Comparative Efficacy of Different Protein Supplements on Muscle Mass, Strength, and Physical Indices of Sarcopenia among Community-Dwelling, Hospitalized or Institutionalized Older Adults Undergoing Resistance Training: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Protocol
2.2. Search Strategy
2.3. Criteria for Selecting Studies
2.4. Main Outcomes
2.5. Data Extraction
2.6. Risks of Bias in Individual Study and across Studies
2.7. Data Synthesis and Analysis
2.8. Certainty of Evidence
3. Results
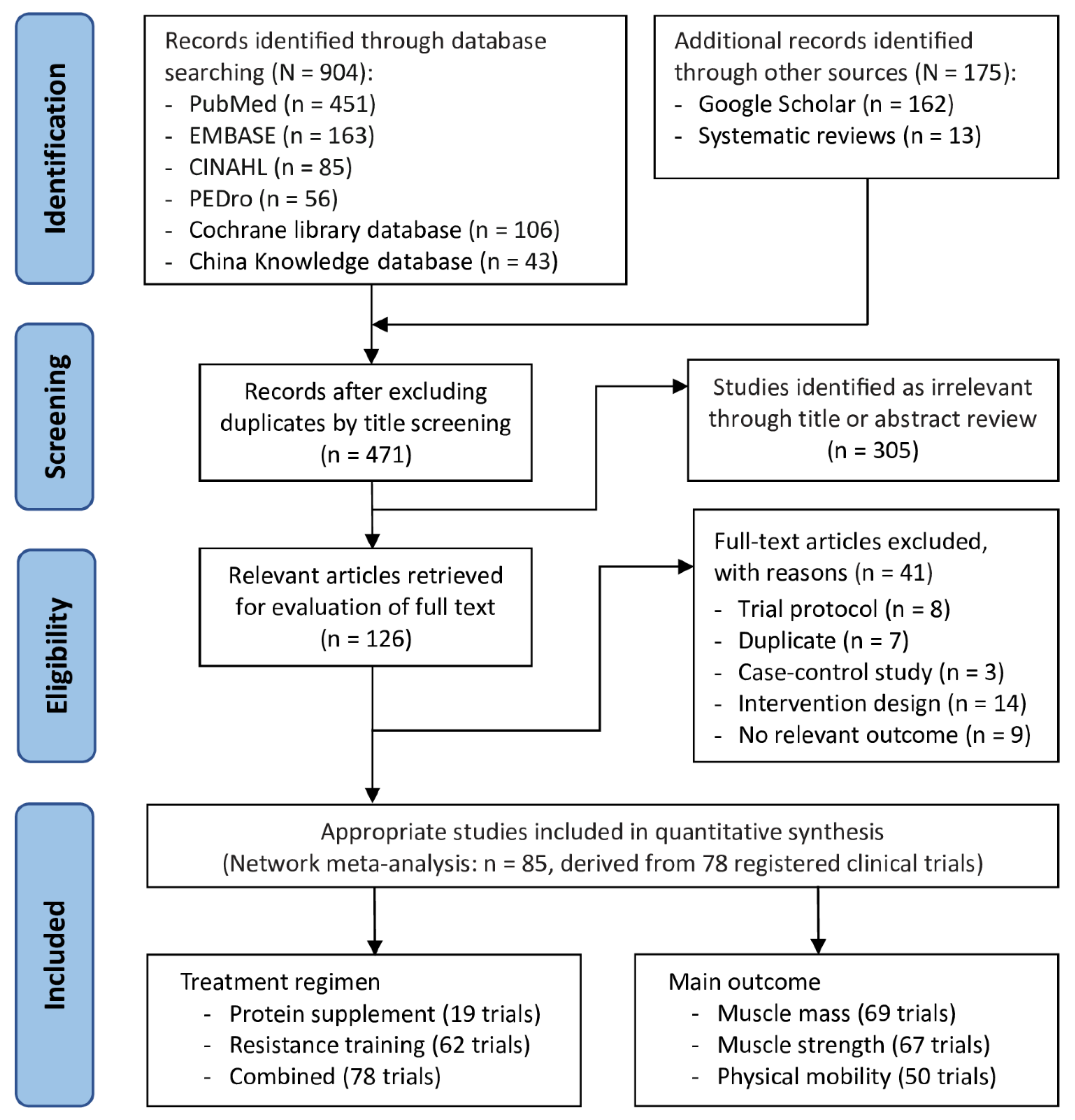
3.1. Trial Selection Flowchart
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Protocol of Protein Supplementation
3.4. Protocol of Resistance Training
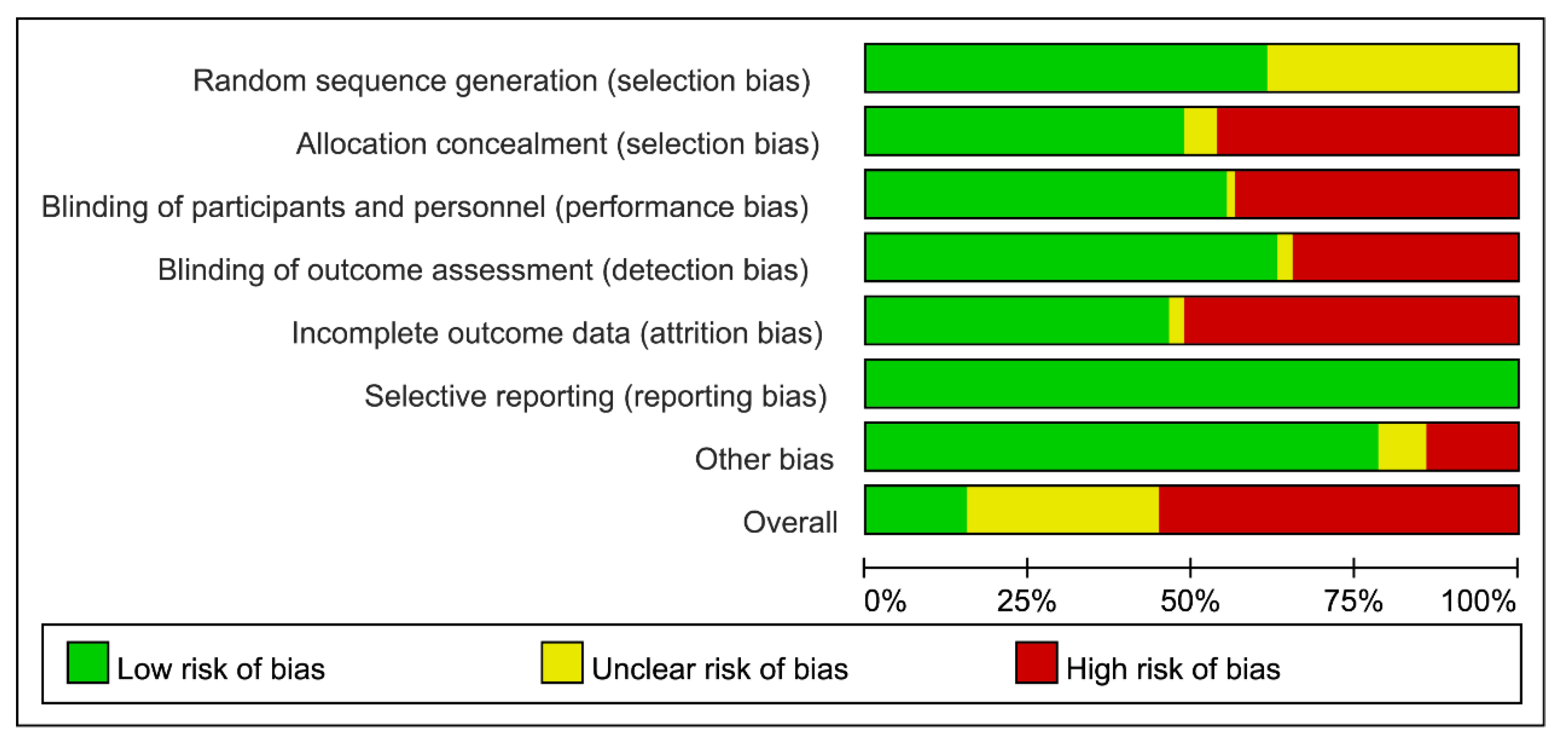
3.5. Risks of Bias in Individual Study and Across Studies
3.6. Treatment Efficacy for Muscle Mass
3.6.1. Conventional Pairwise Meta-Analysis
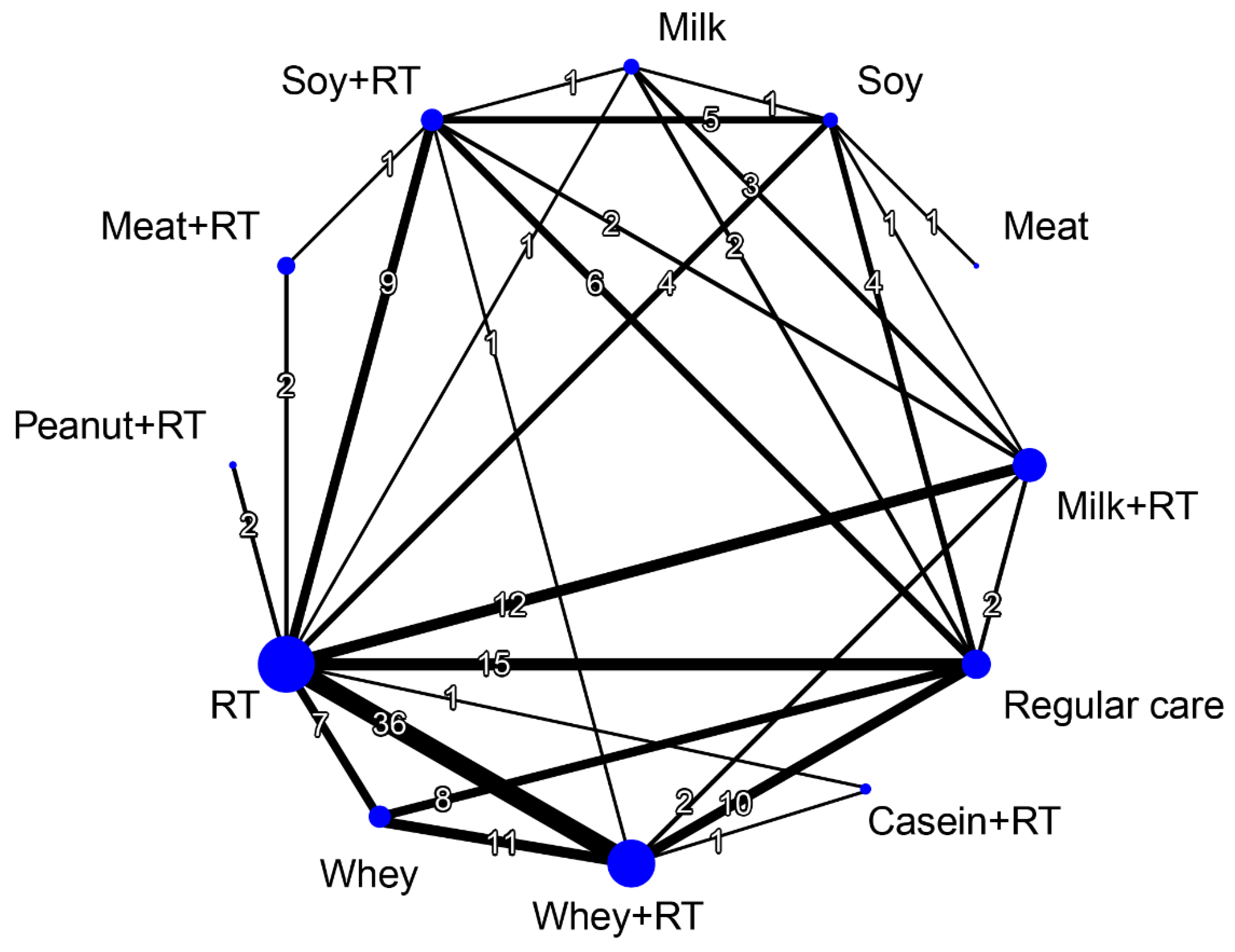
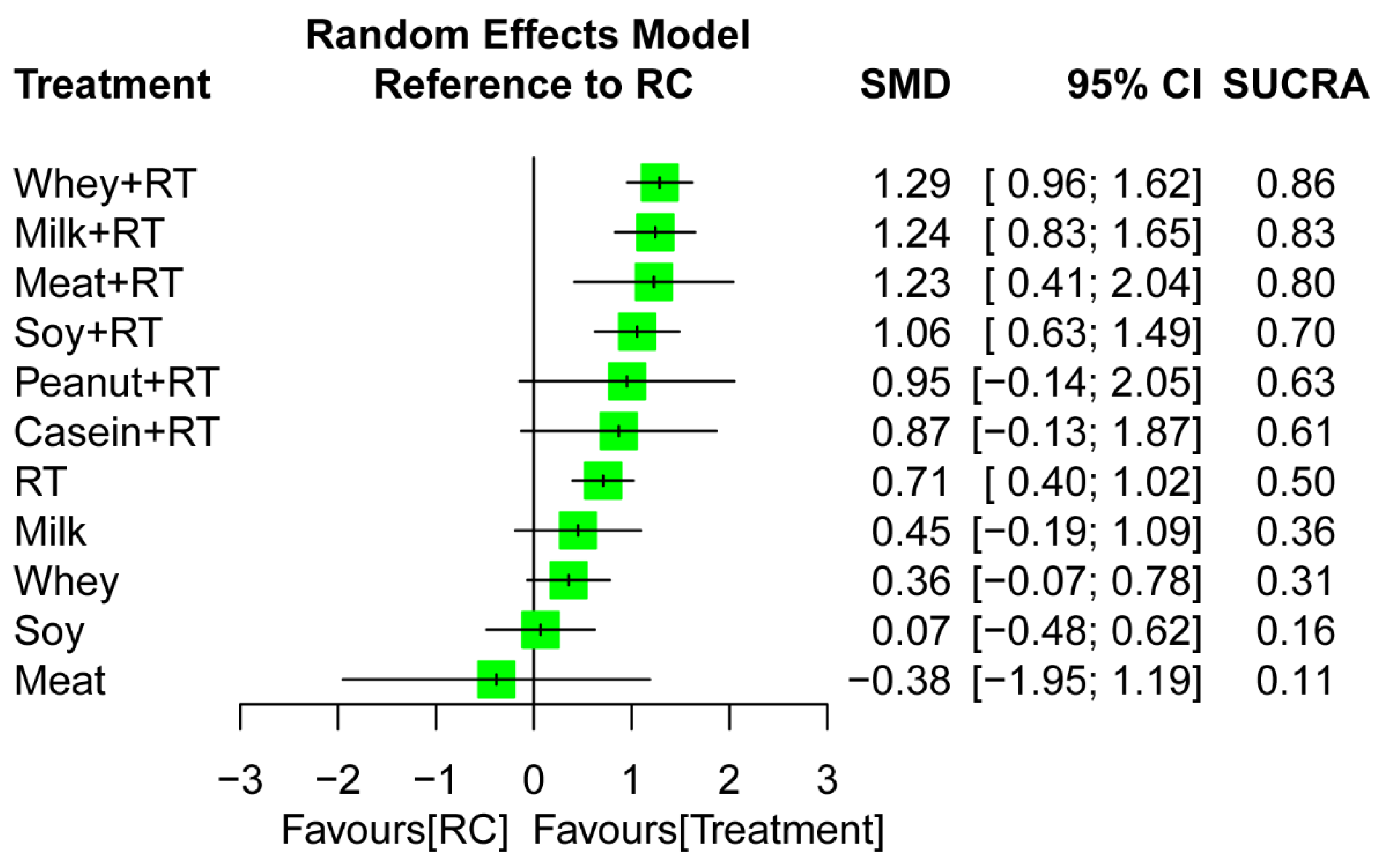
3.6.2. Network Meta-Analysis
3.6.3. Subgroup Analysis Based on Follow-Up Time
3.7. Treatment Efficacy for Muscle Strength
3.7.1. Conventional Pairwise Meta-Analysis
3.7.2. Network Meta-Analysis
3.7.3. Subgroup Analysis Based on Follow-Up Time
3.8. Effectiveness of Treatment for Physical Mobility
3.8.1. Conventional Pairwise Meta-Analysis
3.8.2. Network Meta-Analysis
3.8.3. Subgroup Analysis Based on Follow-Up Time
3.9. Network Meta-Regression Anlyses
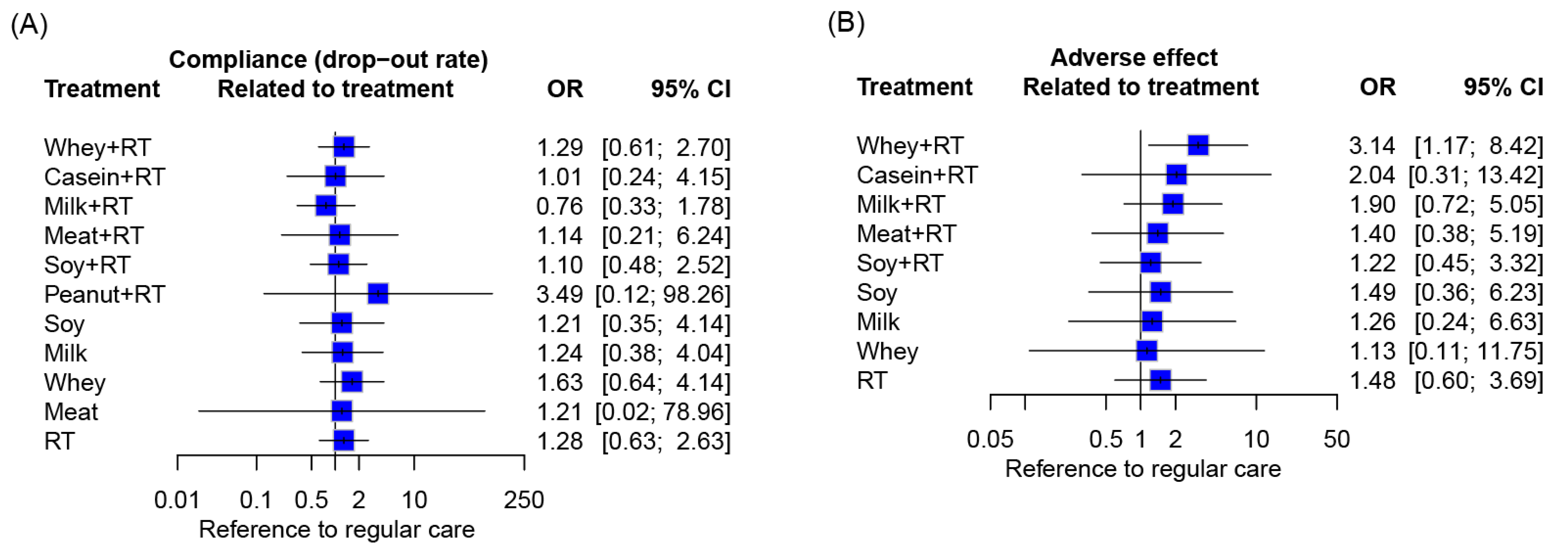
3.10. Compliance and Side Effects
3.11. Publication Bias
3.12. Certainty of the Evidence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, L.K.; Woo, J.; Assantachai, P.; Auyeung, T.W.; Chou, M.Y.; Iijima, K.; Jang, H.C.; Kang, L.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 300–307.e302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyere, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Tanaka, S.; Kataoka, S.; Tanaka, R. Association of sarcopenia, pre-sarcopenia, and dynapenia with the onset and progression of locomotive syndrome in Japanese older adults: A cross-sectional study. J. Physiol. Anthropol. 2023, 42, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longobucco, Y.; Krumpoch, S.; Lauretani, F.; Angileri, V.; Sieber, C.; Marzetti, E.; Calvani, R.; Cherubini, A.; Landi, F.; Bernabei, R.; et al. Gait characteristics in community-dwelling older persons with low skeletal muscle mass and low physical performance. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 34, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolland, Y.; Lauwers-Cances, V.; Cristini, C.; Abellan van Kan, G.; Janssen, I.; Morley, J.E.; Vellas, B. Difficulties with physical function associated with obesity, sarcopenia, and sarcopenic-obesity in community-dwelling elderly women: The EPIDOS (EPIDemiologie de l’OSteoporose) Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1895–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawthon, P.M.; Orwoll, E.S.; Peters, K.E.; Ensrud, K.E.; Cauley, J.A.; Kado, D.M.; Stefanick, M.L.; Shikany, J.M.; Strotmeyer, E.S.; Glynn, N.W.; et al. Strong Relation between Muscle Mass Determined by D3-creatine Dilution, Physical Performance and Incidence of Falls and Mobility Limitations in a Prospective Cohort of Older Men. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 74, 844–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damluji, A.A.; Alfaraidhy, M.; AlHajri, N.; Rohant, N.N.; Kumar, M.; Al Malouf, C.; Bahrainy, S.; Ji Kwak, M.; Batchelor, W.B.; Forman, D.E.; et al. Sarcopenia and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circulation 2023, 147, 1534–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickering, M.E.; Chapurlat, R. Where Two Common Conditions of Aging Meet: Osteoarthritis and Sarcopenia. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2020, 107, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shorter, E.; Sannicandro, A.J.; Poulet, B.; Goljanek-Whysall, K. Skeletal Muscle Wasting and Its Relationship With Osteoarthritis: A Mini-Review of Mechanisms and Current Interventions. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2019, 21, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlietstra, L.; Stebbings, S.; Meredith-Jones, K.; Abbott, J.H.; Treharne, G.J.; Waters, D.L. Sarcopenia in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: The association with self-reported fatigue, physical function and obesity. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torii, M.; Itaya, T.; Minamino, H.; Katsushima, M.; Fujita, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Oshima, Y.; Watanabe, R.; Ito, H.; Arai, H.; et al. Management of sarcopenia in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol./Jpn. Rheum. Assoc. 2023, 33, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Liu, R.Y.; Zhang, G.W.; Hu, F.; Jin, Y.H.; Liu, B.Y. Possible sarcopenia and risk of new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus in older adults in China: A 7-year longitudinal cohort study. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Choi, H.; Kim, K.Y.; Lee, H.S.; Jung, J.M. Appendicular Skeletal Muscle Mass Associated with Sarcopenia as a Predictor of Poor Functional Outcomes in Ischemic Stroke. Clin. Interv. Aging 2023, 18, 1009–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, J.E.; Anker, S.D.; von Haehling, S. Prevalence, incidence, and clinical impact of sarcopenia: Facts, numbers, and epidemiology-update 2014. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2014, 5, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Hirayama, K.; Han, T.F.; Izutsu, M.; Yuki, M. Sarcopenia Prevalence and Risk Factors among Japanese Community Dwelling Older Adults Living in a Snow-Covered City According to EWGSOP2. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiee, G.; Keshtkar, A.; Soltani, A.; Ahadi, Z.; Larijani, B.; Heshmat, R. Prevalence of sarcopenia in the world: A systematic review and meta- analysis of general population studies. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2017, 16, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makizako, H.; Nakai, Y.; Tomioka, K.; Taniguchi, Y. Prevalence of sarcopenia defined using the Asia Working Group for Sarcopenia criteria in Japanese community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phys. Ther. Res. 2019, 22, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, P.; Dou, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xie, X.; Zhou, J.; Zeng, Y. Falls among older adults with sarcopenia dwelling in nursing home or community: A meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Tao, W.; Dou, Q.; Yang, Y. Sarcopenia as a predictor of hospitalization among older people: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr. 2018, 18, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hao, Q.; Hai, S.; Wang, H.; Cao, L.; Dong, B. Sarcopenia as a predictor of all-cause mortality among community-dwelling older people: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Maturitas 2017, 103, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Dou, Q.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Y.; Xie, X. Sarcopenia as a predictor of all-cause mortality among older nursing home residents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e021252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Tang, H. Sarcopenia for predicting falls and hospitalization in community-dwelling older adults: EWGSOP versus EWGSOP2. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinedo-Villanueva, R.; Westbury, L.D.; Syddall, H.E.; Sanchez-Santos, M.T.; Dennison, E.M.; Robinson, S.M.; Cooper, C. Health Care Costs Associated With Muscle Weakness: A UK Population-Based Estimate. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2019, 104, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goates, S.; Du, K.; Arensberg, M.B.; Gaillard, T.; Guralnik, J.; Pereira, S.L. Economic Impact of Hospitalizations in US Adults with Sarcopenia. J. Frailty Aging 2019, 8, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, B.T.; Gorissen, S.H.; Pennings, B.; Koopman, R.; Groen, B.B.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J. Aging Is Accompanied by a Blunted Muscle Protein Synthetic Response to Protein Ingestion. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.T.; Ang, S.J.; Tsai, S.Y. Sarcopenia: Tilting the Balance of Protein Homeostasis. Proteomics 2020, 20, e1800411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedmer, P.; Jung, T.; Castro, J.P.; Pomatto, L.C.D.; Sun, P.Y.; Davies, K.J.A.; Grune, T. Sarcopenia—Molecular mechanisms and open questions. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 65, 101200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Xing, F. Influencing factors of sarcopenia in older adults based on the Newman system model: A case-control study. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2023, 14, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, S.; Granic, A.; Sayer, A.A. Nutrition and Muscle Strength, As the Key Component of Sarcopenia: An Overview of Current Evidence. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvani, R.; Picca, A.; Coelho-Júnior, H.J.; Tosato, M.; Marzetti, E.; Landi, F. Diet for the prevention and management of sarcopenia. Metabolism 2023, 146, 155637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiberger, E.; Sieber, C.; Pfeifer, K. Physical activity, exercise, and sarcopenia—Future challenges. Wien. Med. Wochenschr. 2011, 161, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Li, S. Advances in nutritional supplementation for sarcopenia management. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1189522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, J.H.T.; Yiu, T.; Ong, M.T.Y.; Lee, W.Y.W. Sarcopenia: Current treatments and new regenerative therapeutic approaches. J. Orthop. Transl. 2020, 23, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, F.; Calvani, R.; Cesari, M.; Tosato, M.; Martone, A.M.; Ortolani, E.; Savera, G.; Salini, S.; Sisto, A.; Picca, A.; et al. Sarcopenia: An Overview on Current Definitions, Diagnosis and Treatment. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2018, 19, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutz, N.E.; Bauer, J.M.; Barazzoni, R.; Biolo, G.; Boirie, Y.; Bosy-Westphal, A.; Cederholm, T.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.; Krznaric, Z.; Nair, K.S.; et al. Protein intake and exercise for optimal muscle function with aging: Recommendations from the ESPEN Expert Group. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Ling, X.Y.; Fang, Z.L.; Lu, Y.F. Optimal exercise to improve physical ability and performance in older adults with sarcopenia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Geriatr. Nurs. 2023, 52, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, C.; Robinson, S.M.; Witham, M.D.; Dodds, R.M.; Granic, A.; Buckland, C.; De Biase, S.; Finnegan, S.; Rochester, L.; Skelton, D.A.; et al. Resistance exercise as a treatment for sarcopenia: Prescription and delivery. Age Ageing 2022, 51, afac003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLeod, J.C.; Stokes, T.; Phillips, S.M. Resistance Exercise Training as a Primary Countermeasure to Age-Related Chronic Disease. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giallauria, F.; Cittadini, A.; Smart, N.A.; Vigorito, C. Resistance training and sarcopenia. Monaldi Arch. Chest Dis. 2016, 84, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tessier, A.J.; Chevalier, S. An Update on Protein, Leucine, Omega-3 Fatty Acids, and Vitamin D in the Prevention and Treatment of Sarcopenia and Functional Decline. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Pan, T.; Tong, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Z. The effects of nutritional supplementation on older sarcopenic individuals who engage in resistance training: A meta-analysis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1109789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Liu, C.W. Effect of Whey Protein Supplementation in Postmenopausal Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, R.P.; Mazidi, M.; Rodríguez García, C.; Lane, K.E.; Jafari, A.; Butler, T.; Perez de Heredia, F.; Davies, I.G. Protein interventions augment the effect of resistance exercise on appendicular lean mass and handgrip strength in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 115, 897–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.P.; Condello, G.; Kuo, C.H. Effects of Milk Protein in Resistance Training-Induced Lean Mass Gains for Older Adults Aged ≥ 60 y: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.F.; Santos, J.S.; Costa, R.R.; Cadore, E.L.; Macedo, R.C.O. Effects of Protein Supplementation Associated with Resistance Training on Body Composition and Muscle Strength in Older Adults: A Systematic Review of Systematic Reviews with Meta-analyses. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 2511–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Roh, Y. Which intervention is more effective in improving sarcopenia in older adults? A systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2023, 210, 111773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcelén-Fraile, M.D.C.; Lorenzo-Nocino, M.F.; Afanador-Restrepo, D.F.; Rodríguez-López, C.; Aibar-Almazán, A.; Hita-Contreras, F.; Achalandabaso-Ochoa, A.; Castellote-Caballero, Y. Effects of different intervention combined with resistance training on musculoskeletal health in older male adults with sarcopenia: A systematic review. Front. Public Health 2023, 10, 1037464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negm, A.M.; Lee, J.; Hamidian, R.; Jones, C.A.; Khadaroo, R.G. Management of Sarcopenia: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2022, 23, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.D.; Wu, Y.T.; Tsauo, J.Y.; Chen, P.R.; Tu, Y.K.; Chen, H.C.; Liou, T.H. Effects of Protein Supplementation Combined with Exercise Training on Muscle Mass and Function in Older Adults with Lower-Extremity Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuyul-Vásquez, I.; Pezo-Navarrete, J.; Vargas-Arriagada, C.; Ortega-Díaz, C.; Sepúlveda-Loyola, W.; Hirabara, S.M.; Marzuca-Nassr, G.N. Effectiveness of Whey Protein Supplementation during Resistance Exercise Training on Skeletal Muscle Mass and Strength in Older People with Sarcopenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.D.; Tsauo, J.Y.; Wu, Y.T.; Cheng, C.P.; Chen, H.C.; Huang, Y.C.; Chen, H.C.; Liou, T.H. Effects of protein supplementation combined with resistance exercise on body composition and physical function in older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1078–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, C.H.; Saddler, N.I.; Devries, M.C.; McGlory, C.; Baker, S.K.; Phillips, S.M. Leucine supplementation enhances integrative myofibrillar protein synthesis in free-living older men consuming lower- and higher-protein diets: A parallel-group crossover study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 1594–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trommelen, J.; Betz, M.W.; van Loon, L.J.C. The Muscle Protein Synthetic Response to Meal Ingestion Following Resistance-Type Exercise. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landi, F.; Calvani, R.; Tosato, M.; Martone, A.M.; Ortolani, E.; Savera, G.; D’Angelo, E.; Sisto, A.; Marzetti, E. Protein Intake and Muscle Health in Old Age: From Biological Plausibility to Clinical Evidence. Nutrients 2016, 8, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitelseder, S.; Dideriksen, K.; Agergaard, J.; Malmgaard-Clausen, N.M.; Bechshoeft, R.L.; Petersen, R.K.; Serena, A.; Mikkelsen, U.R.; Holm, L. Even effect of milk protein and carbohydrate intake but no further effect of heavy resistance exercise on myofibrillar protein synthesis in older men. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinckaers, P.J.M.; Kouw, I.W.K.; Gorissen, S.H.M.; Houben, L.H.P.; Senden, J.M.; Wodzig, W.; de Groot, L.; Verdijk, L.B.; Snijders, T.; van Loon, L.J.C. The Muscle Protein Synthetic Response to the Ingestion of a Plant-Derived Protein Blend Does Not Differ from an Equivalent Amount of Milk Protein in Healthy Young Males. J. Nutr. 2023, 152, 2734–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanng, S.K.; Oxfeldt, M.; Pedersen, S.S.; Johansen, F.T.; Risikesan, J.; Lejel, T.; Bertram, H.C.; Hansen, M. Influence of protein source (cricket, pea, whey) on amino acid bioavailability and activation of the mTORC1 signaling pathway after resistance exercise in healthy young males. Eur. J. Nutr. 2023, 62, 1295–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colonetti, T.; Grande, A.J.; Milton, K.; Foster, C.; Alexandre, M.C.; Uggioni, M.L.; Rosa, M.I. Effects of whey protein supplement in the elderly submitted to resistance training: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 68, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteyne, A.J.; Coelho, M.O.C.; Porter, C.; Abdelrahman, D.R.; Jameson, T.S.O.; Jackman, S.R.; Blackwell, J.R.; Finnigan, T.J.A.; Stephens, F.B.; Dirks, M.L.; et al. Mycoprotein ingestion stimulates protein synthesis rates to a greater extent than milk protein in rested and exercised skeletal muscle of healthy young men: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 318–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, S.; Monteyne, A.J.; Whelehan, G.; van der Heijden, I.; Abdelrahman, D.R.; Murton, A.J.; Finnigan, T.J.A.; Stephens, F.B.; Wall, B.T. Ingestion of mycoprotein, pea protein, and their blend support comparable postexercise myofibrillar protein synthesis rates in resistance-trained individuals. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 325, E267–E279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burd, N.A.; Yang, Y.; Moore, D.R.; Tang, J.E.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Phillips, S.M. Greater stimulation of myofibrillar protein synthesis with ingestion of whey protein isolate v. micellar casein at rest and after resistance exercise in elderly men. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 958–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.E.; Alexander, D.D.; Perez, V. Effects of Whey Protein and Resistance Exercise on Body Composition: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2014, 33, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, M.; Lynch, H.; Dickinson, J.M.; Reed, K.E. No Difference Between the Effects of Supplementing With Soy Protein Versus Animal Protein on Gains in Muscle Mass and Strength in Response to Resistance Exercise. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 28, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, P.L.; Mata, F.; Morales, J.S.; Castillo-García, A.; Lucia, A. Does Beef Protein Supplementation Improve Body Composition and Exercise Performance? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanini, B.; Simonetto, A.; Zubani, M.; Castellano, M.; Gilioli, G. The Effects of Cow-Milk Protein Supplementation in Elderly Population: Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piri Damaghi, M.; Mirzababaei, A.; Moradi, S.; Daneshzad, E.; Tavakoli, A.; Clark, C.C.T.; Mirzaei, K. Comparison of the effect of soya protein and whey protein on body composition: A meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 127, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.T.; Harris, D.O.; Marshall, R.N.; Quinlan, J.I.; Edwards, S.J.; Allen, S.L.; Breen, L. Protein Source and Quality for Skeletal Muscle Anabolism in Young and Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 1901–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamseer, L.; Moher, D.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: Elaboration and explanation. BMJ 2015, 349, g7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutton, B.; Salanti, G.; Caldwell, D.M.; Chaimani, A.; Schmid, C.H.; Cameron, C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Straus, S.; Thorlund, K.; Jansen, J.P.; et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: Checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutton, B.; Catalá-López, F.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement extension for systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analysis: PRISMA-NMA. Med. Clin. 2016, 147, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thomas, J.; Chandler, J.; Cumpston, M.; Li, T.; Page, M.J.; Welch, V.A. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.4 (Updated August 2023), version 6.4 (updated August 2023) ed.; The Cochrane Collaboration: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begg, C.B.; Mazumdar, M. Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics 1994, 50, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Li, T.; Deeks, J.J. Chapter 6: Choosing effect measures and computing estimates of effect. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.4 (Updated August 2023); Higgins, J.P.T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; Cochrane: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.; Tong, T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences, 2nd ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associates: Hillsdale, MI, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Chaimani, A.; Caldwell, D.M.; Li, T.; Higgins, J.P.T.S.G. Chapter 11: Undertaking network meta-analyses. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 6.3 (Updated February 2022); Higgins, J.P.T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; Cochrane: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, D.; Boddington, P.; White, I.R. The design-by-treatment interaction model: A unifying framework for modelling loop inconsistency in network meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 2016, 7, 329–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salanti, G.; Ades, A.E.; Ioannidis, J.P. Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: An overview and tutorial. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrer, M.; Cuijpers, P.; Furukawa, T.A.; Ebert, D.D. Chapter 12: Network Meta-Analysis. In Doing Meta-Analysis with R: A Hands-On Guide; Harrer, M., Cuijpers, P., Furukawa, T.A., Ebert, D.D., Eds.; Chapman & Hall: London, UK; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Xie, F.; Yan, S.; Hu, X.; Jin, B.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Yin, D.; Xie, Q. Subhealth: Definition, criteria for diagnosis and potential prevalence in the central region of China. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, S.R.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, J.; Rücker, G. Network meta-analysis: Application and practice using R software. Epidemiol. Health 2019, 41, e2019013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brignardello-Petersen, R.; Bonner, A.; Alexander, P.E.; Siemieniuk, R.A.; Furukawa, T.A.; Rochwerg, B.; Hazlewood, G.S.; Alhazzani, W.; Mustafa, R.A.; Murad, M.H.; et al. Advances in the GRADE approach to rate the certainty in estimates from a network meta-analysis. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2018, 93, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papakonstantinou, T.; Nikolakopoulou, A.; Rücker, G.; Chaimani, A.; Schwarzer, G.; Egger, M.; Salanti, G. Estimating the contribution of studies in network meta-analysis: Paths, flows and streams. F1000Res 2018, 7, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, T.A.; Miura, T.; Chaimani, A.; Leucht, S.; Cipriani, A.; Noma, H.; Mitsuyasu, H.; Kanba, S.; Salanti, G. Using the contribution matrix to evaluate complex study limitations in a network meta-analysis: A case study of bipolar maintenance pharmacotherapy review. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salanti, G.; Del Giovane, C.; Chaimani, A.; Caldwell, D.M.; Higgins, J.P. Evaluating the quality of evidence from a network meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiocchia, V.; Nikolakopoulou, A.; Higgins, J.P.T.; Page, M.J.; Papakonstantinou, T.; Cipriani, A.; Furukawa, T.A.; Siontis, G.C.M.; Egger, M.; Salanti, G. ROB-MEN: A tool to assess risk of bias due to missing evidence in network meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aas, S.N.; Seynnes, O.; Benestad, H.B.; Raastad, T. Strength training and protein supplementation improve muscle mass, strength, and function in mobility-limited older adults: A randomized controlled trial. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 32, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amasene, M.; Besga, A.; Echeverria, I.; Urquiza, M.; Ruiz, J.R.; Rodriguez-Larrad, A.; Aldamiz, M.; Anaut, P.; Irazusta, J.; Labayen, I. Effects of Leucine-Enriched Whey Protein Supplementation on Physical Function in Post-Hospitalized Older Adults Participating in 12-Weeks of Resistance Training Program: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amasene, M.; Cadenas-Sanchez, C.; Echeverria, I.; Sanz, B.; Alonso, C.; Tobalina, I.; Irazusta, J.; Labayen, I.; Besga, A. Effects of Resistance Training Intervention along with Leucine-Enriched Whey Protein Supplementation on Sarcopenia and Frailty in Post-Hospitalized Older Adults: Preliminary Findings of a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arciero, P.J.; Baur, D.; Connelly, S.; Ormsbee, M.J. Timed-daily ingestion of whey protein and exercise training reduces visceral adipose tissue mass and improves insulin resistance: The PRISE study. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 117, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnarson, A.; Gudny Geirsdottir, O.; Ramel, A.; Briem, K.; Jonsson, P.V.; Thorsdottir, I. Effects of whey proteins and carbohydrates on the efficacy of resistance training in elderly people: Double blind, randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 67, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, R.; Hooshmand Moghadam, B.; Candow, D.G.; Elliott, B.T.; Wong, A.; Ashtary-Larky, D.; Forbes, S.C.; Rashidlamir, A. Effects of Icelandic yogurt consumption and resistance training in healthy untrained older males. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 127, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemben, M.G.; Witten, M.S.; Carter, J.M.; Eliot, K.A.; Knehans, A.W.; Bemben, D.A. The effects of supplementation with creatine and protein on muscle strength following a traditional resistance training program in middle-aged and older men. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2010, 14, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijeh, N.; Mohammadnia-Ahmadi, M.; Hooshamnd-Moghadam, B.; Eskandari, M.; Golestani, F. Effects of Soy Milk in Conjunction With Resistance Training on Physical Performance and Skeletal Muscle Regulatory Markers in Older Men. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2022, 24, 294–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candow, D.G.; Chilibeck, P.D.; Facci, M.; Abeysekara, S.; Zello, G.A. Protein supplementation before and after resistance training in older men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2006, 97, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candow, D.G.; Little, J.P.; Chilibeck, P.D.; Abeysekara, S.; Zello, G.A.; Kazachkov, M.; Cornish, S.M.; Yu, P.H. Low-dose creatine combined with protein during resistance training in older men. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2008, 40, 1645–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chale, A.; Cloutier, G.J.; Hau, C.; Phillips, E.M.; Dallal, G.E.; Fielding, R.A. Efficacy of whey protein supplementation on resistance exercise-induced changes in lean mass, muscle strength, and physical function in mobility-limited older adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2013, 68, 682–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.M. Effects of resistance training combined with nutritional intervention on alleviating sarcopenia in the elderly. Electron. J. Pract. Clin. Nurs. Sci. 2019, 4, 48–50. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Sheng, Y.L.; Qi, T.; Sheng, X.M.; Jin, X.W. Effects of fortified nutrition combining with resistance exercise on physical function and activity of daily living for elderly patients with sarcopenia. J. Nurs. Sci. 2017, 32, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colonetti, T.; Grande, A.J.; da Rocha, F.R.; Ronconi Dondossola, E.; Tuon, L.; Gomes Batista Teles, H.; Minotto Bom, B.; Colonetti, L.; da Rosa, M.I. Whey protein and vitamin D supplementation in institutionalized older adults: A randomized trial. Nutr. Health 2023, 29, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daly, R.M.; O’Connell, S.L.; Mundell, N.L.; Grimes, C.A.; Dunstan, D.W.; Nowson, C.A. Protein-enriched diet, with the use of lean red meat, combined with progressive resistance training enhances lean tissue mass and muscle strength and reduces circulating IL-6 concentrations in elderly women: A cluster randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Azevedo Bach, S.; Radaelli, R.; Beck Schemes, M.; Neske, R.; Garbelotto, C.; Roschel, H.; Silveira Pinto, R.; Dornelles Schneider, C. Can supplemental protein to low-protein containing meals superimpose on resistance-training muscle adaptations in older adults? A randomized clinical trial. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 162, 111760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Carvalho Bastone, A.; Nobre, L.N.; de Souza Moreira, B.; Rosa, I.F.; Ferreira, G.B.; Santos, D.D.L.; Monteiro, N.; Alves, M.D.; Gandra, R.A.; de Lira, E.M. Independent and combined effect of home-based progressive resistance training and nutritional supplementation on muscle strength, muscle mass and physical function in dynapenic older adults with low protein intake: A randomized controlled trial. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2020, 89, 104098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deer, R.R.; Dickinson, J.M.; Baillargeon, J.; Fisher, S.R.; Raji, M.; Volpi, E. A Phase I Randomized Clinical Trial of Evidence-Based, Pragmatic Interventions to Improve Functional Recovery After Hospitalization in Geriatric Patients. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2019, 74, 1628–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deibert, P.; Solleder, F.; König, D.; Vitolins, M.Z.; Dickhuth, H.H.; Gollhofer, A.; Berg, A. Soy protein based supplementation supports metabolic effects of resistance training in previously untrained middle aged males. Aging Male Off. J. Int. Soc. Study Aging Male 2011, 14, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirks, M.L.; Tieland, M.; Verdijk, L.B.; Losen, M.; Nilwik, R.; Mensink, M.; de Groot, L.C.P.G.M.; van Loon, L.J.C. Protein Supplementation Augments Muscle Fiber Hypertrophy but Does Not Modulate Satellite Cell Content During Prolonged Resistance-Type Exercise Training in Frail Elderly. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2017, 18, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, W.R.; Chilibeck, P.D.; Rooke, J.J.; Kaviani, M.; Krentz, J.R.; Haines, D.M. The effect of bovine colostrum supplementation in older adults during resistance training. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2014, 24, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulac, M.C.; Pion, C.H.; Lemieux, F.C.; Pinheiro Carvalho, L.; El Hajj Boutros, G.; Bélanger, M.; Gaudreau, P.; Chevalier, S.; Morais, J.A.; Noirez, P.; et al. Effects of slow- v. fast-digested protein supplementation combined with mixed power training on muscle function and functional capacities in older men. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 1017–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliot, K.A.; Knehans, A.W.; Bemben, D.A.; Witten, M.S.; Carter, J.; Bemben, M.G. The effects of creatine and whey protein supplementation on body composition in men aged 48 to 72 years during resistance training. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2008, 12, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiatarone, M.A.; O’Neill, E.F.; Ryan, N.D.; Clements, K.M.; Solares, G.R.; Nelson, M.E.; Roberts, S.B.; Kehayias, J.J.; Lipsitz, L.A.; Evans, W.J. Exercise Training and Nutritional Supplementation for Physical Frailty in Very Elderly People. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formica, M.B.; Gianoudis, J.; Nowson, C.A.; O’Connell, S.L.; Milte, C.; Ellis, K.A.; Daly, R.M. Effect of lean red meat combined with a multicomponent exercise program on muscle and cognitive function in older adults: A 6-month randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, P.; Mc Cormack, W.; Toomey, C.; Norton, C.; Saunders, J.; Kerin, E.; Lyons, M.; Jakeman, P. Twelve weeks’ progressive resistance training combined with protein supplementation beyond habitual intakes increases upper leg lean tissue mass, muscle strength and extended gait speed in healthy older women. Biogerontology 2017, 18, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gade, J.; Beck, A.M.; Andersen, H.E.; Christensen, B.; Rønholt, F.; Klausen, T.W.; Vinther, A.; Astrup, A. Protein supplementation combined with low-intensity resistance training in geriatric medical patients during and after hospitalisation: A randomised, double-blind, multicentre trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2019, 122, 1006–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granic, A.; Hurst, C.; Dismore, L.; Stevenson, E.; Sayer, A.A.; Aspray, T. Feasibility and acceptability of a milk and resistance exercise intervention to improve muscle function in community-dwelling older adults (MIlkMAN): Pilot study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffen, C.; Duncan, M.; Hattersley, J.; Weickert, M.O.; Dallaway, A.; Renshaw, D. Effects of resistance exercise and whey protein supplementation on skeletal muscle strength, mass, physical function, and hormonal and inflammatory biomarkers in healthy active older men: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 158, 111651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gronstedt, H.; Vikstrom, S.; Cederholm, T.; Franzen, E.; Luiking, Y.C.; Seiger, A.; Wimo, A.; Faxen-Irving, G.; Bostrom, A.M. Effect of Sit-to-Stand Exercises Combined With Protein-Rich Oral Supplementation in Older Persons: The Older Person’s Exercise and Nutrition Study. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2020, 21, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamarsland, H.; Johansen, M.K.; Seeberg, F.; Brochmann, M.; Garthe, I.; Benestad, H.B.; Raastad, T. Native Whey Induces Similar Adaptation to Strength Training as Milk, despite Higher Levels of Leucine, in Elderly Individuals. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haß, U.; Kochlik, B.; Herpich, C.; Rudloff, S.; Norman, K. Effects of an Omega-3 Supplemented, High-Protein Diet in Combination with Vibration and Resistance Exercise on Muscle Power and Inflammation in Old Adults: A Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haub, M.D.; Wells, A.M.; Campbell, W.W. Beef and soy-based food supplements differentially affect serum lipoprotein-lipid profiles because of changes in carbohydrate intake and novel nutrient intake ratios in older men who resistive-train. Metabolism 2005, 54, 769–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haub, M.D.; Wells, A.M.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Campbell, W.W. Effect of protein source on resistive-training-induced changes in body composition and muscle size in older men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 76, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.N.; Li, D.M. Observation on the Clinical Effect of Dietary Nutrition Intervention Combined with Anti-resistance Training in Elderly Male Patients with Sarcopenia. Smart Healthc. 2022, 8, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, L.; Olesen, J.L.; Matsumoto, K.; Doi, T.; Mizuno, M.; Alsted, T.J.; Mackey, A.L.; Schwarz, P.; Kjaer, M. Protein-containing nutrient supplementation following strength training enhances the effect on muscle mass, strength, and bone formation in postmenopausal women. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 105, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holwerda, A.M.; Overkamp, M.; Paulussen, K.J.M.; Smeets, J.S.J.; van Kranenburg, J.; Backx, E.M.P.; Gijsen, A.P.; Goessens, J.P.B.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J.C. Protein Supplementation after Exercise and before Sleep Does Not Further Augment Muscle Mass and Strength Gains during Resistance Exercise Training in Active Older Men. J. Nutr. 2018, 148, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Kim, N.; Choi, Y.J.; Lee, Y.; Yun, J.; Park, S.J.; Park, H.S.; Chung, Y.S.; Park, Y.K. Leucine-Enriched Protein Supplementation Increases Lean Body Mass in Healthy Korean Adults Aged 50 Years and Older: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karelis, A.D.; Messier, V.; Suppere, C.; Briand, P.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R. Effect of cysteine-rich whey protein (immunocal(R)) supplementation in combination with resistance training on muscle strength and lean body mass in non-frail elderly subjects: A randomized, double-blind controlled study. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2015, 19, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemmler, W.; Kohl, M.; Fröhlich, M.; Jakob, F.; Engelke, K.; von Stengel, S.; Schoene, D. Effects of High-Intensity Resistance Training on Osteopenia and Sarcopenia Parameters in Older Men with Osteosarcopenia-One-Year Results of the Randomized Controlled Franconian Osteopenia and Sarcopenia Trial (FrOST). J Bone Min. Res. 2020, 35, 1634–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmler, W.; Kohl, M.; Jakob, F.; Engelke, K.; von Stengel, S. Effects of High Intensity Dynamic Resistance Exercise and Whey Protein Supplements on Osteosarcopenia in Older Men with Low Bone and Muscle Mass. Final Results of the Randomized Controlled FrOST Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, M.; Crognale, D.; Cogan, K.E.; Contarelli, S.; Egan, B.; Newsholme, P.; De Vito, G. The effects of a combined bodyweight-based and elastic bands resistance training, with or without protein supplementation, on muscle mass, signaling and heat shock response in healthy older people. Exp. Gerontol. 2019, 115, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukuljan, S.; Nowson, C.A.; Bass, S.L.; Sanders, K.; Nicholson, G.C.; Seibel, M.J.; Salmon, J.; Daly, R.M. Effects of a multi-component exercise program and calcium-vitamin-D3-fortified milk on bone mineral density in older men: A randomised controlled trial. Osteoporos. Int. 2009, 20, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukuljan, S.; Nowson, C.A.; Sanders, K.; Daly, R.M. Effects of resistance exercise and fortified milk on skeletal muscle mass, muscle size, and functional performance in middle-aged and older men: An 18-mo randomized controlled trial. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 1864–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J.; Yoshida, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Kim, H.; Suzuki, T.; Lee, Y. Effects of a combined physical training and nutrition intervention on physical performance and health-related quality of life in prefrail older women living in the community: A randomized controlled trial. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2015, 16, e261–e268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamb, D.A.; Moore, J.H.; Smith, M.A.; Vann, C.G.; Osburn, S.C.; Ruple, B.A.; Fox, C.D.; Smith, K.S.; Altonji, O.M.; Power, Z.M.; et al. The effects of resistance training with or without peanut protein supplementation on skeletal muscle and strength adaptations in older individuals. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leenders, M.; Verdijk, L.B.; Van der Hoeven, L.; Van Kranenburg, J.; Nilwik, R.; Wodzig, W.K.; Senden, J.M.; Keizer, H.A.; Van Loon, L.J. Protein supplementation during resistance-type exercise training in the elderly. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2013, 45, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.D.; Liao, Y.H.; Liou, T.H.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Kuo, Y.C.; Chen, H.C. Effects of Protein-Rich Nutritional Composition Supplementation on Sarcopenia Indices and Physical Activity during Resistance Exercise Training in Older Women with Knee Osteoarthritis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maesta, N.; Nahas, E.A.; Nahas-Neto, J.; Orsatti, F.L.; Fernandes, C.E.; Traiman, P.; Burini, R.C. Effects of soy protein and resistance exercise on body composition and blood lipids in postmenopausal women. Maturitas 2007, 56, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltais, M.L.; Ladouceur, J.P.; Dionne, I.J. The Effect of Resistance Training and Different Sources of Postexercise Protein Supplementation on Muscle Mass and Physical Capacity in Sarcopenic Elderly Men. J. Strength Cond. Res./Natl. Strength Cond. Assoc. 2016, 30, 1680–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKenna, C.F.; Salvador, A.F.; Hughes, R.L.; Scaroni, S.E.; Alamilla, R.A.; Askow, A.T.; Paluska, S.A.; Dilger, A.C.; Holscher, H.D.; De Lisio, M. Higher protein intake during resistance training does not potentiate strength, but modulates gut microbiota, in middle-aged adults: A randomized control trial. Am J Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 320, E900–E913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertz, K.H.; Reitelseder, S.; Bechshoeft, R.; Bulow, J.; Højfeldt, G.; Jensen, M.; Schacht, S.R.; Lind, M.V.; Rasmussen, M.A.; Mikkelsen, U.R.; et al. The effect of daily protein supplementation, with or without resistance training for 1 year, on muscle size, strength, and function in healthy older adults: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, E.G.; Nowson, C.A.; Dunstan, D.W.; Kerr, D.A.; Menzies, D.; Daly, R.M. Effects of whey protein plus vitamin D supplementation combined with progressive resistance training on glycaemic control, body composition, muscle function and cardiometabolic risk factors in middle-aged and older overweight/obese adults with type 2 diabetes: A 24-week randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, C.J.; D’Souza, R.F.; Mitchell, S.M.; Figueiredo, V.C.; Miller, B.F.; Hamilton, K.L.; Peelor, F.F., 3rd; Coronet, M.; Pileggi, C.A.; Durainayagam, B.; et al. Impact of dairy protein during limb immobilization and recovery on muscle size and protein synthesis; a randomized controlled trial. J. Appl. Physiol. 2018, 124, 717–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molnar, A.; Jonasne Sztruhar, I.; Csontos, A.A.; Ferencz, C.; Varbiro, S.; Szekacs, B. Special nutrition intervention is required for muscle protective efficacy of physical exercise in elderly people at highest risk of sarcopenia. Physiol. Int. 2016, 103, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, H.; Tokuda, Y. Effect of whey protein supplementation after resistance exercise on the muscle mass and physical function of healthy older women: A randomized controlled trial. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Tokuda, Y. De-Training Effects Following Leucine-Enriched Whey Protein Supplementation and Resistance Training in Older Adults with Sarcopenia: A Randomized Controlled Trial with 24 Weeks of Follow-Up. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2022, 26, 994–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabuco, H.C.G.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Fernandes, R.R.; Sugihara Junior, P.; Cavalcante, E.F.; Cunha, P.M.; Antunes, M.; Nunes, J.P.; Venturini, D.; Barbosa, D.S.; et al. Effect of whey protein supplementation combined with resistance training on body composition, muscular strength, functional capacity, and plasma-metabolism biomarkers in older women with sarcopenic obesity: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 32, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabuco, H.C.G.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Fernandes, R.R.; Sugihara Junior, P.; Cavalcante, E.F.; Venturini, D.; Barbosa, D.S.; Silva, A.M.; Sardinha, L.B.; Cyrino, E.S. Effects of Protein Intake Beyond Habitual Intakes Associated With Resistance Training on Metabolic Syndrome-Related Parameters, Isokinetic Strength, and Body Composition in Older Women. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2019, 27, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabuco, H.C.G.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Sugihara Junior, P.; Fernandes, R.R.; Cavalcante, E.F.; Antunes, M.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Teixeira, D.C.; Silva, A.M.; Sardinha, L.B.; et al. Effects of Whey Protein Supplementation Pre- or Post-Resistance Training on Muscle Mass, Muscular Strength, and Functional Capacity in Pre-Conditioned Older Women: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabuco, H.C.G.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Sugihara Junior, P.; Fernandes, R.R.; Cavalcante, E.F.; Venturini, D.; Barbosa, D.S.; Silva, A.M.; Sardinha, L.B.; Cyrino, E.S. Effects of pre- or post-exercise whey protein supplementation on body fat and metabolic and inflammatory profile in pre-conditioned older women: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. NMCD 2019, 29, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, M.I.; Mikhail, A.; Lan, L.; Di Carlo, A.; Hamilton, B.; Barnard, K.; Hettinga, B.P.; Hatcher, E.; Tarnopolsky, M.G.; Nederveen, J.P.; et al. A Five-Ingredient Nutritional Supplement and Home-Based Resistance Exercise Improve Lean Mass and Strength in Free-Living Elderly. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oesen, S.; Halper, B.; Hofmann, M.; Jandrasits, W.; Franzke, B.; Strasser, E.M.; Graf, A.; Tschan, H.; Bachl, N.; Quittan, M.; et al. Effects of elastic band resistance training and nutritional supplementation on physical performance of institutionalised elderly—A randomized controlled trial. Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 72, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsatti, F.L.; Maestá, N.; de Oliveira, E.P.; Nahas Neto, J.; Burini, R.C.; Nunes, P.R.P.; Souza, A.P.; Martins, F.M.; Nahas, E.P. Adding Soy Protein to Milk Enhances the Effect of Resistance Training on Muscle Strength in Postmenopausal Women. J. Diet. Suppl. 2018, 15, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roschel, H.; Hayashi, A.P.; Fernandes, A.L.; Jambassi-Filho, J.C.; Hevia-Larraín, V.; de Capitani, M.; Santana, D.A.; Gonçalves, L.S.; de Sá-Pinto, A.L.; Lima, F.R.; et al. Supplement-based nutritional strategies to tackle frailty: A multifactorial, double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4849–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seino, S.; Sumi, K.; Narita, M.; Yokoyama, Y.; Ashida, K.; Kitamura, A.; Shinkai, S. Effects of Low-Dose Dairy Protein Plus Micronutrient Supplementation during Resistance Exercise on Muscle Mass and Physical Performance in Older Adults: A Randomized, Controlled Trial. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahar, S.; Kamaruddin, N.S.; Badrasawi, M.; Sakian, N.I.; Abd Manaf, Z.; Yassin, Z.; Joseph, L. Effectiveness of exercise and protein supplementation intervention on body composition, functional fitness, and oxidative stress among elderly Malays with sarcopenia. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S.; Bedi, R.; Sandhu, J.S. Effect of soy isolate protein and resistance exercises on muscle performance and bone health of osteopenic/osteoporotic post-menopausal women. J Women Aging 2013, 25, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, A.L.S.; Machado-Lima, A.; Brech, G.C.; Greve, J.M.D.; Dos Santos, J.R.; Inojossa, T.R.; Rogero, M.M.; Salles, J.E.N.; Santarem-Sobrinho, J.M.; Davis, C.L.; et al. The Influence of Whey Protein on Muscle Strength, Glycemic Control and Functional Tasks in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Resistance Exercise Program: Randomized and Triple Blind Clinical Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugihara Junior, P.; Ribeiro, A.S.; Nabuco, H.C.G.; Fernandes, R.R.; Tomeleri, C.M.; Cunha, P.M.; Venturini, D.; Barbosa, D.S.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Cyrino, E.S. Effects of Whey Protein Supplementation Associated With Resistance Training on Muscular Strength, Hypertrophy, and Muscle Quality in Preconditioned Older Women. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 28, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Yan, X.; Fan, P.; Xu, D.; Li, Y. Analysis of the Clincal Effect ofDietary Nutrition Intervention Combined with Resistance Training on the Cognitive Function of Elderly Male Patients with Sarcopenia. Progr. Mod. Biomed. 2020, 20, 2698–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, R.L.; Brinkworth, G.D.; Noakes, M.; Buckley, J.D. Muscle strength gains during resistance exercise training are attenuated with soy compared with dairy or usual protein intake in older adults: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieland, M.; Dirks, M.L.; van der Zwaluw, N.; Verdijk, L.B.; van de Rest, O.; de Groot, L.C.; van Loon, L.J. Protein supplementation increases muscle mass gain during prolonged resistance-type exercise training in frail elderly people: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2012, 13, 713–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisan, M.C.; Souza, J.M.; Marucci Mde, F. Influence of soy protein intake and weight training on the resting energy expenditure of postmenopausal women. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2010, 56, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unterberger, S.; Aschauer, R.; Zöhrer, P.A.; Draxler, A.; Franzke, B.; Strasser, E.M.; Wagner, K.H.; Wessner, B. Effects of an increased habitual dietary protein intake followed by resistance training on fitness, muscle quality and body composition of seniors: A randomised controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1034–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdijk, L.B.; Jonkers, R.A.M.; Gleeson, B.G.; Beelen, M.; Meijer, K.; Savelberg, H.H.C.M.; Wodzig, K.W.H.W.; Dendale, P.; Van Loon, L.J.C. Protein supplementation before and after exercise does not further augment skeletal muscle hypertrophy after resistance training in elderly men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verreijen, A.M.; Verlaan, S.; Engberink, M.F.; Swinkels, S.; de Vogel-van den Bosch, J.; Weijs, P.J. A high whey protein-, leucine-, and vitamin D-enriched supplement preserves muscle mass during intentional weight loss in obese older adults: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumaran, R.K.; Daly, R.M.; Tan, V.P.S. “We Want More”-Perspectives of Sarcopenic Older Women on the Feasibility of High-Intensity Progressive Resistance Exercises and a Whey-Protein Nutrition Intervention. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1176523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikberg, S.; Sörlén, N.; Brandén, L.; Johansson, J.; Nordström, A.; Hult, A.; Nordström, P. Effects of Resistance Training on Functional Strength and Muscle Mass in 70-Year-Old Individuals With Pre-sarcopenia: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2019, 20, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, M.G.; He, J.; Schroeder, E.T. Periodized resistance training with and without supplementation improve body composition and performance in older men. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 114, 891–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisgarber, K.D.; Candow, D.G.; Farthing, J.P. Whey protein and high-volume resistance training in postmenopausal women. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2015, 19, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Kimura, Y.; Ishiyama, D.; Nishio, N.; Otobe, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Ohji, S.; Koyama, S.; Sato, A.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Synergistic effect of bodyweight resistance exercise and protein supplementation on skeletal muscle in sarcopenic or dynapenic older adults. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2019, 19, 429–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdzieblik, D.; Jendricke, P.; Oesser, S.; Gollhofer, A.; König, D. The Influence of Specific Bioactive Collagen Peptides on Body Composition and Muscle Strength in Middle-Aged, Untrained Men: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Gao, H.L.; Guo, N.Z.; Chea, Z.M.; Wu, X.Y.; He, D.L.; Wei, L.Q.; Shen, X.C.; Lv, W.Y. Effect of health education and whey protein supplementation combined with resistance exercise on the intervention of middle—Aged and elderly people with sarcopenia. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2022, 12, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.Y.; Chan, R.; Kwok, T.; Cheng, K.C.; Ha, A.; Woo, J. Effects of exercise and nutrition supplementation in community-dwelling older Chinese people with sarcopenia: A randomized controlled trial. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorissen, S.H.M.; Trommelen, J.; Kouw, I.W.K.; Holwerda, A.M.; Pennings, B.; Groen, B.B.L.; Wall, B.T.; Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Horstman, A.M.H.; Koopman, R.; et al. Protein Type, Protein Dose, and Age Modulate Dietary Protein Digestion and Phenylalanine Absorption Kinetics and Plasma Phenylalanine Availability in Humans. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burd, N.A.; Gorissen, S.H.; van Vliet, S.; Snijders, T.; van Loon, L.J. Differences in postprandial protein handling after beef compared with milk ingestion during postexercise recovery: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.E.; Moore, D.R.; Kujbida, G.W.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Phillips, S.M. Ingestion of whey hydrolysate, casein, or soy protein isolate: Effects on mixed muscle protein synthesis at rest and following resistance exercise in young men. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, S.B.; Tarnopolsky, M.A.; Macdonald, M.J.; Macdonald, J.R.; Armstrong, D.; Phillips, S.M. Consumption of fluid skim milk promotes greater muscle protein accretion after resistance exercise than does consumption of an isonitrogenous and isoenergetic soy-protein beverage. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Kong, J.; Underwood, C.; Petocz, P.; Hirani, V.; Dawson, B.; O’Leary, F. Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of protein and amino acid supplements in older adults with acute or chronic conditions. Br. J. Nutr. 2018, 119, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.D.; Lee, P.H.; Hsiao, D.J.; Huang, S.W.; Tsauo, J.Y.; Chen, H.C.; Liou, T.H. Effects of Protein Supplementation Combined with Exercise Intervention on Frailty Indices, Body Composition, and Physical Function in Frail Older Adults. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, D.; Lin, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, S.-J. Effect of nutritional supplement combined with exercise intervention on sarcopenia in the elderly: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Sci. 2017, 4, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naclerio, F.; Larumbe-Zabala, E. Effects of Whey Protein Alone or as Part of a Multi-ingredient Formulation on Strength, Fat-Free Mass, or Lean Body Mass in Resistance-Trained Individuals: A Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2016, 46, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.D.; Chen, H.C.; Huang, S.W.; Liou, T.H. The Role of Muscle Mass Gain Following Protein Supplementation Plus Exercise Therapy in Older Adults with Sarcopenia and Frailty Risks: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression Analysis of Randomized Trials. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gade, J.; Pedersen, R.J.; Beck, A.M. Effect of Protein or Essential Amino Acid Supplementation During Prolonged Resistance Exercise Training in Older Adults on Body Composition, Muscle Strength, and Physical Performance Parameters: A Systematic Review. Rehabil. Process Outcome 2018, 7, 1179572718765760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, K.; Chen, G.-C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, X.; Szeto, I.M.Y.; Qin, L.-Q. Effects of milk proteins supplementation in older adults undergoing resistance training: A meta-analysis of randomized control trials. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Jeong, K.; Lim, S.; Lee, S.; Baek, Y. Association of Dietary Protein Sources and Their Adequacy, Body Composition and Risk of Sarcopenic Obesity in South Korean Populations: A Cross-Sectional Study. Metabolites 2024, 14, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Baek, Y.; Jeong, K.; Lee, S. Association of Dietary Factors With Grip Strength, Body Fat, and Prevalence of Sarcopenic Obesity in Rural Korean Elderly With Cardiometabolic Multimorbidity. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 910481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.Y.; Lu, Z.H.; Leung, J.C.S.; Kwok, T.C.Y. Association of dietary protein intake, inflammation with muscle mass, physical performance and incident sarcopenia in Chinese community-dwelling older adults. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2024, 28, 100163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeuninx, B.; McKendry, J.; Wilson, D.; Martin, U.; Breen, L. Age-Related Anabolic Resistance of Myofibrillar Protein Synthesis Is Exacerbated in Obese Inactive Individuals. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 3535–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, I.F.; Verdijk, L.B.; Hamer, H.M.; Verlaan, S.; Luiking, Y.C.; Kouw, I.W.K.; Senden, J.M.; van Kranenburg, J.; Gijsen, A.P.; Bierau, J.; et al. Both basal and post-prandial muscle protein synthesis rates, following the ingestion of a leucine-enriched whey protein supplement, are not impaired in sarcopenic older males. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1440–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, E.A.; Colenso-Semple, L.; McKellar, S.R.; Yau, T.; Ali, M.U.; Fitzpatrick-Lewis, D.; Sherifali, D.; Gaudichon, C.; Tomé, D.; Atherton, P.J.; et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis of protein intake to support muscle mass and function in healthy adults. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herda, A.A.; McKay, B.D.; Herda, T.J.; Costa, P.B.; Stout, J.R.; Cramer, J.T. Changes in Strength, Mobility, and Body Composition Following Self-Selected Exercise in Older Adults. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2021, 29, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallinson, J.E.; Wardle, S.L.; O’Leary, T.J.; Greeves, J.P.; Cegielski, J.; Bass, J.; Brook, M.S.; Wilkinson, D.J.; Smith, K.; Atherton, P.J.; et al. Protein dose requirements to maximize skeletal muscle protein synthesis after repeated bouts of resistance exercise in young trained women. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2023, 33, 2470–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churchward-Venne, T.A.; Pinckaers, P.J.M.; Smeets, J.S.J.; Betz, M.W.; Senden, J.M.; Goessens, J.P.B.; Gijsen, A.P.; Rollo, I.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J.C. Dose-response effects of dietary protein on muscle protein synthesis during recovery from endurance exercise in young men: A double-blind randomized trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 303–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holwerda, A.M.; Paulussen, K.J.M.; Overkamp, M.; Goessens, J.P.B.; Kramer, I.F.; Wodzig, W.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J.C. Dose-Dependent Increases in Whole-Body Net Protein Balance and Dietary Protein-Derived Amino Acid Incorporation into Myofibrillar Protein During Recovery from Resistance Exercise in Older Men. J. Nutr. 2019, 149, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, C.J.; Milan, A.M.; Mitchell, S.M.; Zeng, N.; Ramzan, F.; Sharma, P.; Knowles, S.O.; Roy, N.C.; Sjödin, A.; Wagner, K.H.; et al. The effects of dietary protein intake on appendicular lean mass and muscle function in elderly men: A 10-wk randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 106, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
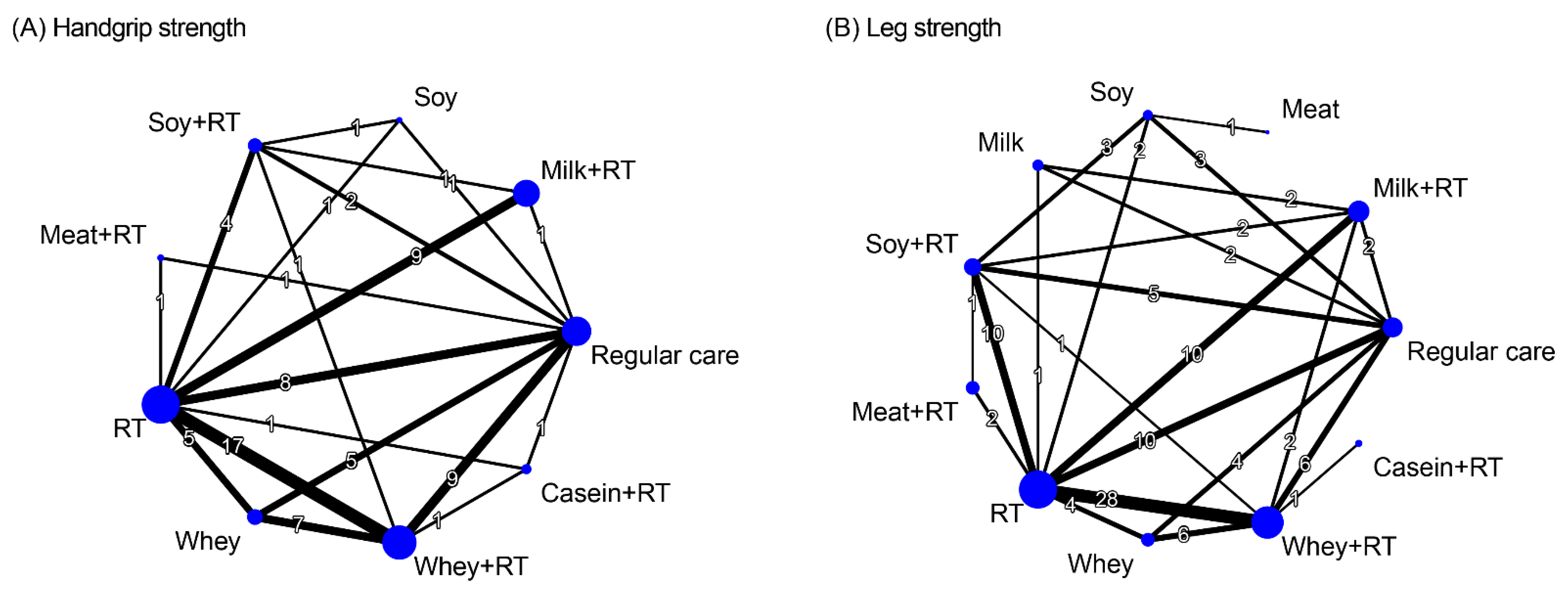
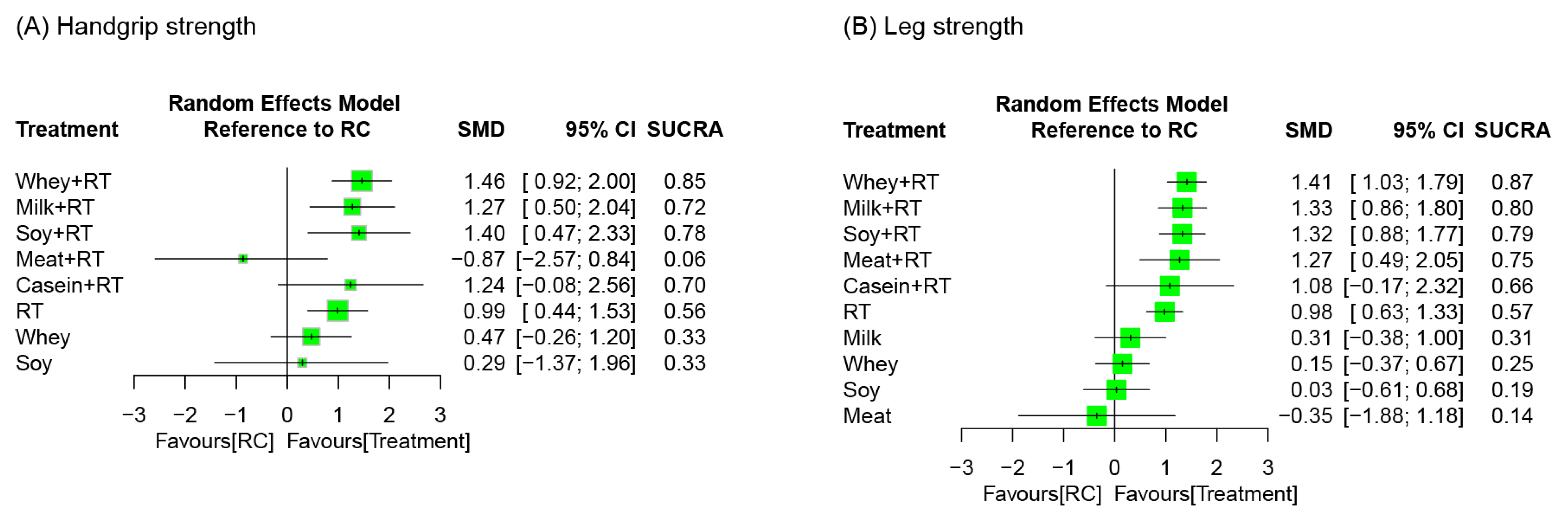
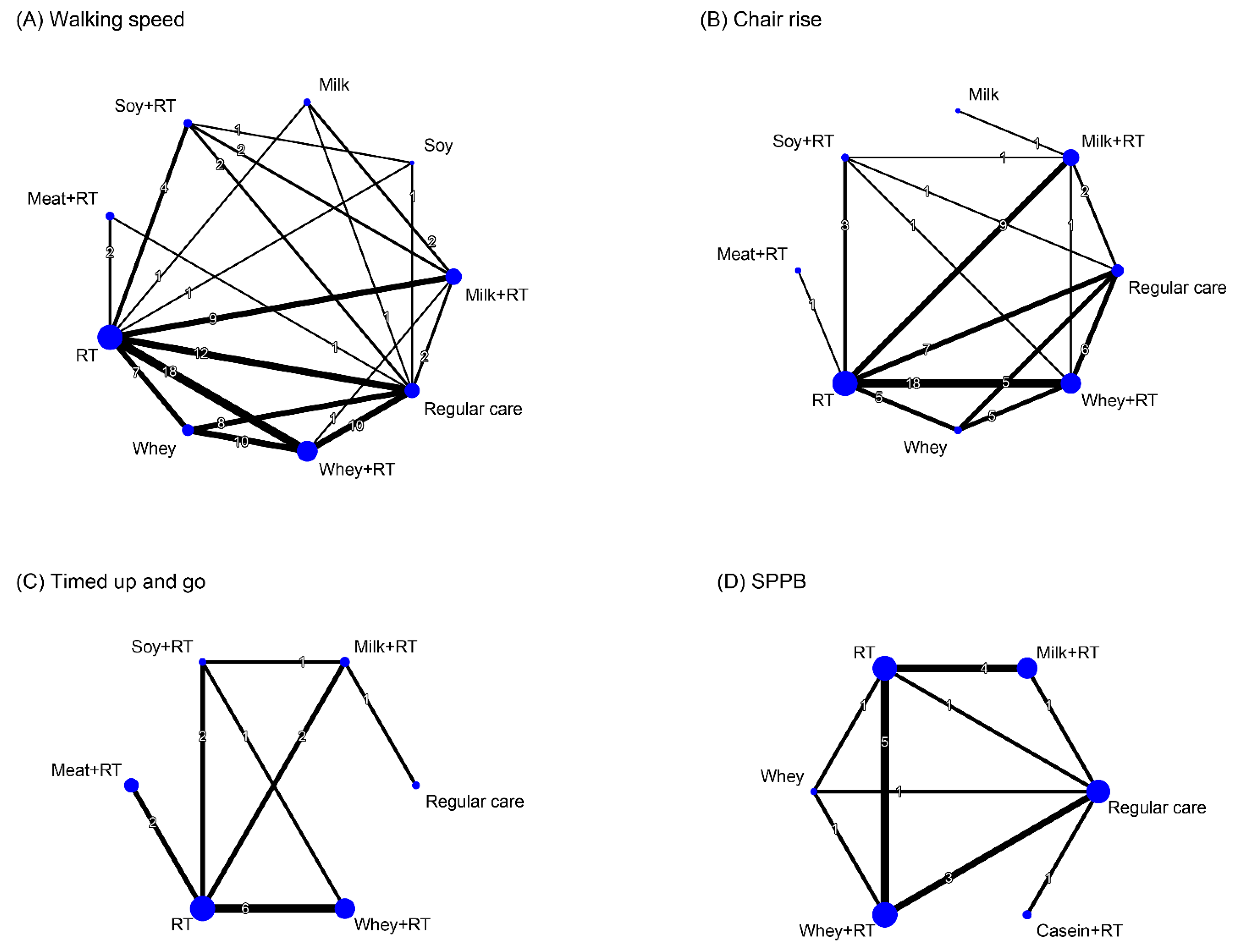
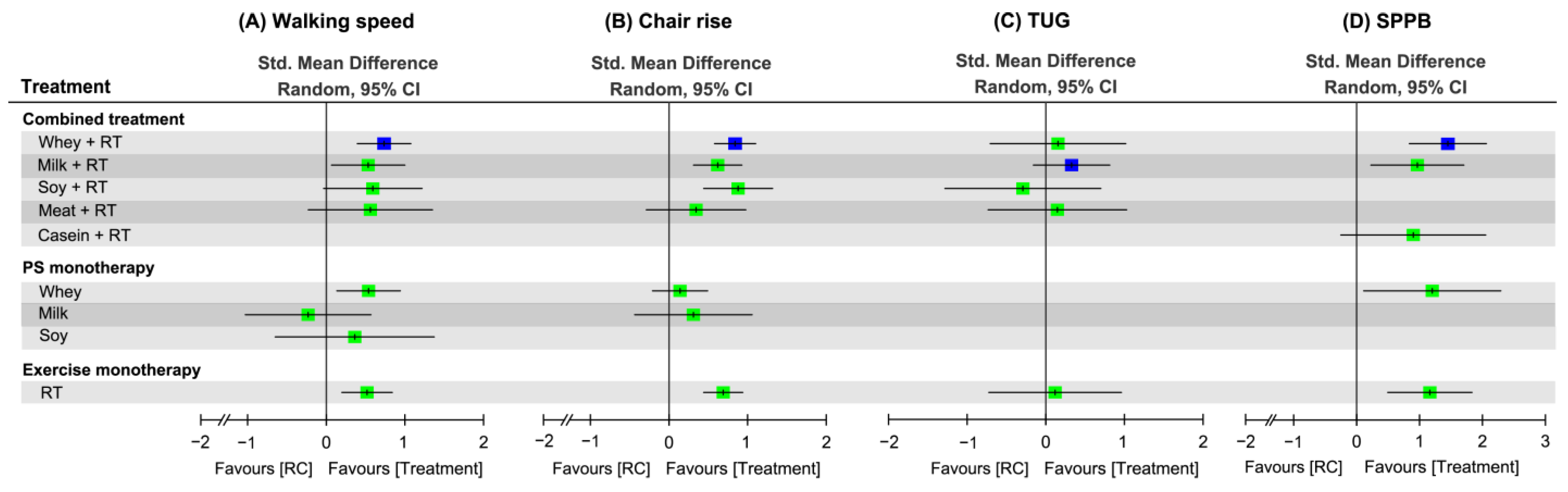
| Study Arm | Combined Treatment | Resistance Training (Combined with or without Placebo Supplement) | Protein Supplementation Alone | Control (Placebo Supplement or Regular Care) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | Trials (Groups), n a | Sample (n) | Mean (Range) b | Trials (Groups), n a | Sample (n) | Mean (Range) b | Trials (Groups), n a | Sample (n) | Mean (Range) b | Trials (Groups), n a | Sample (n) | Mean (Range) b |
| Age, year | 78 (89) | 2458 | 69.8 (47.0–87.2) | 62 (64) | 1664 | 69.8 (47.4–86.2) | 19 (19) | 415 | 68.6 (50.0–85.7) | 27 (27) | 735 | 73.8 (54.1–89.2) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 74 (83) | 2287 | 26.1 (18.8–32.7) | 60 (62) | 1624 | 26.9 (18.8–33.3) | 18 (18) | 400 | 25.5 (18.6–31.0) | 25 (25) | 592 | 24.9 (18.9–30.0) |
| Sex, n, % | ||||||||||||
| Sex-specific trial | ||||||||||||
| Men | 22 (26) | 573 | 100 | 18 (20) | 332 | 100 | 4 (4) | 91 | 100 | 8 (8) | 288 | 100 |
| Women | 16 (17) | 375 | 100 | 14 (14) | 275 | 100 | 5 (5) | 98 | 100 | 3 (3) | 46 | 100 |
| Sex mixed trial | 39 (45) | 1494 | 29 (29) | 1052 | 10 (10) | 226 | 16 (16) | 401 | ||||
| Men | 614 | 42.3 (13.0–87.5) | 422 | 41.5 (9.8–73.7) | 89 | 40.0 (16.7–73.3) | 175 | 44.8 (12.5–80.0) | ||||
| Women | 880 | 57.7 (12.5–87.0) | 630 | 58.5 (26.3–90.2) | 137 | 60.0 (26.7–83.3) | 226 | 55.2 (20.0–87.5) | ||||
| Population (area) | ||||||||||||
| America | 29 (36) | 669 | 25 (27) | 434 | 6 (6) | 107 | 7 (7) | 108 | ||||
| Asia | 18 (18) | 589 | 12 (12) | 333 | 7 (7) | 147 | 11 (11) | 387 | ||||
| Europe | 23 (26) | 710 | 17 (17) | 469 | 5 (5) | 116 | 6 (6) | 109 | ||||
| Oceania | 8 (9) | 490 | 8 (8) | 428 | 1 (1) | 45 | 3 (3) | 131 | ||||
| Physical condition | ||||||||||||
| Untrained healthy | 33 (38) | 947 | 27 (29) | 692 | 8 (8) | 202 | 9 (9) | 199 | ||||
| Dynapenia | 4 (4) | 92 | 3 (3) | 78 | 2 (2) | 39 | 3 (3) | 51 | ||||
| Frailty | 12 (13) | 394 | 12 (12) | 356 | 2 (2) | 44 | 5 (5) | 122 | ||||
| Sarcopenia | 18 (20) | 516 | 11 (11) | 202 | 6 (6) | 105 | 10 (10) | 353 | ||||
| Sedentary or inactive | 7 (9) | 213 | 5 (5) | 100 | 2 (2) | 25 | 1 (1) | 10 | ||||
| Overweight or obesity | 5 (6) | 296 | 5 (5) | 236 | 0 | 0 | ||||||
| Protein source of supplementation | ||||||||||||
| Whey | 43 (47) | 1311 | 11 (11) | 243 | ||||||||
| Milk | 17 (18) | 553 | 2 (2) | 73 | ||||||||
| Soy | 14 (14) | 324 | 6 (6) | 99 | ||||||||
| Casein | 4 (4) | 94 | 0 | |||||||||
| Meat | 5 (5) | 194 | 0 | |||||||||
| Peanut | 1 (1) | 20 | 0 | |||||||||
| Intervention compliance (%) | ||||||||||||
| Protein supplement | 40 (47) | 1287 | 91.5 (64–100) | 37 (37) | 323 | 87.8 (73–100) | ||||||
| Resistance training | 46 (52) | 1505 | 87.3 (44–100) | 38 (38) | 1117 | 86.2 (44–100) | ||||||
| Placebo supplement | 15 (15) | 300 | 93.8 (71.5–100) | 4 (4) | 55 | 89.4 (75–99) | ||||||
| Muscle mass (baseline) | ||||||||||||
| Total lean mass, kg | 41 (47) | 1354 | 45.9 (31.8–59.2) | 36 (37) | 1050 | 46.2 (32.0–60.8) | 7 (7) | 158 | 46.2 (39.9–56.6) | 7 (7) | 117 | 49.0 (47.9–51.5) |
| Appendicular lean mass, kg | 38 (41) | 1160 | 18.8 (7.9–30.5) | 36 (36) | 955 | 18.8 (8.0–30.0) | 9 (9) | 161 | 18.8 (12.8–27.2) | 11 (11) | 260 | 19.2 (12.6–26.7) |
| Total lean index, kg/m2 | 44 (50) | 1406 | 17.2 (13.6–22.9) | 39 (40) | 1143 | 17.4 (13.9–22.5) | 8 (8) | 168 | 17.2 (15.5–19.0) | 8 (8) | 128 | 17.6 (16.6–19.1) |
| Appendicular lean index, kg/m2 | 39 (41) | 1150 | 7.0 (3.0–9.4) | 35 (35) | 935 | 7.1 (3.0–9.4) | 11 (11) | 208 | 7.1 (5.4–8.8) | 11 (11) | 257 | 7.1 (5.2–8.9) |
| Handgrip strength (baseline), kg | ||||||||||||
| Sex-specific trial | ||||||||||||
| Men | 7 (8) | 282 | 30.3 (15.3–41.1) | 4 (4) | 64 | 33.2 (19.7–42.2) | 2 (2) | 37 | 25.5 (18.8–30.0) | 3 (3) | 190 | 18.6 (15.2–21.1) |
| Women | 4 (5) | 93 | 20.2 (15.8–22.4) | 4 (4) | 71 | 20.3 (15.1–23.1) | 1 (1) | 25 | 23 | 0 | ||
| Sex mixed trial | 23 (25) | 819 | 26.5 (13.8–41.2) | 19 (19) | 619 | 26.8 (15.8–41.8) | 6 (6) | 119 | 22.3 (16.4–35.6) | 11 (11) | 300 | 23.1 (15.1–33.6) |
| Physical mobility (baseline) | ||||||||||||
| 5-time chair rise, s | 28 (31) | 1032 | 12.2 (4.6–26.5) | 25 (25) | 850 | 13.6 (4.7–30.0) | 4 (4) | 83 | 12.6 (7.7–18.7) | 7 (7) | 216 | 11.9 (7.8–18.6) |
| Walking speed, m/s | 36 (39) | 1277 | 1.26 (0.44–2.33) | 31 (31) | 956 | 1.18 (0.51–2.05) | 13 (13) | 322 | 1.25 (0.45–2.14) | 15 (15) | 407 | 1.26 (0.47–2.05) |
| Global mobility c | 16 (16) | 402 | 9.0 (6.2–11.4) | 10 (10) | 181 | 9.3 (7.1–11.2) | 1 (1) | 20 | 6.2 | 7 (7) | 224 | 8.6 (7.8–11.0) |
| Treatment (Common Comparator: Regular Care) | GRADE Certainty of Evidence a | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Muscle Mass | Muscle Strength | Physical Mobility | |||||
| Handgrip | Leg Strength | Walking Speed | Chair Rise | Timed Up and Go | SPPB | ||
| Combined therapy | |||||||
| Casein + RT | ⨁⊝⊝⊝ b,d,e | ⨁⊝⊝⊝ b,c,d | ⨁⊝⊝⊝ b,d,e | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,e | |||
| Meat + RT | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,e | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,d | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,e | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,d | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,d | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,d | |
| Milk + RT | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,e | ⨁⨁⨁⊝ b | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,e | ⨁⨁⨁⊝ b | ⨁⨁⨁⊝ b | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,d | ⨁⨁⨁⊝ b |
| Peanut + RT | ⨁⊝⊝⊝ b,d,e | ||||||
| Soy + RT | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,e | ⨁⨁⨁⨁ | ⨁⊝⊝⊝ b,c,e | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,d | ⨁⨁⨁⨁ | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,d | |
| Whey + RT | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,e | ⨁⨁⨁⊝ b | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,e | ⨁⨁⨁⊝ b | ⨁⨁⨁⊝ b | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,d | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,c |
| Monotherapy | |||||||
| Meat | ⨁⊝⊝⊝ b,d,e | ⨁⊝⊝⊝ b,d,e | |||||
| Milk | ⨁⊝⊝⊝ b,d,e | ⨁⊝⊝⊝ b,d,e | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,d | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,d | |||
| Soy | ⨁⊝⊝⊝ b,d,e | ⨁⨁⨁⊝ d | ⨁⊝⊝⊝ b,c,d,e | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,d | |||
| Whey | ⨁⊝⊝⊝ b,d,e | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,d | ⨁⊝⊝⊝ b,d,e | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,c | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,d | ⨁⨁⨁⊝ b | |
| Resistance training | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,e | ⨁⨁⨁⊝ b | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,e | ⨁⨁⨁⊝ b | ⨁⨁⨁⊝ b | ⨁⨁⊝⊝ b,d | ⨁⨁⨁⊝ b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, C.-D.; Huang, S.-W.; Chen, H.-C.; Huang, M.-H.; Liou, T.-H.; Lin, C.-L. Comparative Efficacy of Different Protein Supplements on Muscle Mass, Strength, and Physical Indices of Sarcopenia among Community-Dwelling, Hospitalized or Institutionalized Older Adults Undergoing Resistance Training: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2024, 16, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070941
Liao C-D, Huang S-W, Chen H-C, Huang M-H, Liou T-H, Lin C-L. Comparative Efficacy of Different Protein Supplements on Muscle Mass, Strength, and Physical Indices of Sarcopenia among Community-Dwelling, Hospitalized or Institutionalized Older Adults Undergoing Resistance Training: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2024; 16(7):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070941
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Chun-De, Shih-Wei Huang, Hung-Chou Chen, Mao-Hua Huang, Tsan-Hon Liou, and Che-Li Lin. 2024. "Comparative Efficacy of Different Protein Supplements on Muscle Mass, Strength, and Physical Indices of Sarcopenia among Community-Dwelling, Hospitalized or Institutionalized Older Adults Undergoing Resistance Training: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" Nutrients 16, no. 7: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070941
APA StyleLiao, C.-D., Huang, S.-W., Chen, H.-C., Huang, M.-H., Liou, T.-H., & Lin, C.-L. (2024). Comparative Efficacy of Different Protein Supplements on Muscle Mass, Strength, and Physical Indices of Sarcopenia among Community-Dwelling, Hospitalized or Institutionalized Older Adults Undergoing Resistance Training: A Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients, 16(7), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16070941






