Prevalence and Impact of Malnutrition Risk on Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury and Stroke: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using Electronic Health Records
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
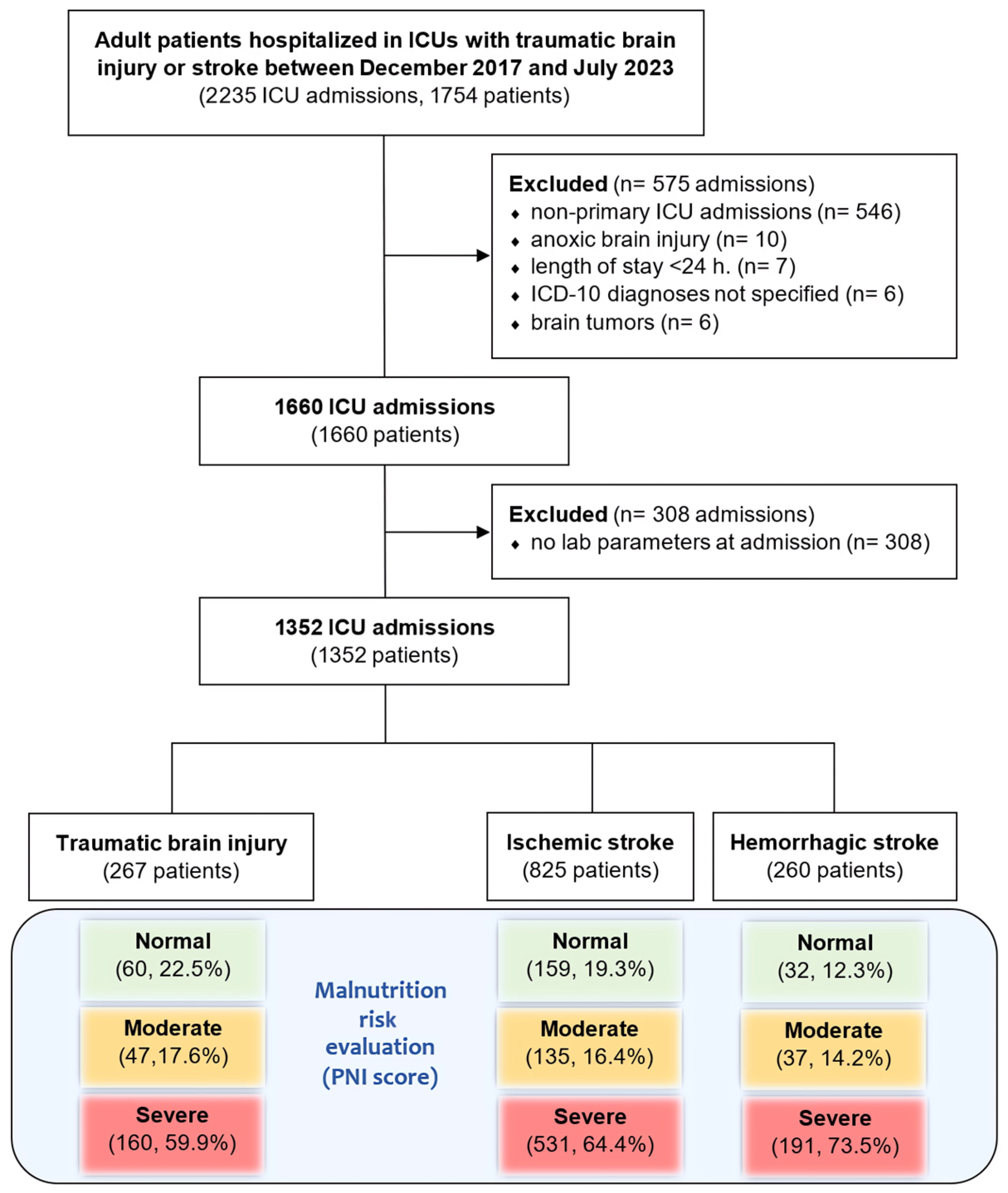
2.2. Selection Criteria
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Outcomes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Prevalence of Malnutrition Risk
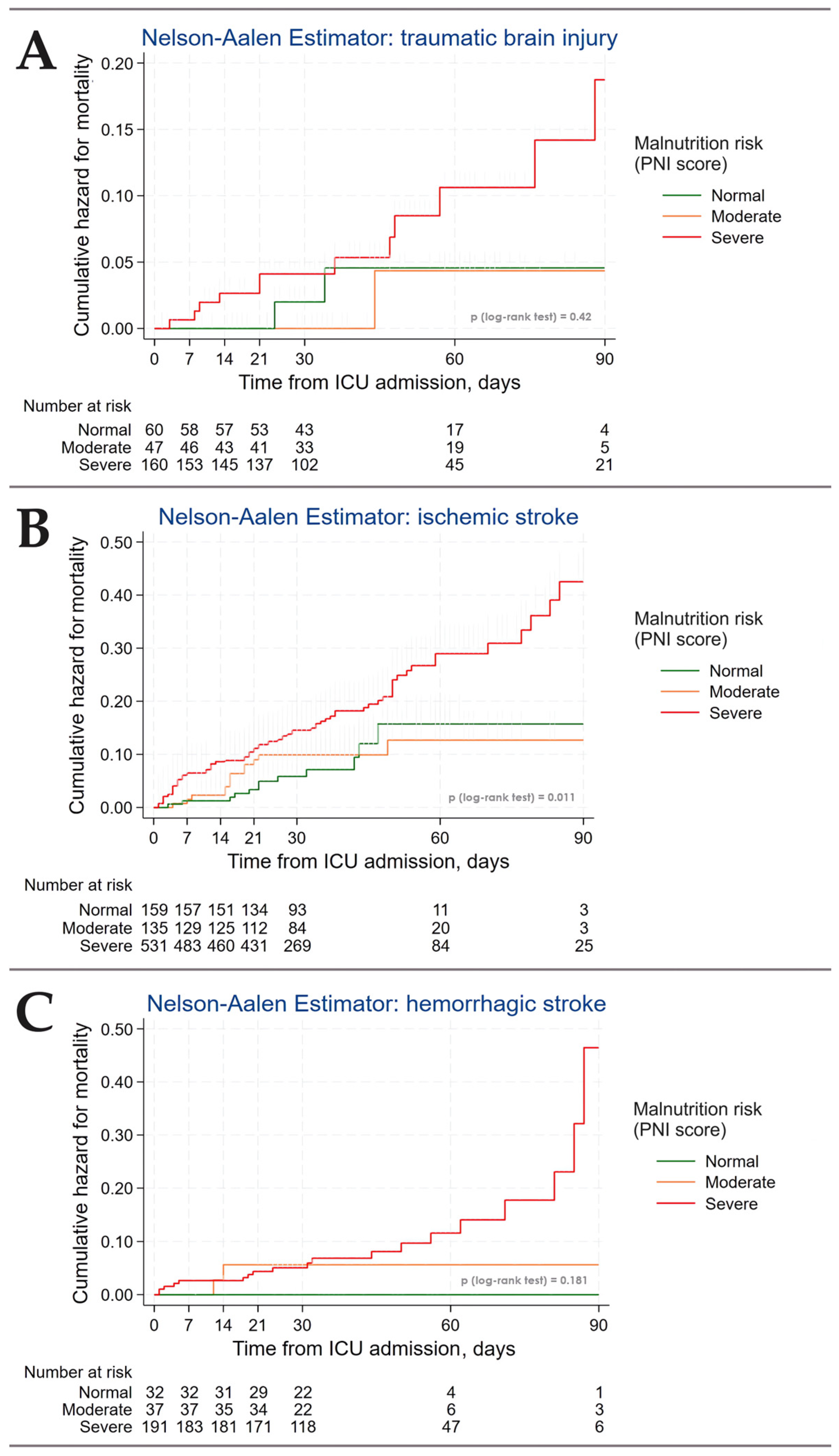
3.3. Outcomes
3.4. Predictors of Malnutrition Risk
| Parameters | Traumatic Brain Injury, n = 267 | Ischemic Stroke, n = 825 | Hemorrhagic Stroke, n = 260 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Nutrition (Not at Risk of Malnutrition) n = 125 PNI ≥ 33.8 † | At Risk of Malnutrition n = 142 PNI < 33.8 † | p Value | Normal Nutrition (Not at Risk of Malnutrition) n = 478 PNI ≥ 30.8 † | At Risk of Malnutrition n = 347 PNI < 30.8 † | p Value | Normal Nutrition (Not at Risk of Malnutrition) n = 124 PNI ≥ 31.6 † | At Risk of Malnutrition n = 136 PNI < 31.6 † | p Value | ||
| Sex | male | 85, 68% | 108, 76% | 0.142 1 | 274, 57% | 175, 50% | 0.05 1 | 82, 66% | 66, 49% | 0.004 1 |
| female | 40, 32% | 34, 24% | 204, 43% | 172, 50% | 42, 34% | 70, 51% | ||||
| Age, years | 34 (IQR 24–48) | 48 (IQR 37–60) | <0.001 2 | 66 (IQR 58–75) | 72 (IQR 63–81) | <0.001 2 | 52.5 (IQR 41–63.5) | 63 (IQR 56–69.5) | <0.001 2 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | * n = 113, 21.6 (IQR 19.0–24.6) | n = 127, 22.1 (IQR 18.9–25.4) | 0.4 2 | n = 425, 26.1 (IQR 23.0–30.5) | n = 319, 26.1 (IQR 22.8–30.8) | 0.8 2 | n = 118, 25.6 (IQR 21.8–29.4) | n = 122, 25.5 (IQR 22.6–30.03) | 0.86 | |
| SOFA at admission, score | n = 78, 2 (IQR 1–3) | n = 104, 3 (IQR 2–5) | <0.001 2 | n = 330, 2 (IQR 1–3) | n = 269, 4 (IQR 3–6) | <0.001 2 | n = 89, 2 (IQR 0–3) | n = 92, 3 (IQR 2–4) | <0.001 2 | |
| FOUR at admission, score | n = 79, 15 (IQR 14–16) | n = 110, 13 (IQR 10–15) | <0.001 2 | n = 352, 16 (IQR 15–16) | n = 269, 13 (IQR 9–16) | <0.001 2 | n = 97, 16 (IQR 14–16) | n = 94, 13 (IQR 11–16) | <0.001 2 | |
| GCS at admission, score | n = 81, 13 (IQR 10–15) | n = 111, 10 (IQR 8–14) | <0.001 2 | n = 358, 15 (IQR 12–15) | n = 277, 11 (IQR 8–14) | <0.001 2 | n = 98, 14 (IQR 12–15) | n = 97, 11 (IQR 9–14) | <0.001 2 | |
| CRS-R at admission, score | n = 59, 14 (IQR 5–22) | n = 69, 10 (IQR 5–18) | 0.037 2 | n = 228, 22 (IQR 17–23) | n = 165, 13 (IQR 5–20) | <0.001 2 | n = 54, 21 (IQR 17–22) | n = 67, 12 (IQR 5–20) | <0.001 2 | |
| Pneumonia at admission | 31, 25% | 57, 40% | 0.008 1 | 108, 23% | 184, 53% | <0.001 1 | 24, 20% | 65, 48% | <0.001 1 | |
| Coronary artery disease | 2, 1.6% | 15, 10.6% | 0.002 3 | 88, 19% | 125, 36% | <0.001 1 | 13, 11% | 31, 23% | 0.008 1 | |
| Arterial hypertension | 23, 18% | 59, 42% | <0.001 1 | 376, 79% | 257, 74% | 0.123 1 | 92, 74% | 105, 77% | 0.6 1 | |
| Type 2 diabetes | 0, 0% | 3, 2.1% | 0.3 3 | 26, 5.4% | 26, 7.5% | 0.2 3 | 6, 4.8% | 5, 3.7% | 0.7 3 | |
| Anemia | 5, 4.0% | 12, 8.5% | 0.2 3 | 7, 1.5% | 13, 3.7% | 0.04 3 | 3, 2.4% | 10, 7.4% | 0.089 3 | |
| WBC, 109/L | 7.4 (IQR 6.2–9.7) | 9.1 (IQR 7.1–11.5) | 0.002 2 | 8.3 (IQR 6.6–10.6) | 9.83 (IQR 7.3–12.6) | <0.001 2 | 8.5 (IQR 6.45–11.575) | 8.7 (IQR 6.6–11.62) | 0.66 | |
| NLR | 3.2 (IQR 2.2–5.3) | 5.0 (IQR 3.2–8.2) | <0.001 2 | 3.9 (IQR 2.6–6.6) | 7.1 (IQR 4.2–12.6) | <0.001 2 | 3.5 (IQR 2.5–7.4) | 6 (IQR 3.9–10.0) | <0.001 2 | |
| Platelets, 109/L | 344 (IQR 260–442) | 325 (IQR 244–416) | 0.3 2 | 264 (IQR 212–332) | 242 (IQR 185–314) | <0.001 2 | 311 (IQR 231–379.5) | 294 (IQR 226–376.5) | 0.5 2 | |
| INR | n = 123, 1.14 (IQR 1.06–1.27) | n = 139, 1.21 (IQR 1.13–1.36) | 0.004 2 | n = 474, 1.11 (IQR 1.02–1.24) | n = 342, 1.225 (IQR 1.1–1.35) | <0.001 2 | n = 123, 1.12 (IQR 1.06–1.22) | n = 135, 1.2 (IQR 1.08–1.35) | 0.001 2 | |
| Albumin, g/L | 37.9 (IQR 35.9–40.7) | 28.35 (IQR 25.1–31.9) | <0.001 2 | 36 (IQR 33.4–38.8) | 26.5 (IQR 23.8–28.7) | <0.001 2 | 35.85 (IQR 33.55–38.15) | 28 (IQR 25.55–30) | <0.001 2 | |
| Total protein, g/L | n = 124, 68.8 (IQR 66.4–72.2) | n = 140, 59.2 (IQR 54.5–64.9) | <0.001 2 | n = 460, 66.2 (IQR 62.2–70.2) | n = 335, 55.4 (IQR 50.7–59.4) | <0.001 2 | n = 119, 65.7 (IQR 62.6–70.1) | n = 135, 57 (IQR 53.2–61.6) | <0.001 2 | |
| Cholesterol, mmol/L | n = 12, 5.71 (IQR 4.52–6.37) | n = 4, 3.79 (IQR 3.13–4.52) | 0.02 2 | n = 39, 4.42 (IQR 3.62–5.43) | n = 25, 3.37 (IQR 2.92–3.82) | 0.002 2 | n = 10, 5.46 (IQR 4.43–6.02) | n = 13, 3.61 (IQR 2.88–4.38) | 0.004 2 | |
| Outcomes | ||||||||||
| Hospital mortality | 4, 3.2% | 14, 9.9% | 0.048 3 | 43, 9.0% | 79, 22.8% | <0.001 3 | 7, 5.6% | 14, 10.3% | 0.181 3 | |
| Hospital length of stay, days | 38 (IQR 27–62) | 39.5 (IQR 22–64) | 0.9 2 | 34 (IQR 23–47) | 25 (IQR 22–47) | <0.001 2 | 36.5 (IQR 26.5–52) | 35 (IQR 23–60) | 0.6 2 | |
| Need for MV | 42, 34% | 84, 59% | <0.001 1 | 123, 26% | 237, 68% | <0.001 1 | 47, 38% | 90, 66% | <0.001 1 | |
| Use of vasoactive drugs | 12, 9.6% | 32, 23% | 0.005 2 | 52, 11% | 92, 27% | <0.001 1 | 11, 8.9% | 23, 16.9% | 0.066 2 | |
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Findings
4.2. Relationship with Previous Studies
4.3. Significance of the Study Findings
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goldman, L.; Siddiqui, E.M.; Khan, A.; Jahan, S.; Rehman, M.U.; Mehan, S.; Sharma, R.; Budkin, S.; Kumar, S.N.; Sahu, A.; et al. Understanding Acquired Brain Injury: A Review. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodruff, T.M.; Thundyil, J.; Tang, S.C.; Sobey, C.G.; Taylor, S.M.; Arumugam, T.V. Pathophysiology, Treatment, and Animal and Cellular Models of Human Ischemic Stroke. Mol. Neurodegener. 2011, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahata, H.; Tsutsumi, K.; Baba, H.; Nagata, I.; Yonekura, M. Early Intervention to Promote Oral Feeding in Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhage: A Retrospective Cohort Study. BMC Neurol. 2011, 11, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherbakov, N.; Doehner, W. Sarcopenia in Stroke-Facts and Numbers on Muscle Loss Accounting for Disability after Stroke. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2011, 2, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aquilani, R.; Sessarego, P.; Iadarola, P.; Barbieri, A.; Boschi, F. Nutrition for Brain Recovery after Ischemic Stroke: An Added Value to Rehabilitation. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2011, 26, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brazinova, A.; Rehorcikova, V.; Taylor, M.S.; Buckova, V.; Majdan, M.; Psota, M.; Peeters, W.; Feigin, V.; Theadom, A.; Holkovic, L.; et al. Epidemiology of Traumatic Brain Injury in Europe: A Living Systematic Review. J. Neurotrauma 2021, 38, 1411–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saghaleini, S.H.; Dehghan, K.; Shadvar, K.; Sanaie, S.; Mahmoodpoor, A.; Ostadi, Z. Pressure Ulcer and Nutrition. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 22, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Liu, W.; Chen, Y.; She, Q.; Li, M.; Zhao, H.Y.; Zhao, W.; Peng, Z.; Wu, J. Effect of Poor Nutritional Status and Comorbidities on the Occurrence and Outcome of Pneumonia in Elderly Adults. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 719530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, N.; Wang, Y.; Dimachkie, M.M.; Barohn, R.J. Nutritional Neuropathies. Neurol. Clin. 2013, 31, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, L.M.; Ouma, J.R. A Descriptive Study of Malnutrition in Traumatic Brain Injury Patients. Panam. J. Trauma Crit. Care Emerg. Surg. 2022, 10, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poblete, R.A.; Yaceczko, S.; Aliakbar, R.; Saini, P.; Hazany, S.; Breit, H.; Louie, S.G.; Lyden, P.D.; Partikian, A. Optimization of Nutrition after Brain Injury: Mechanistic and Therapeutic Considerations. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Kim, J.H.; Choo, Y.H.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.; Ha, E.J.; Oh, J. Nutrition Therapy for Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury: A Narrative Review. Korean J. Neurotrauma 2023, 19, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.-H.; Shin, Y.-I. Nutritional Supplementation in Stroke Rehabilitation: A Narrative Review. Brain Neurorehabilit. 2022, 15, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.H.; Kim, J.S.; Kwon, S.U.; Yun, S.C.; Koh, J.Y.; Kang, D.W. Undernutrition as a Predictor of Poor Clinical Outcomes in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. Arch. Neurol. 2008, 65, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansare, M.L.; Kouda, D.A.; Diallo, I.M.; Bakhoum, M.; Mourabit, S.; Toure, K.; Ndiaye, M.; Diop, A.G.; Ndiaye, M.M. What Is the Nutritional Status of Your Patients Suffering from Strokes. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 176, 366–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouziana, S.D.; Tziomalos, K. Malnutrition in Patients with Acute Stroke. J. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 2011, 167898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrigan, M.L.; Escuro, A.A.; Celestin, J.; Kirby, D.F. Nutrition in the Stroke Patient. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2011, 26, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgos, R.; Bretón, I.; Cereda, E.; Desport, J.C.; Dziewas, R.; Genton, L.; Gomes, F.; Jésus, P.; Leischker, A.; Muscaritoli, M.; et al. ESPEN Guideline Clinical Nutrition in Neurology. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 354–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grechko, A.V.; Yadgarov, M.Y.; Yakovlev, A.A.; Berikashvili, L.B.; Kuzovlev, A.N.; Polyakov, P.A.; Kuznetsov, I.V.; Likhvantsev, V.V. Russian Intensive Care Dataset–RICD. Obs. Reanimatol. 2024, 20, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russian Intensive Care Dataset–RICD. Available online: https://fnkcrr-database.ru/ (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- Shirakabe, A.; Hata, N.; Kobayashi, N.; Okazaki, H.; Matsushita, M.; Shibata, Y.; Nishigoori, S.; Uchiyama, S.; Asai, K.; Shimizu, W. The Prognostic Impact of Malnutrition in Patients with Severely Decompensated Acute Heart Failure, as Assessed Using the Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) and Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) Score. Heart Vessels 2018, 33, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.; Chen, Y.; Ruan, J.; Yu, H.; Zhu, P.; Zhu, Y.Z. Correlation between the Prognostic Nutritional Index and Outcomes in Older Patients Aged ≥ 60 Years with Chronic Heart Failure. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2023, 45, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, M.; Mo, H.J.; Kim, C.; Sohn, J.H.; Yu, K.H.; Lee, S.H. The Association between Malnutrition Status and Hemorrhagic Transformation in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke Receiving Intravenous Thrombolysis. BMC Neurol. 2023, 23, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Vincenzo, O.; Luisi, M.L.E.; Alicante, P.; Ballarin, G.; Biffi, B.; Gheri, C.F.; Scalfi, L. The Assessment of the Risk of Malnutrition (Undernutrition) in Stroke Patients. Nutrients 2023, 15, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, N.C.; Salter, K.L.; Robertson, J.; Teasell, R.W.; Woodbury, M.G. Which Reported Estimate of the Prevalence of Malnutrition after Stroke Is Valid? Stroke 2009, 40, e66–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, P.; Blaser, A.R.; Berger, M.M.; Calder, P.C.; Casaer, M.; Hiesmayr, M.; Mayer, K.; Montejo-Gonzalez, J.C.; Pichard, C.; Preiser, J.C.; et al. ESPEN Practical and Partially Revised Guideline: Clinical Nutrition in the Intensive Care Unit. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 1671–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabbouh, T.; Torbey, M.T. Malnutrition in Stroke Patients: Risk Factors, Assessment, and Management. Neurocrit. Care 2018, 29, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Baek, S.; Jang, Y.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, E.S.; Byun, H.; Oh, M.K. Malnutrition and Associated Factors in Acute and Subacute Stroke Patients with Dysphagia. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, A.; Li, Y.; Xi, X.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Luo, X.; Zeng, X. Analysis of Risk Factors and Development of Predictive Model for Malnutrition in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury. Nutr. Neurosci. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, M. Poor Nutritional Status on Admission Predicts Poor Outcomes after Stroke Observational Data from the Food Trial. Stroke 2003, 34, 1450–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendavid, I.; Zusman, O.; Kagan, I.; Theilla, M.; Cohen, J.; Singer, P. Early Administration of Protein in Critically Ill Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compher, C.; Chittams, J.; Sammarco, T.; Nicolo, M.; Heyland, D.K. Greater Protein and Energy Intake May Be Associated with Improved Mortality in Higher Risk Critically Ill Patients: A Multicenter, Multinational Observational Study. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Leigh, J.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Choi, Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, J.E.; Cho, W.S.; Seo, H.G.; Oh, B.M. Decreasing Incidence and Mortality in Traumatic Brain Injury in Korea, 2008–2017: A Population-Based Longitudinal Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Kang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wei, Y. Application of Prognostic Nutritional Index in the Predicting of Prognosis in Young Adults with Acute Ischemic Stroke. World Neurosurg. 2023, 178, e292–e299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nergiz, S.; Ozturk, U. The Effect of Prognostic Nutritional Index on Infection in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients. Medicina 2023, 59, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grechko, A.V.; Gurkova, M.M.; Zhdanova, M.A.; Zurabov, A.Y.; Zurabov, F.M.; Kuzovlev, A.N.; Petrova, M.V.; Polyakov, P.A.; Cheboksarov, D.V.; Chernevskaya, E.A.; et al. Prevention of Nosocomial Pneumonia Recurrence Using a Bacteriophage Cocktail in Intensive Care Unit. Russ. J. Anesthesiol. Reanimatol. 2024, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderle, C.; Gomes, F.; Schuetz, P.; Stumpf, F.; Austin, P.; Ballesteros-Pomar, M.D.; Cederholm, T.; Fletcher, J.; Laviano, A.; Norman, K.; et al. ESPEN Guideline on Nutritional Support for Polymorbid Medical Inpatients. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 1545–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serón-Arbeloa, C.; Labarta-Monzón, L.; Puzo-Foncillas, J.; Mallor-Bonet, T.; Lafita-López, A.; Bueno-Vidales, N.; Montoro-Huguet, M. Malnutrition Screening and Assessment. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arfsten, H.; Cho, A.; Prausmüller, S.; Spinka, G.; Novak, J.; Goliasch, G.; Bartko, P.E.; Raderer, M.; Gisslinger, H.; Kornek, G.; et al. Inflammation-Based Scores as a Common Tool for Prognostic Assessment in Heart Failure or Cancer. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 725903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de van der Schueren, M.A.E.; Keller, H.; Cederholm, T.; Barazzoni, R.; Compher, C.; Correia, M.I.T.D.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Jager-Wittenaar, H.; Pirlich, M.; Steiber, A.; et al. Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition (GLIM): Guidance on Validation of the Operational Criteria for the Diagnosis of Protein-Energy Malnutrition in Adults. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 2872–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameters | Traumatic Brain Injury (1), n = 267 | Ischemic Stroke (2), n = 825 | Hemorrhagic Stroke (3), n = 260 | p 1–2–3 | p 1–2 † | p 1–3 † | p 2–3 † | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | male | 193, 72% | 449, 54% | 148, 57% | <0.001 1 | <0.001 1 | <0.001 1 | 0.51 |
| female | 74, 28% | 376, 46% | 112, 43% | |||||
| Age, years | 42 (IQR 29–56) | 69 (IQR 60–78) | 59 (IQR 48–68) | <0.001 2 | <0.001 4 | <0.001 4 | <0.001 4 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 | * n = 240, 21.8 (IQR 18.9–24.9) | n = 744, 26.1 (IQR 23–30.6) | n = 240, 25.6 (IQR 22.4–29.8) | <0.001 2 | <0.001 4 | <0.001 4 | 0.4 4 | |
| Transfer from other hospital | 250, 64% | 803, 97% | 254, 98% | 0.016 3 | 0.007 3 | 0.031 3 | 0.9 3 | |
| APACHE II at admission, score | n = 15, 6 (IQR 3–10) | n = 28, 7.5 (IQR 5–13.5) | n = 10, 8 (IQR 6–14) | 0.4 2 | - | - | - | |
| SOFA at admission, score | n = 182, 3 (IQR 2–4) | n = 599, 3 (IQR 1–5) | n = 181, 3 (IQR 1–4) | 0.111 2 | - | - | - | |
| FOUR at admission, score | n = 189, 14 (IQR 11–16) | n = 621, 16 (IQR 13–16) | n = 191, 15 (IQR 12–16) | <0.001 2 | <0.001 4 | 0.1 4 | 0.7 4 | |
| GCS at admission, score | n = 192, 11 (IQR 9–14) | n = 635, 14 (IQR 10–15) | n = 195, 14 (IQR 10–15) | <0.001 2 | <0.001 4 | <0.001 4 | 0.9 4 | |
| CRS-R at admission, score | n = 128, 11 (IQR 6–19) | n = 393, 20 (IQR 11–23) | n = 121, 18 (IQR 8–22) | <0.001 2 | <0.001 4 | 0.017 4 | 0.042 4 | |
| Pneumonia at admission | 88, 33% | 292, 35% | 89, 34% | 0.8 1 | - | - | - | |
| Comorbidity | ||||||||
| Coronary artery disease | 17, 6.4% | 213, 26% | 44, 17% | <0.001 3 | <0.001 1 | <0.001 1 | 0.003 1 | |
| Arterial hypertension | 82, 31% | 633, 77% | 197, 76% | <0.001 1 | <0.001 1 | <0.001 1 | 0.8 1 | |
| Type 2 diabetes | 3, 1.1% | 52, 6.3% | 11, 4.2% | <0.001 3 | <0.001 3 | 0.031 3 | 0.3 3 | |
| Anemia | 17, 6.4% | 20, 1.4% | 13, 5.0% | 0.005 3 | 0.005 3 | 0.6 3 | 0.06 3 | |
| Laboratory parameters and malnutrition risk assessment at admission | ||||||||
| PNI score | 33.4 (IQR 28.2–37.7) | 32.2 (IQR 27.3–36.7) | 31.3 (IQR 27.9–35.3) | 0.025 2 | 0.1 4 | 0.016 4 | 0.7 4 | |
| Status | Normal | 60, 23% | 159, 20% | 32, 12% | 0.012 1 | 0.4 1 | 0.002 1 | 0.014 1 |
| Moderate | 47, 18% | 135, 16% | 37, 14% | |||||
| Severe | 160, 60% | 531, 64% | 191, 74% | |||||
| WBC, 109/L | 8.2 (IQR 6.6–11) | 8.8 (IQR 6.8–11.5) | 8.6 (IQR 6.5–11.6) | 0.127 2 | - | - | - | |
| Lymphocyte count, 109/L | 1.4 (IQR 1.1–1.8) | 1.2 (IQR 0.9–1.8) | 1.2 (IQR 0.9–1.8) | 0.005 2 | 0.004 4 | 0.1 4 | 0.9 4 | |
| Neutrophil count, 109/L | 5.6 (IQR 4.3–8.4) | 6.4 (IQR 4.5–9.2) | 6.4 (IQR 4.5–8.9) | 0.027 2 | 0.024 4 | 0.1 4 | 0.9 4 | |
| NLR | 4.3 (IQR 2.6–6.9) | 5 (IQR 3.1–9) | 5 (IQR 2.9–8.7) | <0.001 2 | 0.001 4 | 0.02 4 | 0.9 4 | |
| Platelets, 109/L | 337 (IQR 251–429) | 255 (IQR 201–328) | 305 (IQR 228.5–379.5) | <0.001 2 | <0.001 4 | 0.01 4 | <0.001 4 | |
| INR | n = 262, 1.18 (IQR 1.1–1.3) | n = 816, 1.15 (IQR 1.1–1.3) | n = 258, 1.15 (IQR 1.1–1.3) | 0.026 2 | 0.02 4 | 0.4 4 | 0.9 4 | |
| Albumin, g/L | 33.4 (IQR 28.2–37.7) | 32.2 (IQR 27.3–36.7) | 31.3 (IQR 27.9–35.3) | 0.025 2 | 0.1 4 | 0.025 4 | 0.7 4 | |
| Total protein, g/L | n = 264, 65.1 (IQR 58.5–69.7) | n = 795, 62 (IQR 56.1–67.6) | n = 254, 61.8 (IQR 56.2–66.3) | <0.001 2 | <0.001 4 | <0.001 4 | 0.9 4 | |
| Cholesterol, mmol/L | n = 16, 4.9 (IQR 4.4–6.3) | n = 64, 3.9 (IQR 3.1–4.7) | n = 23, 4.4 (IQR 3.1–5.6) | 0.009 2 | 0.008 4 | 0.3 4 | 0.7 4 | |
| Outcomes | ||||||||
| Hospital mortality | 18, 6.7% | 122, 14.8% | 21, 8.1% | <0.001 3 | <0.001 3 | 0.6 3 | 0.004 3 | |
| Hospital length of stay, days | 39 (IQR 24–63) | 31 (IQR 22–47) | 36 (IQR 24–56) | <0.001 2 | <0.001 4 | 0.9 4 | 0.001 4 | |
| Need for MV | 126, 47% | 360, 44% | 137, 53% | 0.035 1 | 0.3 1 | 0.2 1 | 0.011 1 | |
| Use of vasoactive drugs | 44, 17% | 144, 18% | 34, 13% | 0.3 1 | - | - | - | |
| Discharge department | ICU palliative psych. ward neurorehabilitation | 126, 43% | 386, 47% | 130, 50% | 0.5 1 | - | - | - |
| 69, 26% | 209, 25% | 72, 28% | ||||||
| 72, 27% | 230, 28% | 58, 22% | ||||||
| Parameters | Univariate Analysis HR (95% CI) | p Value | Multivariable Analysis adj. HR (95% CI) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (ref. male) | 1.59 (1.16–2.16) | 0.003 | 0.8 | |
| Age * | 1.044 (1.032–1.055) | <0.001 | 1.038 (1.023–1.052) | <0.001 |
| SOFA * | 1.37 (1.30–1.45) | <0.001 | 1.33 (1.26–1.41) | <0.001 |
| FOUR | 0.85 (0.82–0.89) | <0.001 | 0.4 | |
| GCS | 0.85 (0.81–0.90) | <0.001 | 0.2 | |
| CRS-R | 0.94 (0.91–0.97) | <0.001 | ||
| Pneumonia at admission | 2.17(1.59–2.96) | <0.001 | 0.3 | |
| Coronary artery disease | 2.23 (1.58–3.14) | <0.001 | 0.1 | |
| Arterial hypertension | 1.84 (1.28–2.64) | <0.001 | 0.9 | |
| Type 2 diabetes | 2.08 (1.12–3.86) | 0.020 | 0.9 | |
| Anemia | 0.67 (0.21–2.11) | 0.5 | - | |
| Ischemic stroke (ref. TBI) | 3.06 (1.85–5.04) | <0.001 | 0.4 | |
| Hemorrhagic stroke (ref. TBI) | 1.45 (0.77–2.73) | 0.3 | - | |
| PNI score | 0.918 (0.893–0.943) | <0.001 | 0.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shestopalov, A.E.; Yakovleva, A.V.; Yadgarov, M.Y.; Sergeev, I.V.; Kuzovlev, A.N. Prevalence and Impact of Malnutrition Risk on Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury and Stroke: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using Electronic Health Records. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152396
Shestopalov AE, Yakovleva AV, Yadgarov MY, Sergeev IV, Kuzovlev AN. Prevalence and Impact of Malnutrition Risk on Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury and Stroke: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using Electronic Health Records. Nutrients. 2024; 16(15):2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152396
Chicago/Turabian StyleShestopalov, Alexander E., Alexandra V. Yakovleva, Mikhail Ya. Yadgarov, Ivan V. Sergeev, and Artem N. Kuzovlev. 2024. "Prevalence and Impact of Malnutrition Risk on Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury and Stroke: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using Electronic Health Records" Nutrients 16, no. 15: 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152396
APA StyleShestopalov, A. E., Yakovleva, A. V., Yadgarov, M. Y., Sergeev, I. V., & Kuzovlev, A. N. (2024). Prevalence and Impact of Malnutrition Risk on Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury and Stroke: A Retrospective Cohort Study Using Electronic Health Records. Nutrients, 16(15), 2396. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16152396






