Contemporary Perspectives on the Role of Vitamin D in Enhancing Gut Health and Its Implications for Preventing and Managing Intestinal Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
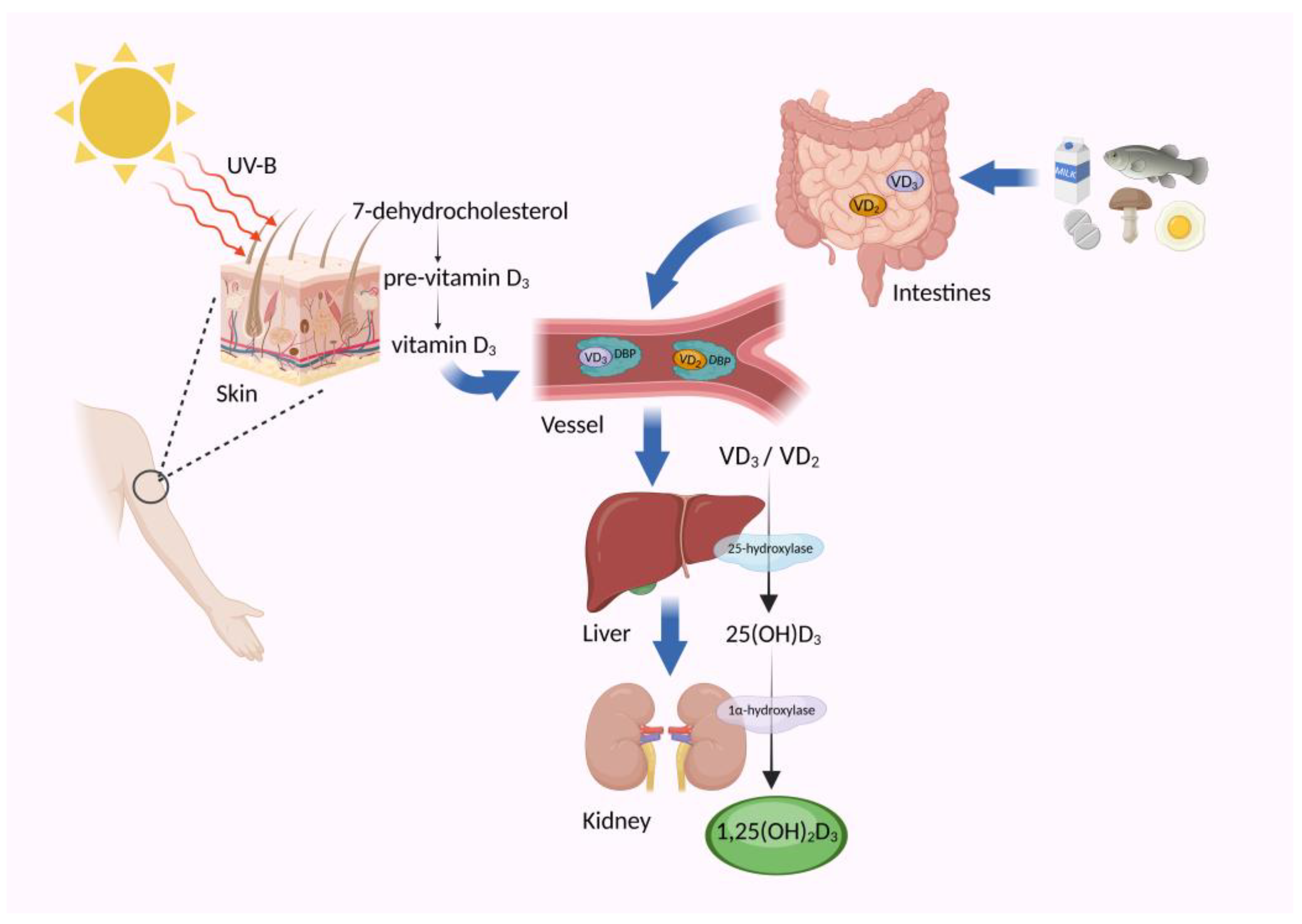
2. Understanding Vitamin D: Definition and Sources
3. The Dynamic Interplay: Impact of Vitamin D on the Gut Microbiome and Intestinal Barrier Function
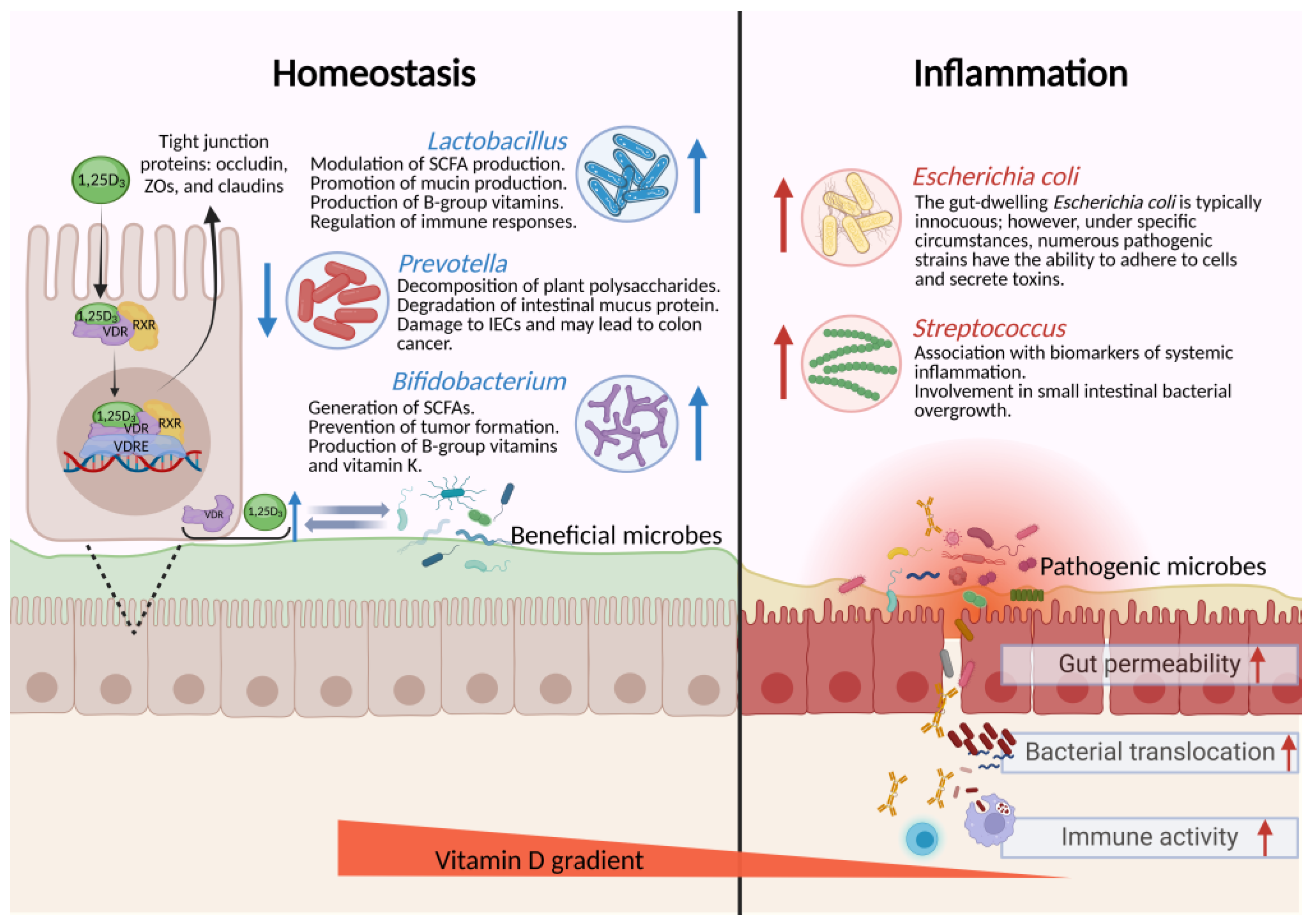
3.1. Regulation of Vitamin D on the Composition of the Gut Microbiota
3.2. Contribution of the Gut Microbiome to Vitamin D Metabolism
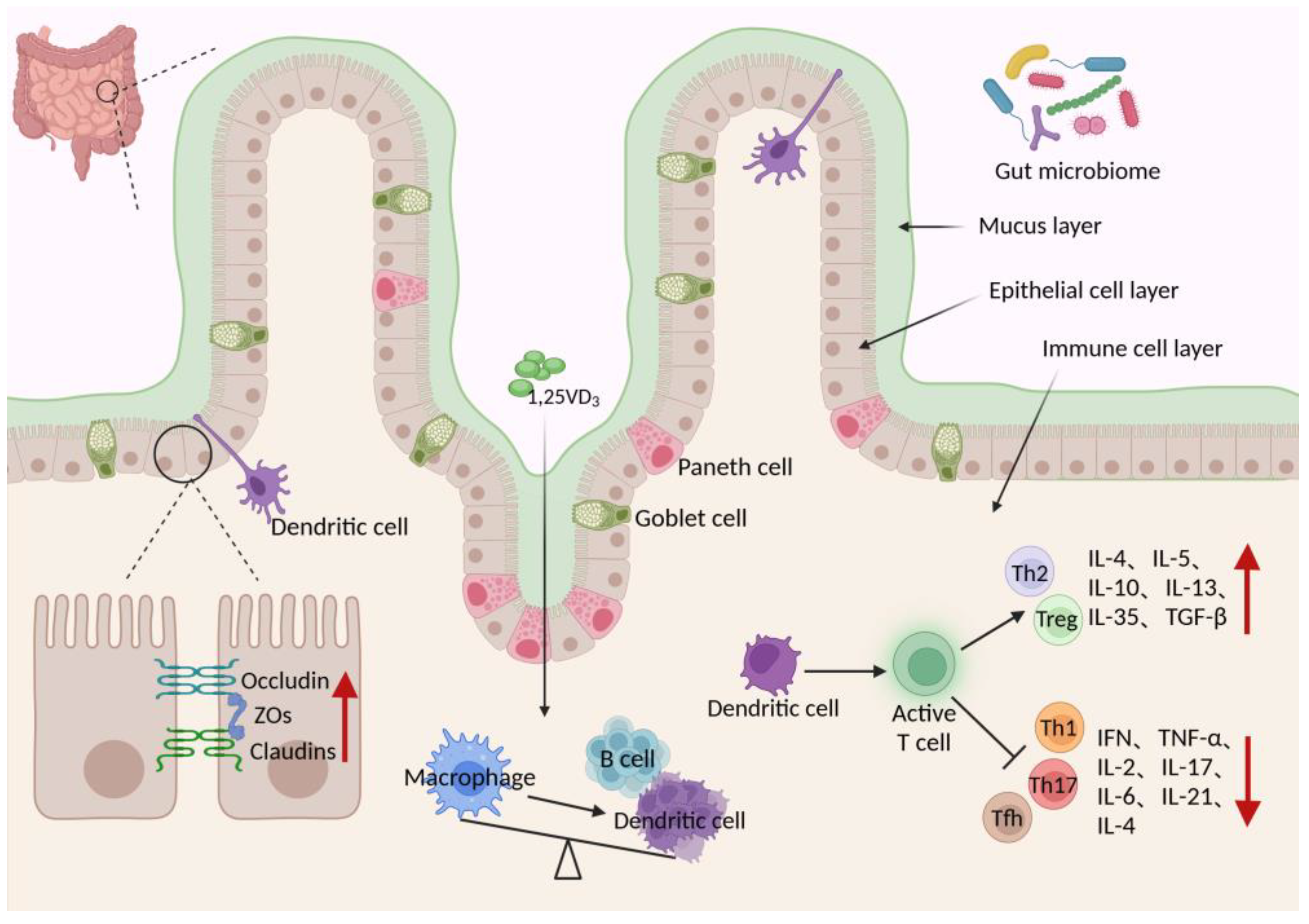
3.3. Role of Vitamin D in Preserving Intestinal Barrier Function
3.4. Consequences of Vitamin D Deficiency on Intestinal Barrier Function
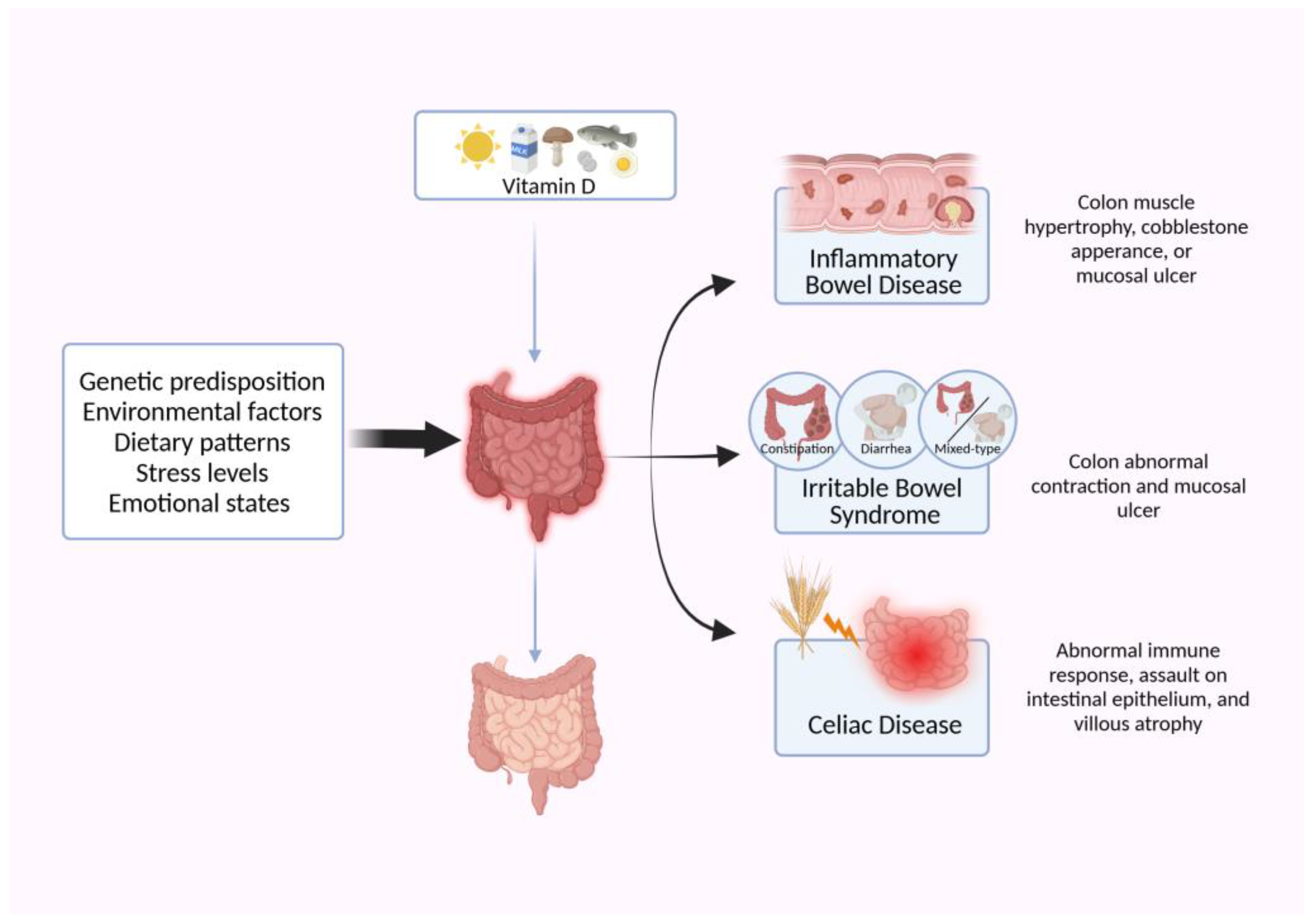
4. Unraveling the Nexus: Association of Vitamin D with Gut Diseases
4.1. Vitamin D and Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
4.2. Implications of Vitamin D in Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
4.3. Influence of Vitamin D in Celiac Disease (CeD)
5. Limitations and Future Aspects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wacker, M.; Holick, M.F. Sunlight and Vitamin D: A global perspective for health. Dermato-Endocrinology 2013, 5, 51–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleet, J.C. Vitamin D and Gut Health. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1390, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thursby, E.; Juge, N. Introduction to the human gut microbiota. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, P.; Ishimoto, T.; Fu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y. The Gut Microbiota in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 733992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Feng, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chao, G.; Zhang, S. Gut microbiota and intestinal immunity—A crosstalk in irritable bowel syndrome. Immunology 2024, 172, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sone, T.; Scott, R.A.; Hughes, M.R.; Malloy, P.J.; Feldman, D.; O’Malley, B.W.; Pike, J.W. Mutant vitamin D receptors which confer hereditary resistance to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in humans are transcriptionally inactive in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 20230–20234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Singh, A.; Cabral, C.; Kumar, R.; Ganguly, R.; Kumar Rana, H.; Gupta, A.; Rosaria Lauro, M.; Carbone, C.; Reis, F.; Pandey, A.K. Beneficial Effects of Dietary Polyphenols on Gut Microbiota and Strategies to Improve Delivery Efficiency. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangestani, H.; Boroujeni, H.K.; Djafarian, K.; Emamat, H.; Shab-Bidar, S. Vitamin D and The Gut Microbiota: A Narrative Literature Review. Clin. Nutr. Res. 2021, 10, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martens, P.J.; Gysemans, C.; Verstuyf, A.; Mathieu, A.C. Vitamin D’s Effect on Immune Function. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pinto, R.; Pietropaoli, D.; Chandar, A.K.; Ferri, C.; Cominelli, F. Association Between Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Vitamin D Deficiency: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2708–2717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, N.; Wang, D.; Zhang, J.; Gong, X. Efficacy of vitamin D in treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e12662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valvano, M.; Magistroni, M.; Cesaro, N.; Carlino, G.; Monaco, S.; Fabiani, S.; Vinci, A.; Vernia, F.; Viscido, A.; Latella, G. Effectiveness of Vitamin D Supplementation on Disease Course in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients: Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2024, 30, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bikle, D.D. Vitamin D: Production, Metabolism and Mechanisms of Action. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., Hofland, J., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.J.; Pandohee, J.; Xu, B.J. Recent developments and emerging trends in dietary vitamin D sources and biological conversion. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, S.; Yuan, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, J. The role of vitamin D deficiency in the development of paediatric diseases. Ann. Med. 2023, 55, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggeletopoulou, I.; Tsounis, E.P.; Mouzaki, A.; Triantos, C. Exploring the Role of Vitamin D and the Vitamin D Receptor in the Composition of the Gut Microbiota. Front. Biosci. Landmark 2023, 28, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, J.P.; Reinhardt, T.A.; Horst, R.L. Enzymes and factors controlling vitamin D metabolism and action in normal and milk fever cows. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 4022–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D deficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiamenghi, V.I.; de Mello, E.D. Vitamin D deficiency in children and adolescents with obesity: A meta-analysis. J. Pediatr. 2021, 97, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, W.; Hammond, L.A.; Cotter, E.; Osborne, G.W.; Alexander, S.A.; Nink, V.; Cui, X.Y.; Eyles, D.W. Developmental Vitamin D (DVD) Deficiency Reduces Nurr1 and TH Expression in Post-mitotic Dopamine Neurons in Rat Mesencephalon. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 2443–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, P.; Agarwal, Y.; Hameed, M. Recent Advances in Association between Vitamin D Levels and Cardiovascular Disorders. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2023, 25, 185–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangha, A.; Quon, M.; Pfeffer, G.; Orton, S.M. The Role of Vitamin D in Neuroprotection in Multiple Sclerosis: An Update. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon, R.; LeBoff, M.S.; Neale, R.E. Health Effects of Vitamin D Supplementation: Lessons Learned from Randomized Controlled Trials and Mendelian Randomization Studies. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2023, 38, 1391–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, D.; Zhang, Y.G.; Wu, S.; Lu, R.; Lin, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, H.; Cs-Szabo, G.; Sun, J. Vitamin D receptor is a novel transcriptional regulator for Axin1. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 165, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safari, S.; Rafraf, M.; Malekian, M.; Molani-Gol, R.; Asghari-Jafarabadi, M.; Mobasseri, M. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on metabolic parameters, serum irisin and obesity values in women with subclinical hypothyroidism: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1306470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Yan, J.; Zhi, C.; Zhou, Q.; Yuan, X. 1,25(OH)2D3 deficiency-induced gut microbial dysbiosis degrades the colonic mucus barrier in Cyp27b1 knockout mouse model. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assa, A.; Vong, L.; Pinnell, L.J.; Rautava, J.; Avitzur, N.; Johnson-Henry, K.C.; Sherman, P.M. Vitamin D deficiency predisposes to adherent-invasive Escherichia coli-induced barrier dysfunction and experimental colonic injury. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.T.; Stenger, S.; Li, H.; Wenzel, L.; Tan, B.H.; Krutzik, S.R.; Ochoa, M.T.; Schauber, J.; Wu, K.; Meinken, C.; et al. Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response. Science 2006, 311, 1770–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agmon-Levin, N.; Theodor, E.; Segal, R.M.; Shoenfeld, Y. Vitamin D in systemic and organ-specific autoimmune diseases. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013, 45, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, M.; Masenga, S.K.; Ishimwe, J.A.; Demirci, M.; Ahmad, T.; Jamison, S.; Albritton, C.F.; Mwesigwa, N.; Porcia Haynes, A.; White, J.; et al. Recent Advances in Understanding Peripheral and Gut Immune Cell-Mediated Salt-Sensitive Hypertension and Nephropathy. Hypertension 2024, 81, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.F.; Ji, F.; Fan, P.; Denryter, K. Swine Gastrointestinal Microbiota and the Effects of Dietary Amino Acids on Its Composition and Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.L.; Zhang, H.T.; Shan, C.F.; Guo, Y.L.; Gong, X.; Cui, M.M.; Li, X.B.; Tang, M. Correlation between the gut microbiome and neurodegenerative diseases: A review of metagenomics evidence. Neural Regen. Res. 2024, 19, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.H.; Wang, Q.C.; Liu, Y.X.; Wang, L.; Ge, Z.; Li, Z.Z.; Feng, S.L.; Wu, C.M. Gut microbiota and hypertension: Association, mechanisms and treatment. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2023, 45, 2195135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamza, F.N.; Daher, S.; Fakhoury, H.M.A.; Grant, W.B.; Kvietys, P.R.; Al-Kattan, K. Immunomodulatory Properties of Vitamin D in the Intestinal and Respiratory Systems. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munem, F.; Thianhlun, P.C.K.; Anderson, P.H.; Stringer, A.M. Vitamin D is a potential treatment for the management of gastrointestinal mucositis. Curr. Opin. Support. Palliat. Care 2023, 17, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, L.; Sun, T.; Guo, K.; Geng, S. Dysbiosis of gut microbiota and its correlation with dysregulation of cytokines in psoriasis patients. BMC Microbiol. 2021, 21, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stec, A.; Sikora, M.; Maciejewska, M.; Paralusz-Stec, K.; Michalska, M.; Sikorska, E.; Rudnicka, L. Bacterial Metabolites: A Link between Gut Microbiota and Dermatological Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faradina, A.; Tinkov, A.A.; Skalny, A.V.; Chang, J.S. Micronutrient (iron, selenium, vitamin D) supplementation and the gut microbiome. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2024, 10–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Rawat, A.; Alwakeel, M.; Sharif, E.; Al Khodor, S. The potential role of vitamin D supplementation as a gut microbiota modifier in healthy individuals. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boughanem, H.; Ruiz-Limon, P.; Pilo, J.; Lisbona-Montanez, J.M.; Tinahones, F.J.; Moreno Indias, I.; Macias-Gonzalez, M. Linking serum vitamin D levels with gut microbiota after 1-year lifestyle intervention with Mediterranean diet in patients with obesity and metabolic syndrome: A nested cross-sectional and prospective study. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2249150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Sun, J. Imbalance of the intestinal virome and altered viral-bacterial interactions caused by a conditional deletion of the vitamin D receptor. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1957408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.G.; Lu, R.; Xia, Y.; Dong, H.; Sun, J. Lack of Vitamin D Receptor Causes Dysbiosis and Changes the Functions of the Murine Intestinal Microbiome. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 996–1009.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, H.; Waterhouse, M.; Rahman, S.; Baxter, C.; Duarte Romero, B.; McLeod, D.S.A.; Ebeling, P.R.; English, D.R.; Hartel, G.; O’Connell, R.L.; et al. The effect of vitamin D supplementation on the gut microbiome in older Australians—Results from analyses of the D-Health Trial. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2221429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderpoor, N.; Mousa, A.; Fernanda Gomez Arango, L.; Barrett, H.L.; Dekker Nitert, M.; de Courten, B. Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Faecal Microbiota: A Randomised Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdaca, G.; Tagliafico, L.; Page, E.; Paladin, F.; Gangemi, S. Gender Differences in the Interplay between Vitamin D and Microbiota in Allergic and Autoimmune Diseases. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellerba, F.; Muzio, V.; Gnagnarella, P.; Facciotti, F.; Chiocca, S.; Bossi, P.; Cortinovis, D.; Chiaradonna, F.; Serrano, D.; Raimondi, S.; et al. The Association between Vitamin D and Gut Microbiota: A Systematic Review of Human Studies. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, V.T.; Fehlbaum, S.; Seifert, N.; Richard, N.; Bruins, M.J.; Sybesma, W.; Rehman, A.; Steinert, R.E. Effects of colon-targeted vitamins on the composition and metabolic activity of the human gut microbiome—A pilot study. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shieh, A.; Lee, S.M.; Lagishetty, V.; Gottleib, C.; Jacobs, J.P.; Adams, J.S. Pilot Trial of Vitamin D3 and Calcifediol in Healthy Vitamin D Deficient Adults: Does It Change the Fecal Microbiome? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 3464–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellerba, F.; Serrano, D.; Johansson, H.; Pozzi, C.; Segata, N.; NabiNejad, A.; Piperni, E.; Gnagnarella, P.; Macis, D.; Aristarco, V.; et al. Colorectal cancer, Vitamin D and microbiota: A double-blind Phase II randomized trial (ColoViD) in colorectal cancer patients. Neoplasia 2022, 34, 100842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, A.; Gold, D.R.; Weiss, S.T.; Litonjua, A.A.; Lee-Sarwar, K.; Liu, Y.Y. Association of Vitamin D Level and Maternal Gut Microbiome during Pregnancy: Findings from a Randomized Controlled Trial of Antenatal Vitamin D Supplementation. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Park, H.K.; Kang, C.D.; Choi, D.H.; Park, S.C.; Park, J.M.; Nam, S.J.; Chae, G.B.; Lee, K.Y.; Cho, H.; et al. High Dose Intramuscular Vitamin D3 Supplementation Impacts the Gut Microbiota of Patients with Clostridioides Difficile Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 904987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.L.; Jiang, L.; Adams, J.S.; Xu, Z.Z.; Shen, J.; Janssen, S.; Ackermann, G.; Vanderschueren, D.; Pauwels, S.; Knight, R.; et al. Vitamin D metabolites and the gut microbiome in older men. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Yoon, S.; Zhang, Y.G.; Lu, R.; Xia, Y.; Wan, J.; Petrof, E.O.; Claud, E.C.; Chen, D.; Sun, J. Vitamin D receptor pathway is required for probiotic protection in colitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2015, 309, G341–G349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.L.; Martoni, C.J.; Prakash, S. Oral supplementation with probiotic L. reuteri NCIMB 30242 increases mean circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D: A post hoc analysis of a randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2944–2951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khaldy, N.S.; Al-Musharaf, S.; Aljazairy, E.A.; Hussain, S.D.; Alnaami, A.M.; Al-Daghri, N.; Aljuraiban, G. Serum Vitamin D Level and Gut Microbiota in Women. Healthcare 2023, 11, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Ananaba, G.A.; Patrickson, J.; Pitts, S.; Yi, Y.; Yan, F.; Eko, F.O.; Lyn, D.; Black, C.M.; Igietseme, J.U.; et al. Chlamydial infection in vitamin D receptor knockout mice is more intense and prolonged than in wild-type mice. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 135, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizawa, M.; Akagi, D.; Makishima, M. Lithocholic Acid Is a Vitamin D Receptor Ligand That Acts Preferentially in the Ileum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.C.; Chen, Y.; Du, J. Critical roles of intestinal epithelial vitamin D receptor signaling in controlling gut mucosal inflammation. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 148, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, B.; Juillerat, P.; Oyas, O.; Ramon, C.; Bravo, F.D.; Franc, Y.; Fournier, N.; Michetti, P.; Mueller, C.; Geuking, M.; et al. Microbial network disturbances in relapsing refractory Crohn’s disease. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 323–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, M.; Garner, A.; Vlamakis, H.; Xavier, R.J. Microbial genes and pathways in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasoodanan, P.K.V.; Sharma, A.K.; Mahajan, S.; Dhakan, D.B.; Maji, A.; Scaria, J.; Sharma, V.K. Western and non-western gut microbiomes reveal new roles of Prevotella in carbohydrate metabolism and mouth-gut axis. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untersmayr, E.; Brandt, A.; Koidl, L.; Bergheim, I. The Intestinal Barrier Dysfunction as Driving Factor of Inflammaging. Nutrients 2022, 14, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Yu, Z.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Surface components and metabolites of probiotics for regulation of intestinal epithelial barrier. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiippala, K.; Jouhten, H.; Ronkainen, A.; Hartikainen, A.; Kainulainen, V.; Jalanka, J.; Satokari, R. The Potential of Gut Commensals in Reinforcing Intestinal Barrier Function and Alleviating Inflammation. Nutrients 2018, 10, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moens, E.; Veldhoen, M. Epithelial barrier biology: Good fences make good neighbours. Immunology 2012, 135, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.V.; Gordon, J.I. Commensal host-bacterial relationships in the gut. Science 2001, 292, 1115–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, J.; Wells, J.; Cani, P.D.; García-Ródenas, C.L.; MacDonald, T.; Mercenier, A.; Whyte, J.; Troost, F.; Brummer, R.J. Human Intestinal Barrier Function in Health and Disease. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowat, A.M.; Agace, W.W. Regional specialization within the intestinal immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, R.F.; Liu, P.T.; Modlin, R.L.; Adams, J.S.; Hewison, M. Impact of vitamin D on immune function: Lessons learned from genome-wide analysis. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piemonti, L.; Monti, P.; Sironi, M.; Fraticelli, P.; Leone, B.E.; Dal Cin, E.; Allavena, P.; Di Carlo, V. Vitamin D3 affects differentiation, maturation, and function of human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 4443–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.H. Vitamin D metabolism and signaling in the immune system. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2012, 13, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeke, F.; Takiishi, T.; Korf, H.; Gysemans, C.; Mathieu, C. Vitamin D: Modulator of the immune system. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Essen, M.R.; Kongsbak, M.; Schjerling, P.; Olgaard, K.; Odum, N.; Geisler, C. Vitamin D controls T cell antigen receptor signaling and activation of human T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 344–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badalato, G.M.; Hemal, A.K.; Menon, M.; Badani, K.K. Current role of robot-assisted pyelolithotomy for the management of large renal calculi: A contemporary analysis. J. Endourol. 2009, 23, 1719–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakura, Y.; Ishigame, H.; Saijo, S.; Nakae, S. Functional specialization of interleukin-17 family members. Immunity 2011, 34, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, N.; Li, H.; Bian, Y.; Wen, W.; Kong, X.; Wang, F. The dynamic shifts of IL-10-producing Th17 and IL-17-producing Treg in health and disease: A crosstalk between ancient “Yin-Yang” theory and modern immunology. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, A.; Ohno, H.; Satoh-Takayama, N. Disease pathogenesis and barrier functions regulated by group 3 innate lymphoid cells. Semin. Immunopathol. 2024, 45, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickie, L.J.; Church, L.D.; Coulthard, L.R.; Mathews, R.J.; Emery, P.; McDermott, M.F. Vitamin D3 down-regulates intracellular Toll-like receptor 9 expression and Toll-like receptor 9-induced IL-6 production in human monocytes. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 1466–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miossec, P.; Kolls, J.K. Targeting IL-17 and TH17 cells in chronic inflammation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbi, J.; Pardoll, D.; Pan, F. Treg functional stability and its responsiveness to the microenvironment. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 259, 115–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, H.K.; Maiers, J.L.; DeMali, K.A. Interplay between tight junctions & adherens junctions. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 358, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenwald, M.A.; Turner, J.R. The intestinal epithelial barrier: A therapeutic target? Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sadi, R.; Boivin, M.; Ma, T. Mechanism of cytokine modulation of epithelial tight junction barrier. Front. Biosci. 2009, 14, 2765–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hausmann, A.; Steenholdt, C.; Nielsen, O.H.; Jensen, K.B. Immune cell-derived signals governing epithelial phenotypes in homeostasis and inflammation. Trends Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, C.Y.; Chiang Chiau, J.S.; Cheng, M.L.; Chan, W.T.; Jiang, C.B.; Chang, S.W.; Liu, C.Y.; Chang, C.W.; Lee, H.C. Effects of Vitamin D-Deficient Diet on Intestinal Epithelial Integrity and Zonulin Expression in a C57BL/6 Mouse Model. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 649818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assa, A.; Vong, L.; Pinnell, L.J.; Avitzur, N.; Johnson-Henry, K.C.; Sherman, P.M. Vitamin D deficiency promotes epithelial barrier dysfunction and intestinal inflammation. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, J.; Zhang, Z.; Musch, M.W.; Ning, G.; Sun, J.; Hart, J.; Bissonnette, M.; Li, Y.C. Novel role of the vitamin D receptor in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal mucosal barrier. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G208–G216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetta, H.F.; Muhammad, K.; El-Masry, E.A.; Taha, A.E.; Ahmed, E.A.; Phares, C.; Kader, H.A.; Waheed, Y.; Zahran, A.M.; Yahia, R.; et al. The interplay between vitamin D and COVID-19: Protective or bystander? Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 25, 2131–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stio, M.; Retico, L.; Annese, V.; Bonanomi, A.G. Vitamin D regulates the tight-junction protein expression in active ulcerative colitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Lu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Xu, C. The efficacy of vitamin D supplementation for irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Nutr. J. 2022, 21, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vici, G.; Camilletti, D.; Polzonetti, V. Possible Role of Vitamin D in Celiac Disease Onset. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trasciatti, S.; Grizzi, F. Vitamin D and celiac disease. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2024, 109, 249–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, C.; Gordon, M.; Sinopoulou, V.; Limketkai, B.N. Vitamin D for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 10, CD011806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Jia, X.; Zhu, Z.; Ye, D.; Wu, Y.; Guo, R.; Jiang, M. Vitamin D improves irritable bowel syndrome symptoms: A meta-analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Maizels, R.M. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Evol. Med. Public Health 2014, 2014, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ungaro, R.; Mehandru, S.; Allen, P.B.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Colombel, J.F. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet 2017, 389, 1756–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, J.; Mehandru, S.; Colombel, J.F.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Crohn’s disease. Lancet 2017, 389, 1741–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGovern, D.P.; Kugathasan, S.; Cho, J.H. Genetics of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1163–1176.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, S.; Raffals, L.E. The Microbiome in Crohn’s Disease: Role in Pathogenesis and Role of Microbiome Replacement Therapies. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 46, 481–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.C.; Shi, H.Y.; Hamidi, N.; Underwood, F.E.; Tang, W.; Benchimol, E.I.; Panaccione, R.; Ghosh, S.; Wu, J.C.Y.; Chan, F.K.L.; et al. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: A systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet 2017, 390, 2769–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, J.H.; Li, Y.; Rogers, C.J.; Cantorna, M.T. Vitamin D regulates the gut microbiome and protects mice from dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, W.; Sun, T.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Deb, D.K.; Yoon, D.; Kong, J.; Thadhani, R.; Li, Y.C. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D promotes negative feedback regulation of TLR signaling via targeting microRNA-155-SOCS1 in macrophages. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3687–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Wu, S.; Lu, R.; Zhou, D.; Zhou, J.; Carmeliet, G.; Petrof, E.; Claud, E.C.; Sun, J. Tight junction CLDN2 gene is a direct target of the vitamin D receptor. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vernia, F.; Valvano, M.; Longo, S.; Cesaro, N.; Viscido, A.; Latella, G. Vitamin D in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Implications. Nutrients 2022, 14, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagishetty, V.; Misharin, A.V.; Liu, N.Q.; Lisse, T.S.; Chun, R.F.; Ouyang, Y.; McLachlan, S.M.; Adams, J.S.; Hewison, M. Vitamin D deficiency in mice impairs colonic antibacterial activity and predisposes to colitis. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 2423–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubatan, J.; Chou, N.D.; Nielsen, O.H.; Moss, A.C. Systematic review with meta-analysis: Association of vitamin D status with clinical outcomes in adult patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 1146–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.C.; Manson, J.E.; Abrams, S.A.; Aloia, J.F.; Brannon, P.M.; Clinton, S.K.; Durazo-Arvizu, R.A.; Gallagher, J.C.; Gallo, R.L.; Jones, G.; et al. The 2011 report on dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin D from the Institute of Medicine: What clinicians need to know. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, J.; Cooper, S.C.; Ghosh, S.; Hewison, M. The Role of Vitamin D in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Mechanism to Management. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohouli, M.H.; Farahmand, F.; Alimadadi, H.; Rahmani, P.; Motamed, F.; da Silva Magalhaes, E.I.; Rohani, P. Vitamin D therapy in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Pediatr. 2023, 19, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, M.; Hendy, P.; Ding, J.N.; Shaw, S.; Hold, G.; Hart, A. The Effect of Vitamin D on Intestinal Inflammation and Faecal Microbiota in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. J. Crohns Colitis 2018, 12, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.C.; Sperber, A.D.; Corsetti, M.; Camilleri, M. Irritable bowel syndrome. Lancet 2020, 396, 1675–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mearin, F.; Lacy, B.E.; Chang, L.; Chey, W.D.; Lembo, A.J.; Simren, M.; Spiller, R. Bowel Disorders. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1393–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, M.; Yao, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, E.; Yuan, J.; Wang, F.; Yang, K.; Bian, Z.; Zhong, L.L.D. The level and prevalence of depression and anxiety among patients with different subtypes of irritable bowel syndrome: A network meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamani, M.; Alizadeh-Tabari, S.; Zamani, V. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The prevalence of anxiety and depression in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, T. The brain-gut axis in irritable bowel syndrome—Clinical aspects. Med. Sci. Monit. 2004, 10, RA125–RA131. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.M.; Denou, E.; Verdu, E.F.; Bercik, P. The putative role of the intestinal microbiota in the irritable bowel syndrome. Dig. Liver Dis. 2009, 41, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Malley, D.; Quigley, E.M.; Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Do interactions between stress and immune responses lead to symptom exacerbations in irritable bowel syndrome? Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khayyat, Y.; Attar, S. Vitamin D Deficiency in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Does it Exist? Oman Med. J. 2015, 30, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.E.; Williams, E.A.; Corfe, B.M. Vitamin D status in irritable bowel syndrome and the impact of supplementation on symptoms: What do we know and what do we need to know? Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 72, 1358–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalighi Sikaroudi, M.; Mokhtare, M.; Janani, L.; Faghihi Kashani, A.H.; Masoodi, M.; Agah, S.; Abbaspour, N.; Dehnad, A.; Shidfar, F. Vitamin D3 Supplementation in Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients: The Effects on Symptoms Improvement, Serum Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone, and Interleukin-6—A Randomized Clinical Trial. Complement. Med. Res. 2020, 27, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickup, J.C. Inflammation and activated innate immunity in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The pro- and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.E.; Williams, E.A.; Corfe, B.M. Vitamin D supplementation in people with IBS has no effect on symptom severity and quality of life: Results of a randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.Y.; Kang, A.H.; Green, A.; Gwee, K.A.; Ho, K.Y. Systematic review: Worldwide variation in the frequency of coeliac disease and changes over time. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 38, 226–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindfors, K.; Ciacci, C.; Kurppa, K.; Lundin, K.E.A.; Makharia, G.K.; Mearin, M.L.; Murray, J.A.; Verdu, E.F.; Kaukinen, K. Coeliac disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catassi, C.; Verdu, E.F.; Bai, J.C.; Lionetti, E. Coeliac disease. Lancet 2022, 399, 2413–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, P.H.; Lebwohl, B.; Greywoode, R. Celiac disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 1099–1106, quiz 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, M.N. Gluten, major histocompatibility complex, and the small intestine. A molecular and immunobiologic approach to the spectrum of gluten sensitivity (‘celiac sprue’). Gastroenterology 1992, 102, 330–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohi, S.; Mustalahti, K.; Kaukinen, K.; Laurila, K.; Collin, P.; Rissanen, H.; Lohi, O.; Bravi, E.; Gasparin, M.; Reunanen, A.; et al. Increasing prevalence of coeliac disease over time. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 26, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.A.; Jeong, J.; Underwood, F.E.; Quan, J.; Panaccione, N.; Windsor, J.W.; Coward, S.; deBruyn, J.; Ronksley, P.E.; Shaheen, A.A.; et al. Incidence of Celiac Disease Is Increasing over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 507–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorini, F.; Tonacci, A. Vitamin D: An Essential Nutrient in the Dual Relationship between Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases and Celiac Disease—A Comprehensive Review. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez-Polo, M.; Churruca, I.; Perez-Junkera, G.; Larretxi, I.; Lasa, A.; Esparta, J.; Cantero-Ruiz de Eguino, L.; Navarro, V. Study Protocol for a Controlled Trial of Nutrition Education Intervention about Celiac Disease in Primary School: ZELIAKIDE Project. Nutrients 2024, 16, 338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, J.A.; Wassaf, D.; Dunn, K.; Arora, S.; Winkle, P.; Stacey, H.; Cooper, S.; Goldstein, K.E.; Manchanda, R.; Kontos, S.; et al. Safety and tolerability of KAN-101, a liver-targeted immune tolerance therapy, in patients with coeliac disease (ACeD): A phase 1 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 735–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tye-Din, J.A.; Daveson, A.J.M.; Goel, G.; Goldstein, K.E.; Hand, H.L.; Neff, K.M.; Popp, A.; Taavela, J.; Maki, M.; Isola, J.; et al. Efficacy and safety of gluten peptide-based antigen-specific immunotherapy (Nexvax2) in adults with coeliac disease after bolus exposure to gluten (RESET CeD): An interim analysis of a terminated randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 2 study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo Perez, L.; Castillejo de Villasante, G.; Cano Ruiz, A.; Leon, F. Non-dietary therapeutic clinical trials in coeliac disease. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 23, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanpowpong, P.; Obuch, J.C.; Jiang, H.; McCarty, C.E.; Katz, A.J.; Leffler, D.A.; Kelly, C.P.; Weir, D.C.; Leichtner, A.M.; Camargo, C.A., Jr. Multicenter study on season of birth and celiac disease: Evidence for a new theoretical model of pathogenesis. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capriati, T.; Francavilla, R.; Castellaneta, S.; Ferretti, F.; Diamanti, A. Impact of the birth’s season on the development of celiac disease in Italy. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2015, 174, 1657–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantin, C.; Huber, W.D.; Granditsch, G.; Weghofer, M.; Valenta, R. Different profiles of wheat antigens are recognised by patients suffering from coeliac disease and IgE-mediated food allergy. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2005, 138, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, P.H.; Cellier, C. Celiac disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1731–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barera, G.; Maruca, K.; Sgaramella, P.; Di Stefano, M.; Mora, S. Short-term, low dose vitamin D supplementation in young patients with celiac disease: A pilot study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 32, 663–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blazina, S.; Bratanic, N.; Campa, A.S.; Blagus, R.; Orel, R. Bone mineral density and importance of strict gluten-free diet in children and adolescents with celiac disease. Bone 2010, 47, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Number of Participants | Country | Subject Information | Vitamin D Supplementation | Changes of Gut Microbiome | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 835 | Australia | Australians aged 60–84 years | 60,000 IU of vitamin D3/month for 5 years | No significant changes | [43] |
| 36 | Ireland | Healthy volunteers | 60 µg vitamin D3 per day for four weeks | Bacteroidetes↓; Actinobacteria↑; Bifidobacterium longum↑; Coprococcus↑ | [47] |
| 26 | Australia | 18–60 years, with vitamin D deficiency (serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) concentration ≤ 50 nmol/L) | 4000 IU/day for 16 weeks | Lachnospira↑; Blautia↓ | [44] |
| 18 | United States | Adults ≥ 18 years with vitamin D deficiency (25-hydroxyvitamin D [25(OH)D] < 20 ng/mL) | Vitamin D3 (60 µg [2400 IU]/day) or 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (20 µg/day) for 8 weeks | Firmicutes↓ | [48] |
| 74 | Italy | 35–75 years old colorectal cancer patients with resected colorectal cancer stage I–III in the last 24 months | 2000 IU vitamin D3 per day for 1 year | Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides↑; Bacteroides gallinarum↑; Christensenella timonensis↑; Ruminococcus YE78↑; Faecalibacterium prausnitzii↑; Holdemanella biformis↑; Eubacterium brachy↓; Bacteroides coprocola↓ | [49] |
| 870 | United States | 10–18 weeks of gestation | 4400 IU vitamin D3 per day between enrollment and delivery | Desulfovibrio↓ | [50] |
| 18 | Korea | Patients with Clostridioides difficile infections (CDI) and vitamin D insufficiency (vitamin D level < 17 ng/mL) | 200,000 IU vitamin D3 per day for 2 weeks | Proteobacteria↓; Lachnospiraceae↑; Ruminococcaceae↑; Akkermansiaceae↑; Bifidobacteriaceae↑ | [51] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Mei, L.; Hao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Ji, Y. Contemporary Perspectives on the Role of Vitamin D in Enhancing Gut Health and Its Implications for Preventing and Managing Intestinal Diseases. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142352
Wang J, Mei L, Hao Y, Xu Y, Yang Q, Dai Z, Yang Y, Wu Z, Ji Y. Contemporary Perspectives on the Role of Vitamin D in Enhancing Gut Health and Its Implications for Preventing and Managing Intestinal Diseases. Nutrients. 2024; 16(14):2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142352
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jiaxin, Lihua Mei, Yanling Hao, Yajun Xu, Qing Yang, Zhaolai Dai, Ying Yang, Zhenlong Wu, and Yun Ji. 2024. "Contemporary Perspectives on the Role of Vitamin D in Enhancing Gut Health and Its Implications for Preventing and Managing Intestinal Diseases" Nutrients 16, no. 14: 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142352
APA StyleWang, J., Mei, L., Hao, Y., Xu, Y., Yang, Q., Dai, Z., Yang, Y., Wu, Z., & Ji, Y. (2024). Contemporary Perspectives on the Role of Vitamin D in Enhancing Gut Health and Its Implications for Preventing and Managing Intestinal Diseases. Nutrients, 16(14), 2352. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142352









