Anorexia and Bulimia Nervosa in Spanish Middle-Aged Adults: Links to Sociodemographic Factors, Diet, and Lifestyle
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sampling
2.2. Ethical Considerations
2.3. Instrument and Variables
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Statistical Analyses
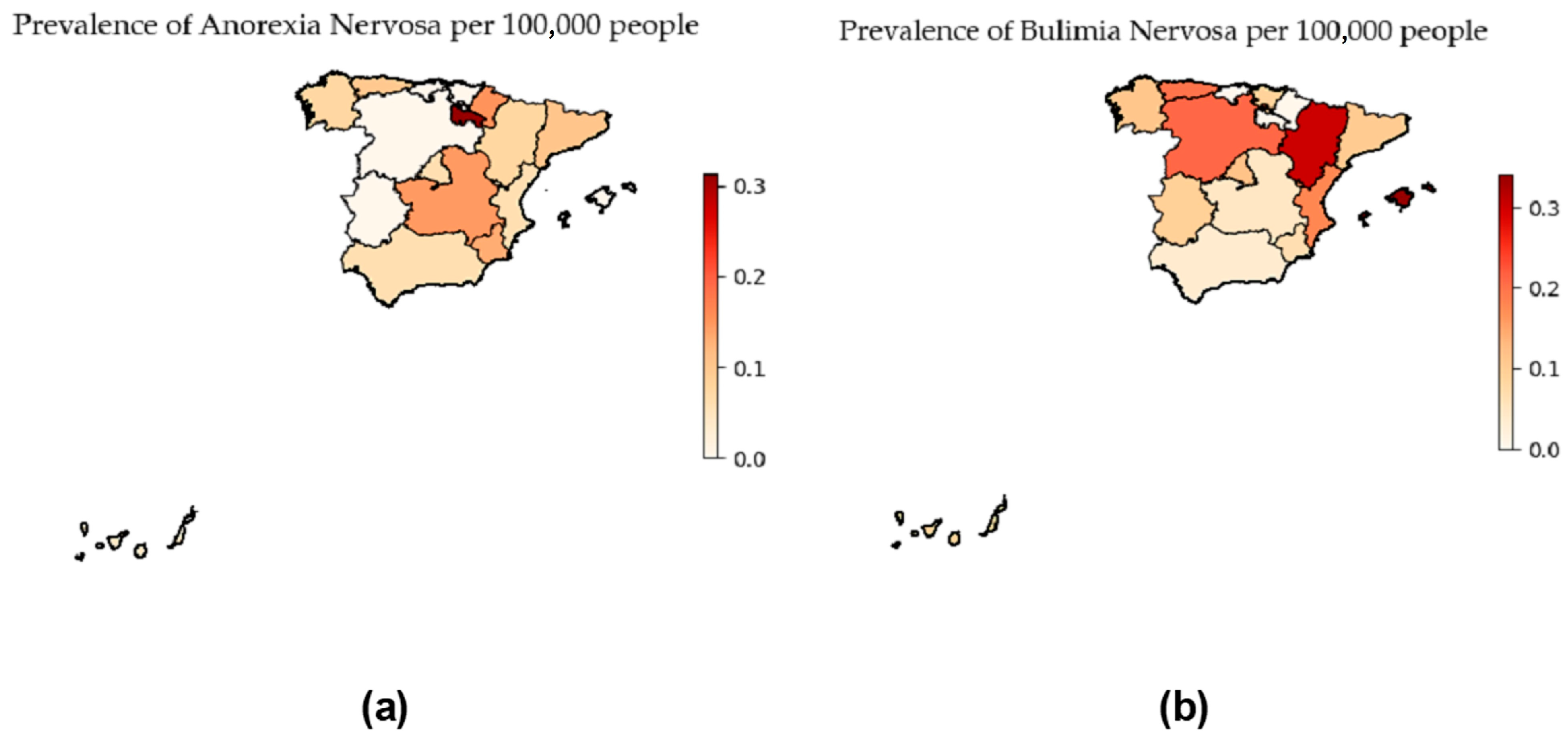
3. Results
4. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
- Concerns about body image and lack of control over food intake were reported by 50% and 28%, respectively, suggesting potential undiagnosed disorders.
- Significant BMI differences were noted between healthy individuals and those with anorexia or bulimia.
- A growing prevalence of eating disorders is found among both women and men and across various age groups, challenging entrenched stereotypes.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association (APA). Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Association (APA): Washington, DC, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, H.; Wan, Y.; Li, C.; Yu, D. An update on the prevalence of eating disorders in the general population: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eat. Weight Disord. EWD 2022, 27, 415–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sansfaçon, J.; Booij, L.; Gauvin, L.; Fletcher, É.; Islam, F.; Israël, M.; Steiger, H. Pretreatment motivation and therapy outcomes in eating disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2020, 53, 1879–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteleone, P.; Brambilla, F. Multiple Comorbidities in People with Eating Disorders. Comorb. Ment. Phys. Disord. 2014, 179, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solmi, M.; Monaco, F.; Højlund, M.; Monteleone, A.M.; Trott, M.; Firth, J.; Carfagno, M.; Eaton, M.; De Toffol, M.; Vergine, M.; et al. Outcomes in people with eating disorders: A transdiagnostic and disorder-specific systematic review, meta-analysis and multivariable meta-regression analysis. World Psychiatry 2024, 23, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, S.N.; Fitzsimmons-Craft, E.E.; Austin, S.B.; Wilfley, D.E.; Taylor, C.B. Estimated prevalence of eating disorders in Singapore. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2020, 54, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galmiche, M.; Déchelotte, P.; Lambert, G.; Tavolacci, M.P. Prevalence of eating disorders over the 2000–2018 period: A systematic literature review. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchison, D.; Hay, P.; Griffiths, S.; Murray, S.B.; Bentley, C.; Gratwick-Sarll, K.; Harrison, C.; Mond, J. Disentangling body image: The relative associations of overvaluation, dissatisfaction, and preoccupation with psychological distress and eating disorder behaviors in male and female adolescents. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2016, 50, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfalahi, M.; Mahadevan, S.; Balushi, R.; Chan, M.F.; Saadon, M.A.; Al-Adawi, S.; Qoronfleh, M.W. Prevalence of eating disorders and disordered eating in Western Asia: A systematic review and meta-Analysis. Eat. Disord. 2021, 30, 556–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapa, D.A.N.; Johnson, S.N.; Richson, B.N.; Bjorlie, K.; Won, Y.Q.; Nelson, S.V.; Ayres, J.; Jun, D.; Forbush, K.T.; Christensen, K.A.; et al. Eating-disorder psychopathology in female athletes and non-athletes: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2022, 55, 861–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackard, D.M.; Richter, S.; Frisch, M.J.; Mangham, D.; Cronemeyer, C.L. Eating disorder treatment among women forty and older: Increases in prevalence over time and comparisons to young adult patients. J. Psychosom. Res. 2013, 74, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elran-Barak, R.; Fitzsimmons-Craft, E.E.; Benyamini, Y.; Crow, S.J.; Peterson, C.B.; Hill, L.L.; Crosby, R.D.; Mitchell, J.E.; Le Grange, D. Anorexia Nervosa, Bulimia Nervosa, and Binge Eating Disorder in Midlife and Beyond. J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2015, 203, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangweth-Matzek, B.; Hoek, H.W. Epidemiology and treatment of eating disorders in men and women of middle and older age. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2017, 30, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, J.H.; Runfola, C.D. Eating disorders in midlife women: A perimenopausal eating disorder? Maturitas 2016, 85, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksen, C.A.; Mackenzie, C.S.; Fergusson, P.; Bouchard, D.R. Does Age Impact the Clinical Presentation of Adult Women Seeking Specialty Eating Disorder Treatment? J. Nerv. Ment. Dis. 2020, 208, 742–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellard, A.M.; Cornelissen, P.L.; Mian, E.; Cazzato, V. The ageing body: Contributing attitudinal factors towards perceptual body size estimates in younger and middle-aged women. Arch. Women’s Ment. Health 2021, 24, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hockey, A.; Barlow, F.K.; Shiels, A.L.; Donovan, C.L. Body dissatisfaction in midlife women: The applicability of the tripartite influence model. Body Image 2021, 39, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biernacki, P.; Waldorf, D. Snowball Sampling: Problems and Techniques of Chain Referral Sampling. Sociol. Methods Res. 1981, 10, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2008, 61, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandri, E.; Piredda, M.; De Maria, M.; Mancin, S.; Sguanci, M.; Cabo, A.; Cerdá Olmedo, G. Development and psychometric testing of the nutritional and social health habits scale (NutSo-HH): A methodological review of existing tools. MethodsX 2024, 12, 102768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancato, G.; Macchia, S.; Murgia, M.; Signore, M.; Simeoni, G. Handbook of Recommended Practices for Questionnarie Development and Testing in European Statistical Systems; Italian National Institute of Statistics (ISTAT): Rome, Italy, 2004; 162p, Available online: https://www.istat.it/it/files/2013/12/Handbook_questionnaire_development_2006.pdf (accessed on 16 April 2024).
- Norte Navarro, A.I.; Ortiz Moncada, R. Quality of the Spanish Diet According to the Healthy Eating Index. Nutr. Hosp. 2011, 26, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grupo Colaborativo de la Sociedad Española de Nutrición Comunitaria (SENC). Guías Alimentarias Para La Población Española; La Nueva Pirámide de La Alimentación Saludable. Nutr. Hosp. 2016, 33, 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- Sandri, E.; Borghesi, D.; Cantín Larumbe, E.; Cerdá Olmedo, G.; Vega-Bello, M.J.; Bernalte Martí, V. Intermittent Fasting: Socio-Economic Profile of Spanish Citizens Who Practice It and the Influence of This Dietary Pattern on the Health and Lifestyle Habits of the Population. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandri, E.; Sguanci, M.; Cantín Larumbe, E.; Cerdá Olmedo, G.; Werner, L.U.; Piredda, M.; Mancin, S. Plant-Based Diets versus the Mediterranean Dietary Pattern and Their Socio-Demographic Determinants in the Spanish Population: Influence on Health and Lifestyle Habits. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangha, S.; Oliffe, J.L.; Kelly, M.T.; McCuaig, F. Eating Disorders in Males: How Primary Care Providers Can Improve Recognition, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Am. J. Men’s Health 2019, 13, 155798831985742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Effatpanah, M.; Nakhostin-Ansari, A.; Gorgani, F.; Khotbehsara, S.T.; Seifi, S.; Nasoori, H.; Memari, A.H.; Darijani, S.R. Burden and Epidemiology of Mental Disorders in the Middle East and North Africa from 1990 to 2019: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study. Balk. Med. J. 2024, 41, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulik, C.M.; Coleman JR, I.; Hardaway, J.A.; Breithaupt, L.; Watson, H.J.; Bryant, C.D.; Breen, G. Genetics and neurobiology of eating disorders. Nat. Neurosci. 2022, 25, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falvey, S.E.; Hahn, S.L.; Anderson, O.S.; Lipson, S.K.; Sonneville, K.R. Diagnosis of Eating Disorders Among College Students: A Comparison of Military and Civilian Students. Mil. Med. 2021, 186, 975–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiotsa, B.; Naccache, B.; Duval, M.; Rocher, B.; Grall-Bronnec, M. Social media use and body image disorders: Association between frequency of comparing one’s own physical appearance to that of people being followed on social media and body dissatisfaction and drive for thinness. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparicio-Martinez, P.; Perea-Moreno, A.J.; Martinez-Jimenez, M.P.; Redel-Macías, M.D.; Pagliari, C.; Vaquero-Abellan, M. Social Media, Thin-Ideal, Body Dissatisfaction and Disordered Eating Attitudes: An Exploratory Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nechita, D.; Bud, S.; David, D. Shame and eating disorders symptoms: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 54, 1899–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciwoniuk, N.; Wayda-Zalewska, M.; Kucharska, K. Distorted Body Image and Mental Pain in Anorexia Nervosa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallaram, G.K.; Sharma, P.; Kattula, D.; Singh, S.; Pavuluru, P. Body image perception, eating disorder behavior, self-esteem and quality of life: A cross-sectional study among female medical students. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoletić, E.; Duraković-Belko, E. Body image distortion, perfectionism and eating disorder symptoms in risk group of female ballet dancers and models and in control group of female students. Psychiatr. Danub. 2009, 21, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hicks, R.E.; Kenny, B.; Stevenson, S.; Vanstone, D.M. Risk factors in body image dissatisfaction: Gender, maladaptive perfectionism, and psychological wellbeing. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koutra, K.; Mouatsou, C.; Psoma, S. The Influence of Positive and Negative Aspects of Perfectionism on Psychological Distress in Emerging Adulthood: Exploring the Mediating Role of Self-Compassion. Behav. Sci. 2023, 13, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swami, V. Negative body image and eating disorder symptomatology among young women identifying with goth subculture. Body Image 2017, 21, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.E.; Lechtenberg, E. Nutrition through the Life Cycle; Cengage Leaning: Boston, MA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dalle Grave, R.; Calugi, S.; Marchesini, G. Compulsive exercise to control shape or weight in eating disorders: Prevalence, associated features, and treatment outcome. Compr. Psychiatry 2008, 49, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Qi, L.; Liu, S.; Hu, W.; Cao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Tang, M.; Lv, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, Y. Body Dissatisfaction and Disordered Eating Behaviors: The Mediation Role of Smartphone Addiction and Depression. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, S.; McLean, S.A.; Bryant, E.; Le, A.; Marks, P.; National Eating Disorder Research Consortium; Touyz, S.; Maguire, S. Risk factors for eating disorders: Findings from a rapid review. J. Eat. Disord. 2023, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, P.; Mitchison, D. Urbanization and eating disorders. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2021, 34, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorrell, S.; Trainor, C.; Le Grange, D. The impact of urbanization on risk for eating disorders. Curr. Opin. Psychiatry 2019, 32, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Son, G.E.; Van Hoeken, D.; Bartelds, A.I.M.; Van Furth, E.F.; Hoek, H.W. Urbanisation and the incidence of eating disorders. Br. J. Psychiatry 2006, 189, 562–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freizinger, M.; Jhe, G.B.; Dahlberg, S.E.; Pluhar, E.; Raffoul, A.; Slater, W.; Shrier, L.A. Binge-eating behaviors in adolescents and young adults during the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Eat. Disord. 2022, 10, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madani, S.; Ahmadi, A.; Shoaei-Jouneghani, F.; Moazen, M.; Sasani, N. The relationship between the Mediterranean diet and Axis I disorders: A systematic review of observational studies. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 10, 3241–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalindjian, N.; Hirot, F.; Stona, A.C.; Huas, C.; Godart, N. Early Detection of Eating Disorders: A Scoping Review. Eat. Weight Disord. 2022, 27, 21–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicula, M.; Pellegrini, D.; Grennan, L.; Bhatnagar, N.; McVey, G.; Couturier, J. Help-seeking attitudes and behaviours among youth with eating disorders: A scoping review. J. Eat. Disord. 2022, 10, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Y. Social media usage for health purposes: Systematic review. J. Med. Internet Res. 2020, 23, e17917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, M.M.; Burgermaster, M.; Mamykina, L. The use of social media in nutrition interventions for adolescents and young adults-A systematic review. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2018, 120, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, H.; Paul, T.; Jain, E.; Loh, H.; Kazmi, S.H.; Dua, R.; Rodriguez, R.; Naqvi, S.A.; Bidika, E. A Clinical Overview of Anorexia Nervosa and Overcoming Treatment Resistance. Avicenna J. Med. 2022, 13, 003–014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, P.; Palavras, M.A.; da Luz, F.Q.; Dos Anjos Garnes, S.; Sainsbury, A.; Touyz, S.; Appolinario, J.C.; Claudino, A.M. Physical and mental health outcomes of an integrated cognitive behavioural and weight management therapy for people with an eating disorder characterized by binge eating and a high body mass index: A randomized controlled trial. BMC Psychiatry 2022, 22, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, J.E.; Peterson, C.B. Anorexia Nervosa. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.H. Health concern, food choice motives, and attitudes toward healthy eating: The mediating role of food choice motives. Appetite 2008, 51, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karam, J.; Haddad, C.; Sacre, H.; Serhan, M.; Salameh, P.; Jomaa, L. Financial Wellbeing and Quality of Life Among a Sample of the Lebanese Population: The Mediating Effect of Food Insecurity. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 906646, Erratum in Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1029025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urhan, M.; Okut Aysin, E. Nutritional and health behaviour predictors of the weight gain during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 2993–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, M.; Langiano, E.; Falese, L.; Diotaiuti, P.; Cortis, C.; De Vito, E. Changes in Physical Activity Levels and Eating Behaviours during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Sociodemographic Analysis in University Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Mean ± SD or n (%) | |
|---|---|
| Male | 1650 (16.64%) |
| Female | 8263 (83.36%) |
| Age (years) | 39.35 ± 5.57 |
| Male Age (years) | 39.87 ± 5.55 |
| Female Age (years) | 39.25 ± 5.58 |
| Level of education | |
| Basic education | 2703 (27.27%) |
| Higher education | 7210 (72.73%) |
| Income level | |
| Low | 4032 (40.67%) |
| Medium–high | 5430 (54.78%) |
| Do not know/no answer | 451 (4.55%) |
| Municipality | |
| <2000 | 444 (4.48%) |
| 2000–10,000 | 1603 (16.17%) |
| >10,000 | 7866 (79.35%) |
| Diagnosed Eating Disorder | |
|---|---|
| No ED | 9582 (96.66%) |
| Anorexia nervosa | 36 (0.36%) |
| Bulimia nervosa | 53 (0.53%) |
| More than one ED | 48 (0.48%) |
| Other ED | 194 (1.97%) |
| Never | Rarely | Occasionally | Frequently | Very Often | Always | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obesophobia | 845 (8.50%) | 1552 (15.66%) | 2605 (26.28%) | 2409 (24.30%) | 1421 (14.33%) | 1081 (10.90%) |
| No control | 1393 (14.05%) | 2851 (28.76%) | 2880 (29.05%) | 1553 (15.67%) | 914 (9.22%) | 322 (3.25%) |
| Body image | 287 (2.90%) | 1614 (16.28%) | 3011 (30.37%) | 2691 (27.15%) | 1378 (13.90%) | 932 (9.40%) |
| Never | Rarely | Occasionally | Frequently | Very Often | Always | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obesophobia | 3 | 4 | 10 | 21 | 26 | 25 |
| (3.37%) | (4.49%) | (11.24%) | (23.60%) | (29.21%) | (28.09%) | |
| No control | 7 | 13 | 17 | 23 | 19 | 10 |
| (7.87%) | (14.61%) | (19.10%) | (25.84%) | (21.35%) | (11.24%) | |
| Body image | 1 | 4 | 13 | 29 | 22 | 20 |
| (1.12%) | (4.49%) | (14.61%) | (32.58%) | (24.72%) | (22.47%) |
| Numerical Variable | Healthy Population | Anorexia | Bulimia | p-Value $ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI | 24.34 ± 4.39 | 20.45 ± 2.27 | 25.25 ± 5.57 | H-A (<0.001) |
| H-B (1.00) | ||||
| A-B (<0.001) | ||||
| IASE | 54.18 ± 9.95 | 52.25 ± 10.13 | 51.57 ± 12.03 | 0.21 ‡ |
| Fried food | 2.15 ± 0.78 | 1.86 ± 0.76 | 2.04 ± 0.78 | H-A (0.06) |
| H-B (0.87) | ||||
| A-B (0.81) | ||||
| Fast food | 2.33 ± 0.75 | 1.86 ± 0.83 | 2.42 ± 0.72 | H-A (<0.001) |
| H-B (1.00) | ||||
| A-B (<0.001) | ||||
| Ultra-processed food | 2.46 ± 0.93 | 2.12 ± 1.04 | 2.44 ± 0.95 | 0.40 ‡ |
| Fish | 1.86 ± 0.49 | 1.85 ± 0.55 | 1.83 ± 0.49 | 0.91 ‡ |
| Water | 3.40 ± 0.63 | 3.50 ± 0.61 | 3.49 ± 0.61 | 0.37 ‡ |
| Sugary soft drinks | 1.37 ± 0.65 | 1.33 ± 0.68 | 1.60 ± 0.84 | 0.07 ‡ |
| Juice | 1.20 ± 0.50 | 1.28 ± 0.70 | 1.17 ± 0.43 | 0.94 ‡ |
| Coffee and energy drinks | 1.79 ± 0.72 | 1.94 ± 0.86 | 1.81 ± 0.59 | 0.54 ‡ |
| Sedentary lifestyle | 1.66 ± 0.87 | 1.46 ± 0.76 | 1.55 ± 0.86 | 0.95 ‡ |
| Self-perceived health | 3.82 ± 0.83 | 3.72 ± 0.88 | 3.58 ± 0.89 | 0.06 ‡ |
| Sport | 145.71 ± 165.86 | 267.71 ± 203.37 | 160.19 ± 160.14 | H-A (<0.001) |
| H-B (0.77) | ||||
| A-B (0.047) | ||||
| Sleeping hours | 2.44 ± 0.73 | 2.31 ± 0.75 | 2.08 ± 0.70 | H-A (1.00) |
| H-B (<0.001) | ||||
| A-B (0.33) | ||||
| Getting up rested | 2.52 ± 0.59 | 2.36 ± 0.64 | 2.34 ± 0.59 | H-A (0.34) |
| H-B (0.13) | ||||
| A-B (1.00) | ||||
| Sleep quality | 3.31 ± 1.03 | 2.94 ± 1.04 | 2.89 ± 1.44 | H-A (0.05) |
| H-B (0.14) | ||||
| A-B (1.00) | ||||
| Smoking | 1.22 ± 0.62 | 1.25 ± 0.77 | 1.28 ± 0.66 | 0.46 ‡ |
| Alcohol | 1.74 ± 0.88 | 1.64 ± 0.87 | 1.72 ± 1.03 | 0.54 ‡ |
| Getting drunk | 1.04 ± 0.26 | 1.06 ± 0.23 | 1.23 ± 0.64 | H-A (1.00) |
| H-B (<0.001) | ||||
| A-B (0.14) | ||||
| Night outings | 1.09 ± 0.31 | 1.06 ± 0.23 | 1.11 ± 0.38 | 0.78 ‡ |
| Kerrypnx | Healthy Population n (%) | Anorexia n (%) | Bulimia n (%) | p-Value & |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Men | 1641 (17.13%) | 1 (2.78%) | 2 (3.77%) | <0.001 |
| Women | 7941 (82.87%) | 35 (97.22%) | 51 (96.23%) | |
| 3.51 × 10−3 § | 0.14 § | 0.06 § | ||
| High education | 6985 (72.9%) | 30 (83.33%) | 40 (75.47%) | 0.19 |
| Low education | 2597 (27.1%) | 6 (16.67%) | 13 (24.53%) | |
| Low income | 5273 (57.60%) | 16 (50.00%) | 26 (52.00%) | 0.54 |
| Medium–High income | 3882 (42.40%) | 16 (50.00%) | 24 (48.00%) | |
| Small city | 423 (4.41%) | 2 (5.56%) | 3 (5.66%) | 0.55 |
| Medium city | 1529 (15.96%) | 9 (25.00%) | 10 (18.87%) | |
| Big city | 7630 (79.63%) | 25 (69.44%) | 40 (75.47%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sandri, E.; Cantín Larumbe, E.; Cerdá Olmedo, G.; Luciani, G.; Mancin, S.; Sguanci, M.; Piredda, M. Anorexia and Bulimia Nervosa in Spanish Middle-Aged Adults: Links to Sociodemographic Factors, Diet, and Lifestyle. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162671
Sandri E, Cantín Larumbe E, Cerdá Olmedo G, Luciani G, Mancin S, Sguanci M, Piredda M. Anorexia and Bulimia Nervosa in Spanish Middle-Aged Adults: Links to Sociodemographic Factors, Diet, and Lifestyle. Nutrients. 2024; 16(16):2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162671
Chicago/Turabian StyleSandri, Elena, Eva Cantín Larumbe, Germán Cerdá Olmedo, Gaia Luciani, Stefano Mancin, Marco Sguanci, and Michela Piredda. 2024. "Anorexia and Bulimia Nervosa in Spanish Middle-Aged Adults: Links to Sociodemographic Factors, Diet, and Lifestyle" Nutrients 16, no. 16: 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162671
APA StyleSandri, E., Cantín Larumbe, E., Cerdá Olmedo, G., Luciani, G., Mancin, S., Sguanci, M., & Piredda, M. (2024). Anorexia and Bulimia Nervosa in Spanish Middle-Aged Adults: Links to Sociodemographic Factors, Diet, and Lifestyle. Nutrients, 16(16), 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162671







