Postnatal Consumption of Black Bean Powder Protects against Obesity and Dyslipidemia in Male Adult Rat Offspring from Obese Pregnancies
Abstract
1. Introduction
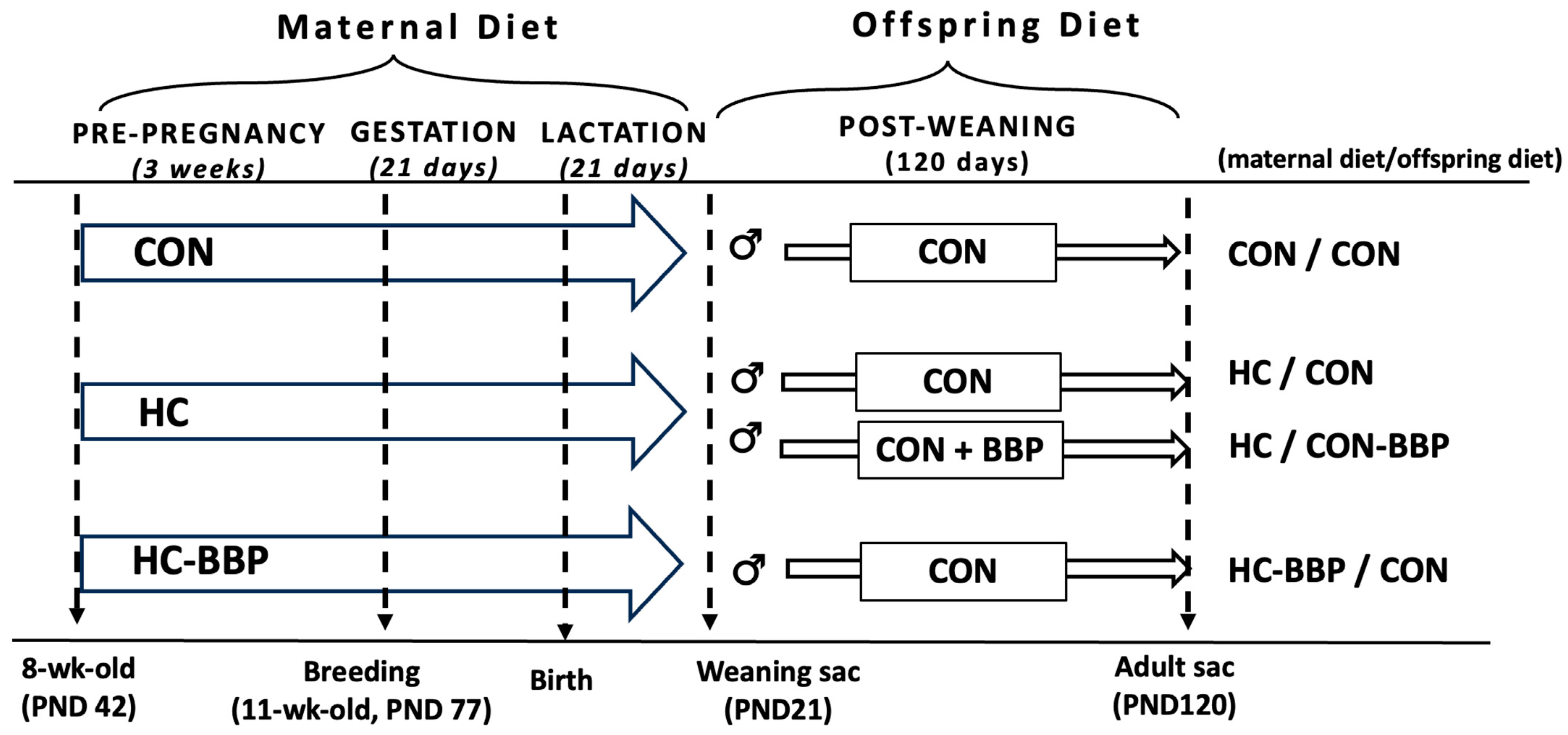
2. Materials and Methods
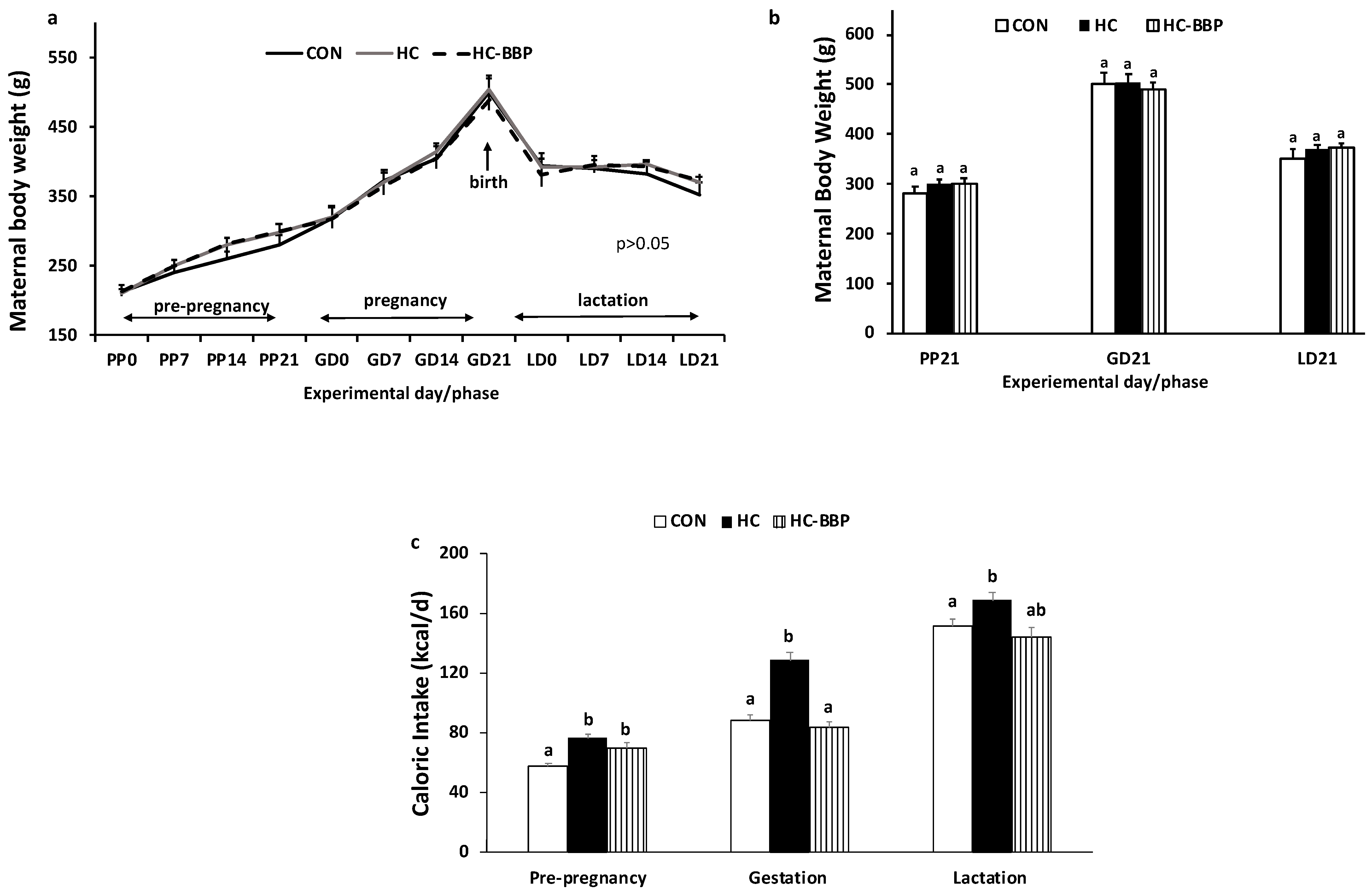
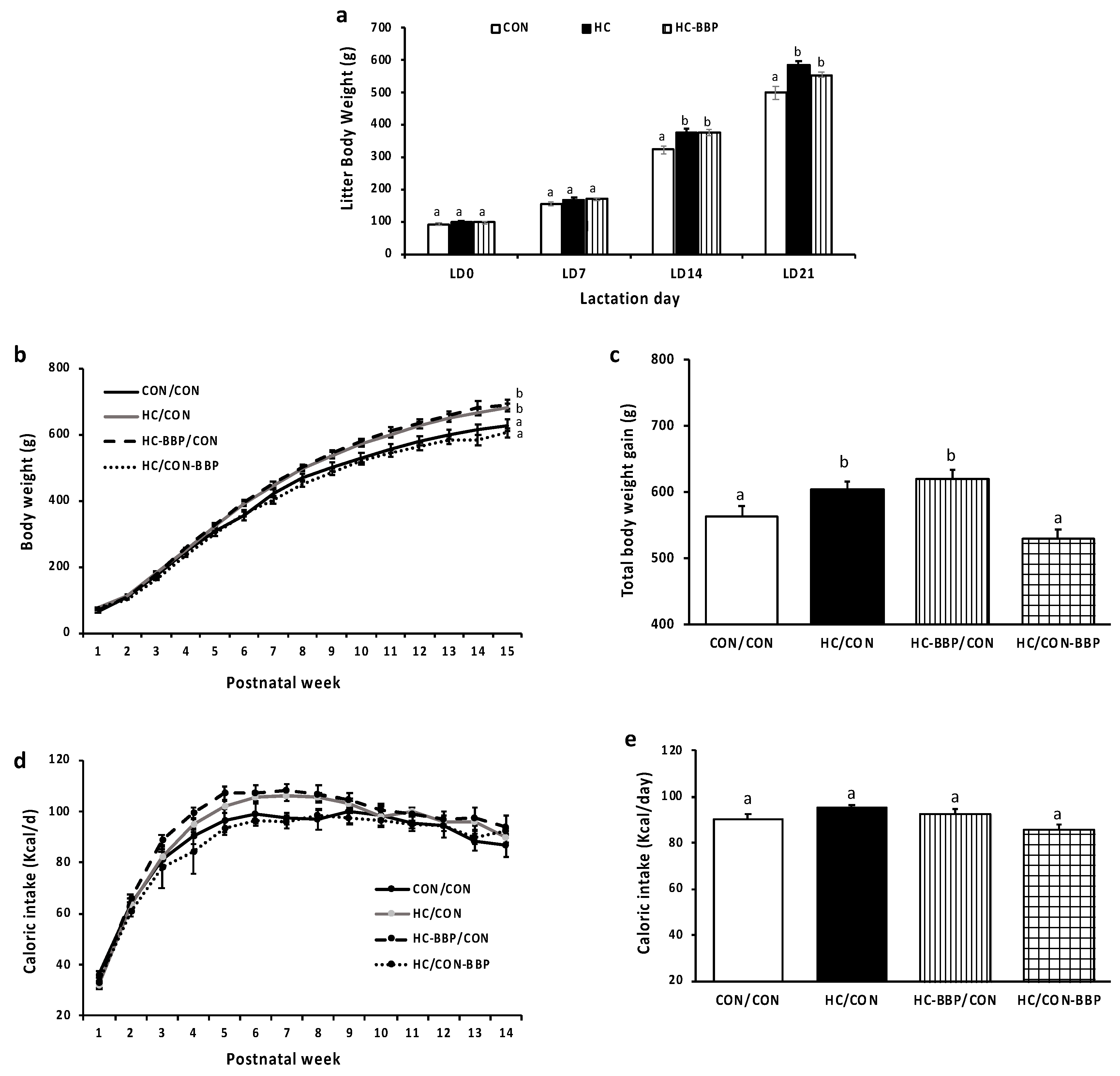
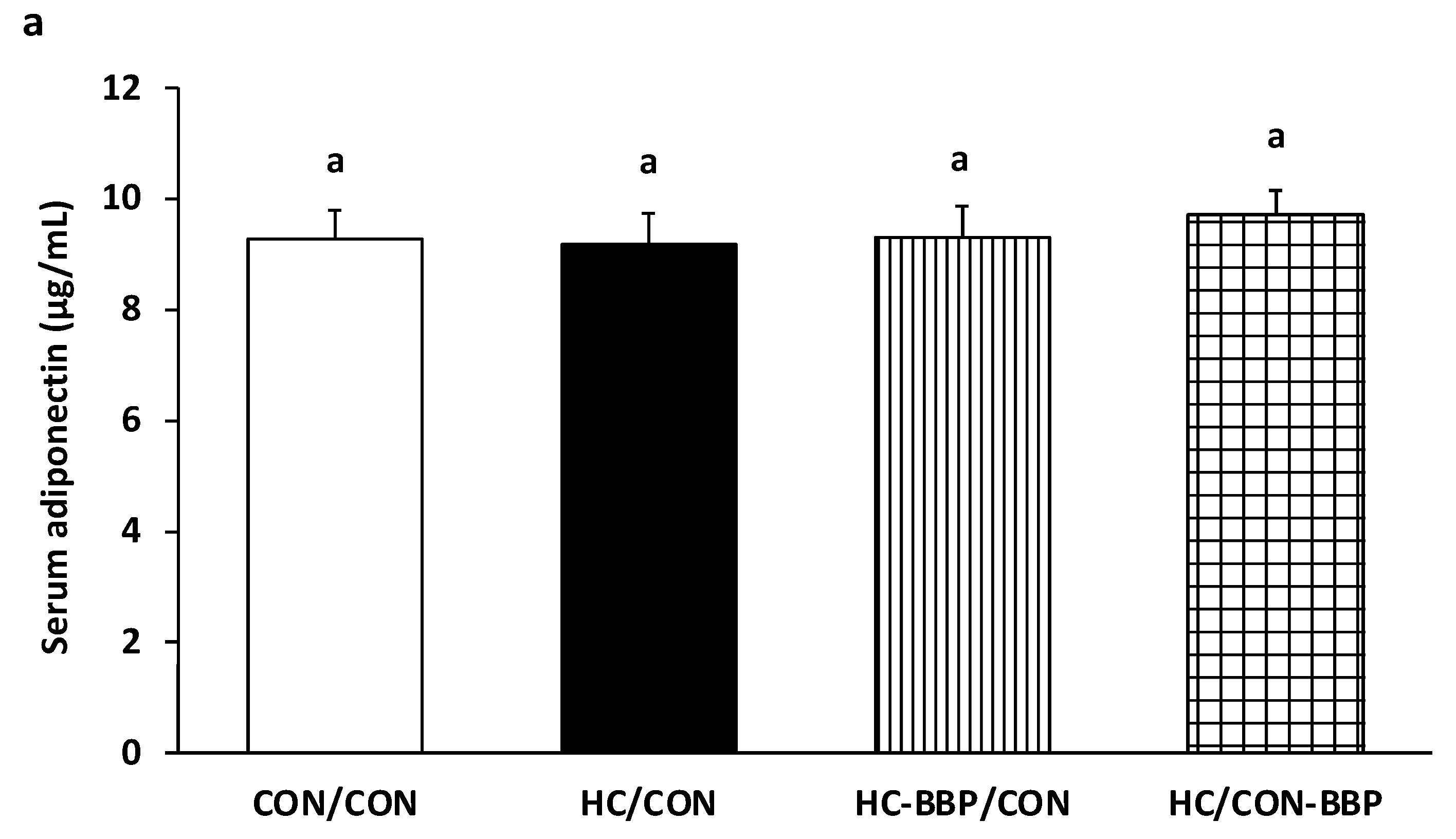
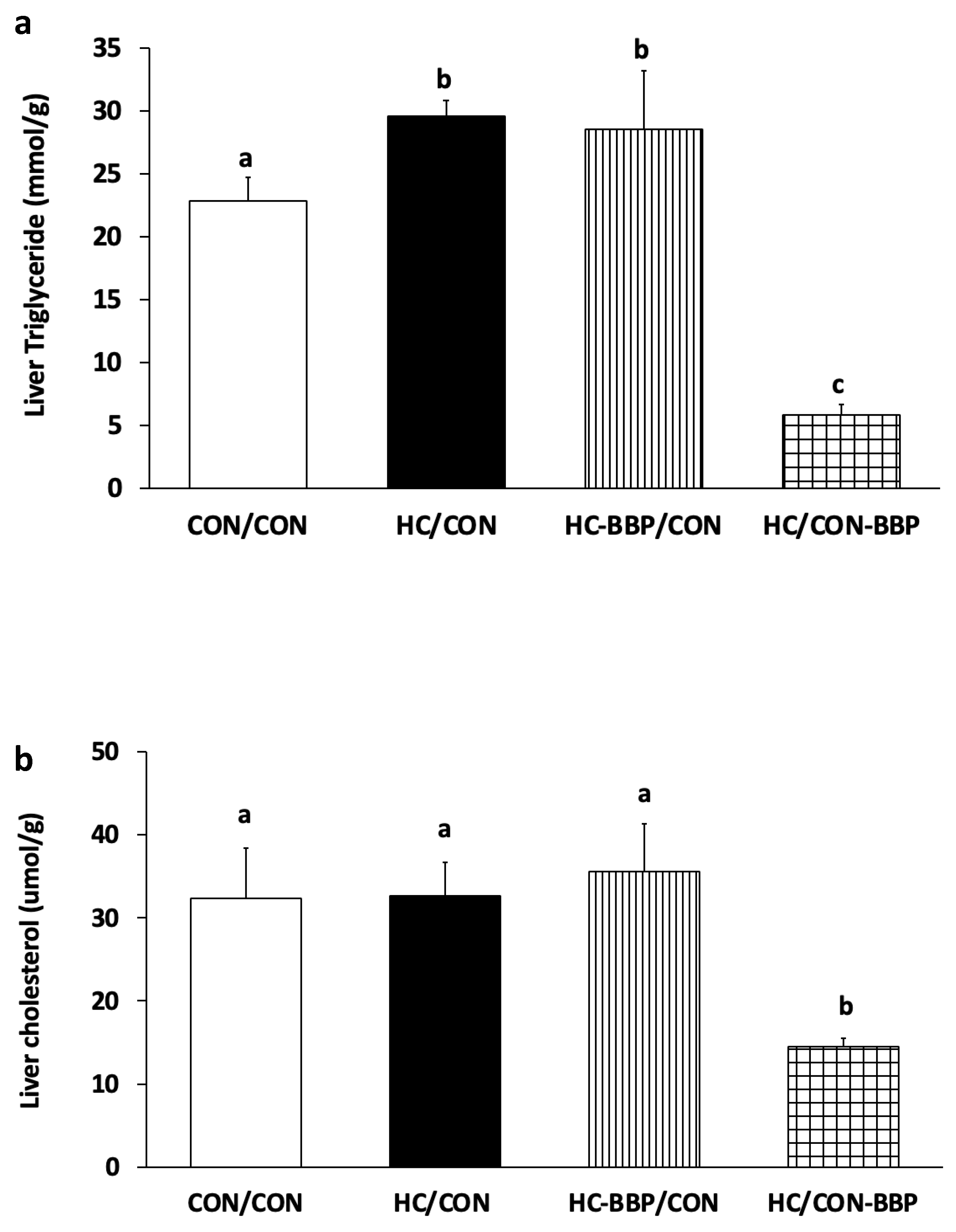
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hales, C.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity among Adults: United States, 2017–2018; NCHS Data Brief; National Center for Health Statistics: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Elshenawy, S.; Simmons, R. Maternal obesity and prenatal programming. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 435, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, M.; Ross, M.G. Maternal-infant nutrition and development programming of offspring appetite and obesity. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, A.R.; Rodrigo, N.; Cao, Q.; Joseph, O.; Gill, A.J.; Saad, S.; Pollock, C.A.; Glastras, S.J. Maternal Weight Intervention in the Perinatal Period Improves Liver Health in the Offspring of Mothers with Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 16, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidl, T.B.; Wager, J.L.; Baker, L.G.; Brightwell, A.L.; Melan, K.M.; Larion, S.; Sarr, O.; Regnault, T.R.; Urbanski, S.J.; Thompson, J.A. High maternal adiposity during pregnancy programs an imbalance in the lipidome and predisposes to diet-induced hepatosteatosis in the offspring. Biosci. Rep. 2023, 43, BSR20231060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan-Martinez, D.H.; Bosquez-Mendoza, V.M.; Ruiz-Noa, Y.; Ibarra-Reynoso, L.D.R.; Barbosa-Sabanero, G.; Lazo-de-la-Vega-Monroy, M.L. Nutritional, pharmacological, and environmental programming of NAFLD in early life. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2023, 324, G99–G114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.; Hafner, H.; Varghese, M.; Griffin, C.; Clemente, J.; Islam, M.; Carlson, Z.; Zhu, A.; Hak, L.; Abrishami, S.; et al. Programming effects of maternal and gestational obesity on offspring metabolism and metabolic inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickers, M.H. Developmental programming and transgenerational transmission of obesity. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 64, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leghi, G.E.; Netting, M.J.; Middleton, P.F.; Wlodek, M.E.; Geddes, D.T.; Muhlhausler, A.B.S. The impact of maternal obesity on human milk macronutrient composition: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellsworth, L.; Perng, W.; Harman, E.; Das, A.; Pennathur, S.; Gregg, B. Impact of maternal overweight and obesity on milk composition and infant growth. Matern. Child. Nutr. 2020, 16, e12979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrettini, S.; Caroli, A.; Torlone, E. Nutrition and metabolic adaptations in physiological and complicated pregnancy: Focus on obesity and gestational diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 611929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.N.; Tain, Y.L. The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly of Pregnancy Nutrients and Developmental Programming of Adult Disease. Nutrients 2019, 11, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, E.; Martinez-Samayoa, P.M.; Rodriguez-Gonzalez, G.L.; Nathanielsz, P.W. Dietary intervention prior to pregnancy reverses metabolic programming in male offspring of obese rats. J. Physiol. 2010, 588, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Peng, H.; Xu, H.; Li, J.; Golovko, M.; Cheng, H.; Lynch, E.C.; Liu, L.; McCauley, N.; Kennedy, L.; et al. Maternal diet intervention before pregnancy primes offspring lipid metabolism in liver. Lab. Investig. 2020, 100, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaxton, L.; Espey, E. Family Planning American Style Redux: Unintended Pregnancy Improves, Barriers Remain. Obs. Gynecol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 44, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero, P.; Milagro, F.I.; Campion, J.; Martinez, J.A. Supplementation with methyl donors during lactation to high-fat-sucrose-fed dams protects offspring against liver fat accumulation when consuming an obesogenic diet. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2014, 5, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, L.; Menikdiwela, K.R.; Clevenger, S.; Eboh, T.; Allen, L.; Koboziev, I.; Scoggin, S.; Rashid, A.M.; Moussa, H.; Moustaid-Moussa, N. Maternal and Postnatal Supplementation of Fish Oil Improves Metabolic Health of Mouse Male Offspring. Obesity 2018, 26, 1740–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, H.S.; Doucet, É.; Power, K.A. Dietary pulses as a means to improve the gut microbiome, inflammation, and appetite control in obesity. Obes. Rev. 2023, 24, e13598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Bamboriya, S.D.; Rani, K.; Meena, R.S.; Sheoran, S.; Loyal, A.; Kumawat, A.; Jhariya, M.K. Grain legumes: A diversified diet for sustainable livelihood, food, and nutritional security. In Advances in Legumes for Sustainable Intensification; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 157–178. [Google Scholar]
- Monk, J.M.; Wu, W.; Lepp, D.; Wellings, H.R.; Hutchinson, A.L.; Liddle, D.M.; Graf, D.; Pauls, K.P.; Robinson, L.E.; Power, K.A. Navy bean supplemented high-fat diet improves intestinal health, epithelial barrier integrity and critical aspects of the obese inflammatory phenotype. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 70, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermsdorff, H.H.; Zulet, M.A.; Abete, I.; Martinez, J.A. A legume-based hypocaloric diet reduces proinflammatory status and improves metabolic features in overweight/obese subjects. Eur. J. Nutr. 2011, 50, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; de Souza, R.J.; Choo, V.L.; Ha, V.; Cozma, A.I.; Chiavaroli, L.; Mirrahimi, A.; Blanco Mejia, S.; Di Buono, M.; Bernstein, A.M.; et al. Effects of dietary pulse consumption on body weight: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.E.; Parnell, J.A.; Tunnicliffe, J.M.; Han, J.; Sturzenegger, T.; Reimer, R.A. Consuming yellow pea fiber reduces voluntary energy intake and body fat in overweight/obese adults in a 12-week randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour-Niazi, S.; Mirmiran, P.; Fallah-Ghohroudi, A.; Azizi, F. Non-soya legume-based therapeutic lifestyle change diet reduces inflammatory status in diabetic patients: A randomised cross-over clinical trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winham, D.M.; Hutchins, A.M.; Thompson, S.V. Glycemic Response to Black Beans and Chickpeas as Part of a Rice Meal: A Randomized Cross-Over Trial. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeysekara, S.; Chilibeck, P.D.; Vatanparast, H.; Zello, G.A. A pulse-based diet is effective for reducing total and LDL-cholesterol in older adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108 (Suppl. S1), S103–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viguiliouk, E.; Glenn, A.J.; Nishi, S.K.; Chiavaroli, L.; Seider, M.; Khan, T.; Bonaccio, M.; Iacoviello, L.; Mejia, S.B.; Jenkins, D.J.A.; et al. Associations between Dietary Pulses Alone or with Other Legumes and Cardiometabolic Disease Outcomes: An Umbrella Review and Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, S308–S319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinangeli, C.P.; Curran, J.; Barr, S.I.; Slavin, J.; Puri, S.; Swaminathan, S.; Tapsell, L.; Patterson, C.A. Enhancing nutrition with pulses: Defining a recommended serving size for adults. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 990–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreani, G.A.; Mahmood, S.; Patel, M.S.; Rideout, T.C. Maternal pea fiber supplementation to a high calorie diet in obese pregnancies protects male offspring from metabolic dysfunction in adulthood. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2024, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rideout, T.C.; Andreani, G.A.; Pembroke, J.; Choudhary, D.; Browne, R.W.; Mahmood, S.; Patel, M.S. Maternal Pea Protein Intake Provides Sex-Specific Protection against Dyslipidemia in Offspring from Obese Pregnancies. Nutrients 2023, 15, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.L.; Loader, T.B.; Anderson, H.D.; Zahradka, P.; Taylor, C.G. Regular Black Bean Consumption Is Necessary to Sustain Improvements in Small-Artery Vascular Compliance in the Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat. Nutrients 2020, 12, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, H.J.; McGinley, J.N.; Neil, E.S.; Brick, M.A. Beneficial Effects of Common Bean on Adiposity and Lipid Metabolism. Nutrients 2017, 9, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmuth-Hoene, A.E.; Schelenz, R. Effect of dietary fiber on mineral absorption in growing rats. J. Nutr. 1980, 110, 1774–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rideout, T.C.; Harding, S.V.; Jones, P.J. Consumption of plant sterols reduces plasma and hepatic triglycerides and modulates the expression of lipid regulatory genes and de novo lipogenesis in C57BL/6J mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2010, 54 (Suppl. S1), S7–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouwels, S.; Sakran, N.; Graham, Y.; Leal, A.; Pintar, T.; Yang, W.; Kassir, R.; Singhal, R.; Mahawar, K.; Ramnarain, D. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A review of pathophysiology, clinical management and effects of weight loss. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalligeros, M.; Vassilopoulos, A.; Vassilopoulos, S.; Victor, D.W.; Mylonakis, E.; Noureddin, M. Prevalence of Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD, MetALD, and ALD) in the United States: NHANES 2017–2020. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, in press. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Dungubat, E.; Kusano, H.; Fukusato, T. Pathology and pathogenesis of metabolic dysfunction-associated Steatotic liver disease-associated hepatic tumors. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwärzler, J.; Grabherr, F.; Grander, C.; Adolph, T.E.; Tilg, H. The pathophysiology of MASLD: An immunometabolic perspective. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2024, 20, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.K.; Chuah, K.H.; Rajaram, R.B.; Lim, L.L.; Ratnasingam, J.; Vethakkan, S.R. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): A State-of-the-Art Review. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 32, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, predictions, risk factors and prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Kim, B.H.; Seo, H.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, H.H.; Son, H.H.; Choi, M.H. Cholesterol-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and atherosclerosis aggravated by systemic inflammation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Lu, L.G. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Dyslipidemia, Risk for Cardiovascular Complications, and Treatment Strategy. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2015, 3, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kneeman, J.M.; Misdraji, J.; Corey, K.E. Secondary causes of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2012, 5, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rooyen, D.M.; Larter, C.Z.; Haigh, W.G.; Yeh, M.M.; Ioannou, G.; Kuver, R.; Lee, S.P.; Teoh, N.C.; Farrell, G.C. Hepatic free cholesterol accumulates in obese, diabetic mice and causes nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1393–1403, 1403 e1391–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, T.A.; Davidson, N.O. Cholesterol and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Renewed focus on an old villain. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1995–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed-Abdul, M.M. Lipid Metabolism in Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Metabolites 2023, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, K.; Teratani, T.; Suzuki, T.; Shimizu, M.; Sato, H.; Narimatsu, K.; Okada, Y.; Kurihara, C.; Irie, R.; Yokoyama, H.; et al. Free cholesterol accumulation in hepatic stellate cells: Mechanism of liver fibrosis aggravation in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. Hepatology 2014, 59, 154–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Link, F.; Han, M.; Chaudhary, R.; Asimakopoulos, A.; Liebe, R.; Yao, Y.; Hammad, S.; Dropmann, A.; Krizanac, M. The Interplay of TGF-β1 and Cholesterol Orchestrating Hepatocyte Cell Fate, EMT, and Signals for HSC Activation. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 17, 567–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayonrinde, O.T.; Oddy, W.H.; Adams, L.A.; Mori, T.A.; Beilin, L.J.; de Klerk, N.; Olynyk, J.K. Infant nutrition and maternal obesity influence the risk of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adolescents. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quek, S.X.Z.; Tan, E.X.; Ren, Y.P.; Muthiah, M.; Loo, E.X.L.; Tham, E.H.; Siah, K.T.H. Factors early in life associated with hepatic steatosis. World J. Hepatol. 2022, 14, 1235–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, C.C.; Perng, W.; Sauder, K.A.; Shapiro, A.L.B.; Starling, A.P.; Friedman, C.; Felix, J.F.; Kupers, L.K.; Moore, B.F.; Hebert, J.R.; et al. Maternal Diet Quality During Pregnancy and Offspring Hepatic Fat in Early Childhood: The Healthy Start Study. J. Nutr. 2023, 153, 1122–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Dong, L.; Hou, D.; Zhou, S. Protective Effects of White Kidney Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) against Diet-Induced Hepatic Steatosis in Mice Are Linked to Modification of Gut Microbiota and Its Metabolites. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, H.; Inaba, Y.; Kimura, K.; Asahara, S.I.; Kido, Y.; Matsumoto, M.; Motoyama, T.; Tachibana, N.; Kaneko, S.; Kohno, M.; et al. Dietary Mung Bean Protein Reduces Hepatic Steatosis, Fibrosis, and Inflammation in Male Mice with Diet-Induced, Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunner, K.T.; Henneberg, C.J.; Wilechansky, R.M.; Long, M.T. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Obesity Treatment. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2019, 8, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, H.J.; Lutsiv, T.; McGinley, J.N.; Fitzgerald, V.K.; Neil, E.S. Consumption of Common Bean Suppresses the Obesogenic Increase in Adipose Depot Mass: Impact of Dose and Biological Sex. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.E.; Ramos-Roman, M.A.; Browning, J.D.; Parks, E.J. Increased de novo lipogenesis is a distinct characteristic of individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parlati, L.; Regnier, M.; Guillou, H.; Postic, C. New targets for NAFLD. JHEP Rep. 2021, 3, 100346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Una, M.; Lopez-Mancheno, Y.; Dieguez, C.; Fernandez-Rojo, M.A.; Novelle, M.G. Unraveling the Role of Leptin in Liver Function and Its Relationship with Liver Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Cortegana, C.; Garcia-Galey, A.; Tami, M.; Del Pino, P.; Carmona, I.; Lopez, S.; Alba, G.; Sanchez-Margalet, V. Role of Leptin in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Tam, C.C.; Meng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Alves, P.; Yokoyama, W. Cooked Black Turtle Beans Ameliorate Insulin Resistance and Restore Gut Microbiota in C57BL/6J Mice on High-Fat Diets. Foods 2021, 10, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ingredient | Experimental Diets 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | HC | HC-BBP | CON-BBP | |
| Casein | 18.96 | 23.31 | 18.00 | 7.00 |
| Corn Starch | 52.13 | 8.33 | 7.00 | 22.88 |
| Maltodextrin | 14.22 | 11.65 | 10.00 | 14.22 |
| Sucrose | 0.38 | 20.60 | 10.00 | 0.38 |
| Cellulose | 4.74 | 5.83 | 5.83 | 6.74 |
| Black bean powder | 0.00 | 0.00 | 20.00 | 40.00 |
| Soybean Oil | 2.37 | 2.91 | 2.91 | 2.00 |
| Lard | 1.90 | 20.69 | 19.85 | 1.50 |
| Cholesterol | 0.00 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.00 |
| Mineral Mix | 4.74 | 5.83 | 5.83 | 4.74 |
| Vitamin Mix | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.12 | 0.09 |
| L-Cystine | 0.28 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.28 |
| Choline Bitartrate | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.23 | 0.19 |
| Energy contribution | ||||
| Total energy (Kcal/g) | 3.82 | 4.69 | 4.56 | 3.51 |
| % energy from fat | 10.04 | 45.26 | 45.36 | 10.18 |
| % energy from protein | 20.13 | 20.16 | 20.59 | 20.02 |
| % energy from Carbohydrate | 69.82 | 34.59 | 34.06 | 69.82 |
| Fiber Content (%) | ||||
| Total fiber | 4.74 | 5.83 | 4.25 | 6.74 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choudhary, D.; Andreani, G.A.; Mahmood, S.; Wen, X.; Patel, M.S.; Rideout, T.C. Postnatal Consumption of Black Bean Powder Protects against Obesity and Dyslipidemia in Male Adult Rat Offspring from Obese Pregnancies. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071029
Choudhary D, Andreani GA, Mahmood S, Wen X, Patel MS, Rideout TC. Postnatal Consumption of Black Bean Powder Protects against Obesity and Dyslipidemia in Male Adult Rat Offspring from Obese Pregnancies. Nutrients. 2024; 16(7):1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071029
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoudhary, Divya, Gabriella A. Andreani, Saleh Mahmood, Xiaozhong Wen, Mulchand S. Patel, and Todd C. Rideout. 2024. "Postnatal Consumption of Black Bean Powder Protects against Obesity and Dyslipidemia in Male Adult Rat Offspring from Obese Pregnancies" Nutrients 16, no. 7: 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071029
APA StyleChoudhary, D., Andreani, G. A., Mahmood, S., Wen, X., Patel, M. S., & Rideout, T. C. (2024). Postnatal Consumption of Black Bean Powder Protects against Obesity and Dyslipidemia in Male Adult Rat Offspring from Obese Pregnancies. Nutrients, 16(7), 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16071029







