Factors Influencing Breast Milk Antibody Titers during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: An Observational Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Maternal and Neonatal Data Collection
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3.1. Neonatal Samples
2.3.2. Breast Milk Samples
2.4. Statistical Analysis
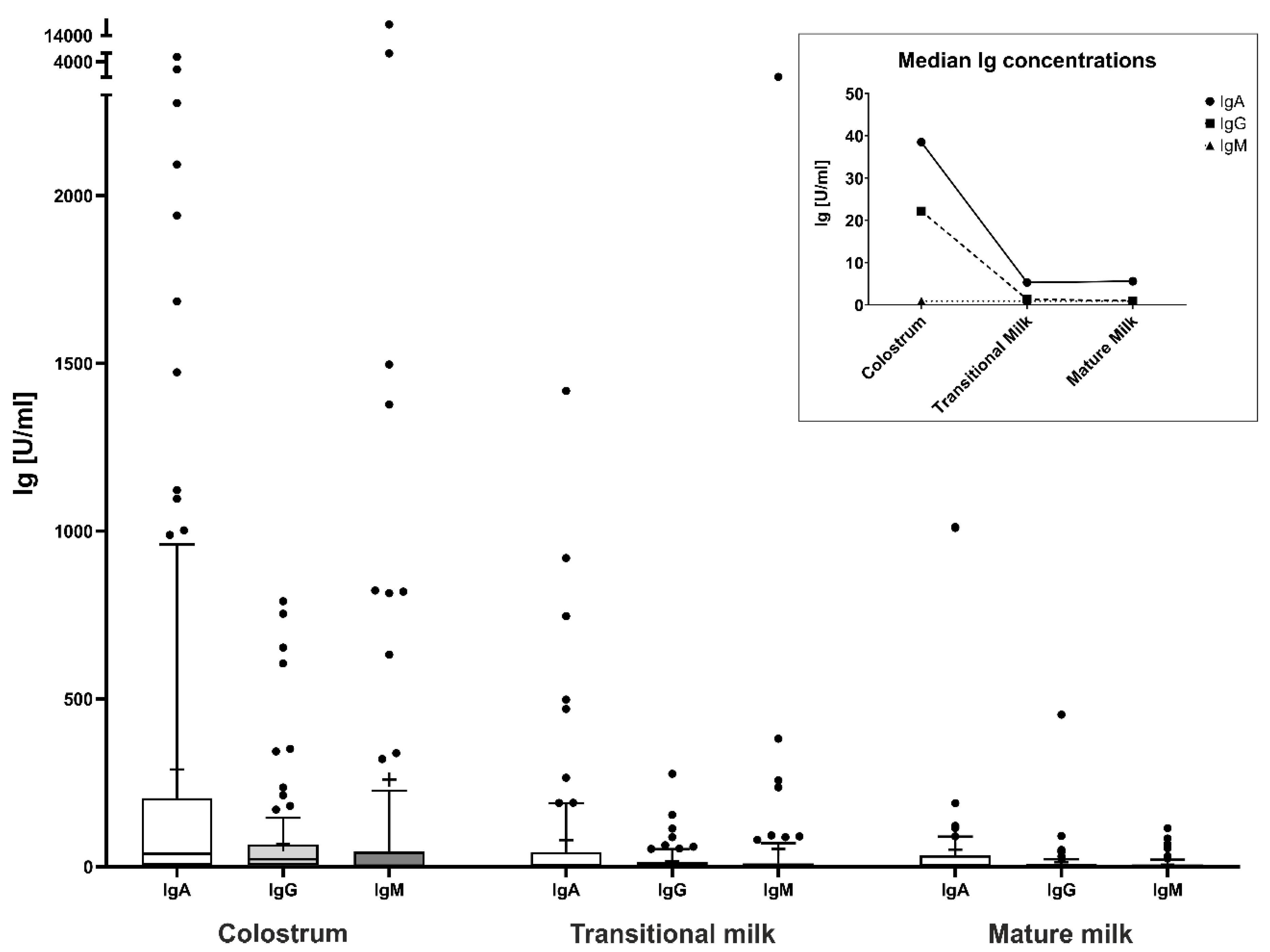
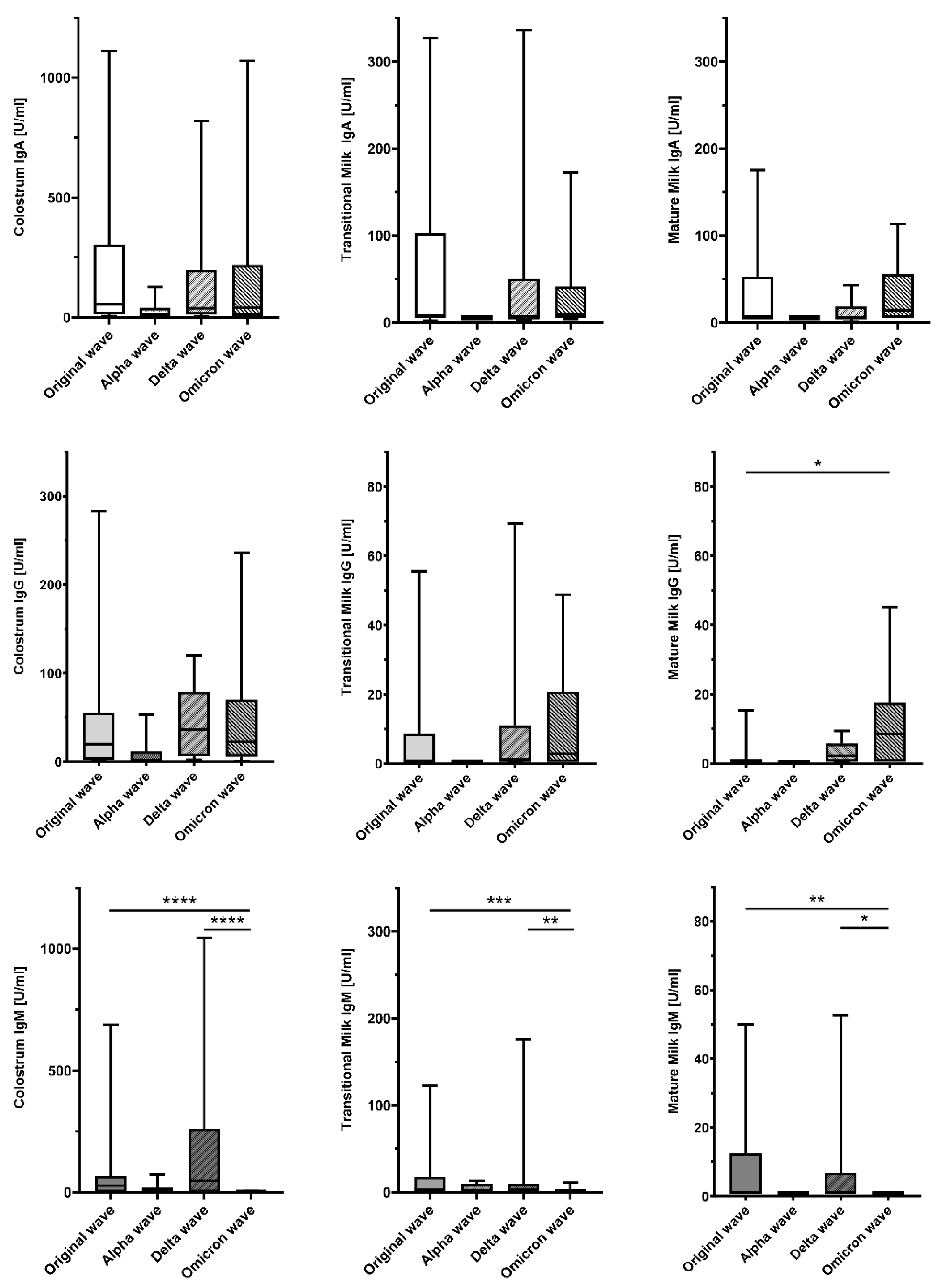
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGES | Austrian Agency for Health and Food Safety GmBH |
| DBS | dried blood spot |
| DT | detection threshold(s) |
| GISAID | Global Initiative on Sharing all Influenza Data |
| Ig | immunoglobulin(s) |
| LOD | limit(s) of detection |
| NICU | neonatal intensive care unit |
| S1RBD | Spike S1 receptor-binding domain |
| TMB | 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine |
References
- Fernández-Buhigas, I.; Rayo, N.; Silos, J.C.; Serrano, B.; Ocón-Hernández, O.; Leung, B.W.; Delgado, J.L.; Fernández, D.S.; Valle, S.; De Miguel, L.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2-specific antibodies in human breast milk following SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy: A prospective cohort study. Int. Breastfeed. J. 2024, 19, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimberlin, D.W.; Puopolo, K.M. Breast Milk and COVID-19: What Do We Know? Clin. Infect Dis. 2021, 72, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, A.; Marino, J.; Amanat, F.; Krammer, F.; Hahn-Holbrook, J.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; Powell, R.L. Robust and Specific Secretory IgA Against SARS-CoV-2 Detected in Human Milk. Iscience 2020, 23, 101735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, R.M.; Williams, J.E.; Järvinen, K.M.; Belfort, M.B.; Pace, C.D.W.; Lackey, K.A.; Gogel, A.C.; Nguyen-Contant, P.; Kanagaiah, P.; Fitzgerald, T.; et al. Characterization of SARS-CoV-2 RNA, Antibodies, and Neutralizing Capacity in Milk Produced by Women with COVID-19. mBio 2021, 12, e03192-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitroglou, M.; Sokou, R.; Iacovidou, N.; Pouliakis, A.; Kafalidis, G.; Boutsikou, T.; Iliodromiti, Z. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Immunoglobulins in Human Milk after Coronavirus Disease or Vaccination-Time Frame and Duration of Detection in Human Milk and Factors That Affect Their Titers: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczygioł, P.; Łukianowski, B.; Kościelska-Kasprzak, K.; Jakuszko, K.; Bartoszek, D.; Krajewska, M.; Królak-Olejnik, B. Antibodies in the breastmilk of COVID-19 recovered women. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2022, 22, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olearo, F.; Radmanesh, L.S.; Felber, N.; von Possel, R.; Emmerich, P.; Pekarek, N.; Pfefferle, S.; Nörz, D.; Hansen, G.; Diemert, A.; et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in breast milk during lactation after infection or vaccination: A cohort study. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2022, 153, 103685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temocin, F.; Çaycı, Y.T.; Seren, C.; Kuruoglu, T.; Atilla, A.; Birinci, A.; Tanyel, E. Investigation of Anti-SARS-CoV-2-specific IgG Levels in Breast Milk after Vaccination or COVID-19 Infection. Am. J. Perinatol. 2024, 41, e3085–e3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pace, R.M.; Williams, J.E.; Järvinen, K.M.; Belfort, M.B.; Pace, C.D.W.; Lackey, K.A.; Gogel, A.C.; Nguyen-Contant, P.; Kanagaiah, P.; Fitzgerald, T.; et al. COVID-19 and human milk: SARS-CoV-2, antibodies, and neutralizing capacity. medRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaidou, V.; Georgiou, R.; Christofidou, M.; Felekkis, K.; Pieri, M.; Papaneophytou, C. Detection of SARS-CoV-2-Specific Antibodies in Human Breast Milk and Their Neutralizing Capacity after COVID-19 Vaccination: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Pregnancy, Childbirth and the Postnatal Period [Place Unknown]. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/question-and-answers-hub/q-a-detail/coronavirus-disease-covid-19-pregnancy-and-childbirth (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. COVID-19 and Breastfeeding USA 2021. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding-special-circumstances/hcp/illnesses-conditions/covid-19.html?CDC_AAref_Val=https://www.cdc.gov/breastfeeding/breastfeeding-special-circumstances/maternal-or-infant-illnesses/covid-19-and-breastfeeding.html (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Pace, R.M.; Williams, J.E.; Järvinen, K.M.; Meehan, C.L.; Martin, M.A.; Ley, S.H.; Barbosa-Leiker, C.; Andres, A.; Yeruva, L.; Belfort, M.B.; et al. Milk From Women Diagnosed With COVID-19 Does Not Contain SARS-CoV-2 RNA but Has Persistent Levels of SARS-CoV-2-Specific IgA Antibodies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 801797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.G.; Terreri, S.; Terrin, G.; Natale, F.; Pietrasanta, C.; Salvatori, G.; Brunelli, R.; Midulla, F.; Papaevangelou, V.; Carsetti, R.; et al. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection Versus Vaccination in Pregnancy: Implications for Maternal and Infant Immunity. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75 (Suppl. S1), S37–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine. Management Considerations for Pregnant Patients with COVID-19. 2020. Available online: https://s3.amazonaws.com/cdn.smfm.org/media/2415/SMFM_COVID_Management_of_COVID_pos_preg_patients_7-2-20.PDF_.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- e.V. FvG. hCoV-19 Variants Dahboard Munich 2024. Available online: https://gisaid.org/hcov-19-variants-dashboard/ (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- GmBh ÖAfGuE. GISIAD Österreich-Report. 2024. Available online: https://www.ages.at/forschung/wissen-aktuell/detail/gisaid-oesterreich-report (accessed on 20 February 2024).
- Sriraman, N.K. The Nuts and Bolts of Breastfeeding: Anatomy and Physiology of Lactation. Curr. Probl. Pediatr. Adolesc. Health Care. 2017, 47, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rio-Aige, K.; Azagra-Boronat, I.; Castell, M.; Selma-Royo, M.; Collado, M.C.; Rodríguez-Lagunas, M.J.; Pérez-Cano, F.J. The Breast Milk Immunoglobulinome. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, A.; Marino, J.; Amanat, F.; Oguntuyo, K.Y.; Hahn-Holbrook, J.; Lee, B.; Zolla-Pazner, S.; Powell, R.L. The IgA in milk induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection is comprised of mainly secretory antibody that is neutralizing and highly durable over time. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0249723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selma-Royo, M.; Bäuerl, C.; Mena-Tudela, D.; Aguilar-Camprubí, L.; Pérez-Cano, F.J.; Parra-Llorca, A.; Lerin, C.; Martínez-Costa, C.; Collado, M.C. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgA and IgG in human milk after vaccination is dependent on vaccine type and previous SARS-CoV-2 exposure: A longitudinal study. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, S.J.; Dickson, J.S.; Barnhart, H.M.; Toledo, R.T.; Eiten-Miller, R.R. IgA, IgG, IgM and Lactoferrin Contents of Human Milk During Early Lactation and the Effect of Processing and Storage. J. Food Prot. 1983, 46, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuidhail, J.; Al-Shudiefat, A.A.; Darwish, M. Alterations of immunoglobulin G and immunoglobulin M levels in the breast milk of mothers with exclusive breastfeeding compared to mothers with non-exclusive breastfeeding during 6 months postpartum: The Jordanian cohort study. Am. J. Hum. Biol. 2019, 31, e23197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakuszko, K.; Kościelska-Kasprzak, K.; Żabińska, M.; Bartoszek, D.; Poznański, P.; Rukasz, D.; Kłak, R.; Królak-Olejnik, B.; Krajewska, M. Immune Response to Vaccination against COVID-19 in Breastfeeding Health Workers. Vaccines 2021, 9, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, H.M.; DiMaggio, L.S.; Perez, M.A.; Chen, X.; Stephens, K.; Gibson, T.; Anderson, E.J.; Rostad, C.A. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Profiles in Maternal Serum and Breast Milk Following mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination: A Longitudinal Prospective Observational Cohort Study. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero Ramírez, D.S.; Lara Pérez, M.M.; Carretero Pérez, M.; Suárez Hernández, M.I.; Martín Pulido, S.; Pera Villacampa, L.; Fernández Vilar, A.M.; Rivero Falero, M.; González Carretero, P.; Reyes Millán, B.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Breast Milk After Vaccination. Pediatrics 2021, 148, e2021052286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutra, L.V.; Silva, M.H.; Lebrão, C.W.; Affonso-Fonseca, F.L.; Suano-Souza, F.I. Impact of the Presence Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgA in the Colostrum of Women Infected by COVID-19 During the Pregnancy in Neonatal Clinical Outcomes: A Cross-Sectional Study. Matern. Child. Health J. 2023, 27, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, R.; Petrova, A. Biologically active breast milk proteins in association with very preterm delivery and stage of lactation. J. Perinatol. 2011, 31, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trend, S.; Strunk, T.; Lloyd, M.L.; Kok, C.H.; Metcalfe, J.; Geddes, D.T.; Lai, C.T.; Richmond, P.; Doherty, D.A.; Simmer, K.; et al. Levels of innate immune factors in preterm and term mothers’ breast milk during the 1st month postpartum. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 115, 1178–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, A.; de Albuquerque Diniz, E.M.; Barbosa, S.F.; Vaz, F.A. Immunologic factors in human milk: The effects of gestational age and pasteurization. J. Hum. Lact. 2005, 21, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, S.J.; Buckley, R.H.; Wakil, S.S.; McAllister, D.C.; David, R.J.; Faix, R.G. Elevated IgA concentration in milk produced by mothers delivered of preterm infants. J. Pediatr. 1981, 99, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total n = 140 (100) | Term Birth n = 110 (78.6) | Preterm Birth n = 30 (21.4) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal characteristics | |||
| Maternal age [years] | 32.0 ± 4.8 | 32.0 ± 4.6 | 31.8 ± 5.6 |
| Gravidity, median (range) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–3) |
| Parity, median (range) | 2 (1–2) | 2 (1–2) | 2 (1–2) |
| Time of infection, n (%) | |||
| during pregnancy | 98 (70.0) | 82 (74.5) | 16 (53.3) |
| peripartum | 42 (30.0) | 28 (25.5) | 14 (46.7) |
| Interval infection—delivery [days] | 44 (7.5; 102.8) | 50 (11; 112.3) | 22.5 (1.5; 86.5) |
| Maternal symptoms, n (%) | |||
| a-/pre-symptomatic | 22 (15.7) | 19 (17.3) | 3 (10.0) |
| mild | 95 (67.9) | 74 (67.3) | 21 (70.0) |
| moderate | 7 (5.0) | 5 (4.5) | 2 (6.7) |
| severe | 3 (2.1) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (10.0) |
| missing information | 13 (9.3) | 12 (10.9) | 1 (3.3) |
| Vaccination, n (%) | |||
| Non-vaccinated | 94 (67.1) | 72 (65.5) | 22 (73.3) |
| 1× vaccinated | 5 (3.6) | 3 (2.7) | 2 (6.7) |
| 2× vaccinated | 12 (8.6) | 10 (9.1) | 2 (6.7) |
| 3× vaccinated | 29 (20.7) | 25 (22.7) | 4 (13.3) |
| Virus wave, n (%) | |||
| Original wave | 38 (27.2) | 27 (24.5) | 11 (36.7) |
| Alpha wave | 9 (6.4) | 8 (7.3) | 1 (3.3) |
| Delta wave | 29 (20.7) | 19 (17.3) | 10 (33.3) |
| Omicron wave | 64 (45.7) | 56 (50.9) | 9 (26.7) |
| Neonatal characteristics | |||
| Number of participants, n (%) | 144 (100) | 111 (77.1) | 33 (22.9) |
| Multiple birth (twins), n (%) | 4 (2.8) | 1 (0.9) | 3 (9.1) |
| Infant sex, n (%) | |||
| male | 85 (59.0) | 65 (58.6) | 20 (60.6) |
| female | 59 (41.0) | 46 (41.4) | 13 (39.4) |
| Delivery mode | |||
| vaginal | 70 (48.6) | 62 (55.9) | 8 (24.2) |
| vacuum extraction | 6 (4.2) | 6 (5.4) | 0 (0.0) |
| C-section | 68 (47.2) | 43 (38.7) | 25 (75.8) |
| Gestational age [weeks] | 38.7 (37.0; 39.8) | 39.1 (38.1; 40.1) | 34.4 (34.1; 35.3) |
| Birth weight [g] | 3047.3 ± 624.47 | 3277.4 ± 455.08 | 2273.2 ± 478.61 |
| z-score birth weight | −0.32 ± 1.00 | −0.32 ± 1.00 | −0.30 ± 0.83 |
| Birth length [cm] | 48.6 ± 3.29 | 49.7 ± 2.28 | 44.7 ± 3.30 |
| z-score birth length | −0.72 ± 1.05 | −0.70 ± 0.99 | −0.81 ± 1.26 |
| Birth head circumference [cm] | 34.1 ± 2.21 | 34.8 ± 1.63 | 31.8 ± 2.27 |
| z-score birth head circumference | −0.18 ± 1.18 | −0.15 ± 1.24 | −0.28 ± 0.98 |
| Apgar scores | |||
| 1 min | 9 (8; 9) | 9 (9; 9) | 8 (6; 9) |
| 5 min | 10 (9; 10) | 10 (9.8; 10) | 9 (8; 10) |
| 10 min | 10 (10; 10) | 10 (10; 10) | 9 (9; 10) |
| Umbilical cord arterial pH | 7.259 ± 0.073 | 7.251 ± 0.085 | 7.293 ± 0.064 |
| Umbilical cord arterial base excess [mmol/L] | −2.7 ± 4.4 | −3.0 ± 4.3 | −0.9 ± 4.6 |
| Neonate tested positive for SARS-CoV-2, n (%) | 3 (2.1) | 3 (2.7) | 0 (0.0) |
| Neonate admitted to NICU, n (%) | 34 (23.6) | 12 (10.8) | 22 (66.7) |
| DBS umbilical cord blood available, n (%) | 85 (59.0) | 67 (60.3) | 18 (54.5) |
| DBS venous blood neonate 48 h available, n (%) | 13 (9.0) | 10 (9.0) | 3 (9.1) |
| DBS anti-S1RBD-IgG concentrations § | 90.8 (23.4; 314.4) | 104.3 (27.1; 338.1) | 54.6 (15.8; 141.4) |
| DBS anti-S1RBD-IgM concentrations $ | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| Type of Breast Milk | Maternal Characteristic | IgA Median (Q1; Q3) | p-Value * | IgG Median (Q1; Q3) | p-Value * | IgM Median (Q1; Q3) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colostrum | |||||||
| Infection during pregnancy | 51.3 (14.0; 221.7) | 23.0 (3.7; 60.2) | 0.9 (0.9; 51.4) | ||||
| Peripartum infection | 23.2 (5.3; 187.9) | 0.131 | 19.3 (4.8; 71.3) | 0.896 | 0.9 (0.9; 3.2) | 0.063 | |
| Infection only | 24.0 (5.3; 128.5) | 11.3 (2.2; 47.2) | 7.5 (0.9; 78.7) | ||||
| Infection + vaccination | 98.0 (12.0; 457.0) | 0.013 | 42.2 (4.0; 112.5) | 0.001 | 0.9 (0.9; 0.9) | <0.001 | |
| Asymptomatic/mild disease | 48.9 (5.7; 214.2) | 23.0 (4.8; 66.2) | 0.9 (0.9; 47.5) | ||||
| Moderate/severe disease | 29.9 (5.3; 1176.0) | 0.642 | 36.3 (9.8; 131.4) | 0.206 | 17.6 (0.9; 475.9) | 0.196 | |
| Term birth | 38.5 (5.3; 204.8) | 20.7 (3.3; 63.9) | 0.9 (0.9; 31.2) | ||||
| Preterm birth | 36.0 (5.3; 217.7) | 0.930 | 32.9 (10.0; 87.7) | 0.236 | 18.3 (0.9; 183.1) | 0.065 | |
| Age < 35 years | 40.0 (5.3; 190.2) | 22.5 (4.8; 67.7) | 0.9 (0.9; 51.4) | ||||
| Age ≥ 35 years | 26.0 (5.3; 502.1) | 0.619 | 20.2 (3.1; 59.8) | 0.916 | 0.9 (0.9; 16.2) | 0.186 | |
| Transitional milk | |||||||
| Infection during pregnancy | 5.3 (5.3; 42.5) | 0.7 (0.5; 12.2) | 0.9 (0.9; 6.6) | ||||
| Peripartum infection | 12.5 (5.3; 46.7) | 0.308 | 2.7 (0.5; 21.0) | 0.439 | 0.9 (0.9; 21.2) | 0.296 | |
| Infection only | 5.3 (5.3; 36.0) | 0.5 (0.5; 7.7) | 0.9 (0.9; 12.6) | ||||
| Infection + vaccination | 20.5 (0.0; 58.6) | 0.086 | 7.3 (0.5; 33.3) | 0.008 | 0.9 (0.9; 0.9) | 0.013 | |
| Asymptomatic/mild disease | 5.3 (5.3; 39.2) | 0.8 (0.5; 11.4) | 0.9 (0.9; 10.6) | ||||
| Moderate/severe disease | 46.7 (33.7; 468.5) | 0.012 | 20.7 (3.6; 82.4) | 0.026 | 12.2 (0.9; 89.5) | 0.151 | |
| Term birth | 5.3 (5.3; 39.2) | 1.4 (0.5; 12.2) | 0.9 (0.9; 6.6) | ||||
| Preterm birth | 10.6 (5.3; 121.5) | 0.325 | 1.2 (0.5; 44.0) | 0.795 | 0.9 (0.9; 11.9) | 0.671 | |
| Age < 35 years | 5.3 (5.3; 41.0) | 1.2 (0.5; 8.9) | 0.9 (0.9; 6.6) | ||||
| Age ≥ 35 years | 17.5 (5.3; 102.8) | 0.440 | 3.4 (0.5; 32.3) | 0.311 | 0.9 (0.9; 55.6) | 0.333 | |
| Mature milk | |||||||
| Infection during pregnancy | 5.3 (5.3; 18.4) | 0.5 (0.5; 4.6) | 0.9 (0.9; 0.9) | ||||
| Peripartum infection | 22.5 (8.5; 69.9) | 0.004 | 8.5 (2.1; 15.7) | 0.001 | 0.9 (0.9; 14.4) | 0.248 | |
| Infection only | 5.3 (5.3; 18.8) | 0.5 (0.5; 2.3) | 0.9 (0.9; 5.1) | ||||
| Infection + vaccination | 20.4 (4.0; 59.7) | 0.015 | 10.0 (5.6; 22.8) | <0.001 | 0.9 (0.9; 0.9) | 0.016 | |
| Asymptomatic/mild disease | 5.3 (5.3; 32.9) | 0.6 (0.5; 9.0) | 0.9 (0.9; 0.9) | ||||
| Moderate/severe disease | 62.0 (21.2; 545.7) | 0.012 | 8.2 (3.3; 51.6) | 0.136 | 30.8 (0.9; 69.5) | 0.026 | |
| Term birth | 5.3 (5.3; 32.9) | 0.6 (0.5; 9.3) | 0.9 (0.9; 0.9) | ||||
| Preterm birth | 15.6 (5.3; 59.7) | 0.649 | 2.3 (0.5; 8.5) | 0.600 | 0.9 (0.9; 6.9) | 0.018 | |
| Age < 35 years | 5.3 (5.3; 20.4) | 0.5 (0.5; 7.7) | 0.9 (0.9; 0.9) | ||||
| Age ≥ 35 years | 22.5 (5.3; 69.9) | 0.168 | 5.6 (0.5; 21.6) | 0.050 | 0.9 (0.9; 3.2) | 0.722 |
| Type of Breast Milk | Virus Wave | IgA Median (Q1; Q3) | p-Value * | IgG Median (Q1; Q3) | p-Value * | IgM Median (Q1; Q3) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colostrum | |||||||
| Original wave | 54.6 (13.2; 304.4) | 21.5 (2.4; 46.2) | 27.2 (0.9; 67.4) | ||||
| Alpha wave | 10.7 (1.0; 40.0) | 0.9 (0.5; 11.7) | 0.9 (0.9; 19.2) | ||||
| Delta wave | 38.3 (11.7; 198.7) | 36.3 (5.9; 78.8) | 47.8 (0.9; 260.8) | ||||
| Omicron wave | 41.2 (5.3; 218.7) | 0.276 | 22.2 (5.7; 70.3) | 0.075 | 0.9 (0.9; 0.9) | <0.001 | |
| Transitional milk | |||||||
| Original wave | 8.0 (5.3; 102.8) | 0.5 (0.5; 8.8) | 3.2 (0.9; 18.1) | ||||
| Alpha wave | 5.3 (5.3; 5.3) | 0.5 (0.5; 0.5) | 0.9 (0.9; 10.0) | ||||
| Delta wave | 5.3 (5.3; 50.7) | 1.2 (0.5; 11.1) | 6.2 (0.9; 45.1) | ||||
| Omicron wave | 9.6 (5.3; 41.3) | 0.697 | 2.9 (0.5; 20.8) | 0.141 | 0.9 (0.9; 0.9) | 0.005 | |
| Mature milk | |||||||
| Original wave | 5.3 (5.3; 52.5) | 0.5 (0.5; 0.9) | 0.9 (0.9; 12.4) | ||||
| Alpha wave | 5.3 (5.3; 5.3) | 0.5 (0.5; 0.6) | 0.9 (0.9; 0.9) | ||||
| Delta wave | 5.3 (4.3; 18.8) | 2.3 (0.5; 5.8) | 0.9 (0.9; 6.8) | ||||
| Omicron wave | 14.4 (5.3; 55.6) | 0.189 | 8.5 (0.5; 17.6) | 0.004 | 0.9 (0.9; 0.9) | 0.004 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hochmayr, C.; Winkler, I.; Hammerl, M.; Höller, A.; Huber, E.; Urbanek, M.; Kiechl-Kohlendorfer, U.; Griesmaier, E.; Posod, A. Factors Influencing Breast Milk Antibody Titers during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: An Observational Study. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142320
Hochmayr C, Winkler I, Hammerl M, Höller A, Huber E, Urbanek M, Kiechl-Kohlendorfer U, Griesmaier E, Posod A. Factors Influencing Breast Milk Antibody Titers during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: An Observational Study. Nutrients. 2024; 16(14):2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142320
Chicago/Turabian StyleHochmayr, Christoph, Ira Winkler, Marlene Hammerl, Alexander Höller, Eva Huber, Martina Urbanek, Ursula Kiechl-Kohlendorfer, Elke Griesmaier, and Anna Posod. 2024. "Factors Influencing Breast Milk Antibody Titers during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: An Observational Study" Nutrients 16, no. 14: 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142320
APA StyleHochmayr, C., Winkler, I., Hammerl, M., Höller, A., Huber, E., Urbanek, M., Kiechl-Kohlendorfer, U., Griesmaier, E., & Posod, A. (2024). Factors Influencing Breast Milk Antibody Titers during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic: An Observational Study. Nutrients, 16(14), 2320. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16142320







