Epigenetic Effects of Resveratrol on Oncogenic Signaling in Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.2. DNA Isolation and Pyrosequencing
2.3. RNA Isolation, cDNA Synthesis, and qRT-PCR
2.4. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and Quantitative ChIP (qChIP)
2.5. Phospho-Antibody Wnt Signaling Array
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genes, That Are Hypermethylated upon Exposure to Resveratrol (RSV), Are Associated with Numerous Oncogenic Signaling Pathways
3.2. GLI2 and WNT4 from Hedgehog and Wnt Signaling Pathways, Respectively, Are Hypermethylated and Downregulated in Response to Resveratrol (RSV)
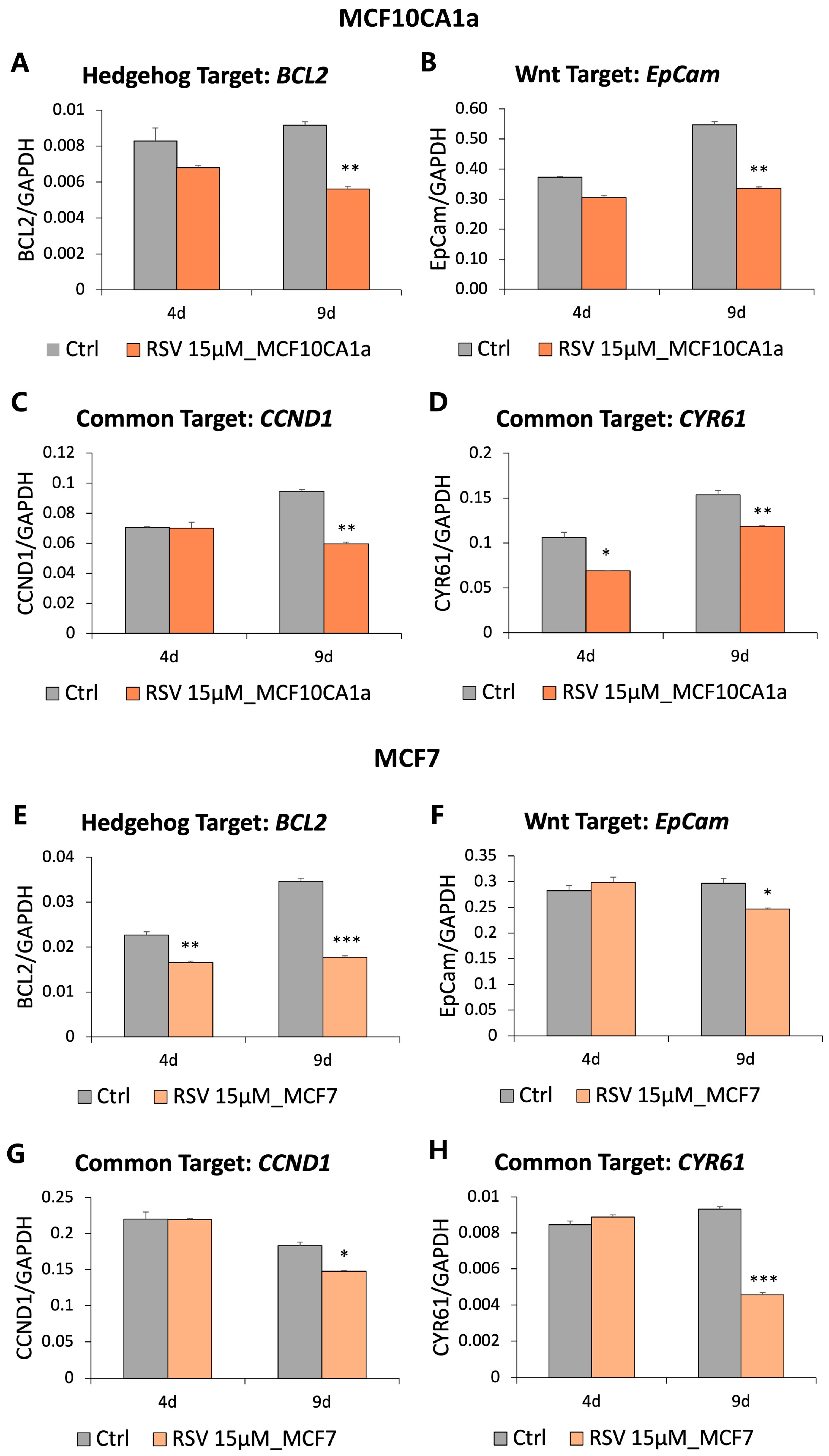
3.3. Genes Downstream of the Hedgehog and Wnt Signaling Are Downregulated in Response to Resveratrol (RSV)
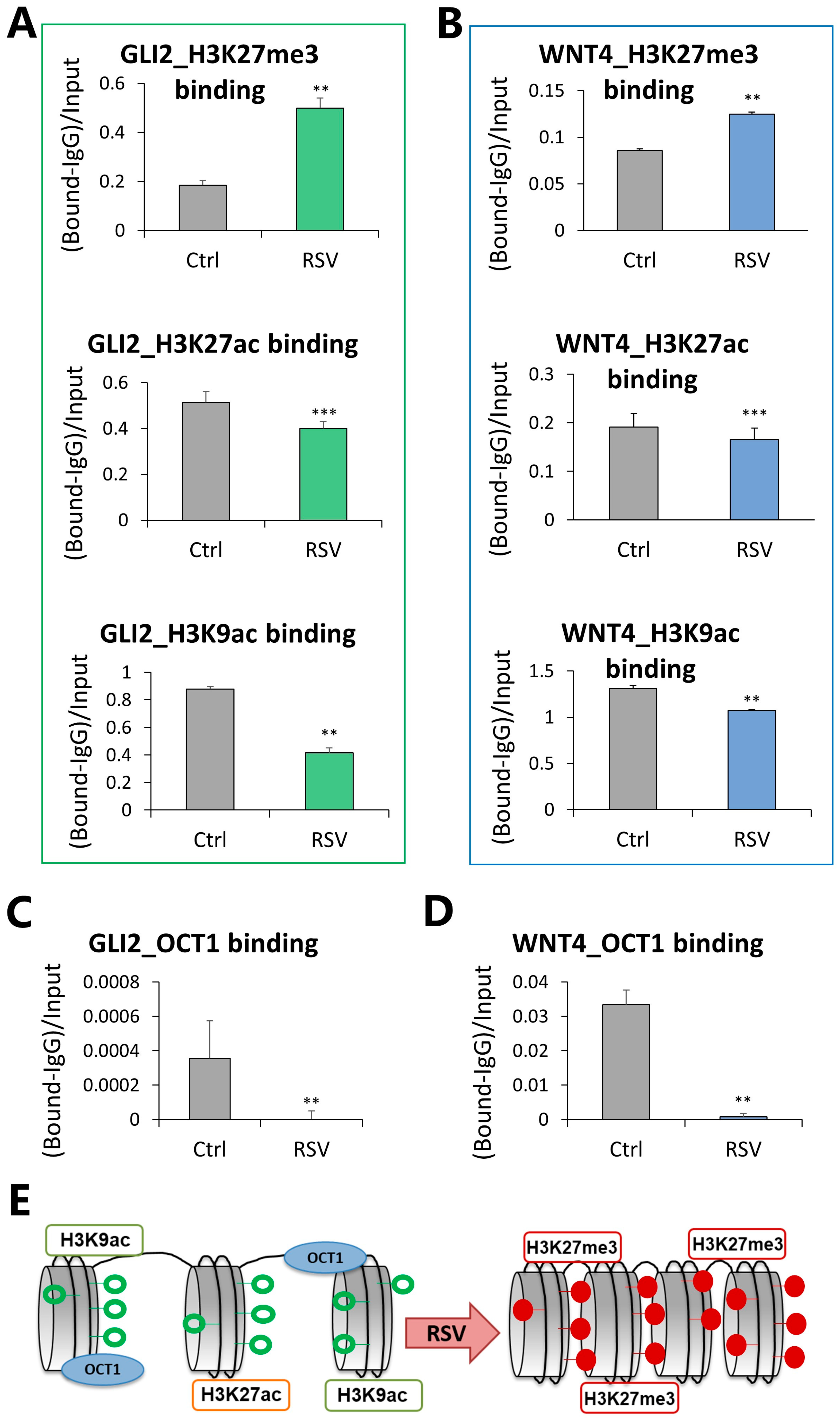
3.4. Compacted Chromatin Structure and Decreased OCT1 Transcription Factor Occupancy at Regulatory Regions of GLI2 and WNT4 in Response to Resveratrol (RSV)
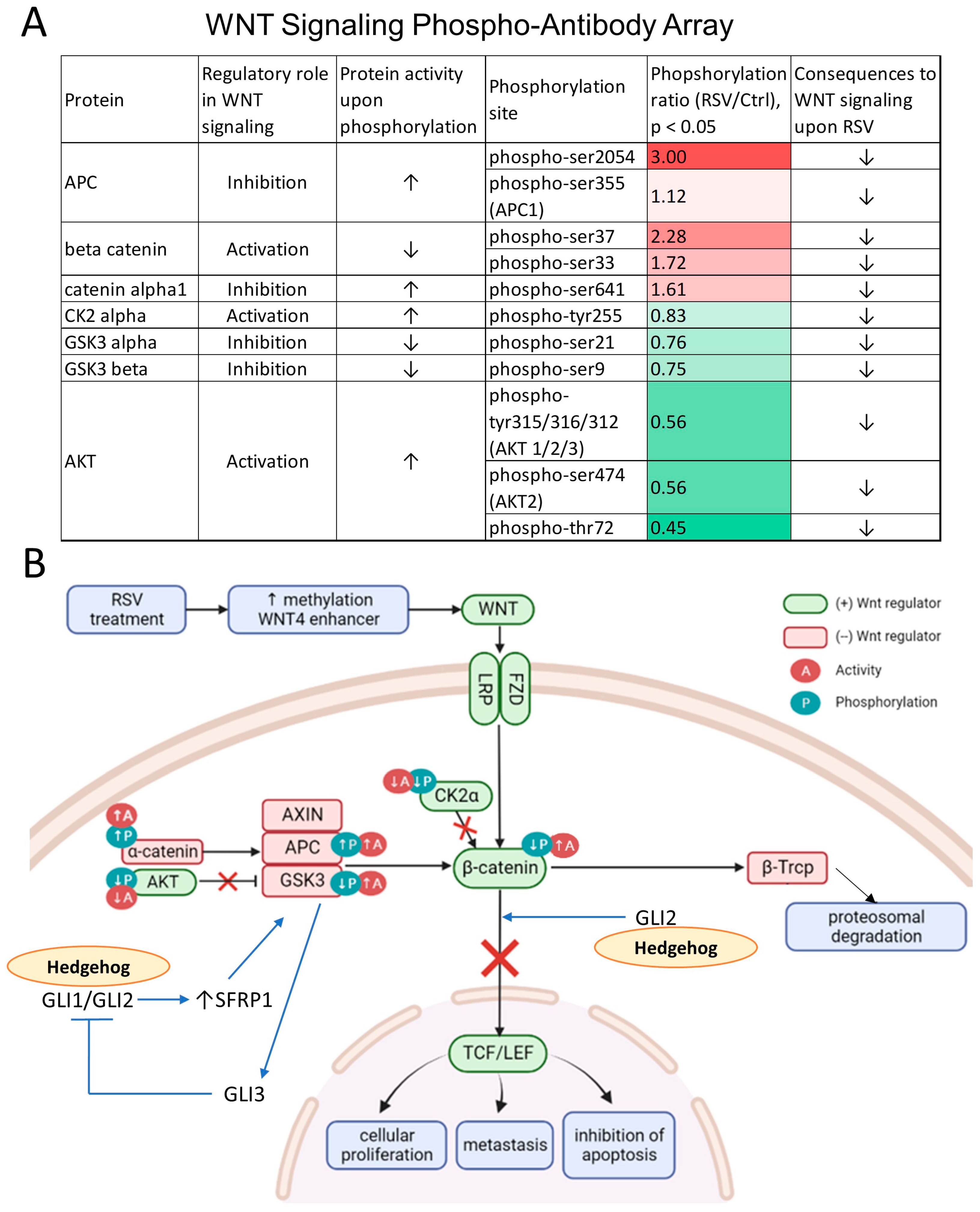
3.5. The Wnt Pathway Activity Is Attenuated as Reflected by Changes in Protein Phosphorylation upon Exposure to Resveratrol (RSV)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT1 | AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase 1 |
| AKT3 | AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase 3 |
| APC | APC Regulator of WNT Signaling Pathway |
| BCL2 | BCL2 Apoptosis Regulator |
| CCND1 | Cyclin D1 |
| CK2α | Casein Kinase Two Alpha |
| CYR61 | Cysteine-rich Angiogenic Inducer 61 |
| EpCam | Epithelial Cell Adhesion Molecule |
| FZD | Frizzled Class Receptor |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase |
| GLI | GLI Family Zinc Finger |
| GSK3α (GSK3-alpha) | Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Alpha |
| GSK3β (GSK3-beta) | Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta |
| JAK/STAT | Janus Kinase/Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription |
| KRAS | KRAS Proto-oncogene, GTPase |
| LRP | LDL Receptor-related Protein |
| MAML2 | Mastermind-like Transcriptional Coactivator 2 |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase |
| NENF | Neudesin Neurotrophic Factor |
| NOTCH | Notch Receptor |
| NOTCH2 | Notch Receptor 2 |
| OCT1(SLC22A1) | Solute Carrier Family 22 Member 1 |
| PITX2 | Paired-like Homeodomain 2 |
| PLCG2 | Phospholipase C Gamma 2 |
| PRKCA | Protein Kinase C Alpha |
| PRKCB | Protein Kinase C Beta |
| PTCH1 | Patched 1 |
| PTCHD1 | Patched Domain Containing 1 |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog |
| RARβ | Retinoic Acid Receptor Beta |
| RASAL2 | RAS Protein Activator Like 2 |
| RPS6KA2 | Ribosomal Protein S6 Kinase A2 |
| RSV | Resveratrol |
| SFRP1 | Secreted Frizzled-related Protein 1 |
| SMO | Smoothened, Frizzled Class Receptor |
| STAT3 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 |
| STAT4 | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 4 |
| STAT5B | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 5B |
| SUFU | SUFU Negative Regulator of Hedgehog Signaling |
| TCF/LEF | T-cell Factor/Lymphoid Enhancer Factor |
| TGF-β pathway | Transforming Growth Factor-beta |
| Wnt signaling | Wingless-related Integration Site |
| WNT16 | Wnt Family Member 16 |
| WNT4 | Wnt Family Member 4 |
| WNT6 | Wnt Family Member 6 |
| Β-Trcp (BTRC) | Beta-transducin Repeat Containing E3 Ubiquitin Protein |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vietri, M.T.; D’Elia, G.; Benincasa, G.; Ferraro, G.; Caliendo, G.; Nicoletti, G.F.; Napoli, C. DNA methylation and breast cancer: A way forward (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 59, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussos Torres, E.T.; Connolly, R.M. Breast cancer epigenetics (Chapter 13). In Epigenetic Cancer Therapy—Translational Epigenetics; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; pp. 275–299. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, B.D.; Rossi, E.; Pichardo, C.; Wooten, W.; Pichardo, M.; Tang, W.; Dorsey, T.H.; Ajao, A.; Hutchison, R.; Moubadder, L.; et al. Neighborhood Deprivation and DNA Methylation and Expression of Cancer Genes in Breast Tumors. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2341651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, A.; Nakanishi, M. Navigating the DNA methylation landscape of cancer. Trends Genet. 2021, 37, 1012–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanska, B.; Salame, P.; Bednarek, A.; Fabianowska-Majewska, K. Comparative effects of retinoic acid, vitamin D and resveratrol alone and in combination with adenosine analogues on methylation and expression of phosphatase and tensin homologue tumour suppressor gene in breast cancer cells. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Kroller, L.; Miao, B.; Boekhoff, H.; Bauer, A.S.; Buchler, M.W.; Hackert, T.; Giese, N.A.; Taipale, J.; Hoheisel, J.D. Promoter Hypermethylation Promotes the Binding of Transcription Factor NFATc1, Triggering Oncogenic Gene Activation in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanska, B.; Huang, J.; Bhattacharyya, B.; Suderman, M.; Hallett, M.; Han, Z.G.; Szyf, M. Definition of the landscape of promoter DNA hypomethylation in liver cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5891–5903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanska, B.; Cheishvili, D.; Suderman, M.; Arakelian, A.; Huang, J.; Hallett, M.; Han, Z.G.; Al-Mahtab, M.; Akbar, S.M.; Khan, W.A.; et al. Genome-wide study of hypomethylated and induced genes in patients with liver cancer unravels novel anticancer targets. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3118–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayol, G.; Martin-Subero, J.I.; Rios, J.; Queiros, A.; Kulis, M.; Sunol, M.; Esteller, M.; Gomez, S.; Garcia, I.; de Torres, C.; et al. DNA hypomethylation affects cancer-related biological functions and genes relevant in neuroblastoma pathogenesis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukeir, N.; Stefanska, B.; Parashar, S.; Chik, F.; Arakelian, A.; Szyf, M.; Rabbani, S.A. Pharmacological methyl group donors block skeletal metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 2769–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakneshan, P.; Szyf, M.; Farias-Eisner, R.; Rabbani, S.A. Reversal of the hypomethylation status of urokinase (uPA) promoter blocks breast cancer growth and metastasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 31735–31744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukeir, N.; Pakneshan, P.; Chen, G.; Szyf, M.; Rabbani, S.A. Alteration of the methylation status of tumor-promoting genes decreases prostate cancer cell invasiveness and tumorigenesis in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9202–9210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harandi-Zadeh, S.; Boycott, C.; Beetch, M.; Yang, T.; Martin, B.J.E.; Ren, K.; Kwasniak, A.; Dupuis, J.H.; Lubecka, K.; Yada, R.Y.; et al. Pterostilbene Changes Epigenetic Marks at Enhancer Regions of Oncogenes in Breast Cancer Cells. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beetch, M.; Boycott, C.; Harandi-Zadeh, S.; Yang, T.; Martin, B.J.E.; Dixon-McDougall, T.; Ren, K.; Gacad, A.; Dupuis, J.H.; Ullmer, M.; et al. Pterostilbene leads to DNMT3B-mediated DNA methylation and silencing of OCT1-targeted oncogenes in breast cancer cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2021, 98, 108815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubecka, K.; Kurzava, L.; Flower, K.; Buvala, H.; Zhang, H.; Teegarden, D.; Camarillo, I.; Suderman, M.; Kuang, S.; Andrisani, O.; et al. Stilbenoids remodel the DNA methylation patterns in breast cancer cells and inhibit oncogenic NOTCH signaling through epigenetic regulation of MAML2 transcriptional activity. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 656–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Aguilar, R.; Perez-Plasencia, C.; Marchat, L.A.; Gariglio, P.; Garcia Mena, J.; Rodriguez Cuevas, S.; Ruiz-Garcia, E.; Astudillo-de la Vega, H.; Hernandez Juarez, J.; Flores-Perez, A.; et al. Methylation Landscape of Human Breast Cancer Cells in Response to Dietary Compound Resveratrol. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigafoos, A.N.; Paradise, B.D.; Fernandez-Zapico, M.E. Hedgehog/GLI Signaling Pathway: Transduction, Regulation, and Implications for Disease. Cancers 2021, 13, 3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.; Yu, C.; Li, F.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Wu, C.; Wang, C.; Ye, L. Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in cancers and targeted therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, M.; Xu, F.; Jiang, S. Wnt signaling in breast cancer: Biological mechanisms, challenges and opportunities. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, S.G.; Brook, N.; Agostino, M.; Arfuso, F.; Kumar, A.P.; Dharmarajan, A. Wnt signaling in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riobo-Del Galdo, N.A.; Lara Montero, A.; Wertheimer, E.V. Role of Hedgehog Signaling in Breast Cancer: Pathogenesis and Therapeutics. Cells 2019, 8, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, S.C.; Tong, L.; Li, Y.; Do, R.; Walz, S.; Fitzgerald, K.N.; Gouw, A.M.; Baylot, V.; Gutgemann, I.; Eilers, M.; et al. MYC regulates the antitumor immune response through CD47 and PD-L1. Science 2016, 352, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipitsin, M.; Campbell, L.L.; Argani, P.; Weremowicz, S.; Bloushtain-Qimron, N.; Yao, J.; Nikolskaya, T.; Serebryiskaya, T.; Beroukhim, R.; Hu, M.; et al. Molecular definition of breast tumor heterogeneity. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Wu, J.F.; Luo, Q.C.; Liu, Q.F.; Wu, Q.W.; Ye, G.D.; She, H.Q.; Li, B.A. Pygo2 activates MDR1 expression and mediates chemoresistance in breast cancer via the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4787–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Samant, R.S.; Shevde, L.A. Nonclassical activation of Hedgehog signaling enhances multidrug resistance and makes cancer cells refractory to Smoothened-targeting Hedgehog inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 11824–11833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Haaf, A.; Bektas, N.; von Serenyi, S.; Losen, I.; Arweiler, E.C.; Hartmann, A.; Knuchel, R.; Dahl, E. Expression of the glioma-associated oncogene homolog (GLI) 1 in human breast cancer is associated with unfavourable overall survival. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiris-Pages, M.; Sotgia, F.; Lisanti, M.P. Chemotherapy induces the cancer-associated fibroblast phenotype, activating paracrine Hedgehog-GLI signalling in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10728–10745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, W.P.; Zhao, M.R. Crosstalk between Wnt/beta-catenin and Hedgehog/Gli signaling pathways in colon cancer and implications for therapy. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Wang, X. Antagonism between Hedgehog and Wnt signaling pathways regulates tumorigenicity. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 6327–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, P.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Chen, F.; Chen, W. Crosstalk between Hh and Wnt signaling promotes osteosarcoma progression. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 12, 768–773. [Google Scholar]
- Takada, T. Activation of the Hedgehog and Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathways in Basal Cell Carcinoma. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2021, 13, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, K.M.; Pohlig, R.T.; Sims-Mourtada, J. Co-activation of Hedgehog and Wnt signaling pathways is associated with poor outcomes in triple negative breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 5285–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, A.A.; Khalid, S.; Ahmad, A. Regulation of Cell Signaling Pathways and miRNAs by Resveratrol in Different Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behroozaghdam, M.; Dehghani, M.; Zabolian, A.; Kamali, D.; Javanshir, S.; Hasani Sadi, F.; Hashemi, M.; Tabari, T.; Rashidi, M.; Mirzaei, S.; et al. Resveratrol in breast cancer treatment: From cellular effects to molecular mechanisms of action. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Chang, H.; Peng, X.; Bai, Q.; Yi, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, J.; Mi, M. Resveratrol inhibits breast cancer stem-like cells and induces autophagy via suppressing Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, W.; Xu, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, F.; Ke, A.; Wang, X.; Guo, C. Resveratrol inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis through the hedgehog signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer cell. Pancreatology 2011, 11, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Gan, H.Z.; Peng, Q. Resveratrol inhibits the hedgehog signaling pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and suppresses gastric cancer invasion and metastasis. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 2381–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, X.; Peng, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Li, M. Resveratrol Induces Apoptosis, Suppresses Migration, and Invasion of Cervical Cancer Cells by Inhibiting the Hedgehog Signaling Pathway. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 8453011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Cao, L.; Chen, X.; Lei, J.; Ma, Q. Resveratrol inhibits hypoxia-driven ROS-induced invasive and migratory ability of pancreatic cancer cells via suppression of the Hedgehog signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 1718–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tost, J.; Gut, I.G. DNA methylation analysis by pyrosequencing. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 2265–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.E.; Suderman, M.J.; Hallett, M.; Szyf, M. DNA demethylation induced by the methyl-CpG-binding domain protein MBD3. Gene 2008, 420, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beetch, M.; Lubecka, K.; Shen, K.; Flower, K.; Harandi-Zadeh, S.; Suderman, M.; Flanagan, J.M.; Stefanska, B. Stilbenoid-Mediated Epigenetic Activation of Semaphorin 3A in Breast Cancer Cells Involves Changes in Dynamic Interactions of DNA with DNMT3A and NF1C Transcription Factor. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1801386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Scott, E.; Kholghi, A.; Andreadi, C.; Rufini, A.; Karmokar, A.; Britton, R.G.; Horner-Glister, E.; Greaves, P.; Jawad, D.; et al. Cancer chemoprevention: Evidence of a nonlinear dose response for the protective effects of resveratrol in humans and mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 298ra117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mai, Y.; Su, J.; Yang, C.; Xia, C.; Fu, L. The strategies to cure cancer patients by eradicating cancer stem-like cells. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Johnson, L.M.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Patel, D.J. DNA methylation pathways and their crosstalk with histone methylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 16, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaissiere, T.; Sawan, C.; Herceg, Z. Epigenetic interplay between histone modifications and DNA methylation in gene silencing. Mutat. Res. 2008, 659, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsompana, M.; Buck, M.J. Chromatin accessibility: A window into the genome. Epigenetics Chromatin 2014, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Loh, Y.P.; Tng, J.Q.; Lim, M.C.; Cao, Z.; Raju, A.; Lieberman Aiden, E.; Li, S.; Manikandan, L.; et al. H3K27me3-rich genomic regions can function as silencers to repress gene expression via chromatin interactions. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creyghton, M.P.; Cheng, A.W.; Welstead, G.G.; Kooistra, T.; Carey, B.W.; Steine, E.J.; Hanna, J.; Lodato, M.A.; Frampton, G.M.; Sharp, P.A.; et al. Histone H3K27ac separates active from poised enhancers and predicts developmental state. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21931–21936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, Q.; Xiong, J.; Zhu, B. Histone H3K27 acetylation is dispensable for enhancer activity in mouse embryonic stem cells. Genome Biol. 2020, 21, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazi, S.; Zahiri, J. Posttranslational modifications in proteins: Resources, tools and prediction methods. Database 2021, 2021, baab012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardito, F.; Giuliani, M.; Perrone, D.; Troiano, G.; Lo Muzio, L. The crucial role of protein phosphorylation in cell signaling and its use as targeted therapy (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, K.; Kazi, J.U. Phosphorylation-Dependent Regulation of WNT/Beta-Catenin Signaling. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 858782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Xiao, G.; Hu, J. Regulation of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling by posttranslational modifications. Cell Biosci. 2014, 4, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qadir Nanakali, N.M.; Maleki Dana, P.; Sadoughi, F.; Asemi, Z.; Sharifi, M.; Asemi, R.; Yousefi, B. The role of dietary polyphenols in alternating DNA methylation in cancer. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 12256–12269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, A.; Meir, A.Y.; Hagemann, T.; Czechowski, P.; Muller, L.; Engelmann, B.; Haange, S.B.; Rolle-Kampczyk, U.; Tsaban, G.; Zelicha, H.; et al. A polyphenol-rich green Mediterranean diet enhances epigenetic regulatory potential: The DIRECT PLUS randomized controlled trial. Metabolism 2023, 145, 155594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, I.; Sharma, M.; Tollefsbol, T.O. Combinatorial Epigenetics Impact of Polyphenols and Phytochemicals in Cancer Prevention and Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Pan, Y.; Ji, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Qin, L. Roles and action mechanisms of WNT4 in cell differentiation and human diseases: A review. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vouyovitch, C.M.; Perry, J.K.; Liu, D.X.; Bezin, L.; Vilain, E.; Diaz, J.J.; Lobie, P.E.; Mertani, H.C. WNT4 mediates the autocrine effects of growth hormone in mammary carcinoma cells. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, 571–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreibich, E.; Kleinendorst, R.; Barzaghi, G.; Kaspar, S.; Krebs, A.R. Single-molecule footprinting identifies context-dependent regulation of enhancers by DNA methylation. Mol. Cell 2023, 83, 787–802.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Lu, C. The interplay between DNA and histone methylation: Molecular mechanisms and disease implications. EMBO Rep. 2021, 22, e51803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Sun, Y.; Cao, S.; Zeng, H.; Jin, N.; Shou, M.; Tang, S.; Chen, Y.; Huang, M. Hedgehog pathway orchestrates the interplay of histone modifications and tailors combination epigenetic therapies in breast cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2601–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Mir, R.; Galande, S. Epigenetic Regulation of the Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Cancer. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 681053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wils, L.J.; Bijlsma, M.F. Epigenetic regulation of the Hedgehog and Wnt pathways in cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 121, 23–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Li, Q.; Shang, R.; Yao, L.; Wu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Xu, M.; Lu, Z.; Zhou, J.; et al. WNT4 secreted by tumor tissues promotes tumor progression in colorectal cancer by activation of the Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Shen, Y.; Lai, J.; Su, Q.; Zhao, J.; Xu, J. FOXE1 supports the tumor promotion of Gli2 on papillary thyroid carcinoma by the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 17739–17748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, H.; Deng, S.; Qin, Y.; He, J.; Hu, F.; Zhu, X.; Feng, X.; Wang, J.; et al. Dual activation of Hedgehog and Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway caused by downregulation of SUFU targeted by miRNA-150 in human gastric cancer. Aging 2021, 13, 10749–10769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracci, L.; Fabbri, A.; Del Corno, M.; Conti, L. Dietary Polyphenols: Promising Adjuvants for Colorectal Cancer Therapies. Cancers 2021, 13, 4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakobusic Brala, C.; Karkovic Markovic, A.; Kugic, A.; Toric, J.; Barbaric, M. Combination Chemotherapy with Selected Polyphenols in Preclinical and Clinical Studies-An Update Overview. Molecules 2023, 28, 3746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, J.; Ahamad, J.; Algahtani, M.S.; Garg, A.; Shahzad, N.; Ahmad, M.Z.; Imam, S.S. Nanotechnology-mediated delivery of resveratrol as promising strategy to improve therapeutic efficacy in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC): Progress and promises. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2024; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.L.; Lin, S.G.; Mao, Y.W.; Wu, J.X.; Hu, C.D.; Lv, R.; Zeng, H.D.; Zhang, M.H.; Lin, L.Z.; Ouyang, S.S.; et al. Wnt/beta-catenin signalling pathway in breast cancer cells and its effect on reversing tumour drug resistance by alkaloids extracted from traditional Chinese medicine. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2023, 25, e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Han, Y.; Wu, X.; Cao, X.; Gao, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, M.; Xiao, H. Gut Microbiota-Derived Resveratrol Metabolites, Dihydroresveratrol and Lunularin, Significantly Contribute to the Biological Activities of Resveratrol. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 912591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Springer, M.; Moco, S. Resveratrol and Its Human Metabolites-Effects on Metabolic Health and Obesity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guthrie, A.R.; Chow, H.S.; Martinez, J.A. Effects of resveratrol on drug- and carcinogen-metabolizing enzymes, implications for cancer prevention. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2017, 5, e00294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurzava Kendall, L.; Ma, Y.; Yang, T.; Lubecka, K.; Stefanska, B. Epigenetic Effects of Resveratrol on Oncogenic Signaling in Breast Cancer. Nutrients 2024, 16, 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050699
Kurzava Kendall L, Ma Y, Yang T, Lubecka K, Stefanska B. Epigenetic Effects of Resveratrol on Oncogenic Signaling in Breast Cancer. Nutrients. 2024; 16(5):699. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050699
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurzava Kendall, Lucinda, Yuexi Ma, Tony Yang, Katarzyna Lubecka, and Barbara Stefanska. 2024. "Epigenetic Effects of Resveratrol on Oncogenic Signaling in Breast Cancer" Nutrients 16, no. 5: 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050699
APA StyleKurzava Kendall, L., Ma, Y., Yang, T., Lubecka, K., & Stefanska, B. (2024). Epigenetic Effects of Resveratrol on Oncogenic Signaling in Breast Cancer. Nutrients, 16(5), 699. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050699





