Genes Involved in Susceptibility to Obesity and Emotional Eating Behavior in a Romanian Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Samples
2.2. Anthropometric Measurements
2.3. Emotional Eating Measurement
2.4. Genetic Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
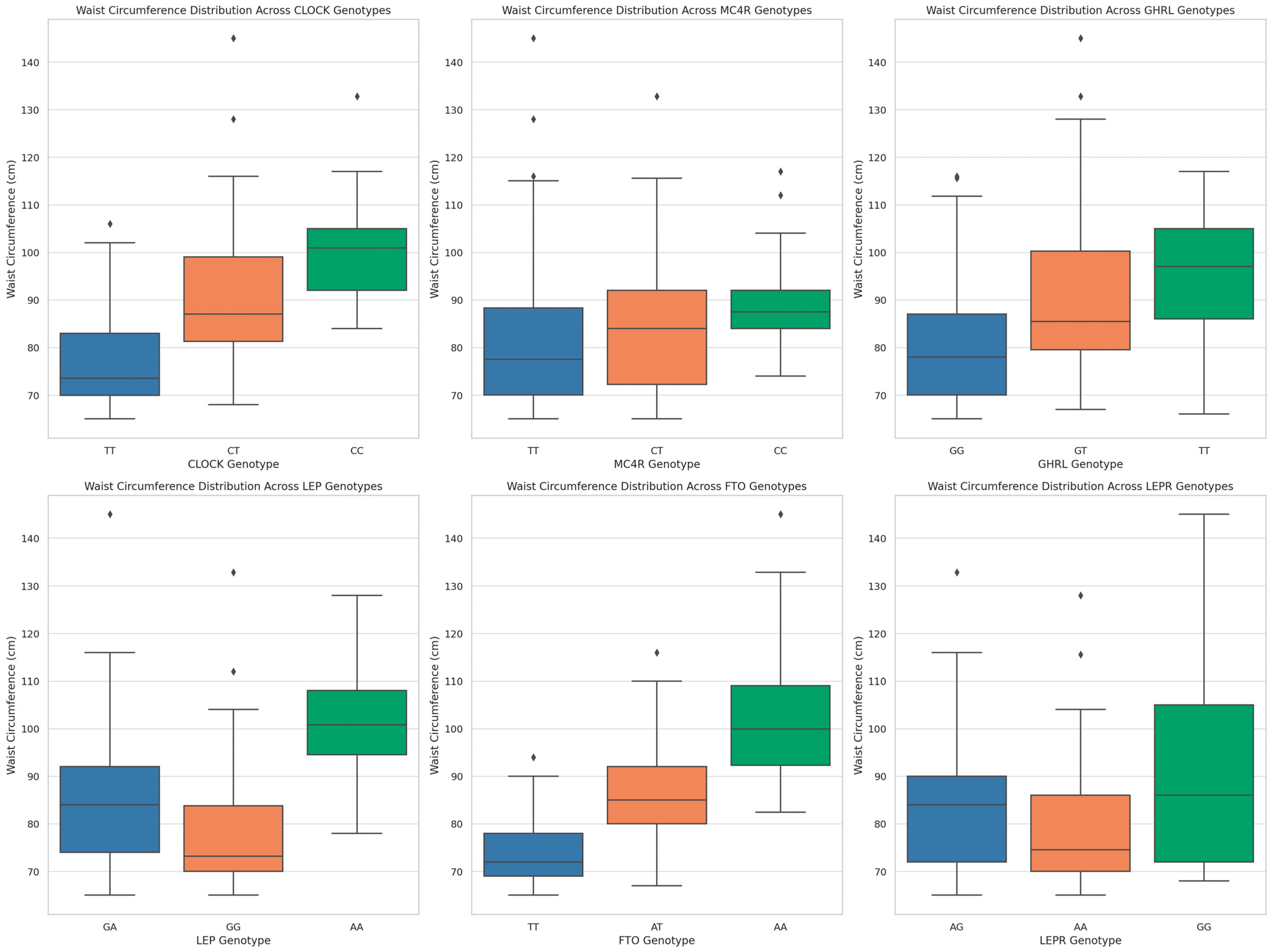
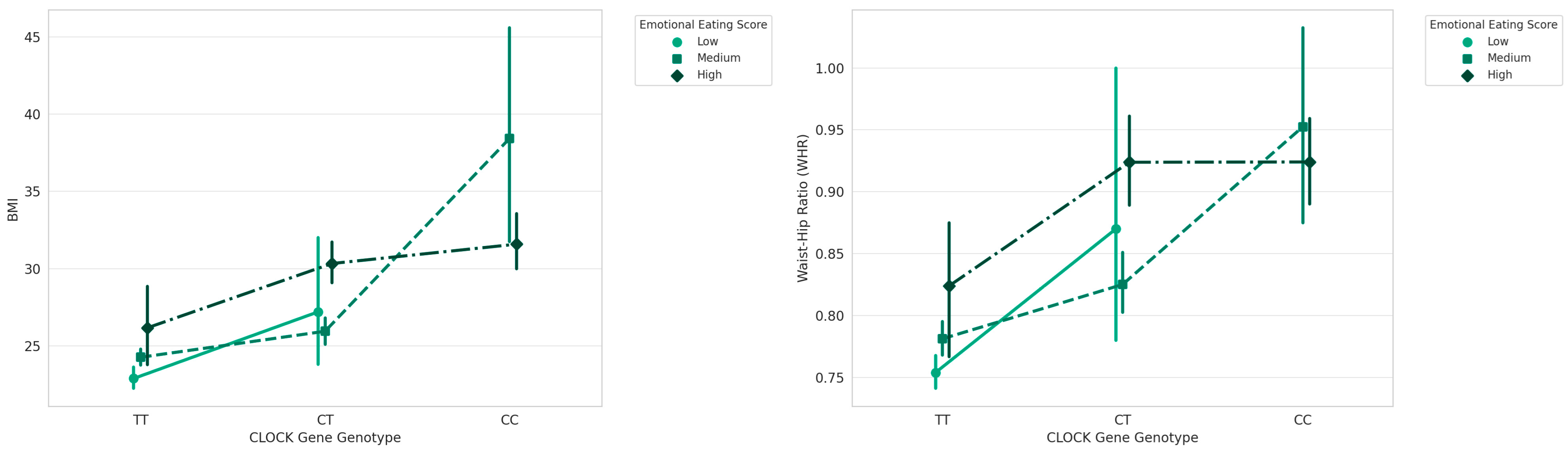
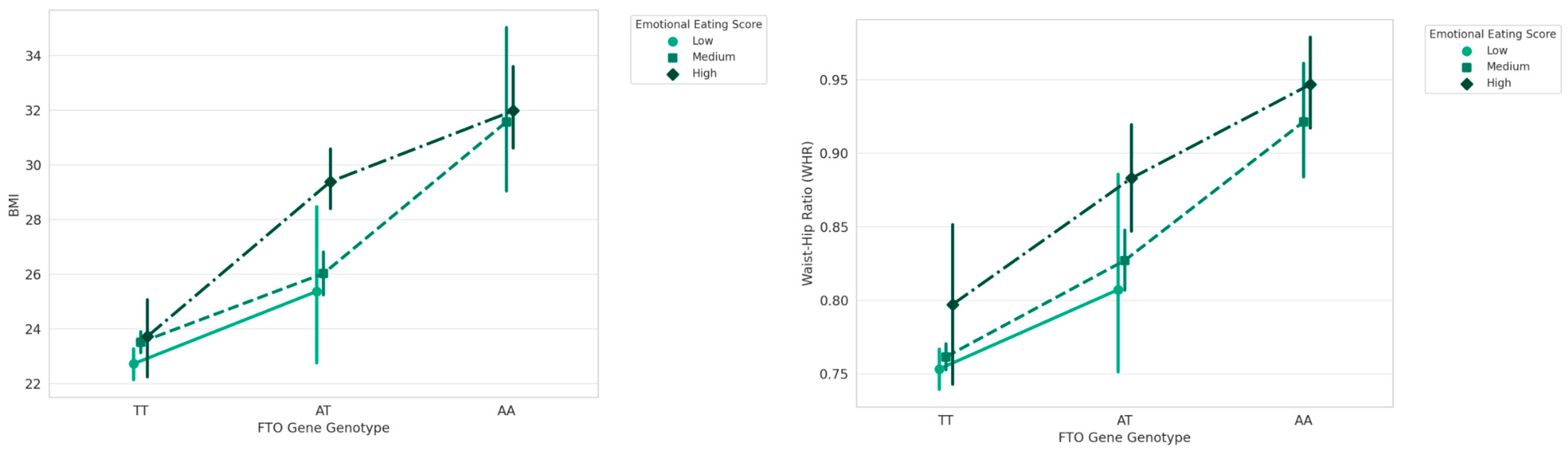
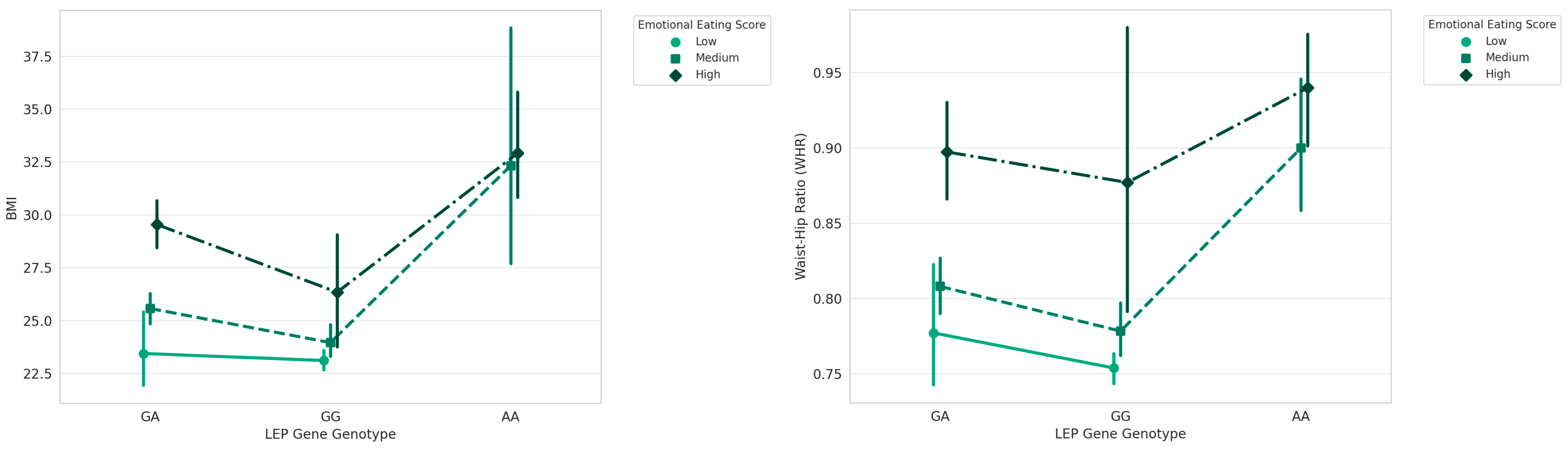
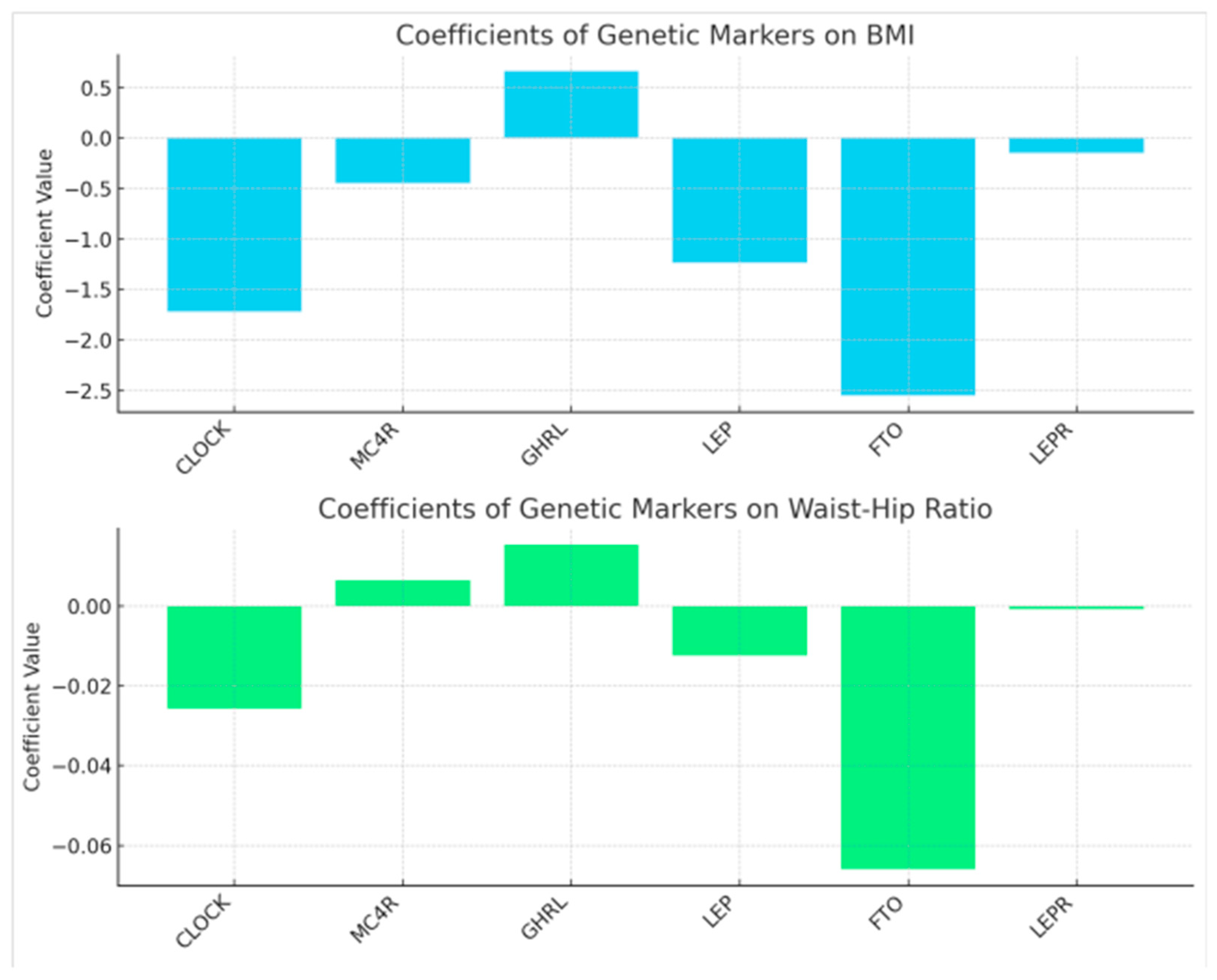
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herle, M.; Smith, A.D.; Kininmonth, A.; Llewellyn, C. The Role of Eating Behaviours in Genetic Susceptibility to Obesity. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremmel, M.; Gerdtham, U.G.; Nilsson, P.M.; Saha, S. Economic Burden of Obesity: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obesity and Overweight. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- Nour, T.Y.; Altintaş, K.H. Effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on obesity and it is risk factors: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popa, S.; Moţa, M.; Popa, A.; Moţa, E.; Serafinceanu, C.; Guja, C.; Catrinoiu, D.; Hâncu, N.; Lichiardopol, R.; Bala, C.; et al. Prevalence of overweight/obesity, abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome and atypical cardiometabolic phenotypes in the adult Romanian population: PREDATORR study. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2016, 39, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineda, E.; Sanchez-Romero, L.M.; Brown, M.; Jaccard, A.; Jewell, J.; Galea, G.; Webber, L.; Breda, J. Forecasting Future Trends in Obesity across Europe: The Value of Improving Surveillance. Obes. Facts 2018, 11, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Li, H. Obesity: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Therapeutics. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 706978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez-Fernández, D.; Mercado-Celis, G.; Flores-Morales, J.; Clavellina-Gaytán, D.; Vidrio, R.; Vidrio, E.; Mosti, M.; Sánchez-Aguilar, H.; Rodriguez, D.; León, P.; et al. Analysis of Gene Candidate SNP and Ancestral Origin Associated to Obesity and Postoperative Weight Loss in a Cohort of Obese Patients Undergoing RYGB. Obes. Surg. 2017, 27, 1481–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, R.J.F.; Yeo, G.S.H. The genetics of obesity: From discovery to biology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2021, 23, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzi, M.O. Genetics of obesity: What genetic association studies have taught us about the biology of obesity and its complications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankinen, T.; Zuberi, A.; Chagnon, Y.C.; Weisnagel, S.J.; Argyropoulos, G.; Walts, B.; Pérusse, L.; Bouchard, C. The human obesity gene map: The 2005 update. Obesity 2006, 14, 529–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, F.R.; Loos, R.J.F. Developments in obesity genetics in the era of genome-wide association studies. J. Nutrigenet. Nutrigenom. 2011, 4, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.R.; Klimentidis, Y.C.; Dulin-Keita, A.; Casazza, K. Genetic influences in childhood obesity: Recent progress and recommendations for experimental designs. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Loos, R.J.F. Obesity genomics: Assessing the transferability of susceptibility loci across diverse populations. Genome Med. 2013, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favara, G.; Maugeri, A.; Magnano San Lio, R.; Barchitta, M.; Agodi, A. Exploring Gene-Diet Interactions for Mother-Child Health: A Systematic Review of Epidemiological Studies. Nutrients 2024, 16, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deram, S.; Villares, S.M.F. Genetic variants influencing effectiveness of weight loss strategies. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2009, 53, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahati, S.; Qorbani, M.; Naghavi, A.; Nia, M.H.; Pishva, H. Association between CLOCK 3111 T/C polymorphism with ghrelin, GLP-1, food timing, sleep and chronotype in overweight and obese Iranian adults. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2022, 22, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Montes, E.; Rodríguez-Barranco, M.; Ching-López, A.; Artacho, R.; Huerta, J.M.; Amiano, P.; Lasheras, C.; Moreno-Iribas, C.; Jimenez-Zabala, A.; Chirlaque, M.D.; et al. Circadian clock gene variants and their link with chronotype, chrononutrition, sleeping patterns and obesity in the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (EPIC) study. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 1977–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becer, E.; Ergoren, M.C. Dual Effect of the GHRL Gene Variant in the Molecular Pathogenesis of Obesity. Balkan J. Med. Genet. 2021, 24, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atalayer, D.; Gibson, C.; Konopacka, A.; Geliebter, A. Ghrelin and Eating Disorders. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 40, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalla, M.A.; Stengel, A. The Role of Ghrelin in Anorexia Nervosa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, M.; Adam, V.; Palomera, E.; Blesa, S.; Díaz, G.; Buquet, X.; Serra-Prat, M.; Martín-Escudero, J.C.; Palanca, A.; Chaves, J.F.; et al. Ghrelin Gene Variants Influence on Metabolic Syndrome Components in Aged Spanish Population. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, R.J.F.; Yeo, G.S.H. The bigger picture of FTO: The first GWAS-identified obesity gene. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, D.S.; Calton, M.A.; Kim, M.J.; Kwok, P.Y.; Miljkovic, I.; Harris, T.; Koster, A.; Liu, Y.; Tranah, G.J.; Ahituv, N.; et al. Genetic association study of adiposity and melanocortin-4 receptor (MC4R) common variants: Replication and functional characterization of non-coding regions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leońska-Duniec, A.; Jastrzȩbski, Z.; Zarȩbska, A.; Smółka, W.; Ciȩszczyk, P. Impact of the Polymorphism Near MC4R (rs17782313) on Obesity- and Metabolic-Related Traits in Women Participating in an Aerobic Training Program. J. Hum. Kinet. 2017, 58, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Murguia, T.; Torres-Castillo, N.; Magaña-De la Vega, L.; Rodríguez-Reyes, S.C.; Campos-Pérez, W.; Martínez-López, E. Role of Leu72Met of GHRL and Gln223Arg of LEPR Variants on Food Intake, Subjective Appetite, and Hunger-Satiety Hormones. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauber, E.; Last, K.S.; Olive, P.J.W.; Kyriacou, C.P. Clock gene evolution and functional divergence. J. Biol. Rhythms 2004, 19, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagannath, A.; Taylor, L.; Wakaf, Z.; Vasudevan, S.R.; Foster, R.G. The genetics of circadian rhythms, sleep and health. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, R128–R138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rijo-Ferreira, F.; Takahashi, J.S. Genomics of circadian rhythms in health and disease. Genome Med. 2019, 11, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, W.; Wang, X. Studies on the fat mass and obesity-associated (FTO) gene and its impact on obesity-associated diseases. Genes Dis. 2022, 10, 2351–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Serri, A.; Alroughani, R.; Al-Temaimi, R.A. The FTO gene polymorphism rs9939609 is associated with obesity and disability in multiple sclerosis patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Lu, X.Z.; Yang, X.X.; Wang, H.; Geng, H.Y.; Gong, G.; Zhan, Y.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Yang, Z.J. GHRL Gene Leu72Met Polymorphism and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis Involving 8,194 Participants. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Proenca, R.; Maffei, M.; Barone, M.; Leopold, L.; Friedman, J.M. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 1994, 372, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.C.; Trujillo, J.; Farias, D.R.; Kac, G. Polymorphisms in the leptin (rs7799039) gene are associated with an increased risk of excessive gestational weight gain but not with leptin concentration during pregnancy. Nutr. Res. 2017, 47, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskiliene, A.; Smalinskiene, A.; Kriaucioniene, V.; Lesauskaite, V.; Petkeviciene, J. Associations of MC4R, LEP, and LEPR Polymorphisms with Obesity-Related Parameters in Childhood and Adulthood. Genes 2021, 12, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartaglia, L.A.; Dembski, M.; Weng, X.; Deng, N.; Culpepper, J.; Devos, R.; Richards, G.J.; Campfield, L.A.; Clark, F.T.; Deeds, J.; et al. Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, OB-R. Cell 1995, 83, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Pasero, H.; Aguilar-Aguilar, E.; Colmenarejo, G.; de Molina, A.R.; Reglero, G.; Loria-Kohen, V. The Q223R Polymorphism of the Leptin Receptor Gene as a Predictor of Weight Gain in Childhood Obesity and the Identification of Possible Factors Involved. Genes 2020, 11, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.X. The melanocortin-4 receptor: Physiology, pharmacology, and pathophysiology. Endocr. Rev. 2010, 31, 506–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinau, G.; Heyder, N.A.; Tao, Y.X.; Scheerer, P. Structural Complexity and Plasticity of Signaling Regulation at the Melanocortin-4 Receptor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drabsch, T.; Gatzemeier, J.; Pfadenhauer, L.; Hauner, H.; Holzapfel, C. Associations between Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms and Total Energy, Carbohydrate, and Fat Intakes: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2018, 9, 425–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Zheng, Y.; Hruby, A.; Williamson, D.A.; Bray, G.A.; Shen, Y.; Sacks, F.M.; Qi, L. Dietary Protein Modifies the Effect of the MC4R Genotype on 2-Year Changes in Appetite and Food Craving: The POUNDS Lost Trial. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garaulet, M.; Canteras, M.; Morales, E.; López-Guimera, G.; Sánchez-Carracedo, D.; Corbalán-Tutau, M.D. Validation of a questionnaire on emotional eating for use in cases of obesity: The Emotional Eater Questionnaire (EEQ). Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saliva DNA Extraction & WGA Amplification. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/RO/en/technical-documents/protocol/genomics/dna-and-rna-purification/extraction-of-dna-from-saliva (accessed on 28 June 2024).
- Graffelman, J.; Jain, D.; Weir, B. A genome-wide study of Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium with next generation sequence data. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dina, C.; Meyre, D.; Gallina, S.; Durand, E.; Körner, A.; Jacobson, P.; Carlsson, L.M.S.; Kiess, W.; Vatin, V.; Lecoeur, C.; et al. Variation in FTO contributes to childhood obesity and severe adult obesity. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 724–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Guimerà, G.; Dashti, H.S.; Smith, C.E.; Sánchez-Carracedo, D.; Ordovas, J.M.; Garaulet, M. CLOCK 3111 T/C SNP interacts with emotional eating behavior for weight-loss in a Mediterranean population. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S. Association between CLOCK Gene Polymorphisms and Insomnia Risk According to Food Groups: A KoGES Longitudinal Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.B.; Neufeld, E.V.; Dolezal, B.A.; Martin, J.L. Sleep deprivation and obesity in adults: A brief narrative review. BMJ open Sport Exerc. Med. 2018, 4, 2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaulet, M.; Sánchez-Moreno, C.; Smith, C.E.; Lee, Y.C.; Nicolás, F.; Ordovás, J.M. Ghrelin, Sleep Reduction and Evening Preference: Relationships to CLOCK 3111 T/C SNP and Weight Loss. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e000392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garaulet, M.; Lee, Y.C.; Shen, J.; Parnell, L.D.; Arnett, D.K.; Tsai, M.Y.; Lai, C.Q.; Ordovas, J.M. CLOCK genetic variation and metabolic syndrome risk: Modulation by monounsaturated fatty acids. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wei, L.; Zhao, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y. Resveratrol Maintains Lipid Metabolism Homeostasis via One of the Mechanisms Associated with the Key Circadian Regulator Bmal1. Molecules 2019, 24, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Song, Y.; Cheng, X.R.; Xia, S.; Rahman, M.R.T.; Shi, Y.; Le, G. Resveratrol restores the circadian rhythmic disorder of lipid metabolism induced by high-fat diet in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melhorn, S.J.; Askren, M.K.; Chung, W.K.; Kratz, M.; Bosch, T.A.; Tyagi, V.; Webb, M.F.; De Leon, M.R.B.; Grabowski, T.J.; Leibel, R.L.; et al. FTO genotype impacts food intake and corticolimbic activation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cecil, J.E.; Tavendale, R.; Watt, P.; Hetherington, M.M.; Palmer, C.N.A. An obesity-associated FTO gene variant and increased energy intake in children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2558–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karra, E.; O’Daly, O.G.; Choudhury, A.I.; Yousseif, A.; Millership, S.; Neary, M.T.; Scott, W.R.; Chandarana, K.; Manning, S.; Hess, M.E.; et al. A link between FTO, ghrelin, and impaired brain food-cue responsivity. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 3539–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heffernan, S.M.; Stebbings, G.K.; Kilduff, L.P.; Erskine, R.M.; Day, S.H.; Morse, C.I.; McPhee, J.S.; Cook, C.J.; Vance, B.; Ribbans, W.J.; et al. Fat mass and obesity associated (FTO) gene influences skeletal muscle phenotypes in non-resistance trained males and elite rugby playing position. BMC Genet. 2017, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livingstone, K.M.; Celis-Morales, C.; Papandonatos, G.D.; Erar, B.; Florez, J.C.; Jablonski, K.A.; Razquin, C.; Marti, A.; Heianza, Y.; Huang, T.; et al. FTO genotype and weight loss: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 9563 individual participant data from eight randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2016, 354, i4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merritt, D.C.; Jamnik, J.; El-Sohemy, A. FTO genotype, dietary protein intake, and body weight in a multiethnic population of young adults: A cross-sectional study. Genes Nutr. 2018, 13, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza García, A.S.; Martínez Moreno, A.G.; Reyes Castillo, Z. The role of ghrelin and leptin in feeding behavior: Genetic and molecular evidence. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2021, 68, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sovetkina, A.; Nadir, R.; Fung, J.N.M.; Nadjarpour, A.; Beddoe, B. The Physiological Role of Ghrelin in the Regulation of Energy and Glucose Homeostasis. Cureus 2020, 12, e7941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.N.; Huang, M.C.; Chang, W.T.; Ko, A.M.S.; Tsai, E.M.; Liu, C.S.; Lee, C.H.; Ko, Y.C. G-2548A polymorphism of the leptin gene is correlated with extreme obesity in Taiwanese aborigines. Obesity 2006, 14, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, S.; Rüstemoǧlu, A.; Tekcan, A.; Taşliyurt, T.; Güven, H.; Yiǧit, S. Investigation of associations between obesity and LEP G2548A and LEPR 668A/G polymorphisms in a Turkish population. Dis. Markers 2013, 35, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Ali, S.; Kallel, A.; Ftouhi, B.; Sediri, Y.; Feki, M.; Slimane, H.; Jemaa, R.; Kaabachi, N. Association of G-2548A LEP polymorphism with plasma leptin levels in Tunisian obese patients. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 42, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soskic, S.; Stokic, E.; Obradovic, M.; Sudar, E.; Tanic, N.; Kupusinac, A.; Djordjevic, J.; Isenovic, E.R. Association of leptin gene polymorphism G-2548A with metabolic and anthropometric parameters in obese patients in a Serbian population: Pilot study. Clin. Lipidol. 2014, 9, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portolés, O.; Sorlí, J.V.; Francés, F.; Coltell, O.; González, J.I.; Sáiz, C.; Corella, D. Effect of genetic variation in the leptin gene promoter and the leptin receptor gene on obesity risk in a population-based case-control study in Spain. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 21, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysalol, E.P.; Uysalol, M.; Serin, I.; Pehlivan, M.; Oyaci, Y.; Pehlivan, S.; Karakas, Z. The effect of leptin gene polymorphisms (LEP rs7799039 and LEPR rs1137101) on febrile neutropenia. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantin, A.; Costache, G.; Sima, A.V.; Glavce, C.S.; Vladica, M.; Popov, D.L. Leptin G-2548A and leptin receptor Q223R gene polymorphisms are not associated with obesity in Romanian subjects. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penes, O.N.; Weber, B.; Pop, A.L.; Bodnarescu-Cobanoglu, M.; Varlas, V.N.; Kucukberksun, A.S.; Cretoiu, D.; Varlas, R.G.; Zetu, C. Gene Polymorphisms LEP, LEPR, 5HT2A, GHRL, NPY, and FTO-Obesity Biomarkers in Metabolic Risk Assessment: A Retrospective Pilot Study in Overweight and Obese Population in Romania. Cardiogenetics 2024, 14, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstmann, A.; Kovacs, P.; Kabisch, S.; Boettcher, Y.; Schloegl, H.; Tönjes, A.; Stumvoll, M.; Pleger, B.; Villringer, A. Common genetic variation near MC4R has a sex-specific impact on human brain structure and eating behavior. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, H.D.; Chen, C.; Gaynor, B.; Shao, J.; Urban, J.F. The porcine translational research database: A manually curated, genomics and proteomics-based research resource. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Molokin, A.; Urban, J.; Solano-Aguilar, G. Effects of fat sources on high fat induced changes in inflammation and lipid metabolism in juvenile pigs (822.3). FASEB J. 2014, 28, 822.3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Chromosome Location | Gene Product | Variant | Function of Protein |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLOCK | 4q12 | A basic helix loop-helix-PAS transcription factor | rs1801260; 3111 T > C | Sleep disorders, metabolic syndrome, obesity, emotional eating |
| FTO | 16q12.2 | 2-oxoglutarate (2-OG) Fe (II) dependent demethylase | rs9939609; T > A | Control of daily food intake, appetite, and satiety-overeating control, nutrients preferences |
| GHRL | 3p25–26 | Ghrelin-obestatin prepropeptide | rs696217 G > T | Obesity, eating disorders, metabolic syndrome |
| LEP | 7q32.1 | Leptin | rs7799039; G > A | Regulates appetite, increases in energy expenditure, body composition |
| LEPR | 1p31.3 | Leptin receptor | rs1137101; A > G Gln223Arg | Mediating leptin signaling |
| MC4R | 18q21.32 | Melanocortin 4 receptor | rs17782313; T > C | One of the major regulator of food intake and energy expenditure |
| Gender | Count | Height (cm) (±SD) | Weight (kg) (±SD) | BMI (kg/m2) (±SD) | Waist Circumferences (cm) (±SD) | HIP Circumferences (cm) (±SD) | WHR (±SD) | SQ (±SD) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MEN | 88 | 178.42 ± 5.02 | 86.09 ± 14.84 | 26.91 ± 3.69 | 92.10 ± 14.42 | 104.38 ± 7.20 | 0.88 ± 0.10 | 7.38 ± 3.85 |
| WOMEN | 132 | 164.97 ± 4.29 | 69.92 ± 12.66 | 25.69 ± 4.97 | 77.97 ± 11.34 | 99.01 ± 6.76 | 0.78 ± 0.07 | 6.07 ± 3.47 |
| Gene | p Value | Chi-Squared Statistic |
|---|---|---|
| CLOCK | 0.120592 | 4.230683 |
| FTO | 0.369244 | 1.992597 |
| GHRL | 0.028898 | 7.087998 |
| LEP | 0.000005 | 24.439422 |
| LEPR | 0.008863 | 9.451751 |
| MC4R | 0.099333 | 4.618563 |
| Genes | Genotype | Distribution (N) |
|---|---|---|
| CLOCK rs1801260; 3111 T > C | TT | 128 |
| CT | 66 | |
| CC | 26 | |
| FTO rs9939609; T > A | TT | 110 |
| AT | 64 | |
| AA | 46 | |
| GHRL rs696217 G > T | GG | 147 |
| GT | 60 | |
| TT | 13 | |
| LEP rs7799039; G > A | GG | 23 |
| GA | 111 | |
| AA | 86 | |
| LEPR rs1137101; A > G | AA | 70 |
| AG | 101 | |
| GG | 49 | |
| MC4R rs17782313; T > C | TT | 124 |
| CT | 70 | |
| CC | 26 |
| Genes | Genotype | BMI Mean (±SD) | N | F (ANOVA) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLOCK | TT | 24.07 ± 2.67 | 128 | 50.041 | 0.001 |
| CT | 27.88 ± 3.75 | 66 | |||
| CC | 32.63 ± 5.86 | 26 | |||
| MC4R | TT | 25.53 ± 3.85 | 124 | 5.085 | 0.002 |
| CT | 26.50 ± 5.13 | 70 | |||
| CC | 28.93 ± 5.13 | 26 | |||
| GHRL | GG | 25.14 ± 3.77 | 147 | 14.441 | 0.001 |
| GT | 27.90 ± 4.60 | 60 | |||
| TT | 30.00 ± 7.33 | 13 | |||
| LEP | GG | 23.96 ± 2.75 | 86 | 37.833 | 0.001 |
| GA | 26.68 ± 3.68 | 111 | |||
| AA | 32.73 ± 6.17 | 23 | |||
| FTO | TT | 23.33 ± 1.78 | 110 | 125.922 | 0.001 |
| AT | 27.00 ± 3.17 | 64 | |||
| AA | 31.85 ± 4.95 | 46 | |||
| LEPR | GG | 27.64 ± 5.39 | 49 | 4.401 | 0.013 |
| AG | 26.17± 4.02 | 101 | |||
| AA | 25.17± 4.36 | 70 |
| Gene | Genotypes | EES (±SD) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emotional Eaters | GHRL | TT | 11.38 ± 3.86 |
| CLOCK | CC | 11.12 ± 2.82 | |
| Low Emotional Eaters | CLOCK | CT | 8.13 ± 3.85 |
| MC4R | CT | 6.94 ± 3.67 | |
| TT | 6.25 ± 3.66 | ||
| CC | 7.81 ± 3.81 | ||
| GHRL | GT | 8.13 ± 3.74 | |
| GG | 5.54 ± 3.04 | ||
| LEP | GA | 7.16 ± 3.83 | |
| AA | 10.04 ± 3.72 | ||
| FTO | TA | 7.25 ± 3.59 | |
| AA | 10.13 ± 3.36 | ||
| LEPR | AG | 6.38 ± 3.54 | |
| GG | 7.45 ± 3.70 | ||
| AA | 6.30 ± 3.81 | ||
| Non-Emotional Eaters | LEP | GG | 5.02 ± 2.49 |
| CLOCK | TT | 4.90 ± 2.49 | |
| GHRL | GG | 5.54 ± 3.04 | |
| FTO | TT | 4.73 ± 2.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vranceanu, M.; Filip, L.; Hegheș, S.-C.; de Lorenzo, D.; Cozma-Petruț, A.; Ghitea, T.C.; Stroia, C.M.; Banc, R.; Mîrza, O.M.; Miere, D.; et al. Genes Involved in Susceptibility to Obesity and Emotional Eating Behavior in a Romanian Population. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162652
Vranceanu M, Filip L, Hegheș S-C, de Lorenzo D, Cozma-Petruț A, Ghitea TC, Stroia CM, Banc R, Mîrza OM, Miere D, et al. Genes Involved in Susceptibility to Obesity and Emotional Eating Behavior in a Romanian Population. Nutrients. 2024; 16(16):2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162652
Chicago/Turabian StyleVranceanu, Maria, Lorena Filip, Simona-Codruța Hegheș, David de Lorenzo, Anamaria Cozma-Petruț, Timea Claudia Ghitea, Carmina Mariana Stroia, Roxana Banc, Oana Maria Mîrza, Doina Miere, and et al. 2024. "Genes Involved in Susceptibility to Obesity and Emotional Eating Behavior in a Romanian Population" Nutrients 16, no. 16: 2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162652
APA StyleVranceanu, M., Filip, L., Hegheș, S.-C., de Lorenzo, D., Cozma-Petruț, A., Ghitea, T. C., Stroia, C. M., Banc, R., Mîrza, O. M., Miere, D., Cozma, V., & Popa, D.-S. (2024). Genes Involved in Susceptibility to Obesity and Emotional Eating Behavior in a Romanian Population. Nutrients, 16(16), 2652. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162652













