Nutritional Status Impact on Hip Fracture Patients in a Rural Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sociodemographic Variables
2.2. Surgical Procedure Variables
2.3. Nutritional Value Variables
2.4. Ethical Aspects
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Surgical Procedure
3.2. Nutritional Values
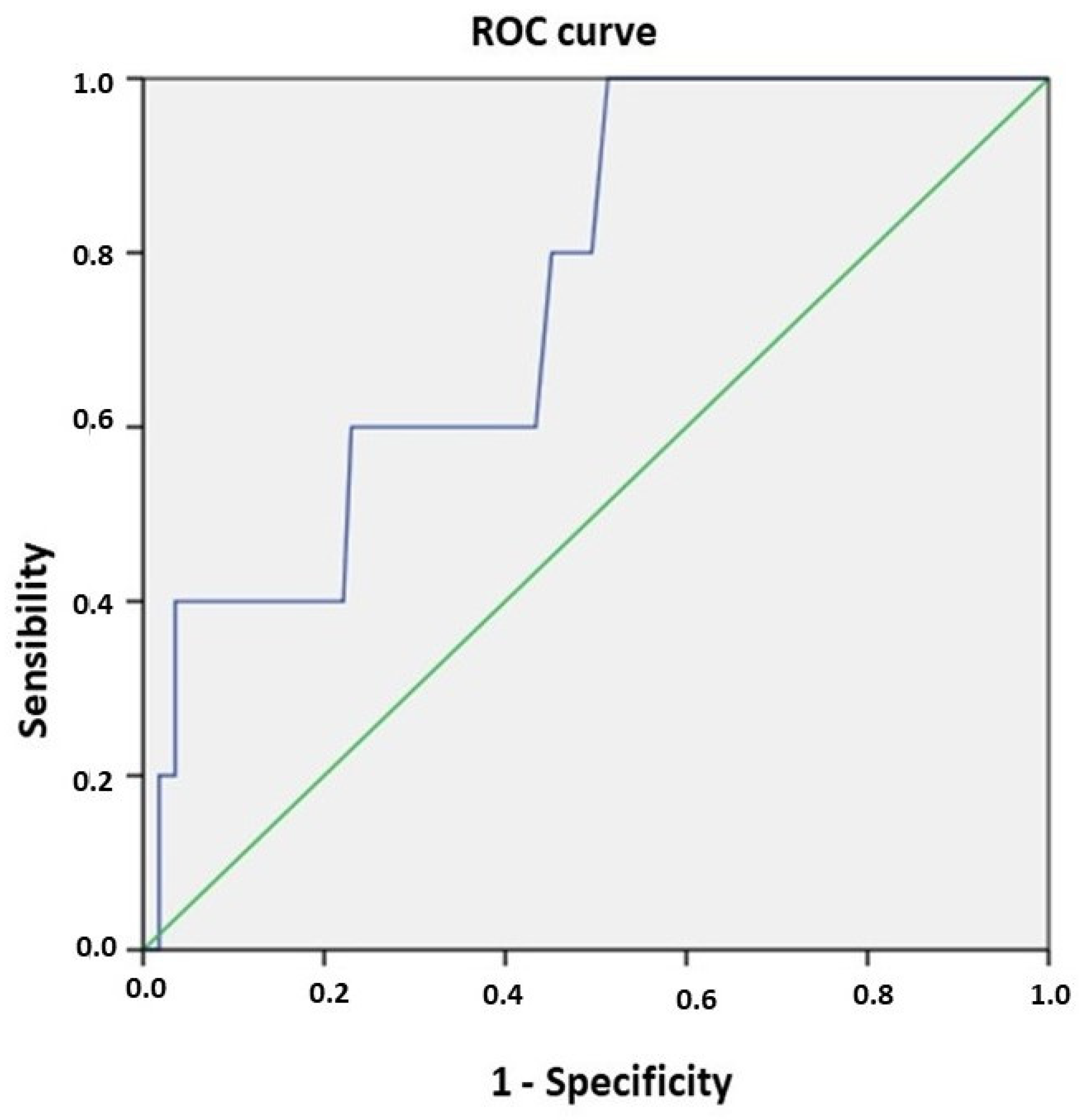
3.3. Mortality Predictors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sáez-López, P. Informe Anual de RNFC [Internet]. Grupo de Trabajo RNFC: Madrid, Spain, 2022; p. 82. Available online: https://rnfc.es/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Informe-RNFC-2022_compressed.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2024).
- Patel, J.N.; Klein, D.S.; Sreekumar, S.; Liporace, F.A.; Yoon, R.S. Outcomes in Multidisciplinary Team-based Approach in Geriatric Hip Fracture Care: A Systematic Review. JAAOS J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2020, 28, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.Y.; Yan, S.; Low, L.L.; Vasanwala, F.F.; Low, S.G. Predictors of poor functional outcomes and mortality in patients with hip fracture: A systematic review. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veronese, N.; Maggi, S. Epidemiology and social costs of hip fracture. Injury 2018, 49, 1458–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, H.E.; Tverdal, A.; Falch, J.A.; Pedersen, J.I. Factors associated with mortality after hip fracture. Osteoporos. Int. 2000, 11, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, H.; Wakabayashi, H.; Yoshimura, Y.; Yamada, M.; Kim, H.; Harada, A. Chapter 4 Treatment of sarcopenia. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18 (Suppl. 1), 28–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradeanu, A.V.; Ciubara, A.B.; Burlea, S.L.; Ciubara, A. The Socio-Economic Impact Produced by Patients with Dementia and Hip Fractures. BRAIN Broad Res. Artif. Intell. Neurosci. 2020, 11 (Suppl. 1), 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koren-Hakim, T.; Weiss, A.; Hershkovitz, A.; Otzrateni, I.; Grosman, B.; Frishman, S.; Salai, M.; Beloosesky, Y. The relationship between nutritional status of hip fracture operated elderly patients and their functioning, comorbidity and outcome. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 31, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmi, M.; Veronese, N.; Correll, C.U.; Favaro, A.; Santonastaso, P.; Caregaro, L.; Vancampfort, D.; Luchini, C.; De Hert, M.; Stubbs, B. Bone mineral density, osteoporosis, and fractures among people with eating disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Psychiatric. Scand. 2016, 133, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, J.J.; Bauer, J.D.; Capra, S.; Pulle, R.C. Multidisciplinary, multi-modal nutritional care in acute hip fracture inpatients—Results of a pragmatic intervention. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, T.; Maeda, K.; Nagano, A.; Shimizu, A.; Ueshima, J.; Murotani, K.; Sato, K.; Tsubaki, A. Undernutrition, Sarcopenia, and Frailty in Fragility Hip Fracture: Advanced Strategies for Improving Clinical Outcomes. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Llanos, J.P. Controversia 1. Papel de la albúmina en la valoración nutricional. Nutr. Hosp. 2023, 40, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Álvarez, J.; Del Río, J.; Planas, M.; Peris, P.G.; de Lorenzo, A.G.; Calvo, V.; Olveira, G.; Irles, J.A.; Piñeiro, G.; Grupo de Documentación de SENPE. Documento SENPE-SEDOM sobre la codificación de la desnutrición hospitalaria. Nutr. Hosp. 2008, 23, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weimann, A.; Braga, M.; Harsanyi, L.; Laviano, A.; Ljungqvist, O.; Soeters, P.; Jauch, K.; Kemen, M.; Hiesmayr, J.; Horbach, T.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Enteral Nutrition: Surgery including organ transplantation. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 224–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, D.C.; Corkins, M.R.; Malone, A.; Miller, S.; Mogensen, K.M.; Guenter, P.; Jensen, G.L.; the ASPEN Malnutrition Committee. ASPEN Malnutrition Committee. The Use of Visceral Proteins as Nutrition Markers: An ASPEN Position Paper. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2021, 36, 22–28, Erratum in Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2021, 36, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, D.C. The systemic inflammation-based Glasgow Prognostic Score: A decade of experience in patients with cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2013, 39, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishioka, S.; Wakabayashi, H.; Momosaki, R. Nutritional Status Changes and Activities of Daily Living after Hip Fracture in Convalescent Rehabilitation Units: A Retrospective Observational Cohort Study from the Japan Rehabilitation Nutrition Database. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Carson, J.L.; Schlussel, Y.; Noveck, H.; Shapses, S.A. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with reduced mobility after hip fracture surgery: A prospective study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajada, S.; Smith, A.; Morgan, D. Preoperative nutritional serum parameters as predictors of failure after internal fixation in undisplaced intracapsular proximal femur fractures. Injury 2015, 46, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrobot, A.; Demkow, U.; Wachowska, M. Immunomodulatory role of vitamin D: A review. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Broe, K.E.; Chen, T.C.; Weinberg, J.; Bischoff-Ferrari, H.A.; Holick, M.F.; Kiel, D.P. A higher dose of vitamin D reduces the risk of falls in nursing home residents: A randomized, multiple-dose study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2007, 55, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekinci, O.; Yanık, S.; Terzioğlu Bebitoğlu, B.; Yılmaz Akyüz, E.; Dokuyucu, A.; Erdem, Ş. Effect of Calcium β-Hydroxy-β-Methylbutyrate (CaHMB), Vitamin D, and Protein Supplementation on Postoperative Immobilization in Malnourished Older Adult Patients With Hip Fracture: A Randomized Controlled Study. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2016, 31, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez, R.R.A.; García, R.L.; Romero, C.E.A.; Mendoza, K.G.; Quijano, M.G.M.; Solares, A.P.; Rohenes, L.C.M. Mortality of patients with hip fracture in five years of evolution at Regional Hospital General Ignacio Zaragoza. Rev. Espec. Méd.-Quir. 2013, 18, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Hao, Q.; Dong, B. Sarcopenia predicts readmission and mortality in elderly patients in acute care wards: A prospective study. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, V.G.; Perez, M.; Lourenço, R.A. Prevalence of sarcopenia and its associated factors: The impact of muscle mass, gait speed, and handgrip strength reference values on reported frequencies. Clinics 2019, 74, e477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dripps, R.D.; Lamont, A.; Eckenhoff, J.E. The role of anesthesia in surgical mortality. JAMA 1961, 178, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malafarina, V.; Reginster, J.-Y.; Cabrerizo, S.; Bruyère, O.; Kanis, J.A.; Martinez, J.A.; Zulet, M.A. Nutritional Status and Nutritional Treatment Are Related to Outcomes and Mortality in Older Adults with Hip Fracture. Nutrients 2018, 10, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Lázaro, M.; Montero Pérez-Barquero, M.; Carpintero Benítez, P. Importancia de la malnutrición y otros factores médicos en la evolución de los pacientes con fractura de cadera [The role of malnutrition and other medical factors in the evolution of patients with hip fracture]. An. Med. Interna 2004, 21, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Prentice, R.L.; Pettinger, M.B.; Jackson, R.D.; Wactawski-Wende, J.; LaCroix, A.Z.; Anderson, G.L.; Chlebowski, R.T.; Manson, J.E.; Van Horn, L.; Vitolins, M.Z.; et al. Health risks and benefits from calcium and vitamin D supplementation: Women’s Health Initiative clinical trial and cohort study. Osteoporos. Int. 2013, 24, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Sun, T. Prognostic Role of Serum Albumin, Total Lymphocyte Count, and Mini Nutritional Assessment on Outcomes After Geriatric Hip Fracture Surgery: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. J. Arthroplast. 2019, 34, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Daly, B.J.; Walsh, J.C.; Quinlan, J.F.; Falk, G.A.; Stapleton, R.; Quinlan, W.R.; O’Rourke, S.K. Serum albumin and total lymphocyte count as predictors of outcome in hip fractures. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 29, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsagari, A.; Papakitsou, E.; Dionyssiotis, Y.; Rizou, S.; Galanos, A.; Lyritis, G.P. Evaluation of commonly used nutritional assessment methods in hip fracture patients. J. Frailty Sarcopenia Falls 2017, 2, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldebeyan, S.; Nooh, A.; Aoude, A.; Weber, M.H.; Harvey, E.J. Hypoalbuminaemia—A marker of malnutrition and predictor of postoperative complications and mortality after hip fractures. Injury 2017, 48, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizaur-Utrilla, A.; Gonzalez-Navarro, B.; Vizcaya-Moreno, M.F.; Lopez-Prats, F.A. Altered seric levels of albumin, sodium and parathyroid hormone may predict early mortality following hip fracture surgery in elderly. Int. Orthop. 2019, 43, 2825–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoang, H.; Silverstone, F.A.; Leventer, S.; Wolf-Klein, G.P.; Foley, C.J. The effect of nutritional status on length of stay in elderly hip fracture patients. J. Nutr. Health Aging 1998, 2, 159–161. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bohl, D.D.; Shen, M.R.; Hannon, C.P.; Fillingham, Y.A.; Darrith, B.; Della Valle, C.J. Serum Albumin Predicts Survival and Postoperative Course Following Surgery for Geriatric Hip Fracture. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2017, 99, 2110–2118, Erratum in J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2018, 100, e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avenell, A.; Curtain, J.P.; Mak, J.C.; Myint, P.K. Nutritional supplementation for hip fracture aftercare in older people. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 11, CD001880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, S.J.; Borgbjerg, F.M.; Schousboe, B.; Pedersen, B.D.; Jørgensen, H.L.; Duus, B.R.; Lauritzen, J.B.; Hip Fracture Group of Bispebjerg Hospital. A Comprehensive Hip Fracture Program Reduces Complication Rates and Mortality. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 1831–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varsavsky, M.; Moreno, P.R.; Fernández, A.B.; Fernández, I.L.; Gómez, J.M.Q.; Rubio, V.; Martín, A.G.; Berdonces, M.C.; Cortés, S.N.; Muñoz, M.R.; et al. Recomendaciones de vitamina D para la población general. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2017, 64, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Wang, J.; Zou, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, J.; Chen, M. High blood urea nitrogen to creatinine ratio is associated with increased risk of sarcopenia in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Exp. Gerontol. 2022, 169, 111960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Shi, K.; Chen, X.; Gao, M.; Han, Y.; Fang, Y. Blood Profiles of Community-Dwelling People with Sarcopenia: Analysis Based on the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study. Gerontology 2024, 70, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, N.; Ünal, A.M. Standard and Newly Defined Prognostic Factors Affecting Early Mortality After Hip Fractures. Cureus 2022, 14, e21464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.H.; Dennison, E.M.; Aihie Sayer, A.; Fielding, R.; Cooper, C. Osteoporosis and sarcopenia in older age. Muscle Bone Interact 2015, 80, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groff, H.; Kheir, M.M.; George, J.; Azboy, I.; Higuera, C.A.; Parvizi, J. Causes of in-hospital mortality after hip fractures in the elderly. Hip Int. 2020, 30, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzo, A.; Francescutti, C.; Simon, G. Risk factors correlated with postoperative mortality for hip fracture surgery in the elderly: A population-based approach. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 20, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Reig, J.; Salvador Marín, J.; Pérez Alba, J.M.; Ferrández Martínez, J.; Orozco Beltrán, D.; Martínez López, J.F. Risk factors for in-hospital mortality following hip fracture. Rev. Esp. Cir. Ortop. Traumatol. 2017, 61, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frost, S.A.; Nguyen, N.D.; Black, D.A.; Eisman, J.A.; Nguyen, T.V. Risk factors for in-hospital post-hip fracture mortality. Bone 2011, 49, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilley, E.; Herrmann, F.; Rapin, C.-H.; Hoffmeyer, P.; Rizzoli, R.; Chevalley, T. Socioeconomic and living conditions are determinants of hip fracture incidence and age occurrence among community-dwelling elderly. Osteoporos. Int. 2011, 22, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llombart, R.; Mariscal, G.; Barrios, C.; de la Rubia Ortí, J.E.; Llombart-Ais, R. Does vitamin D deficiency affect functional outcomes in hip fracture patients? A meta-analysis of cohort studies. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2024, 47, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Rodríguez, D.; Marco, E.; Dávalos-Yerovi, V.; López-Escobar, J.; Messaggi-Sartor, M.; Barrera, C.; Ronquillo-Moreno, N.; Vázquez-Ibar, O.; Calle, A.; Inzitari, M.; et al. Translation and Validation of the Spanish Version of the SARC-F Questionnaire to Assess Sarcopenia in Older People. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2019, 23, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkisas, S.; Baudry, S.; Bauer, J.; Beckwée, D.; De Cock, A.-M.; Hobbelen, H.; Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Kasiukiewicz, A.; Landi, F.; Marco, E.; et al. Application of ultrasound for muscle assessment in sarcopenia: Towards standardized measurements. Eur. Geriatr. Med. 2018, 9, 739–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malafarina, V.; Uriz-Otano, F.; Malafarina, C.; Martinez, J.A.; Zulet, M.A. Effectiveness of nutritional supplementation on sarcopenia and recovery in hip fracture patients. A multicentre randomized trial. Maturitas 2017, 101, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Tokuda, Y. Effect of whey protein supplementation after resistance exercise on the muscle mass and physical function of healthy older women: A randomized controlled trial. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| BUN | Vit D | Albumin | Mortality | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intracapsular non-displaced (25–20.2%) | 26.9 ± 6.4 | 9.6 ± 6.6 | 3.69 ± 0.4 | 8% |
| Pertrochanteric (37–29.8%) | 30.5 ± 13.4 | 12.8 ± 10.6 | 3.59 ± 0.4 | 8.1% |
| Subtrochanteric (55–44.3%) | 32.0 ± 14.9 | 13.3 ± 9.7 | 3.53 ± 0.4 | 7.4% |
| Intracapsular displaced (7–5.6%) | 33.3 ± 8.0 | 13.3 ± 11.1 | 3.66 ± 0.4 | 14.3% |
| p value | 0.529 | 0.551 | 0.566 | 0.455 |
| BUN | Vit D | Albumin | Hospital Stay | Mortality | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intramedullary nail (63–50.8%) | 32.2 ± 13.8 | 13.0 ± 9.5 | 3.56 ± 0.4 | 10.5 ± 4.0 | 8.6% |
| Partial prosthesis (26–20.9%) | 28.3 ± 12.4 | 11.5 ± 8.0 | 3.64 ± 0.4 | 11.6 ± 4.2 | 3.8% |
| Total prosthesis (35–28.2%) | 30.7 ± 10.3 | 11.3 ± 11.7 | 3.61 ± 0.3 | 9.0 ± 2.4 | 6.3% |
| p value | 0.427 | 0.430 | 0.214 | 0.139 | 0.124 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martín-Nieto, A.; Chana-Valero, P.; Ruiz-Tovar, J.; Escobar-Aguilar, G.; Simarro-González, M.; Rodríguez-Bernal, P.; García-García, E. Nutritional Status Impact on Hip Fracture Patients in a Rural Environment. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3622. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16213622
Martín-Nieto A, Chana-Valero P, Ruiz-Tovar J, Escobar-Aguilar G, Simarro-González M, Rodríguez-Bernal P, García-García E. Nutritional Status Impact on Hip Fracture Patients in a Rural Environment. Nutrients. 2024; 16(21):3622. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16213622
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartín-Nieto, Ana, Pedro Chana-Valero, Jaime Ruiz-Tovar, Gema Escobar-Aguilar, María Simarro-González, Pablo Rodríguez-Bernal, and Elena García-García. 2024. "Nutritional Status Impact on Hip Fracture Patients in a Rural Environment" Nutrients 16, no. 21: 3622. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16213622
APA StyleMartín-Nieto, A., Chana-Valero, P., Ruiz-Tovar, J., Escobar-Aguilar, G., Simarro-González, M., Rodríguez-Bernal, P., & García-García, E. (2024). Nutritional Status Impact on Hip Fracture Patients in a Rural Environment. Nutrients, 16(21), 3622. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16213622






