The Role of Central and Peripheral Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) as a Biomarker of Anorexia Nervosa Reconceptualized as a Metabo-Psychiatric Disorder
Abstract
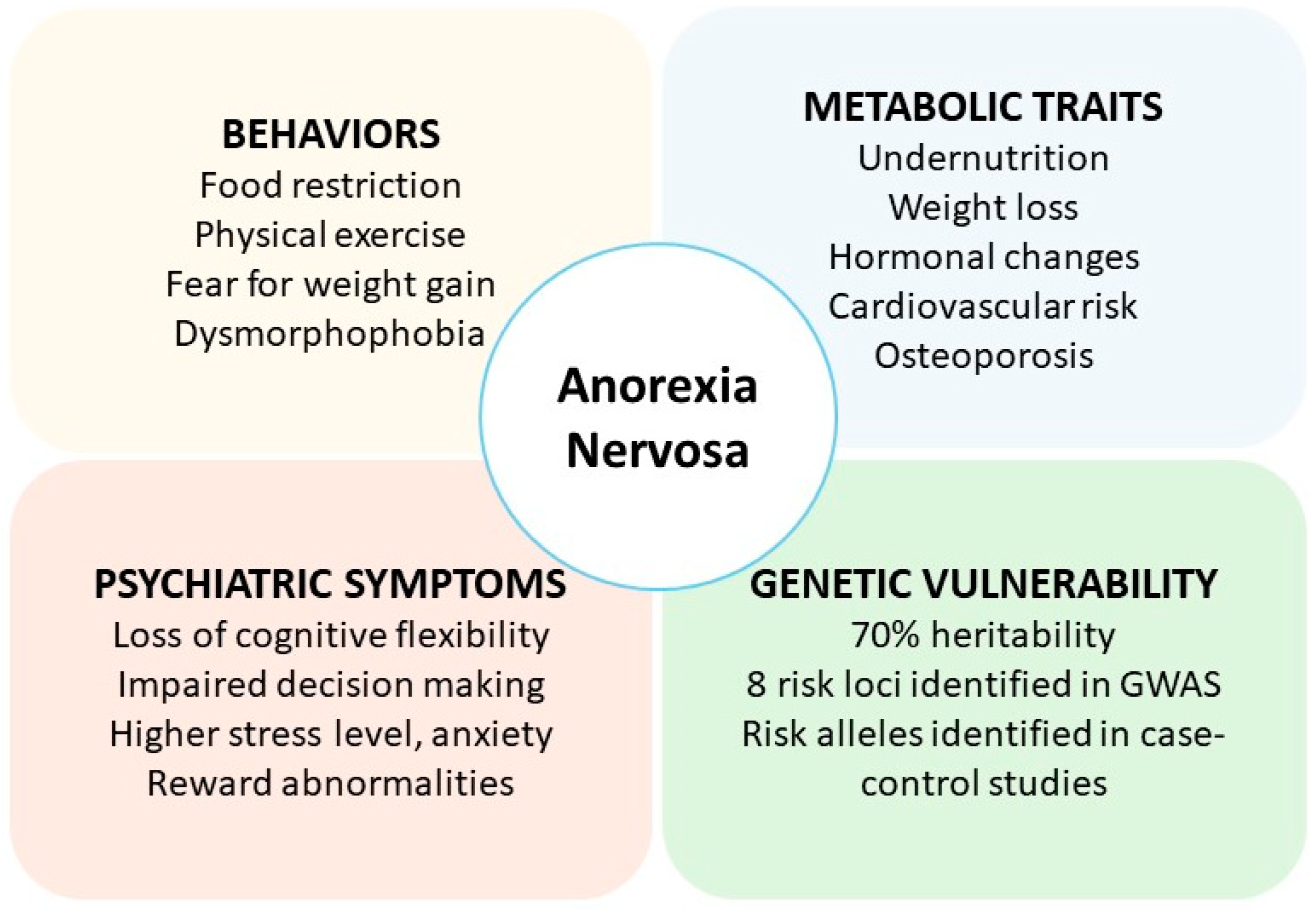
1. AN: A Metabo-Psychiatric Disorder with Complex Etiology
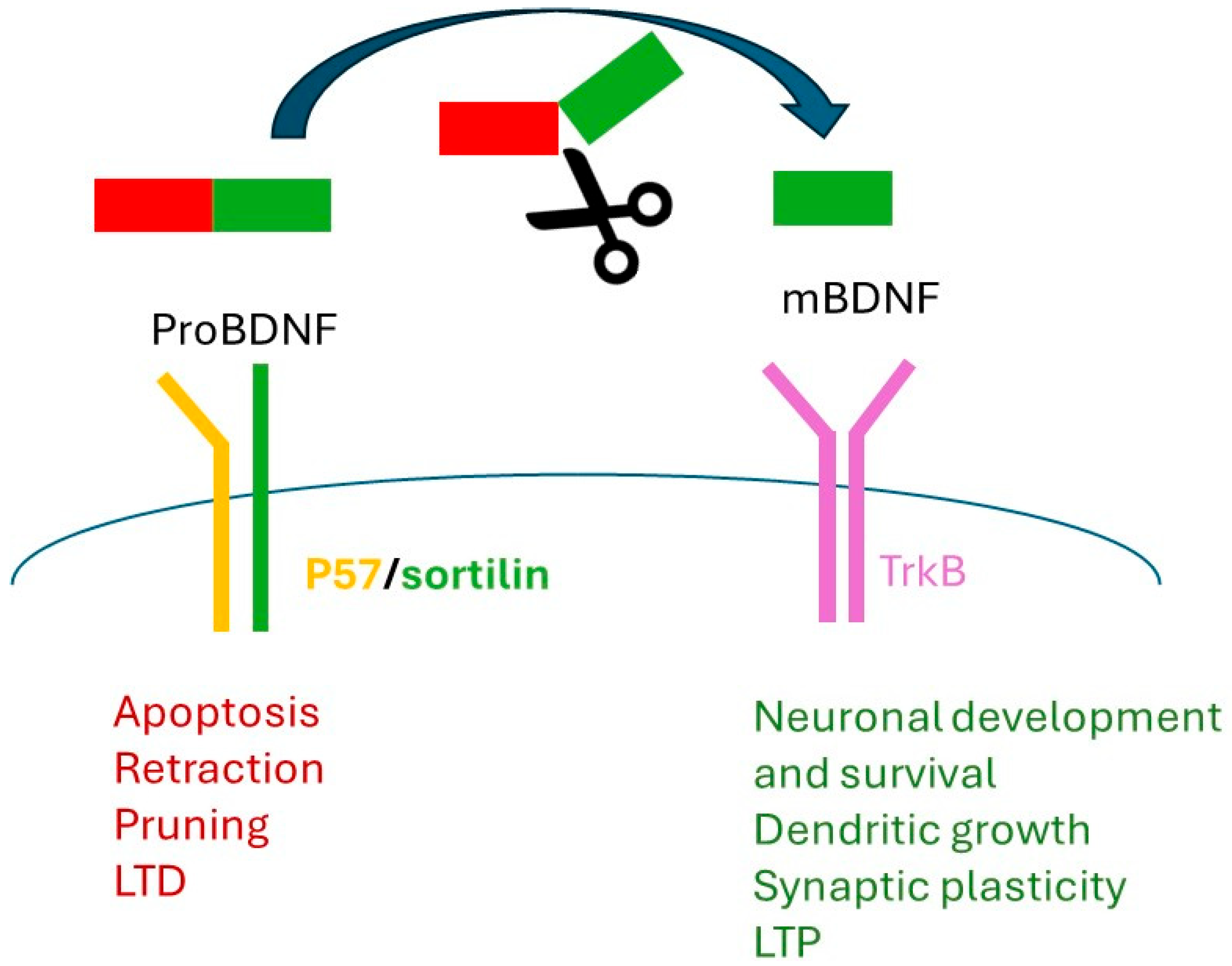
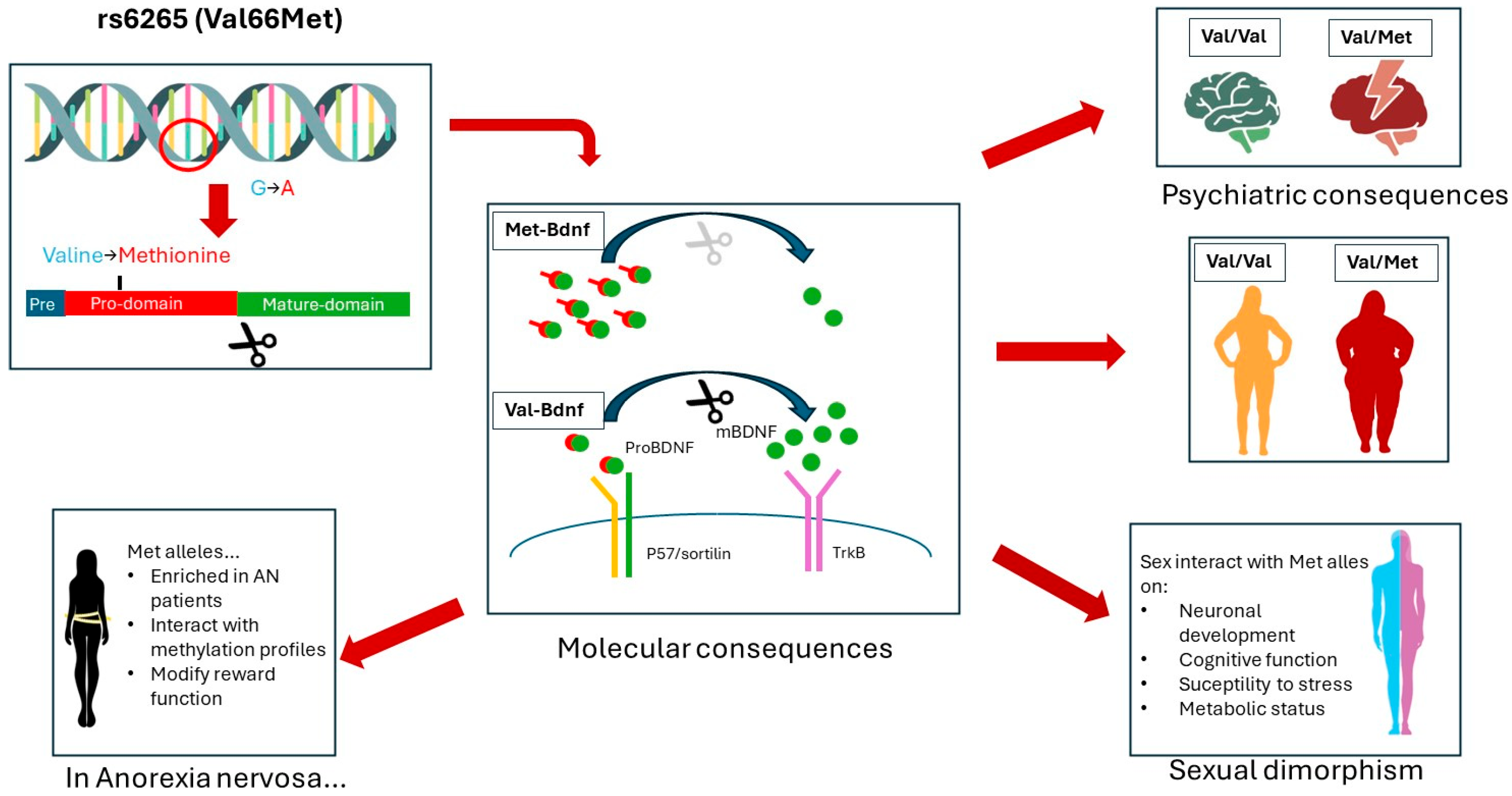
2. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Val66Met Polymorphism
3. BDNF and AN: Clinical Data
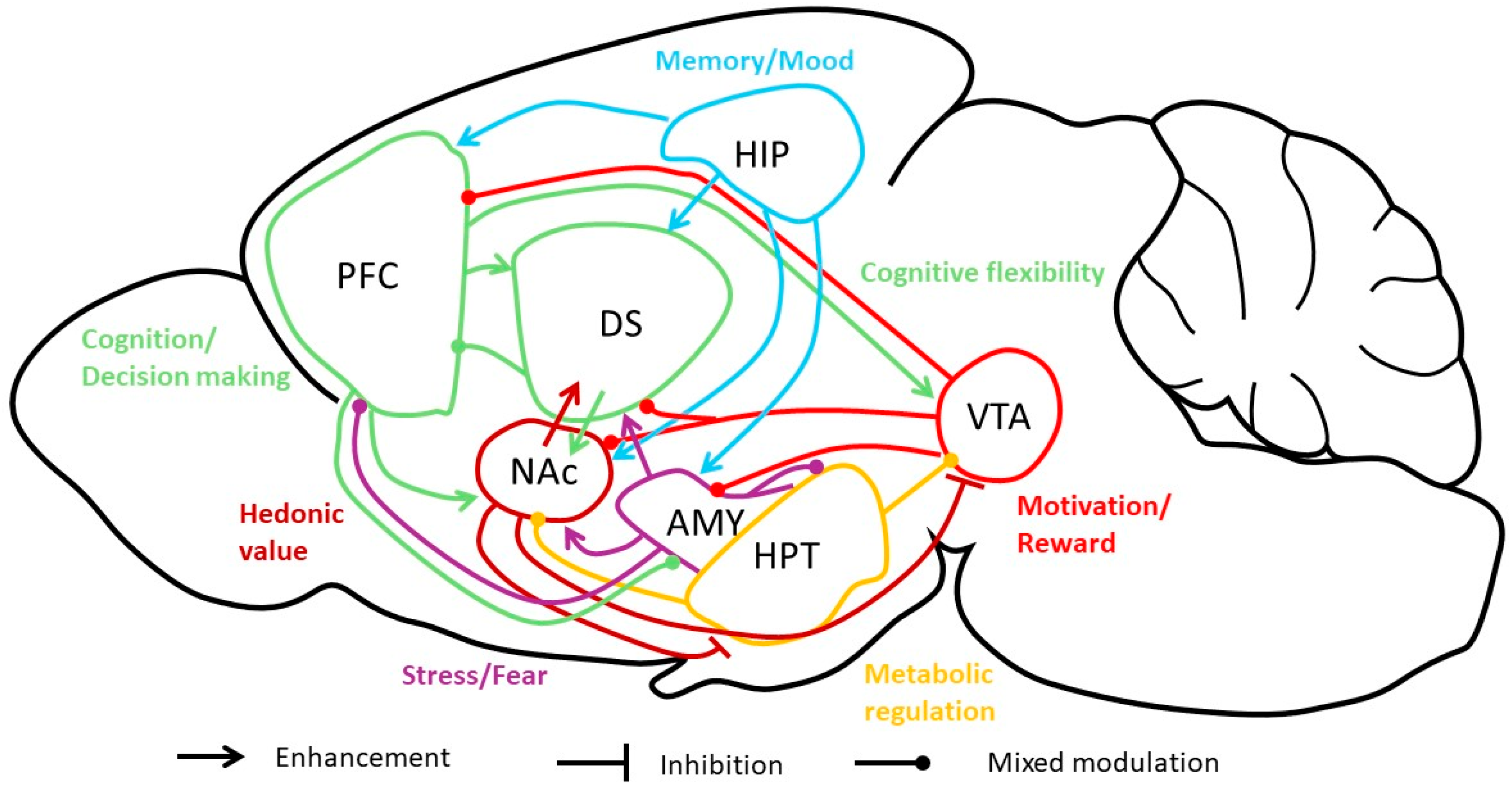
4. BDNF and AN: Inputs from Animal Models
| Tissue | Gene | Calory Restrictions (Chronic) | Fasting (Acute) | Physical Activities | High Fat Diet/Obesity | Chronic Stress | Acute Stress | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Change | Species/Sex | Change | Species/Sex | Change | Species/Sex | Change | Species/Sex | Change | Species/Sex | Change | Species/Sex | ||
| PFC | BDNF | Ns Prot | Rat ♂ [73,74] | ↑ mRNA | Mice ♂ [75] | ↓ Prot | Rats ♂ [76] | ↓ mRNA | Rat ♂ [77] | ↓ mRNA | Rat ♂ [77] | ||
| ↑ Prot | Rat ♀♂ [78,79] | ↑ Prot | Rat ♂ [80] | ||||||||||
| Hippocampus | BDNF | ↑ Prot | Rat ♀♂ [73,78,79] | ↓ Cell Nb | Mice ♂ [81] | Ns mRNA | Mice [75] | ↓ Prot | Rats ♂ [76] | ||||
| ↓ Cell Nb | Rat ♂ [82] | ↑ Prot | Mice ♂ [83] | ↓ mRNA | Mice ♂ [84] | ||||||||
| TrkB | Ns Cell Nb | Rat ♂ [82] | ↓ mRNA | Mice, ♂ [84] | Ns Prot | Rat ♂ [80] | |||||||
| Hypothalamus | BDNF | ↓ mRNA | Mice ♂, Rat ♀♂ [84,85] | ↑ mRNA, prot | Rat ♂ [86] | ↑ mRNA | Rat ♂ [87] | ||||||
| TrkB | Ns mRNA | Mice ♂ [84] | |||||||||||
| DS | BDNF | ↑ Prot | Mice ♂ [88] | ↑ mRNA,prot | Mice ♂ [89] | ||||||||
| NAc | BDNF | Ns Prot | Rat ♂ [74] | ↑ mRNA | Human ♀♂ [90] | ↑ Prot | Rat ♂ [91] | ||||||
| TrkB | ↑ Prot | Rat ♂ [91] | |||||||||||
| VTA | BDNF | Ns mRNA, prot | Rat ♂ [74] | ↑ Prot | Rat ♂ [91] | ||||||||
| TrkB | ↓ Prot | Rat ♂ [74] | ↑ Prot | Rat ♂ [91] | |||||||||
| Amygdala | BDNF | ↑ Prot | Rat ♂ [73] | ↓ mRNA | Rats ♀ (ABA) [66] | ↓ mRNA, prot | Rat ♂ [92] | ||||||
| Serum/Plasma | BDNF | Ns Prot | Rat ♂ [79] | ↑ Prot | Human ♂ [93] | ↓ Prot | Human ♀ [94] | ↑ Prot | Human ♂ [95] | ↑ Prot | Human ♂ [95] | ||
5. BDNF and Stress-Related Mood Disorders
6. BDNF and Metabolism
7. Discussion
7.1. Role of BDNF in AN Etiology and Prognosis
7.2. Exploring the Biomarker Potential of Circulating BDNF
7.3. Metabolic Implications and Sexual Dimorphism
7.4. The Paradox of Physical Activity
7.5. Limitations and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vanevski, F.; Xu, B. Molecular and Neural Bases Underlying Roles of BDNF in the Control of Body Weight. Front. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 43608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, S.; Keller, L.; Herpertz-Dahlmann, B.; Seitz, J. The Role of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in Anorexia Nervosa. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2023, 151, 106069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. Available online: https://dsm.psychiatryonline.org/doi/book/10.1176/appi.books.9780890425596 (accessed on 15 November 2022).
- DaCosta, M.; Halmi, K.A. Classifications of Anorexia Nervosa: Question of Subtypes. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 1992, 11, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micali, N.; Hagberg, K.W.; Petersen, I.; Treasure, J.L. The Incidence of Eating Disorders in the UK in 2000–2009: Findings from the General Practice Research Database. BMJ Open 2013, 3, e002646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Treasure, J.; Stein, D.; Maguire, S. Has the Time Come for a Staging Model to Map the Course of Eating Disorders from High Risk to Severe Enduring Illness? An Examination of the Evidence. Early Interv. Psychiatry 2015, 9, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcelus, J.; Mitchell, A.J.; Wales, J.; Nielsen, S. Mortality Rates in Patients With Anorexia Nervosa and Other Eating Disorders: A Meta-Analysis of 36 Studies. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 724–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westmoreland, P.; Krantz, M.J.; Mehler, P.S. Medical Complications of Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia. Am. J. Med. 2016, 129, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, E.; Bakshi, N.; Watters, A.; Rosen, H.R.; Mehler, P.S. Hepatic Complications of Anorexia Nervosa. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 2977–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Aranda, F.; Pinheiro, A.P.; Tozzi, F.; Thornton, L.M.; Fichter, M.M.; Halmi, K.A.; Kaplan, A.S.; Klump, K.L.; Strober, M.; Woodside, D.B.; et al. Symptom Profile of Major Depressive Disorder in Women with Eating Disorders. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2007, 41, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinbourne, J.M.; Touyz, S.W. The Co-Morbidity of Eating Disorders and Anxiety Disorders: A Review. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. J. Eat. Disord. Assoc. 2007, 15, 253–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompili, M.; Mancinelli, I.; Girardi, P.; Ruberto, A.; Tatarelli, R. Suicide in Anorexia Nervosa: A Meta-analysis. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2004, 36, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, J.C.; Blackmore, E.; Sutandar-Pinnock, K.; Woodside, D.B. Relapse in Anorexia Nervosa: A Survival Analysis. Psychol. Med. 2004, 34, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhausen, H.-C. Outcome of Eating Disorders. Child Adolesc. Psychiatr. Clin. N. Am. 2009, 18, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duriez, P.; Maatoug, R.; Verbe, J. Failure of Electroconvulsive Therapy to Improve Anorexia Nervosa in the Absence of Other Psychiatric Comorbidities: A Case Report. J. ECT 2020, 36, e44–e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zipfel, S.; Giel, K.E.; Bulik, C.M.; Hay, P.; Schmidt, U. Anorexia Nervosa: Aetiology, Assessment, and Treatment. Lancet Psychiatry 2015, 2, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, H.J.; Yilmaz, Z.; Thornton, L.M.; Hübel, C.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Gaspar, H.A.; Bryois, J.; Hinney, A.; Leppä, V.M.; Mattheisen, M.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Eight Risk Loci and Implicates Metabo-Psychiatric Origins for Anorexia Nervosa. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilenfeld, L.R.; Kaye, W.H.; Greeno, C.G.; Merikangas, K.R.; Plotnicov, K.; Pollice, C.; Rao, R.; Strober, M.; Bulik, C.M.; Nagy, L. A Controlled Family Study of Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia Nervosa: Psychiatric Disorders in First-Degree Relatives and Effects of Proband Comorbidity. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1998, 55, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strober, M.; Freeman, R.; Lampert, C.; Diamond, J.; Kaye, W. Controlled Family Study of Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia Nervosa: Evidence of Shared Liability and Transmission of Partial Syndromes. Am. J. Psychiatry 2000, 157, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulik, C.; Yilmaz, Z.; HArdaway, A. Genetics and Epigenetics of Eating Disorders. Adv. Genomics Genet. 2015, 2015, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versini, A.; Ramoz, N.; Le Strat, Y.; Scherag, S.; Ehrlich, S.; Boni, C.; Hinney, A.; Hebebrand, J.; Romo, L.; Guelfi, J.-D.; et al. Estrogen Receptor 1 Gene (ESR1) Is Associated with Restrictive Anorexia Nervosa. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 1818–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.H.; Schaumberg, K.; Munn-Chernoff, M.A. Genetics of Anorexia Nervosa. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2017, 19, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou Al Hassan, S.; Cutinha, D.; Mattar, L. The Impact of COMT, BDNF and 5-HTT Brain-Genes on the Development of Anorexia Nervosa: A Systematic Review. Eat. Weight Disord. EWD 2021, 26, 1323–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybakowski, F.; Dmitrzak-Weglarz, M.; Szczepankiewicz, A.; Skibinska, M.; Slopien, A.; Rajewski, A.; Hauser, J. Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor Gene Val66Met and -270C/T Polymorphisms and Personality Traits Predisposing to Anorexia Nervosa. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2007, 28, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clarke, J.; Ramoz, N.; Fladung, A.-K.; Gorwood, P. Higher Reward Value of Starvation Imagery in Anorexia Nervosa and Association with the Val66Met BDNF Polymorphism. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aid, T.; Kazantseva, A.; Piirsoo, M.; Palm, K.; Timmusk, T. Mouse and Rat BDNF Gene Structure and Expression Revisited. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 85, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barde, Y.A.; Edgar, D.; Thoenen, H. Purification of a New Neurotrophic Factor from Mammalian Brain. EMBO J. 1982, 1, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R.; Parada, L.F.; Coulier, F.; Barbacid, M. TrkB, a Novel Tyrosine Protein Kinase Receptor Expressed during Mouse Neural Development. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 3701–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R.; Nanduri, V.; Jing, S.; Lamballe, F.; Tapley, P.; Bryant, S.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Jones, K.R.; Reichardt, L.F.; Barbacid, M. The TrkB Tyrosine Protein Kinase Is a Receptor for Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Neurotrophin-3. Cell 1991, 66, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keifer, J.; Sabirzhanov, B.E.; Zheng, Z.; Li, W.; Clark, T.G. Cleavage of ProBDNF to BDNF by a Tolloid-Like Metalloproteinase Is Required for Acquisition of In Vitro Eyeblink Classical Conditioning. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 14956–14964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barde, Y.-A. The Nerve Growth Factor Family. Prog. Growth Factor Res. 1990, 2, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderson, R.F.; Alterman, A.L.; Barde, Y.-A.; Lindsay, R.M. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Increases Survival and Differentiated Functions of Rat Septal Cholinergic Neurons in Culture. Neuron 1990, 5, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindholm, D.; Dechant, G.; Heisenberg, C.-P.; Thoenen, H. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Is a Survival Factor for Cultured Rat Cerebellar Granule Neurons and Protects Them Against Glutamate-Induced Neurotoxicity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1993, 5, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Pang, P.T.; Feng, L.; Lu, B. Cyclic AMP Controls BDNF-Induced TrkB Phosphorylation and Dendritic Spine Formation in Mature Hippocampal Neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Christian, K.; Lu, B. BDNF: A Key Regulator for Protein-Synthesis Dependent LTP and Long-Term Memory? Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2008, 89, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, H.K.; Teng, K.K.; Lee, R.; Wright, S.; Tevar, S.; Almeida, R.D.; Kermani, P.; Torkin, R.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Lee, F.S.; et al. ProBDNF Induces Neuronal Apoptosis via Activation of a Receptor Complex of P75NTR and Sortilin. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 5455–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, K.K.; Park, K.J.; Hong, E.J.; Kramer, B.M.; Greenberg, M.E.; Kaplan, D.R.; Miller, F.D. Developmental Axon Pruning Mediated by BDNF-P75NTR–Dependent Axon Degeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orefice, L.L.; Shih, C.-C.; Xu, H.; Waterhouse, E.G.; Xu, B. Control of Spine Maturation and Pruning through ProBDNF Synthesized and Released in Dendrites. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2016, 71, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ernfors, P.; Lee, K.F.; Jaenisch, R. Mice Lacking Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Develop with Sensory Deficits. Nature 1994, 368, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves-Pereira, M.; Mundo, E.; Muglia, P.; King, N.; Macciardi, F.; Kennedy, J.L. The Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Gene Confers Susceptibility to Bipolar Disorder: Evidence from a Family-Based Association Study. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 71, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egan, M.F.; Kojima, M.; Callicott, J.H.; Goldberg, T.E.; Kolachana, B.S.; Bertolino, A.; Zaitsev, E.; Gold, B.; Goldman, D.; Dean, M.; et al. The BDNF Val66met Polymorphism Affects Activity-Dependent Secretion of BDNF and Human Memory and Hippocampal Function. Cell 2003, 112, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Patel, P.D.; Sant, G.; Meng, C.-X.; Teng, K.K.; Hempstead, B.L.; Lee, F.S. Variant Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) (Met66) Alters the Intracellular Trafficking and Activity-Dependent Secretion of Wild-Type BDNF in Neurosecretory Cells and Cortical Neurons. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 4401–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiaruttini, C.; Vicario, A.; Li, Z.; Baj, G.; Braiuca, P.; Wu, Y.; Lee, F.S.; Gardossi, L.; Baraban, J.M.; Tongiorgi, E. Dendritic Trafficking of BDNF MRNA Is Mediated by Translin and Blocked by the G196A (Val66Met) Mutation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16481–16486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ursini, G.; Cavalleri, T.; Fazio, L.; Angrisano, T.; Iacovelli, L.; Porcelli, A.; Maddalena, G.; Punzi, G.; Mancini, M.; Gelao, B.; et al. BDNF Rs6265 Methylation and Genotype Interact on Risk for Schizophrenia. Epigenetics 2016, 11, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tongiorgi, E.; Righi, M.; Cattaneo, A. Activity-Dependent Dendritic Targeting of BDNF and TrkB MRNAs in Hippocampal Neurons. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 9492–9505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McHughen, S.A.; Rodriguez, P.F.; Kleim, J.A.; Kleim, E.D.; Crespo, L.M.; Procaccio, V.; Cramer, S.C. BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism Influences Motor System Function in the Human Brain. Cereb. Cortex 2010, 20, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelmann, E.; Leßmann, V.; Brigadski, T. Pre- and Postsynaptic Twists in BDNF Secretion and Action in Synaptic Plasticity. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76, 610–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieraci, A.; Mallei, A.; Popoli, M. Social Isolation Stress Induces Anxious-Depressive-Like Behavior and Alterations of Neuroplasticity-Related Genes in Adult Male Mice. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 6212983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uegaki, K.; Kumanogoh, H.; Mizui, T.; Hirokawa, T.; Ishikawa, Y.; Kojima, M. BDNF Binds Its Pro-Peptide with High Affinity and the Common Val66Met Polymorphism Attenuates the Interaction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandys, M.K.; Kas, M.J.H.; van Elburg, A.A.; Ophoff, R.; Slof-Op’t Landt, M.C.T.; Middeldorp, C.M.; Boomsma, D.I.; van Furth, E.F.; Slagboom, P.E.; Adan, R.A.H. The Val66Met Polymorphism of the BDNF Gene in Anorexia Nervosa: New Data and a Meta-Analysis. World J. Biol. Psychiatry Off. J. World Fed. Soc. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 14, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisoway, A.; Sonley, A.; Law, J.; Zai, C.; Chapman, A.; McMain, S.; Kennedy, J. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF Val66Met) in Borderline Personality Disorder: Associated with Eating Disorder Comorbidity but Not Psychotherapy Response. Pers. Med. Psychiatry 2024, 43–44, 100114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribases, M.; Gratacos, M.; Fernandez-Aranda, F.; Bellodi, L.; Boni, C.; Anderluh, M.; Cavallini, M.C.; Cellini, E.; Bella, D.D.; Erzegovesi, S.; et al. Association of BDNF with Restricting Anorexia Nervosa and Minimum Body Mass Index: A Family-Based Association Study of Eight European Populations. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 13, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Itoh, K.; Nakazato, M.; Shimizu, E.; Ohgake, S.; Koike, K.; Okamura, N.; Matsushita, S.; Suzuki, K.; et al. Association between the Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor 196G/A Polymorphism and Eating Disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2004, 127B, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercader, J.M.; Ribasés, M.; Gratacòs, M.; González, J.R.; Bayés, M.; de Cid, R.; Badía, A.; Fernández-Aranda, F.; Estivill, X. Altered Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Blood Levels and Gene Variability Are Associated with Anorexia and Bulimia. Genes Brain Behav. 2007, 6, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyszkiewicz-Nwafor, M.; Rybakowski, F.; Dmitrzak-Weglarz, M.; Skibinska, M.; Paszynska, E.; Dutkiewicz, A.; Słopien, A. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Oxytocin Signaling in Association With Clinical Symptoms in Adolescent Inpatients With Anorexia Nervosa—A Longitudinal Study. Front. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsdorf, B.; Dahmen, B.; Buehren, K.; Dempfle, A.; Egberts, K.; Ehrlich, S.; Fleischhaker, C.; Konrad, K.; Schwarte, R.; Timmesfeld, N.; et al. BDNF Levels in Adolescent Patients with Anorexia Nervosa Increase Continuously to Supranormal Levels 2.5 Years after First Hospitalization. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2021, 46, E568–E578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, M.; Ellenbroek, B.; Shao, F.; Wang, W. Effects of Adolescent Social Stress and Antidepressant Treatment on Cognitive Inflexibility and Bdnf Epigenetic Modifications in the MPFC of Adult Mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 88, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houlton, J.; Zhou, L.Y.Y.; Barwick, D.; Gowing, E.K.; Clarkson, A.N. Stroke Induces a BDNF-Dependent Improvement in Cognitive Flexibility in Aged Mice. Neural Plast. 2019, 2019, 1460890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, E.; Portella, M.J.; Piñol-Ripoll, G.; López, R.; Cuadras, D.; Forcada, I.; Teres, M.; Vieta, E.; Mur, M. High BDNF Serum Levels Are Associated to Good Cognitive Functioning in Bipolar Disorder. Eur. Psychiatry 2019, 60, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazato, M.; Tchanturia, K.; Schmidt, U.; Campbell, I.C.; Treasure, J.; Collier, D.A.; Hashimoto, K.; Iyo, M. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Set-Shifting in Currently Ill and Recovered Anorexia Nervosa (AN) Patients. Psychol. Med. 2009, 39, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamero-Villarroel, C.; Gordillo, I.; Carrillo, J.A.; García-Herráiz, A.; Flores, I.; Jiménez, M.; Monge, M.; Rodríguez-López, R.; Gervasini, G. BDNF Genetic Variability Modulates Psychopathological Symptoms in Patients with Eating Disorders. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2014, 23, 669–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, T.G.; Chen, Y.-W.; Aoki, C. Using the Activity-Based Anorexia Rodent Model to Study the Neurobiological Basis of Anorexia Nervosa. J. Vis. Exp. 2015, 22, 52927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duriez, P.; Nilsson, I.A.K.; Le Thuc, O.; Alexandre, D.; Chartrel, N.; Rovere, C.; Chauveau, C.; Gorwood, P.; Tolle, V.; Viltart, O. Exploring the Mechanisms of Recovery in Anorexia Nervosa through a Translational Approach: From Original Ecological Measurements in Human to Brain Tissue Analyses in Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelegen, C.; Van Den Heuvel, J.; Collier, D.A.; Campbell, I.C.; Oppelaar, H.; Hessel, E.; Kas, M.J.H. Dopaminergic and Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor Signalling in Inbred Mice Exposed to a Restricted Feeding Schedule. Genes Brain Behav. 2008, 7, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, E.V.; Klenotich, S.J.; McMurray, M.S.; Dulawa, S.C. Activity-Based Anorexia Alters the Expression of BDNF Transcripts in the Mesocorticolimbic Reward Circuit. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottarlini, F.; Rizzi, B.; Targa, G.; Fumagalli, F.; Caffino, L. Long-Lasting BDNF Signaling Alterations in the Amygdala of Adolescent Female Rats Exposed to the Activity-Based Anorexia Model. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1087075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennerley, S.W.; Walton, M.E. Decision Making and Reward in Frontal Cortex: Complementary Evidence from Neurophysiological and Neuropsychological Studies. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 125, 297–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, G.K.W. Altered Brain Reward Circuits in Eating Disorders: Chicken or Egg? Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2013, 15, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruscitti, C.; Rufino, K.; Goodwin, N.; Wagner, R. Difficulties in Emotion Regulation in Patients with Eating Disorders. Borderline Personal. Disord. Emot. Dysregulation 2016, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trutti, A.C.; Mulder, M.J.; Hommel, B.; Forstmann, B.U. Functional Neuroanatomical Review of the Ventral Tegmental Area. NeuroImage 2019, 191, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Gao, H.; Tong, L.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Q.; Yan, B. Emotion Regulation of Hippocampus Using Real-Time FMRI Neurofeedback in Healthy Human. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lodovico, L.; Versini, A.; Lachatre, M.; Marcheselli, J.; Ramoz, N.; Gorwood, P. Is Decision-Making Impairment an Endophenotype of Anorexia Nervosa? Eur. Psychiatry 2022, 65, e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Arco, A.; Segovia, G.; de Blas, M.; Garrido, P.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Pamplona, R.; Mora, F. Prefrontal Cortex, Caloric Restriction and Stress during Aging: Studies on Dopamine and Acetylcholine Release, BDNF and Working Memory. Behav. Brain Res. 2011, 216, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Chau, L.; Liu, S.; Avshalumov, M.V.; Rice, M.E.; Carr, K.D. A Food Restriction Protocol That Increases Drug Reward Decreases Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase B in the Ventral Tegmental Area, with No Effect on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor or Tropomyosin Receptor Kinase B Protein Levels in Dopaminergic Forebrain Regions. Neuroscience 2011, 197, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranowski, B.J.; Hayward, G.C.; Marko, D.M.; MacPherson, R.E.K. Examination of BDNF Treatment on BACE1 Activity and Acute Exercise on Brain BDNF Signaling. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 665867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanoski, S.; Meisel, R.; Mullins, A.; Davidson, T. The Effects of Energy-Rich Diets on Discrimination Reversal Learning and on BDNF in the Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex of the Rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 182, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, S.; Imbe, H.; Morikawa, Y.; Kubo, C.; Senba, E. Chronic Stress, as Well as Acute Stress, Reduces BDNF MRNA Expression in the Rat Hippocampus but Less Robustly. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 53, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptan, Z.; Akgün-Dar, K.; Kapucu, A.; Dedeakayoğulları, H.; Batu, Ş.; Üzüm, G. Long Term Consequences on Spatial Learning-Memory of Low-Calorie Diet during Adolescence in Female Rats; Hippocampal and Prefrontal Cortex BDNF Level, Expression of NeuN and Cell Proliferation in Dentate Gyrus. Brain Res. 2015, 1618, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, W.; Lee, J.; Guo, Z.; Mattson, M.P. Dietary Restriction Stimulates BDNF Production in the Brain and Thereby Protects Neurons Against Excitotoxic Injury. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2001, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, M.; Poddighe, L.; Boi, M.; Sanna, F.; Piludu, M.; Sanna, F.; Corda, M.; Giorgi, O.; Quartu, M. Effect of Acute Stress on the Expression of BDNF, TrkB, and PSA-NCAM in the Hippocampus of the Roman Rats: A Genetic Model of Vulnerability/Resistance to Stress-Induced Depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilland, K.E.; Fox, E.A. Effect of Food Deprivation or Short-Term Western Diet Feeding on BDNF Protein Expression in the Hypothalamic Arcuate, Paraventricular, and Ventromedial Nuclei. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2017, 312, R611–R625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, J.P.; Mesquita, R.; Assunção, M.; Pereira, P.A. Effects of Food Restriction on Synthesis and Expression of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Tyrosine Kinase B in Dentate Gyrus Granule Cells of Adult Rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 399, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, S.; Rajeev, V.; Fann, D.Y.; Jo, D.; Arumugam, T.V. Intermittent Fasting Increases Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Huang, X.-F. Energy-Restricted Pair-Feeding Normalizes Low Levels of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor/Tyrosine Kinase B MRNA Expression in the Hippocampus, but Not Ventromedial Hypothalamic Nucleus, in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Neuroscience 2009, 160, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, Z.; Kalyani, M.; Janik, J.M.; Shi, H. Effects of Energy Status and Diet on Bdnf Expression in the Ventromedial Hypothalamus of Male and Female Rats. Physiol. Behav. 2014, 130, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rage, F.; Givalois, L.; Marmigère, F.; Tapia-Arancibia, L.; Arancibia, S. Immobilization Stress Rapidly Modulates BDNF MRNA Expression in the Hypothalamus of Adult Male Rats. Neuroscience 2002, 112, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaich, C.L.; Wellman, T.L.; Einwag, Z.; Dutko, R.A.; Erdos, B. Inhibition of BDNF Signaling in the Paraventricular Nucleus of the Hypothalamus Lowers Acute Stress-Induced Pressor Responses. J. Neurophysiol. 2018, 120, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastioli, G.; Arnold, J.C.; Mancini, M.; Mar, A.C.; Gamallo-Lana, B.; Saadipour, K.; Chao, M.V.; Rice, M.E. Voluntary Exercise Boosts Striatal Dopamine Release: Evidence for the Necessary and Sufficient Role of BDNF. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 4725–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyanishi, H.; Muramatsu, S.-I.; Nitta, A. Striatal Shati/Nat8l-BDNF Pathways Determine the Sensitivity to Social Defeat Stress in Mice through Epigenetic Regulation. Neuropsychopharmacol. Off. Publ. Am. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 46, 1594–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, V.; Han, M.-H.; Graham, D.L.; Berton, O.; Renthal, W.; Russo, S.J.; LaPlant, Q.; Graham, A.; Lutter, M.; Lagace, D.C.; et al. Molecular Adaptations Underlying Susceptibility and Resistance to Social Defeat in Brain Reward Regions. Cell 2007, 131, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, M.P.; Sanna, F.; Boi, M.; Poddighe, L.; Secci, L.; Trucas, M.; Fernández-Teruel, A.; Corda, M.G.; Giorgi, O.; Quartu, M. Acute Stress Induces Different Changes on the Expression of BDNF and TrkB in the Mesocorticolimbic System of Two Lines of Rats Differing in Their Response to Stressors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Zhu, Z.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Cheng, S.; Qin, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, D.; Pan, F. Effects of Traumatic Stress in Adolescence on PTSD-like Behaviors, Dendrite Development, and H3K9me2/BDNF Expression in the Amygdala of Male Rats. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 296, 388–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, T.; Hashimoto, S.; Yanamoto, H.; Ikawa, M.; Nakano, Y.; Sekiyama, T.; Kou, K.; Kashiwamura, S.; Takeda, C.; Fujioka, H. Response of Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor to Combining Cognitive and Physical Exercise. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 1119–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Xiong, J.; Lim, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Huang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Zhong, J.; Xiao, Z.; Zhou, X.-F. Upregulation of Blood ProBDNF and Its Receptors in Major Depression. J. Affect. Disord. 2013, 150, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herhaus, B.; Heni, M.; Bloch, W.; Petrowski, K. Acute and Chronic Psychosocial Stress by the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Male Humans: A Highly Standardized and Controlled Study. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeler, J.; Burghardt, N. Activity-Based Anorexia for Modeling Vulnerability and Resilience in Mice. Bio-Protocol 2021, 11, e4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrucci, C.L.; Milton, L.K.; Greaves, E.; Stefanidis, A.; van den Buuse, M.; Oldfield, B.J.; Foldi, C.J. The BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism Does Not Increase Susceptibility to Activity-Based Anorexia in Rats. Biology 2022, 11, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-W.; Surgent, O.; Rana, B.S.; Lee, F.; Aoki, C. Variant BDNF-Val66Met Polymorphism Is Associated with Layer-Specific Alterations in GABAergic Innervation of Pyramidal Neurons, Elevated Anxiety and Reduced Vulnerability of Adolescent Male Mice to Activity-Based Anorexia. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 3980–3993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Madra, M.; Zeltser, L.M. BDNF-Val66Met Variant and Adolescent Stress Interact to Promote Susceptibility to Anorexic Behavior in Mice. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohoe, T.P. Stress-Induced Anorexia: Implications for Anorexia Nervosa. Life Sci. 1984, 34, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarda, A.S.; Schreyer, C.C.; Boersma, G.J.; Tamashiro, K.L.; Moran, T.H. Anorexia Nervosa as a Motivated Behavior: Relevance of Anxiety, Stress, Fear and Learning. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 152, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlovsky, N.; Matar, M.A.; Kaplan, Z.; Kotler, M.; Zohar, J.; Cohen, H. Long-Term down-Regulation of BDNF MRNA in Rat Hippocampal CA1 Subregion Correlates with PTSD-like Behavioural Stress Response. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2007, 10, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Qi, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, G.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Du, Z.; Sun, L. Applying Ketamine to Alleviate the PTSD-like Effects by Regulating the HCN1-Related BDNF. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 86, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Zhang, J.; Hong, L.; Huang, W.; Dai, X.; Ye, Q.; Chen, X. Metformin Ameliorates Stress-Induced Depression-like Behaviors via Enhancing the Expression of BDNF by Activating AMPK/CREB-Mediated Histone Acetylation. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 260, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisch, A.J.; Bolaños, C.A.; de Wit, J.; Simonak, R.D.; Pudiak, C.M.; Barrot, M.; Verhaagen, J.; Nestler, E.J. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Ventral Midbrain-Nucleus Accumbens Pathway: A Role in Depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 54, 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berton, O.; McClung, C.A.; Dileone, R.J.; Krishnan, V.; Renthal, W.; Russo, S.J.; Graham, D.; Tsankova, N.M.; Bolanos, C.A.; Rios, M.; et al. Essential Role of BDNF in the Mesolimbic Dopamine Pathway in Social Defeat Stress. Science 2006, 311, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvas, M.; Palmiter, R.D. Contributions of Striatal Dopamine Signaling to the Modulation of Cognitive Flexibility. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 69, 704–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyanishi, H.; Nitta, A. A Role of BDNF in the Depression Pathogenesis and a Potential Target as Antidepressant: The Modulator of Stress Sensitivity “Shati/Nat8l-BDNF System” in the Dorsal Striatum. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taliaz, D.; Nagaraj, V.; Haramati, S.; Chen, A.; Zangen, A. Altered Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Expression in the Ventral Tegmental Area, but Not in the Hippocampus, Is Essential for Antidepressant-Like Effects of Electroconvulsive Therapy. Biol. Psychiatry 2013, 74, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Ghosh, A.K.; Ghosh, B.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Mondal, A.C. Decreased MRNA and Protein Expression of BDNF, NGF, and Their Receptors in the Hippocampus from Suicide: An Analysis in Human Postmortem Brain. Clin. Med. Insights Pathol. 2013, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wang, D.-D.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Lee, F.S.; Chen, Z.-Y. Variant Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Val66Met Polymorphism Alters Vulnerability to Stress and Response to Antidepressants. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 4092–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosang, G.M.; Shiles, C.; Tansey, K.E.; McGuffin, P.; Uher, R. Interaction between Stress and the BDNFVal66Met Polymorphism in Depression: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro-Catala, M.; van Nierop, M.; Barrantes-Vidal, N.; Cristóbal-Narváez, P.; Sheinbaum, T.; Kwapil, T.R.; Peña, E.; Jacobs, N.; Derom, C.; Thiery, E.; et al. Childhood Trauma, BDNF Val66Met and Subclinical Psychotic Experiences. Attempt at Replication in Two Independent Samples. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 83, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehto, K.; Mäestu, J.; Kiive, E.; Veidebaum, T.; Harro, J. BDNF Val66Met Genotype and Neuroticism Predict Life Stress: A Longitudinal Study from Childhood to Adulthood. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. J. Eur. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 26, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Castro, T.B.; Salas-Magaña, M.; Juárez-Rojop, I.E.; López-Narváez, M.L.; Tovilla-Zárate, C.A.; Hernández-Díaz, Y. Exploring the Association between BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism and Suicidal Behavior: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2017, 94, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatt, J.M.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Dobson-Stone, C.; Paul, R.H.; Bryant, R.A.; Schofield, P.R.; Gordon, E.; Kemp, A.H.; Williams, L.M. Interactions between BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism and Early Life Stress Predict Brain and Arousal Pathways to Syndromal Depression and Anxiety. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Li, X.; McGue, M. Interacting Effect of BDNF VAL66MET Polymorphism and Stressful Life Events on Adolescent Depression. Genes Brain Behav. 2012, 11, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ji, M.; Xu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhu, S.; Li, W. Sevoflurane Attenuates Stress-Enhanced Fear Learning by Regulating Hippocampal BDNF Expression and Akt/GSK-3β Signaling Pathway in a Rat Model of Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder. J. Anesth. 2015, 29, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalev, I.; Lerer, E.; Israel, S.; Uzefovsky, F.; Gritsenko, I.; Mankuta, D.; Ebstein, R.P.; Kaitz, M. BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism Is Associated with HPA Axis Reactivity to Psychological Stress Characterized by Genotype and Gender Interactions. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, N.; Osinsky, R.; Schmitz, A.; Mueller, E.; Kuepper, Y.; Hennig, J. The BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism Affects HPA-Axis Reactivity to Acute Stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2010, 35, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo-Martínez, L.; Rupérez, F.J.; Martos-Moreno, G.Á.; Graell, M.; Barbas, C.; Argente, J.; García, A. Unveiling Metabolic Phenotype Alterations in Anorexia Nervosa through Metabolomics. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, J. PVN Pathways Controlling Energy Homeostasis. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.J.; Liao, G.-Y.; Kinney, C.E.; Sahibzada, N.; Xu, B. Discrete BDNF Neurons in the Paraventricular Hypothalamus Control Feeding and Energy Expenditure. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelleymounter, M.A.; Cullen, M.J.; Wellman, C.L. Characteristics of BDNF-Induced Weight Loss. Exp. Neurol. 1995, 131, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Loh, K.H.; Wu, M.; Morgan, D.A.; Schneeberger, M.; Yu, X.; Chi, J.; Kosse, C.; Kim, D.; Rahmouni, K.; et al. A Leptin-BDNF Pathway Regulating Sympathetic Innervation of Adipose Tissue. Nature 2020, 583, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-W.; Xu, B. Rapid and Lasting Effects of Activating BDNF-Expressing PVH Neurons on Energy Balance. eNeuro 2022, 9, ENEURO.0009-22.2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.-Y.; Bouyer, K.; Kamitakahara, A.; Sahibzada, N.; Wang, C.-H.; Rutlin, M.; Simerly, R.B.; Xu, B. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Is Required for Axonal Growth of Selective Groups of Neurons in the Arcuate Nucleus. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Sobue, G.; Yamamoto, K.; Terao, S.; Mitsuma, T. Expression of MRNAs for Neurotrophic Factors (NGF, BDNF, NT-3, and GDNF) and Their Receptors (P75NGFR, TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC) in the Adult Human Peripheral Nervous System and Nonneural Tissues. Neurochem. Res. 1996, 21, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donovan, M.J.; Miranda, R.C.; Kraemer, R.; McCaffrey, T.A.; Tessarollo, L.; Mahadeo, D.; Sharif, S.; Kaplan, D.R.; Tsoulfas, P.; Parada, L.; et al. Neurotrophin and Neurotrophin Receptors in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Am. J. Pathol. 1995, 147, 309–324. [Google Scholar]
- Expression of neurotrophins in skeletal muscle: Quantitative comparison and significance for motoneuron survival and maintenance of function. J. Neurosci. Res. 1995, 42, 21–33. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lommatzsch, M.; Braun, A.; Mannsfeldt, A.; Botchkarev, V.A.; Botchkareva, N.V.; Paus, R.; Fischer, A.; Lewin, G.R.; Renz, H. Abundant Production of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor by Adult Visceral Epithelia. Implications for Paracrine and Target-Derived Neurotrophic Functions. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 1183–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassiman, D.; Denef, C.; Desmet, V.J.; Roskams, T. Human and Rat Hepatic Stellate Cells Express Neurotrophins and Neurotrophin Receptors. Hepatology 2001, 33, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sornelli, F.; Fiore, M.; Chaldakov, G.N.; Aloe, L. Adipose Tissue-Derived Nerve Growth Factor and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor: Results from Experimental Stress and Diabetes. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2009, 28, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kharitonenkov, A.; Shiyanova, T.L.; Koester, A.; Ford, A.M.; Micanovic, R.; Galbreath, E.J.; Sandusky, G.E.; Hammond, L.J.; Moyers, J.S.; Owens, R.A.; et al. FGF-21 as a Novel Metabolic Regulator. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1627–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teillon, S.; Calderon, G.A.; Rios, M. Diminished Diet-Induced Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia and Enhanced Expression of PPARalpha and FGF21 in Mice with Hepatic Ablation of Brain-Derived Neurotropic Factor. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 205, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Genzer, Y.; Chapnik, N.; Froy, O. Effect of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) on Hepatocyte Metabolism. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 88, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, U.J.; Choi, M.-S. Obesity and Its Metabolic Complications: The Role of Adipokines and the Relationship between Obesity, Inflammation, Insulin Resistance, Dyslipidemia and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184–6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camerino, C.; Conte, E.; Cannone, M.; Caloiero, R.; Fonzino, A.; Tricarico, D. Nerve Growth Factor, Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Osteocalcin Gene Relationship in Energy Regulation, Bone Homeostasis and Reproductive Organs Analyzed by MRNA Quantitative Evaluation and Linear Correlation Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, M.; Itakura, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Nakagawa, T.; Noguchi, H.; Taiji, M. Comparison of the Antidiabetic Effects of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Thiazolidinediones in Obese Diabetic Mice. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2007, 9, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, V.B.; Aström, M.-B.; Chan, M.H.S.; Bruce, C.R.; Krabbe, K.S.; Prelovsek, O.; Akerström, T.; Yfanti, C.; Broholm, C.; Mortensen, O.H.; et al. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Is Produced by Skeletal Muscle Cells in Response to Contraction and Enhances Fat Oxidation via Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwa, M.; Yamamoto, K.-I.; Nakano, H.; Sasaki, H.; Radak, Z.; Kumagai, S. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Treatment Increases the SkeletalMuscle Glucose Transporter 4 Protein Expression in Mice. Physiol. Res. 2010, 59, 619–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Brobst, D.; Chan, W.S.; Tse, M.C.L.; Herlea-Pana, O.; Ahuja, P.; Bi, X.; Zaw, A.M.; Kwong, Z.S.W.; Jia, W.; et al. Muscle-Generated BDNF Is a Sexually Dimorphic Myokine That Controls Metabolic Flexibility. Sci. Signal. 2019, 12, eaau1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baeza-Raja, B.; Sachs, B.D.; Li, P.; Christian, F.; Vagena, E.; Davalos, D.; Le Moan, N.; Ryu, J.K.; Sikorski, S.L.; Chan, J.P.; et al. P75 Neurotrophin Receptor Regulates Energy Balance in Obesity. Cell Rep. 2016, 14, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandrini, L.; Di Minno, A.; Amadio, P.; Ieraci, A.; Tremoli, E.; Barbieri, S.S. Association between Obesity and Circulating Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Levels: Systematic Review of Literature and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckers, S.; Peeters, A.; Zegers, D.; Mertens, I.; Van Gaal, L.; Van Hul, W. Association of the BDNF Val66Met Variation with Obesity in Women. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2008, 95, 110–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shugart, Y.Y.; Chen, L.; Day, I.N.M.; Lewis, S.J.; Timpson, N.J.; Yuan, W.; Abdollahi, M.R.; Ring, S.M.; Ebrahim, S.; Golding, J.; et al. Two British Women Studies Replicated the Association between the Val66Met Polymorphism in the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and BMI. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. EJHG 2009, 17, 1050–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skledar, M.; Nikolac, M.; Dodig-Curkovic, K.; Curkovic, M.; Borovecki, F.; Pivac, N. Association between Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Val66Met and Obesity in Children and Adolescents. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2012, 36, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, B.; Cheng, H.; Shen, Y.; Chandak, G.R.; Zhao, X.; Hou, D.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Mi, J. Study of 11 BMI-Associated Loci Identified in GWAS for Associations with Central Obesity in the Chinese Children. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalenda, A.; Landgraf, K.; Löffler, D.; Kovacs, P.; Kiess, W.; Körner, A. The BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism Is Associated with Lower BMI, Lower Postprandial Glucose Levels and Elevated Carbohydrate Intake in Children and Adolescents. Pediatr. Obes. 2018, 13, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidović, V.; Maksimović, N.; Novaković, I.; Damnjanović, T.; Jekić, B.; Vidović, S.; Majkić Singh, N.; Stamenković-Radak, M.; Nikolić, D.; Marisavljević, D. Association of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Val66Met Polymorphism with Body Mass Index, Fasting Glucose Levels and Lipid Status in Adolescents. Balk. J. Med. Genet. BJMG 2020, 23, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-L.; Lee, S.-Y.; Chang, Y.-H.; Chen, S.-H.; Chu, C.-H.; Wang, T.-Y.; Chen, P.-S.; Lee, I.-H.; Yang, Y.-K.; Hong, J.-S.; et al. The BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism and Plasma Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Levels in Han Chinese Patients with Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 51, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; De, A.; Chowdhury, A. Epidemiology of Non-Alcoholic and Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Assis, G.G.; Hoffman, J.R.; Bojakowski, J.; Murawska-Ciałowicz, E.; Cięszczyk, P.; Gasanov, E.V. The Val66 and Met66 Alleles-Specific Expression of BDNF in Human Muscle and Their Metabolic Responsivity. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 14, 638176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rylander, M.; Brinton, J.T.; Sabel, A.L.; Mehler, P.S.; Gaudiani, J.L. A Comparison of the Metabolic Complications and Hospital Course of Severe Anorexia Nervosa by Binge-Purge and Restricting Subtypes. Eat. Disord. 2017, 25, 345–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, N.; Galusca, B.; Grouselle, D.; Frere, D.; Billard, S.; Epelbaum, J.; Estour, B. Ghrelin and Obestatin Circadian Levels Differentiate Bingeing-Purging from Restrictive Anorexia Nervosa. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 3057–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Encinas, A.; Sepúlveda, A.R.; Kurland, V.; Lacruz, T.; Nova, E.; Graell, M. Identifying Psychosocial and Familial Correlates and the Impact of the Stressful Life Events in the Onset of Anorexia Nervosa: Control-Case Study (ANOBAS): Psychosocial and Familial Correlates and Stressful Life Events in AN. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 284, 112768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakova, M.; Stuke, K.; Schuemberg, K.; Mueller, K.; Schoenknecht, P.; Schroeter, M.L. BDNF as a Biomarker for Successful Treatment of Mood Disorders: A Systematic & Quantitative Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2015, 174, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colle, R.; Trabado, S.; David, D.J.; Brailly-Tabard, S.; Hardy, P.; Falissard, B.; Fève, B.; Becquemont, L.; Verstuyft, C.; Corruble, E. Plasma BDNF Level in Major Depression: Biomarker of the Val66Met BDNF Polymorphism and of the Clinical Course in Met Carrier Patients. Neuropsychobiology 2017, 75, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutt, R.; Shankar, N.; Srivastava, S.; Yadav, A.; Ahmed, R.S. Cardiac Autonomic Tone, Plasma BDNF Levels and Paroxetine Response in Newly Diagnosed Patients of Generalised Anxiety Disorder. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2020, 24, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, L.; Sun, X.; Jia, X.; Li, D.; Gao, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J. The Relationship Among BDNF Val66Met Polymorphism, Plasma BDNF Level, and Trait Anxiety in Chinese Patients with Panic Disorder. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 932235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaleri, D.; Moretti, F.; Bartoccetti, A.; Mauro, S.; Crocamo, C.; Carrà, G.; Bartoli, F. The Role of BDNF in Major Depressive Disorder, Related Clinical Features, and Antidepressant Treatment: Insight from Meta-Analyses. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 149, 105159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duriez, P.; Ramoz, N.; Gorwood, P.; Viltart, O.; Tolle, V. A Metabolic Perspective on Reward Abnormalities in Anorexia Nervosa. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 30, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tommasi, M.; Sergi, M.R.; Konstantinidou, F.; Franzago, M.; Pesce, M.; Fratta, I.L.; Grilli, A.; Stuppia, L.; Picconi, L.; Saggino, A.; et al. Association of COMT, BDNF and 5-HTT Functional Polymorphisms with Personality Characteristics. Front. Biosci. Landmark Ed. 2021, 26, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauls, A.; Dimitropoulos, G.; Marcoux-Louie, G.; Singh, M.; Patten, S.B. Psychological Characteristics and Childhood Adversity of Adolescents with Atypical Anorexia Nervosa versus Anorexia Nervosa. Eat. Disord. 2022, 30, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katuri, R.B.; Gaur, G.S.; Sahoo, J.P.; Bobby, Z.; Shanmugavel, K. Association of Circulating Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor with Cognition among Adult Obese Population. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 30, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irani, H.; Abiri, B.; Khodami, B.; Yari, Z.; Lafzi Ghazi, M.; Hosseinzadeh, N.; Saidpour, A. Effect of Time Restricted Feeding on Anthropometric Measures, Eating Behavior, Stress, Serum Levels of BDNF and LBP in Overweight/Obese Women with Food Addiction: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutr. Neurosci. 2024, 27, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araya, A.V.; Orellana, X.; Espinoza, J. Evaluation of the Effect of Caloric Restriction on Serum BDNF in Overweight and Obese Subjects: Preliminary Evidences. Endocrine 2008, 33, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farinetti, A.; Aspesi, D.; Marraudino, M.; Marzola, E.; Amianto, F.; Abbate-Daga, G.; Gotti, S. Sexually Dimorphic Behavioral Effects of Maternal Separation in Anorexic Rats. Dev. Psychobiol. 2020, 62, 297–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Babyak, M.A.; Brummett, B.H.; Siegler, I.C.; Kuhn, C.M.; Williams, R.B. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Val66Met Polymorphism Interacts with Gender to Influence Cortisol Responses to Mental Stress. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2017, 79, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Weisbrod, A.S.; Barry, E.S.; Graham, A.M.; Eklund, M.; Grunberg, N.E. Decreased BDNF in Female but Not Male Rats after Exposure to Stress: A Sex-Sensitive Rat Model of Stress? Stress 2019, 22, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, P.; Ng, C.F.; Pang, B.P.S.; Chan, W.S.; Tse, M.C.L.; Bi, X.; Kwan, H.-L.R.; Brobst, D.; Herlea-Pana, O.; Yang, X.; et al. Muscle-Generated BDNF (Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor) Maintains Mitochondrial Quality Control in Female Mice. Autophagy 2022, 18, 1367–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, J.M.; Vargas, R.; Sanders, A.E.; Stuart, E.; Downey, A.E.; Chaphekar, A.V.; Nguyen, A.; Ganson, K.T.; Buckelew, S.M.; Garber, A.K. Clinical Characteristics of Hospitalized Male Adolescents and Young Adults with Atypical Anorexia Nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2024, 57, 1008–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.B.; Nagata, J.M.; Griffiths, S.; Calzo, J.P.; Brown, T.A.; Mitchison, D.; Blashill, A.J.; Mond, J.M. The Enigma of Male Eating Disorders: A Critical Review and Synthesis. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2017, 57, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridout, S.J.; Ridout, K.K.; Kole, J.; Fitzgerald, K.L.; Donaldson, A.A.; Alverson, B. Comparison of Eating Disorder Characteristics and Depression Comorbidity in Adolescent Males and Females: An Observational Study. Psychiatry Res. 2021, 296, 113650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulfvebrand, S.; Birgegård, A.; Norring, C.; Högdahl, L.; von Hausswolff-Juhlin, Y. Psychiatric Comorbidity in Women and Men with Eating Disorders Results from a Large Clinical Database. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 230, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, D.; Petrigna, L.; Pereira, F.C.; Muscella, A.; Bianco, A.; Tavares, P. The Impact of Physical Exercise on the Circulating Levels of BDNF and NT 4/5: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmati, M.; Lee, S.; Yon, D.K.; Lee, S.W.; Udeh, R.; McEvoy, M.; Oh, H.; Butler, L.; Keyes, H.; Barnett, Y.; et al. Physical Activity and Prevention of Mental Health Complications: An Umbrella Review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2024, 160, 105641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noetel, M.; Sanders, T.; Gallardo-Gómez, D.; Taylor, P.; del Pozo Cruz, B.; van den Hoek, D.; Smith, J.J.; Mahoney, J.; Spathis, J.; Moresi, M.; et al. Effect of Exercise for Depression: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomised Controlled Trials. BMJ 2024, 384, e075847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Banks, W.A.; Fasold, M.B.; Bluth, J.; Kastin, A.J. Transport of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor across the Blood–Brain Barrier. Neuropharmacology 1998, 37, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.B.; Williamson, R.; Santini, M.A.; Clemmensen, C.; Ettrup, A.; Rios, M.; Knudsen, G.M.; Aznar, S. Blood BDNF Concentrations Reflect Brain-Tissue BDNF Levels across Species. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2011, 14, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfving, B.; Plougmann, P.H.; Müller, H.K.; Mathé, A.A.; Rosenberg, R.; Wegener, G. Inverse Correlation of Brain and Blood BDNF Levels in a Genetic Rat Model of Depression. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2010, 13, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cain, S.W.; Chang, A.-M.; Vlasac, I.; Tare, A.; Anderson, C.; Czeisler, C.A.; Saxena, R. Circadian Rhythms in Plasma Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Differ in Men and Women. J. Biol. Rhythms 2017, 32, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, J.; Gorwood, P.; Ramoz, N.; Viltart, O. The Role of Central and Peripheral Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) as a Biomarker of Anorexia Nervosa Reconceptualized as a Metabo-Psychiatric Disorder. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162617
Cao J, Gorwood P, Ramoz N, Viltart O. The Role of Central and Peripheral Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) as a Biomarker of Anorexia Nervosa Reconceptualized as a Metabo-Psychiatric Disorder. Nutrients. 2024; 16(16):2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162617
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Jingxian, Philip Gorwood, Nicolas Ramoz, and Odile Viltart. 2024. "The Role of Central and Peripheral Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) as a Biomarker of Anorexia Nervosa Reconceptualized as a Metabo-Psychiatric Disorder" Nutrients 16, no. 16: 2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162617
APA StyleCao, J., Gorwood, P., Ramoz, N., & Viltart, O. (2024). The Role of Central and Peripheral Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) as a Biomarker of Anorexia Nervosa Reconceptualized as a Metabo-Psychiatric Disorder. Nutrients, 16(16), 2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16162617







