The Validity of Quadriceps Muscle Thickness as a Nutritional Risk Indicator in Patients with Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
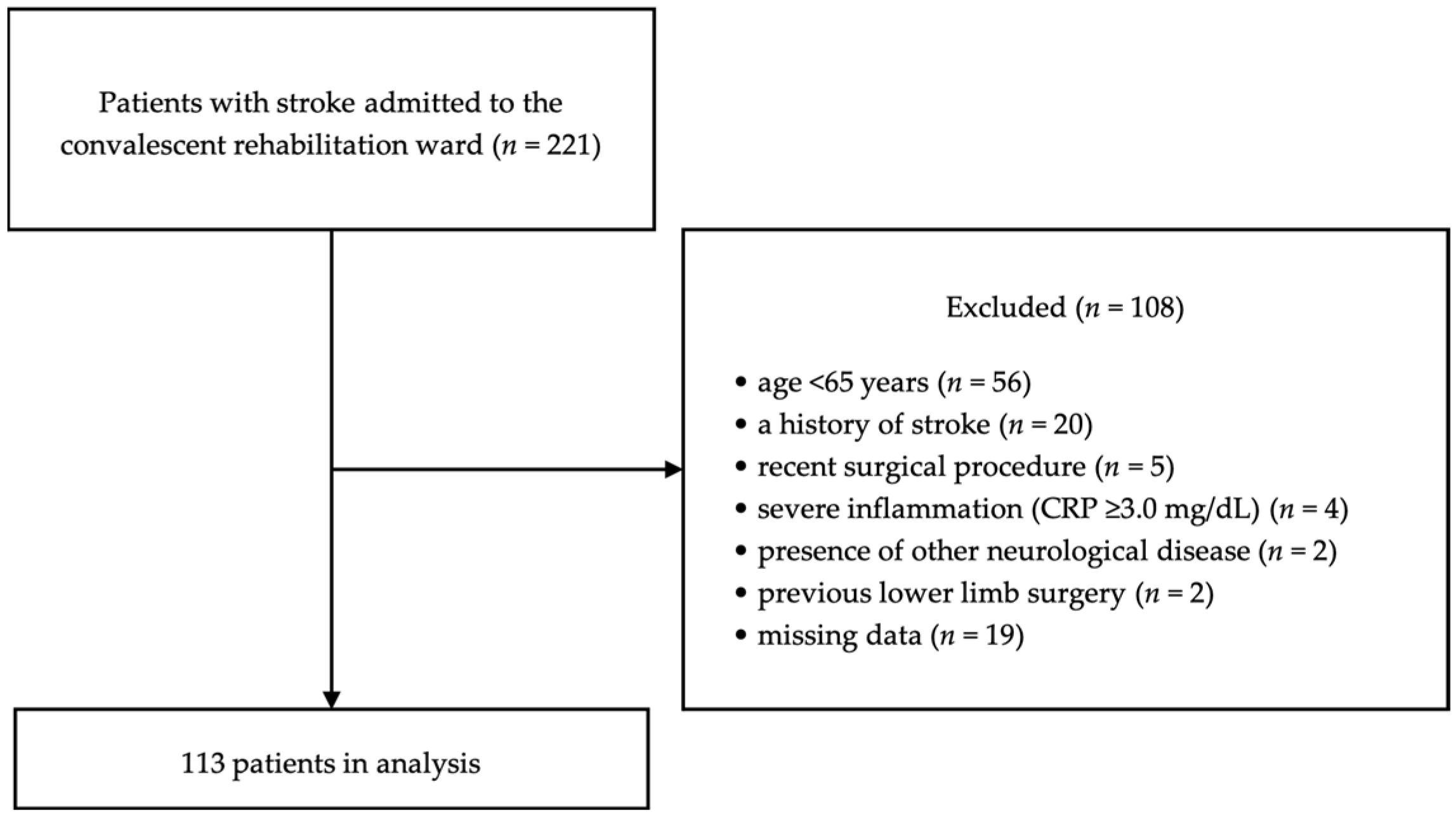
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Nutritional Risk Assessment
2.4. Muscle Mass Assessment
2.5. Outcome
2.6. Rehabilitation Program and Nutritional Management
2.7. Sample Size Calculation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
2.9. Ethics
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Watanabe, Y.; Ikenaga, M.; Yoshimura, E.; Yamada, Y.; Kimura, M. Association between Echo Intensity and Attenuation of Skeletal Muscle in Young and Older Adults: A Comparison between Ultrasonography and Computed Tomography. Clin. Interv. Aging 2018, 13, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokura, Y.; Nishioka, S.; Maeda, K.; Wakabayashi, H. Ultrasound Utilized by Registered Dietitians for Body Composition Measurement, Nutritional Assessment, and Nutritional Management. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 57, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.J.S.; et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition—A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, N.C.; Salter, K.L.; Robertson, J.; Teasell, R.W.; Woodbury, M.G. Which Reported Estimate of the Prevalence of Malnutrition after Stroke Is Valid? Stroke 2009, 40, e66–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, K.; Nakagawa, N.; Koyama, S.; Maruyama, J.; Hasebe, N. Malnutrition Increases the Incidence of Death, Cardiovascular Events, and Infections in Patients with Stroke after Rehabilitation. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Zhu, S.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, P.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, W.; Sun, W.; et al. Association between Malnutrition and Long-Term Mortality in Older Adults with Ischemic Stroke. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 2535–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, M.; Ido, Y.; Yoshimura, Y.; Mutai, H. Relationship of Malnutrition During Hospitalization With Functional Recovery and Postdischarge Destination in Elderly Stroke Patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2019, 28, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, H.; Nezu, T.; Hosomi, N.; Aoki, S.; Kinoshita, N.; Kuga, J.; Shimomura, R.; Araki, M.; Ueno, H.; Ochi, K.; et al. Controlling Nutritional Status Score for Predicting 3-Mo Functional Outcome in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Nutrition 2018, 55–56, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Xia, J.; Shao, X.; Pu, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Zheng, J.; Wu, D.; Chen, B. The Relationship between the Baseline Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index (GNRI) and Neurological Function at the Convalescence Stage in Patients with Stroke: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Geriatr. 2023, 23, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ni, J.; Li, Y. Malnutrition Defined by Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index Predicts Outcomes in Severe Stroke Patients: A Propensity Score-Matched Analysis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.K.; Kim, T.J.; Kim, Y.; Nam, K.-W.; Jeong, H.-Y.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, J.S.; Ko, S.-B.; Yoon, B.-W. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index Predicts Poor Outcomes in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke—Automated Undernutrition Screen Tool. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Lim, J.-S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, C.-H.; Lee, S.-H.; Jang, M.U.; Oh, M.S.; Lee, B.-C.; Yu, K.-H. Association between Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index and Post-Stroke Cognitive Outcomes. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irisawa, H.; Mizushima, T. Correlation of Body Composition and Nutritional Status with Functional Recovery in Stroke Rehabilitation Patients. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Vincenzo, O.; Pagano, E.; Cervone, M.; Natale, R.; Morena, A.; Esposito, A.; Pasanisi, F.; Scalfi, L. High Nutritional Risk Is Associated with Poor Functional Status and Prognostic Biomarkers in Stroke Patients at Admission to a Rehabilitation Unit. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scrutinio, D.; Lanzillo, B.; Guida, P.; Passantino, A.; Spaccavento, S.; Battista, P. Association Between Malnutrition and Outcomes in Patients With Severe Ischemic Stroke Undergoing Rehabilitation. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 101, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huppertz, V.; Guida, S.; Holdoway, A.; Strilciuc, S.; Baijens, L.; Schols, J.; van Helvoort, A.; Lansink, M.; Muresanu, D.F. Impaired Nutritional Condition After Stroke From the Hyperacute to the Chronic Phase: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 780080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojzischke, J.; van Wijngaarden, J.; van den Berg, C.; Cetinyurek-Yavuz, A.; Diekmann, R.; Luiking, Y.; Bauer, J. Nutritional status and functionality in geriatric rehabilitation patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2020, 11, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsutsumiuchi, K.; Wakabayashi, H.; Maeda, K.; Shamoto, H. Impact of Malnutrition on Post-Stroke Cognitive Impairment in Convalescent Rehabilitation Ward Inpatients. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2021, 12, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.; Emery, P.W.; Weekes, C.E. Risk of Malnutrition Is an Independent Predictor of Mortality, Length of Hospital Stay, and Hospitalization Costs in Stroke Patients. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, S.; Wakabayashi, H. Interaction between Malnutrition and Physical Disability in Older Adults: Is There a Malnutrition-Disability Cycle? Nutr. Rev. 2023, 81, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillanne, O.; Morineau, G.; Dupont, C.; Coulombel, I.; Vincent, J.-P.; Nicolis, I.; Benazeth, S.; Cynober, L.; Aussel, C. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index: A New Index for Evaluating at-Risk Elderly Medical Patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignacio de Ulíbarri, J.; González-Madroño, A.; de Villar, N.G.P.; González, P.; González, B.; Mancha, A.; Rodríguez, F.; Fernández, G. CONUT: A Tool for Controlling Nutritional Status. First Validation in a Hospital Population. Nutr. Hosp. 2005, 20, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka, S.; Wakabayashi, H.; Yoshida, T. Accuracy of Non-Paralytic Anthropometric Data for Nutritional Screening in Older Patients with Stroke and Hemiplegia. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portero-McLellan, K.C.; Staudt, C.; Silva, F.R.; Delbue Bernardi, J.L.; Baston Frenhani, P.; Leandro Mehri, V.A. The use of calf circumference measurement as an anthropometric tool to monitor nutritional status in elderly inpatients. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2010, 14, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seron-Arbeloa, C.; Labarta-Monzon, L.; Puzo-Foncillas, J.; Mallor-Bonet, T.; Lafita-Lopez, A.; Bueno-Vidales, N.; Montoro-Huguet, M. Malnutrition Screening and Assessment. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, Y.; Maeda, K.; Nonogaki, T.; Shimizu, A.; Yamanaka, Y.; Matsuyama, R.; Kato, R.; Mori, N. Impact of Edema on Length of Calf Circumference in Older Adults. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2019, 19, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraiz, G.M.; Gallo, L.H.; Rabito, E.I.; Gomes, A.R.S.; Schieferdecker, M.E.M. Relationship between Muscle Thickness and Calf Circumference in Healthy Older Women. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2020, 86, 103942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokura, Y.; Kato, M.; Taniguchi, Y.; Kimoto, K.; Okada, Y. Energy Intake during the Acute Phase and Changes in Femoral Muscle Thickness in Older Hemiplegic Inpatients with Stroke. Nutrition 2020, 70, 110582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozoe, M.; Kanai, M.; Kubo, H.; Kitamura, Y.; Shimada, S.; Mase, K. Changes in Quadriceps Muscle Thickness in Acute Non-Ambulatory Stroke Survivors. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2016, 23, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridker, P.M. C-reactive protein, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease: Clinical update. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2005, 32, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Lin, G.-H.; Huang, Y.-J.; Song, C.-Y.; Lee, Y.-C.; How, M.-J.; Chen, Y.-M.; Hsueh, I.-P.; Chen, M.-H.; Hsieh, C.-L. Improving the Utility of the Brunnstrom Recovery Stages in Patients with Stroke: Validation and Quantification. Medicine 2016, 95, e4508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumney, D.; Nollinger, K.; Shesko, K.; Skop, K.; Spencer, M.; Newton, R.A. Ability of Functional Independence Measure to Accurately Predict Functional Outcome of Stroke-Specific Population: Systematic Review. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2010, 47, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, K.; Furuya, R.; Takita, T.; Maruyama, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Ohkawa, S.; Kumagai, H. Simplified Nutritional Screening Tools for Patients on Maintenance Hemodialysis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokura, Y.; Maeda, K.; Wakabayashi, H.; Nishioka, S.; Higashi, S. High Nutritional-Related Risk on Admission Predicts Less Improvement of Functional Independence Measure in Geriatric Stroke Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, 1335–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, P.; Alasmar, M.; McLaughlin, J.; Ang, Y.; McPhee, J.; Heire, P.; Sultan, J. The Current Use of Ultrasound to Measure Skeletal Muscle and Its Ability to Predict Clinical Outcomes: A Systematic Review. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 2298–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rech, A.; Radaelli, R.; Goltz, F.R.; da Rosa, L.H.T.; Schneider, C.D.; Pinto, R.S. Echo Intensity Is Negatively Associated with Functional Capacity in Older Women. Age 2014, 36, 9708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, G.C.-H.; Chen, C.H.; Petrella, R.; Thind, A. Rehabilitation Impact Indices and Their Independent Predictors: A Systematic Review. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e003483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicco, D.; Jurman, G. The Advantages of the Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC) over F1 Score and Accuracy in Binary Classification Evaluation. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Sato, A.; Fujimoto, Y.; Minematsu, T.; Sugama, J.; Sanada, H. Temporal Muscle Thickness as a New Indicator of Nutritional Status in Older Individuals. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2019, 19, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, F.; Kikutani, T.; Tohara, T.; Yoshida, M.; Yaegaki, K. Tongue Thickness Relates to Nutritional Status in the Elderly. Dysphagia 2012, 27, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.-Y.; Ong, S.P.; Ng, C.C.; Yap, C.S.L.; Engkasan, J.P.; Barakatun-Nisak, M.Y.; Heyland, D.K.; Hasan, M.S. Association between Ultrasound Quadriceps Muscle Status with Premorbid Functional Status and 60-Day Mortality in Mechanically Ventilated Critically Ill Patient: A Single-Center Prospective Observational Study. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1338–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Paris, A.; González-Fernandez, M.; Hueso-Del Río, L.E.; Ferrer-Lahuerta, E.; Monge-Vazquez, A.; Losfablos-Callau, F.; Sanclemente-Hernández, T.; Sanz-Arque, A.; Arbones-Mainar, J.M. Muscle Thickness and Echogenicity Measured by Ultrasound Could Detect Local Sarcopenia and Malnutrition in Older Patients Hospitalized for Hip Fracture. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos-Angulo, A.; Galán-Mercant, A.; Cuesta-Vargas, A.I. Ultrasound Muscle Assessment and Nutritional Status in Institutionalized Older Adults: A Pilot Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besharat, S.; Grol-Prokopczyk, H.; Gao, S.; Feng, C.; Akwaa, F.; Gewandter, J.S. Peripheral Edema: A Common and Persistent Health Problem for Older Americans. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0260742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukumoto, Y.; Ikezoe, T.; Yamada, Y.; Tsukagoshi, R.; Nakamura, M.; Mori, N.; Kimura, M.; Ichihashi, N. Skeletal Muscle Quality Assessed from Echo Intensity Is Associated with Muscle Strength of Middle-Aged and Elderly Persons. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasser, E.M.; Draskovits, T.; Praschak, M.; Quittan, M.; Graf, A. Association between ultrasound measurements of muscle thickness, pennation angle, echogenicity and skeletal muscle strength in the elderly. Age 2013, 35, 2377–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akazawa, N.; Harada, K.; Okawa, N.; Tamura, K.; Moriyama, H. Muscle Mass and Intramuscular Fat of the Quadriceps Are Related to Muscle Strength in Non-Ambulatory Chronic Stroke Survivors: A Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Imada, K.; Ishida, K.; Akima, H. Quadriceps Thickness and Echo Intensity Predict Gait Independence in Individuals with Severe and Mild Hemiparetic Stroke. Eur. Neurol. 2020, 83, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.X.M.; Yao, J.; Zirek, Y.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Maier, A.B. Muscle Mass, Strength, and Physical Performance Predicting Activities of Daily Living: A Meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2020, 11, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechelli, F.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Stokes, M.; Agyapong-Badu, S. Validity of Ultrasound Imaging Versus Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Measuring Anterior Thigh Muscle, Subcutaneous Fat, and Fascia Thickness. Methods Protoc. 2019, 2, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheean, P.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Prado, C.M.; McKeever, L.; Hall, A.M.; Braunschweig, C.A. American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition Clinical Guidelines: The Validity of Body Composition Assessment in Clinical Populations. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 12–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variables | Total (N = 113) | Men (N = 58) | Women (N = 55) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years (IQR) | 76.0 (71.0–82.0) | 74.0 (71.0–80.8) | 78.0 (72.0–83.0) | 0.456 a |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 (SD) | 22.6 (3.6) | 22.3 (3.4) | 22.8 (3.8) | 0.404 b |
| Stroke subtype, n (%) | 0.197 c | |||
| Cerebral infarction | 75 (66.4) | 37 (63.8) | 38 (69.1) | |
| Cerebral hemorrhage | 33 (29.2) | 20 (34.5) | 13 (23.6) | |
| Subarachnoid hemorrhage | 5 (4.4) | 1 (1.7) | 4 (7.3) | |
| Brunnstrom recovery stage (lower limb) (IQR) | 5 (4–6) | 5 (5–6) | 5 (4–6) | 0.220 a |
| Days from onset, days (IQR) | 17 (12–22) | 17 (12–22) | 16 (13–23) | 0.854 a |
| Laboratory data | ||||
| Serum albumin, g/dL (SD) | 3.7 (0.4) | 3.7 (0.4) | 3.6 (0.4) | 0.321 b |
| C-reactive protein, mg/dL (IQR) | 0.13 (0.06–0.61) | 0.11 (0.06–0.34) | 0.17 (0.07–0.74) | 0.186 a |
| FIM-total upon admission, score (IQR) | 73 (45–92) | 75 (46–99) | 69 (47–90) | 0.352 a |
| FIM-motor upon admission, score (IQR) | 50.0 (32.0–69.0) | 53.5 (33.3–69.8) | 46.0 (30.5–64.5) | 0.267 a |
| FIM-motor upon discharge, score (IQR) | 76.0 (55.0–84.0) | 77.0 (55.8–84.0) | 75.0 (52.0–84.5) | 0.579 a |
| FIM effectiveness, % | 54.5 (34.6–73.3) | 51.1 (32.0–71.1) | 57.1 (36.4–73.8) | 0.636 a |
| GNRI, score (SD) | 94.3 (7.0) | 94.8 (6.8) | 93.7 (7.3) | 0.414 b |
| Risk of malnutrition (<92), n (%) | 40 (35.4) | 19 (32.8) | 21 (38.2) | |
| Normal (≥92), n (%) | 73 (64.6) | 39 (67.2) | 34 (61.8) | |
| QMT on the non-paretic side, mm (SD) | 51.2 (12.1) | 53.6 (11.8) | 48.6 (12.0) | 0.028 b |
| CC on the non-paretic side, cm (SD) | 32.5 (3.2) | 32.7 (2.9) | 32.2 (3.5) | 0.392 b |
| SFT on the non-paretic side, mm (IQR) | 4.71 (3.25–6.65) | 3.51 (2.71–4.61) | 6.45 (5.17–7.96) | <0.001 a |
| Variables | Men (N = 58) | Women (N = 55) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Correlation Coefficient (95% CI) | p | Correlation Coefficient (95% CI) | p | |
| QMT on the non-paretic side | 0.583 (0.382, 0.731) | <0.001 | 0.650 (0.465, 0.781) | <0.001 |
| CC on the non-paretic side | 0.580 (0.379, 0.729) | <0.001 | 0.601 (0.399, 0.747) | <0.001 |
| Variables | β | B | 95% CI | p | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | −0.13 | −0.50 | −1.23, 0.22 | 0.172 | 1.17 |
| Sex (women) | 0.05 | 2.90 | −6.74, 12.54 | 0.552 | 1.04 |
| BRS (lower limb) | 0.24 | 4.98 | 1.18, 8.78 | 0.011 | 1.11 |
| Days from onset | −0.18 | −0.55 | −1.13, 0.03 | 0.061 | 1.15 |
| Nutritional risk-QMT | −0.25 | −14.81 | −26.07, −3.55 | 0.010 | 1.21 |
| Variables | β | B | 95% CI | p | VIF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | −0.16 | −0.63 | −1.38, 0.11 | 0.094 | 1.17 |
| Sex (women) | 0.07 | 3.85 | −5.99, 13.68 | 0.440 | 1.04 |
| BRS (lower limb) | 0.22 | 4.68 | 0.74, 8.62 | 0.020 | 1.14 |
| Days from onset | −0.24 | −0.75 | −1.31, −0.19 | 0.009 | 1.04 |
| Nutritional risk-CC | −0.12 | −6.84 | −17.16, 3.49 | 0.192 | 1.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maruyama, M.; Kagaya, Y.; Kajiwara, S.; Oikawa, T.; Horikawa, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Sasaki, M. The Validity of Quadriceps Muscle Thickness as a Nutritional Risk Indicator in Patients with Stroke. Nutrients 2024, 16, 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040540
Maruyama M, Kagaya Y, Kajiwara S, Oikawa T, Horikawa M, Fujimoto M, Sasaki M. The Validity of Quadriceps Muscle Thickness as a Nutritional Risk Indicator in Patients with Stroke. Nutrients. 2024; 16(4):540. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040540
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaruyama, Motoki, Yuki Kagaya, Sota Kajiwara, Takuto Oikawa, Manabu Horikawa, Mika Fujimoto, and Masahiro Sasaki. 2024. "The Validity of Quadriceps Muscle Thickness as a Nutritional Risk Indicator in Patients with Stroke" Nutrients 16, no. 4: 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040540
APA StyleMaruyama, M., Kagaya, Y., Kajiwara, S., Oikawa, T., Horikawa, M., Fujimoto, M., & Sasaki, M. (2024). The Validity of Quadriceps Muscle Thickness as a Nutritional Risk Indicator in Patients with Stroke. Nutrients, 16(4), 540. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16040540





