Green Onion-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles Prevent Ferroptotic Cell Death Triggered by Glutamate: Implication for GPX4 Expression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
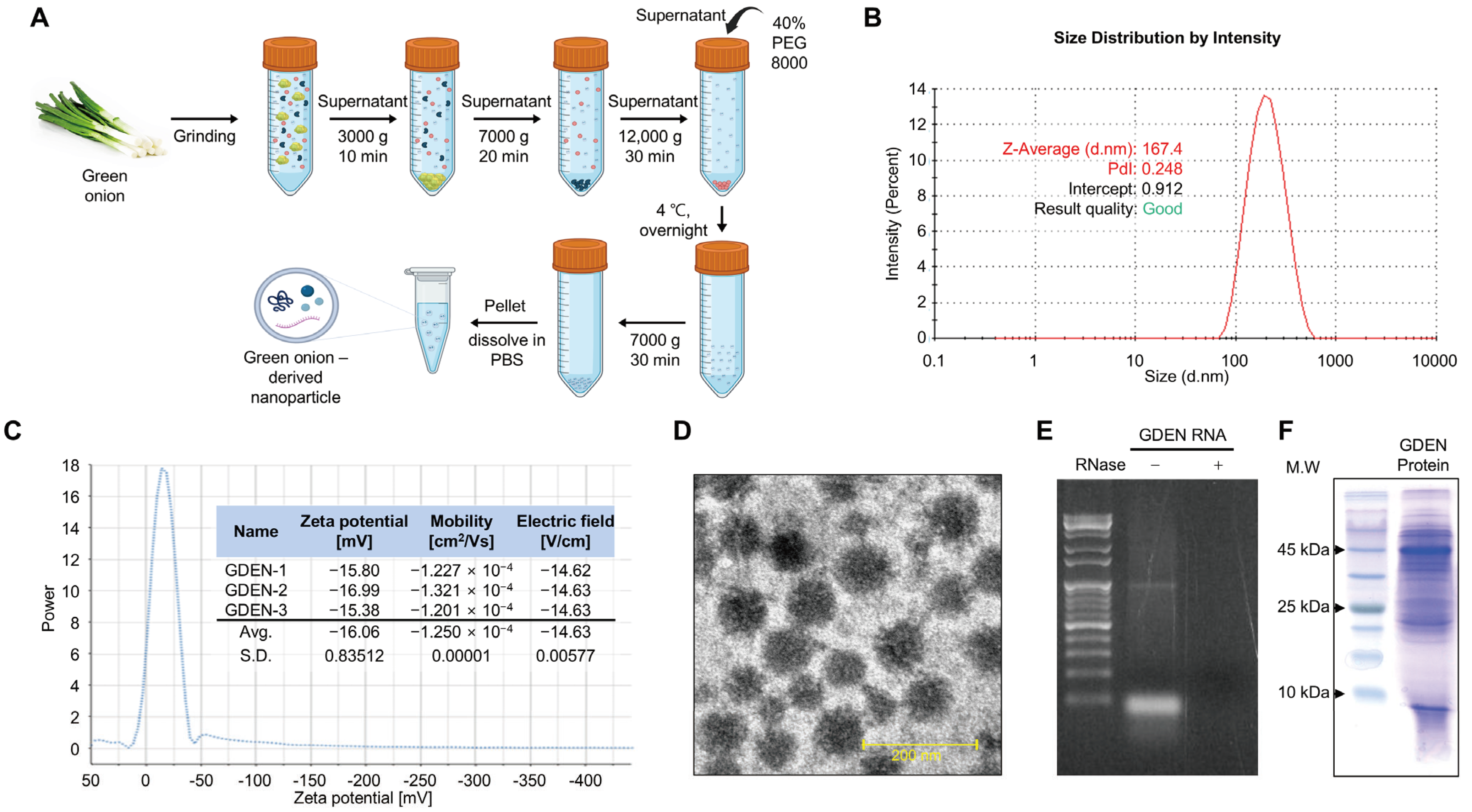
2.3. Isolation of Green Onion-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles (GDENs)
2.4. Characterization of GDENs
2.5. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.6. Measurements of Calcium Influx and Lipid Peroxidation
2.7. Measurement of Intracellular Iron Levels
2.8. Total Glutathione Quantification
2.9. Western Blot
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Characterization of GDENs
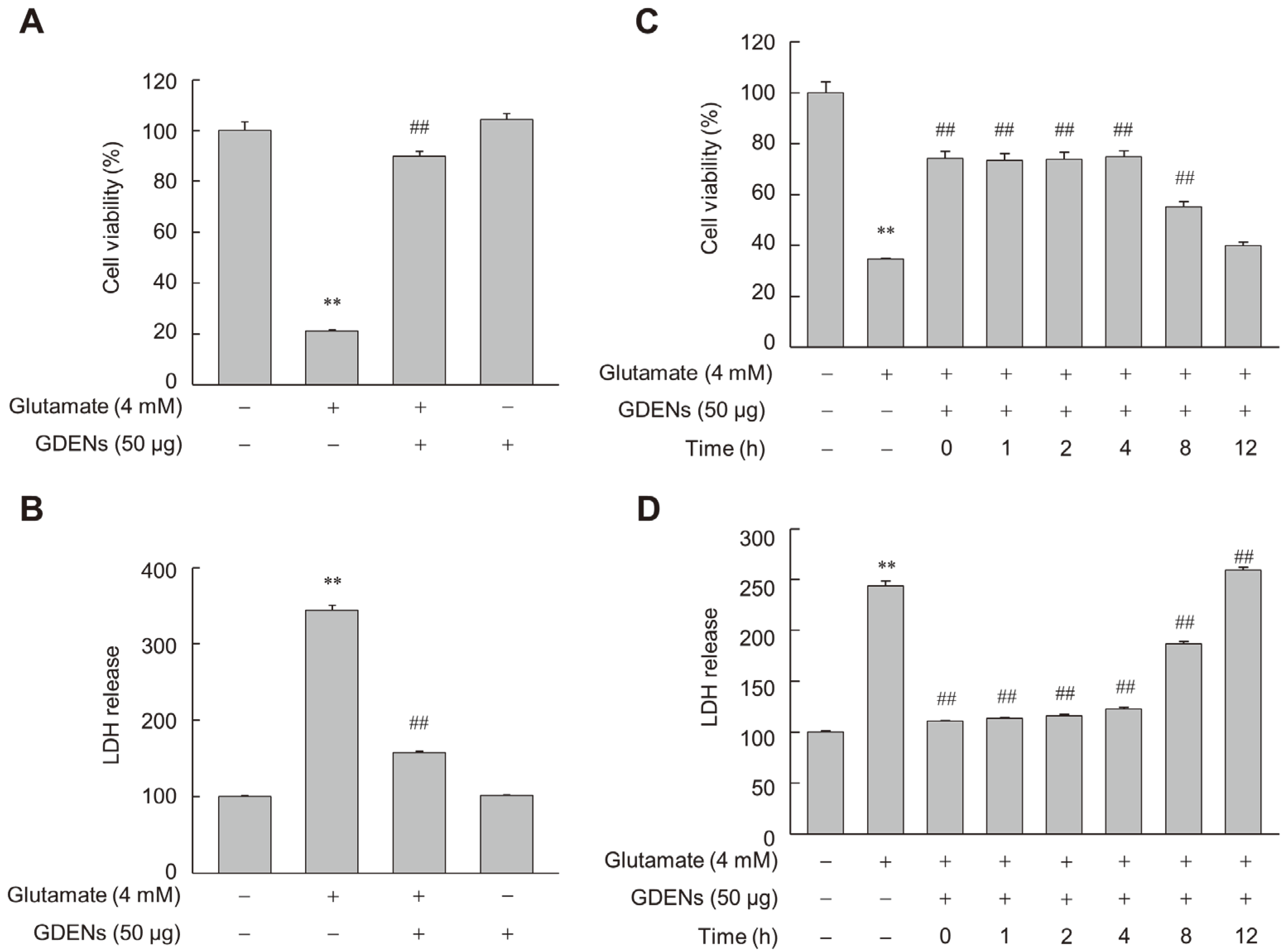
3.2. GDENs Inhibit Glutamate-Induced Ferroptotic Cell Death in HT-22 Cells
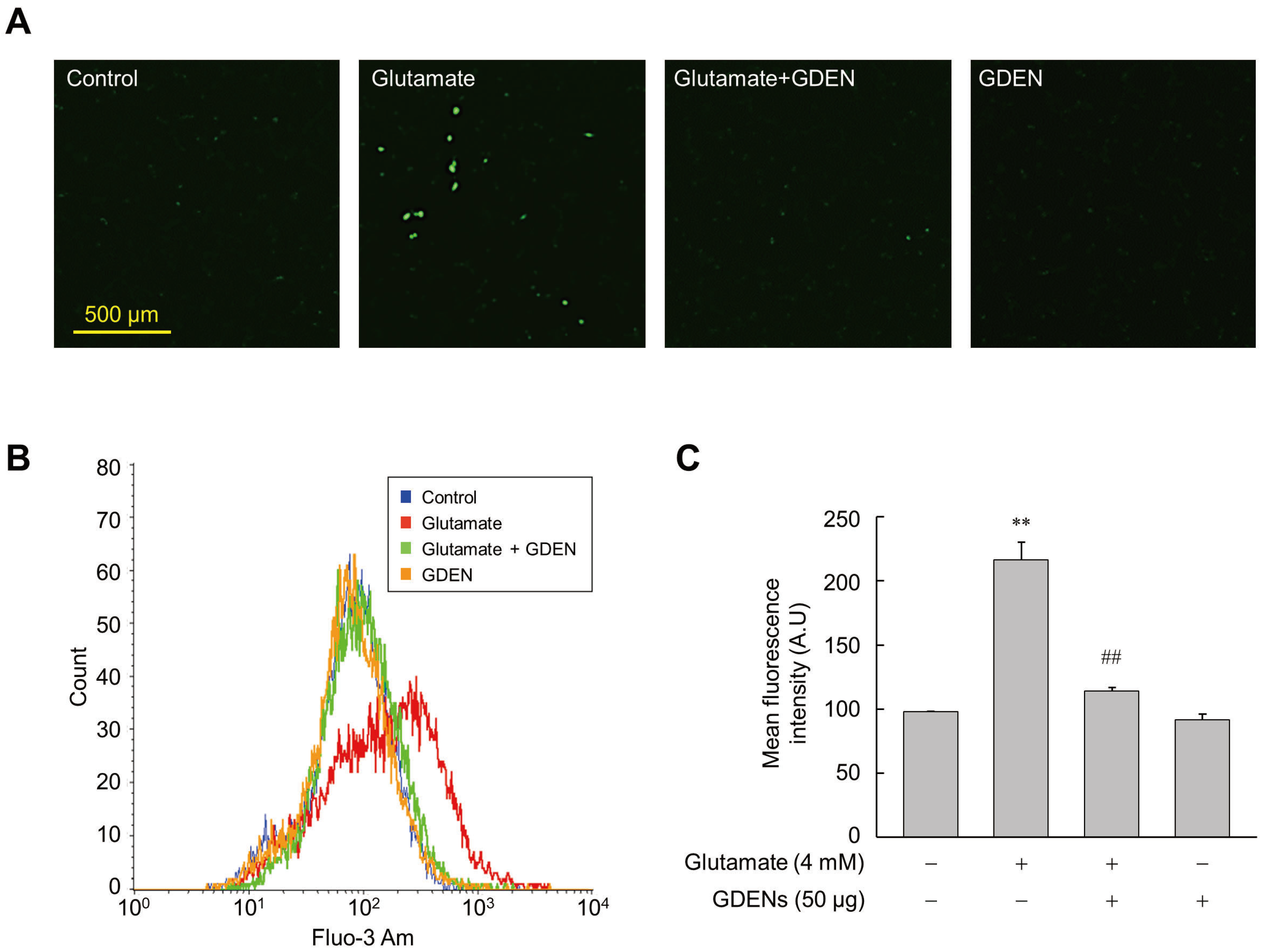
3.3. GDENs Inhibit Glutamate-Induced Calcium Influx
3.4. GDENs Attenuate the Labile Iron Pool by Regulating Iron Metabolism-Related Proteins
3.5. GDENs Suppress Glutamate-Induced Lipid Peroxidation by Up-Regulating GPX4 Expression
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Guo, P.; Xie, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G. Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death, and its relationships with tumourous diseases. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, R.J.; Zucca, F.A.; Duyn, J.H.; Crichton, R.R.; Zecca, L. The role of iron in brain ageing and neurodegenerative disorders. Lancet Neurol. 2014, 13, 1045–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.X.; Sun, X.; Yan, X.L.; Guo, Z.N.; Yang, Y. Ferroptosis in neurological diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Stockwell, B.R.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, A.; Jeandriens, J.; Parkes, H.G.; So, P.W. Iron dyshomeostasis, lipid peroxidation and perturbed expression of cystine/glutamate antiporter in Alzheimer’s disease: Evidence of ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2020, 32, 101494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Wang, D.W.; Xu, S.F.; Zhang, S.; Fan, Y.G.; Yang, Y.Y.; Guo, S.Q.; Wang, S.; Guo, T.; Wang, Z.Y.; et al. α-Lipoic acid improves abnormal behavior by mitigation of oxidative stress, inflammation, ferroptosis, and tauopathy in P301S Tau transgenic mice. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Liu, M.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y. The initiator of neuroexcitotoxicity and ferroptosis in ischemic stroke: Glutamate accumulation. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2023, 16, 1113081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrera, L.; Espiritu, R.A.; Ros, U.; Weber, J.; Schmitt, A.; Stroh, J.; Hailfinger, S.; von Karstedt, S.; García-Sáez, A.J. Ferroptotic pores induce Ca2+ fluxes and ESCRT-III activation to modulate cell death kinetics. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1644–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gao, Z.; He, W.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.; Yan, L.; Mao, S.; Shi, X.; Fan, W.; et al. The gut microbiota metabolite glycochenodeoxycholate activates TFR-ACSL4-mediated ferroptosis to promote the development of environmental toxin-linked MAFLD. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 193, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Tang, M.; Zhou, S.; Xu, D.; Zhao, J.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Tian, X.; Li, M.; Zeng, X. Programmed cell death pathways in the pathogenesis of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 783616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; SriRamaratnam, R.; Welsch, M.E.; Shimada, K.; Skouta, R.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Cheah, J.H.; Clemons, P.A.; Shamji, A.F.; Clish, C.B.; et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 2014, 156, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Gould, S.J. Exosomes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 487–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.J.; Lim, J.W.; Moritz, R.L.; Mathivanan, S. Exosomes: Proteomic insights and diagnostic potential. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2009, 6, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lässer, C.; O’Neil, S.E.; Shelke, G.V.; Sihlbom, C.; Hansson, S.F.; Gho, Y.S.; Lundbäck, B.; Lötvall, J. Exosomes in the nose induce immune cell trafficking and harbour an altered protein cargo in chronic airway inflammation. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salem, K.Z.; Moschetta, M.; Sacco, A.; Imberti, L.; Rossi, G.; Ghobrial, I.M.; Manier, S.; Roccaro, A.M. Exosomes in Tumor Angiogenesis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1464, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howitt, J.; Hill, A.F. Exosomes in the Pathology of Neurodegenerative Diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 26589–26597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Ji, W.; Zhao, R.; Yang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X. Exosome: A significant nano-scale drug delivery carrier. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 7591–7608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logozzi, M.; Di Raimo, R.; Mizzoni, D.; Fais, S. The Potentiality of Plant-Derived Nanovesicles in Human Health-A Comparison with Human Exosomes and Artificial Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J. Plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles and their therapeutic activities. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 17, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanly, C.; Alfieri, M.; Ambrosone, A.; Leone, A.; Fiume, I.; Pocsfalvi, G. Grapefruit-Derived Micro and Nanovesicles Show Distinct Metabolome Profiles and Anticancer Activities in the A375 Human Melanoma Cell Line. Cells 2020, 9, 2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldini, N.; Torreggiani, E.; Roncuzzi, L.; Perut, F.; Zini, N.; Avnet, S. Exosome-like Nanovesicles Isolated from Citrus limon L. Exert Antioxidative Effect. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2018, 19, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Lu, Y.; Chen, X.; Muthuraj, P.G.; Li, X.; Pattabiraman, M.; Zempleni, J.; Kachman, S.D.; Natarajan, S.K.; Yu, J. Protective Role of Shiitake Mushroom-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles in D-Galactosamine and Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, K.; Miller, D.P.; Kumar, A.; Teng, Y.; Sayed, M.; Mu, J.; Lei, C.; Sriwastva, M.K.; Zhang, L.; Yan, J.; et al. Plant-Derived Exosomal Nanoparticles Inhibit Pathogenicity of Porphyromonas gingivalis. iScience 2020, 23, 100869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarasati, A.; Syahruddin, M.H.; Nuryanti, A.; Ana, I.D.; Barlian, A.; Wijaya, C.H.; Ratnadewi, D.; Wungu, T.D.K.; Takemori, H. Plant-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications and Regenerative Therapy. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Yoon, J.B.; Han, J.; Seo, Y.A.; Kang, B.H.; Lee, J.; Ochar, K. Green Onion (Allium fistulosum): An Aromatic Vegetable Crop Esteemed for Food, Nutritional and Therapeutic Significance. Foods 2023, 12, 4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenwick, G.R.; Hanley, A.B. The genus Allium—Part 1. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1985, 22, 199–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.S.; Choi, E.J.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, G.H. Evaluation of Allium Vegetables for Anti-Adipogenic, Anti-Cancer, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities In Vitro. J. Life Sci. 2013, 5, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.T.; Shin, E.J.; Chung, M.Y.; Park, J.H.; Chung, S.; Choi, H.K. Ethanol Extract of Allium fistulosum Inhibits Development of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2018, 12, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.J.; Bian, Y.P.; Wang, Q.H.; Yin, F.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, J.H. Blueberry-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles Ameliorate Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Attenuating Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Xu, J.; Tang, R.; Zeng, P.; Li, Z.; You, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, T.; Ma, X.; He, Y.; et al. Edible Pueraria lobata-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles Ameliorate Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis Associated Lung Inflammation Through Modulating Macrophage Polarization. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 170, 116098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.J.; Lee, H.G.; Hur, J.; Lee, G.H.; Won, J.P.; Kim, E.; Hwang, J.S.; Seo, H.G. PPARδ Activation Mitigates 6-OHDA-Induced Neuronal Damage by Regulating Intracellular Iron Levels. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, J.P.; Kim, E.; Hur, J.; Lee, H.G.; Lee, W.J.; Seo, H.G. Red Clover (Trifolium pratense L.) Extract Inhibits Ferroptotic Cell Death by Modulating Cellular Iron Homeostasis. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 308, 116267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, U.; Abbina, S.; Gill, A.; Bhagat, V.; Kizhakkedathu, J.N. A Facile Colorimetric Method for the Quantification of Labile Iron Pool and Total Iron in Cells and Tissue Specimens. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.M.; Wiemann, S.; Ambreen, G.; Zhou, J.; Engelhardt, K.; Brüßler, J.; Bakowsky, U.; Li, S.M.; Mandic, R.; Pocsfalvi, G.; et al. Cucumber-Derived Exosome-like Vesicles and Plant Crystals for Improved Dermal Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, N.; Li, J.; Zeng, L.; You, J.; Li, R.; Qin, A.; Liu, X.; Yan, F.; Zhou, Z. Plant-Derived Exosome-Like Nanovesicles: Current Progress and Prospects. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 4987–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuela, N.; Muhammad, D.R.; Iriawati; Wijaya, C.H.; Ratnadewi, Y.M.D.; Takemori, H.; Ana, I.D.; Yuniati, R.; Handayani, W.; Wungu, T.D.K.; et al. Isolation of Plant-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles (PDENs) from Solanum nigrum L. Berries and Their Effect on Interleukin-6 Expression as a Potential Anti-inflammatory Agent. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0296259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Han, Q.; Chen, J.; Wu, T.; Cheng, Y.; Li, F.; Xia, W. Celery (Apium graveolens L.) Exosome-like Nanovesicles as a New-Generation Chemotherapy Drug Delivery Platform against Tumor Proliferation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 8413–8424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.E.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.M.; et al. Yam-Derived Exosome-like Nanovesicles Stimulate Osteoblast Formation and Prevent Osteoporosis in Mice. J. Control. Release 2023, 355, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Yan, L.; Yu, Q.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, L.; Zheng, L. Characterization of the MicroRNA Profile of Ginger Exosome-like Nanoparticles and Their Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Intestinal Caco-2 Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 4725–4734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Yao, X.; Yue, J.; Fang, Y.; Cao, G.; Midgley, A.C.; Nishinari, K.; Yang, Y. Advances in Bioactivity of MicroRNAs of Plant-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles and Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 6285–6299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akao, Y.; Kuranaga, Y.; Heishima, K.; Sugito, N.; Morikawa, K.; Ito, Y.; Soga, T.; Ito, T. Plant hvu-MIR168-3p Enhances Expression of Glucose Transporter 1 (SLC2A1) in Human Cells by Silencing Genes Related to Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain Complex I. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2022, 101, 108922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Xu, F.; Zhang, X.; Mu, J.; Sayed, M.; Hu, X.; Lei, C.; Sriwastva, M.; Kumar, A.; Sundaram, K.; et al. Plant-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Inhibit Lung Inflammation Induced by Exosomes SARS-CoV-2 Nsp12. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 2424–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhivotovsky, B.; Orrenius, S. Calcium and Cell Death Mechanisms: A Perspective from the Cell Death Community. Cell Calcium 2011, 50, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.H.; Miyamoto, M.; Sastre, A.; Schnaar, R.L.; Coyle, J.T. Glutamate Toxicity in a Neuronal Cell Line Involves Inhibition of Cystine Transport Leading to Oxidative Stress. Neuron 1989, 2, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.B.; Maher, P. Protein Kinase C Activation Inhibits Glutamate-Induced Cytotoxicity in a Neuronal Cell Line. Brain Res. 1994, 644, 169–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, S.; Mueller, C.; Pfeiffer, S.; Kraft, V.A.N.; Merl-Pham, J.; Bao, X.; Feederle, R.; Jin, X.; Hauck, S.M.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; et al. MS4A15 Drives Ferroptosis Resistance through Calcium-Restricted Lipid Remodeling. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 670–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleitze, S.; Paula-Lima, A.; Núñez, M.T.; Hidalgo, C. The Calcium-Iron Connection in Ferroptosis-Mediated Neuronal Death. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 175, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, S.; He, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Piao, M.; Chi, G.; Luo, Y.; Ge, P. RSL3 Drives Ferroptosis through NF-κB Pathway Activation and GPX4 Depletion in Glioblastoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2023, 518, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambright, W.S.; Fonseca, R.S.; Chen, L.; Na, R.; Ran, Q. Ablation of Ferroptosis Regulator Glutathione Peroxidase 4 in Forebrain Neurons Promotes Cognitive Impairment and Neurodegeneration. Redox Biol. 2017, 12, 45521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Meng, Z.; Yu, S.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Wu, H. Baicalein Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Ferroptosis via Regulating GPX4/ACSL4/ACSL3 Axis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 366, 110137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Zhao, W.; Lowe, S.; Bentley, R.; Hu, G.; Mei, H.; Jiang, X.; Sun, C.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y. Quercetin alleviates kainic acid-induced seizure by inhibiting the Nrf2-mediated ferroptosis pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2022, 191, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Wang, H. Kaempferol Ameliorates Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation-Induced Neuronal Ferroptosis by Activating Nrf2/SLC7A11/GPX4 Axis. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Fang, Z.M.; Yi, X.; Wei, X.; Jiang, D.S. The interaction between ferroptosis and inflammatory signaling pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Jang, H.; Park, D.; Park, B.; Jang, Y.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.H.; Shim, M.K.; Yang, Y. Oral Delivery of Photoresponsive Milk-Derived Exosomes for the Local Therapy of Glioblastoma. ACS Mater. Lett. 2024, 6, 4019–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Zaldívar, H.M.; Polakovicova, I.; Salas-Huenuleo, E.; Corvalán, A.H.; Kogan, M.J.; Yefi, C.P.; Andia, M.E. Extracellular Vesicles Through the Blood-Brain Barrier: A Review. Fluids Barriers CNS 2022, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, H.J.; Won, J.P.; Lee, H.G.; Seo, H.G. Green Onion-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles Prevent Ferroptotic Cell Death Triggered by Glutamate: Implication for GPX4 Expression. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193257
Yoon HJ, Won JP, Lee HG, Seo HG. Green Onion-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles Prevent Ferroptotic Cell Death Triggered by Glutamate: Implication for GPX4 Expression. Nutrients. 2024; 16(19):3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193257
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Han Jun, Jun Pil Won, Hyuk Gyoon Lee, and Han Geuk Seo. 2024. "Green Onion-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles Prevent Ferroptotic Cell Death Triggered by Glutamate: Implication for GPX4 Expression" Nutrients 16, no. 19: 3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193257
APA StyleYoon, H. J., Won, J. P., Lee, H. G., & Seo, H. G. (2024). Green Onion-Derived Exosome-like Nanoparticles Prevent Ferroptotic Cell Death Triggered by Glutamate: Implication for GPX4 Expression. Nutrients, 16(19), 3257. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16193257




