Infant Milk Formula Enriched in Dairy Cream Brings Its Digestibility Closer to Human Milk and Supports Intestinal Health in Pre-Clinical Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Infant Simulated Gastrointestinal In Vitro Digestion Method
2.3. Protein Digestibility
2.3.1. Free Amino Acid Analysis
2.3.2. Molecular Weight Distribution of Peptides
2.3.3. Proteomics
2.4. Free Fatty Acid Analysis
2.5. Mineral Analysis
2.6. Analysis of Intestinal Health
2.6.1. Intestinal Barrier Cell Culture Model
2.6.2. Cytotoxicity Assays
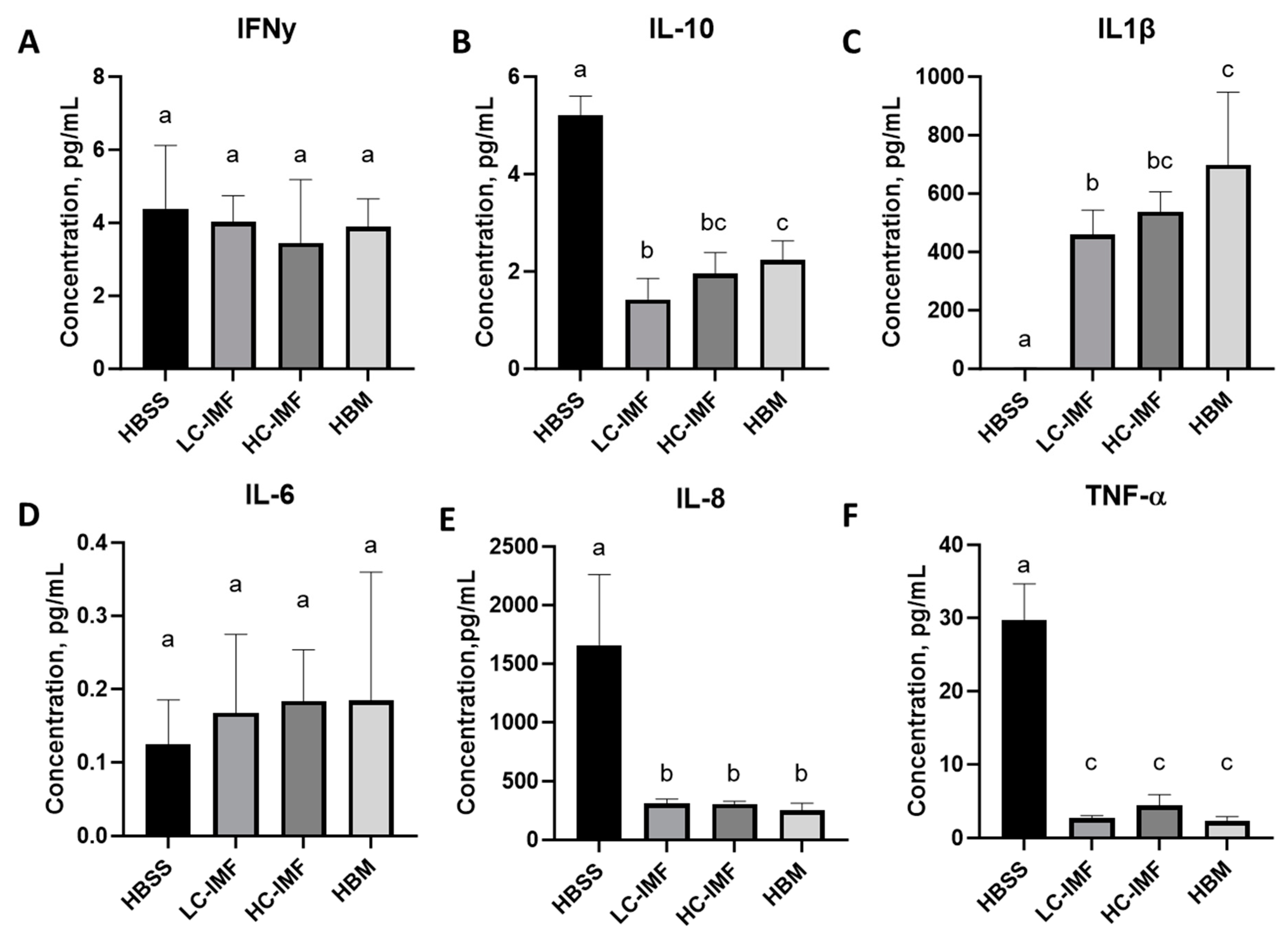
2.6.3. Immunomodulation Analysis
2.6.4. Satiety Analysis
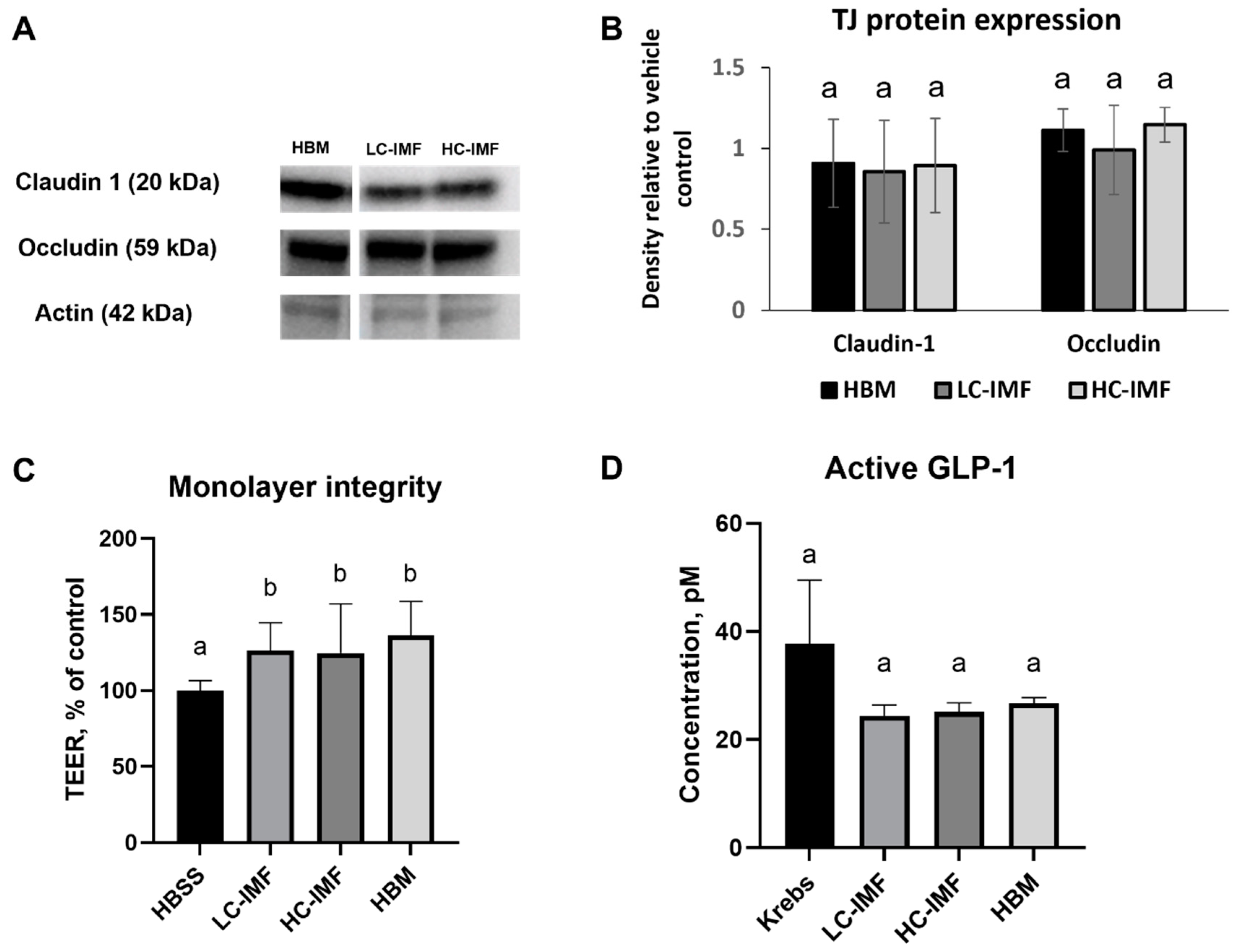
2.6.5. Tight Junction (TJ) Protein Analysis
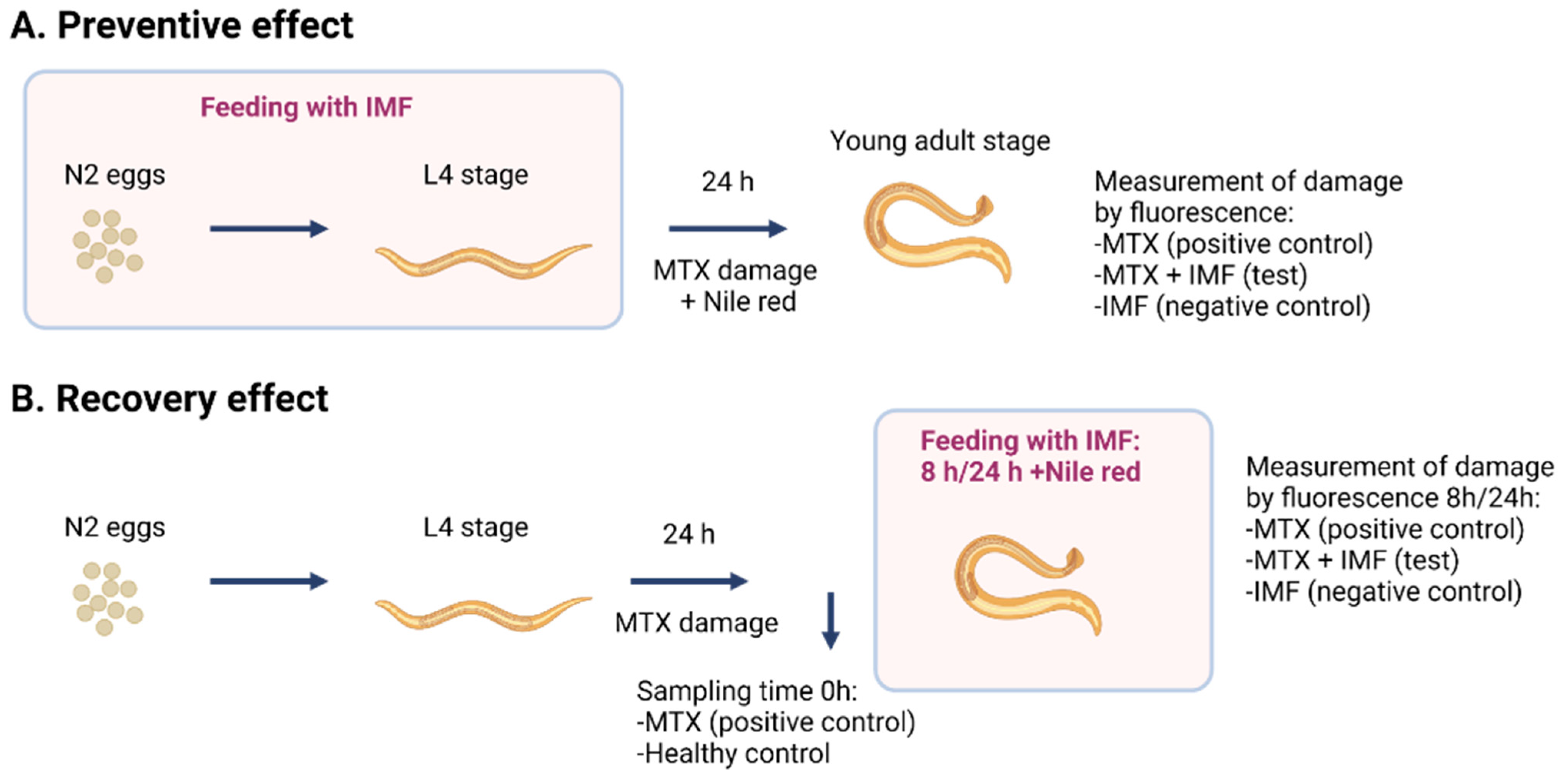
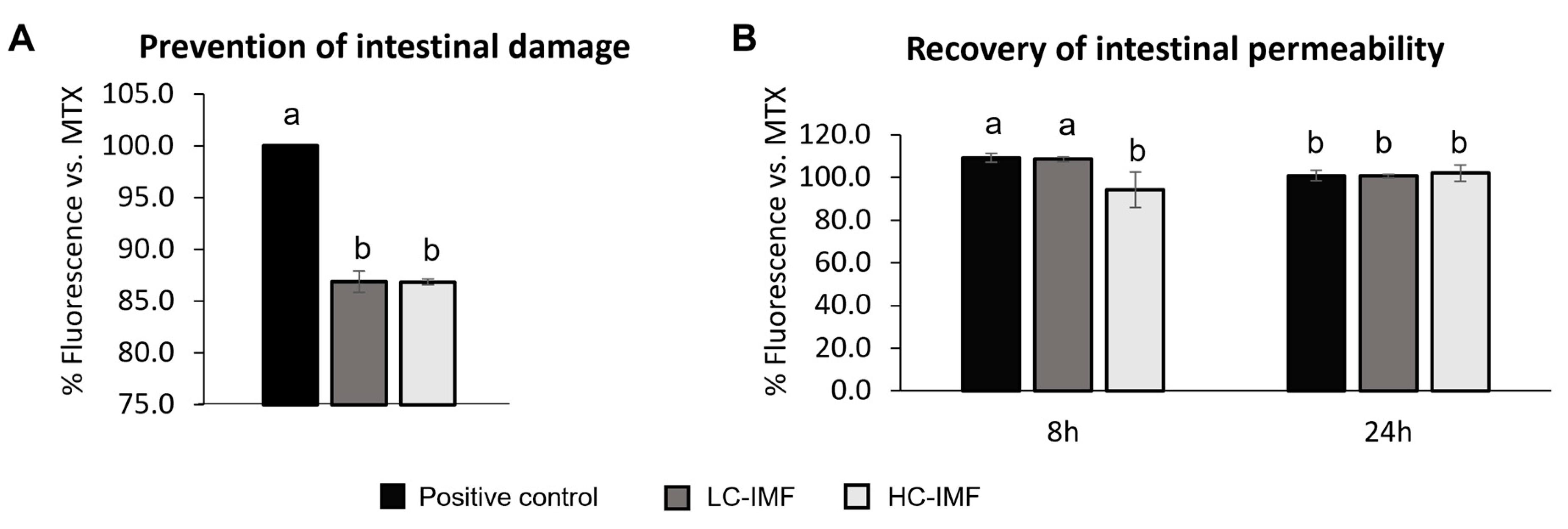
2.6.6. Evaluation of Gut Barrier Integrity with C. elegans
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Digestion and Bioavailability
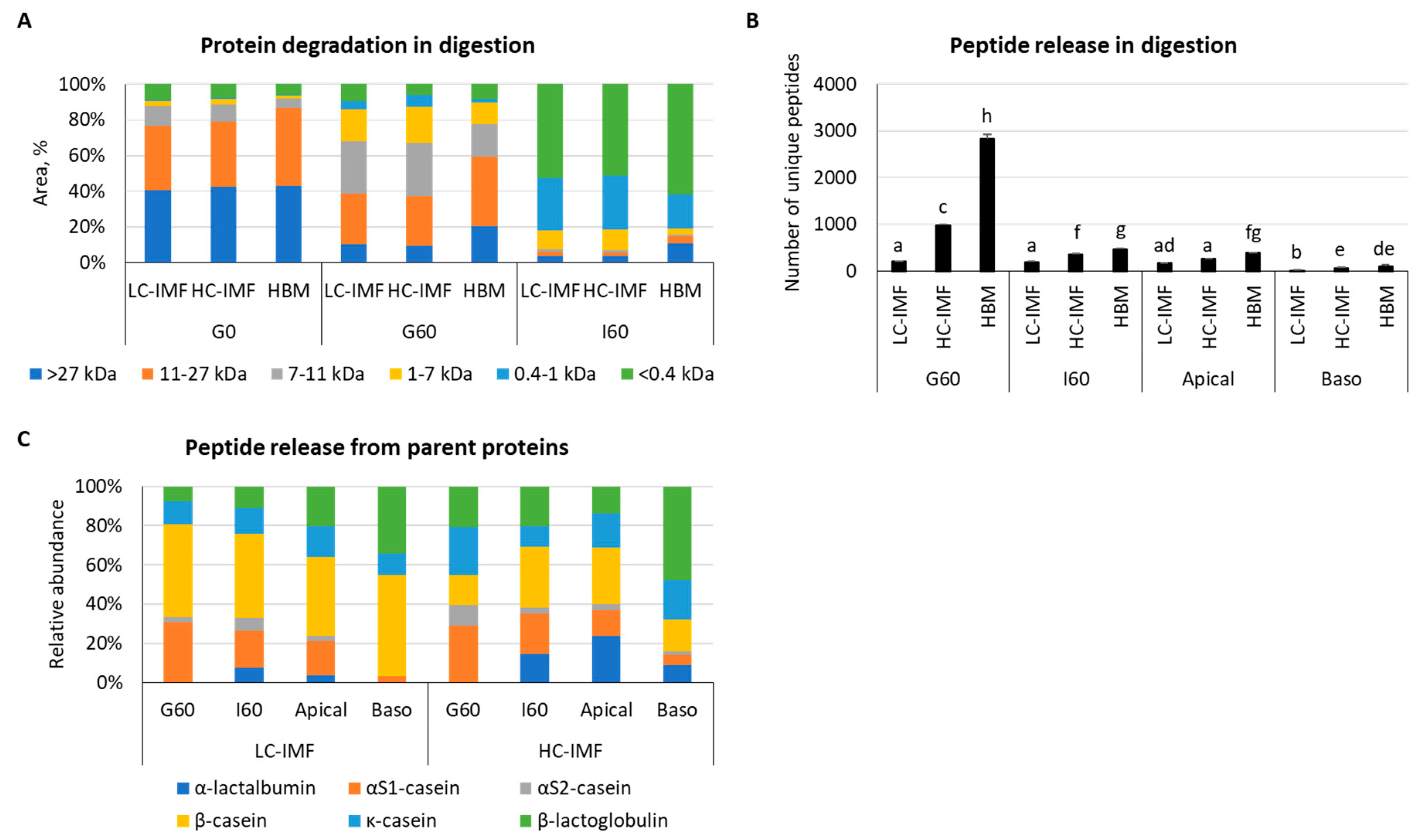
3.1.1. Protein Digestion: Peptide Size Distribution by HPLC
3.1.2. Peptide Release and Bioavailability
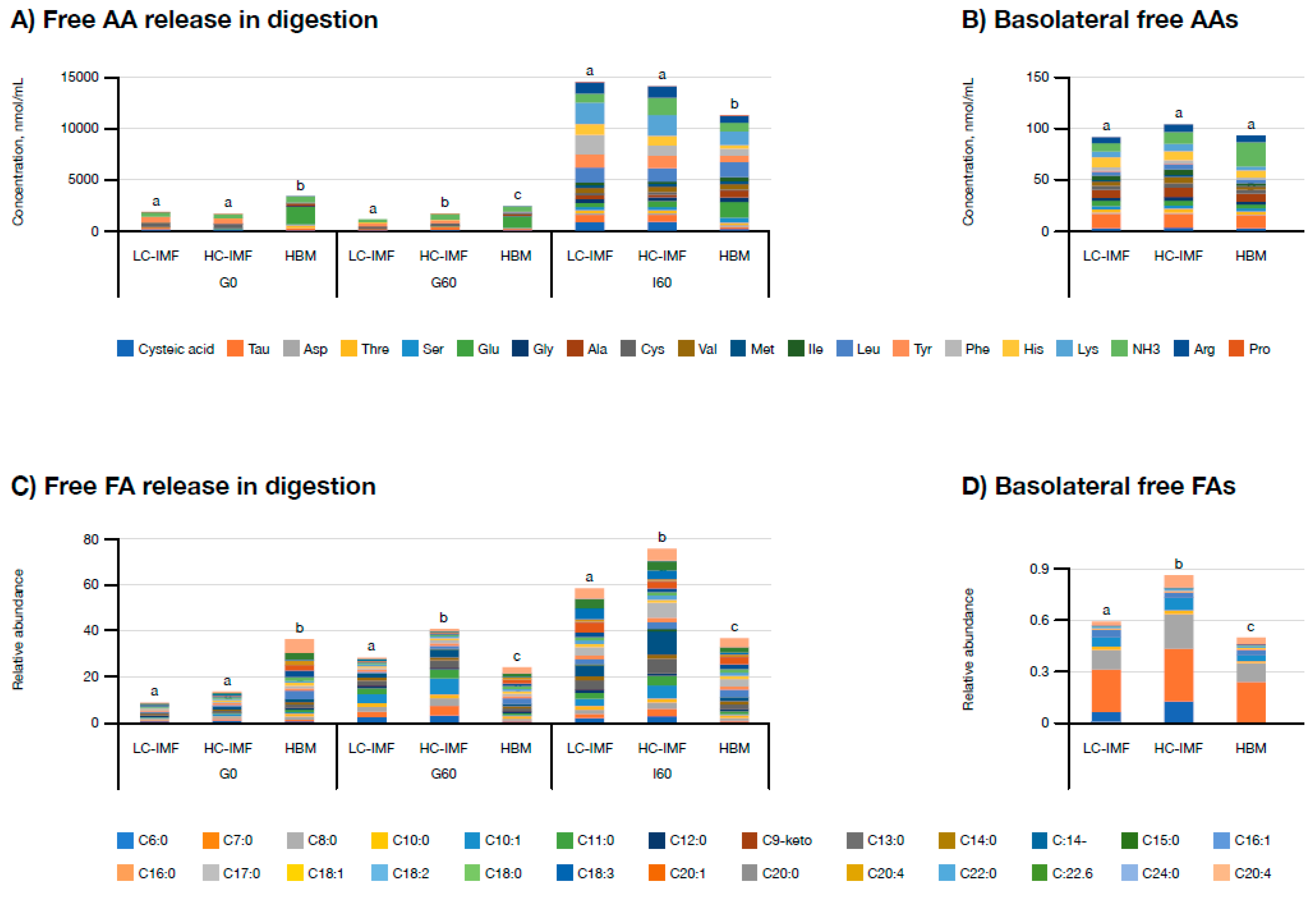
3.1.3. Free Amino Acid (AA) and Fatty Acid (FA) Release and Bioavailability
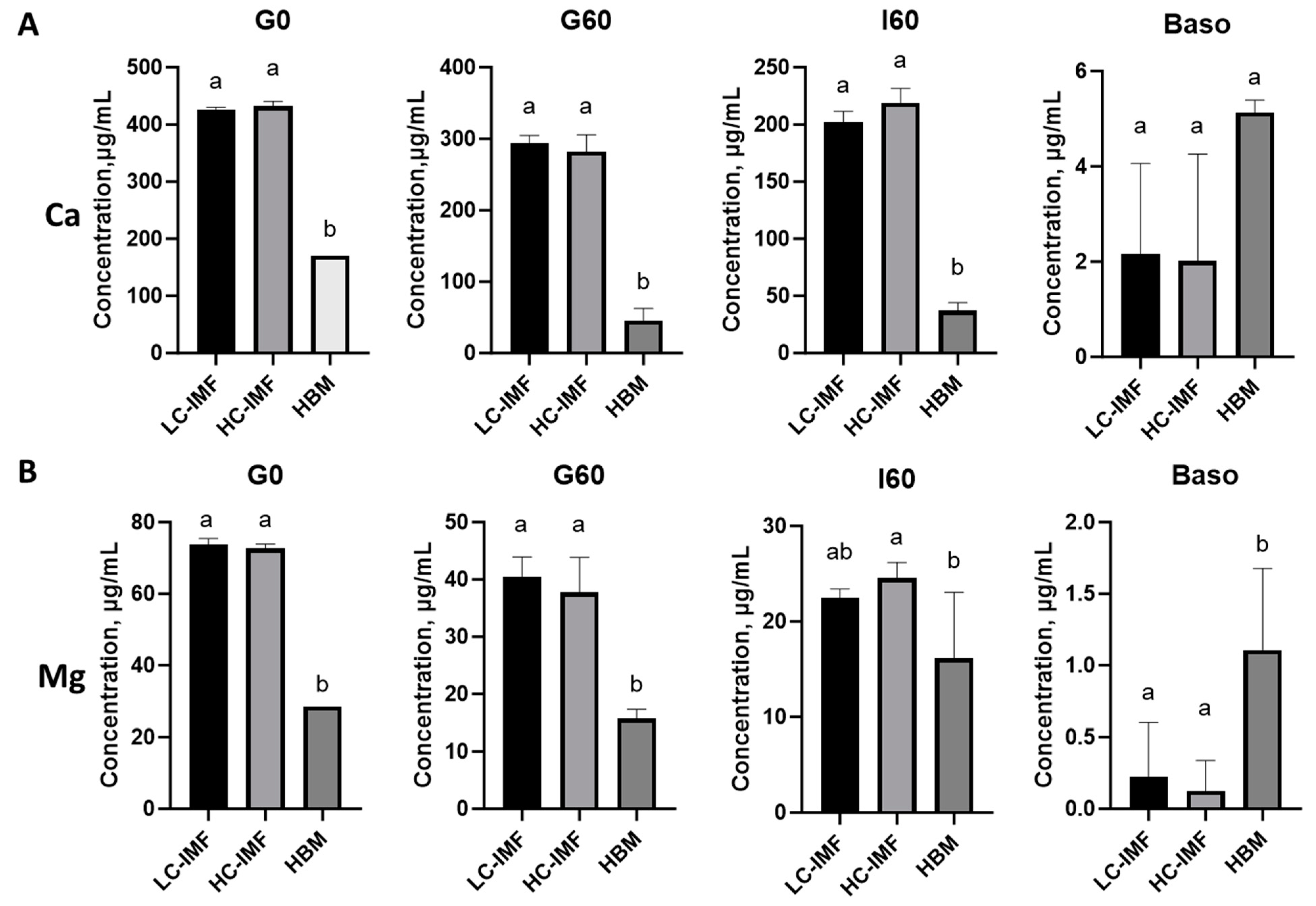
3.1.4. Mineral Release and Bioavailability
3.2. Functionality of HBM, LC-IMF and HC-IMF
3.2.1. Intestinal Health
3.2.2. Satiety
3.2.3. Immunity/Inflammation
3.2.4. Intestinal Health Effect in C. elegans
4. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Nutrition Targets 2025. Breastfeeding Policy Brief. 2014. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/WHO-NMH-NHD-14.7 (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Martin, C.R.; Ling, P.-R.; Blackburn, G.L. Review of Infant Feeding: Key Features of Breast Milk and Infant Formula. Nutrients 2016, 8, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Yi, D.Y. Components of human breast milk: From macronutrient to microbiome and microRNA. Clin. Exp. Pediatr. 2020, 63, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, L.; Espinosa-Martos, I.; García-Carral, C.; Manzano, S.; McGuire, M.K.; Meehan, C.L.; McGuire, M.A.; Williams, J.E.; Foster, J.; Sellen, D.W.; et al. What’s Normal? Immune Profiling of Human Milk from Healthy Women Living in Different Geographical and Socioeconomic Settings. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvalatchmanan, J.; Rukmini, A.; Ji, S.; Triebl, A.; Gao, L.; Bendt, A.K.; Wenk, M.R.; Gooley, J.J.; Torta, F. VariabilityVariability of Lipids in Human Milk. Metabolites 2021, 11, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hageman, J.H.; Danielsen, M.; Nieuwenhuizen, A.G.; Feitsma, A.L.; Dalsgaard, T.K. Comparison of bovine milk fat and vegetable fat for infant formula: Implications for infant health. Int. Dairy J. 2019, 92, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.; Oh, S.; Imm, J.-Y. Roles of Milk Fat Globule Membrane on Fat Digestion and Infant Nutrition. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2022, 42, 351–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, L.R.; Lönnerdal, B. Milk fat globule membrane: The role of its various components in infant health and development. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2020, 85, 108465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoni, M.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Ottoboni, M.; Tretola, M.; Pinotti, L. Comparative Proteomics of Milk Fat Globule Membrane (MFGM) Proteome across Species and Lactation Stages and the Potentials of MFGM Fractions in Infant Formula Preparation. Foods 2020, 9, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaron, S.; Shachar, D.; Abramas, L.; Riskin, A.; Bader, D.; Litmanovitz, I.; Bar-Yoseph, F.; Cohen, T.; Levi, L.; Lifshitz, Y.; et al. Effect of high beta-palmitate content in infant formula on the intestinal microbiota of term infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 56, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Alvarado, R.; Phinney, B.; Lönnerdal, B. Proteomic characterization of human milk fat globule membrane proteins during a 12 month lactation period. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3530–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernell, O.; Timby, N.; Domellöf, M.; Lönnerdal, B. Clinical Benefits of Milk Fat Globule Membranes for Infants and Children. J. Pediatr. 2016, 173, S60–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, C.; Cauty, C.; Guyomarc’h, F. Organization of lipids in milks, infant milk formulas and various dairy products: Role of technological processes and potential impacts. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2015, 95, 863–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronsky, J.; Campoy, C.; Embleton, N.; Fewtrell, M.; Mis, N.F.; Gerasimidis, K.; Hojsak, I.; Hulst, J.; Indrio, F.; Lapillonne, A.; et al. Palm Oil and Beta-palmitate in Infant Formula: A Position Paper by the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2019, 68, 742–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinlan, P.T.; Lockton, S.; Irwin, J.; Lucas, A.L. The relationship between stool hardness and stool composition in breast- and formula-fed infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1995, 20, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bar-Yoseph, F.; Lifshitz, Y.; Cohen, T.; Malard, P.; Xu, C. SN2-Palmitate Reduces Fatty Acid Excretion in Chinese Formula-fed Infants. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2016, 62, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurnida, D.A.; Rowan, A.M.; Idjradinata, P.; Muchtadi, D.; Sekarwana, N. Association of complex lipids containing gangliosides with cognitive development of 6-month-old infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2012, 88, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timby, N.; Domellöf, E.; Hernell, O.; Lönnerdal, B.; Domellöf, M. Neurodevelopment, nutrition, and growth until 12 mo of age in infants fed a low-energy, low-protein formula supplemented with bovine milk fat globule membranes: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 860–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timby, N.; Hernell, O.; Vaarala, O.; Melin, M.; Lönnerdal, B.; Domellöf, M. Infections in infants fed formula supplemented with bovine milk fat globule membranes. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 384–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timby, N.; Domellöf, M.; Lönnerdal, B.; Hernell, O. Supplementation of Infant Formula with Bovine Milk Fat Globule Membranes. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrożej, D.; Dumycz, K.; Dziechciarz, P.; Ruszczyński, M. Milk Fat Globule Membrane Supplementation in Children: Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corredig, M.; Roesch, R.; Dalgleish, D. Production of a novel ingredient from buttermilk. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 2744–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astaire, J.; Ward, R.; German, J.; Jiménez-Flores, R. Concentration of polar MFGM lipids from buttermilk by microfiltration and supercritical fluid extraction. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 2297–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombaut, R.; Dejonckheere, V.; Dewettinck, K. Filtration of milk fat globule membrane fragments from acid buttermilk cheese whey. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1662–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombaut, R.; Dewettinck, K. Thermocalcic aggregation of milk fat globule membrane fragments from acid buttermilk cheese whey. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 2665–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontecha, J.; Brink, L.; Wu, S.; Pouliot, Y.; Visioli, F.; Jiménez-Flores, R. Sources, Production, and Clinical Treatments of Milk Fat Globule Membrane for Infant Nutrition and Well-Being. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legislation.gov.uk. Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2016/127 of 25 September 2015 supplementing Regulation (EU) No 609/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council as Regards the Specific Compositional and Information Requirements for Infant Formula and Follow-On Formula and as Regards Requirements on Information Relating to Infant and Young Child Feeding 2015. Available online: https://www.legislation.gov.uk/eur/2016/127/contents#:~:text=Commission%20Delegated%20Regulation%20%28EU%29%202016%2F127%20of%2025%20September,and%20young%20child%20feeding%20%28Text%20with%20EEA%20relevance%29 (accessed on 26 April 2023).
- Ménard, O.; Bourlieu, C.; De Oliveira, S.; Dellarosa, N.; Laghi, L.; Carrière, F.; Capozzi, F.; Dupont, D.; Deglaire, A. A first step towards a consensus static in vitro model for simulating full-term infant digestion. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodkorb, A.; Egger, L.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Assunção, R.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Boutrou, R.; Carrière, F.; et al. INFOGEST static in vitro simulation of gastrointestinal food digestion. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 991–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondrashina, A.; Arranz, E.; Cilla, A.; Faria, M.A.; Santos-Hernández, M.; Miralles, B.; Hashemi, N.; Rasmussen, M.K.; Young, J.F.; Barberá, R.; et al. Coupling in vitro food digestion with in vitro epithelial absorption; recommendations for biocompatibility. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Rooney, H.; Dold, C.; Bavaro, S.; Tobin, J.; Callanan, M.J.; Brodkorb, A.; Lawlor, P.G.; Giblin, L. Membrane filtration processing of infant milk formula alters protein digestion in young pigs. Food Res. Int. 2023, 166, 112577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizcaíno, J.A.; Deutsch, E.W.; Wang, R.; Csordas, A.; Reisinger, F.; Ríos, D.; Dianes, J.A.; Sun, Z.; Farrah, T.; Bandeira, N.; et al. ProteomeXchange provides globally coordinated proteomics data submission and dissemination. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smart, K.F.; Aggio, R.B.M.; Van Houtte, J.R.; Villas-Bôas, S.G. Analytical platform for metabolome analysis of microbial cells using methyl chloroformate derivatization followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1709–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsen, L.G.; Skou, P.B.; Khakimov, B.; Bro, R. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry data processing made easy. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1503, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondrashina, A.; Brodkorb, A.; Giblin, L. Sodium butyrate converts Caco-2 monolayers into a leaky but healthy intestinal barrier resembling that of a newborn infant. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 5066–5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondrashina, A.; Papkovsky, D.; Giblin, L. Physiological Gut Oxygenation Alters GLP-1 Secretion from the Enteroendocrine Cell Line STC-1. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavaro, S.L.; Mamone, G.; Picariello, G.; Callanan, M.J.; Chen, Y.; Brodkorb, A.; Giblin, L. Thermal or membrane processing for Infant Milk Formula: Effects on protein digestion and integrity of the intestinal barrier. Food Chem. 2021, 347, 129019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorell, P.; Alvarez, B.; Llopis, S.; Navarro, V.; Ortiz, P.; Gonzalez, N.; Balaguer, F.; Rojas, A.; Chenoll, E.; Ramon, D.; et al. Heat-Treated Bifidobacterium longum CECT-7347: A Whole-Cell Postbiotic with Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory, and Gut-Barrier Protection Properties. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Robinson, R.C.; Wang, J.; Krishnakumar, N.; Manning, C.J.; Lor, Y.; Breck, M.; Barile, D.; German, J.B. Peptidomic profiling of human milk with LC-MS/MS reveals pH-specific proteolysis of milk proteins. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 766–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, Y.; Lönnerdal, B. Bioactive peptides derived from human milk proteins: An update. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2020, 23, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, N.; Beverly, R.L.; Scottoline, B.P.; Dallas, D.C. Peptides Derived from In Vitro and In Vivo Digestion of Human Milk Are Immunomodulatory in THP-1 Human Macrophages. J. Nutr. 2021, 152, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, R.; Meisel, H. Food-derived peptides with biological activity: From research to food applications. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2007, 18, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrat-Melin, B.; Le, T.T.; Møller, H.S.; Larsen, L.B.; Young, J.F. Short communication: Inhibition of angiotensin 1-converting enzyme by peptides derived from variants of bovine beta-casein upon apical exposure to a Caco-2 cell monolayer. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagaoka, S.; Futamura, Y.; Miwa, K.; Awano, T.; Yamauchi, K.; Kanamaru, Y.; Tadashi, K.; Kuwata, T. Identification of novel hypocholesterolemic peptides derived from bovine milk beta-lactoglobulin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 281, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pihlanto-Leppälä, A.; Koskinen, P.; Piilola, K.; Tupasela, T.; Korhonen, H. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory properties of whey protein digests: Concentration and characterization of active peptides. J. Dairy Res. 2000, 67, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavares, T.; Contreras, M.d.M.; Amorim, M.; Pintado, M.; Recio, I.; Malcata, F.X. Novel whey-derived peptides with inhibitory effect against angiotensin-converting enzyme: In vitro effect and stability to gastrointestinal enzymes. Peptides 2011, 32, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, B.; Okuyan, B.; Sener, G.; Tunali-Akbay, T. Investigation of beta-lactoglobulin derived bioactive peptides against SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): In silico analysis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 891, 173781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohl, C.H.K.; Thibane, J. Antifungal free fatty acids: A review. Sci. Against Microb. Pathog. Commun. Curr. Res. Technol. Adv. 2011, 1, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Kristmundsdóttir, T.; Árnadóttir, S.G.; Bergsson, G.; Thormar, H. Development and evaluation of microbicidal hydrogels containing monoglyceride as the active ingredient. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Xue, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Yang, X.; Guo, C. Medium-Chain fatty acids enhanced the excretion of fecal cholesterol and cholic acid in C57BL/6J mice fed a cholesterol-rich diet. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 1390–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, C.; Guo, C. Medium-chain fatty acids decrease serum cholesterol via reduction of intestinal bile acid reabsorption in C57BL/6J mice. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 15, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, G.J.; Sánchez, G. Cytokine modulation (IL-6, IL-8, IL-10) by human breast milk lipids on intestinal epithelial cells (Caco-2). J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2016, 29, 2505–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, W.-H.; Shin, S.Y.; Song, J.H.; Kang, N.M. Effect of human breast milk on innate immune response: Up-regulation of bacterial pattern recognition receptors and innate cytokines in THP-1 monocytic cells. Eur. J. Inflamm. 2021, 19, 20587392211026107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, M.A.; Kelly, Y.J.; Sacker, A. Breastfeeding and hospitalization for diarrheal and respiratory infection in the United Kingdom Millennium Cohort Study. Pediatrics 2007, 119, e837–e842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duijts, L.; Ramadhani, M.K.; Moll, H.A. Breastfeeding protects against infectious diseases during infancy in industrialized countries. A systematic review. Matern. Child Nutr. 2009, 5, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duijts, L.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; Hofman, A.; Moll, H.A. Prolonged and exclusive breastfeeding reduces the risk of infectious diseases in infancy. Pediatrics 2010, 126, e18–e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quigley, C.; Taut, C.; Zigman, T.; Gallagher, L.; Campbell, H.; Zgaga, L. Association between home birth and breast feeding outcomes: A cross-sectional study in 28 125 mother-infant pairs from Ireland and the UK. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e010551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| LC-IMF | HC-IMF | HBM | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peptide | Intensity, 106 | Peptide | Intensity, 106 | Peptide | Intensity, 106 |
| (βLg)-VEELKPTPE | 16.59 | (βLg)-VEELKPTPE | 132.31 | (βCn)-FDPQIPK | 1116.60 |
| (βLg)-YVEELKPTPE | 9.82 | (βLg)-YVEELKPTPE | 42.15 | (βCn)-PEIMEVPK_Oxidation (M) | 176.72 |
| (βLg)-YVEELKPTPE_Lac(K) | 7.04 | (βLg)-GLDIQ | 40.65 | (βCn)-QQVPQPIPQ | 74.41 |
| (βLg)-VEELKPTPE_Lac (K) | 4.85 | (βLg)-EELKPTPE | 35.76 | (βCn)-DPQIPK | 15.85 |
| (βCn)-EMPFPK | 31.18 | (βLg)-VEELKPTPE_Lac (K) | 24.33 | (βCn)-PLMQQVPQPI | 12.75 |
| (βCn)-HLPLPL | 9.62 | (βLg)-IPAVFK | 13.33 | (αS1Cn/Casoxin-D)-VQVP | 88.95 |
| (βCn)-QEPVLGPV | 7.40 | (βLg)-ELKPTPEGDLEIL | 10.89 | (αLA)-FLDDDITDDI | 32.45 |
| (βCn)-IPPLTQTPV | 6.61 | (βLg)-DAQSAPL | 8.32 | (multiple *)-RMD | 1017.60 |
| (βCn)-MHQPHQPLPPT | 5.54 | (βCn)-EMPFPK | 69.03 | (multiple)-EDLSDEAERDE | 10.60 |
| (βCn)-NIPPLTQTPV | 5.53 | (βCn)-EMPFPK_Oxidation (M) | 29.22 | (multiple)-DLSDEAERDE | 9.58 |
| (βCn)-VVPPFLQPEV | 4.18 | (βCn)-VVPPFLQPE | 24.51 | (multiple)-NEESTIPR | 7.62 |
| (βCn)-VYPFPGPIPN | 3.96 | (βCn)-HLPLPL | 24.03 | (multiple)-KHE | 5.57 |
| (βCn)-HQPHQPLPPT | 3.33 | (βCn)-VYPFPGPIPN | 10.66 | (multiple)-YQL | 4.94 |
| (KCn)-NQDKTEIPT | 6.07 | (βCn)-HQPHQPLPPT | 10.01 | (multiple)-MKT | 4.92 |
| (KCn)-ESPPEINT | 4.20 | (βCn)-VVPPFLQPEV | 8.66 | (multiple)-VNEESTIPR | 3.81 |
| (αS1Cn)-APSFSDIPNPI | 4.84 | (KCn)-NQDKTEIPT | 78.77 | (multiple)-YLH | 2.68 |
| (αS1Cn)-HQGLPQ | 3.60 | (multiple)-YYP | 1.03 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kondrashina, A.; Mamone, G.; Giblin, L.; Lane, J.A. Infant Milk Formula Enriched in Dairy Cream Brings Its Digestibility Closer to Human Milk and Supports Intestinal Health in Pre-Clinical Studies. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183065
Kondrashina A, Mamone G, Giblin L, Lane JA. Infant Milk Formula Enriched in Dairy Cream Brings Its Digestibility Closer to Human Milk and Supports Intestinal Health in Pre-Clinical Studies. Nutrients. 2024; 16(18):3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183065
Chicago/Turabian StyleKondrashina, Alina, Gianfranco Mamone, Linda Giblin, and Jonathan A. Lane. 2024. "Infant Milk Formula Enriched in Dairy Cream Brings Its Digestibility Closer to Human Milk and Supports Intestinal Health in Pre-Clinical Studies" Nutrients 16, no. 18: 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183065
APA StyleKondrashina, A., Mamone, G., Giblin, L., & Lane, J. A. (2024). Infant Milk Formula Enriched in Dairy Cream Brings Its Digestibility Closer to Human Milk and Supports Intestinal Health in Pre-Clinical Studies. Nutrients, 16(18), 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16183065






