Rosa sterilis Juice Alleviated Breast Cancer by Triggering the Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway and Suppressing the Jak2/Stat3 Pathway
Abstract
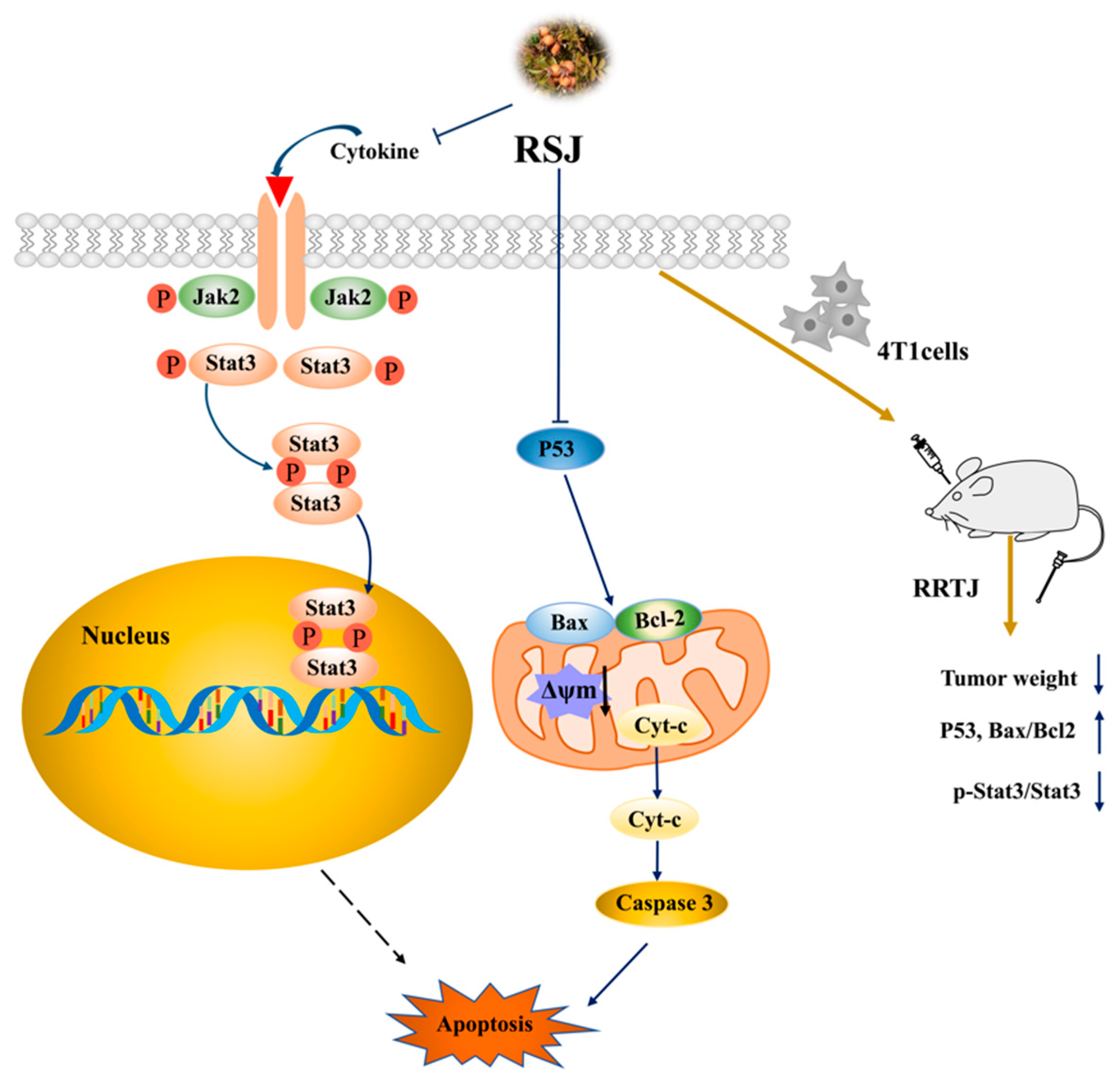
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of RSJ
2.2. Exploring the Protective Effects of RSJ on BC In Vitro
2.2.1. Cell Culture
2.2.2. Cell Viability Assay
2.2.3. Cell Morphology Assay
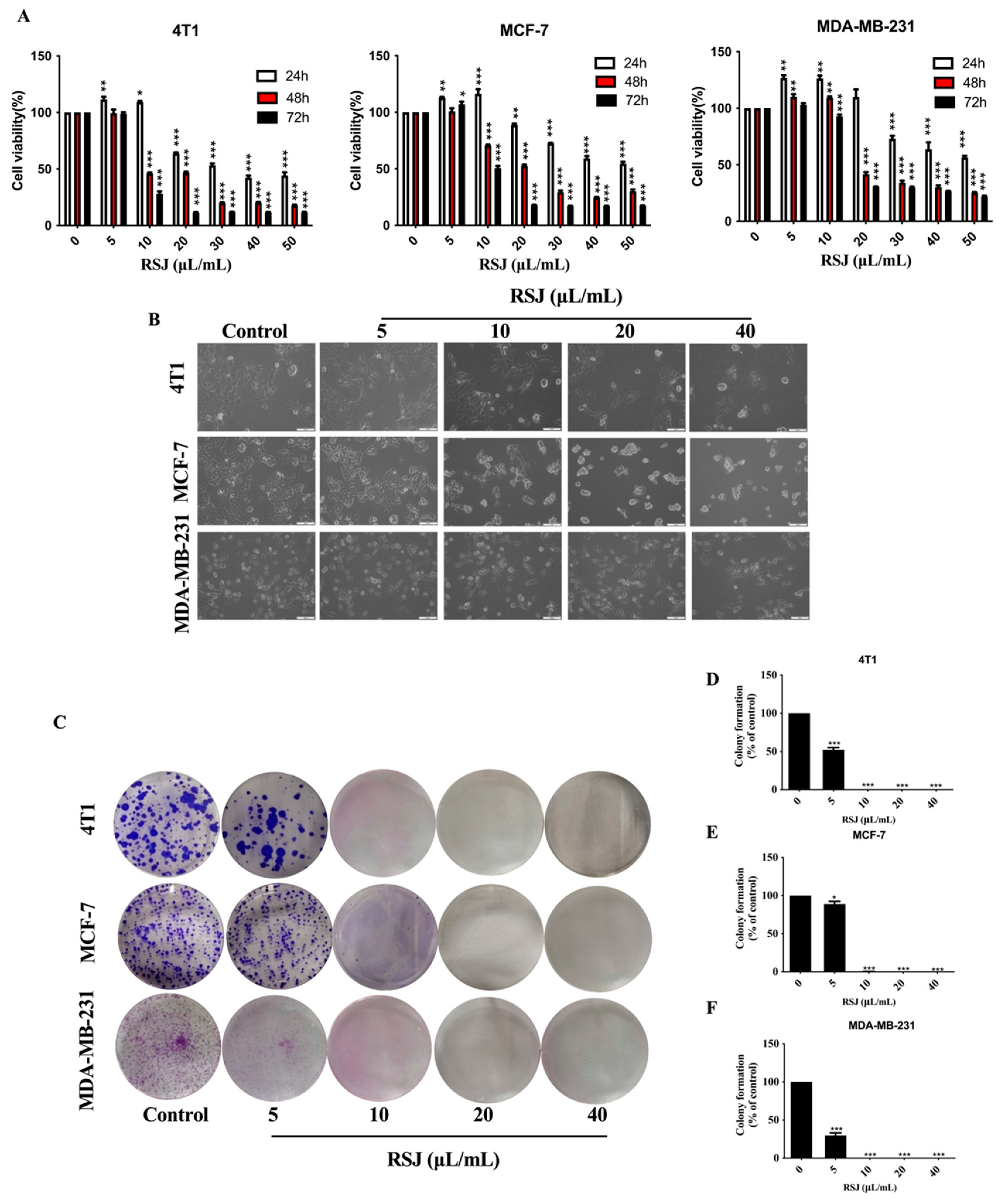
2.2.4. Colony Formation Assay
2.2.5. Apoptosis Assay Using Flow Cytometry (FCM)
2.2.6. Determination of the Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (Δψm)
2.3. Exploring the Protective Effects of RSJ on BC In Vivo
2.3.1. Establishment of Animal Tumor Model
2.3.2. Hematoxylin–Eosin (H&E) Staining and Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
2.3.3. Western Blot
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
3.1. The Anti-Breast Cancer Effect of RSJ In Vitro
3.1.1. RSJ Inhibits the Proliferation of BC Cells While Promoting Their Apoptosis
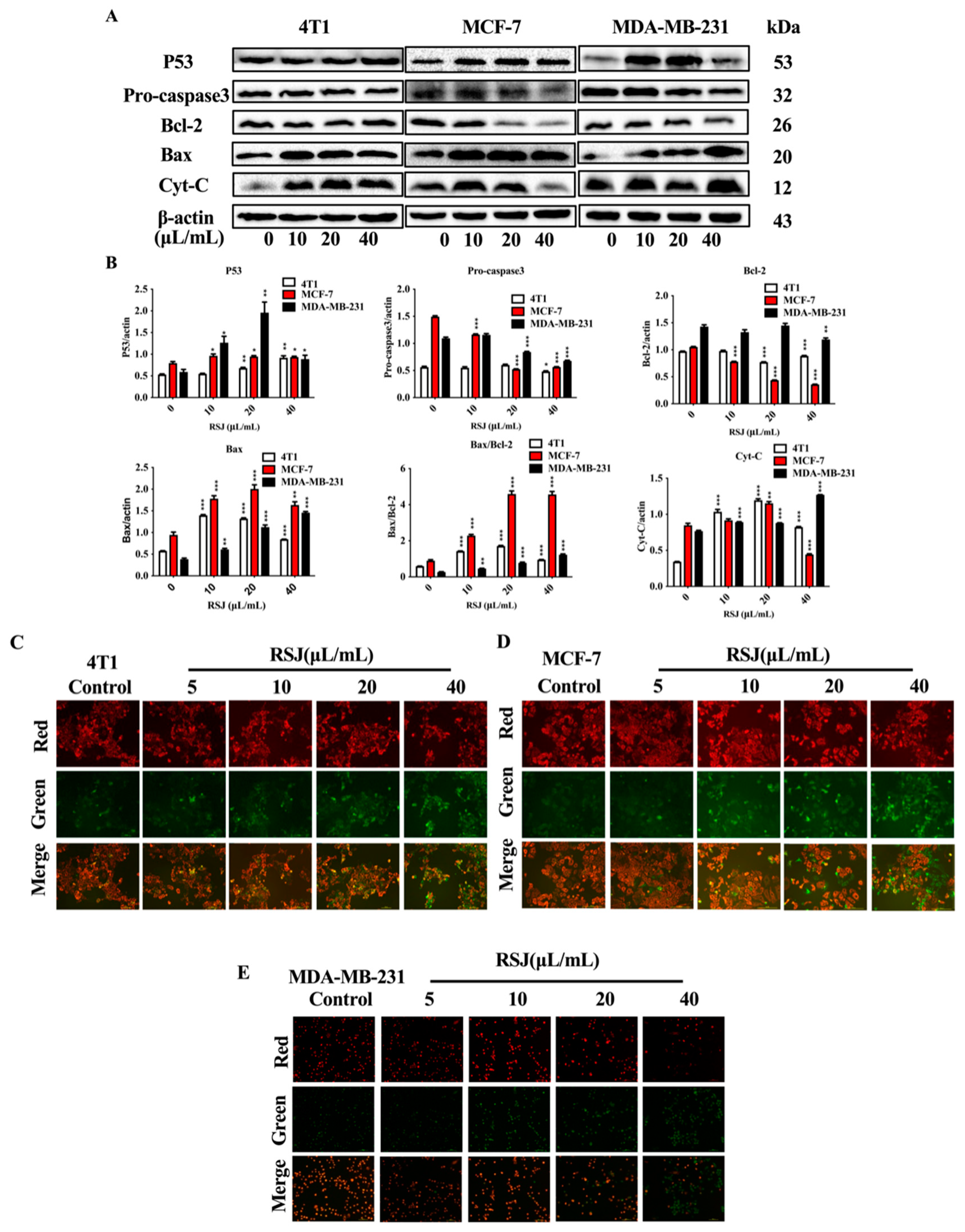
3.1.2. RSJ Triggers the Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway
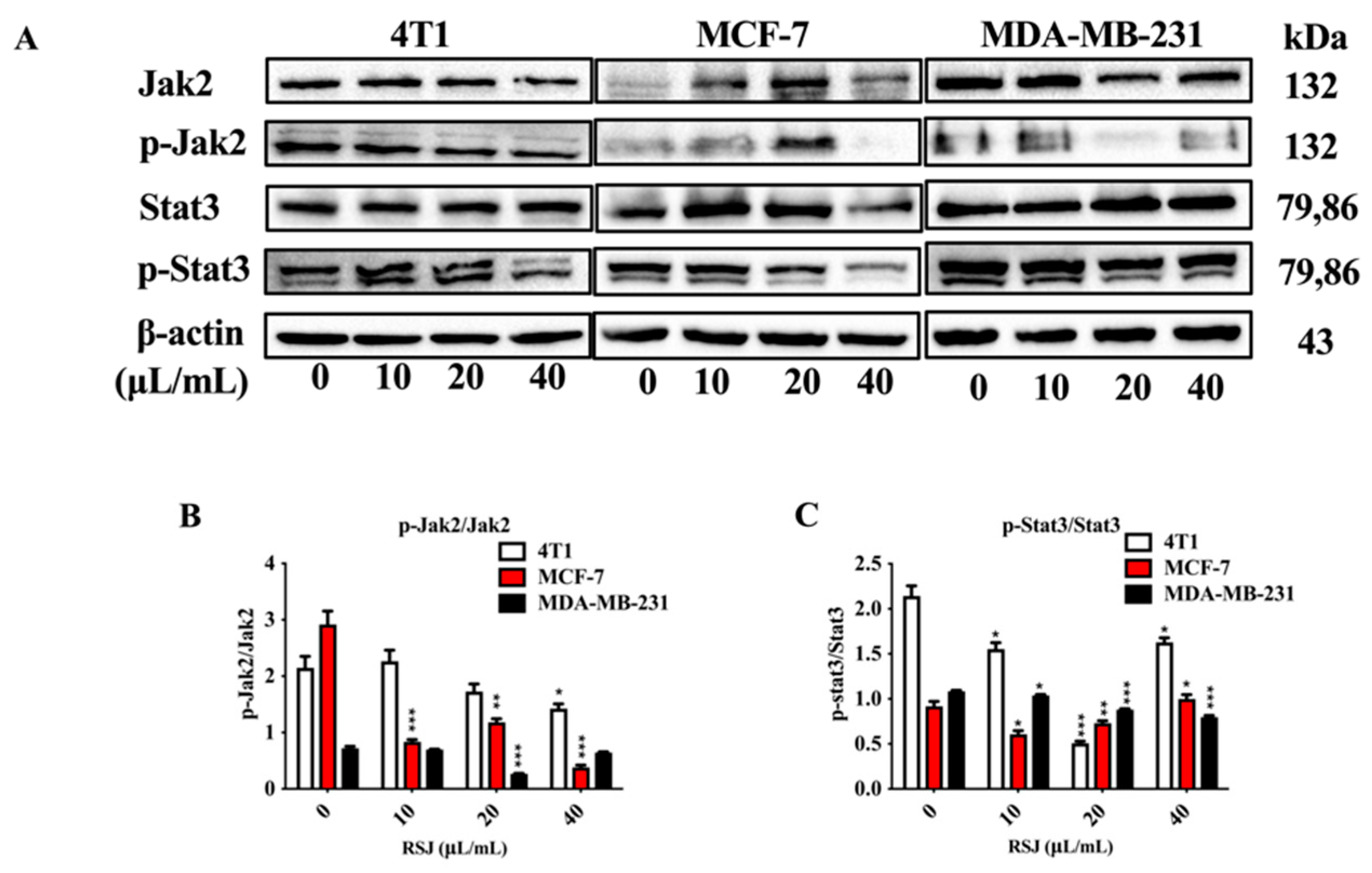
3.1.3. RSJ Suppresses the Jak2/Stat3 Signaling Pathway
3.2. The Protective Effects of RSJ on BC In Vivo
3.2.1. RSJ Inhibits BC Growth In Vivo
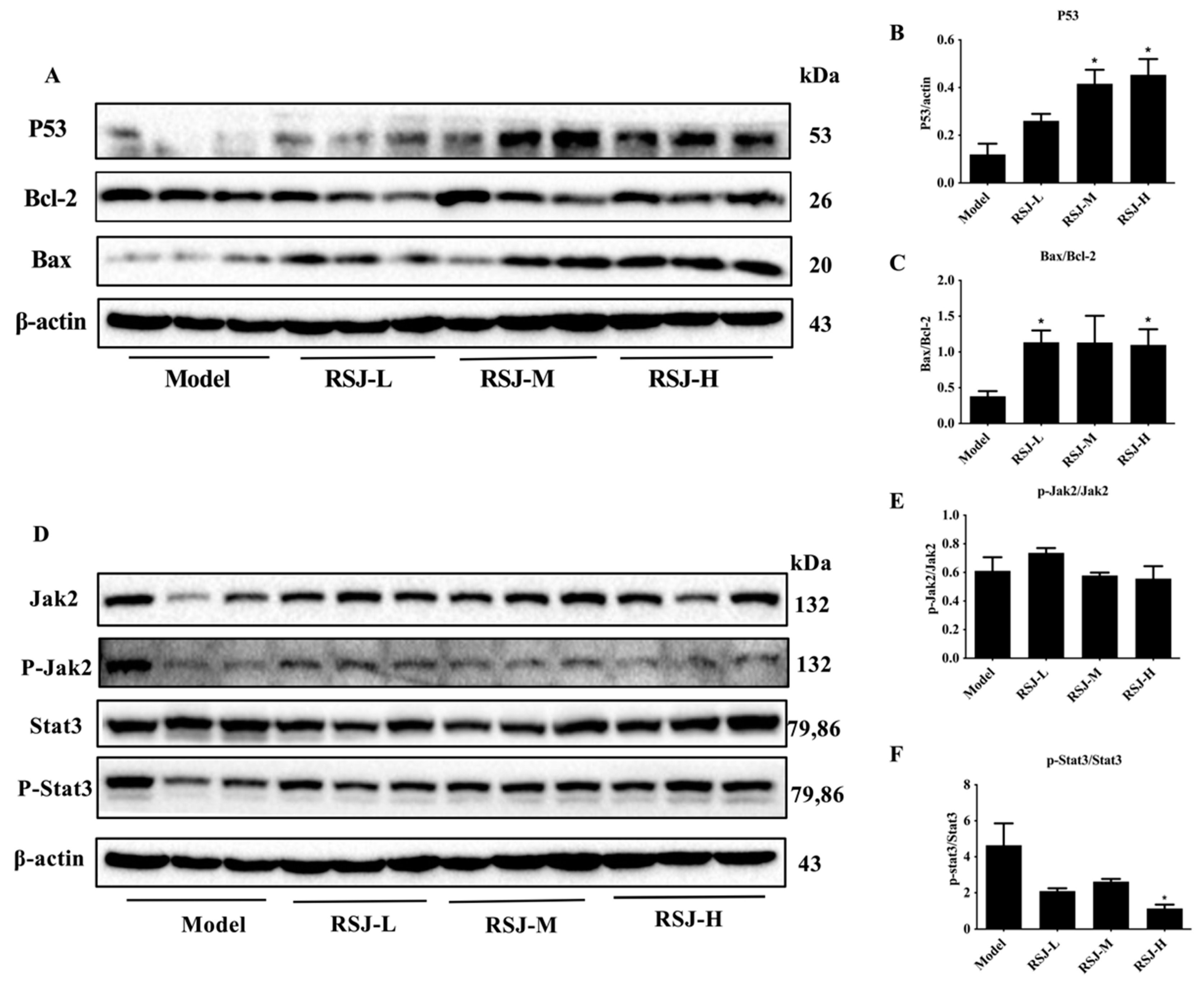
3.2.2. RSJ Exerts Anti-Tumor Activity by Promoting Apoptosis
3.2.3. RSJ Inhibits the Jak2/Stat3 Signaling Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Bsc, M.F.B.; Me, J.F.; Soerjomataram, M.I.; et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.-S.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Z.-N.; Xu, F.; Lu, H.-J.; Zhu, Z.-Y.; Shi, W.; Jiang, J.; Yao, P.-P.; Zhu, H.-P. Risk Factors and Preventions of Breast Cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lalani, N.; Voduc, K.D.; Jimenez, R.B.; Levasseur, N.; Gondara, L.; Speers, C.; Lohrisch, C.; Nichol, A. Breast Cancer Molecular Subtype as a Predictor of Radiation Therapy Fractionation Sensitivity. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 109, 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, I.E.; Lee-Felker, S. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Multimodality Appearance. Curr. Radiol. Rep. 2023, 11, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes, W.D.; Smith, I.E.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Triple-negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1938–1948. [Google Scholar]
- Holliday, D.L.; Speirs, V. Choosing the right cell line for breast cancer research. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, 215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garrido-Castro, A.C.; Lin, N.U.; Polyak, K. Insights into Molecular Classifications of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Improving Patient Selection for Treatment. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 176–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quintela-Fandino, M.; Soberon, N.; Lluch, A.; Manso, L.; Calvo, I.; Cortes, J.; Moreno-Antón, F.; Gil-Gil, M.; Martinez-Jánez, N.; Gonzalez-Martin, A.; et al. Critically short telomeres and toxicity of chemotherapy in early breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 21472–21482. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.-Q.; Zhang, D.; Farha, A.K.; Yang, X.; Li, H.-B.; Kong, K.-W.; Zhang, J.-R.; Chan, C.-L.; Lu, W.-Y.; Corke, H.; et al. Phytochemicals, essential oils, and bioactivities of an underutilized wild fruit Cili (Rosa roxburghii). Ind. Crop. Prod. 2020, 143, 111928. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, D.J.; Cragg, G.M. Natural Products as Sources of New Drugs over the Nearly Four Decades from 01/1981 to 09/2019. J. Nat. Prod. 2020, 83, 770–803. [Google Scholar]
- Naeem, M.; Iqbal, M.O.; Khan, H.; Ahmed, M.M.; Farooq, M.; Aadil, M.M.; Jamaludin, M.I.; Hazafa, A.; Tsai, W.-C. A Review of Twenty Years of Research on the Regulation of Signaling Pathways by Natural Products in Breast Cancer. Molecules 2022, 27, 3412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Meng, X.; Gan, R.-Y.; Zhang, J.-J.; Li, H.-B. Dietary Natural Products for Prevention and Treatment of Breast Cancer. Nutrients 2017, 9, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Cai, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S.; Li, P.; Li, X. Promoting Apoptosis, a Promising Way to Treat Breast Cancer with Natural Products: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 801662. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Wei, T.; Zheng, L.; Jiang, F.; Ma, W.; Lu, M.; Wu, X.; An, H. Recent Advances on Main Active Ingredients, Pharmacological Activities of Rosa roxbughii and Its Development and Utilization. Foods 2023, 12, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fang, W.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y. Physicochemical, biological properties, and flavour profile of Rosa roxburghii Tratt, Pyracantha fortuneana, and Rosa laevigata Michx fruits: A comprehensive review. Food Chem. 2022, 366, 130509. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.T.; Lv, M.J.; An, J.Y.; Fan, X.H.; Dong, M.Z.; Zhang, S.D.; Wang, J.D.; Wang, Y.Q.; Cai, Z.H.; Fu, Y.J. Botanical characteristics, phytochemistry and related biological activities of Rosa roxburghii Tratt fruit, and its potential use in functional foods: A review. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1432–1451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Zhang, S.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, M.; Tang, L.; Wang, P.; Liu, Y.; Xu, C.; Luo, P.; Gao, X. Fermented Rosa roxburghii Tratt Juice Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperlipidemia in Rats by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 883629. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Xia, R.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; Yao, Y.; et al. Component analysis and anti-pulmonary fibrosis effects of Rosa sterilis juice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 12915–12924. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, D.; Xu, J.; Liu, S.; Nasser, M.I.; Wei, W.; Mao, T.; Liu, X.; Zou, X.; Li, J.; Li, X. Rosmanol induces breast cancer cells apoptosis by regulating PI3K/AKT and STAT3/JAK2 signaling pathways. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 631. [Google Scholar]
- Saleem, M.Z.; Nisar, M.A.; Alshwmi, M.; Din, S.R.U.; Gamallat, Y.; Khan, M.; Ma, T. Brevilin A Inhibits STAT3 Signaling and Induces ROS-Dependent Apoptosis, Mitochondrial Stress and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 435–450. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Wang, B.; Xu, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Ye, X. In-vitro and in-vivo anti-breast cancer activity of synergistic effect of berberine and exercise through promoting the apoptosis and immunomodulatory effects. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 87, 106787. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Gan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Fan, C.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Inhibition of Stat3 Signaling Pathway by Natural Product Pectolinarigenin Attenuates Breast Cancer Metastasis. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1195. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Tian, L.; Wang, L.; Yang, W.; Chen, L.; He, F.; Yin, W. Flavonoid-rich extracts from okra flowers exert antitumor activity in colorectal cancer through induction of mitochondrial dysfunction-associated apoptosis, senescence and autophagy. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 10448–10466. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, G.; Liu, S.; Huang, M.; Jiang, X.; Yang, M. Cadmium induces apoptosis of human granulosa cell line KGN via mitochondrial dysfunction-mediated pathways. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, K.; Resat, H. Constitutive activation of STAT3 in breast cancer cells: A review. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 138, 2570–2578. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fisusi, F.A.; Akala, E.O. Drug Combinations in Breast Cancer Therapy. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2019, 7, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Waks, A.G.; Winer, E.P. Breast Cancer Treatment. JAMA 2019, 321, 288. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, M.; Lin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Laurent, I.; Zhong, Y.; Li, J. Ampelopsin Inhibits Breast Cancer Cell Growth through Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 44, 1738–1745. [Google Scholar]
- Pfanner, N.; Warscheid, B.; Wiedemann, N. Mitochondrial proteins: From biogenesis to functional networks. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 267–284. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, S.; Ma, Z.; Li, S.; Zhang, W. Casticin inhibits esophageal cancer cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis by regulating mitochondrial apoptotic and JNK signaling pathways. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 2019, 392, 177–187. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Yu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhou, T.; Nie, T.; Cheng, M.; Liu, H.; Dai, M.; Zhang, B. ABT-737 potentiates cisplatin-induced apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells via the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2301–2308. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Zhang, J.; Xu, F.; Deng, H.; Zhang, W.; Kang, S.; Liang, W. Stomatin-like protein 2 inhibits cisplatin-induced apoptosis through MEK/ERK signaling and the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway in cervical cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1357–1368. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wu, D.-D.; Zhang, J.-X.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.-J.; Hu, X.; Dong, W.-G. Mitochondrial pathway mediated by reactive oxygen species involvement in α-hederin-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 1901–1910. [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland, M.C.; Jarodsky, J.M.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Baker, D.; Kranz, R.G. Structurally Mapping Endogenous Heme in the CcmCDE Membrane Complex for Cytochrome c Biogenesis. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 1065–1080. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kurokawa, M.; Kornbluth, S. Caspases and Kinases in a Death Grip. Cell 2009, 138, 838–854. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, K.D.; Galbraith, M.D.; Andrysik, Z.; Espinosa, J.M. Mechanisms of transcriptional regulation by p53. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 25, 133–143. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Xiong, W.; Song, L.; Li, B.; Zhou, T.; Yu, Y.; Yang, X.; et al. Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 Promotes Alveolar Epithelial Cell Apoptosis and Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury Through P53 Pathway. Shock 2021, 57, 140–150. [Google Scholar]
- E Sabaawy, H.; Ryan, B.M.; Khiabanian, H.; Pine, S.R. JAK/STAT of all trades: Linking inflammation with cancer development, tumor progression and therapy resistance. Carcinogenesis 2021, 42, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Mengie Ayele, T.; Tilahun Muche, Z.; Behaile Teklemariam, A.; Bogale Kassie, A.; Chekol Abebe, E. Role of JAK2/STAT3 Signaling Pathway in the Tumorigenesis, Chemotherapy Resistance, and Treatment of Solid Tumors: A Systemic Review. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 1349–1364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.-H.; Qin, L.; Li, X. Role of STAT3 signaling pathway in breast cancer. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walker, S.R.; Xiang, M.; Frank, D.A. Distinct roles of STAT3 and STAT5 in the pathogenesis and targeted therapy of breast cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 382, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Subramaniam, A.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Perumal, E.; Li, F.; Nachiyappan, A.; Dai, X.; Swamy, S.N.; Ahn, K.S.; Kumar, A.P.; Tan, B.K.; et al. Potential role of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)3 signaling pathway in inflammation, survival, proliferation and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1835, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsu, J.D.; Kao, S.H.; Ou, T.T.; Chen, Y.J.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, C.J. Gallic Acid Induces G2/M Phase Arrest of Breast Cancer Cell MCF-7 through Stabilization of p27Kip1 Attributed to Disruption of p27Kip1/Skp2 Complex. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 1996–2003. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Satari, A.; Ghasemi, S.; Habtemariam, S.; Asgharian, S.; Lorigooini, Z. Rutin: A Flavonoid as an Effective Sensitizer for Anticancer Therapy; Insights into Multifaceted Mechanisms and Applicability for Combination Therapy. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2021, 2021, 9913179. [Google Scholar]
- Turkoglu, B.; Mansuroglu, B. Catechin Loaded Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) Nanoparticles: Characterization, Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activity Against MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 5313–5321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Huang, S.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Ling, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, D.; Yin, W. Rosa sterilis Juice Alleviated Breast Cancer by Triggering the Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway and Suppressing the Jak2/Stat3 Pathway. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2784. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162784
Wang W, Huang S, Li S, Li X, Ling Y, Wang X, Zhang S, Zhou D, Yin W. Rosa sterilis Juice Alleviated Breast Cancer by Triggering the Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway and Suppressing the Jak2/Stat3 Pathway. Nutrients. 2024; 16(16):2784. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162784
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenxi, Shaolin Huang, Sha Li, Xingjie Li, Yihan Ling, Xiaomeng Wang, Shuwen Zhang, Dingzi Zhou, and Wenya Yin. 2024. "Rosa sterilis Juice Alleviated Breast Cancer by Triggering the Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway and Suppressing the Jak2/Stat3 Pathway" Nutrients 16, no. 16: 2784. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162784
APA StyleWang, W., Huang, S., Li, S., Li, X., Ling, Y., Wang, X., Zhang, S., Zhou, D., & Yin, W. (2024). Rosa sterilis Juice Alleviated Breast Cancer by Triggering the Mitochondrial Apoptosis Pathway and Suppressing the Jak2/Stat3 Pathway. Nutrients, 16(16), 2784. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162784




