The Relationship between Birth Weight and the Risk of Overweight and Obesity among Chinese Children and Adolescents Aged 7–17 Years
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
2.3. Data Collection and Measurements
2.4. Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Characteristics of the Research Population
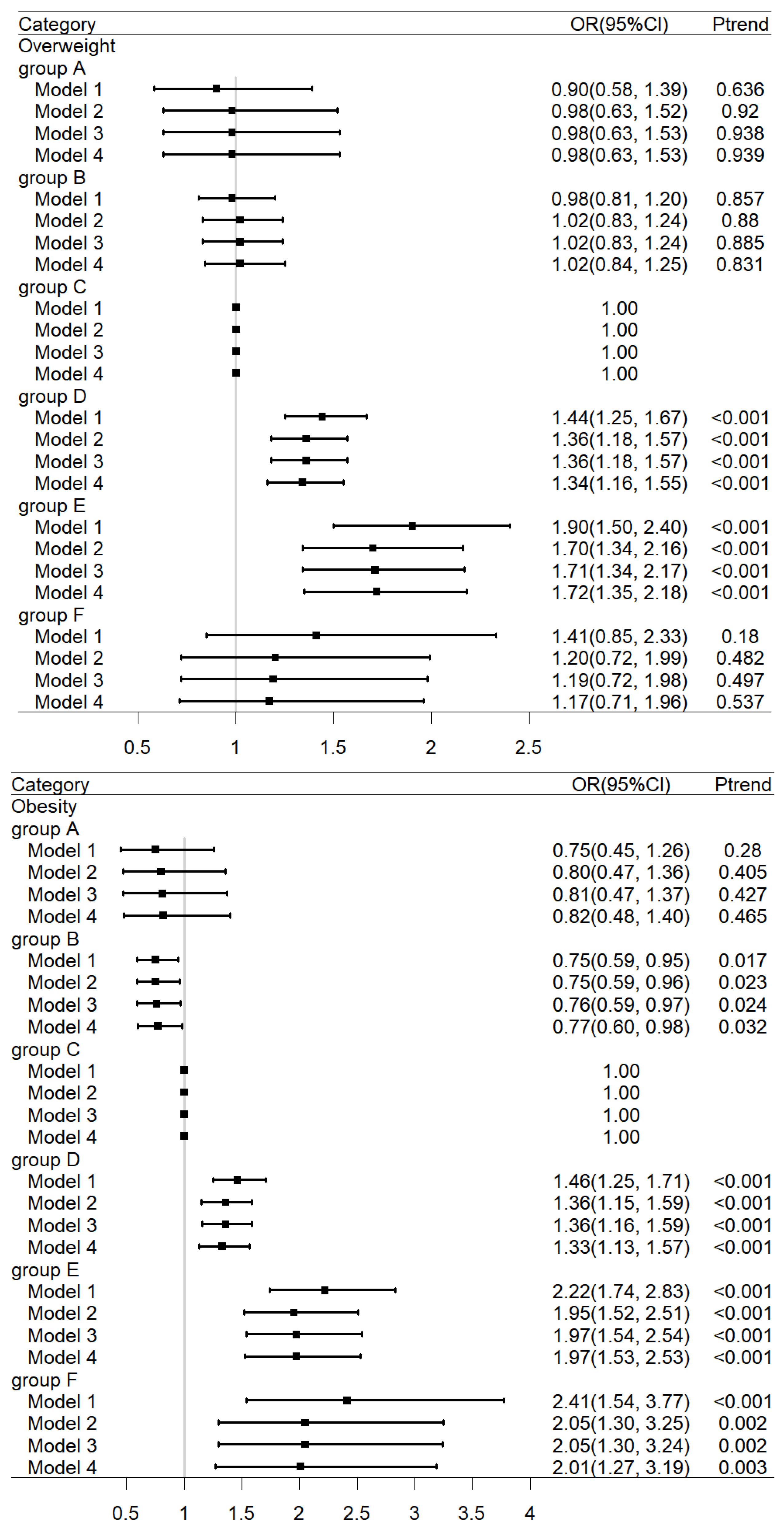
3.2. The Relationship between Birth Weight and the Risk of Overweight or Obesity
3.3. The Relationship between Birth Weight and the Risk of Overweight or Obesity with Age
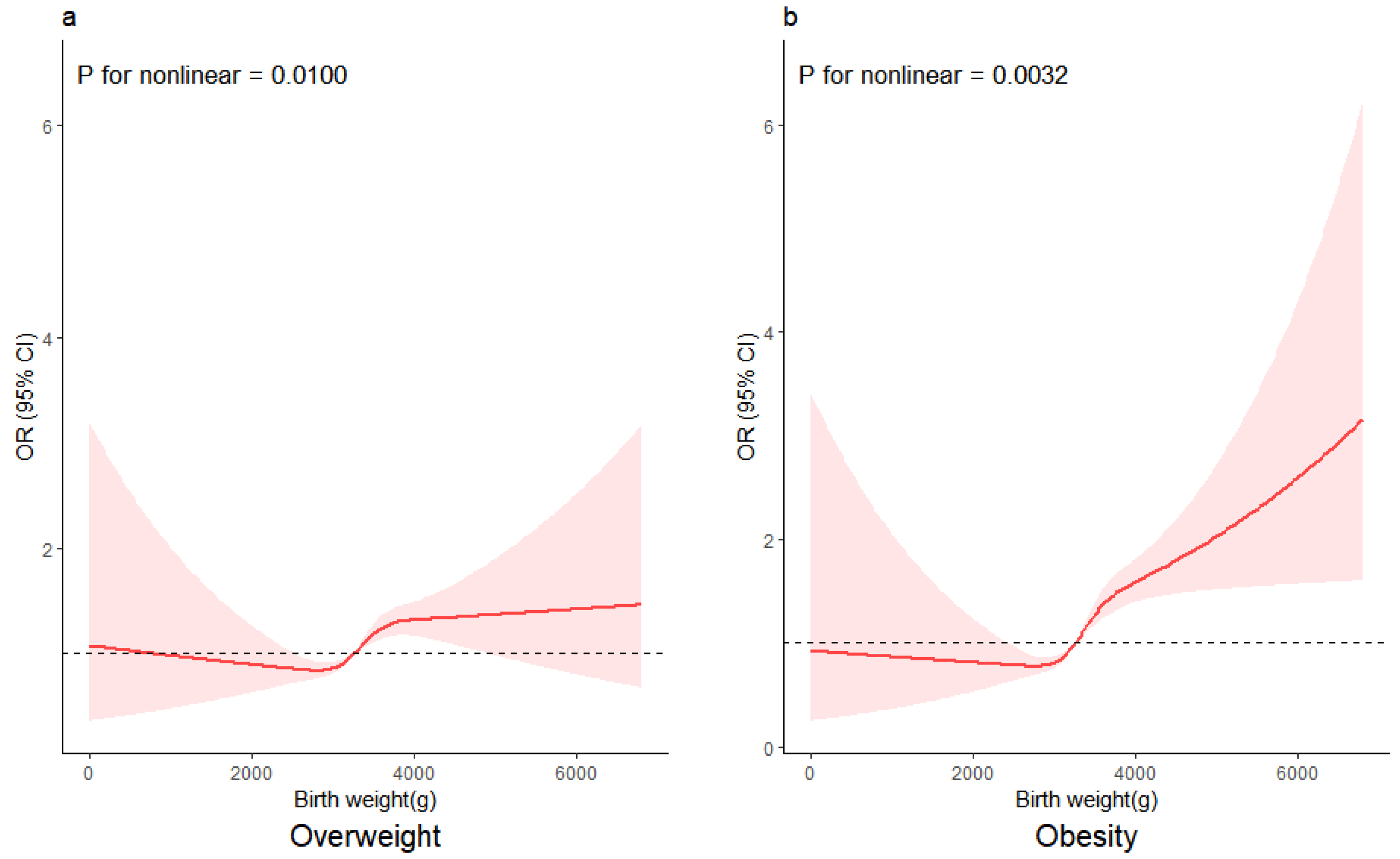
3.4. The Relationship between Birth Weight as a Continuous Variable and the Risk of Being Overweight and Obese
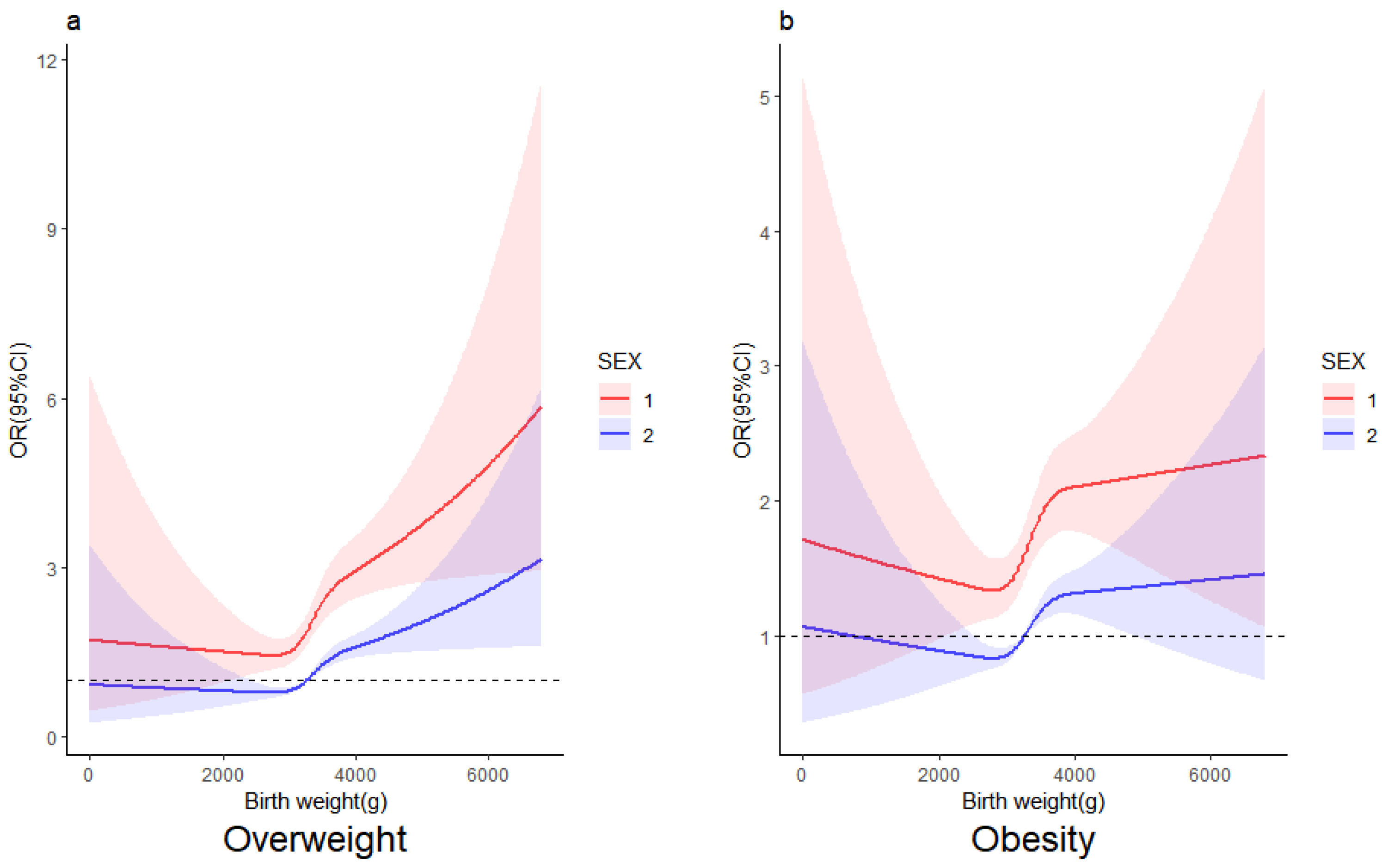
3.5. The Relationship between Birth Weight and the Risk of Overweight and Obesity by Gender
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Facts and Figures on Childhood Obesity. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- The State Council Information Office of the People’s Republic of China. The Report on Chinese Resident’s Chronic Diseases and Nutrition. 2020; People’s Health Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2021; p. 148. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.-F. Childhood Obesity: A Growing Global Health Hazard Extending to Adulthood. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2013, 54, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, M.; Fleming, T.; Robinson, M.; Thomson, B.; Graetz, N.; Margono, C.; Mullany, E.C.; Biryukov, S.; Abbafati, C.; Abera, S.F.; et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet 2014, 384, 766–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas-Eapen, N. Childhood Obesity. Prim. Care Clin. Off. Pract. 2021, 48, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Obesity Federation. World Obesity Atlas 2023. Available online: https://www.worldobesity.org/ (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Smith, J.D.; Fu, E.; Kobayashi, M.A. Prevention and Management of Childhood Obesity and Its Psychological and Health Comorbidities. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2020, 16, 351–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulgaron, E.R.; Delamater, A.M. Obesity and type 2 diabetes in children: Epidemiology and treatment. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2014, 14, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, U.; Dixon, A.E.; Forno, E. Obesity and asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litwin, M.; Kułaga, Z. Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and primary hypertension. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2021, 36, 825–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piché, M.E.; Tchernof, A.; Després, J.P. Obesity Phenotypes, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revision Committee of Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Childhood Obesity. Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Childhood Obesity 2021; People’s Health Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2021; p. 99. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, P.; Wang, W.J.; Yu, H.T.; Zang, J.J.; Qian, N.S.; He, X.; Gao, W.J.; Yu, C.Q.; Li, L.M.; Wu, F. Differences and Correlation Analysis of Birth Weight and Overweight/Obesity in Shanghai Twin Cohort. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. Off. J. Int. Soc. Twin Stud. 2021, 24, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.R.; Walker, B.F. Fetal nutrition and cardiovascular disease in adult life. Lancet 1993, 341, 1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, K.B.A.; Leal, V.S.; Oliveira, J.S.; Pereira, C.; Gonçalves, F.; Andrade, I.S.; Eickmann, S.H.; Lira, P.I.C.; Lima, M.C. Birth weight and overweight in adolescents: The erica project in the city of recife, pernambuco. Rev. Paul. Pediatr. Orgao Of. Soc. Pediatr. Sao Paulo 2021, 39, e2019380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, J.; Weres, A.; Czenczek-Lewandowska, E.; Leszczak, J.; Kalandyk-Osinko, K.; Mazur, A. Relationship between Children’s Birth Weight and Birth Length and a Risk of Overweight and Obesity in 4–15-Year-Old Children. Medicina 2019, 55, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, C.E.; de Vasconcelos, F.d.A. Relationship between birth weight and overweight/obesity among students in Florianópolis, Santa Catarina, Brazil: A retrospective cohort study. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2014, 132, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wen, D. Association between Marginally Low Birth Weight and Obesity-Related Outcomes and Indirect Effects via Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Abnormal Eating. Obes. Facts 2022, 15, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschler, V.; Edit, S.; Miorin, C.; Guntsche, Z.; Maldonado, N.; Garcia, C.; Lapertosa, S.; Gonzalez, C.D. Association Between High Birth Weight and Later Central Obesity in 9-Year-Old Schoolchildren. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2021, 19, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Xu, C.; Liu, Q.; Fan, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, L.; Hang, D.; Shang, H.; Gu, A. Association between birth weight and risk of cardiovascular disease: Evidence from UK Biobank. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 31, 2637–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Niu, H.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Yan, S.; Li, M.; Jiang, S.; Ma, X.; Li, B.; Wu, H. Analysis of Dose-response Relationship between BMI and Hypertension in Northeastern China Using Restricted Cubic Spline Functions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schellong, K.; Schulz, S.; Harder, T.; Plagemann, A. Birth weight and long-term overweight risk: Systematic review and a meta-analysis including 643,902 persons from 66 studies and 26 countries globally. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.B.; Han, S.P.; Zhu, G.Z.; Zhu, C.; Wang, X.J.; Cao, X.G.; Guo, X.R. Birth weight and subsequent risk of obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2011, 12, 525–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, D.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Yang, L.; Huang, J.; Fang, H.; Guo, Q.; Xu, X.; Ju, L.; et al. China Nutrition and Health Surveys (1982–2017). China CDC Wkly. 2021, 3, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Yu, J.; Chang, X.; Wang, M.; An, L. Prevalence and Correlates of Metabolic Syndrome in Chinese Children: The China Health and Nutrition Survey. Nutrients 2017, 9, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Wang, Y.; Xie, W.; Zhang, J.; Ni, Y.; Peng, X.; Sun, G.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, Y. Multilevel Analysis of the Nutritional and Health Status among Children and Adolescents in Eastern China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Q.; Cai, H.; Xiang, Y.B.; Zhou, P.; Li, H.; Yang, G.; Jiang, Y.; Shu, X.O.; Zheng, W.; Xu, W.H. Prospective cohort studies of birth weight and risk of obesity, diabetes, and hypertension in adulthood among the Chinese population. J. Diabetes 2019, 11, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rito, A.I.; Buoncristiano, M.; Spinelli, A.; Salanave, B.; Kunešová, M.; Hejgaard, T.; García Solano, M.; Fijałkowska, A.; Sturua, L.; Hyska, J.; et al. Association between Characteristics at Birth, Breastfeeding and Obesity in 22 Countries: The WHO European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative—COSI 2015/2017. Obes. Facts 2019, 12, 226–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauder, K.A.; Hockett, C.W.; Ringham, B.M.; Glueck, D.H.; Dabelea, D. Fetal overnutrition and offspring insulin resistance and β-cell function: The Exploring Perinatal Outcomes among Children (EPOCH) study. Diabet. Med. J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2017, 34, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheatcroft, S.B.; Kearney, M.T.; Shah, A.M.; Ezzat, V.A.; Miell, J.R.; Modo, M.; Williams, S.C.R.; Cawthorn, W.P.; Medina-Gomez, G.; Vidal-Puig, A.; et al. IGF-Binding Protein-2 Protects Against the Development of Obesity and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozanne, S.E.; Fernandez-Twinn, D.; Hales, C.N. Fetal growth and adult diseases. Semin. Perinatol. 2004, 28, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, E.; Wang, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, B.; Zhang, Z.; Li, N.; Hu, G. Association of early pregnancy body mass index and children’s birth weight with risk of being overweight in childhood. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2018, 30, e23174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberico, S.; Montico, M.; Barresi, V.; Monasta, L.; Businelli, C.; Soini, V.; Erenbourg, A.; Ronfani, L.; Maso, G. The role of gestational diabetes, pre-pregnancy body mass index and gestational weight gain on the risk of newborn macrosomia: Results from a prospective multicentre study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2014, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Han, S.; Zhu, J.; Sun, X.; Ji, C.; Guo, X. Pre-pregnancy body mass index in relation to infant birth weight and offspring overweight/obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bateson, P.; Barker, D.; Clutton-Brock, T.; Deb, D.; D’Udine, B.; Foley, R.A.; Gluckman, P.; Godfrey, K.; Kirkwood, T.; Lahr, M.M.; et al. Developmental plasticity and human health. Nature 2004, 430, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.P.; Yang, M.; Liang, L.; Fu, J.F.; Xiong, F.; Liu, G.L.; Gong, C.X.; Luo, F.H.; Chen, S.K.; Zhang, D.D.; et al. Possible role of birth weight on general and central obesity in Chinese children and adolescents: A cross-sectional study. Ann. Epidemiol. 2015, 25, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooney, B.L.; Mathiason, M.A.; Schauberger, C.W. Predictors of obesity in childhood, adolescence, and adulthood in a birth cohort. Matern. Child Health J. 2011, 15, 1166–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigante, D.P.; Victora, C.G.; Matijasevich, A.; Horta, B.L.; Barros, F.C. Association of family income with BMI from childhood to adult life: A birth cohort study. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zeng, L.; Wang, D.; Li, C.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H.; Xiao, Y. Effects of birth weight on body composition and overweight/obesity at early school age. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 1778–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldroyd, J.; Renzaho, A.; Skouteris, H. Low and high birth weight as risk factors for obesity among 4 to 5-year-old Australian children: Does gender matter? Eur. J. Pediatr. 2011, 170, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Katzmarzyk, P.T.; Chaput, J.P.; Fogelholm, M.; Johnson, W.D.; Kuriyan, R.; Kurpad, A.; et al. Birth weight and childhood obesity: A 12-country study. Int. J. Obes. Suppl. 2015, 5, S74–S79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.F.; Wang, L.; Pan, A. Epidemiology and determinants of obesity in China. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 373–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Pearce, A.; Li, L. Weight gain in early years and subsequent body mass index trajectories across birth weight groups: A prospective longitudinal study. Eur. J. Public Health 2020, 30, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total | Birth Weight, n (%) | p | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Characteristics | A | B | C | D | E | F | ||
| Participants, n (%) | 10,041 (100.0) | 263 (2.6) | 1466 (14.6) | 4824 (48.0) | 2720 (27.1) | 619 (6.2) | 149 (1.5) | |
| Sex, n (%) | <0.001 | |||||||
| boys | 5025 (50.0) | 108 (41.1) | 629 (42.9) | 2325 (48.2) | 1504 (55.3) | 367 (59.3) | 92 (61.7) | |
| Age group, % | 0.166 | |||||||
| pre-pubertal | 4833 (48.1) | 131 (49.8) | 739 (50.4) | 2265 (47.0) | 1328 (48.8) | 308 (49.8) | 62 (41.6) | |
| pubertal | 2772 (27.6) | 68 (25.9) | 406 (27.7) | 1371 (28.4) | 714 (26.3) | 165 (26.7) | 48 (32.2) | |
| post-pubertal | 2436 (24.3) | 64 (24.3) | 321 (21.9) | 1188 (24.6) | 678 (24.9) | 146 (23.6) | 39 (26.2) | |
| Birth length, % | <0.001 | |||||||
| low | 1728 (17.2) | 151 (57.4) | 375 (25.6) | 712 (14.8) | 377 (13.9) | 79 (12.8) | 34 (22.8) | |
| normal | 7332 (73.0) | 107 (40.7) | 1018 (69.4) | 3731 (77.3) | 2017 (74.2) | 384 (62.0) | 75 (50.3) | |
| high | 981 (9.8) | 5 (1.9) | 73 (5.0) | 381 (7.9) | 326 (12.0) | 156 (25.2) | 40 (26.9) | |
| Nutritional status, % | <0.001 | |||||||
| underweight | 906 (9.0) | 39 (14.8) | 214 (14.6) | 430 (8.9) | 183 (6.7) | 29 (4.7) | 11 (7.4) | |
| normal | 7006 (69.8) | 184 (70.0) | 1019 (69.5) | 3485 (72.2) | 1840 (67.7) | 385 (62.2) | 93 (62.4) | |
| overweight | 1184 (11.8) | 24 (9.1) | 145 (9.9) | 505 (10.5) | 385 (14.2) | 106 (17.1) | 19 (12.8) | |
| obesity | 945 (9.4) | 16 (6.1) | 88 (6.0) | 404 (8.4) | 312 (11.5) | 99 (16.0) | 26 (17.5) | |
| Residence area, % | <0.001 | |||||||
| urban | 4953 (49.3) | 122 (46.4) | 713 (48.6) | 2218 (46.0) | 1448 (53.2) | 352 (56.9) | 100 (67.1) | |
| rural | 5088 (50.7) | 141 (53.6) | 753 (51.4) | 2606 (54.0) | 1272 (46.8) | 267 (43.1) | 49 (32.9) | |
| Total energy, kcal/d | 1827.4 (884.2) | 1810.4 (781.9) | 1800.0 (883.6) | 1817.2 (882.6) | 1835.2 (904.2) | 1883.1 (923.9) | 1911.9 (781.6) | 0.078 |
| Physical activity, % | 0.573 | |||||||
| low | 3483 (34.7) | 98 (37.3) | 499 (34.0) | 1641 (34.0) | 976 (35.9) | 216 (34.9) | 53 (35.6) | |
| high | 4356 (43.4) | 109 (41.4) | 639 (43.6) | 2101 (43.6) | 1159 (42.6) | 287 (46.4) | 61 (40.9) | |
| unknown | 2202 (21.9) | 56 (21.3) | 328 (22.4) | 1082 (22.4) | 585 (21.5) | 116 (18.7) | 35 (23.5) | |
| Electronic/video time, % | 0.424 | |||||||
| <2 h | 6984 (69.6) | 173 (65.8) | 1025 (69.9) | 3389 (70.3) | 1878 (69.0) | 416 (67.2) | 103 (69.1) | |
| ≥2 h | 3057 (30.5) | 90 (34.2) | 441 (30.1) | 1435 (29.8) | 842 (31.0) | 203 (32.8) | 46 (30.9) | |
| Engel’s coefficient, % | <0.001 | |||||||
| ≥60% | 203 (2.0) | 4 (1.5) | 29 (2.0) | 98 (2.0) | 63 (2.3) | 8 (1.3) | 1 (0.7) | |
| 50–59% | 277 (2.8) | 4 (1.5) | 52 (3.6) | 133 (2.8) | 72 (2.7) | 14 (2.3) | 2 (1.3) | |
| 40–49% | 272 (2.7) | 5 (1.9) | 53 (3.6) | 133 (2.8) | 65 (2.4) | 15 (2.4) | 1 (0.7) | |
| 30–39% | 686 (6.8) | 12 (4.6) | 109 (7.4) | 353 (7.3) | 171 (6.3) | 38 (6.1) | 3 (2.0) | |
| <30% | 1710 (17.0) | 33 (12.6) | 219 (14.9) | 878 (18.2) | 464 (17.1) | 91 (14.7) | 25 (16.8) | |
| unknown | 6893 (68.7) | 205 (78.0) | 1004 (68.5) | 3229 (66.9) | 1885 (69.3) | 453 (73.2) | 117 (78.5) | |
| Group | Pre-Pubertal Stage | Pubertal Stage | Post-Pubertal Stage | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95%CI) | p | OR (95%CI) | p | OR (95%CI) | p | |
| A | ||||||
| Overweight | 1.05 (0.55–1.98) | 0.890 | 0.59 (0.23–1.54) | 0.282 | 1.28 (0.55–2.97) | 0.574 |
| Obesity | 0.74 (0.36–1.53) | 0.419 | 0.40 (0.09–1.69) | 0.212 | 2.42 (0.88–6.67) | 0.087 |
| B | ||||||
| Overweight | 1.00 (0.75–1.33) | 0.981 | 1.00 (0.68–1.45) | 0.984 | 1.03 (0.68–1.56) | 0.894 |
| Obesity | 0.73 (0.54–1.01) | 0.057 | 0.93 (0.58–1.49) | 0.764 | 0.64 (0.31–1.34) | 0.238 |
| C | ||||||
| Overweight | reference | reference | reference | |||
| Obesity | reference | reference | reference | |||
| D | ||||||
| Overweight | 1.16 (0.93–1.45) | 0.182 | 1.53 (1.17–2.01) | 0.002 | 1.46 (1.10–1.96) | 0.010 |
| Obesity | 1.18 (0.95–1.46) | 0.135 | 1.43 (1.04–1.99) | 0.030 | 1.69 (1.14–2.50) | 0.009 |
| E | ||||||
| Overweight | 1.89 (1.34–2.66) | <0.001 | 1.33 (0.82–2.16) | 0.245 | 2.00 (1.23–3.27) | 0.006 |
| Obesity | 1.86 (1.33–2.61) | <0.001 | 1.82 (1.09–3.07) | 0.023 | 3.18 (1.75–5.80) | <0.001 |
| F | ||||||
| Overweight | 1.35 (0.63–2.88) | 0.444 | 1.01 (0.40–2.53) | 0.991 | 1.00 (0.34–3.00) | 0.994 |
| Obesity | 1.85 (0.96–3.57) | 0.066 | 2.29 (0.99–5.31) | 0.052 | 2.97 (0.96–9.18) | 0.059 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, J.; Guo, Q.; Fang, H.; Cheng, X.; Ju, L.; Wei, X.; Zhao, L.; Cao, Q.; Yuan, X.; He, L. The Relationship between Birth Weight and the Risk of Overweight and Obesity among Chinese Children and Adolescents Aged 7–17 Years. Nutrients 2024, 16, 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050715
Shi J, Guo Q, Fang H, Cheng X, Ju L, Wei X, Zhao L, Cao Q, Yuan X, He L. The Relationship between Birth Weight and the Risk of Overweight and Obesity among Chinese Children and Adolescents Aged 7–17 Years. Nutrients. 2024; 16(5):715. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050715
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Jiaqi, Qiya Guo, Hongyun Fang, Xue Cheng, Lahong Ju, Xiaoqi Wei, Liyun Zhao, Qiuye Cao, Xiaolin Yuan, and Li He. 2024. "The Relationship between Birth Weight and the Risk of Overweight and Obesity among Chinese Children and Adolescents Aged 7–17 Years" Nutrients 16, no. 5: 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050715
APA StyleShi, J., Guo, Q., Fang, H., Cheng, X., Ju, L., Wei, X., Zhao, L., Cao, Q., Yuan, X., & He, L. (2024). The Relationship between Birth Weight and the Risk of Overweight and Obesity among Chinese Children and Adolescents Aged 7–17 Years. Nutrients, 16(5), 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050715






