Effect of Fermented Soybean (FSB) Supplementation on Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
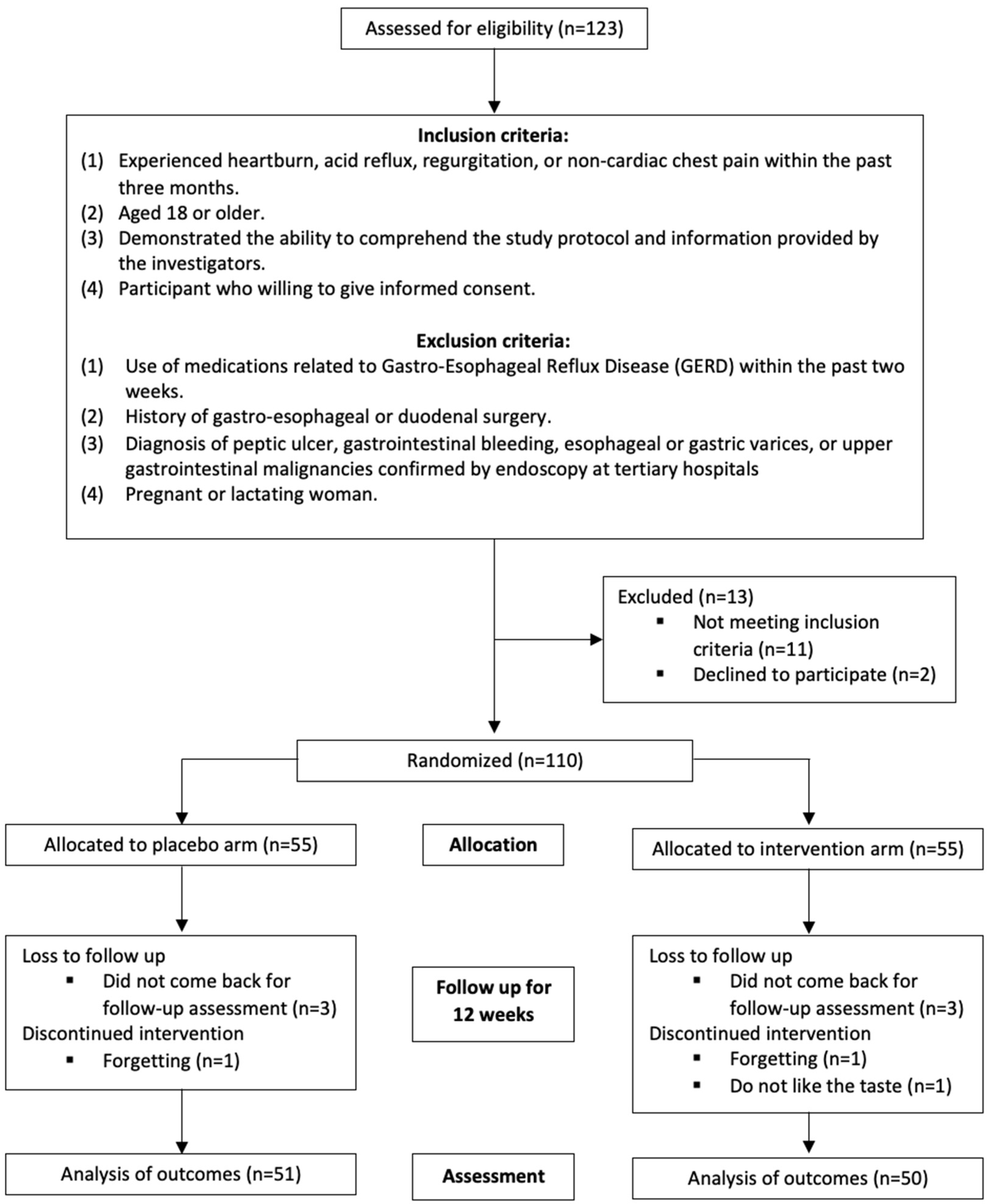
2.1. Participant Recruitment
2.2. Supplementation
2.3. Instruments (Participant-Reported Outcomes)
2.4. Laboratory Examination
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fass, R.; Boeckxstaens, G.E.; El-Serag, H.; Rosen, R.; Sifrim, D.; Vaezi, M.F. Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirwan, J.S.; Hasan, S.S.; Babar, Z.-U.-D.; Conway, B.R.; Ghori, M.U. Global Prevalence and Risk Factors of Gastro-oesophageal Reflux Disease (GORD): Systematic Review with Meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yang, W.L.; Cai, M.H.; Chen, X.; Zhao, R.; Li, M.T.; Yan, X.L.; Xue, L.W.; Hong, L.; Tang, M.Y. Burden of gastroesophageal reflux disease in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of disease study 2019. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Wang, R. Global, regional and national burden of gastroesophageal reflux disease, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 study. Ann. Med. 2022, 54, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahoney, L.B.; Rosen, R. The Spectrum of Reflux Phenotypes. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 15, 646–654. [Google Scholar]
- Eslick, G.D.; Talley, N.J. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Risk Factors, and Impact on Quality of Life—A Population-based Study. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2009, 43, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.; Lee, T.Y.; Lien, H.C.; Peng, Y.C.; Yeh, H.J.; Chang, C.S. Correlation Between Symptom Severity and Health-Related Life Quality of a Population With Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Gastroenterol. Res. 2017, 10, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlqvist, P.; Karlsson, M.; Johnson, D.; Carlsson, J.; Bolge, S.; Wallander, M.A. Relationship between symptom load of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease and health-related quality of life, work productivity, resource utilization and concomitant diseases: Survey of a US cohort. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 960–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiklund, I. Review of the quality of life and burden of illness in gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dig. Dis. 2004, 22, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlqvist, P. Symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease, perceived productivity, and health-related quality of life. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, S57–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, K.-H.; Musial, F.; Eypasch, E.; Meining, A. Gastrointestinal Quality of Life in Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review. Digestion 2022, 103, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belobrajdic, D.P.; James-Martin, G.; Jones, D.; Tran, C.D. Soy and Gastrointestinal Health: A Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokuruka, M. Effects of processing on soybean nutrients and potential impact on consumer health: An overview. Afr. J. Food Agric. Nutr. Dev. 2011, 11, 5000–5017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatani, A.; Vaher, K.; Rivero-Mendoza, D.; Alabasi, K.; Dahl, W.J. Fermented soy supplementation improves indicators of quality of life: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial in adults experiencing heartburn. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Ren, Y.; Guo, X.; Ye, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z.; Yu, K. Postbiotics from Lactobacillus delbrueckii Alleviate Intestinal Inflammation by Promoting the Expansion of Intestinal Stem Cells in, S. Typhimurium-Induced Mice. Foods 2024, 13, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Li, Y.H.; Yang, L.Y.; Yin, J.; He, J.H.; Hou, D.X.; Liu, Y.L.; Huang, X.G. Effects of Dietary Supplementation of Lactobacillus delbrueckii on Gut Microbiome and Intestinal Morphology in Weaned Piglets. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 692389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, T.D.; Bradley, S.; Buckley, N.D.; Green-Johnson, J.M. Interactions of lactic acid bacteria with human intestinal epithelial cells: Effects on cytokine production. J. Food Prot. 2003, 66, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ethier, R.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Jeffrey, M.; Tompkins, T.A. Profiling of Metabolites in a Fermented Soy Dietary Supplement Reinforces its Role in the Management of Intestinal Inflammation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, 2300770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrick, L. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): A Review of Conventional and Alternative Treatments. Altern. Med. Rev. 2011, 16, 116. [Google Scholar]
- Zacny, J.; Zamakhshary, M.; Sketris, I.; Veldhuyzen van Zanten, S. Systematic review: The efficacy of intermittent and on-demand therapy with histamine H2-receptor antagonists or proton pump inhibitors for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease patients. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 21, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisbury, B.H.; Terrell, J.M. Antacids. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.C.; Lall, R.; Srivastava, A. Nutraceuticals: Efficacy, Safety and Toxicity; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wierzejska, R.E. Dietary Supplements—For Whom? The Current State of Knowledge about the Health Effects of Selected Supplement Use. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leo, T.K.; Tan, E.S.S.; Amini, F.; Rehman, N.; Ng, E.S.C.; Tan, C.K. Effect of rice (Oryza sativa L.) ceramides supplementation on improving skin barrier functions and depigmentation: An open-label prospective study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Normina, A.B.; Noradhiah, T.; YB, H.; CK, T.; Kandiah, M.; Aris, A.Z.; Tan, E.S. Consumption of Malay Herbal Medicine (MHMs) During Pregnancy and Postpartum. Indian J. Public Health 2019, 10, 1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, R.; Ravichandran, V.; Tan, C.K. Role of dietary supplements in the continuous battle against COVID-19. Phytother. Res. 2024, 38, 1071–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaptchuk, T.J.; Shaw, J.; Kerr, C.E.; Conboy, L.A.; Kelley, J.M.; Csordas, T.J.; Lembo, A.J.; Jacobson, E.E. “Maybe I Made Up the Whole Thing”: Placebos and Patients’ Experiences in a Randomized Controlled Trial. Cult. Med. Psychiatry 2009, 33, 382–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, M.; Dent, J.; Beebe, T.; Junghard, O.; Wiklund, I.; Lind, T.; Johnsson, F. The Reflux Disease Questionnaire: A measure for assessment of treatment response in clinical trials. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2008, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, J.; Vakil, N.; Jones, R.; Bytzer, P.; Schöning, U.; Halling, K.; Junghard, O.; Lind, T. Accuracy of the diagnosis of GORD by questionnaire, physicians and a trial of proton pump inhibitor treatment: The Diamond Study. Gut 2010, 59, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiklund, I.K.; Junghard, O.; Grace, E.; Talley, N.J.; Kamm, M.; Veldhuyzen van Zanten, S.; Pare, P.; Chiba, N.; Leddin, D.S.; Bigard, M.-A. Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia patients. Psychometric documentation of a new disease-specific questionnaire (QOLRAD). Eur. J. Surg. Suppl. Acta Chir. Suppl. 1998, 583, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Maret-Ouda, J.; Markar, S.R.; Lagergren, J. Gastroesophageal reflux disease: A review. Jama 2020, 324, 2536–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, M.; Gelhot, A.R. Gastroesophageal reflux disease: Diagnosis and management. Am. Fam. Physician 1999, 59, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar]
- Eusebi, L.H.; Ratnakumaran, R.; Yuan, Y.; Solaymani-Dodaran, M.; Bazzoli, F.; Ford, A.C. Global prevalence of, and risk factors for, gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms: A meta-analysis. Gut 2018, 67, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, N.F.; Sjahid, A.S.; Tuan Kamauzaman, T.H.; Lee, Y.Y.; Islam, M.A. Efficacy and safety of domperidone in combination with proton pump inhibitors in gastroesophageal reflux disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-W.; Chang, C.-S. Impact of overlapping functional gastrointestinal disorders on the quality of life in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 27, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirac, M.A.; Safiri, S.; Tsoi, D.; Adedoyin, R.A.; Afshin, A.; Akhlaghi, N.; Alahdab, F.; Almulhim, A.M.; Amini, S.; Ausloos, F. The global, regional, and national burden of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Shang, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, X.; Xin, C.; Yan, X.; Zhai, Y.; Yin, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z. Current advancement on the dynamic mechanism of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, Q.; Fass, R.; Gyawali, C.P.; Miwa, H.; Pandolfino, J.E.; Zerbib, F. Esophageal disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N. Esophageal Diseases. In Sex/Gender-Specific Medicine in Clinical Areas; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 55–93. [Google Scholar]
- Ozkahraman Kırık, M.; Uslu Coskun, B. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. In Airway Diseases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Aghayeva, S.; Katzka, D.; Afandiyeva, N.; Bor, S.; Babayeva, G.; Hidayatov, A.; Mammadzada, G. The Prevalence of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease in Azerbaijan: A Population-Based Cross-sectional Study. Turk. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 34, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhre Yaseri, H. Gender is a risk factor in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran 2017, 31, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belete, M.; Tesfaye, W.; Akalu, Y.; Adane, A.; Yeshaw, Y. Gastroesophageal reflux disease symptoms and associated factors among university students in Amhara region, Ethiopia, 2021: A cross-sectional study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023, 23, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setiawan, M.A.; Fasrini, U.U.; Amir, A.; Miro, S. Characteristics of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Patients at RSUP Dr. M. Djamil Padang during 2018–2021 Period: A Cross-Sectional Study. Indones. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Dig. Endosc. 2024, 24, 227. [Google Scholar]
- Aladag, H.; Aladag, M. Frequency of GERD in women of childbearing age in Malatya region. Med. Sci. 2023, 12, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höllwarth, M.E.; Solari, V. Gastroesophageal reflux disease. In Pediatric Surgery: Diagnosis and Management; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 753–776. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Fan, W.; Yu, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, D.; Song, M.; Liu, S.; Zuo, X.; Zhang, R. Differences in Dietary and Lifestyle Triggers between Non-Erosive Reflux Disease and Reflux Esophagitis—A Multicenter Cross-Sectional Survey in China. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela, M.F. Diagnostic work-up of GERD. Gastrointest. Endosc. Clin. 2014, 24, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, P.O.; Gerson, L.B.; Vela, M.F. Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2013, 108, 308–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisbert, J.P.; Cooper, A.; Karagiannis, D.; Hatlebakk, J.; Agréus, L.; Jablonowski, H.; Zapardiel, J. Impact of gastroesophageal reflux disease on patients’ daily lives: A European observational study in the primary care setting. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2009, 7, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.T.; Posner, S.; Harbrecht, M.; Koutlas, N.; Reichstein, J.; Cantrell, S.; Leiman, D.A. Reflux Disease Questionnaire Scoring and Utilization: A Scoping Review. Foregut 2024, 4, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, C.; Gleddie, S.; Xiao, C.-W. Soybean bioactive peptides and their functional properties. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.; Jo, S.; Kim, O.-K.; Lee, J. Gastro-Protective Effect of Fermented Soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merr.) in a Rat Model of Ethanol/HCl-Induced Gastric Injury. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Descazeaux, M.; Brouquières, D.; Didier, A.; Lescouzères, M.; Napoléon, M.F.; Escamilla, R.; Guilleminault, L. Obesity Predicts Treatment Response to Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy in Patients with Chronic Cough. Lung 2020, 198, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swami, O.C.; Shah, N.J. Functional dyspepsia and the role of digestive enzymes supplement in its therapy. Int. J. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 6, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, K.M.; Jacobs, J.R.; Merritt, R.J.; Murray, R.D. Decreased regurgitation with a soy formula containing added soy fiber. Clin. Pediatr. 2006, 45, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvatore, S.; Tabbers, M.; Singendonk, M.; Savino, F.; Staiano, A.; Benninga, M.; Huysentruyt, K.; Vandenplas, Y. The management of infant regurgitation. In Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children: GER in Children; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 269–288. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, S.; Hsieh, J.; Ho, Y.; Kao, C. Effects of butter and soybean oils on solid-phase gastric emptying in patients with functional dyspepsia. Abdom. Imaging 2000, 25, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otaki, F.; Iyer, P.G. Gastroesophageal reflux disease and Barrett esophagus in the elderly. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2021, 37, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandulski, A.; Malfertheiner, P. Gastroesophageal reflux disease—From reflux episodes to mucosal inflammation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Meroni, M.; Casati, S.; Goldoni, R.; Thomaz, D.V.; Kehr, N.S.; Galimberti, D.; Del Fabbro, M.; Tartaglia, G.M. Salivary biomarkers: Novel noninvasive tools to diagnose chronic inflammation. Int. J. Oral Sci. 2023, 15, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Yoshida, N.; Tomatsuri, N.; Takayama, R.; Katada, K.; Takagi, T.; Ichikawa, H.; Naito, Y.; Okanoue, T.; Yoshikawa, T. Cytokine-induced neutrophil accumulation in the pathogenesis of acute reflux esophagitis in rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2005, 16, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N.; Uchiyama, K.; Kuroda, M.; Sakuma, K.; Kokura, S.; Ichikawa, H.; Naito, Y.; Takemura, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Okanoue, T. Interleukin-8 expression in the esophageal mucosa of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2004, 39, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isomoto, H.; Saenko, V.A.; Kanazawa, Y.; Nishi, Y.; Ohtsuru, A.; Inoue, K.; Akazawa, Y.; Takeshima, F.; Omagari, K.; Miyazaki, M. Enhanced expression of interleukin-8 and activation of nuclear factor kappa-B in endoscopy-negative gastroesophageal reflux disease. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2004, 99, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zong, X.; Wang, C.; Shi, C.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z. Peptides derived from fermented soybean meal suppresses intestinal inflammation and enhances epithelial barrier function in piglets. Food Agric. Immunol. 2020, 31, 120–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagar, L.; Champagne, C.; Buckley, N.; Raymond, Y.; Green-Johnson, J. Immunomodulatory properties of fermented soy and dairy milks prepared with lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, M423–M430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, F.; Cheng, L.; Harnett, K.M.; Chak, A.; Cooper, G.S.; Isenberg, G.; Ray, M.; Katz, J.A.; Catanzaro, A.; O’Shea, R.; et al. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease–Associated Esophagitis Induces Endogenous Cytokine Production Leading to Motor Abnormalities. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Nakamoto, M.; Shuto, E.; Hata, A.; Aki, N.; Shikama, Y.; Bando, Y.; Ichihara, T.; Minamigawa, T.; Kuwamura, Y. Associations between intake of dietary fermented soy food and concentrations of inflammatory markers: A cross-sectional study in Japanese workers. J. Med. Investig. 2018, 65, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Permata, F.; Roosdiana, A.; Anggraini, V. The effect of fermented Glycine max (L.) Merr. to rats induced CCl4 toward hepatic IL-6 expression and ALT-AST level. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2020, 1430, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semeniuk, J.; Wasilewska, J.; Kaczmarski, M. Serum interleukin–4 and tumor necrosis factor alpha concentrations in children with primary acid gastroesophageal reflux and acid gastroesophageal reflux secondary to cow’s milk allergy. Adv. Med. Sci. 2012, 57, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yosef, T.M.; ElMetwally, A.A.; Mansour, A.; AbuFayyoud, M.A.; ElGhandour, A.M. Evaluation of serum levels of Interleukin-4 in Egyptian patients with refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease. Alex. J. Med. 2020, 56, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivashkin, V.; Evsyutina, Y.; Trukhmanov, A.; Lyamina, S.; Malyshev, I. Systemic inflammatory response in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2015, 3, 64–69. [Google Scholar]
- Das, D.; Sarkar, S.; Wann, S.B.; Kalita, J.; Manna, P. Current perspectives on the anti-inflammatory potential of fermented soy foods. Food Res. Int. 2022, 152, 110922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, Y.-P.; Hung, C.-Y.; Yang, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-L. Immune modulation effects of soya bean fermentation food evaluated by an animal model. Food Agric. Immunol. 2015, 26, 463–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.S.S.; Chin, S.A.F.X.; Sathapan, M.S.P.; Dewi, A.D.; Amini, F.; Bustami, N.A.; Tan, P.Y.; Ho, Y.B.; Tan, C.K. Mental Health and the COVID-19 Pandemic: Observational Evidence from Malaysia. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, L.; Baldasseroni, S.; Bandinelli, S.; De Alfieri, W.; Cartei, A.; Calvani, D.; Baldini, A.; Masotti, G.; Marchionni, N. Disease severity and health-related quality of life across different chronic conditions. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2000, 48, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, C.; Versluijs, Y.; Furay, E.; Reese-White, D.; Holan, C.; Alexander, J.; Doggett, S.; Ring, D.; Buckley, F. Psychoemotional factors and their influence on the quality of life in patients with GERD. Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 7219–7226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulich, K.R.; Madisch, A.; Pacini, F.; Piqué, J.M.; Regula, J.; Van Rensburg, C.J.; Újszászy, L.; Carlsson, J.; Halling, K.; Wiklund, I.K. Reliability and validity of the Gastrointestinal Symptom Rating Scale (GSRS) and Quality of Life in Reflux and Dyspepsia (QOLRAD) questionnaire in dyspepsia: A six-country study. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2008, 6, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, X.-L.; Wang, H. Quality of life scales for patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease: A literature review. Int. J. Nurs. Sci. 2015, 2, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenti, A.D.; Guyatt, G.H.; Wiklund, I.; Heels-Ansdell, D.; Armstrong, D.; Fallone, C.A.; Tanser, L.; Van Zanten, S.V.; El-Dika, S.; Chiba, N. The influence of demographic factors and health-related quality of life on treatment satisfaction in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease treated with esomeprazole. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2005, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flook, N.W.; Wiklund, I. Accounting for the effect of GERD symptoms on patients’ health-related quality of life: Supporting optimal disease management by primary care physicians. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2007, 61, 2071–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juniper, E.F.; Guyatt, G.H.; Willan, A.; Griffith, L.E. Determining a minimal important change in a disease-specific quality of life questionnaire. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1994, 47, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aanen, M.; Numans, M.; Weusten, B.; Smout, A. Diagnostic value of the reflux disease questionnaire in general practice. Digestion 2006, 74, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Zanten, S.V.; Armstrong, D.; Barkun, A.; Junghard, O.; White, R.J.; Wiklund, I.K. Symptom overlap in patients with upper gastrointestinal complaints in the Canadian confirmatory acid suppression test (CAST) study: Further psychometric validation of the reflux disease questionnaire. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 25, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wang, Q.; Yao, D.; Li, J.; Bai, G. Association Between Psychosocial Disorders and Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2022, 28, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Abbas, M.S.; Nassar, S.T.; Tasha, T.; Desai, A.; Bajgain, A.; Ali, A.; Dutta, C.; Pasha, K.; Khan, S. Correlation of Anxiety and Depression to the Development of Gastroesophageal Disease in the Younger Population. Cureus 2022, 14, e32712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampa, J.; Westman, M.; Kadetoff, D.; Agréus, A.N.; Le Maître, E.; Gillis-Haegerstrand, C.; Andersson, M.; Khademi, M.; Corr, M.; Christianson, C.A. Peripheral inflammatory disease associated with centrally activated IL-1 system in humans and mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12728–12733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivimäki, M.; Shipley, M.J.; Batty, G.D.; Hamer, M.; Akbaraly, T.N.; Kumari, M.; Jokela, M.; Virtanen, M.; Lowe, G.D.; Ebmeier, K.P. Long-term inflammation increases risk of common mental disorder: A cohort study. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 149–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharangi, A.B.; Das, S. Healing indigestion: A phytotherapeutic review. Adv. Tradit. Med. 2022, 22, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.-P.; Li, S.-M.; Shen, T.; Zhang, Y.-Y. Correlation between sleep impairment and functional dyspepsia. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 0300060520937164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoormans, D.; van Es, B.; Mols, F.; Wasowicz, D.; Beijer, S.; Ezendam, N.P.M. The relation between sleep quality, sleep quantity, and gastrointestinal problems among colorectal cancer survivors: Result from the PROFILES registry. Support. Care Cancer 2022, 30, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| Gender (n/%) | |
| Male | 36 (35.6) |
| Female | 65 (64.4) |
| Age (years) (n/%) | |
| ≤25 | 9 (8.9) |
| 26–35 | 16 (15.8) |
| 36–45 | 45 (44.6) |
| 46–55 | 23 (22.8) |
| >55 | 8 (7.9) |
| Body Mass Index (BMI) (n/%) | |
| Underweight (<18.5) | 7 (6.9) |
| Normal Weight (18.5–24.9) | 60 (59.4) |
| Overweight (25–29.9) | 25 (24.8) |
| Obese (≥30) | 9 (8.9) |
| RDQ Domains | Group | Baseline | First Follow-Up | Second Follow-Up | Third Follow-Up | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heartburn | Intervention | 0.420 ± 0.065 | 0.445 ± 0.061 | 0.690 ± 0.028 | 0.220 ± 0.007 | <0.01 * |
| Placebo | 0.490 ± 0.038 | 0.779 ± 0.045 | 0.603 ± 0.039 | 0.515 ± 0.051 | ||
| Dyspepsia | Intervention | 0.575 ± 0.093 | 0.570 ± 0.087 | 0.750 ± 0.057 | 0.340 ± 0.076 | 0.466 |
| Placebo | 0.564 ± 0.097 | 0.583 ± 0.093 | 0.613 ± 0.088 | 0.466 ± 0.016 | ||
| Regurgitation | Intervention | 0.905 ± 0.073 | 0.785 ± 0.076 | 0.785 ± 0.059 | 0.335 ± 0.056 | <0.001 * |
| Placebo | 0.897 ± 0.023 | 0.912 ± 0.042 | 0.373 ± 0.093 | 0.740 ± 0.017 |
| Inflammation Levels | Group | Baseline | First Follow-Up | Second Follow-Up | Third Follow-Up | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interleukin-4 (pg/mL) | Intervention | 129.97 ± 37.73 | 108.73 ± 27.06 | 108.24 ± 10.49 | 94.80 ± 24.32 | <0.01 * |
| Placebo | 137.29 ± 22.55 | 139.81 ± 26.57 | 171.20 ± 19.37 | 149.45 ± 33.68 | ||
| Interleukin-6 (pg/mL) | Intervention | 4.407 ± 0.715 | 4.236 ± 1.138 | 5.012 ± 1.242 | 2.494 ± 0.483 | <0.05 * |
| Placebo | 4.747 ± 1.246 | 3.418 ± 0.874 | 3.284 ± 0.592 | 4.982 ± 0.943 | ||
| Interleukin-8 (pg/mL) | Intervention | 231.82 ± 49.67 | 223.12 ± 36.85 | 205.54 ± 26.19 | 185.83 ± 19.76 | <0.05 * |
| Placebo | 209.78 ± 34.43 | 213.31 ± 22.21 | 206.27 ± 19.84 | 220.19 ± 25.66 |
| QOLRAD | Group | Baseline | First Follow-Up | Second Follow-Up | Third Follow-Up | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall | Intervention | 5.268 ± 1.955 | 5.712 ± 1.675 | 5.642 ± 1.741 | 5.971 ± 1.999 | <0.05 * |
| Placebo | 5.466 ± 1.850 | 5.621 ± 1.077 | 5.549 ± 1.799 | 5.512 ± 2.005 | ||
| Vitality | Intervention | 5.027 ± 1.647 | 5.633 ± 1.024 | 5.567 ± 1.889 | 5.873 ± 2.010 | <0.05 * |
| Placebo | 5.255 ± 1.647 | 5.536 ± 1.024 | 5.353 ± 1.889 | 5.405 ± 2.010 | ||
| Emotional Distress | Intervention | 5.287 ± 1.003 | 5.730 ± 1.691 | 5.613 ± 1.785 | 5.980 ± 1.036 | <0.05 * |
| Placebo | 5.484 ± 1.929 | 5.608 ± 1.153 | 5.578 ± 1.814 | 5.546 ± 2.032 | ||
| Sleep Disturbance | Intervention | 5.340 ± 2.022 | 5.748 ± 1.741 | 5.612 ± 1.787 | 5.996 ± 1.061 | 0.535 |
| Placebo | 5.509 ± 1.958 | 5.678 ± 1.148 | 5.580 ± 1.797 | 5.816 ± 2.025 | ||
| Food/Drink Problems | Intervention | 5.143 ± 1.995 | 5.667 ± 1.670 | 5.670 ± 1.708 | 5.917 ± 1.987 | 0.339 |
| Placebo | 5.135 ± 1.847 | 5.614 ± 1.979 | 5.477 ± 1.773 | 5.602 ± 1.975 | ||
| Physical/Social Functioning | Intervention | 5.468 ± 1.101 | 5.780 ± 1.722 | 5.720 ± 1.797 | 6.060 ± 2.030 | <0.05 * |
| Placebo | 5.565 ± 1.950 | 5.643 ± 1.142 | 5.690 ± 1.896 | 5.565 ± 2.068 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, E.S.S.; Zaman, R.; Memon, M.A.; Tan, C.K. Effect of Fermented Soybean (FSB) Supplementation on Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). Nutrients 2024, 16, 2779. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162779
Tan ESS, Zaman R, Memon MA, Tan CK. Effect of Fermented Soybean (FSB) Supplementation on Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). Nutrients. 2024; 16(16):2779. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162779
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Eugenie Sin Sing, Rahela Zaman, Muhammad Akbar Memon, and Chung Keat Tan. 2024. "Effect of Fermented Soybean (FSB) Supplementation on Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)" Nutrients 16, no. 16: 2779. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162779
APA StyleTan, E. S. S., Zaman, R., Memon, M. A., & Tan, C. K. (2024). Effect of Fermented Soybean (FSB) Supplementation on Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD). Nutrients, 16(16), 2779. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162779






