Beyond Nutritional Treatment: Effects of Fitwalking on Physical Capacity and Intestinal Barrier Integrity in BMI-Stratified IBS Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
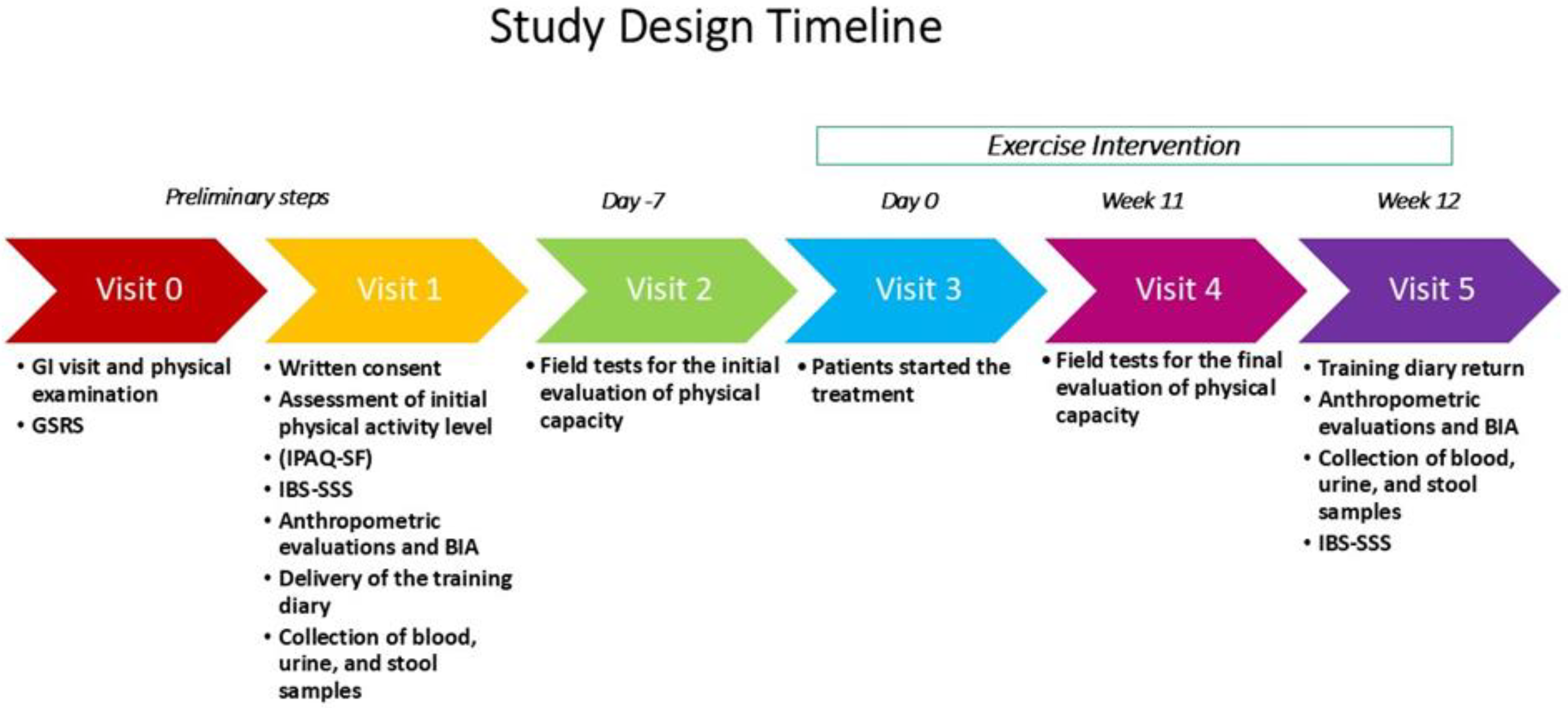
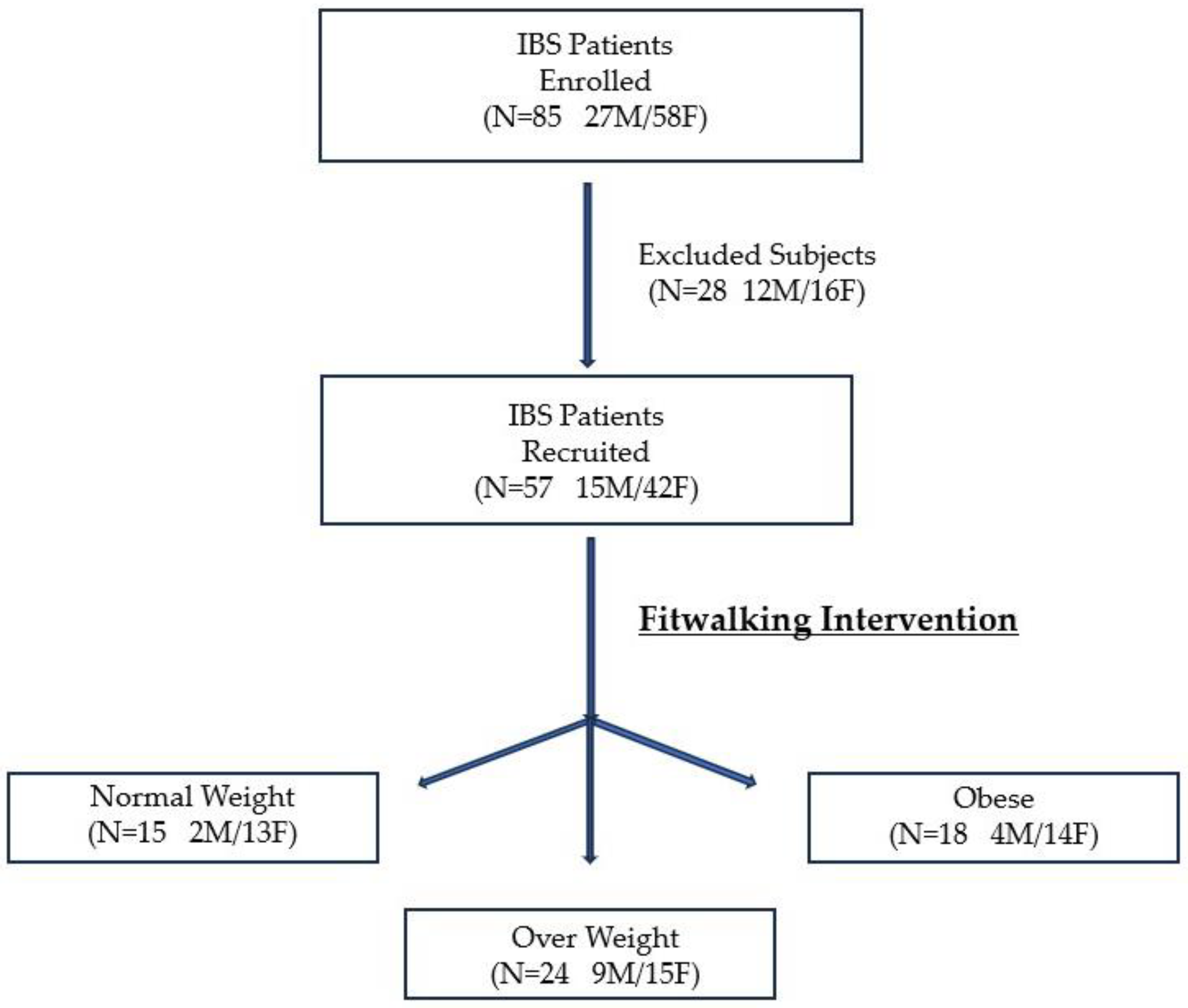
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Exercise Protocol
2.3.1. Physical Capacity Evaluation Test
2.3.2. Fitwalking Intervention
2.3.3. Training Diary
2.3.4. Global Physical Capacity Score
2.4. Biomarkers of Intestinal Barrier Function and Dysbiosis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients’ Characteristics
3.2. Effects of Fitwalking on GPCS
3.3. Effects of Fitwalking on the Biochemical Parameters
3.4. Effects of Fitwalking on the Markers of Intestinal Barrier and Fermentative Dysbiosis
3.5. Correlations Between BMI, GPCS, and the Markers of Intestinal Barrier Function and Integrity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lovell, R.M.; Ford, A.C. Global prevalence of and risk factors for irritable bowel syndrome: A meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 712–721.e714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Obesity Day 2022-Accelerating Action to Stop Obesity. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/04-03-2022-world-obesity-day-2022-accelerating-action-to-stop-obesity (accessed on 12 November 2024).
- Phelps, N.H.; Singleton, R.K.; Zhou, B.; Heap, R.A.; Mishra, A.; Bennett, J.E.; Paciorek, C.J.; Lhoste, V.P.; Carrillo-Larco, R.M.; Stevens, G.A. Worldwide trends in underweight and obesity from 1990 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 3663 population-representative studies with 222 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2024, 403, 1027–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damms-Machado, A.; Louis, S.; Schnitzer, A.; Volynets, V.; Rings, A.; Basrai, M.; Bischoff, S.C. Gut permeability is related to body weight, fatty liver disease, and insulin resistance in obese individuals undergoing weight reduction. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vancamelbeke, M.; Vermeire, S. The intestinal barrier: A fundamental role in health and disease. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 11, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Barbara, G.; Buurman, W.; Ockhuizen, T.; Schulzke, J.D.; Serino, M.; Tilg, H.; Watson, A.; Wells, J.M. Intestinal permeability—A new target for disease prevention and therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Després, J.P.; Lemieux, I. Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature 2006, 444, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamprecht, M.; Frauwallner, A. Exercise, intestinal barrier dysfunction and probiotic supplementation. Med. Sport Sci. 2012, 59, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A. Intestinal zonulin: Open sesame! Gut 2001, 49, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Seethaler, B.; Basrai, M.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Nazare, J.-A.; Walter, J.; Delzenne, N.M.; Bischoff, S.C. Biomarkers for assessment of intestinal permeability in clinical practice. Am. J. Physiol. -Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2021, 321, G11–G17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serek, P.; Oleksy-Wawrzyniak, M. The effect of bacterial infections, probiotics and zonulin on intestinal barrier integrity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, A.P.; Texeira, T.F.; Ferreira, A.B.; Peluzio Mdo, C.; Alfenas Rde, C. Influence of a high-fat diet on gut microbiota, intestinal permeability and metabolic endotoxaemia. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendyala, S.; Walker, J.M.; Holt, P.R. A high-fat diet is associated with endotoxemia that originates from the gut. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1100–1101.e1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburton, D.E.; Bredin, S.S. Health benefits of physical activity: A systematic review of current systematic reviews. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2017, 32, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, M.H.; Nevill, A.M.; Murtagh, E.M.; Holder, R.L. The effect of walking on fitness, fatness and resting blood pressure: A meta-analysis of randomised, controlled trials. Prev. Med. 2007, 44, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zheng, X.; Ding, H.; Zhang, D.; Cheung, P.M.; Yang, Z.; Tam, K.W.; Zhou, W.; Chan, D.C.; Wang, W.; et al. The Effect of Walking on Depressive and Anxiety Symptoms: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2024, 10, e48355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzato, M.; Parodi, G.; Rossi, D.; Stasi, E.; Roccatello, D. Fitwalking: A New Frontier for Kidney Patients. A Center’s Experience. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2024, 49, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, F.; Riezzo, G.; Orlando, A.; Linsalata, M.; D’Attoma, B.; Prospero, L.; Ignazzi, A.; Giannelli, G. A Comparison of the Low-FODMAPs Diet and a Tritordeum-Based Diet on the Gastrointestinal Symptom Profile of Patients Suffering from Irritable Bowel Syndrome-Diarrhea Variant (IBS-D): A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prospero, L.; Riezzo, G.; Linsalata, M.; Orlando, A.; D’Attoma, B.; Russo, F. Psychological and gastrointestinal symptoms of patients with irritable bowel syndrome undergoing a low-FODMAP diet: The role of the intestinal barrier. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riezzo, G.; Prospero, L.; D’Attoma, B.; Ignazzi, A.; Bianco, A.; Franco, I.; Curci, R.; Campanella, A.; Bonfiglio, C.; Osella, A.R.; et al. The Impact of a Twelve-Week Moderate Aerobic Exercise Program on Gastrointestinal Symptom Profile and Psychological Well-Being of Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients: Preliminary Data from a Southern Italy Cohort. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, A.; Russo, F.; Franco, I.; Riezzo, G.; Donghia, R.; Curci, R.; Bonfiglio, C.; Prospero, L.; D’Attoma, B.; Ignazzi, A. Enhanced Physical Capacity and Gastrointestinal Symptom Improvement in Southern Italian IBS Patients following Three Months of Moderate Aerobic Exercise. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, F.; Fiasca, F.; Minelli, M.; Maio, D.; Mattei, A.; Vergallo, I.; Cifone, M.G.; Cinque, B.; Minelli, M. The effects of low-nickel diet combined with oral administration of selected probiotics on patients with systemic nickel allergy syndrome (SNAS) and gut dysbiosis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmulson, M.J.; Drossman, D.A. What is new in Rome IV. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 23, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulich, K.R.; Madisch, A.; Pacini, F.; Piqué, J.M.; Regula, J.; Van Rensburg, C.J.; Újszászy, L.; Carlsson, J.; Halling, K.; Wiklund, I.K. Reliability and validity of the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) and Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia (QOLRAD) questionnaire in dyspepsia: A six-country study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2008, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, C.Y.; Morris, J.; Whorwell, P.J. The irritable bowel severity scoring system: A simple method of monitoring irritable bowel syndrome and its progress. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1997, 11, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.H.; Macfarlane, D.J.; Lam, T.H.; Stewart, S.M. Validity of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire Short Form (IPAQ-SF): A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2011, 8, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, S.F.; Mohktar, M.S.; Ibrahim, F. The theory and fundamentals of bioimpedance analysis in clinical status monitoring and diagnosis of diseases. Sensors 2014, 14, 10895–10928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laukkanen, R.; Oja, P.; Pasanen, M.; Vuori, I. Validity of a two kilometre walking test for estimating maximal aerobic power in overweight adults. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 1992, 16, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Pearn, J.; Bullock, K. A portable hand-grip dynamometer. Aust. Paediatr. J. 1979, 15, 107–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmink, K.A.; Kemper, H.C.; de Greef, M.H.; Rispens, P.; Stevens, M. The validity of the sit-and-reach test and the modified sit-and-reach test in middle-aged to older men and women. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport 2003, 74, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; Monahan, K.D.; Seals, D.R. Age-predicted maximal heart rate revisited. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2001, 37, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, D.R.; Soucy, L.; Sénéchal, M.; Dionne, I.J.; Brochu, M. Impact of resistance training with or without caloric restriction on physical capacity in obese older women. Menopause 2009, 16, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, B.; Verne, N.G. Intestinal membrane permeability and hypersensitivity in the irritable bowel syndrome. Pain 2009, 146, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, R.; Singh, A.K.; Chauhan, P. Health benefits of physical activity. CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2006, 175, 776–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, S.F.; Murphy, E.F.; O’Sullivan, O.; Lucey, A.J.; Humphreys, M.; Hogan, A.; Hayes, P.; O’Reilly, M.; Jeffery, I.B.; Wood-Martin, R.; et al. Exercise and associated dietary extremes impact on gut microbial diversity. Gut 2014, 63, 1913–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayles, M.P. ACSM’s Exercise testing and Prescription; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Linsalata, M.; Riezzo, G.; Clemente, C.; D’Attoma, B.; Russo, F. Noninvasive Biomarkers of Gut Barrier Function in Patients Suffering from Diarrhea Predominant-IBS: An Update. Dis Markers 2020, 2020, 2886268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirns, B.H.; Koemel, N.A.; Sciarrillo, C.M.; Anderson, K.L.; Emerson, S.R. Exercise and intestinal permeability: Another form of exercise-induced hormesis? Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 319, G512–G518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.; Kapounková, K.; Struhár, I. The relationship between the gut microbiome and resistance training: A rapid review. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2024, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, M.D.V.; Graça, P.; Afonso, C.; D’Amicis, A.; Lappalainen, R.; Damkjaer, S. Physical activity levels and body weight in a nationally representative sample in the European Union. Public Health Nutr. 1999, 2, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telle-Hansen, V.H.; Christensen, J.J.; Formo, G.A.; Holven, K.B.; Ulven, S.M. A comprehensive metabolic profiling of the metabolically healthy obesity phenotype. Lipids Health Dis. 2020, 19, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasini, E.; Corsetti, G.; Assanelli, D.; Testa, C.; Romano, C.; Dioguardi, F.S.; Aquilani, R. Effects of chronic exercise on gut microbiota and intestinal barrier in human with type 2 diabetes. Minerva Medica 2019, 110, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajamian, M.; Steer, D.; Rosella, G.; Gibson, P.R. Serum zonulin as a marker of intestinal mucosal barrier function: May not be what it seems. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0210728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aasbrenn, M.; Lydersen, S.; Farup, P.G. Changes in serum zonulin in individuals with morbid obesity after weight-loss interventions: A prospective cohort study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2020, 20, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohlsson, B.; Orho-Melander, M.; Nilsson, P.M. Higher levels of serum zonulin may rather be associated with increased risk of obesity and hyperlipidemia, than with gastrointestinal symptoms or disease manifestations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.; Kim, H.J. Intestinal barrier dysfunction orchestrates the onset of inflammatory host–microbiome cross-talk in a human gut inflammation-on-a-chip. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E10539–E10547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasano, A. Intestinal permeability and its regulation by zonulin: Diagnostic and therapeutic implications. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaye, I.K. Haptoglobin, inflammation and disease. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2008, 102, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Lammers, K.M.; Goldblum, S.; Shea-Donohue, T.; Netzel-Arnett, S.; Buzza, M.S.; Antalis, T.M.; Vogel, S.N.; Zhao, A.; Yang, S. Identification of human zonulin, a physiological modulator of tight junctions, as prehaptoglobin-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16799–16804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Uzzau, S.; Goldblum, S.E.; Fasano, A. Human zonulin, a potential modulator of intestinal tight junctions. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 4435–4440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelakkot, C.; Ghim, J.; Ryu, S.H. Mechanisms regulating intestinal barrier integrity and its pathological implications. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żak-Gołąb, A.; Kocełak, P.; Aptekorz, M.; Zientara, M.; Juszczyk, Ł.; Martirosian, G.; Chudek, J.; Olszanecka-Glinianowicz, M. Gut microbiota, microinflammation, metabolic profile, and zonulin concentration in obese and normal weight subjects. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 2013, 674106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, M.-C.; Bistritz, L.; Meddings, J.B. Alterations in intestinal permeability. Gut 2006, 55, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travers, G.; Kippelen, P.; Trangmar, S.J.; González-Alonso, J. Physiological Function during Exercise and Environmental Stress in Humans—An Integrative View of Body Systems and Homeostasis. Cells 2022, 11, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryvoruchko, I.; Sykal, M. Dynamics of changes in plasma fatty acid binding proteins and intestinal zonulin in patients with generalized intra-abdominal infection and abdominal sepsis depending on the severity of patients. Klin. Khirurgiia 2021, 88, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, M.; Fasulo, E.; Ungaro, F.; Massimino, L.; Sinagra, E.; Danese, S.; Mandarino, F.V. Gut dysbiosis in irritable bowel syndrome: A narrative review on correlation with disease subtypes and novel therapeutic implications. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| NW (n. 15) | OW (n. 24) | OB (n. 18) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (Male/Female) | 2 M/13 F | 9 M/15 F | 4 M/14 F | ||
| Age (years) | 55.07 ± 1.29 a | 56.33 ± 1.23 a | 53.78 ± 2.35 a | 0.85 | |
| Waist Circumference | Pre | 78.47 ± 1.68 a | 91.41 ± 1.50 b* | 107.3 ± 2.23 c | <0.0001 |
| Post | 77.66 ± 1.72 a | 89.81 ± 1.57 b* | 106 ± 2.32 c | <0.0001 | |
| Hip Circumference | Pre | 97.43 ± 1.29 a | 103 ± 1.27 a | 116 ± 2.75 b | <0.0001 |
| Post | 97.31 ± 1.39 a | 101.9 ± 1.20 a | 114.5 ± 2.69 b | <0.0001 | |
| Waist/Hip Ratio | Pre | 0.80 ± 0.02 a | 0.88 ± 0.02 ab | 0.87 ± 0.06 b | 0.02 |
| Post | 0.81 ± 0.03 a | 0.87 ± 0.02 ab | 0.93 ± 0.02 b | 0.003 | |
| PhA (degrees) | Pre | 5.94 ± 0.26 a | 6.41 ± 0.19 ab | 6.71 ± 0.15 b | 0.033 |
| Post | 6.37 ± 0.24 a | 6.34 ± 0.16 a | 6.64 ± 0.20 a | 0.56 | |
| BCM (kg) | Pre | 24.4 ± 1.37 a | 28.48 ± 1.33 ab | 31.61 ± 1.41 b | 0.001 |
| Post | 25.13 ± 1.36 a | 28.18 ± 1.23 ab | 31.24 ± 1.24 b | 0.001 | |
| FM (kg) | Pre | 19.95 ± 2.86 a | 23.18 ± 1.17 a | 36.61 ± 2.51 b | <0.001 |
| Post | 16.25 ± 0.82 a | 22.73 ± 1.01 b | 37.98 ± 2.67 c | <0.001 | |
| FFM (kg) | Pre | 45.71 ± 1.73 a | 51.10 ± 1.93 ab | 55.32 ± 2.04 b | 0.003 |
| Post | 45.20 ± 1.59 a | 50.81 ± 1.81 ab | 55.26 ± 1.91 b | 0.0004 | |
| TBW (liters) | Pre | 33.47 ± 1.32 a | 37.11 ± 1.44 ab | 40.47 ± 1.49 b | 0.004 |
| Post | 32.83 ± 1.13 a | 37.06 ± 1.34 ab | 40.40 ± 1.42 b | 0.0005 | |
| ECW (liters) | Pre | 15.43 ± 0.60 a | 16.30 ± 0.60 a | 17.27 ± 0.57 a | 0.080 |
| Post | 14.46 ± 0.38 a | 16.38 ± 0.54 ab | 17.45 ± 0.68 b | 0.004 | |
| IBS-SSS Total Score | Pre | 94.33 ± 5.50 a | 94.38 ± 4.15 a | 92.22 ± 4.79 a | 0.99 |
| Post | 91.67 ± 6.95 a | 92.08 ± 4.39 a | 89.72 ± 4.47 a | 0.96 | |
| IPAQ-SF Categories ° | |||||
| Inactive | 4 (26.7%) | 7 (29.2%) | 4 (22.2%) | ||
| Sufficiently Active | 8 (53.3%) | 11 (45.8%) | 12 (66.7%) | 0.730 | |
| Active/Very Active | 3 (20.0%) | 6 (25%) | 2 (11.1%) |
| NW (n. 15) | OW (n. 24) | OB (n. 18) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSH (μU/mL) | Pre | 2.83 ± 0.52 a | 4.75 ± 0.93 a | 5.59 ± 1.28 a | 0.62 |
| Post | 2.33 ± 0.30 a | 4.46 ± 0.92 a | 6.27 ± 1.38 a | 0.19 | |
| fT3 (pg/mL) | Pre | 3.19 ± 0.11 a | 3.30 ± 0.07 a | 3.31 ± 0.09 a | 0.69 |
| Post | 3.24 ± 0.10 a | 3.30 ± 0.09 a | 3.39 ± 0.10 a | 0.58 | |
| fT4 (pg/mL) | Pre | 1.12 ± 0.06 a | 1.01 ± 0.04 a | 1.03 ± 0.04 a | 0.40 |
| Post | 1.06 ± 0.09 a | 1.06 ± 0.05 a | 1.07 ± 0.05 a | 0.88 | |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | Pre | 87.53 ± 2.88 a | 92.79 ± 2.62 a | 102.8 ± 9.88 a | 0.22 |
| Post | 88.87 ± 2.71 a | 90.79 ± 2.38 a | 94.33 ± 3.44 a | 0.44 | |
| Insulin (μU/mL) | Pre | 5.92 ± 0.49 a | 8.55 ± 0.69 ab | 13.21 ± 1.54 b | 0.0002 |
| Post | 6.17 ± 0.79 a | 9.18 ± 1.07 a | 13.71 ± 1.39 b | 0.0001 | |
| Uric acid (mg/dL) | Pre | 36.60 ± 2.44 a | 37.46 ± 1.23 a | 39.11 ± 2.39 a | 0.76 |
| Post | 36.20 ± 2.56 a | 37.67 ± 2.30 a | 37.78 ± 1.91 a | 0.89 | |
| 25-OH-Vitamin D (ng/mL) | Pre | 30.93 ± 3.62 a | 24.93 ± 2.11 a | 22.62 ± 1.72 a | 0.23 |
| Post | 34.51 ± 3.19 a | 29.19 ± 1.84 a | 25.51 ± 1.60 a | 0.15 | |
| γGT (U/L) | Pre | 28.80 ± 9.35 a | 20.88 ± 2.44 a | 21.67 ± 2.81 a | 0.55 |
| Post | 23.87 ± 7.53 a | 30.67 ± 8.61 a | 22.83 ± 3.45 a | 0.36 | |
| ALT (U/L) | Pre | 18.07 ± 0.89 a | 27.25 ± 3.16b | 25.28 ± 2.20 ab | 0.02 |
| Post | 17.40 ± 1.46 a | 26.79 ± 3.42 ab | 23.72 ± 1.64 b | 0.03 | |
| AST (U/L) | Pre | 19.27 ± 1.73 a | 23.54 ± 1.29 a | 20.67 ± 1.39 a | 0.06 |
| Post | 19.53 ± 1.49 a | 22.46 ± 2.18 a | 19.06 ± 0.99 a | 0.56 | |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | Pre | 203.3 ± 9.73 a | 205.5 ± 5.58 a | 210.7 ± 8.00 a | 0.60 |
| Post | 205.7 ± 10.57 a | 207.2 ± 6.68 a | 217.2 ± 9.13 a | 0.47 | |
| HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL) | Pre | 69.05 ± 5.61 a | 55.21 ± 2.52 ab | 52.68 ± 2.66 b | 0.03 |
| Post | 71.93 ± 6.40 a | 55.81 ± 2.74 ab | 51.80 ± 3.06 b | 0.009 | |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | Pre | 99.13 ± 15.84 a | 93.33 ± 7.71 a | 128.6 ± 9.12 b | 0.008 |
| Post | 133.3 ± 28.83 a | 101.5 ± 7.76 a | 148.1 ± 15.27 a | 0.05 |
| NW (n. 15) | OW (n. 24) | OB (n. 18) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum zonulin (ng/mL) | Pre | 40.91 ± 3.37 a | 50.60 ± 3.93 ab | 57.54 ± 4.74 b* | 0.01 |
| Post | 38.97 ± 2.66 a | 46.93 ± 3.13 a | 47.02 ± 3.83 a* | 0.20 | |
| Fecal zonulin (ng/mL) | Pre | 90.13 ± 10.69 a | 116.40 ± 16.29 a** | 120.60 ± 20.52 a | 0.53 |
| Post | 105.70 ± 17.46 a | 150.3 ± 21.18 a** | 121.80 ± 22.53 a | 0.37 | |
| I-FABP (ng/mL) | Pre | 4.08 ± 0.33 a | 3.69 ± 0.38 a | 4.36 ± 1.31 a | 0.25 |
| Post | 4.26 ± 0.17 a | 3.44 ± 0.38 a | 3.93 ± 0.98 a | 0.06 | |
| Indican (mg/L) | Pre | 42.95 ± 5.46 a | 61.22 ± 6.79 a | 85.22 ± 12.67 a* | 0.64 |
| Post | 44.89 ± 6.45 a | 57.74 ± 6.69 a | 58.62 ± 8.61 a* | 0.40 |
| Parameters | β | Std. Error (β) | p-Value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body Mass Index | −0.067 | 0.032 | 0.043 | −0.004–−0.129 |
| Serum zonulin | −0.033 | 0.010 | 0.001 | −0.014–−0.052 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bianco, A.; Russo, F.; Prospero, L.; Riezzo, G.; Franco, I.; D’Attoma, B.; Ignazzi, A.; Verrelli, N.; Bagnato, C.B.; Goscilo, F.; et al. Beyond Nutritional Treatment: Effects of Fitwalking on Physical Capacity and Intestinal Barrier Integrity in BMI-Stratified IBS Patients. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4181. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234181
Bianco A, Russo F, Prospero L, Riezzo G, Franco I, D’Attoma B, Ignazzi A, Verrelli N, Bagnato CB, Goscilo F, et al. Beyond Nutritional Treatment: Effects of Fitwalking on Physical Capacity and Intestinal Barrier Integrity in BMI-Stratified IBS Patients. Nutrients. 2024; 16(23):4181. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234181
Chicago/Turabian StyleBianco, Antonella, Francesco Russo, Laura Prospero, Giuseppe Riezzo, Isabella Franco, Benedetta D’Attoma, Antonia Ignazzi, Nicola Verrelli, Claudia Beatrice Bagnato, Francesco Goscilo, and et al. 2024. "Beyond Nutritional Treatment: Effects of Fitwalking on Physical Capacity and Intestinal Barrier Integrity in BMI-Stratified IBS Patients" Nutrients 16, no. 23: 4181. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234181
APA StyleBianco, A., Russo, F., Prospero, L., Riezzo, G., Franco, I., D’Attoma, B., Ignazzi, A., Verrelli, N., Bagnato, C. B., Goscilo, F., Mallardi, D., Linsalata, M., Bonfiglio, C., Pesole, P. L., & Ferro, A. (2024). Beyond Nutritional Treatment: Effects of Fitwalking on Physical Capacity and Intestinal Barrier Integrity in BMI-Stratified IBS Patients. Nutrients, 16(23), 4181. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16234181







