Body Composition Changes in Male and Female Elite Soccer Players: Effects of a Nutritional Program Led by a Sport Nutritionist
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Body Composition
2.2.1. Skinfold Thickness
2.2.2. Whole-Body Bioimpedance Analysis (BIA)
2.3. Statistical Analysis
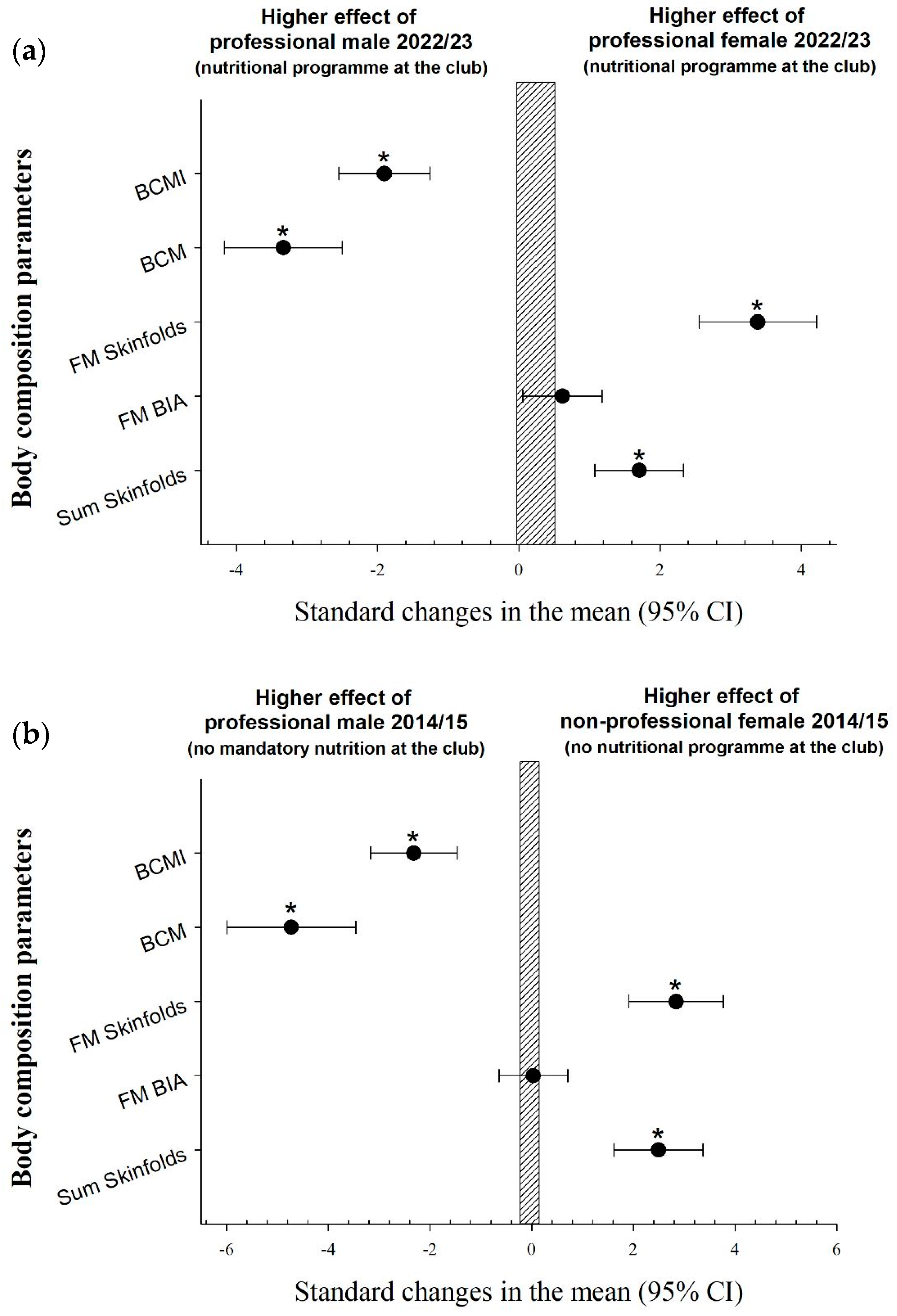
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lago-Peñas, C.; Lorenzo-Martinez, M.; Campo, R.L.-D.; Resta, R.; Rey, E. Evolution of physical and technical parameters in the Spanish LaLiga 2012–2019. Sci. Med. Footb. 2012, 7, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mujika, I. The alphabet of sport science research starts with Q. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2013, 8, 465–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujika, I.; Halson, S.; Burke, L.M.; Balagué, G.; Farrow, D. An Integrated, Multifactorial Approach to Periodization for Optimal Performance in Individual and Team Sports. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 538–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, K.L.; Thomson, J.S.; Swift, R.J.; von Hurst, P.R. Role of nutrition in performance enhancement and postexercise recovery. Open Access J. Sports Med. 2015, 6, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoli, A.; Bianco, A.; Grimaldi, K.A. The Ketogenic diet and sport: A possible marriage? Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2015, 43, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durkalec-Michalski, K.; Zawieja, E.E.; Zawieja, B.E.; Jurkowska, D.; Buchowski, M.S.; Jeszka, J. Effects of Low Versus Moderate Glycemic Index Diets on Aerobic Capacity in Endurance Runners: Three-Week Randomized Controlled Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2018, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, D.; Domínguez, R.; Rodríguez-Fernández, A.; Raya-González, J. Effects of Caffeine Supplementation on Power Performance in a Flywheel Device: A Randomised, Double-Blind Cross-Over Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Fernández, A.; Castillo, D.; Raya-González, J.; Domínguez, R.; Bailey, S.J. Beetroot juice supplementation increases concentric and eccentric muscle power output. Original investigation. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2021, 24, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raya-González, J.; Rendo-Urteaga, T.; Domínguez, R.; Castillo, D.; Rodríguez-Fernández, A.; Grgic, J. Acute Effects of Caffeine Supplementation on Movement Velocity in Resistance Exercise: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2019, 50, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, R.; Beck, K.L.; Manore, M.M.; Gifford, J.; Flood, V.M.; O’connor, H. Effectiveness of Education Interventions Designed to Improve Nutrition Knowledge in Athletes: A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2019, 49, 1769–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murimi, M.W.; Kanyi, M.; Mupfudze, T.; Amin, R.; Mbogori, T.; Aldubayan, K. Factors Influencing Efficacy of Nutrition Education Interventions: A Systematic Review. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2017, 49, 142–165.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, M.R.; Mitchell, N.; Backhouse, S.H. Sports nutrition interventions: A systematic review of behavioural strategies used to promote dietary behaviour change in athletes. Appetite 2020, 150, 104645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, J.; Maughan, R.J.; Gleeson, M.; Bilsborough, J.; Jeukendrup, A.; Morton, J.P.; Phillips, S.M.; Armstrong, L.; Burke, L.M.; Close, G.L.; et al. UEFA expert group statement on nutrition in elite football. Current evidence to inform practical recommendations and guide future research. Br. J. Sports Med. 2021, 55, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutts, A.J. Challenges in developing evidence-based practice in high-performance sport. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2017, 12, 717–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.M. Communicating sports science in the age of the twittersphere. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2017, 27, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, H.; Ekstrand, J.; Hägglund, M. Muscle injury rates in professional football increase with fixture congestion: An 11-year follow-up of the UEFA champions league injury study. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 743–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, G.; Nedelec, M.; McCall, A.; McCormack, D.; Berthoin, S.; Wisløff, U. Effect of 2 soccer matches in a week on physical performance and injury rate. Am. J. Sports Med. 2010, 38, 1752–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melin, A.K.; Heikura, I.A.; Tenforde, A.; Mountjoy, M. Energy Availability in Athletics: Health, Performance, and Physique. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2019, 29, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountjoy, M.; Sundgot-Borgen, J.; Burke, L.; Ackerman, K.E.; Blauwet, C.; Constantini, N.; Lebrun, C.; Lundy, B.; Melin, A.; Meyer, N.; et al. International Olympic Committee (IOC) Consensus Statement on Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S): 2018 Update. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2018, 28, 316–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, F.; Matias, C.N.; Moro, T.; Cerullo, G.; Casolo, A.; Teixeira, F.J.; Paoli, A. Methods over Materials: The Need for Sport-Specific Equations to Accurately Predict Fat Mass Using Bioimpedance Analysis or Anthropometry. Nutrients 2023, 15, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steward, A.; Marfell-Jones, M. International Standards for Anthropometric Assessment; International Society for the Advancement of Kinanthropometry: Lower Hutt, New Zealand, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez-Arrones, L.; Petri, C.; Maldonado, R.A.; Torreno, N.; Munguía-Izquierdo, D.; Di Salvo, V.; Méndez-Villanueva, A. Body fat assessment in elite soccer players: Cross-validation of different field methods. Sci. Med. Footb. 2018, 2, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.A.; Dawson, J.A.; Matias, C.N.; Rocha, P.M.; Minderico, C.S.; Allison, D.B.; Sardinha, L.B.; Silva, A.M. Reference values for body composition and anthropometric measurements in athletes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micheli, M.L.; Pagani, L.; Marella, M.; Gulisano, M.; Piccoli, A.; Angelini, F.; Burtscher, M.; Gatterer, H. Bioimpedance and impedance vector patterns as predictors of league level in male soccer players. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coratella, G.; Campa, F.; Matias, C.N.; Toselli, S.; Koury, J.C.; Andreoli, A.; Sardinha, L.B.; Silva, A.M. Generalized bioelectric impedance-based equations underestimate body fluids in athletes. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2021, 31, 2123–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matias, C.N.; Campa, F.; Cerullo, G.; D’antona, G.; Giro, R.; Faleiro, J.; Reis, J.F.; Monteiro, C.P.; Valamatos, M.J.; Teixeira, F.J. Bioelectrical Impedance Vector Analysis Discriminates Aerobic Power in Futsal Players: The Role of Body Composition. Biology 2022, 11, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascherini, G.; Petri, C.; Galanti, G. Integrated total body composition and localized fat-free mass assessment. Sport Sci. Health 2015, 11, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, E.M.; Maughan, R.J. Requirements for ethics approvals. J. Sports Sci. 2009, 27, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durnin, J.V.; Womersley, J. Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: Measurements on 481 men and women aged from 16 to 72 Years. Br. J. Nutr. 1974, 32, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotler, D.P.; Burastero, S.; Wang, J.; Pierson, R.N., Jr. Prediction of body cell mass, fat-free mass, and total body water with bioelectrical impedance analysis: Effects of race, sex, and disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64, 489S–497S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, F.; Bongiovanni, T.; Rossi, A.; Cerullo, G.; Casolo, A.; Martera, G.; Trecroci, A.; Moro, T.; Paoli, A. Athletic bioimpedance-based equations underestimate fat free mass components in male elite soccer players: Development and validation of new soccer-specific predictive models. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, C.N.; Campa, F.; Santos, D.A.; Lukaski, H.; Sardinha, L.B.; Silva, A.M. Fat-free Mass Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis Predictive Equation for Athletes using a 4-Compartment Model. Int. J. Sports Med. 2021, 42, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, W.; Marshall, S.; Batterham, A.; Hanin, J. Progressive statistics for studies in sports medicine and exercise science. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2009, 41, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehler, K.; Hoerner, N.R.; Gibbs, J.C.; Zinner, C.; Braun, H.; De Souza, M.J.; Schaenzer, W. Low energy availability in exercising men is associated with reduced leptin and insulin but not with changes in other metabolic hormones. J. Sports Sci. 2016, 34, 1921–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, N.L.; Sundgot-Borgen, J.; Lohman, T.G.; Ackland, T.R.; Stewart, A.D.; Maughan, R.J.; Smith, S.; Müller, W. Body composition for health and performance: A survey of body composition assessment practice carried out by the ad hoc research working group on body composition, health and performance under the auspices of the IOC medical commission. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 1044–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundgot-Borgen, J.; Meyer, N.L.; Lohman, T.G.; Ackland, T.R.; Maughan, R.J.; Stewart, A.D.; Müller, W. How to minimise the health risks to athletes who compete in weight-sensitive sports review and position statement on behalf of the ad hoc research working group on body composition, health and performance, under the auspices of the IOC medical commission. Br. J. Sports Med. 2013, 47, 1012–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, M.; Reed, D.B.; Crouse, S.F.; Armstrong, R.B. Pre- and post-season dietary intake, body composition, and performance indices of NCAA division I female soccer players. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2003, 13, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravina, L.; Ruiz, F.; Lekue, J.A.; Irazusta, J.; Gil, S.M. Metabolic impact of a soccer match on female players. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, 1345–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastiá-Rico, J.; Soriano, J.M.; González-Gálvez, N.; Martínez-Sanz, J.M. Body Composition of Male Professional Soccer Players Using Different Measurement Methods: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, V.P.; Riera, J.; Ballarini, P.-A.G.; Martínez, F.D.; Banquells, M.; Ruiz, O. Características antropométricas, composición corporal y somatotipo por deportes.: Datos de referencia del CAR de San Cugat, 1989–2013. Apunts Med. Esport. 2015, 50, 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Cavia, M.; Moreno, A.; Fernández-Trabanco, B.; Carrillo, C.; Alonso-Torre, S. Anthropometric Characteristics and Somatotype of Professional Soccer Players by Position. J. Sports Med. Ther. 2019, 4, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, L.; Scott, M.; Wallace, J.; Reilly, T. Body Composition of English Premier League Soccer Players: Influence of Playing Position, International Status, and Ethnicity. J. Sports Sci. 2009, 27, 1019–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stølen, T.; Chamari, K.; Castagna, C.; Wisløff, U. Physiology of Soccer: An Update. Sports Med. 2005, 35, 501–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, J.L.; Norton, K.I. Evolution of World Cup Soccer Final Games 1966–2010: Game Structure, Speed and Play Patterns. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2014, 17, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassis, G.P.; Massey, A.; Jacobsen, P.; Brito, J.; Randers, M.B.; Castagna, C.; Mohr, M.; Krustrup, P. Elite Football of 2030 Will Not Be the Same as That of 2020: Preparing Players, Coaches, and Support Staff for the Evolution. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2020, 30, 962–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya-Amaya, H.; Molina-López, A.; Berral-Aguilar, A.J.; Rojano-Ortega, D.; Berral-De-La-Rosa, F.J. Migración Del Somatotipo En Jugadores de Fútbol Profesional En Las Últimas Décadas. Int. J. Morphol. 2022, 40, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mountjoy, M.; Sundgot-Borgen, J.K.; Burke, L.M.; Ackerman, K.E.; Blauwet, C.; Constantini, N.; Lebrun, C.; Lundy, B.; Melin, A.K.; Meyer, N.L.; et al. IOC consensus statement on relative energy deficiency in sport (RED-S): 2018 update. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, M.K.; Vlahovich, N.; Hughes, D.; Appaneal, R.; Peterson, K.; Burke, L.; Lundy, B.; Toomey, M.; Watts, D.; Lovell, G.; et al. A multifactorial evaluation of illness risk factors in athletes preparing for the Summer Olympic Games. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2017, 20, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tornberg, Å.B.; Melin, A.; Koivula, F.M.; Johansson, A.; Skouby, S.O.; Faber, J.; Sjödin, A. Reduced neuromuscular performance in amenorrheic elite endurance athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 2478–2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petri, C.; Mascherini, G.; Pengue, L.; Galanti, G. Dietary habits in elite soccer players. Sport Sci. Health 2016, 12, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Professional Female 2022/2023 (n = 44) | Professional Male 2022/2023 (n = 44) | No Professional Female 2014/2015 (n = 44) | Professional Male 2014/2015 (n = 44) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 27.0 ± 5.0 | 26.2 ± 2.9 | 27.3 ± 5.2 | 26.8 ± 3.1 |
| Body mass (kg) | 62.2 ± 5.7 | 80.9 ± 7.7 | 61.0 ± 7.7 | 77.9 ± 6.6 |
| Height (m) | 1.69 ± 0.05 | 1.84 ± 0.05 | 1.69 ± 0.07 | 1.82 ± 0.07 |
| Variable | Professional Female 2022/2023 (n = 44) | Professional Male 2022/2023 (n = 44) | No Professional Female 2014/2015 (n = 44) | Professional Male 2014/2015 (n = 44) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sum 7 SKF (mm) | 61.4 ± 11.8 b,c | 44.0 ± 4.9 c,d | 88.6 ± 17.4 d | 54.5 ± 6.9 b,c |
| Fat-Mass skinfolds (%) | 12.1 ± 2.1 b,c,d | 6.9 ± 0.5 a,c,d | 16.6 ± 2.8 a,b,d | 10.1 ± 1.4 a,b,c |
| Rz (Ohm) | 536.7 ± 56.2 b,d | 436.0 ± 43.2 a,c | 554.7 ± 50.3 b,d | 468.6 ± 31.4 a,c |
| Xc (Ohm) | 69.8 ± 8.7 | 65.8 ± 11.1 | 69.0 ± 6.1 | 65.0 ± 4.7 |
| BCM (Kg) | 29.9 ± 3.2 b,d | 45.4 ± 5.7 a,c,d | 28.2 ± 2.6 b,d | 40.4 ± 2.7 a,b,c |
| BCMI (Kg/m2) | 10.4 ± 0.8 b,d | 13.4 ± 1.3 a,c,d | 10.0 ± 1.0 b,d | 12.3 ± 0.9 a,b,c |
| Phase angle (degree) | 7.4 ± 0.6 b | 8.6 ± 1.5 a,c | 7.1 ± 0.5 b | 7.9 ± 0.5 |
| Fat-Mass BIA (%) | 12.8 ± 3.9 | 10.4 ± 3.7 | 12.8 ± 3.9 | 12.0 ± 3.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Petri, C.; Pengue, L.; Bartolini, A.; Pistolesi, D.; Arrones, L.S. Body Composition Changes in Male and Female Elite Soccer Players: Effects of a Nutritional Program Led by a Sport Nutritionist. Nutrients 2024, 16, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030334
Petri C, Pengue L, Bartolini A, Pistolesi D, Arrones LS. Body Composition Changes in Male and Female Elite Soccer Players: Effects of a Nutritional Program Led by a Sport Nutritionist. Nutrients. 2024; 16(3):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030334
Chicago/Turabian StylePetri, Cristian, Luca Pengue, Alice Bartolini, Duccio Pistolesi, and Luis Suarez Arrones. 2024. "Body Composition Changes in Male and Female Elite Soccer Players: Effects of a Nutritional Program Led by a Sport Nutritionist" Nutrients 16, no. 3: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030334
APA StylePetri, C., Pengue, L., Bartolini, A., Pistolesi, D., & Arrones, L. S. (2024). Body Composition Changes in Male and Female Elite Soccer Players: Effects of a Nutritional Program Led by a Sport Nutritionist. Nutrients, 16(3), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16030334






