Malnutrition in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Insights from Morphofunctional Assessment and Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition Criteria
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Clinical Variables
2.2.1. Anthropometric Measurements
2.2.2. Phase Angle and Body Composition Parameters
2.2.3. Muscle Strength
2.2.4. Biochemical Analysis
2.3. Physical Performance
2.4. Malnutrition Disease Related Diagnosis
2.5. Disease Progression
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Characterization of the Population Study
3.2. Morphofunctional Status
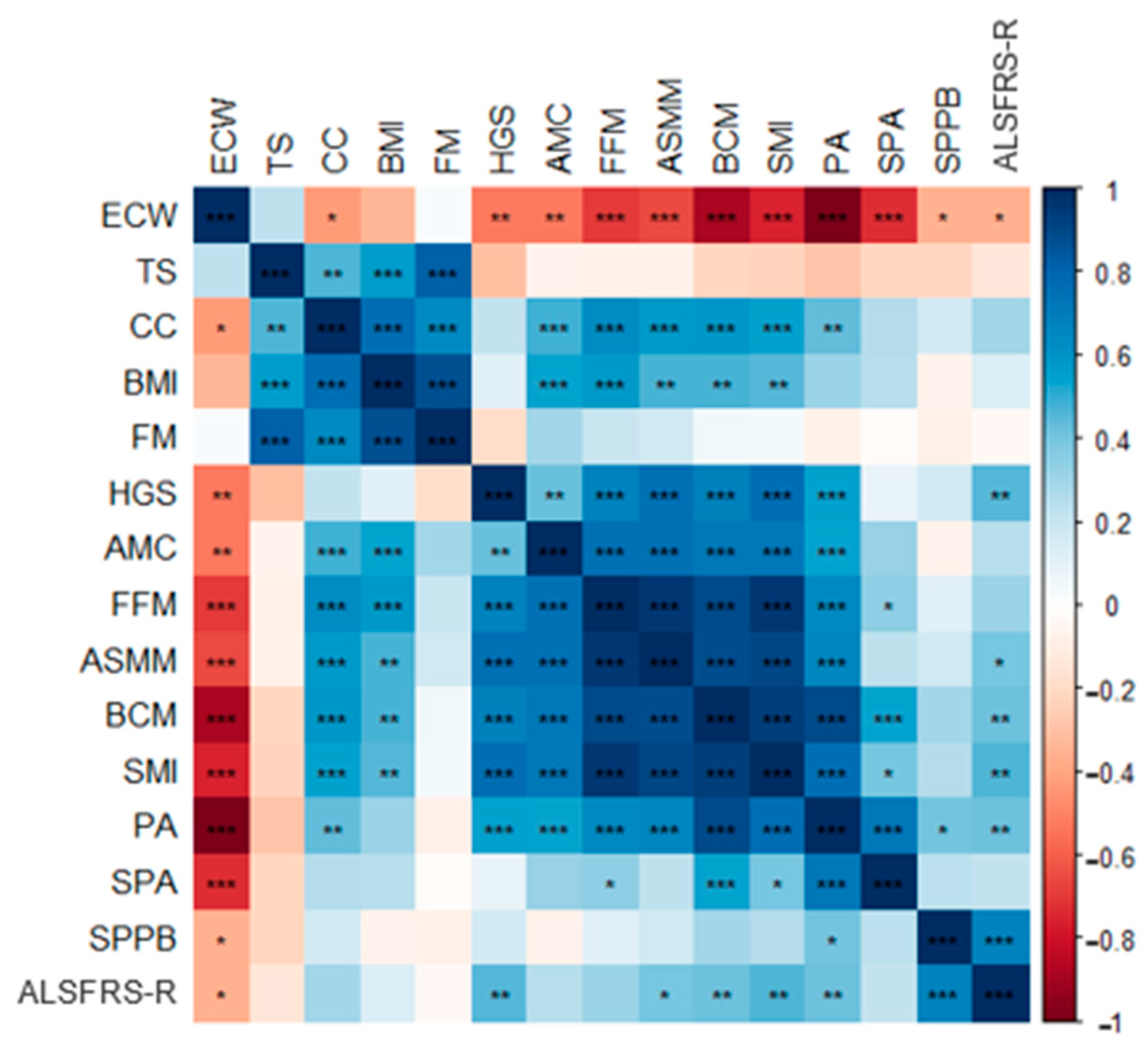
3.3. Correlation between Nutritional Parameters
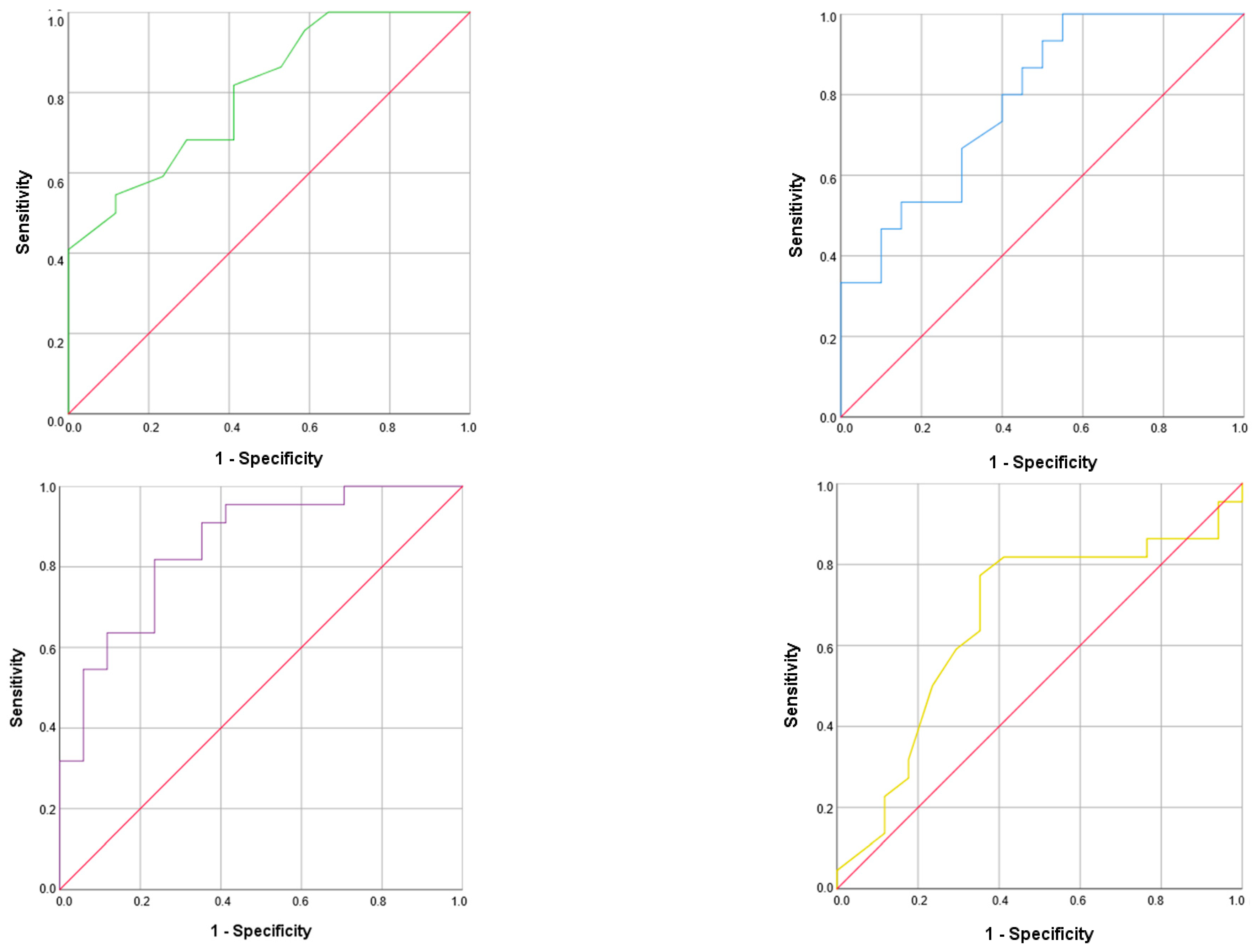
3.4. Malnutrition Risk Factors and Related Morphofunctional Parameter Cut-Off Values
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Couratier, P.; Corcia, P.; Lautrette, G.; Nicol, M.; Preux, P.M.; Marin, B. Epidemiology of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A review of literature. Rev. Neurol. 2016, 172, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, C.S.; Stanich, P.; Salvioni, C.C.S.; Diccini, S. Assessment and nutrition education in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2016, 74, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mitchell, J.D.; Borasio, G.D. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet 2007, 369, 2031–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiò, A.; Logroscino, G.; Hardiman, O.; Swingler, R.; Mitchell, D.; Beghi, E.; Traynor, B.G.; Eurals Consortium. Prognostic factors in ALS: A critical review. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2009, 10, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, A.; Coccurello, R. What is ‘Hyper’ in the ALS Hypermetabolism? Mediat. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 7821672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Olmo García, M.D.; Virgili Casas, N.; Cantón Blanco, A.; Lozano Fuster, F.M.; Wanden-Berghe, C.; Avilés, V.; Ashbaugh Enguídanos, R.; Ferrero López, I.; Molina Soria, J.B.; Montejo González, J.C.; et al. [Nutritional management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Summary of recommendations]. Nutr. Hosp. 2018, 35, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essat, M.; Coates, E.; Clowes, M.; Beever, D.; Hackney, G.; White, S.; Stavroulakis, T.; Halliday, V.; McDermott, C. Understanding the current nutritional management for people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis—A mapping review. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 49, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgos, R.; Bretón, I.; Cereda, E.; Desport, J.C.; Dziewas, R.; Genton, L.; Gomes, F.; Jésus, P.; Leischker, A.; Muscaritoli, M.; et al. ESPEN guideline clinical nutrition in neurology. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 354–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desport, J.C.; Preux, P.M.; Bouteloup-Demange, C.; Clavelou, P.; Beaufrère, B.; Bonnet, C.; Couratier, P.P. Validation of bioelectrical impedance analysis in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1179–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Almeida, J.M.; García García, C.; Vegas Aguilar, I.M.; Bellido Castañeda, V.; Bellido Guerrero, D. Morphofunctional assessment of patient’s nutritional status: A global approach. Nutr. Hosp. 2021, 38, 592–600. [Google Scholar]
- Rofes, L.; Arreola, V.; Clavé, P. The volume-viscosity swallow test for clinical screening of dysphagia and aspiration. Nestle Nutr. Inst. Workshop Ser. 2012, 72, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.P.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Orlandi, S.P.; Bielemann, R.M.; Barbosa-Silva, T.G.; Heymsfield, S.B.; COCONUT Study Group. New Prediction Equations to Estimate Appendicular Skeletal Muscle Mass Using Calf Circumference: Results from NHANES 1999–2006. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2019, 43, 998–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, A.; Rossi, B.; Pillon, L.; Bucciante, G. A new method for monitoring body fluid variation by bioimpedance analysis: The RXc graph. Kidney Int. 1994, 46, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, I.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Baumgartner, R.N.; Ross, R. Estimation of skeletal muscle mass by bioelectrical impedance analysis. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000, 89, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, U.G.; Genton, L.; Karsegard, L.; Slosman, D.O.; Pichard, C. Single prediction equation for bioelectrical impedance analysis in adults aged 20–94 years. Nutrition 2001, 17, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccoli, A.; Nigrelli, S.; Caberlotto, A.; Bottazzo, S.; Rossi, B.; Pillon, L.; Maggiore, Q. Bivariate normal values of the bioelectrical impedance vector in adult and elderly populations. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 61, 269–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Bahat, G.; Bauer, J.; Boirie, Y.; Bruyère, O.; Cederholm, T.; Cooper, C.; Landi, F.; Rolland, Y.; Sayer, A.A.; et al. Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019, 48, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guralnik, J.M.; Simonsick, E.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Glynn, R.J.; Berkman, L.F.; Blazer, D.G.; Scherr, P.A.; Wallace, R.B. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: Association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. J. Gerontol. 1994, 49, M85–M94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.; Crivelli, A.; Evans, D.; Gramlich, L.; Fuchs-Tarlovsky, V.; Keller, H.; Llido, L.; et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition—A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, T.S.; Rodríguez-Santos, F.; Esteban, J.; Vázquez, P.C.; Mora Pardina, J.S.; Carmona, A.C. Spanish adaptation of the revised Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Functional Rating Scale (ALSFRS-R). Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2010, 11, 475–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedarbaum, J.M.; Stambler, N.; Malta, E.; Fuller, C.; Hilt, D.; Thurmond, B.; Nakanishi, A. The ALSFRS-R: A revised ALS functional rating scale that incorporates assessments of respiratory function. BDNF ALS Study Group (Phase III). J. Neurol. Sci. 1999, 169, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roubeau, V.; Blasco, H.; Maillot, F.; Corcia, P.; Praline, J. Nutritional assessment of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in routine practice: Value of weighing and bioelectrical impedance analysis. Muscle Nerve 2015, 51, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvioni, C.; Oda, A.L.; Orsini, M.; Pauli, M.; Frabasile, L.M.; Alves, P.C.L.; Borges, R.M.; Sierra, H.N.M.; Menegatti, G.; Pinho, M.O.; et al. Association between Body Composition and Dysphagia in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurol. Int. 2021, 13, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvioni, C.C.D.S.; Stanich, P.; Oliveira, A.S.B.; Orsini, M. Anthropometry of Arm: Nutritional Risk Indicator in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurol. Int. 2015, 7, 5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gómez, J.J.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.D.; Torres-Torres, B.; De la Maza, B.P.; Penacho-Lázaro, M.Á.; Palacio-Mures, J.M.; Abreu-Padín, C.; López-Guzmán, A.; De Luis-Román, D.A. Malnutrition at diagnosis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (als) and its influence on survival: Using glim criteria. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, R.; Kurihara, M.; Ogawa, N.; Kitamura, A.; Yamakawa, I.; Bamba, S.; Sanada, M.; Sasaki, M.; Urushitani, M. Prognostic prediction by hypermetabolism varies depending on the nutritional status in early amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M.; Leo, A.D.; de van der Schueren, M.A.E. Malnutrition assessment by Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition criteria in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nutrition 2023, 109, 111997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasarskis, E.J.; Berryman, S.; English, T.; Nyland, J.; Vanderleest, J.G.; Schneider, A.; Berger, R.; McClain, C. The use of upper extremity anthropometrics in the clinical assessment of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 1997, 20, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Sun, X.H.; Cai, Z.Y.; Shen, D.C.; Yang, X.Z.; Liu, M.S.; Cui, L.Y. Correlation of weight and body composition with disease progression rate in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Yoon, S.H.; Sung, J.J.; Lee, J.H. Association Between Fat Depletion and Prognosis of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: CT-Based Body Composition Analysis. Ann. Neurol. 2023, 94, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaski, H.C.; Kyle, U.G.; Kondrup, J. Assessment of adult malnutrition and prognosis with bioelectrical impedance analysis: Phase angle and impedance ratio. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2017, 20, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorst, J.; Weydt, P.; Brenner, D.; Witzel, S.; Kandler, K.; Huss, A.; Herrmann, C.; Wiesenfarth, M.; Knehr, A.; Günther, K.; et al. Metabolic alterations precede neurofilament changes in presymptomatic ALS gene carriers. eBioMedicine 2023, 90, 104521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukaski, H.C.; Talluri, A. Phase angle as an index of physiological status: Validating bioelectrical assessments of hydration and cell mass in health and disease. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2023, 24, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Gómez, J.J.; Izaola-Jauregui, O.; Almansa-Ruiz, L.; Jiménez-Sahagún, R.; Primo-Martín, D.; Pedraza-Hueso, M.I.; Ramos-Bachiller, B.; González-Gutiérrez, J.; De Luis-Román, D. Use of Muscle Ultrasonography in Morphofunctional Assessment of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS). Nutrients 2024, 16, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desport, J.C.; Marin, B.; Funalot, B.; Preux, P.M.; Couratier, P. Phase angle is a prognostic factor for survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2008, 9, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barone, M.; Viggiani, M.T.; Introna, A.; D’errico, E.; Scarafino, A.; Iannone, A.; Di Leo, A.; Simone, I.L. Nutritional prognostic factors for survival in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients undergone percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy placement. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Front. Degener. 2019, 20, 490–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Almeida, J.M.; García-García, C.; Vegas-Aguilar, I.M.; Ballesteros Pomar, M.D.; Cornejo-Pareja, I.M.; Fernández Medina, B.; de Luis Román, D.A.; Bellido Guerrero, D.; Bretón Lesmes, I.; Tinahones Madueño, F.J. Nutritional ultrasound®: Conceptualisation, technical considerations and standardisation. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2023, 70 (Suppl. 1), 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, W.; Umehara, T.; Iwamoto, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Katayama, N. Phase Angle Is Associated with Handgrip Strength in Older Patients with Heart Failure. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2023, 47, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.G.; Mitchell, J.D.; Moore, D.H. Riluzole for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)/motor neuron disease (MND). Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2012, CD001447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, N.; Hashida, G.; Kobayashi, M.; Konaka, K. Physical therapy improves lower limb muscle strength but not function in individuals with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A case series study. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 61, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victoria-Montesinos, D.; García-Muñoz, A.M.; Navarro-Marroco, J.; Lucas-Abellán, C.; Mercader-Ros, M.T.; Serrano-Martínez, A.; Abellán-Aynés, O.; Barcina-Pérez, P.; Hernández-Sánchez, P. Phase Angle, Handgrip Strength, and Other Indicators of Nutritional Status in Cancer Patients Undergoing Different Nutritional Strategies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavasini, R.; Guralnik, J.; Brown, J.C.; Di Bari, M.; Cesari, M.; Landi, F.; Vaes, B.; Legrand, D.; Verghese, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Short Physical Performance Battery and all-cause mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. 2016, 14, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes, J.; Cheng, B.; Diamond, B.; Doorish, C.; Mitsumoto, H.; Gordon, P.H. The Timed Up and Go test: Predicting falls in ALS. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2007, 8, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Total (n = 45) | Non-Malnutrition (n = 28/62%) | Malnutrition (n = 17/38%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | 0.02 | |||
| Male | 62.2 | 75.0 | 41.2 | |
| Female | 37.8 | 25.0 | 58.8 | |
| Age (years) | 65 ± 9.9 | 62 ± 10 | 70 ± 9 | 0.01 |
| Disease evolution (months) | 32 ± 27 | 37 ± 31 | 23 ± 19 | 0.15 |
| Dysphagia diagnosis (%) | 49 | 29 | 83 | <0.001 |
| PRG/PEG use (%) | 15.6 | 3.6 | 35.3 | 0.01 |
| NIMV (%) | 20 | 14.3 | 29.4 | 0.40 |
| ALSFRS-R (points) | 32 | 34 | 30 | 0.02 |
| Total (n = 45) | Non-Malnutrition (n = 28, 62%) | Malnutrition (n = 17, 38%) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropometric measures | ||||
| Weight (kg) | 69.3 ± 13.7 | 75.1 ± 10.2 | 59.6 ± 13.5 | <0.001 |
| Weight loss (%) | 9.5 ± 8.2 | 5.8 ± 2.5 | 11.8 ± 9.6 | 0.03 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 25.16 ± 4.64 | 27.4 ± 4.1 | 24.2 ± 2.8 | <0.001 |
| AC (cm) | 27.8 ± 4 | 29.35 ± 3.7 | 25.4 ± 3.3 | 0.001 |
| TS (mm) | 15 ± 3.6 | 15.7 ± 7.7 | 13.8 ± 7 | 0.43 |
| AMC (cm) | 23.1 ± 3.4 | 24.3 ± 2.7 | 21 ± 3.4 | 0.001 |
| CC (cm) | 34.7 ± 3.6 | 33.3 ± 2.6 | 32.6 ± 2.3 | 0.39 |
| ASMI (kg/m2) | 6.4 ± 1.4 | 6.9 ± 1.4 | 5.6 ± 1.2 | 0.01 |
| BIVA | ||||
| Rz (Ohm) | 593.6 ± 106.1 | 549.8 ± 77.1 | 651.9 ± 113.6 | 0.01 |
| Xc (Ohm) | 48.6 ± 8.8 | 50.4 ± 9.2 | 46.2 ± 7.8 | 0.17 |
| PA (°) | 4.63 ± 0.96 | 5.09 ± 0.8 | 4.05 ± 0.8 | <0.001 |
| SPA | −0.85 ± 1.19 | −0.55 ± 0.94 | −1.26 ± 1.38 | 0.08 |
| TBW (kg/m) | 21.5 ± 3.4 | 23.1 ± 2.7 | 19.5 ± 3.3 | 0.001 |
| ECW (%/TBW) | 53.1 ± 6 | 50.3 ± 4.4 | 56.7 ± 6 | 0.001 |
| ECW/ICW | 1.17 ± 0.32 | 1.03 ± 0.18 | 1.36 ± 0.36 | 0.01 |
| FFM (kg/m) | 29 ± 4.4 | 31.2 ± 3.1 | 26.2 ± 3.8 | <0.001 |
| FM (kg/m) | 11.9 ± 5.5 | 13.7 ± 5.7 | 9.5 ± 3.4 | 0.02 |
| BCM (kg/m) | 13.3 ± 3.6 | 15.2 ± 3.0 | 10.8 ± 2.8 | <0.001 |
| ASMM (kg) | 17.4 ± 4.3 | 19.4 ± 3.4 | 14.8 ± 4.1 | 0.001 |
| SMI (kg2/m2) | 7.9 ± 1.7 | 8.7 ± 1.3 | 6.9 ± 1.6 | <0.001 |
| Functional status | ||||
| HGS max (kg) | 20 ± 10.3 | 22 ± 9.8 | 17 ± 10.9 | 0.18 |
| SPPB | 5 | 7 | 4 | 0.19 |
| ORc (95%CI) | p-Value | ORadj (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rz | 1.01 (1.00–1.02) | 0.01 | 1.01 (0.99–1.02) | 0.07 |
| Xc | 0.94 (0.86–1.03) | 0.17 | 0.94 (0.84–1.06) | 0.36 |
| PA | 0.21 (0.07–0.60) | 0.004 | 0.25 (0.08–0.80) | 0.02 |
| SPA | 0.56 (0.30–1.10) | 0.10 | 0.23 (0.06–0.90) | 0.03 |
| %ECW | 1.30 (1.06–1.55) | 0.01 | 1.23 (0.99–1.50) | 0.051 |
| BCM/h | 0.60 (0.43–0.93) | 0.02 | 0.60 (0.43–0.90) | 0.001 |
| SMI | 0.39 (0.20–0.73) | 0.004 | 0.39 (0.14–1.07) | 0.07 |
| FM/h | 0.80 (0.70–0.94) | 0.03 | 0.80 (0.60–0.98) | 0.04 |
| ALSFRS-R | 0.92 (0.85–0.99) | 0.02 | 0.93 (0.86–1.02) | 0.12 |
| SPPB | 0.90 (0.80–1.04) | 0.17 | 0.94 (0.80–1.10) | 0.45 |
| HGS | 0.58 (0.04–4.50) | 0.60 | 0.19 (0.01–2.01) | 0.17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zarco-Martín, M.T.; Freire, C.; Andreo-López, M.C.; Leyva-Martínez, S.; Fernández-Soto, M.L. Malnutrition in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Insights from Morphofunctional Assessment and Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition Criteria. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162625
Zarco-Martín MT, Freire C, Andreo-López MC, Leyva-Martínez S, Fernández-Soto ML. Malnutrition in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Insights from Morphofunctional Assessment and Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition Criteria. Nutrients. 2024; 16(16):2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162625
Chicago/Turabian StyleZarco-Martín, María Teresa, Carmen Freire, María Carmen Andreo-López, Socorro Leyva-Martínez, and María Luisa Fernández-Soto. 2024. "Malnutrition in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Insights from Morphofunctional Assessment and Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition Criteria" Nutrients 16, no. 16: 2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162625
APA StyleZarco-Martín, M. T., Freire, C., Andreo-López, M. C., Leyva-Martínez, S., & Fernández-Soto, M. L. (2024). Malnutrition in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Insights from Morphofunctional Assessment and Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition Criteria. Nutrients, 16(16), 2625. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162625








