lambert, W.; Gregory, J.F.; Schubert, K.; Hugenholtz, J.; Van Der Straeten, D.; Hanson, A.D. Folate biofortification in food plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson, A.D.; Gregory, J.F. Folate Biosynthesis, Turnover, and Transport in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2011, 62, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stover, P.J. Physiology of Folate and Vitamin B12 in Health and Disease. Nutr. Rev. 2004, 62, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kósa, M.; Galla, Z.; Lénárt, I.; Baráth, Á.; Grecsó, N.; Rácz, G.; Bereczki, C.; Monostori, P. Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin): Its Fate from Ingestion to Metabolism with Particular Emphasis on Diagnostic Approaches of Acquired Neonatal/Infantile Deficiency Detected by Newborn Screening. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Leary, F.; Samman, S. Vitamin B12 in Health and Disease. Nutrients 2010, 2, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Zadeh, M.; Mohamadzadeh, M. Vitamin B12 Regulates the Transcriptional, Metabolic, and Epigenetic Programing in Human Ileal Epithelial Cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Zadeh, M.; Mohamadzadeh, M. Vitamin B12 coordinates ileal epithelial cell and microbiota functions to resist Salmonella infection in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20220057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.; Thio, J.; Thomas, R.S.; Phillips, J. Pernicious anaemia. BMJ 2020, 369, m1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman-Garcia, P.; Quiros-Gonzalez, I.; Mottram, L.; Lieben, L.; Sharan, K.; Wangwiwatsin, A.; Tubio, J.; Lewis, K.; Wilkinson, D.; Santhanam, B.; et al. Vitamin B12–dependent taurine synthesis regulates growth and bone mass. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2988–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, A.M.; Kirke, P.N.; Brody, L.C.; Scott, J.M.; Mills, J.L. Effects of folate and vitamin B12 deficiencies during pregnancy on fetal, infant, and child development. Food Nutr. Bull. 2008, 29, S101–S111; discussion S112–S115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.M.; Arthurs, A.L.; Smith, M.D.; Roberts, C.T.; Jankovic-Karasoulos, T. High Folate, Perturbed One-Carbon Metabolism and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Ge, X.; Huang, K.; Mao, L.; Yan, S.; Xu, Y.; Huang, S.; Hao, J.; Zhu, P.; Niu, Y.; et al. Folic Acid Supplement Intake in Early Pregnancy Increases Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Evidence From a Prospective Cohort Study. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, e36–e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, J.S.; Pang, W.W.; Cai, S.; Lee, Y.S.; Chan, J.K.Y.; Shek, L.P.C.; Yap, F.K.P.; Tan, K.H.; Godfrey, K.M.; van Dam, R.M.; et al. High folate and low vitamin B12 status during pregnancy is associated with gestational diabetes mellitus. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhowmik, B.; Siddique, T.; Majumder, A.; Mdala, I.; Hossain, I.A.; Hassan, Z.; Jahan, I.; Moreira, N.; Alim, A.; Basit, A.; et al. Maternal BMI and nutritional status in early pregnancy and its impact on neonatal outcomes at birth in Bangladesh. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2019, 19, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; He, Y.; Sun, X.; He, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, C. Maternal High Folic Acid Supplement Promotes Glucose Intolerance and Insulin Resistance in Male Mouse Offspring Fed a High-Fat Diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6298–6313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.D.; Linarelli, L.E.; Liu, L.; Wall, S.S.; Greenawald, M.H.; Seidel, R.W.; Estabrooks, P.A.; Almeida, F.A.; Cheng, Z. Insulin resistance is associated with epigenetic and genetic regulation of mitochondrial DNA in obese humans. Clin. Epigenet. 2015, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santander Ballestín, S.; Giménez Campos, M.I.; Ballestín Ballestín, J.; Luesma Bartolomé, M.J. Is Supplementation with Micronutrients Still Necessary during Pregnancy? A Review. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ojo, O.; Weldon, S.M.; Thompson, T.; Vargo, E.J. The Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Glycaemic Control in Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burris, H.H.; Camargo, C.A. Vitamin D and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2013, 14, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartley, J. Vitamin D: Emerging roles in infection and immunity. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2014, 8, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsori, D.H.; Hammoud, M.S. Vitamin D deficiency in mothers, neonates and children. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 175, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Review Dietary Reference Intakes for Vitamin D and Calcium. The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health. In Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D; Ross, A.C., Taylor, C.L., Yaktine, A.L., Del Valle, H.B., Eds.; National Academies Press (US): Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mansur, J.L.; Oliveri, B.; Giacoia, E.; Fusaro, D.; Costanzo, P.R. Vitamin D: Before, during and after Pregnancy: Effect on Neonates and Children. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawodu, A.; Wagner, C.L. Mother-child vitamin D deficiency: An international perspective. Arch. Dis. Child. 2007, 92, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, R.E.; Victora, C.G.; Walker, S.P.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Christian, P.; de Onis, M.; Ezzati, M.; Grantham-McGregor, S.; Katz, J.; Martorell, R.; et al. Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet 2013, 382, 427–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, V.T.; Thorstensen, E.B.; Mourath, D.; Jones, M.B.; McCowan, L.M.E.; Kenny, L.C.; Baker, P.N. The relationship between 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration in early pregnancy and pregnancy outcomes in a large, prospective cohort. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 116, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.-X.; Pan, G.-T.; Guo, J.-F.; Li, B.-Y.; Qin, L.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-L. Vitamin D Deficiency Increases the Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8366–8375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghian, M.; Asadi, M.; Rahmani, S.; Akhavan Zanjani, M.; Sadeghi, O.; Hosseini, S.A.; Zare Javid, A. Circulating vitamin D and the risk of gestational diabetes: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Endocrine 2020, 70, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, A.W.; Frankel, J.B.; Heldt, A.M.; Grodsky, G.M. Vitamin D deficiency inhibits pancreatic secretion of insulin. Science 1980, 209, 823–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez, J.A.; Ashraf, A. Role of Vitamin D in Insulin Secretion and Insulin Sensitivity for Glucose Homeostasis. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 2010, 351385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farebrother, J.; Zimmermann, M.B.; Andersson, M. Excess iodine intake: Sources, assessment, and effects on thyroid function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2019, 1446, 44–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, B.; Dupuy, C.; Miot, F.; Dumont, J. Chapter 2 Thyroid Hormone Synthesis And Secretion. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hofland, J., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, M.B. Iodine Deficiency. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 376–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouga, M.; Lean, M.E.J.; Combet, E. Contemporary challenges to iodine status and nutrition: The role of foods, dietary recommendations, fortification and supplementation. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2018, 77, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, M.B.; Jooste, P.L.; Pandav, C.S. Iodine-deficiency disorders. Lancet 2008, 372, 1251–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krela-Kaźmierczak, I.; Czarnywojtek, A.; Skoracka, K.; Rychter, A.M.; Ratajczak, A.E.; Szymczak-Tomczak, A.; Ruchała, M.; Dobrowolska, A. Is There an Ideal Diet to Protect against Iodine Deficiency? Nutrients 2021, 13, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwattisaiwong, S.; Burman, K.D.; Li-Ng, M. Iodine deficiency: Clinical implications. Cleve Clin. J. Med. 2017, 84, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Peng, S.; Fan, C.; Teng, W.; Shan, Z. Effect of Iodine Nutrition on Pregnancy Outcomes in an Iodine-Sufficient Area in China. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2017, 182, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva de Morais, N.; Ayres Saraiva, D.; Corcino, C.; Berbara, T.; Schtscherbyna, A.; Moreira, K.; Vaisman, M.; Alexander, E.K.; Teixeira, P. Consequences of Iodine Deficiency and Excess in Pregnancy and Neonatal Outcomes: A Prospective Cohort Study in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Thyroid 2020, 30, 1792–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neven, K.Y.; Marien, C.B.D.; Janssen, B.G.; Roels, H.A.; Waegeneers, N.; Nawrot, T.S.; Ruttens, A. Variability of iodine concentrations in the human placenta. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, R.; Azizi, F.; Hedayati, M.; Mirmiran, P.; O’Herlihy, C.; Smyth, P.P.A. Is placental iodine content related to dietary iodine intake? Clin. Endocrinol. 2011, 75, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.; O’Herlihy, C.; Smyth, P.P.A. The Placenta as a Compensatory Iodine Storage Organ. Thyroid 2011, 21, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neven, K.Y.; Cox, B.; Cosemans, C.; Gyselaers, W.; Penders, J.; Plusquin, M.; Roels, H.A.; Vrijens, K.; Ruttens, A.; Nawrot, T.S. Lower iodine storage in the placenta is associated with gestational diabetes mellitus. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, R.J.; Alsweiler, J.; Moore, A.E.; Brown, S.; Middleton, P.; Shepherd, E.; Crowther, C.A. Interventions to prevent women from developing gestational diabetes mellitus: An overview of Cochrane Reviews. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2020, 2020, CD012394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijatovic-Vukas, J.; Capling, L.; Cheng, S.; Stamatakis, E.; Louie, J.; Cheung, N.; Markovic, T.; Ross, G.; Senior, A.; Brand-Miller, J.; et al. Associations of Diet and Physical Activity with Risk for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vounzoulaki, E.; Khunti, K.; Abner, S.C.; Tan, B.K.; Davies, M.J.; Gillies, C.L. Progression to type 2 diabetes in women with a known history of gestational diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 2020, 369, m1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Nutrients | Recommendations |
|---|---|
| Energy |
|
| Carbohydrates |
|
| Protein |
|
| Fat |
|
| Folate and vitamin B12 |
|
| Vitamin D |
|
| Iodine |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, X.; Zou, H.; Zhang, T.; Huo, Y.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: What Can Medical Nutrition Therapy Do? Nutrients 2024, 16, 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081217
Wei X, Zou H, Zhang T, Huo Y, Yang J, Wang Z, Li Y, Zhao J. Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: What Can Medical Nutrition Therapy Do? Nutrients. 2024; 16(8):1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081217
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Xiaoyi, Hong Zou, Tingting Zhang, Yanling Huo, Jianzhong Yang, Zhi Wang, Yu Li, and Jiuxiang Zhao. 2024. "Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: What Can Medical Nutrition Therapy Do?" Nutrients 16, no. 8: 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081217
APA StyleWei, X., Zou, H., Zhang, T., Huo, Y., Yang, J., Wang, Z., Li, Y., & Zhao, J. (2024). Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: What Can Medical Nutrition Therapy Do? Nutrients, 16(8), 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16081217