In Vitro Lactic Acid Bacteria Anti-Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Effect and Modulation of the Intestinal Microbiota in Fecal Cultures from HBV-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients
Abstract
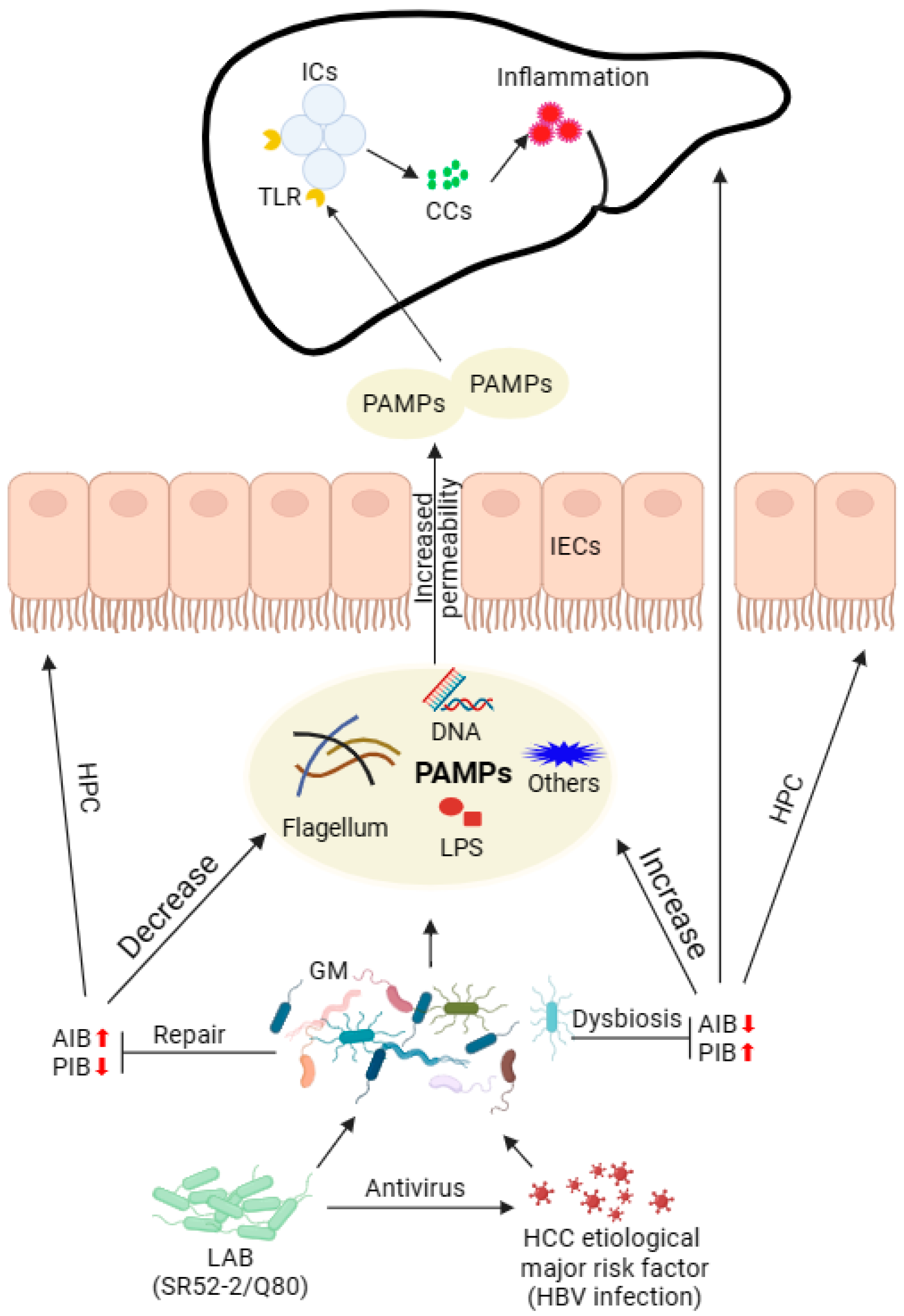
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of LAB Fermentation Supernatants (LFSs)
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability
2.4. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerasechain Reaction (RT-qPCR) Analysis
2.5. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.6. Fecal Sample Collection
2.7. In Vitro Human Fecal Fermentation (HFF)
2.8. DNA Extraction and 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing
2.9. Gas Chromatography (GC)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Subjects
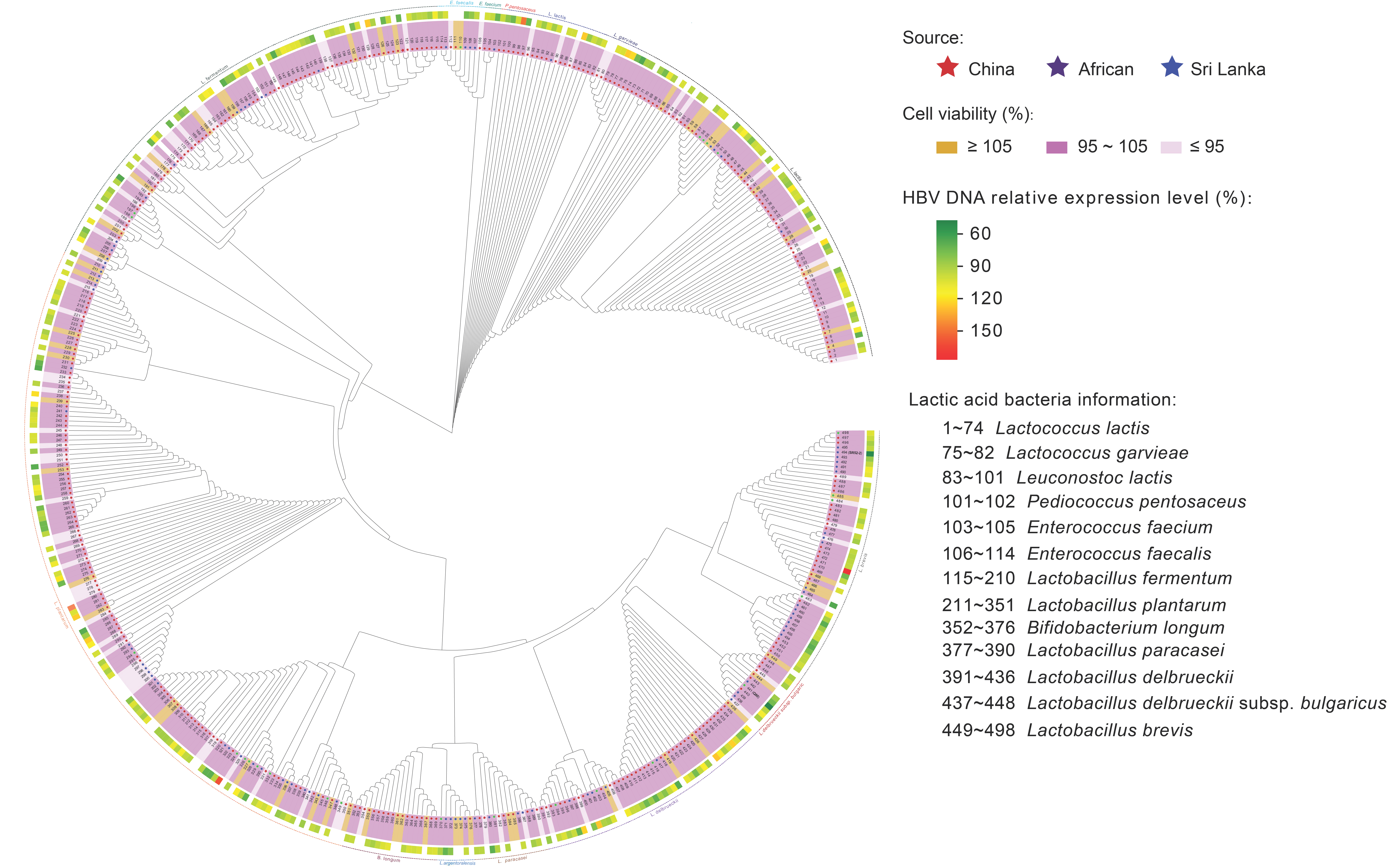
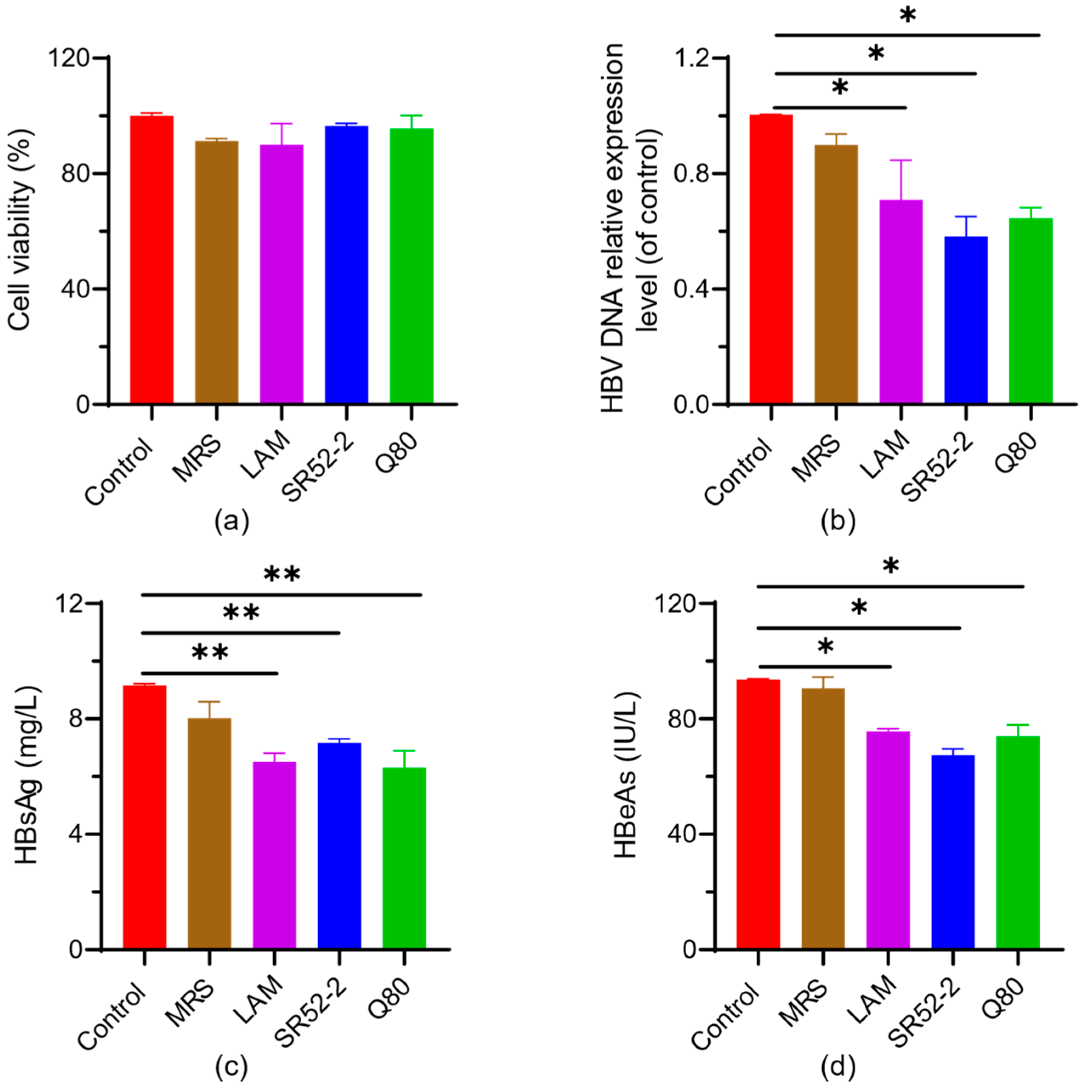
3.2. In Vitro Screening of Probiotics for Anti-Virus
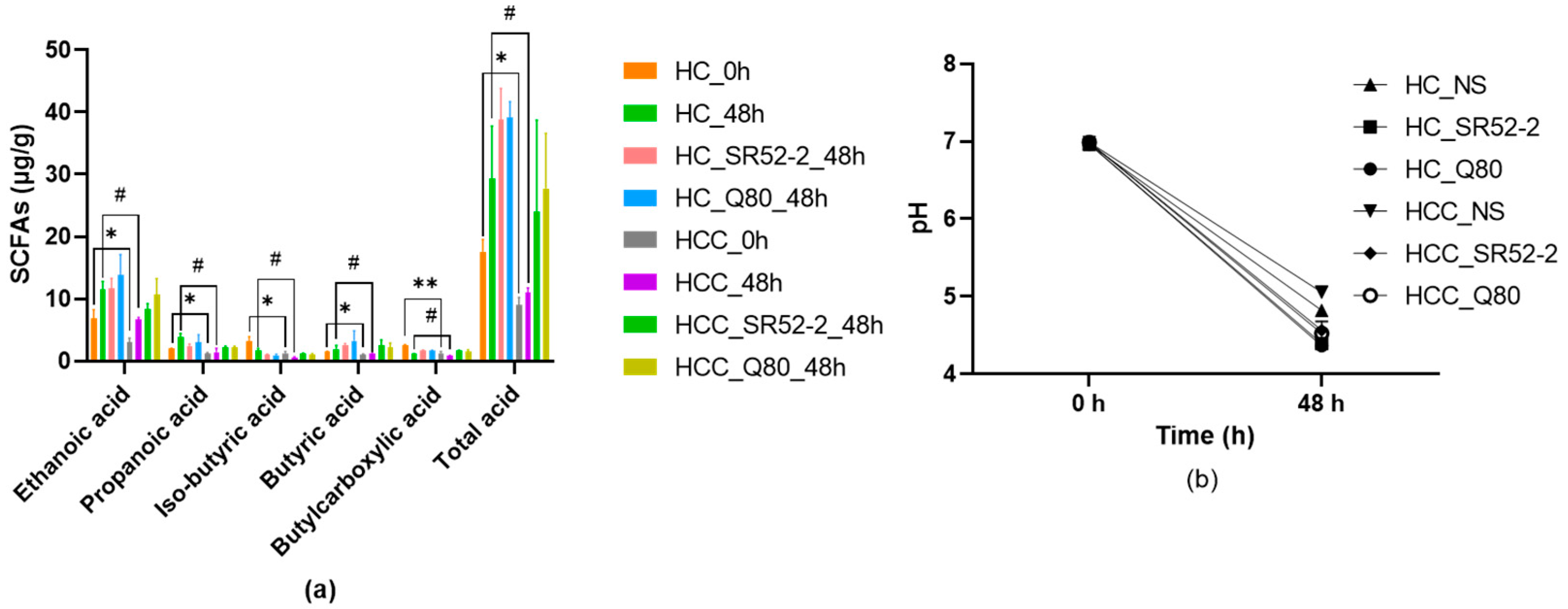
3.3. SCFAs and pH Profiles during In Vitro HFF
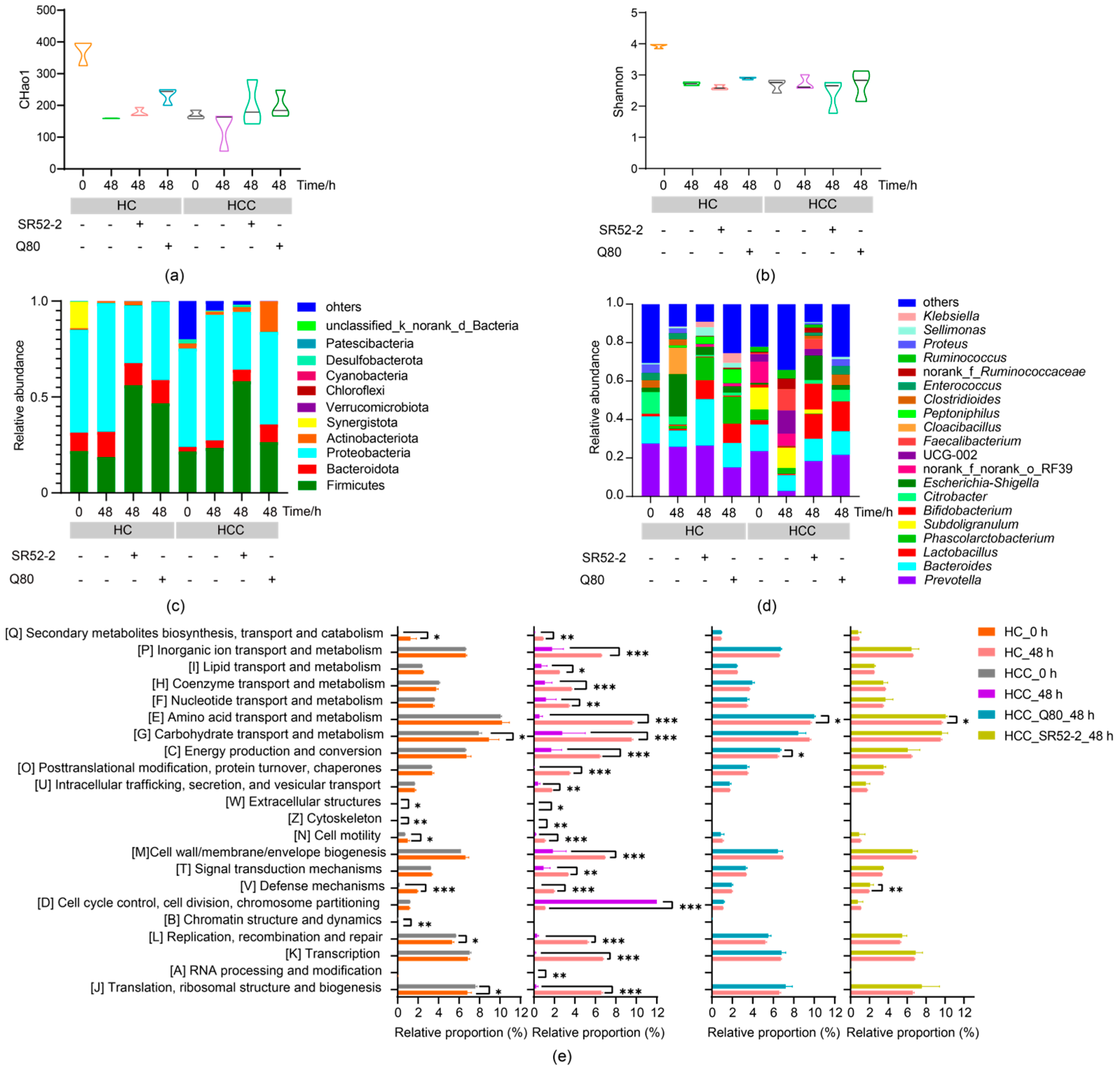
3.4. Effects of LAB on Intestinal Microbiota Diversity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wong, G.L.H.; Gane, E.; Lok, A.S.F. How to achieve functional cure of HBV: Stopping nucs, adding interferon or new drug development? J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 1249–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborators, G.R.F. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Pedersen, O. Gut microbiota in human metabolic health and disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kåhrström, C.T.; Pariente, N.; Weiss, U. Intestinal microbiota in health and disease. Nature 2016, 535, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeder, B.O.; Bäckhed, F. Signals from the gut microbiota to distant organs in physiology and disease. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Adolph, T.E.; Trauner, M. Gut-liver axis: Pathophysiological concepts and clinical implications. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1700–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabst, O.; Hornef, M.W.; Schaap, F.G.; Cerovic, V.; Clavel, T.; Bruns, T. Gut-liver axis: Barriers and functional circuits. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.L.; Schnabl, B. The gut-liver axis and gut microbiota in health and liver disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aron-Wisnewsky, J.; Warmbrunn, M.V.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Clément, K. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Modulating gut microbiota to improve severity? Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1881–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Tang, R.; Li, B.; Ma, X.; Schnabl, B.; Tilg, H. Gut microbiome, liver immunology, and liver diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, F.; Zhang, Q.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, B.; Bi, Y.; Wang, X. Gut microbiota dysbiosis with hepatitis B virus liver disease and association with immune response. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1152987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Ren, Z.; Gao, X.; Hu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, J.; Lu, H.; Yin, S.; Ji, J.; Zhou, L.; et al. Integrated analysis of microbiome and host transcriptome reveals correlations between gut microbiota and clinical outcomes in HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blázquez-Bondia, C.; Parera, M.; Català-Moll, F.; Casadellà, M.; Elizalde-Torrent, A.; Aguiló, M.; Espadaler-Mazo, J.; Santos, J.R.; Paredes, R.; Noguera-Julian, M. Probiotic effects on immunity and microbiome in HIV-1 discordant patients. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1066036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piewngam, P.; Khongthong, S.; Roekngam, N.; Theapparat, Y.; Sunpaweravong, S.; Faroongsarng, D.; Otto, M. Probiotic for pathogen-specific Staphylococcus aureus decolonisation in thailand: A phase 2, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Microbe 2023, 4, e75–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.G.; Cha, K.H.; Kim, G.C.; Im, S.H.; Kwon, H.K. Exploring probiotic effector molecules and their mode of action in gut-immune interactions. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2023, 47, fuad046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suez, J.; Zmora, N.; Segal, E.; Elinav, E. The pros, cons, and many unknowns of probiotics. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Xie, H.; Wei, C.; Mei, C.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, N.; Qin, K.; et al. Lactobacillus rhamnosus gg ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by regulating the Th17/Treg balance and gut microbiota structure. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2190304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumbeck, J.A.; Rasmussen, H.E.; Hutkins, R.W.; Clarke, J.; Shawron, K.; Keshavarzian, A.; Walter, J. Probiotic Bifidobacterium strains and galactooligosaccharides improve intestinal barrier function in obese adults but show no synergism when used together as synbiotics. Microbiome 2018, 6, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Li, J.; Hou, W.; Pan, C.; Liu, J. Mucosal immunity-mediated modulation of the gut microbiome by oral delivery of probiotics into peyer’s patches. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf0677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legesse Bedada, T.; Feto, T.K.; Awoke, K.S.; Garedew, A.D.; Yifat, F.T.; Birri, D.J. Probiotics for cancer alternative prevention and treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother 2020, 129, 110409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welzel, T.M.; Miley, W.J.; Parks, T.L.; Goedert, J.J.; Whitby, D.; Ortiz-Conde, B.A. Real-time pcr assay for detection and quantification of hepatitis B virus genotypes a to g. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 3325–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Department of Medical Administration, National Health and Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of primary liver cancer in china (2019 edition). Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2020, 28, 112–128. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Gonzalez, N.; Comas, J.C.; Harris, H.M.B.; Strain, C.; Stanton, C.; Hill, C.; Corsetti, A.; Gahan, C.G.M. Impact of food origin Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strains on the human intestinal microbiota in an in vitro system. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 832513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Jiang, T.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Dong, B.; Wu, Q.; Gu, B. Carbohydrate-active enzyme profiles of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strain 84-3 contribute to flavor formation in fermented dairy and vegetable products. Food Chem. X 2023, 20, 101036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Li, S.; Chen, W.; Han, Y.; Yao, Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Xiao, Q.; Wei, J.; Liu, Z.; et al. Postoperative probiotics administration attenuates gastrointestinal complications and gut microbiota dysbiosis caused by chemotherapy in colorectal cancer patients. Nutrients 2023, 15, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, J.; Jin, C.; Yang, J.; Zheng, C.; Chen, K.; Xie, Y.; Yang, Y.; Bo, Z.; Wang, J.; et al. Association of gut microbiome and primary liver cancer: A two-sample mendelian randomization and case-control study. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, S.J.; Wolf, Y.; Boursi, B.; Lynn, D.J. Role of the microbiota in response to and recovery from cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, K.; Kodama, Y.; Inokuchi, S.; Schnabl, B.; Aoyama, T.; Ohnishi, H.; Olefsky, J.M.; Brenner, D.A.; Seki, E. Toll-like receptor 9 promotes steatohepatitis by induction of interleukin-1beta in mice. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 323–334.e327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, M.; Chen, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, L.; Dong, Z.; Zhu, W.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Q. Programmable probiotics modulate inflammation and gut microbiota for inflammatory bowel disease treatment after effective oral delivery. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Xue, L.; Shang, Y.; Cai, W.; Xie, X.; Jiang, T.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Determination of antiviral mechanism of centenarian gut-derived Limosilactobacillus fermentum against Norovirus. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 812623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.; Jiang, C.; Li, W.; Wei, J.; Hong, H.; Li, J.; Feng, L.; Wei, H.; Xin, H.; Chen, T. A phase II randomized clinical trial and mechanistic studies using improved probiotics to prevent oral mucositis induced by concurrent radiotherapy and chemotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 618150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Liang, T.; Du, M.; Yang, L.; Yang, J.; Yang, R.; Zhao, H.; Chen, M.; et al. Bifidobacterium longum 070103 fermented milk improve glucose and lipid metabolism disorders by regulating gut microbiota in mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.K.; Kang, J.Y.; Shin, H.S.; Park, I.H.; Ha, N.J. Antiviral activity of Bifidobacterium daolescentis spm0212 against hepatitis B virus. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 2013, 36, 1525–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenartova, P.D.; Hockickova, I.; Janicko, M.; Jarcuska, P.; Drazilova, S.; Lami, F.; Schreter, I.; Kristian, P. Importance of chb’s grey zone: Analysis of patients with hbeag negative chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2024, 125, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Q.; Tamaki, N.; Lee, H.W.; Park, S.Y.; Lee, Y.R.; Lee, H.W.; Lim, S.G.; Lim, T.S.; Kurosaki, M.; Marusawa, H.; et al. Outcome of untreated low-level viremia versus antiviral therapy-induced or spontaneous undetectable HBV-DNA in compensated cirrhosis. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1746–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, M.F.; Heo, J.; Jang, J.W.; Yoon, J.H.; Kweon, Y.O.; Park, S.J.; Tami, Y.; You, S.; Yates, P.; Tao, Y.; et al. Safety, tolerability and antiviral activity of the antisense oligonucleotide bepirovirsen in patients with chronic hepatitis B: A phase 2 randomized controlled trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1725–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.H.; Wang, J.; Chai, X.Q.; Li, Z.C.; Jiang, Y.H.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Fan, J.; Cai, J.B.; Liu, F. The intratumoral bacterial metataxonomic signature of hepatocellular carcinoma. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0098322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. Flash: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Ho, C.L. Recent development of probiotic Bifidobacteria for treating human diseases. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 770248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From dietary fiber to host physiology: Short-chain fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBrearty, N.; Arzumanyan, A.; Bichenkov, E.; Merali, S.; Merali, C.; Feitelson, M. Short chain fatty acids delay the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in HBx transgenic mice. Neoplasia 2021, 23, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Cheng, W.; Shen, J.; Liang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Chai, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; et al. Single-cell and spatiotemporal transcriptomic analyses reveal the effects of microorganisms on immunity and metabolism in the mouse liver. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 3466–3477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geuking, M.B.; McCoy, K.D.; Macpherson, A.J. Metabolites from intestinal microbes shape treg. Cell Res. 2013, 23, 1339–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costabile, A.; Bergillos-Meca, T.; Landriscina, L.; Bevilacqua, A.; Gonzalez-Salvador, I.; Corbo, M.R.; Petruzzi, L.; Sinigaglia, M.; Lamacchia, C. An in vitro fermentation study on the effects of gluten friendly (TM) bread on microbiota and short chain fatty acids of fecal samples from healthy and celiac subjects. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Yang, W.; Guo, X.; Wang, T.; Tan, S.; Sun, R.; Xiao, R.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, D.; Xu, Y.; et al. Early life gut microbiota sustains liver-resident natural killer cells maturation via the butyrate-IL-18 axis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Chen, G.; Guo, Q.; Duan, Y.; Feng, H.; Xia, Q. Gut microbial metabolite butyrate improves anticancer therapy by regulating intracellular calcium homeostasis. Hepatology 2023, 78, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, H.C.; Zhang, X.; Ji, F.; Lin, Y.; Liang, W.; Li, Q.; Chen, D.; Fong, W.; Kang, X.; Liu, W.; et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus suppresses non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatocellular carcinoma through producing valeric acid. EBioMedicine 2024, 100, 104952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, N.; Mizukoshi, E.; Yamashita, T.; Yutani, M.; Seishima, J.; Wang, Z.; Arai, K.; Okada, H.; Yamashita, T.; Sakai, Y.; et al. Chronic liver disease enables gut enterococcus faecalis colonization to promote liver carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 2, 1039–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hu, L.; Tang, W.; Li, D.; Ma, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Dong, L.; Shen, X.; et al. Hepatic NOD2 promotes hepatocarcinogenesis via a RIP2-mediated proinflammatory response and a novel nuclear autophagy-mediated DNA damage mechanism. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chassaing, B.; Etienne-Mesmin, L.; Gewirtz, A.T. Microbiota-liver axis in hepatic disease. Hepatology 2014, 59, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| HC | HCC | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 49.33 ± 8.18 | 57.67 ± 11.09 |
| Male/female | 2/1 | 2/1 |
| HBV DNA (IU/mL) | 0 | 352.30 ± 225.85 |
| HBcAb (S/CO) | 4.75 ± 3.36 | 8.98 ± 0.66 |
| HBeAb (S/CO) | 1.03 ± 0.72 | 0.98 ± 0.69 |
| HBsAb (mIU/mL) | 155.08 ± 81.55 | 1.05 ± 1.06 |
| HBeAg (S/CO) | 0 | 9.25 ± 10.63 |
| HBsAg (IU/mL) | 0 | 93.24 ± 111.51 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Gao, H.; Zhang, T.; Fan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, L.; Zhao, H.; Yang, L.; et al. In Vitro Lactic Acid Bacteria Anti-Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Effect and Modulation of the Intestinal Microbiota in Fecal Cultures from HBV-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Nutrients 2024, 16, 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050600
Yang J, Gao H, Zhang T, Fan Y, Wu Y, Zhao X, Li Y, Wu L, Zhao H, Yang L, et al. In Vitro Lactic Acid Bacteria Anti-Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Effect and Modulation of the Intestinal Microbiota in Fecal Cultures from HBV-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Nutrients. 2024; 16(5):600. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050600
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Juan, He Gao, Tiantian Zhang, Yong Fan, Yuwei Wu, Xinyu Zhao, Ying Li, Lei Wu, Hui Zhao, Lingshuang Yang, and et al. 2024. "In Vitro Lactic Acid Bacteria Anti-Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Effect and Modulation of the Intestinal Microbiota in Fecal Cultures from HBV-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients" Nutrients 16, no. 5: 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050600
APA StyleYang, J., Gao, H., Zhang, T., Fan, Y., Wu, Y., Zhao, X., Li, Y., Wu, L., Zhao, H., Yang, L., Zhong, H., Li, L., Xie, X., & Wu, Q. (2024). In Vitro Lactic Acid Bacteria Anti-Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Effect and Modulation of the Intestinal Microbiota in Fecal Cultures from HBV-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Nutrients, 16(5), 600. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16050600






