Abstract
High-fat diets (HFDs) have pervaded modern dietary habits, characterized by their excessive saturated fat content and low nutritional value. Epidemiological studies have compellingly linked HFD consumption to obesity and the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Moreover, the synergistic interplay of HFD, obesity, and diabetes expedites the aging process and prematurely fosters age-related diseases. However, the underlying mechanisms driving these associations remain enigmatic. One of the most conspicuous hallmarks of aging is the accumulation of highly inflammatory senescent cells, with mounting evidence implicating increased cellular senescence in the pathogenesis of age-related diseases. Our hypothesis posits that HFD consumption amplifies senescence burden across multiple organs. To scrutinize this hypothesis, we subjected mice to a 6-month HFD regimen, assessing senescence biomarker expression in the liver, white adipose tissue, and the brain. Aging is intrinsically linked to impaired cellular stress resilience, driven by dysfunction in Nrf2-mediated cytoprotective pathways that safeguard cells against oxidative stress-induced senescence. To ascertain whether Nrf2-mediated pathways shield against senescence induction in response to HFD consumption, we explored senescence burden in a novel model of aging: Nrf2-deficient (Nrf2+/−) mice, emulating the aging phenotype. Our initial findings unveiled significant Nrf2 dysfunction in Nrf2+/− mice, mirroring aging-related alterations. HFD led to substantial obesity, hyperglycemia, and impaired insulin sensitivity in both Nrf2+/− and Nrf2+/+ mice. In control mice, HFD primarily heightened senescence burden in white adipose tissue, evidenced by increased Cdkn2a senescence biomarker expression. In Nrf2+/− mice, HFD elicited a significant surge in senescence burden across the liver, white adipose tissue, and the brain. We postulate that HFD-induced augmentation of senescence burden may be a pivotal contributor to accelerated organismal aging and the premature onset of age-related diseases.
Keywords:
senescence; stress resistance; obesity; unhealthy diet; prediabetes; high-fat diet; endothelial cells; ageing 1. Introduction
As the global population undergoes a remarkable demographic transformation marked by a substantial increase in life expectancy, society faces unprecedented challenges associated with unhealthy aging [1,2,3,4,5,6]. The longevity revolution brings forth a pressing concern: the escalating burden of age-related diseases exacerbated by lifestyle risk factors [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16]. These diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disorders, and diseases of the central nervous system, pose substantial threats to the well-being of older individuals and the sustainability of healthcare systems worldwide [17,18,19,20,21].
A critical dimension of aging is the profound impact of lifestyle choices, particularly dietary habits [5,20,22,23,24,25,26], on the trajectory of aging and the risk of age-related diseases [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39]. In this context, high-fat diets (HFDs) have emerged as a pervasive element of modern dietary patterns, characterized by their excessive consumption of saturated fats and relatively low nutritional value [40,41,42,43]. Epidemiological studies have compellingly established a robust association between HFD consumption, obesity, and the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) [44,45,46,47,48]. These findings, also supported by the results of preclinical studies, underscore the intimate connection between dietary choices and metabolic health, as well as their potential influence on the aging process [49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56]. What further compounds the challenges posed by HFDs, obesity, and diabetes is their synergistic interplay in accelerating the aging process and promoting the premature emergence of age-related diseases [57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67]. Despite the compelling epidemiological evidence linking these factors, the intricate mechanisms that drive these associations remain insufficiently understood [42,43,68,69,70,71,72,73].
One of the most prominent hallmarks of aging is the accumulation of highly inflammatory senescent cells [74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85]. These cells are characterized by an irreversible cell cycle arrest and the secretion of a plethora of pro-inflammatory mediators known as the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) [86,87,88]. The emergence of cellular senescence is a multifaceted process, influenced by factors such as oxidative stress-mediated DNA damage [89,90] and mitochondrial damage [91,92]. Increasing evidence supports the pivotal role of cellular senescence in the pathogenesis of a wide range of age-related diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular disorders, vascular cognitive impairment (VCI), and neurodegenerative conditions [93,94,95,96,97,98], primarily through the promotion of chronic low-grade inflammation, aptly termed “inflammaging” [99,100,101]. Thus, investigating the extent to which HFD consumption amplifies senescence burden across multiple organs becomes crucial in elucidating the mechanisms driving accelerated, unhealthy aging and the development of age-related diseases [102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112].
Impaired stress resilience, the incapacity to restore homeostasis following exposure to stressful conditions, is a hallmark of aging and plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of various age-related diseases [113,114,115]. A critical and evolutionarily conserved cellular mechanism responsible for maintaining redox homeostasis is the Nuclear factor-erythroid-2-related factor (Nrf2)-antioxidant response element (ARE) signaling pathway [116]. Nrf2 is a transcription factor that orchestrates the coordinated expression of numerous antioxidant and DNA repair genes, conferring cytoprotective effects against oxidative damage during periods of stress [117]. Significantly, aging is associated with Nrf2 dysfunction [117,118]. Furthermore, our previous research has demonstrated that the adverse consequences of high-fat diet (HFD) consumption, including impaired endothelial function, cerebral blood flow regulation, blood-brain barrier disruption, neuroinflammation, and cognitive dysfunction, are exacerbated in mouse models with Nrf2 deficiency, effectively mimicking the aging phenotype [59,119]. Nrf2 knockout mice fed a HFD exhibit elevated levels of SASP factors such as IL-1β and TNFα, compared to their wild-type counterparts [119]. Against this backdrop, we postulate that Nrf2 deficiency may accelerate aging by exacerbating cellular senescence.
The present study was designed to investigate whether HFD consumption, leading to obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus, amplifies senescence burden across multiple organs. Additionally, we hypothesized that age-related Nrf2 dysfunction further magnifies the deleterious effects of HFD on senescence. While Nrf2 knockout mice (Nrf2−/−) have yielded invaluable insights into the protective role of Nrf2 in age-related diseases, they do not entirely replicate physiological aging, where there is a partial rather than complete loss of Nrf2 activity. Thus, in this study, we conducted experiments using heterozygous Nrf2+/− mice, characterized by partial Nrf2 activity loss. These mice, along with their wildtype littermates, were subjected to a 6-month HFD regimen, and subsequently, senescence burden in the liver, white adipose tissue, and the brain was assessed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Treatment
To elucidate the interplay between metabolic stress, impaired stress resilience and senescence in a mouse model of accelerated aging with partial Nrf2 deficiency, we created heterozygous Nrf2 knock-out (Nrf2+/−) mice on a p16-3MR background. The p16-3MR senescence reporter mouse model was developed by Dr. Judith Campisi at the Buck Institute on Aging. These mice express the 3MR transgene construct containing luciferase, red fluorescent protein, and thymidine kinase under the control of p16 promoter [120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128]. Crossbreeding was conducted between p16-3MR mice and Nrf2 homozygous knock-out mice (Jackson Labs, Farmington, CT, B6.129X1-Nfe2l2tm1Ywk/J) to generate the Nrf2+/− mice on the p16-, 3MR background. For genotyping, DNA was extracted from ear punches and PCR was performed using the Red Extract-N-Amp PCR kit (Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA). The primers used for the PCR include: GCC TGA GAG CTG TAG GCC C (common forward primer), GGA ATG GAA AAT AGC TCC TGC C (WT reverse) and GAC AGT ATC GGC CTC AGG AA (mutant reverse) (representative genotyping figure differentiating the homozygous and heterozygous Nrf2 mice is provided in Supplementary Figure S1). Wildtype littermates served as controls (Nrf2+/+ mice).
Between 4 to 6 months of age, both Nrf2+/+ and Nrf2+/− mice (15 males and 14 females, total n = 29) were randomly assigned to one of two dietary groups: a standard chow diet (SD, containing 10% calories from fat) or a high-fat diet (HFD, consisting of 60% calories from fat; Research Diets Inc. New Brunswick, NJ, D12450B). The dietary regimen continued for a duration of 6 months, with the mice having ad-libitum access to both food and water. Throughout the experimental period, bi-weekly body weight measurements were recorded. Upon completion of the 6-month treatment period, all animals underwent perfusion with ice-cold PBS. Subsequently, brain, epididymal fat, and liver tissues were collected, rapidly frozen in liquid nitrogen, and preserved at −80 °C until further analysis. The animal protocols adhered to the ethical guidelines and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (Protocol number#21-030, approval date—5 December 2021) at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center.
2.2. Fasting Glucose and Insulin Measurements
During the fifth month of dietary intervention, we collected blood samples from overnight-fasted animals to measure glucose levels using the OneTouch Ultra Blue glucometer and insulin levels using the Ultra-Sensitive Mouse Insulin ELISA Kit from CystalChem, Elk Grove Village, IL. To assess insulin resistance, we calculated the Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance (HOMA-IR) index using the formula [fasting serum glucose × fasting serum insulin/22.5].
2.3. Nrf2 Activity Assay
Nuclear proteins were isolated from frozen liver and cortex samples using the Nuclear Extraction Kit from Active Motif, Carlsbad, CA, USA. We quantified the protein concentrations using the Micro BCA assay from Thermo Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA. Equal concentrations of isolated nuclear protein (30 µg) were employed to assess Nrf2 DNA-binding capability using the TransAM Nrf2 transcription factor assay kit from Active Motif. In brief, nuclear protein extracts were added to a 96-well plate coated with antioxidant-response element (ARE) sequence oligos and incubated at room temperature for 1 h. After washes to remove unbound proteins, anti-Nrf2 antibodies (1:1000) were added to the wells and incubated for 1 h. Following further washes, HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies were added and incubated for another hour. After additional washes, a substrate solution was added for color development, and optical density (OD) values were measured at 450 nm using a Tecan Spark multimode microplate reader.
2.4. In Vivo Bioluminescence Measurements
Mice were injected with 15 μg of Xenolight RediJect Coelentarazine h intraperitoneally. After 25 min, the mice were anesthetized with isofluorane, and luminescence was measured with a Xenogen IVIS-200 Optical in vivo imaging System (5 min exposure time).
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
Brains collected after perfusion with ice-cold PBS were fixed in 4% PFA for 24 h and subsequently cryoprotected through immersion in 30% sucrose, followed by embedding in OCT medium. Frozen brain OCT blocks were cryosectioned at a thickness of 35 µm, and the sections were stored in cryoprotectant solution at −20 °C until staining. The free-floating sections were immunolabeled using an anti-endomucin primary antibody (1:75, EMD Millipore, Burlington, MA, MAB2624) and an anti-rat Alexa 488 secondary antibody (1:500, Invitrogen, Molecular Probes, Carlsbad, CA, USA) to identify capillary endothelial cells in the mouse brain. Nuclear counterstaining was performed using DAPI (Sigma). Confocal images were acquired using a Leica SP8 MP confocal laser scanning microscope. Senescent endothelial cells were identified in 20× images by co-localizing RFP (p16+ senescent cells) with Alexa 488 green fluorescence signal in the hippocampal region. Double-positive cells were quantified using the Image J count plugin and expressed as the average number of senescent endothelial cells per field in each group.
2.6. Real-Time PCR
RNA extraction from frozen tissue samples was carried out using the RNeasy Miniprep kit from Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA. Equal amounts of RNA (1 µg) were reverse transcribed to cDNA using the High-Capacity RNA to cDNA kit from Applied Biosystems, San Francisco, CA, USA. Real-time PCR reactions were performed in a QuantStudio 12K Flex Real-Time PCR System from Applied Biosystems using validated TaqMan probes for p16, Nrf2, and the housekeeping gene, β-actin (Applied Biosystems), with 50 ng cDNA per reaction as previously reported [119,129]. Data were analyzed using the 2ΔΔCT method, where CT represents the threshold cycle.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All data are presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test or Student’s t-test as appropriate. A p-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Partial Nrf2 Ablation in Nrf2+/− Mice and Its Impact on Nrf2 Activity
To assess whether Nrf2+/− mice exhibited a physiological age-related reduction in Nrf2 rather than complete ablation, we examined Nrf2 transcript levels and activity in both the brain cortex and liver tissues. As anticipated, Nrf2+/− mice displayed an approximate 50% reduction in Nrf2 mRNA levels in the cortex (Figure 1A). Similarly, we observed a significant decrease in Nrf2 activity, as indicated by DNA binding ability in nuclear extracts, in the cortex and a nearly significant reduction in Nrf2 activity in the liver (Figure 1B,C).
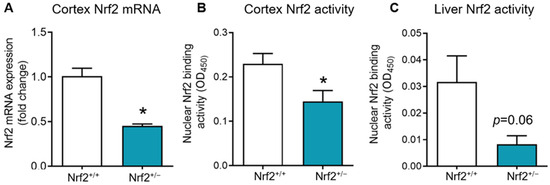
Figure 1.
Nrf2 gene expression and DNA binding activity in Nrf2+/+ and Nrf2+/− mice. (A): Nrf2 mRNA levels in the cortex of Nrf2+/+ and Nrf2+/− mice (n = 3–5). (B,C): DNA binding ability of Nrf2 assessed in the nuclear extracts of the cortex and liver of Nrf2+/+ (n = 4) and Nrf2+/− (n = 4–5) mice using Trans−AM motif assay. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. * indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05) from Nrf2+/+ mice.
3.2. Metabolic Parameters in Nrf2+/− Mice and the Effects of HFD
Next, we investigated the impact of partial Nrf2 ablation and HFD on metabolic parameters. Both Nrf2+/+ and Nrf2+/− mice exhibited comparable increases in final body weight and fasting glucose levels when compared with their SD controls (Figure 2A,B). HFD treatment also induced similar increases in fasting insulin levels and HOMA-IR, a measure of insulin resistance, in both groups, although it reached statistical significance only in the Nrf2+/+ group when compared to their SD controls (Figure 2C,D).
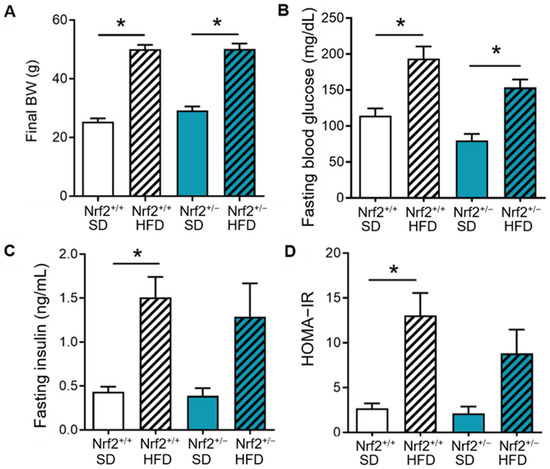
Figure 2.
Impact of partial Nrf2 ablation and HFD on metabolic parameters. Nrf2+/+ and Nrf2+/− mice were fed with standard diet (SD) or high-fat diet (HFD) for 20 weeks. (A–D): Final body weight (BW), fasting blood glucose, fasting insulin, and HOMA-IR index measured in Nrf2+/+ (n = 7–9) and Nrf2+/− (n = 6–7) mice after 20 weeks of respective dietary treatment. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. * denotes a significant difference (p < 0.05) from the indicated group.
3.3. Impact of Partial Nrf2 Ablation on Senescence Induction in Various Tissues
Previously, we demonstrated that both aging and HFD-induced oxidative stress promoted the induction of p16-mediated senescence in Nrf2 knock-out mice (complete ablation of Nrf2 gene and activity) [119,129]. In this study, we aimed to investigate whether partial Nrf2 ablation, which mimics physiological aging, could recapitulate the effects of HFD-induced metabolic stress on senescence. First, we measured luminescence signals from renilla luciferase expressed in p16+ cells as a surrogate marker for senescence in vivo. HFD treatment significantly increased whole-body luminescence in Nrf2+/− mice compared to Nrf2+/+ group (Supplementary Figure S2). Next, we assessed the expression levels of the well-established senescence marker, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16INK4a (Cdkn2a), in multiple tissues.
In the liver, HFD did tended to increase Cdkn2a expression in the Nrf2+/+ group, but this change did not reach statistical significance. In contrast, we observed a several-fold increase in p16 mRNA levels in Nrf2+/− mice on HFD compared to SD-fed Nrf2+/− mice and both Nrf2+/+ groups (Figure 3A), suggesting a significant interaction between diet and partial Nrf2 deficiency in accelerating hepatic senescence. In the visceral adipose tissue (eWAT), HFD significantly increased Cdkn2a expression both in Nrf2+/+ and Nrf2+/− mice, with Nrf2 deficiency not exerting an additive effect (Figure 3B).
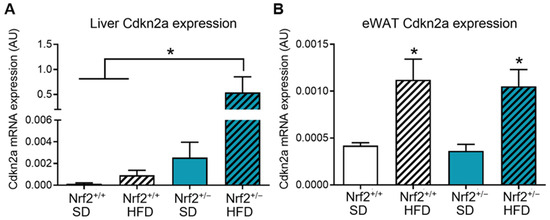
Figure 3.
Partial Nrf2 ablation increases the expression of senescence markers in peripheral tissues. Analysis of Cdkn2a (p16INK4a) gene expression in the liver (A) and epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT) (B) samples from Nrf2+/+ and Nrf2+/− mice after 20 weeks of consuming a standard diet (SD) or high fat diet (HFD) (n = 3−6/group). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. * indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05) from the indicated group.
Given that senescent cells constitute a rare population in the brain (comprising 1–2% of total brain cells), we employed mRFP as a biomarker to identify and quantify p16+ senescent cells in the brain, focusing on senescent endothelial cells in particular, as recent single-cell sequencing studies indicate their heightened susceptibility to senescence in the aging brain [130]. The analysis of p16+/endomucin+ cells revealed that in the hippocampi of Nrf2+/+ mice, a significant increase in the number of senescent endothelial cells was not observed following HFD. Conversely, in the hippocampi of Nrf2+/− mice, HFD resulted in a noteworthy increase in the population of senescent endothelial cells (Figure 4A,B). Overall, our findings suggest that partial Nrf2 ablation was sufficient to accelerate metabolic stress-induced senescence in multiple organs, mimicking the aging phenotype.
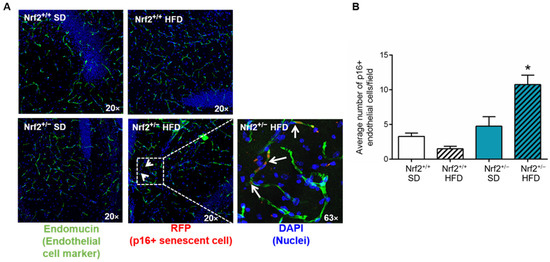
Figure 4.
Induction of senescence in brain microvascular endothelial cells due to partial Nrf2 ablation. (A) Representative images of immunofluorescent labeling used to detect p16-RFP in endomucin+ endothelial cells in the hippocampus of Nrf2+/+ and Nrf2+/− mice after 20 weeks of consuming a standard diet (SD) or high fat diet (HFD) (n = 4/group). White arrows indicate the presence of mRFP positive senescent endothelial cells in the hippocampus. (B) Quantification of the p16-RFP+/endomucin+ endothelial cells in the hippocampi of all the groups. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05.
4. Discussion
In this study, we delved into the intricate relationship between HFDs, partial Nrf2 deficiency, and cellular senescence to decipher their collective impact on the process of aging. Our investigation yielded several important initial findings that collectively contribute to our understanding of the complex mechanisms governing senescence and unhealthy aging. We observed that partial Nrf2 ablation in Nrf2+/− mice closely resembled the physiological age-related reduction in Nrf2, indicating a relevant model for exploring the influence of moderate Nrf2 deficiency on senescence induction. Additionally, both Nrf2+/+ and Nrf2+/− mice exhibited similar metabolic responses to HFD, including increases in body weight and fasting glucose levels, with a tendency toward insulin resistance. Notably, the effects of HFD and Nrf2 deficiency on senescence markers varied across tissues, highlighting the intricate interplay of factors in different physiological contexts. Importantly, in the brain, we uncovered a significant increase in senescent endothelial cells in Nrf2+/− mice exposed to HFD, a finding with potential implications for age-related cognitive decline.
Aging is a multifaceted process influenced by a dynamic interplay of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors, all of which collectively contribute to the emergence of age-related diseases. Among these factors, dietary choices, notably the consumption of high-fat diets (HFDs), have emerged as a focal point of scientific inquiry due to their pronounced association with conditions such as obesity, diabetes, accelerated aging, and heightened susceptibility to age-related diseases, leading to increased morbidity and mortality [51,55,69,72,115,131,132,133,134,135,136]. In the context of unhealthy aging, our study endeavors to illuminate the intricate relationship between HFDs, Nrf2 deficiency, and the phenomenon of cellular senescence.
The age-related decline in Nrf2 or its homolog levels and activity has been well-documented across various tissue types [137,138,139,140] and in diverse species, spanning from invertebrates to humans [140,141,142,143]. It can be attributed to a convergence of factors that collectively contribute to Nrf2 dysfunction and impaired stress resilience. Under normal physiological conditions, Nrf2 is kept at low levels in the cytoplasm through interaction with the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, primarily composed of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein (KEAP1). This complex plays a pivotal role in negatively regulating Nrf2 by facilitating its ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation. However, increased oxidative stress induces conformational changes in the Nrf2-KEAP1 complex prevent ubiquitination, leading to the accumulation of Nrf2 and its subsequent translocation to the nucleus. In the nucleus, Nrf2 forms heterodimers with small MAF (sMAF) proteins and binds to antioxidant response element (ARE) sequences in gene promoter regions, initiating the transcription of crucial cytoprotective genes [144]. In aging, the dysregulation of this finely tuned system, driven by factors such as alterations in KEAP1-Nrf2 interactions, and the diminished availability of critical cofactors, ultimately contributes to Nrf2 dysfunction and impaired stress resilience [119,129,138,145]. These intricate molecular changes collectively underlie the age-related decline in Nrf2 activity, rendering cells and tissues more vulnerable to the detrimental effects of oxidative stresses. Our results demonstrate that partial Nrf2 ablation in Nrf2+/− mice closely mimics the physiological age-related reduction in Nrf2, evident by a significant decrease in Nrf2 mRNA levels and Nrf2 activity in both the cortex and liver tissues. This partial loss of Nrf2 function in Nrf2+/− mice allowed us to explore the impact of moderate Nrf2 deficiency, which is more representative of physiological aging, on senescence induction.
Impairment in Nrf2 signaling during the aging process leads to maladaptive stress responses and stands as a pivotal contributor to the pathogenesis of age-related diseases [119,138,146,147]. Metabolic stress is a well-established factor in promoting cellular senescence [102,148,149]. Our studies underscore the significant role of Nrf2 in preserving redox homeostasis [138,141] and mitigating cellular senescence under conditions of HFD-induced metabolic stress, which closely resemble the conditions of unhealthy aging in humans. Specifically, we observed that partial Nrf2 deficiency (Nrf2+/−) was adequate to exacerbate HFD-induced senescence within cerebromicrovascular endothelial cells situated in the hippocampus—a brain region vital for the regulation of learning and memory function. These findings expand upon our prior research, where complete Nrf2 ablation (Nrf2−/−) induced senescence in cerebral arteries, hastening cerebromicrovascular dysfunction and cognitive decline in HFD-fed mice [119]. Furthermore, in addition to metabolic stressors, complete absence of Nrf2 signaling (Nrf2−/−) amplified the impact of age-related oxidative stress on senescence and inflammation within the cerebral vasculature [129]. Taken together, these collective findings underscore the protective role of Nrf2 signaling in mitigating senescence among cerebromicrovascular endothelial cells, particularly in the context of unhealthy brain aging and obesity-related metabolic stressors.
Dysfunction in Nrf2 has been intricately linked to the development and progression of age-related diseases, including the pathogenesis of VCI [59,119,129,138,145,150]. Notably, previous investigations conducted by our research group have provided compelling evidence that Nrf2 deficiency exacerbates metabolic stress-induced cerebromicrovascular dysfunction [59,119,150]. This dysfunction is characterized by heightened blood-brain barrier permeability, neurovascular uncoupling, and neuroinflammation [59,119]. It is plausible that this accelerated aging phenotype observed in the brain due to Nrf2 deficiency can be mechanistically attributed to the induction of senescence under metabolic stress conditions within the cerebral microcirculation [119,129].
Supporting this hypothesis, substantial evidence indicates that senescence exerts detrimental effects on endothelial-dependent dilation by diminishing endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activity [95,151], impairs angiogenesis [138], reduces the expression of tight junction proteins [152], and increases barrier permeability [153]. Furthermore, in addition to directly promoting tissue dysfunction and inflammation, senescent cells also profoundly influence the function and phenotype of neighboring cells through the paracrine secretion of SASP factors, which amplify the effects of a small population of senescent cells. Notably, robust evidence suggests that the elimination of senescent cells from the brain, utilizing various senolytic strategies, can effectively restore blood-brain barrier integrity, enhance the regulation of cerebral blood flow, and augment brain capillarization in a range of aging and accelerated brain aging models [95,97,121,154]. These improvements are closely correlated with heightened cognitive performance. Importantly, these models encompass not only mouse models of aging but also instances of cognitive decline induced by whole-brain irradiation and chemotherapy [97,121]. Therefore, further investigations are warranted to rigorously evaluate the efficacy of senolytic treatments within the context of HFD-induced accelerated brain senescence, representing a critical area that merits comprehensive exploration.
An intriguing finding of our study pertains to the differential impact of HFD and Nrf2 deficiency on senescence burden in various tissues. Notably, in the liver, HFD did not significantly elevate senescence burden in Nrf2+/+ mice. However, in Nrf2+/− mice, we observed a substantial increase in senescence burden upon exposure to HFD, suggesting a robust interaction between diet and Nrf2 deficiency in driving hepatic senescence. Furthermore, in the context of visceral adipose tissue, HFD induced senescence regardless of genotype, with no additional impact of Nrf2 deficiency. These tissue-specific variations underscore the complexity of senescence regulation influenced by distinct factors and emphasize the necessity for further investigations into their specific molecular mechanisms. Importantly, understanding the implications of liver and adipose senescence for brain aging phenotypes is essential and warrants focused exploration in future research endeavors. Moreover, it is noteworthy that SASP factors secreted by senescent cells [84,155] within the liver and adipose tissue are likely to exert significant influences on BBB integrity [156,157,158,159] and cerebromicrovascular endothelial function and phenotype [160,161,162,163], further accentuating the intricate interplay between these organs in the context of unhealthy aging.
5. Conclusions
In summary, our study aligns with the conclusions of previous research, highlighting the detrimental effects of HFDs on the aging process. Our study provides valuable insights into the complex web of interactions between HFDs, Nrf2 deficiency, and cellular senescence in the context of unhealthy aging (Figure 5). These findings enhance our understanding of the multifaceted mechanisms governing senescence and the potential implications for age-related diseases. Our research has underscored the pivotal role of Nrf2 in alleviating senescence, particularly under conditions of metabolic stress affecting the cerebral microcirculation. This emphasizes the potential significance of Nrf2 in mitigating age-related cognitive decline. To unravel the complexities of the involved molecular pathways and to explore potential therapeutic interventions targeting the Nrf2-ARE pathway for ameliorating the detrimental consequences of unhealthy aging, further in-depth investigations are warranted.
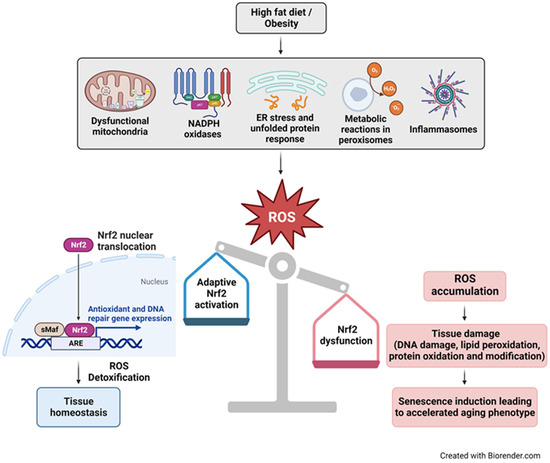
Figure 5.
Schematic illustration of the relationship between consumption of HFD/obesity, oxidative stress, Nrf2 deficiency, and cellular senescence in accelerated aging. Dysfunctional mitochondria, NADPH oxidases, ER stress from misfolded proteins, metabolic processes in peroxisomes, and inflammasomes are major sources of increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels in obesity. Nrf2 plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular redox homeostasis. Under conditions of oxidative stress, Nrf2 is released from the Keap1−Cul3−RBX1 complex, after which it translocates into the nucleus, forms heterodimers with small Maf proteins (sMaf), and binds to antioxidant response elements (AREs). This activation leads to the transcription of genes encoding antioxidant enzymes, DNA repair mechanisms and proteins that confer anti-inflammatory effects, facilitating ROS detoxification and restoration of cellular homeostasis. Conversely, impaired Nrf2 activation results in the accumulation of toxic levels of ROS, inducing macromolecular damage like DNA breaks, and triggering senescence, ultimately leading to an accelerated aging phenotype.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of these molecular pathways, it becomes increasingly imperative to translate these discoveries into practical strategies for promoting healthy aging. Aligning with well-established knowledge, the pivotal role of dietary choices in fostering healthy aging warrants heightened attention. Experts in the field strongly advocate for the maintenance of a well-balanced and nutritionally rich diet, one replete with antioxidants and anti-inflammatory foods, which play a fundamental role in supporting Nrf2 activity while counteracting oxidative stress and inflammation [72,164]. Specifically, consideration should be given to phytochemicals such as sulforaphane from broccoli, curcumin from turmeric, and resveratrol from grapes which have shown promise in activating Nrf2 and exerting beneficial effects on aging-related processes. Some of the putative mechanisms behind the anti-aging effects of these phytochemicals include increased anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, improved mitochondrial function and improved autophagy and proteostasis [165,166]. Findings from clinical studies also support this by demonstrating a positive association between higher phytochemical intake with lowered risk for cardiometabolic and neurodegenerative diseases [167,168]. Such dietary choices are pivotal in mitigating metabolic stress and the associated risks that can accelerate senescence. To fully harness the potential of these insights, it is imperative that we invest in further research and clinical studies aimed at evaluating the effectiveness of dietary interventions designed to enhance Nrf2-mediated cellular resilience and mitigate the onset of cellular senescence. In doing so, we can aim to transform scientific knowledge into practical, evidence-based strategies firmly grounded in geroscience. These strategies empower individuals to embrace and embark on the path of healthy aging.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu16070952/s1; Figure S1: Representative pictures of agarose gel electrophoresis for genotyping Nrf2 transgenic mice. The Nrf2 homozygous knock out were identified with a mutant band at 400 bp while the Nrf2 heterozygous mice expressed both the WT and the mutant bands at 262 and 400 bp, respectively. Figure S2. Partial Nrf2 loss increases whole-body senescence. (A) Mice were injected with coelentarazine, and luminescence was quantified using a Xenogen IVIS Imaging system 25 min after the injection with a 5-min exposure time. Representative images from Nrf2+/+ and Nrf2+/− mice on HFD are shown. (B) Quantification of luminescence counts indicates a significant incprease in senescent cell burden in Nrf2+/− mice compared to Nrf2+/+ mice on HFD (n = 5/group). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. * indicates a significant difference (p < 0.05) from the indicated group.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.U. and A.C.; methodology, P.B., T.K., Z.U. and A.C.; validation, P.B., T.K., Z.U. and A.C.; formal analysis, P.B., T.K., R.G., A.N.T., S.T. and A.Y.; investigation, P.B., T.K., R.G., A.N.T., S.T. and A.Y.; resources, Z.U. and A.C.; data curation, P.B., T.K., R.G., A.N.T., S.T. and A.Y.; writing—original draft preparation, P.B. and Z.U.; writing—review and editing, P.B. and Z.U.; visualization, P.B. and Z.U.; supervision, Z.U. and A.C.; project administration, Z.U. and A.C.; funding acquisition, Z.U. and A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the American Heart Association (AHA834339 to AN, CDA1048544 to PB and CDA941290 to ST), the Oklahoma Center for the Advancement of Science and Technology, the National Institute on Aging (RF1AG072295, R01AG055395, R01AG068295; R01AG070915, R03AG070479, K01AG073613 and K01AG073614), the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (R01NS100782), the National Cancer Institute (R01CA255840), the Oklahoma Shared Clinical and Translational Resources (U54GM104938) with an Institutional Development Award (IDeA) from NIGMS, the Presbyterian Health Foundation, the Reynolds Foundation, the Oklahoma Nathan Shock Center (P30AG050911), and the Cellular and Molecular GeroScience CoBRE (P20GM125528). The authors would also like to thank Unity Biotechnology, Inc. for providing the p16-3MR mouse model.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal protocols adhered to the ethical guidelines and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (Protocol number#21-030, approval date—5 December 2021) at the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data for further analysis will be available to interested researchers upon direct request to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Valsdottir, V.; Magnusdottir, B.B.; Chang, M.; Sigurdsson, S.; Gudnason, V.; Launer, L.J.; Jonsdottir, M.K. Cognition and brain health among older adults in Iceland: The AGES-Reykjavik study. Geroscience 2022, 44, 2785–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dinther, M.; Schram, M.T.; Jansen, J.F.A.; Backes, W.H.; Houben, A.; Berendschot, T.; Schalkwijk, C.G.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; van Oostenbrugge, R.J.; Staals, J. Extracerebral microvascular dysfunction is related to brain MRI markers of cerebral small vessel disease: The Maastricht Study. Geroscience 2022, 44, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doan, L.N.; Takata, Y.; Hooker, K.; Mendez-Luck, C.; Irvin, V.L. Trends in Cardiovascular Disease by Asian American, Native Hawaiian, and Pacific Islander Ethnicity, Medicare Health Outcomes Survey 2011–2015. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Botoseneanu, A.; Markwardt, S.; Nagel, C.L.; Allore, H.G.; Newsom, J.T.; Dorr, D.A.; Quinones, A.R. Multimorbidity Accumulation Among Middle-Aged Americans: Differences by Race/Ethnicity and Body Mass Index. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, e89–e97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, Z.S.; Gioscia-Ryan, R.A.; Justice, J.N.; Lubieniecki, K.L.; Hutton, D.A.; Rossman, M.J.; Zigler, M.C.; Seals, D.R. Lifelong physical activity attenuates age- and Western-style diet-related declines in physical function and adverse changes in skeletal muscle mass and inflammation. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 157, 111632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Lai, E.T.C.; Leung, G.; Ho, S.C.; Woo, J. Intrinsic capacity and 10-year mortality: Findings from a cohort of older people. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 167, 111926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.S.; Liu, I.T.; Li, C.C.; Sun, Z.J.; Chao, T.H.; Liang, F.W.; Wu, C.H. Optimal body composition indices cutoff values based on all-cause mortality in the elderly. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 171, 112026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feter, N.; Mielke, G.I.; Leite, J.S.; Brown, W.J.; Coombes, J.S.; Rombaldi, A.J. Physical activity in later life and risk of dementia: Findings from a population-based cohort study. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 143, 111145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberia-Latasa, M.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; de la Fuente-Arrillaga, C.; Bes-Rastrollo, M.; Carlos, S.; Gea, A. Predictors of total mortality and their differential association on premature or late mortality in the SUN cohort. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 172, 112048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobreva, I.; Marston, L.; Mukadam, N. Which components of the Mediterranean diet are associated with dementia? A UK Biobank cohort study. Geroscience 2022, 44, 2541–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, A.P.; Nagaraj, N.; Osman, D.H.; Rabinovitch, P.S.; Marcinek, D.J. Are fat and sugar just as detrimental in old age? Geroscience 2021, 43, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroto-Rodriguez, J.; Delgado-Velandia, M.; Ortola, R.; Carballo-Casla, A.; Garcia-Esquinas, E.; Rodriguez-Artalejo, F.; Sotos-Prieto, M. Plant-based diets and risk of frailty in community-dwelling older adults: The Seniors-ENRICA-1 cohort. Geroscience 2023, 45, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, Y.O.; Bithi, N.; Yang, J.; Link, C.; Zhang, A.; Baron, B.; Maina, E.; Hine, C. A long-term obesogenic high-fat diet in mice partially dampens the anti-frailty benefits of late-life intermittent fasting. Geroscience 2023, 45, 1247–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, V.M.; Sommerer, Y.; Kalies, C.H.; Spira, D.; Bertram, L.; Demuth, I. Vitamin D supplementation is associated with slower epigenetic aging. Geroscience 2022, 44, 1847–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, Y.O.; Bithi, N.; Link, C.; Yang, J.; Schugar, R.; Llarena, N.; Brown, J.M.; Hine, C. Late-life intermittent fasting decreases aging-related frailty and increases renal hydrogen sulfide production in a sexually dimorphic manner. Geroscience 2021, 43, 1527–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duregon, E.; Pomatto-Watson, L.; Bernier, M.; Price, N.L.; de Cabo, R. Intermittent fasting: From calories to time restriction. Geroscience 2021, 43, 1083–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrelly, C. 50 years of the “war on cancer”: Lessons for public health and geroscience. Geroscience 2021, 43, 1229–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, J.T.; Thao, L.T.P.; Murray, A.M.; Callander, E.; Carr, P.R.; Nelson, M.R.; Wolfe, R.; Woods, R.L.; Reid, C.M.; Shah, R.C.; et al. Prediction of disability-free survival in healthy older people. Geroscience 2022, 44, 1641–1655. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Neumann, J.T.; Thao, L.T.P.; Callander, E.; Chowdhury, E.; Williamson, J.D.; Nelson, M.R.; Donnan, G.; Woods, R.L.; Reid, C.M.; Poppe, K.K.; et al. Cardiovascular risk prediction in healthy older people. Geroscience 2022, 44, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, S.; Pullen, H.; Ritchie, C.W.; Shannon, O.M.; Stevenson, E.J.; Muniz-Terrera, G. Mediterranean diet and structural neuroimaging biomarkers of Alzheimer’s and cerebrovascular disease: A systematic review. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 172, 112065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fekete, M.; Major, D.; Feher, A.; Fazekas-Pongor, V.; Lehoczki, A. Geroscience and pathology: A new frontier in understanding age-related diseases. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2024, 30, 1611623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, M.U.; Khan, M.K.I.; Riaz, S.; Nazir, A.; Maan, A.A.; Amin, U.; Saeed, F.; Afzaal, M. Role of fruits in aging and age-related disorders. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 162, 111763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, G.N.; Sanlier, N. The relationship between nutrition and depression in the life process: A mini-review. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 172, 112072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezzati, A.; Pak, V.M. The effects of time-restricted eating on sleep, cognitive decline, and Alzheimer’s disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2023, 171, 112033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcez, M.L.; Bellettini-Santos, T.; Schiavo, G.L.; Calixto, K.V.; Mina, F.; Medeiros, E.B.; Zabot, G.C.; Pereira, N.S.; Nascimento, N.B.D.; Tomaz, D.B.; et al. Long-term administration of soft drink causes memory impairment and oxidative damage in adult and middle-aged rats. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 166, 111873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, F.Y.; Peng, L.N.; Lee, W.J.; Chen, L.K. Higher dietary diversity and better healthy aging: A 4-year study of community-dwelling middle-aged and older adults from the Taiwan Longitudinal Study of Aging. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 168, 111929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunan, E.; Wright, C.L.; Semola, O.A.; Subramanian, M.; Balasubramanian, P.; Lovern, P.C.; Fancher, I.S.; Butcher, J.T. Obesity as a premature aging phenotype—Implications for sarcopenic obesity. Geroscience 2022, 44, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodgers, J.; Cuevas, A.G.; Williams, D.R.; Kawachi, I.; Subramanian, S.V. The relative contributions of behavioral, biological, and psychological risk factors in the association between psychosocial stress and all-cause mortality among middle- and older-aged adults in the USA. Geroscience 2021, 43, 655–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, L.T.; Jiang, Y.W.; Feng, L.; Pan, A.; Koh, W.P. Dietary Total Antioxidant Capacity and Late-Life Cognitive Impairment: The Singapore Chinese Health Study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palta, P.; Griswold, M.; Ranadive, R.; Bandeen-Roche, K.; Folsom, A.R.; Petruski-Ivleva, N.; Burgard, S.; Kucharska-Newton, A.; Windham, B.G. Midlife Cardiovascular Health and Robust Versus Frail Late-Life Status: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortola, R.; Garcia-Esquinas, E.; Sotos-Prieto, M.; Struijk, E.A.; Caballero, F.F.; Lopez-Garcia, E.; Rodriguez-Artalejo, F. Mediterranean Diet and Changes in Frequency, Severity, and Localization of Pain in Older Adults: The Seniors-ENRICA Cohorts. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merono, T.; Zamora-Ros, R.; Hidalgo-Liberona, N.; Rabassa, M.; Bandinelli, S.; Ferrucci, L.; Fedecostante, M.; Cherubini, A.; Andres-Lacueva, C. Animal Protein Intake Is Inversely Associated With Mortality in Older Adults: The InCHIANTI Study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroto-Rodriguez, J.; Delgado-Velandia, M.; Ortola, R.; Garcia-Esquinas, E.; Martinez-Gomez, D.; Struijk, E.A.; Lopez-Garcia, E.; Rodriguez-Artalejo, F.; Sotos-Prieto, M. A Mediterranean Lifestyle and Frailty Incidence in Older Adults: The Seniors-ENRICA-1 Cohort. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, 1845–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Schupf, N.; Cruz, E.; Stern, Y.; Mayeux, R.P.; Gu, Y. Association Between Mediterranean Diet and Functional Status in Older Adults: A Longitudinal Study Based on the Washington Heights-Inwood Columbia Aging Project. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, 1873–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.F.; Song, X.Y.; Pan, X.F.; Feng, L.; Luo, N.; Yuan, J.M.; Pan, A.; Koh, W.P. Association Between Combined Lifestyle Factors and Healthy Ageing in Chinese Adults: The Singapore Chinese Health Study. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 1796–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tessier, A.J.; Presse, N.; Rahme, E.; Ferland, G.; Bherer, L.; Chevalier, S. Milk, Yogurt, and Cheese Intake Is Positively Associated With Cognitive Executive Functions in Older Adults of the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 2223–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talegawkar, S.A.; Jin, Y.; Xue, Q.L.; Tanaka, T.; Simonsick, E.M.; Tucker, K.L.; Ferrucci, L. Dietary Pattern Trajectories in Middle Age and Physical Function in Older Age. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotos-Prieto, M.; Ortola, R.; Lopez-Garcia, E.; Rodriguez-Artalejo, F.; Garcia-Esquinas, E. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Physical Resilience in Older Adults: The Seniors-ENRICA Cohort. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, L.; Wang, Y.; Holland, T.; Agarwal, P.; Aggarwal, N.; Morris, M.C. DASH and Mediterranean-Dash Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) Diets Are Associated With Fewer Depressive Symptoms Over Time. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, J.K.; de Cabo, R.; Mattison, J.A. Resveratrol Blunts Mitochondrial Loss in Slow and Mixed Skeletal Muscle Phenotypes of Non-Human Primates following a Long-Term High Fat/Sugar Diet. J. Diet. Suppl. 2023, 20, 563–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.; Mirzaei, H.; Guidi, N.; Vinciguerra, M.; Mouton, A.; Linardic, M.; Rappa, F.; Barone, R.; Navarrete, G.; Wei, M.; et al. Fasting-mimicking diet prevents high-fat diet effect on cardiometabolic risk and lifespan. Nat. Metab. 2021, 3, 1342–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zong, C.; Jiang, M.; Hu, H.; Cheng, X.; Ni, J.; Yi, X.; Jiang, B.; Tian, F.; Chang, M.W.; et al. Hepatic HuR modulates lipid homeostasis in response to high-fat diet. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Francesco, A.; Choi, Y.; Bernier, M.; Zhang, Y.; Diaz-Ruiz, A.; Aon, M.A.; Kalafut, K.; Ehrlich, M.R.; Murt, K.; Ali, A.; et al. NQO1 protects obese mice through improvements in glucose and lipid metabolism. NPJ Aging Mech. Dis. 2020, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, A.; Juszczyk, D.; van Jaarsveld, C.H.M.; Gulliford, M.C. Body Mass Index and Incident Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes in Children and Young Adults: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Endocr. Soc. 2017, 1, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, J.P. The importance of weight management in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2014, 68, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosia, A.D.; Palencia, R.; Khan, S. Prevalence of hypertension and obesity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in observational studies: A systematic literature review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2013, 6, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Amiri, E.; Abdullatif, M.; Abdulle, A.; Al Bitar, N.; Afandi, E.Z.; Parish, M.; Darwiche, G. The prevalence, risk factors, and screening measure for prediabetes and diabetes among Emirati overweight/obese children and adolescents. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Hu, F.B. Epidemiology of Obesity and Diabetes and Their Cardiovascular Complications. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 1723–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachtschneider, K.M.; Schook, L.B.; Meudt, J.J.; Shanmuganayagam, D.; Zoller, J.A.; Haghani, A.; Li, C.Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, A.; Raj, K.; et al. Epigenetic clock and DNA methylation analysis of porcine models of aging and obesity. Geroscience 2021, 43, 2467–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce-Keller, A.J.; White, C.L.; Gupta, S.; Knight, A.G.; Pistell, P.J.; Ingram, D.K.; Morrison, C.D.; Keller, J.N. NOX activity in brain aging: Exacerbation by high fat diet. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, S.; Dey, A.; Yu, X.; Stranahan, A.M. Dietary obesity reversibly induces synaptic stripping by microglia and impairs hippocampal plasticity. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 51, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Labrador, R.; Trueba-Saiz, A.; Martinez-Rachadell, L.; Fernandez de Sevilla, M.E.; Zegarra-Valdivia, J.A.; Pignatelli, J.; Diaz-Pacheco, S.; Fernandez, A.M.; Torres Aleman, I. Circulating Insulin-Like Growth Factor I is Involved in the Effect of High Fat Diet on Peripheral Amyloid beta Clearance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, C.D.; Pistell, P.J.; Ingram, D.K.; Johnson, W.D.; Liu, Y.; Fernandez-Kim, S.O.; White, C.L.; Purpera, M.N.; Uranga, R.M.; Bruce-Keller, A.J.; et al. High fat diet increases hippocampal oxidative stress and cognitive impairment in aged mice: Implications for decreased Nrf2 signaling. J. Neurochem. 2010, 114, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistell, P.J.; Morrison, C.D.; Gupta, S.; Knight, A.G.; Keller, J.N.; Ingram, D.K.; Bruce-Keller, A.J. Cognitive impairment following high fat diet consumption is associated with brain inflammation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2010, 219, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreyer, S.A.; Wilson, D.L.; LeBoeuf, R.C. C57BL/6 mice fed high fat diets as models for diabetes-accelerated atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 1998, 136, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, C.L.; Pistell, P.J.; Purpera, M.N.; Gupta, S.; Fernandez-Kim, S.O.; Hise, T.L.; Keller, J.N.; Ingram, D.K.; Morrison, C.D.; Bruce-Keller, A.J. Effects of high fat diet on Morris maze performance, oxidative stress, and inflammation in rats: Contributions of maternal diet. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 35, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, D.G.A.; Faragher, R.G.A. Obesity and type-2 diabetes as inducers of premature cellular senescence and ageing. Biogerontology 2018, 19, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryder, J.R.; Northrop, E.; Rudser, K.D.; Kelly, A.S.; Gao, Z.; Khoury, P.R.; Kimball, T.R.; Dolan, L.M.; Urbina, E.M. Accelerated Early Vascular Aging Among Adolescents With Obesity and/or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucsek, Z.; Toth, P.; Tarantini, S.; Sosnowska, D.; Gautam, T.; Warrington, J.P.; Giles, C.B.; Wren, J.D.; Koller, A.; Ballabh, P.; et al. Aging exacerbates obesity-induced cerebromicrovascular rarefaction, neurovascular uncoupling, and cognitive decline in mice. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 1339–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wubishet, B.L.; Byles, J.E.; Harris, M.L.; Jagger, C. Impact of Diabetes on Life and Healthy Life Expectancy Among Older Women. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 914–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espeland, M.A.; Justice, J.N.; Bahnson, J.; Evans, J.K.; Munshi, M.; Hayden, K.M.; Simpson, F.R.; Johnson, K.C.; Johnston, C.; Kritchevsky, S.R. Eight-Year Changes in Multimorbidity and Frailty in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Associations With Cognitive and Physical Function and Mortality. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingston, A.; Byles, J.; Kiely, K.; Anstey, K.J.; Jagger, C. The Impact of Smoking and Obesity on Disability-Free Life Expectancy in Older Australians. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Cruz, L.L.; Vesentini, G.; Sinzato, Y.K.; Villaverde, A.; Volpato, G.T.; Damasceno, D.C. Effects of high-fat diet-induced diabetes on autophagy in the murine liver: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Life Sci. 2022, 309, 121012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrenbruck, A.R.; Bollinger, L.M. Role of skeletal muscle autophagy in high-fat-diet-induced obesity and exercise. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, S.; Geetha, T.; Broderick, T.L.; Babu, J.R. High Fat With High Sucrose Diet Leads to Obesity and Induces Myodegeneration. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.T.; Ferreira, L.J.D.; Macedo, A.P.A.; Santos, L.S.; Santo, D.A.E.; Codeiro, G.S.; Pereira, M.U.; Medeiros, I.O.R.; da Costa, C.A.S.; Medeiros, J.M.B. Effects of a high-fat diet on the bone structure of Wistar rats: A systematic review. Nutr. Rev. 2023, 81, 1441–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhomoibhi, T.O.; Okobi, T.J.; Okobi, O.E.; Koko, J.O.; Uhomoibhi, O.; Igbinosun, O.E.; Ehibor, U.D.; Boms, M.G.; Abdulgaffar, R.A.; Hammed, B.L.; et al. High-Fat Diet as a Risk Factor for Breast Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Cureus 2022, 14, e32309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedeke, L.; Murt, K.N.; Di Francesco, A.; Camporez, J.P.; Nasiri, A.R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Cline, G.W.; de Cabo, R.; Shulman, G.I. Sex- and strain-specific effects of mitochondrial uncoupling on age-related metabolic diseases in high-fat diet-fed mice. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernier, M.; Wahl, D.; Ali, A.; Allard, J.; Faulkner, S.; Wnorowski, A.; Sanghvi, M.; Moaddel, R.; Alfaras, I.; Mattison, J.A.; et al. Resveratrol supplementation confers neuroprotection in cortical brain tissue of nonhuman primates fed a high-fat/sucrose diet. Aging 2016, 8, 899–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, J.S.; Perez, E.J.; Fukui, K.; Carpenter, P.; Ingram, D.K.; de Cabo, R. Prolonged metformin treatment leads to reduced transcription of Nrf2 and neurotrophic factors without cognitive impairment in older C57BL/6J mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2016, 301, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.J.; Martin-Montalvo, A.; Mercken, E.M.; Palacios, H.H.; Ward, T.M.; Abulwerdi, G.; Minor, R.K.; Vlasuk, G.P.; Ellis, J.L.; Sinclair, D.A.; et al. The SIRT1 activator SRT1720 extends lifespan and improves health of mice fed a standard diet. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattison, J.A.; Wang, M.; Bernier, M.; Zhang, J.; Park, S.S.; Maudsley, S.; An, S.S.; Santhanam, L.; Martin, B.; Faulkner, S.; et al. Resveratrol prevents high fat/sucrose diet-induced central arterial wall inflammation and stiffening in nonhuman primates. Cell Metab. 2014, 20, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minor, R.K.; Baur, J.A.; Gomes, A.P.; Ward, T.M.; Csiszar, A.; Mercken, E.M.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Shin, Y.K.; Canto, C.; Scheibye-Knudsen, M.; et al. SRT1720 improves survival and healthspan of obese mice. Sci. Rep. 2011, 1, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodig, S.; Cepelak, I.; Pavic, I. Hallmarks of senescence and aging. Biochem. Med. 2019, 29, 030501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgoulis, V.; Adams, P.D.; Alimonti, A.; Bennett, D.C.; Bischof, O.; Bishop, C.; Campisi, J.; Collado, M.; Evangelou, K.; Ferbeyre, G.; et al. Cellular Senescence: Defining a Path Forward. Cell 2019, 179, 813–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teuliere, J.; Bernard, C.; Corel, E.; Lapointe, F.J.; Martens, J.; Lopez, P.; Bapteste, E. Network analyses unveil ageing-associated pathways evolutionarily conserved from fungi to animals. Geroscience 2023, 45, 1059–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnaevskiy, N.; Oshima, J.; Mendenhall, A.R. Rapid emergence of transcriptional heterogeneity upon molecular stress predisposes cells to two distinct states of senescence. Geroscience 2023, 45, 1115–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Pang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ye, F.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yao, L.; Gao, J. Single-cell transcriptomics identifies premature aging features of TERC-deficient mouse brain and bone marrow. Geroscience 2022, 44, 2139–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, M.L.; Sell, C.; Azizkhan-Clifford, J. DNA damage-induced degradation of Sp1 promotes cellular senescence. Geroscience 2022, 44, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matacchione, G.; Perugini, J.; Di Mercurio, E.; Sabbatinelli, J.; Prattichizzo, F.; Senzacqua, M.; Storci, G.; Dani, C.; Lezoche, G.; Guerrieri, M.; et al. Senescent macrophages in the human adipose tissue as a source of inflammaging. Geroscience 2022, 44, 1941–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fielding, R.A.; Atkinson, E.J.; Aversa, Z.; White, T.A.; Heeren, A.A.; Achenbach, S.J.; Mielke, M.M.; Cummings, S.R.; Pahor, M.; Leeuwenburgh, C.; et al. Associations between biomarkers of cellular senescence and physical function in humans: Observations from the lifestyle interventions for elders (LIFE) study. Geroscience 2022, 44, 2757–2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavanagh, K.; Sherrill, C.; Ruggiero, A.; Block, M.; Vemuri, R.; Davis, M.; Olivier, A. Biomarkers of senescence in non-human primate adipose depots relate to aging. Geroscience 2021, 43, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, O.; Alon, U. Senescent cell accumulation mechanisms inferred from parabiosis. Geroscience 2021, 43, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefzadeh, M.J.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Hughes, B.; Gadela, N.; Ladiges, W.C.; Vo, N.; Niedernhofer, L.J.; Huffman, D.M.; Robbins, P.D. Heterochronic parabiosis regulates the extent of cellular senescence in multiple tissues. Geroscience 2020, 42, 951–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Lei, Q.; Xie, J.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Gou, X. Potential Regulators of the Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype During Senescence and Aging. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2022, 77, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basisty, N.; Kale, A.; Jeon, O.H.; Kuehnemann, C.; Payne, T.; Rao, C.; Holtz, A.; Shah, S.; Sharma, V.; Ferrucci, L.; et al. A proteomic atlas of senescence-associated secretomes for aging biomarker development. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchkonia, T.; Zhu, Y.; van Deursen, J.; Campisi, J.; Kirkland, J.L. Cellular senescence and the senescent secretory phenotype: Therapeutic opportunities. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 966–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes-Paciencia, S.; Saint-Germain, E.; Rowell, M.C.; Ruiz, A.F.; Kalegari, P.; Ferbeyre, G. The senescence-associated secretory phenotype and its regulation. Cytokine 2019, 117, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childs, B.G.; Durik, M.; Baker, D.J.; van Deursen, J.M. Cellular senescence in aging and age-related disease: From mechanisms to therapy. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, S.I.; Tucker, J.R.; Lim, J.; Thomas, T.G.; Stoddard, G.J.; Lesniewski, L.A.; Donato, A.J. Aging results in DNA damage and telomere dysfunction that is greater in endothelial versus vascular smooth muscle cells and is exacerbated in atheroprone regions. Geroscience 2022, 44, 2741–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamuri, S.; Sure, V.N.; Wang, X.; Bix, G.; Fonseca, V.A.; Mostany, R.; Katakam, P.V.G. Amyloid [Formula: See text] (1-42) peptide impairs mitochondrial respiration in primary human brain microvascular endothelial cells: Impact of dysglycemia and pre-senescence. Geroscience 2022, 44, 2721–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamuri, S.; Sure, V.N.; Kolli, L.; Liu, N.; Evans, W.R.; Sperling, J.A.; Busija, D.W.; Wang, X.; Lindsey, S.H.; Murfee, W.L.; et al. Glycolytic and Oxidative Phosphorylation Defects Precede the Development of Senescence in Primary Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Geroscience 2022, 44, 1975–1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussian, T.J.; Aziz, A.; Meyer, C.F.; Swenson, B.L.; van Deursen, J.M.; Baker, D.J. Clearance of senescent glial cells prevents tau-dependent pathology and cognitive decline. Nature 2018, 562, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Wang, Y.; Shao, L.; Laberge, R.M.; Demaria, M.; Campisi, J.; Janakiraman, K.; Sharpless, N.E.; Ding, S.; Feng, W.; et al. Clearance of senescent cells by ABT263 rejuvenates aged hematopoietic stem cells in mice. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantini, S.; Balasubramanian, P.; Delfavero, J.; Csipo, T.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Kiss, T.; Nyul-Toth, A.; Mukli, P.; Toth, P.; Ahire, C.; et al. Treatment with the BCL-2/BCL-xL inhibitor senolytic drug ABT263/Navitoclax improves functional hyperemia in aged mice. Geroscience 2021, 43, 2427–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaria, M.; O’Leary, M.N.; Chang, J.; Shao, L.; Liu, S.; Alimirah, F.; Koenig, K.; Le, C.; Mitin, N.; Deal, A.M.; et al. Cellular Senescence Promotes Adverse Effects of Chemotherapy and Cancer Relapse. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahire, C.; Nyul-Toth, A.; DelFavero, J.; Gulej, R.; Faakye, J.A.; Tarantini, S.; Kiss, T.; Kuan-Celarier, A.; Balasubramanian, P.; Ungvari, A.; et al. Accelerated cerebromicrovascular senescence contributes to cognitive decline in a mouse model of paclitaxel (Taxol)-induced chemobrain. Aging Cell 2023, 22, e13832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorigatti, A.O.; Riordan, R.; Yu, Z.; Ross, G.; Wang, R.; Reynolds-Lallement, N.; Magnusson, K.; Galvan, V.; Perez, V.I. Brain cellular senescence in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Geroscience 2022, 44, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, F.; Prattichizzo, F.; Grillari, J.; Balistreri, C.R. Cellular Senescence and Inflammaging in Age-Related Diseases. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 9076485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, L.; Fabbri, E. Inflammageing: Chronic inflammation in ageing, cardiovascular disease, and frailty. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccon, T.D.; Nagpal, R.; Yadav, H.; Cavalcante, M.B.; Nunes, A.D.C.; Schneider, A.; Gesing, A.; Hughes, B.; Yousefzadeh, M.; Tchkonia, T.; et al. Senolytic Combination of Dasatinib and Quercetin Alleviates Intestinal Senescence and Inflammation and Modulates the Gut Microbiome in Aged Mice. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 1895–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogrodnik, M.; Zhu, Y.; Langhi, L.G.P.; Tchkonia, T.; Kruger, P.; Fielder, E.; Victorelli, S.; Ruswhandi, R.A.; Giorgadze, N.; Pirtskhalava, T.; et al. Obesity-Induced Cellular Senescence Drives Anxiety and Impairs Neurogenesis. Cell Metab. 2019, 29, 1061–1077.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Hornsby, P.J.; Meng, Q.; Vandeberg, J.F.; Vandeberg, J.L. Longitudinal analysis of short-term high-fat diet on endothelial senescence in baboons. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 3, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, Q.; Hubbard, G.B.; Kushwaha, R.S.; Rainwater, D.; Thomas, C.A., 3rd; Leland, M.M.; Vandeberg, J.L.; Wang, X.L. Endothelial senescence after high-cholesterol, high-fat diet challenge in baboons. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 292, H2913–H2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, G.B.; Zhou, D.; Pan, Y.X. High-fat diet modifies expression of hepatic cellular senescence gene p16(INK4a) through chromatin modifications in adult male rats. Genes Nutr. 2018, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Li, Z.; Xu, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z. Resveratrol Protects against High-Fat Diet Induced Renal Pathological Damage and Cell Senescence by Activating SIRT1. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 39, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Nagata, W.; Koizumi, A.; Ishizuka, T. A preliminary therapeutic study of the effects of molecular hydrogen on intestinal dysbiosis and small intestinal injury in high-fat diet-loaded senescence-accelerated mice. Nutrition 2024, 122, 112372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sone, H.; Kagawa, Y. Pancreatic beta cell senescence contributes to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes in high-fat diet-induced diabetic mice. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pini, M.; Czibik, G.; Sawaki, D.; Mezdari, Z.; Braud, L.; Delmont, T.; Mercedes, R.; Martel, C.; Buron, N.; Marcelin, G.; et al. Adipose tissue senescence is mediated by increased ATP content after a short-term high-fat diet exposure. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Xue, Q.; Wang, J.; Tan, J. High-fat diet and dyslipidemia synergistically contribute to T cell senescence in gut associated lymphoid tissue. Exp. Gerontol. 2021, 151, 111404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.R.; Jiang, K.; Ogrodnik, M.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X.Y.; Lohmeier, H.; Ahmed, L.; Tang, H.; Tchkonia, T.; Hickson, L.J.; et al. Increased renal cellular senescence in murine high-fat diet: Effect of the senolytic drug quercetin. Transl. Res. 2019, 213, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Jeon, B.; Baek, J.; Yun, Y.; Kim, D.; Chang, B.; Kim, S.; Kim, S. High fat diet-induced brain damaging effects through autophagy-mediated senescence, inflammation and apoptosis mitigated by ginsenoside F1-enhanced mixture. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukraintseva, S.; Arbeev, K.; Duan, M.; Akushevich, I.; Kulminski, A.; Stallard, E.; Yashin, A. Decline in biological resilience as key manifestation of aging: Potential mechanisms and role in health and longevity. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2021, 194, 111418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Otin, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, A.R.; Lyon, C.J.; Xia, X.; Liu, J.Z.; Tangirala, R.K.; Yin, F.; Boyadjian, R.; Bikineyeva, A.; Pratico, D.; Harrison, D.G.; et al. Age-accelerated atherosclerosis correlates with failure to upregulate antioxidant genes. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, e42–e54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungvari, Z.I.; Bailey-Downs, L.; Gautam, T.; Jimenez, R.; Losonczy, G.; Zhang, C.; Ballabh, P.; Recchia, F.A.; Wilkerson, D.C.; Sonntag, W.E.; et al. Adaptive induction of NF-E2-Related Factor-2-driven antioxidant genes in endothelial cells in response to hyperglycemia. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H1133–H1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungvari, Z.; Tarantini, S.; Nyul-Toth, A.; Kiss, T.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Csipo, T.; Balasubramanian, P.; Lipecz, A.; Benyo, Z.; Csiszar, A. Nrf2 dysfunction and impaired cellular resilience to oxidative stressors in the aged vasculature: From increased cellular senescence to the pathogenesis of age-related vascular diseases. Geroscience 2019, 41, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivandzade, F.; Prasad, S.; Bhalerao, A.; Cucullo, L. NRF2 and NF-B interplay in cerebrovascular and neurodegenerative disorders: Molecular mechanisms and possible therapeutic approaches. Redox Biol. 2019, 21, 101059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantini, S.; Valcarcel-Ares, M.N.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Tucsek, Z.; Hertelendy, P.; Kiss, T.; Gautam, T.; Zhang, X.A.; Sonntag, W.E.; de Cabo, R.; et al. Nrf2 Deficiency Exacerbates Obesity-Induced Oxidative Stress, Neurovascular Dysfunction, Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption, Neuroinflammation, Amyloidogenic Gene Expression, and Cognitive Decline in Mice, Mimicking the Aging Phenotype. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 73, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demaria, M.; Ohtani, N.; Youssef, S.A.; Rodier, F.; Toussaint, W.; Mitchell, J.R.; Laberge, R.M.; Vijg, J.; Van Steeg, H.; Dolle, M.E.; et al. An essential role for senescent cells in optimal wound healing through secretion of PDGF-AA. Dev. Cell 2014, 31, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yabluchanskiy, A.; Tarantini, S.; Balasubramanian, P.; Kiss, T.; Csipo, T.; Fulop, G.A.; Lipecz, A.; Ahire, C.; DelFavero, J.; Nyul-Toth, A.; et al. Pharmacological or genetic depletion of senescent astrocytes prevents whole brain irradiation-induced impairment of neurovascular coupling responses protecting cognitive function in mice. Geroscience 2020, 42, 409–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.; Dong, Q.; Wang, D.; Chang, J.; Wiley, C.; Demaria, M.; Lee, J.; Kang, J.; Niedernhofer, L.J.; Robbins, P.D.; et al. Systemic clearance of p16(INK4a) -positive senescent cells mitigates age-associated intervertebral disc degeneration. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.N.; Chang, J.; Iyer, S.; Han, L.; Campisi, J.; Manolagas, S.C.; Zhou, D.; Almeida, M. Elimination of senescent osteoclast progenitors has no effect on the age-associated loss of bone mass in mice. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Aziz, A.M.; Sun, Y.; Hellmich, C.; Marlein, C.R.; Mistry, J.; Forde, E.; Piddock, R.E.; Shafat, M.S.; Morfakis, A.; Mehta, T.; et al. Acute myeloid leukemia induces protumoral p16INK4a-driven senescence in the bone marrow microenvironment. Blood 2019, 133, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, J.; Campisi, J.; Demaria, M. A novel suicide gene therapy for the treatment of p16(Ink4a)-overexpressing tumors. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 7274–7281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jeon, O.H.; Kim, C.; Laberge, R.M.; Demaria, M.; Rathod, S.; Vasserot, A.P.; Chung, J.W.; Kim, D.H.; Poon, Y.; David, N.; et al. Local clearance of senescent cells attenuates the development of post-traumatic osteoarthritis and creates a pro-regenerative environment. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, S.A.; Venkatasubramanian, R.; Darrah, M.A.; Ludwig, K.R.; VanDongen, N.S.; Greenberg, N.T.; Longtine, A.G.; Hutton, D.A.; Brunt, V.E.; Campisi, J.; et al. Intermittent supplementation with fisetin improves arterial function in old mice by decreasing cellular senescence. Aging Cell 2024, 23, e14060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, Z.S.; Rossman, M.J.; Mahoney, S.A.; Venkatasubramanian, R.; Maurer, G.S.; Hutton, D.A.; VanDongen, N.S.; Greenberg, N.T.; Longtine, A.G.; Ludwig, K.R.; et al. Cellular Senescence Contributes to Large Elastic Artery Stiffening and Endothelial Dysfunction With Aging: Amelioration With Senolytic Treatment. Hypertension 2023, 80, 2072–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulop, G.A.; Kiss, T.; Tarantini, S.; Balasubramanian, P.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Farkas, E.; Bari, F.; Ungvari, Z.; Csiszar, A. Nrf2 deficiency in aged mice exacerbates cellular senescence promoting cerebrovascular inflammation. Geroscience 2018, 40, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, T.; Nyul-Toth, A.; Balasubramanian, P.; Tarantini, S.; Ahire, C.; DelFavero, J.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Csipo, T.; Farkas, E.; Wiley, G.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing identifies senescent cerebromicrovascular endothelial cells in the aged mouse brain. Geroscience 2020, 42, 429–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFadden, T.; Musaus, M.; Nelsen, J.L.; Martin, K.; Jones, N.; Smith, P.; Kugler, H.; Jarome, T.J. Dysregulation of protein degradation in the hippocampus is associated with impaired spatial memory during the development of obesity. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 393, 112787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroz, N.; Tong, M.; Longato, L.; Xu, H.; de la Monte, S.M. Limited Alzheimer-type neurodegeneration in experimental obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2008, 15, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuzzo, D.; Baldassano, S.; Amato, A.; Picone, P.; Galizzi, G.; Caldara, G.F.; Di Carlo, M.; Mule, F. Glucagon-like peptide-2 reduces the obesity-associated inflammation in the brain. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 121, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucsek, Z.; Toth, P.; Sosnowska, D.; Gautam, T.; Mitschelen, M.; Koller, A.; Szalai, G.; Sonntag, W.E.; Ungvari, Z.; Csiszar, A. Obesity in aging exacerbates blood-brain barrier disruption, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress in the mouse hippocampus: Effects on expression of genes involved in beta-amyloid generation and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 1212–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcarcel-Ares, M.N.; Tucsek, Z.; Kiss, T.; Giles, C.B.; Tarantini, S.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Balasubramanian, P.; Gautam, T.; Galvan, V.; Ballabh, P.; et al. Obesity in Aging Exacerbates Neuroinflammation, Dysregulating Synaptic Function-related Genes and Altering Eicosanoid Synthesis in the Mouse Hippocampus: Potential Role in Impaired Synaptic Plasticity and Cognitive Decline. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 74, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baur, J.A.; Pearson, K.J.; Price, N.L.; Jamieson, H.A.; Lerin, C.; Kalra, A.; Prabhu, V.V.; Allard, J.S.; Lopez-Lluch, G.; Lewis, K.; et al. Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature 2006, 444, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounder, S.S.; Kannan, S.; Devadoss, D.; Miller, C.J.; Whitehead, K.J.; Odelberg, S.J.; Firpo, M.A.; Paine, R., 3rd; Hoidal, J.R.; Abel, E.D.; et al. Impaired transcriptional activity of Nrf2 in age-related myocardial oxidative stress is reversible by moderate exercise training. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcarcel-Ares, M.N.; Gautam, T.; Warrington, J.P.; Bailey-Downs, L.; Sosnowska, D.; de Cabo, R.; Losonczy, G.; Sonntag, W.E.; Ungvari, Z.; Csiszar, A. Disruption of Nrf2 signaling impairs angiogenic capacity of endothelial cells: Implications for microvascular aging. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.J.; Shay, K.P.; Thomas, N.O.; Butler, J.A.; Finlay, L.F.; Hagen, T.M. Age-related loss of hepatic Nrf2 protein homeostasis: Potential role for heightened expression of miR-146a. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 89, 1184–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, H.; Davies, K.J.A.; Forman, H.J. Aging-related decline in the induction of Nrf2-regulated antioxidant genes in human bronchial epithelial cells. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungvari, Z.; Bailey-Downs, L.; Gautam, T.; Sosnowska, D.; Wang, M.; Monticone, R.E.; Telljohann, R.; Pinto, J.T.; de Cabo, R.; Sonntag, W.E.; et al. Age-associated vascular oxidative stress, Nrf2 dysfunction, and NF-kappaB activation in the nonhuman primate Macaca mulatta. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2011, 66, 866–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdar, A.; deBeer, J.; Tarnopolsky, M.A. Dysfunctional Nrf2-Keap1 redox signaling in skeletal muscle of the sedentary old. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1487–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Sykiotis, G.P.; Nishimura, M.; Bodmer, R.; Bohmann, D. Declining signal dependence of Nrf2-MafS-regulated gene expression correlates with aging phenotypes. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 554–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumaru, D.; Motohashi, H. The KEAP1-NRF2 System in Healthy Aging and Longevity. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Qin, R.; Chen, J.; Wang, R.; Goltzman, D.; Miao, D. Inhibition of Nrf2 degradation alleviates age-related osteoporosis induced by 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D deficiency. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 178, 246–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, R.S.; Lokhandwala, M.F.; Banday, A.A. Age-Related Mitochondrial Impairment and Renal Injury Is Ameliorated by Sulforaphane via Activation of Transcription Factor NRF2. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riordan, R.; Rong, W.; Yu, Z.; Ross, G.; Valerio, J.; Dimas-Munoz, J.; Heredia, V.; Magnusson, K.; Galvan, V.; Perez, V.I. Effect of Nrf2 loss on senescence and cognition of tau-based P301S mice. Geroscience 2023, 45, 1451–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schafer, M.J.; White, T.A.; Evans, G.; Tonne, J.M.; Verzosa, G.C.; Stout, M.B.; Mazula, D.L.; Palmer, A.K.; Baker, D.J.; Jensen, M.D.; et al. Exercise Prevents Diet-Induced Cellular Senescence in Adipose Tissue. Diabetes 2016, 65, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.K.; Xu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Pirtskhalava, T.; Weivoda, M.M.; Hachfeld, C.M.; Prata, L.G.; van Dijk, T.H.; Verkade, E.; Casaclang-Verzosa, G.; et al. Targeting senescent cells alleviates obesity-induced metabolic dysfunction. Aging Cell 2019, 18, e12950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, P.; Kiss, T.; Tarantini, S.; Nyul-Toth, A.; Ahire, C.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Csipo, T.; Lipecz, A.; Tabak, A.; Institoris, A.; et al. Obesity-induced cognitive impairment in older adults: A microvascular perspective. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2021, 320, H740–H761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, H.; Chang, E.; Glassford, A.J.; Cooke, J.P.; Chiu, C.P.; Tsao, P.S. eNOS activity is reduced in senescent human endothelial cells: Preservation by hTERT immortalization. Circ. Res. 2001, 89, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krouwer, V.J.; Hekking, L.H.; Langelaar-Makkinje, M.; Regan-Klapisz, E.; Post, J.A. Endothelial cell senescence is associated with disrupted cell-cell junctions and increased monolayer permeability. Vasc. Cell 2012, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, Y.; Baker, D.J.; Tachibana, M.; Liu, C.C.; van Deursen, J.M.; Brott, T.G.; Bu, G.; Kanekiyo, T. Vascular Cell Senescence Contributes to Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown. Stroke 2016, 47, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulej, R.; Nyul-Toth, A.; Ahire, C.; DelFavero, J.; Balasubramanian, P.; Kiss, T.; Tarantini, S.; Benyo, Z.; Pacher, P.; Csik, B.; et al. Elimination of senescent cells by treatment with Navitoclax/ABT263 reverses whole brain irradiation-induced blood-brain barrier disruption in the mouse brain. Geroscience 2023, 45, 2983–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, T.; Nyul-Toth, A.; Gulej, R.; Tarantini, S.; Csipo, T.; Mukli, P.; Ungvari, A.; Balasubramanian, P.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Benyo, Z.; et al. Old blood from heterochronic parabionts accelerates vascular aging in young mice: Transcriptomic signature of pathologic smooth muscle remodeling. Geroscience 2022, 44, 953–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhtiari, A.; Vestergaard, M.B.; Benedek, K.; Fagerlund, B.; Mortensen, E.L.; Osler, M.; Lauritzen, M.; Larsson, H.B.W.; Lindberg, U. Changes in hippocampal volume during a preceding 10-year period do not correlate with cognitive performance and hippocampal blood–brain barrier permeability in cognitively normal late-middle-aged men. Geroscience 2023, 45, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagne, A.; Barnes, S.R.; Nation, D.A.; Kisler, K.; Toga, A.W.; Zlokovic, B.V. Imaging subtle leaks in the blood-brain barrier in the aging human brain: Potential pitfalls, challenges, and possible solutions. Geroscience 2022, 44, 1339–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towner, R.A.; Gulej, R.; Zalles, M.; Saunders, D.; Smith, N.; Lerner, M.; Morton, K.A.; Richardson, A. Rapamycin restores brain vasculature, metabolism, and blood-brain barrier in an inflammaging model. Geroscience 2021, 43, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerkhofs, D.; Wong, S.M.; Zhang, E.; Uiterwijk, R.; Hoff, E.I.; Jansen, J.F.A.; Staals, J.; Backes, W.H.; van Oostenbrugge, R.J. Blood-brain barrier leakage at baseline and cognitive decline in cerebral small vessel disease: A 2-year follow-up study. Geroscience 2021, 43, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagi, Z.; Kroenke, C.D.; Fopiano, K.A.; Tian, Y.; Filosa, J.A.; Sherman, L.S.; Larson, E.B.; Keene, C.D.; Degener O’Brien, K.; Adeniyi, P.A.; et al. Association of cerebral microvascular dysfunction and white matter injury in Alzheimer’s disease. Geroscience 2022, 44, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assar, M.E.; Angulo, J.; Garcia-Rojo, E.; Sevilleja-Ortiz, A.; Garcia-Gomez, B.; Fernandez, A.; Sanchez-Ferrer, A.; La Fuente, J.M.; Romero-Otero, J.; Rodriguez-Manas, L. Early manifestation of aging-related vascular dysfunction in human penile vasculature-A potential explanation for the role of erectile dysfunction as a harbinger of systemic vascular disease. Geroscience 2022, 44, 485–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreau, K.L.; Hildreth, K.L.; Klawitter, J.; Blatchford, P.; Kohrt, W.M. Decline in endothelial function across the menopause transition in healthy women is related to decreased estradiol and increased oxidative stress. Geroscience 2020, 42, 1699–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiss, T.; Tarantini, S.; Csipo, T.; Balasubramanian, P.; Nyul-Toth, A.; Yabluchanskiy, A.; Wren, J.D.; Garman, L.; Huffman, D.M.; Csiszar, A.; et al. Circulating anti-geronic factors from heterochonic parabionts promote vascular rejuvenation in aged mice: Transcriptional footprint of mitochondrial protection, attenuation of oxidative stress, and rescue of endothelial function by young blood. Geroscience 2020, 42, 727–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csiszar, A.; Pinto, J.T.; Gautam, T.; Kleusch, C.; Hoffmann, B.; Tucsek, Z.; Toth, P.; Sonntag, W.E.; Ungvari, Z. Resveratrol Encapsulated in Novel Fusogenic Liposomes Activates Nrf2 and Attenuates Oxidative Stress in Cerebromicrovascular Endothelial Cells From Aged Rats. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 70, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, T.; Acton, J.P.; Cocksedge, S.P.; Davies, K.A.B.; Bailey, S.J. The effect of dietary phytochemicals on nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) activation: A systematic review of human intervention trials. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 1745–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga, C.G.; Croft, K.D.; Kennedy, D.O.; Tomas-Barberan, F.A. The effects of polyphenols and other bioactives on human health. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 514–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, A.; Minihane, A.M. The role of metabolism (and the microbiome) in defining the clinical efficacy of dietary flavonoids. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassidy, A.; Mukamal, K.J.; Liu, L.; Franz, M.; Eliassen, A.H.; Rimm, E.B. High anthocyanin intake is associated with a reduced risk of myocardial infarction in young and middle-aged women. Circulation 2013, 127, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).