The Efficacy of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
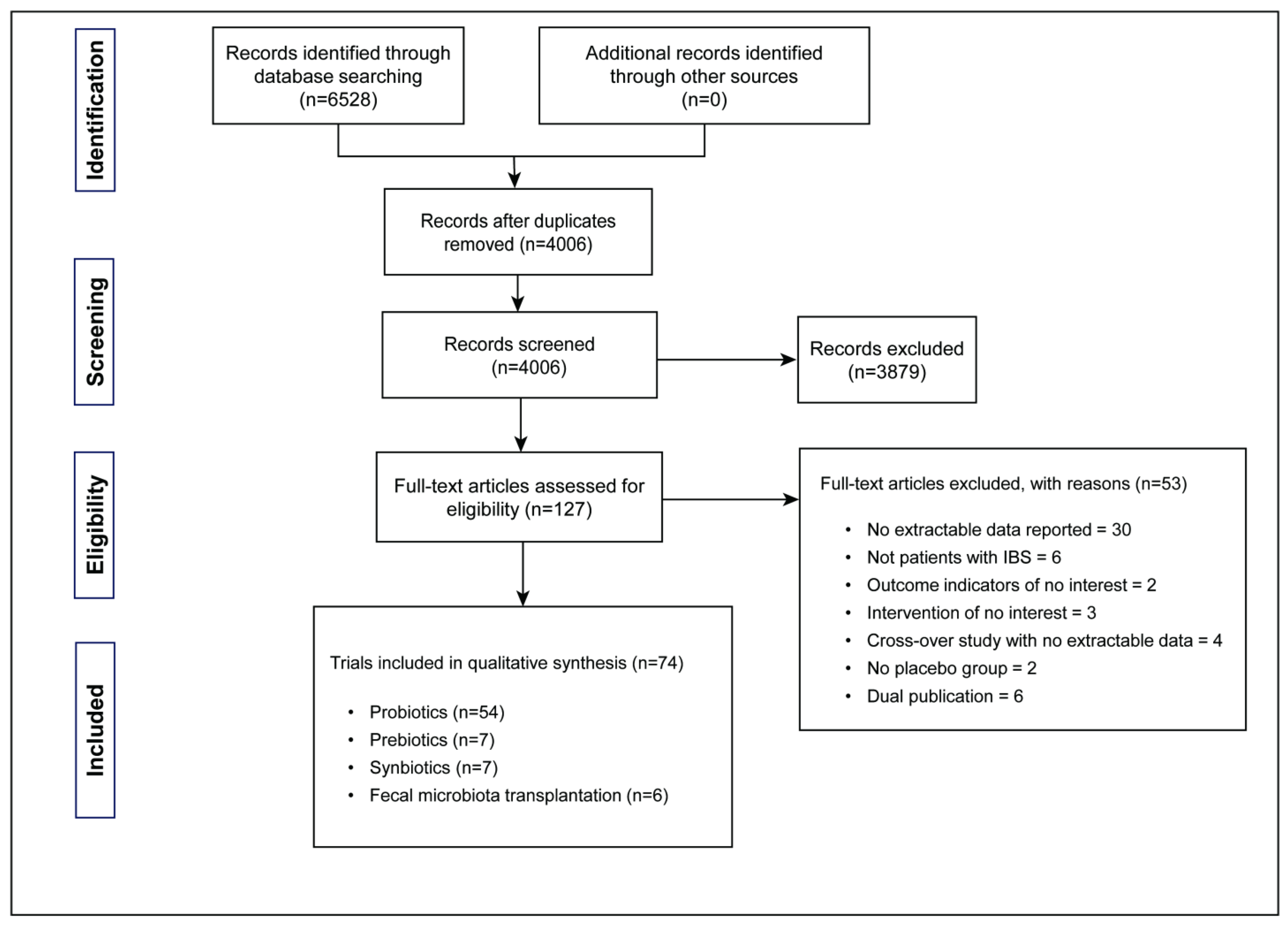
2.1. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.2. Outcome Assessment
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment and Risk of Bias
2.5. Data Synthesis and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Efficacy and Safety of Probiotics
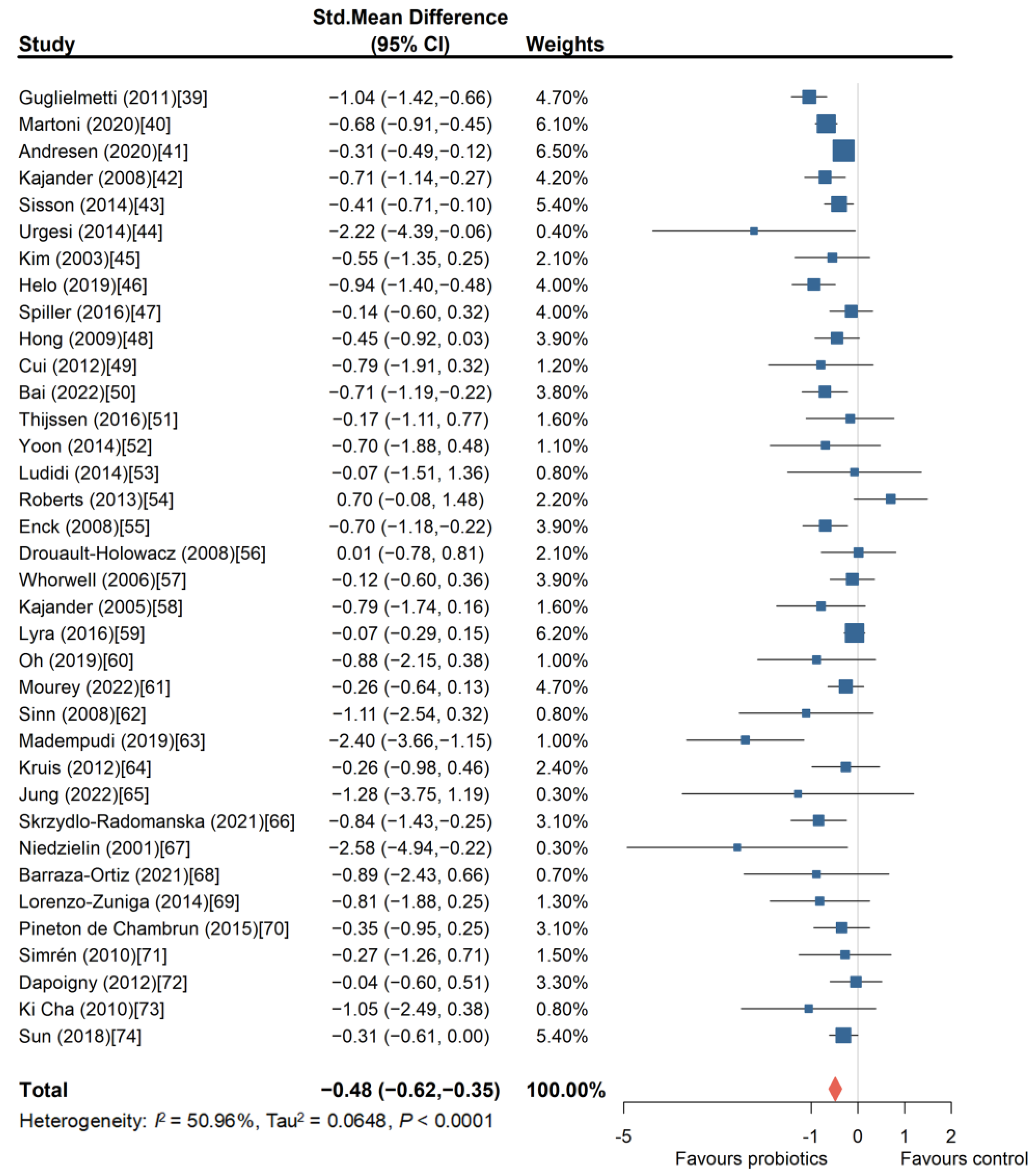
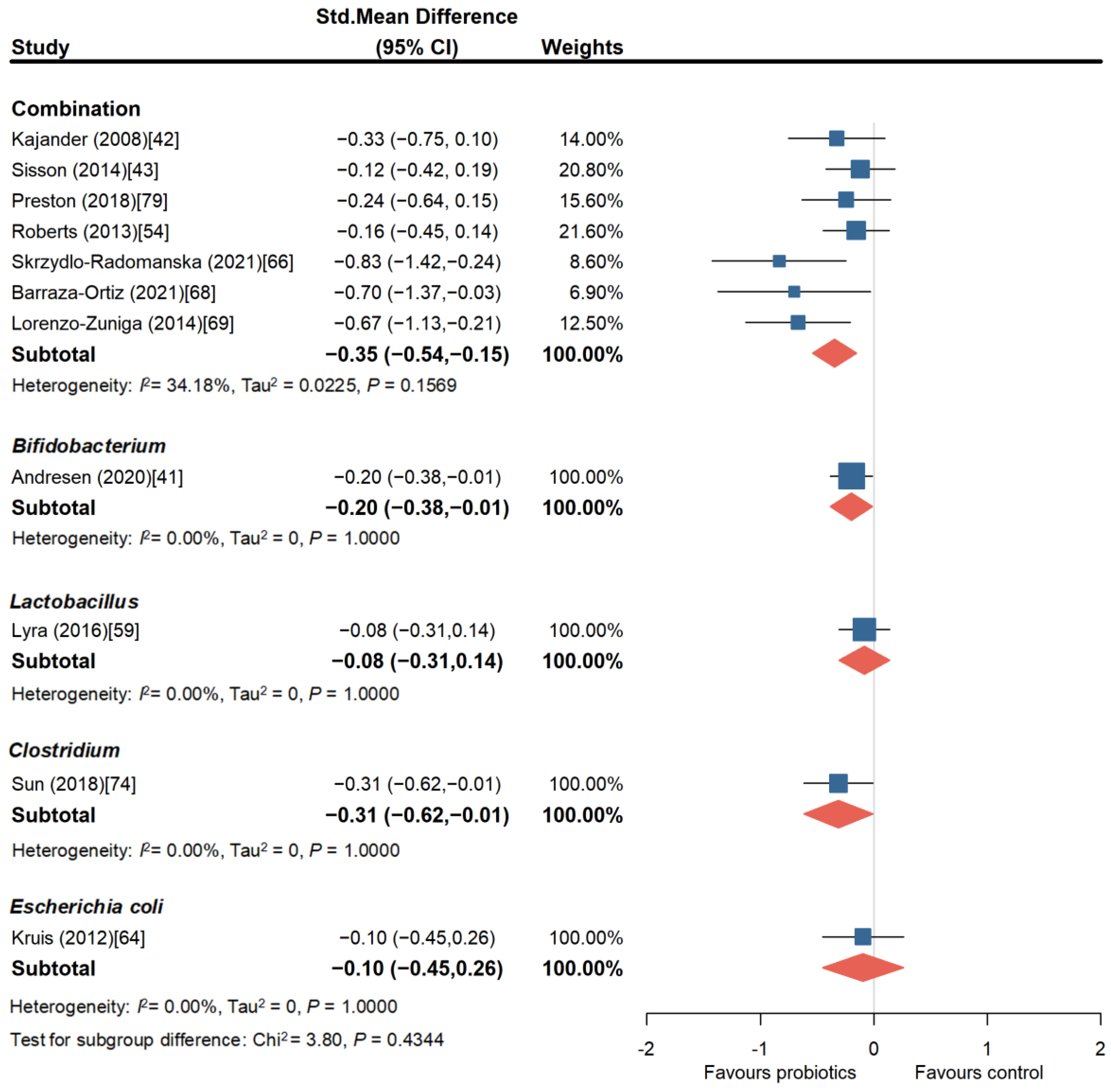
3.1.1. Probiotics Can Effectively Improve Overall Symptoms of IBS
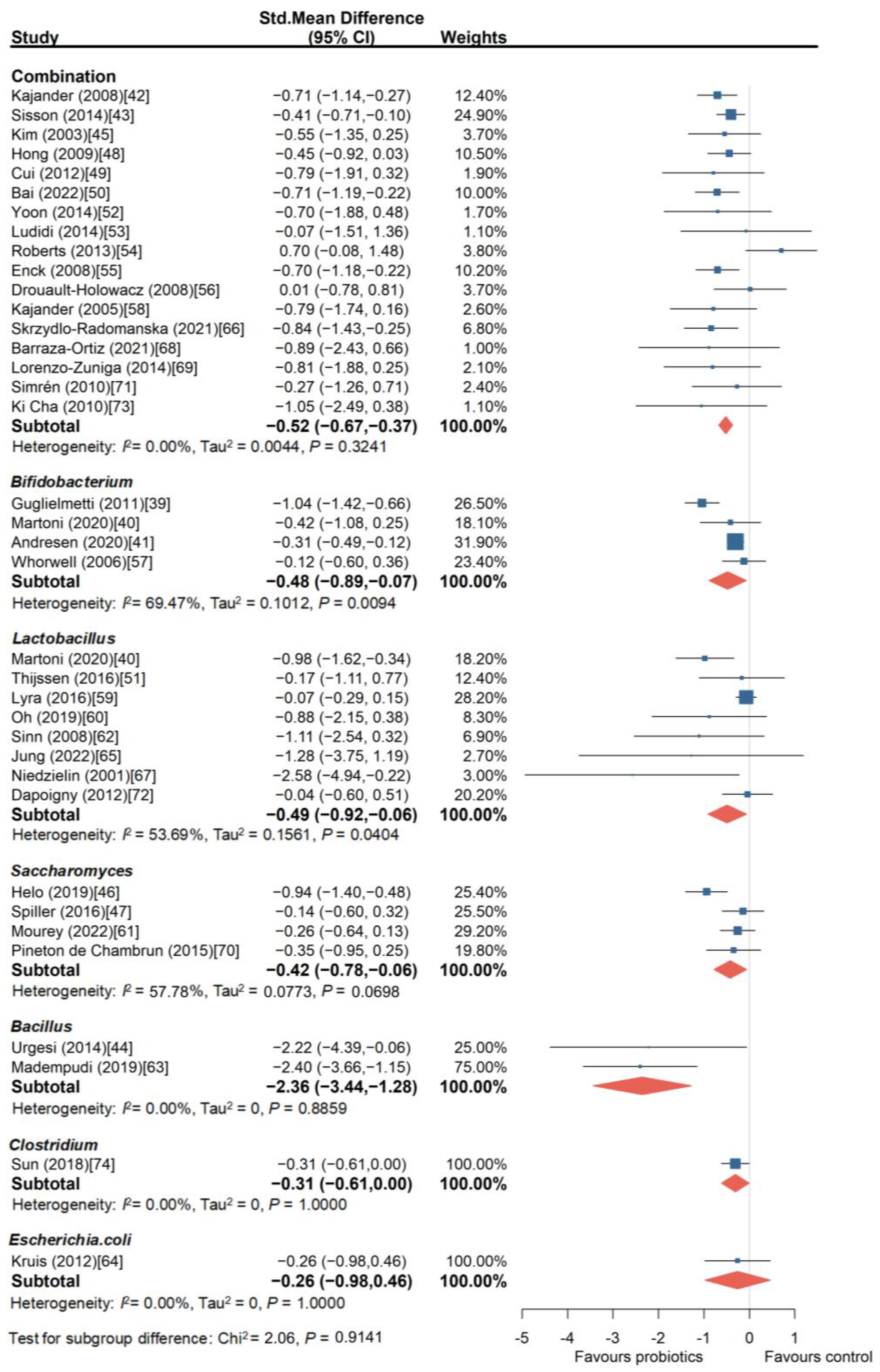
3.1.2. Probiotics Can Effectively Improve Abdominal Pain in Patients with IBS
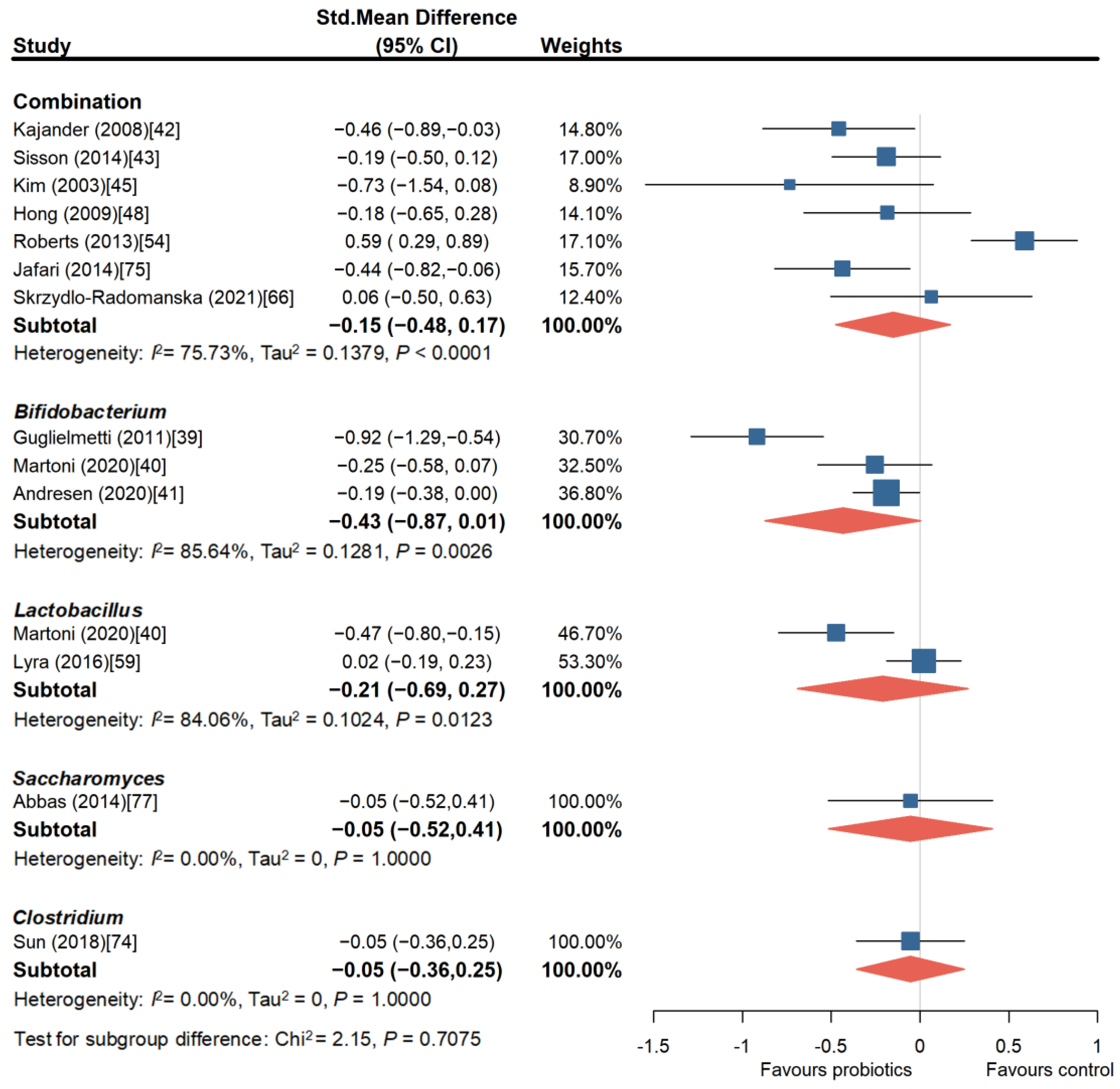
3.1.3. Probiotics Can Partially Improve Bloating in Patients with IBS
3.1.4. Probiotics Can Effectively Improve the Overall Quality of Life in Patients with IBS
3.1.5. Adverse Events with Probiotics
3.2. Efficacy and Safety of Prebiotics
3.3. Efficacy and Safety of Synbiotics
3.4. Efficacy and Safety of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation
3.5. Network Meta-Analysis of the Effectiveness of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | Confidence intervals |
| ENS | Enteric nervous system |
| FMT | Fecal microbiota transplantation |
| IBS | Irritable bowel syndrome |
| IBS-D | Diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome |
| IBS-QoL | IBS quality of life |
| IBS-SSS | IBS symptom severity scale |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| RCT | Randomized controlled trial |
| RR | Relative risk |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SMD | Standardized mean difference |
References
- Lovell, R.M.; Ford, A.C. Global prevalence of and risk factors for irritable bowel syndrome: A meta-analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 712–721.e714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, E.A.; Ryu, H.J.; Bhatt, R.R. The neurobiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 1451–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petitfils, C.; Maurel, S.; Payros, G.; Hueber, A.; Agaiz, B.; Gazzo, G.; Marrocco, R.; Auvray, F.; Langevin, G.; Motta, J.P.; et al. Identification of bacterial lipopeptides as key players in IBS. Gut 2023, 72, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.C.; Sperber, A.D.; Corsetti, M.; Camilleri, M. Irritable bowel syndrome. Lancet 2020, 396, 1675–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringel, Y.; Maharshak, N. Intestinal microbiota and immune function in the pathogenesis of irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 305, G529–G541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camilleri, M. Management Options for Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2018, 93, 1858–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macsharry, J.; O’Mahony, L.; Fanning, A.; Bairead, E.; Sherlock, G.; Tiesman, J.; Fulmer, A.; Kiely, B.; Dinan, T.G.; Shanahan, F.; et al. Mucosal cytokine imbalance in irritable bowel syndrome. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 43, 1467–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtmann, G.J.; Ford, A.C.; Talley, N.J. Pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 1, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Barbara, G.; Buurman, W.; Ockhuizen, T.; Schulzke, J.D.; Serino, M.; Tilg, H.; Watson, A.; Wells, J.M. Intestinal permeability—A new target for disease prevention and therapy. BMC Gastroenterol. 2014, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, C.; Lobo, B.; Pigrau, M.; Ramos, L.; González-Castro, A.M.; Alonso, C.; Guilarte, M.; Guilá, M.; de Torres, I.; Azpiroz, F.; et al. Diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: An organic disorder with structural abnormalities in the jejunal epithelial barrier. Gut 2013, 62, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enck, P.; Aziz, Q.; Barbara, G.; Farmer, A.D.; Fukudo, S.; Mayer, E.A.; Niesler, B.; Quigley, E.M.; Rajilić-Stojanović, M.; Schemann, M.; et al. Irritable bowel syndrome. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.Y.; Cheng, C.W.; Tang, X.D.; Bian, Z.X. Impact of psychological stress on irritable bowel syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 14126–14131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbara, G.; Stanghellini, V.; Cremon, C.; De Giorgio, R.; Corinaldesi, R. What is the effect of inflammation on intestinal function? Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2008, 14 (Suppl. S2), S140–S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbara, G.; Cremon, C.; Carini, G.; Bellacosa, L.; Zecchi, L.; De Giorgio, R.; Corinaldesi, R.; Stanghellini, V. The immune system in irritable bowel syndrome. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2011, 17, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhner, S.; Li, Q.; Vignali, S.; Barbara, G.; De Giorgio, R.; Stanghellini, V.; Cremon, C.; Zeller, F.; Langer, R.; Daniel, H.; et al. Activation of human enteric neurons by supernatants of colonic biopsy specimens from patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbara, G.; Wang, B.; Stanghellini, V.; de Giorgio, R.; Cremon, C.; Di Nardo, G.; Trevisani, M.; Campi, B.; Geppetti, P.; Tonini, M.; et al. Mast cell-dependent excitation of visceral-nociceptive sensory neurons in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canakis, A.; Haroon, M.; Weber, H.C. Irritable bowel syndrome and gut microbiota. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2020, 27, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassinen, A.; Krogius-Kurikka, L.; Mäkivuokko, H.; Rinttilä, T.; Paulin, L.; Corander, J.; Malinen, E.; Apajalahti, J.; Palva, A. The fecal microbiota of irritable bowel syndrome patients differs significantly from that of healthy subjects. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, T.; Liu, R.; Lee, A.; Long, Y.; Du, L.; Lai, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Si, J.; Owyang, C.; et al. Altered Intestinal Microbiota with Increased Abundance of Prevotella Is Associated with High Risk of Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 6961783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salonen, A.; de Vos, W.M.; Palva, A. Gastrointestinal microbiota in irritable bowel syndrome: Present state and perspectives. Microbiology 2010, 156, 3205–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciavilla, P.; Strati, F.; Di Paola, M.; Modesto, M.; Vitali, F.; Cavalieri, D.; Prati, G.M.; Di Vito, M.; Aragona, G.; De Filippo, C.; et al. Gut microbiota profiles and characterization of cultivable fungal isolates in IBS patients. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 3277–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.; Xiong, L.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Chen, M. Alterations of gut microbiota in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.; Tian, Z.; Li, L.; Zeng, Z.; Chen, M.; Xiong, L. Fecal Microbiota Alterations Associated with Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, I.B.; O’Toole, P.W.; Öhman, L.; Claesson, M.J.; Deane, J.; Quigley, E.M.; Simrén, M. An irritable bowel syndrome subtype defined by species-specific alterations in faecal microbiota. Gut 2012, 61, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittayanon, R.; Lau, J.T.; Yuan, Y.; Leontiadis, G.I.; Tse, F.; Surette, M.; Moayyedi, P. Gut Microbiota in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome-A Systematic Review. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Mahony, L.; McCarthy, J.; Kelly, P.; Hurley, G.; Luo, F.; Chen, K.; O’Sullivan, G.C.; Kiely, B.; Collins, J.K.; Shanahan, F.; et al. Lactobacillus and bifidobacterium in irritable bowel syndrome: Symptom responses and relationship to cytokine profiles. Gastroenterology 2005, 128, 541–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdú, E.F.; Bercik, P.; Verma-Gandhu, M.; Huang, X.X.; Blennerhassett, P.; Jackson, W.; Mao, Y.; Wang, L.; Rochat, F.; Collins, S.M. Specific probiotic therapy attenuates antibiotic induced visceral hypersensitivity in mice. Gut 2006, 55, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Li, S.; Lv, L.; Jiang, S.; Xu, L.; Chen, H.; Li, L. Protective effect of Pediococcus pentosaceus Li05 on diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome in rats. Food Funct. 2024, 15, 3692–3708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simrén, M.; Barbara, G.; Flint, H.J.; Spiegel, B.M.; Spiller, R.C.; Vanner, S.; Verdu, E.F.; Whorwell, P.J.; Zoetendal, E.G. Intestinal microbiota in functional bowel disorders: A Rome foundation report. Gut 2013, 62, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staudacher, H.M.; Whelan, K. The low FODMAP diet: Recent advances in understanding its mechanisms and efficacy in IBS. Gut 2017, 66, 1517–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chey, W.D.; Kurlander, J.; Eswaran, S. Irritable bowel syndrome: A clinical review. JAMA 2015, 313, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herndon, C.C.; Wang, Y.P.; Lu, C.L. Targeting the gut microbiota for the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, A.C.; Harris, L.A.; Lacy, B.E.; Quigley, E.M.M.; Moayyedi, P. Systematic review with meta-analysis: The efficacy of prebiotics, probiotics, synbiotics and antibiotics in irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 1044–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooijevaar, R.E.; Terveer, E.M.; Verspaget, H.W.; Kuijper, E.J.; Keller, J.J. Clinical Application and Potential of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation. Annu. Rev. Med. 2019, 70, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savovic, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinn, S. A simple method for converting an odds ratio to effect size for use in meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2000, 19, 3127–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murad, M.H.; Wang, Z.; Chu, H.; Lin, L. When continuous outcomes are measured using different scales: Guide for meta-analysis and interpretation. BMJ 2019, 364, k4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guglielmetti, S.; Mora, D.; Gschwender, M.; Popp, K. Randomised clinical trial: Bifidobacterium bifidum MIMBb75 significantly alleviates irritable bowel syndrome and improves quality of life--a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 33, 1123–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martoni, C.J.; Srivastava, S.; Leyer, G.J. Lactobacillus acidophilus DDS-1 and Bifidobacterium lactis UABla-12 Improve Abdominal Pain Severity and Symptomology in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, V.; Gschossmann, J.; Layer, P. Heat-inactivated Bifidobacterium bifidum MIMBb75 (SYN-HI-001) in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 5, 658–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajander, K.; Myllyluoma, E.; Rajilic-Stojanovic, M.; Kyronpalo, S.; Rasmussen, M.; Jarvenpaa, S.; Zoetendal, E.G.; de Vos, W.M.; Vapaatalo, H.; Korpela, R. Clinical trial: Multispecies probiotic supplementation alleviates the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome and stabilizes intestinal microbiota. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisson, G.; Ayis, S.; Sherwood, R.A.; Bjarnason, I. Randomised clinical trial: A liquid multi-strain probiotic vs. placebo in the irritable bowel syndrome--a 12 week double-blind study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 40, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urgesi, R.; Casale, C.; Pistelli, R.; Rapaccini, G.L.; de Vitis, I. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial on efficacy and safety of association of simethicone and Bacillus coagulans (Colinox(R)) in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Camilleri, M.; McKinzie, S.; Lempke, M.B.; Burton, D.D.; Thomforde, G.M.; Zinsmeister, A.R. A randomized controlled trial of a probiotic, VSL#3, on gut transit and symptoms in diarrhoea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 17, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helo, A.A. Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Saccharomyces Cerevisiae. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Res. 2019, 8, 2919–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiller, R.; Pelerin, F.; Cayzeele Decherf, A.; Maudet, C.; Housez, B.; Cazaubiel, M.; Justen, P. Randomized double blind placebo-controlled trial of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CNCM I-3856 in irritable bowel syndrome: Improvement in abdominal pain and bloating in those with predominant constipation. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2016, 4, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.S.; Kang, H.W.; Im, J.P.; Ji, G.E.; Kim, S.G.; Jung, H.C.; Song, I.S.; Kim, J.S. Effect of probiotics on symptoms in korean adults with irritable bowel syndrome. Gut Liver 2009, 3, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Hu, Y. Multistrain probiotic preparation significantly reduces symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome in a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2012, 5, 238–244. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, T.; Xu, Z.; Xia, P.; Feng, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Yan, G.; Lv, B.; Yan, Z.; et al. The Short-Term Efficacy of Bifidobacterium Quadruple Viable Tablet in Patients with Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Potentially Mediated by Metabolism Rather Than Diversity Regulation. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 118, 1256–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijssen, A.Y.; Clemens, C.H.; Vankerckhoven, V.; Goossens, H.; Jonkers, D.M.; Masclee, A.A. Efficacy of Lactobacillus casei Shirota for patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 28, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.S.; Sohn, W.; Lee, O.Y.; Lee, S.P.; Lee, K.N.; Jun, D.W.; Lee, H.L.; Yoon, B.C.; Choi, H.S.; Chung, W.S.; et al. Effect of multispecies probiotics on irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 29, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludidi, S.; Jonkers, D.M.; Koning, C.J.; Kruimel, J.W.; Mulder, L.; van der Vaart, I.B.; Conchillo, J.M.; Masclee, A.A. Randomized clinical trial on the effect of a multispecies probiotic on visceroperception in hypersensitive IBS patients. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2014, 26, 705–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, L.M.; McCahon, D.; Holder, R.; Wilson, S.; Hobbs, F.D. A randomised controlled trial of a probiotic ‘functional food’ in the management of irritable bowel syndrome. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013, 13, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enck, P.; Zimmermann, K.; Menke, G.; Müller-Lissner, S.; Martens, U.; Klosterhalfen, S. A mixture of Escherichia coli (DSM 17252) and Enterococcus faecalis (DSM 16440) for treatment of the irritable bowel syndrome--a randomized controlled trial with primary care physicians. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2008, 20, 1103–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drouault-Holowacz, S.; Bieuvelet, S.; Burckel, A.; Cazaubiel, M.; Dray, X.; Marteau, P. A double blind randomized controlled trial of a probiotic combination in 100 patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol. 2008, 32, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whorwell, P.J.; Altringer, L.; Morel, J.; Bond, Y.; Charbonneau, D.; O’Mahony, L.; Kiely, B.; Shanahan, F.; Quigley, E.M. Efficacy of an encapsulated probiotic Bifidobacterium infantis 35624 in women with irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajander, K.; Hatakka, K.; Poussa, T.; Färkkilä, M.; Korpela, R. A probiotic mixture alleviates symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome patients: A controlled 6-month intervention. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 22, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyra, A.; Hillila, M.; Huttunen, T.; Mannikko, S.; Taalikka, M.; Tennila, J.; Tarpila, A.; Lahtinen, S.; Ouwehand, A.C.; Veijola, L. Irritable bowel syndrome symptom severity improves equally with probiotic and placebo. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 10631–10642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Jang, Y.S.; Kang, D.; Chang, D.K.; Min, Y.W. Efficacy and Safety of New Lactobacilli Probiotics for Unconstipated Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourey, F.; Decherf, A.; Jeanne, J.F.; Clement-Ziza, M.; Grisoni, M.L.; Machuron, F.; Legrain-Raspaud, S.; Bourreille, A.; Desreumaux, P. Saccharomyces cerevisiae I-3856 in irritable bowel syndrome with predominant constipation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 2509–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinn, D.H.; Song, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.H.; Son, H.J.; Chang, D.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.J.; Rhee, J.C.; Rhee, P.L. Therapeutic effect of Lactobacillus acidophilus-SDC 2012, 2013 in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2008, 53, 2714–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madempudi, R.S.; Ahire, J.J.; Neelamraju, J.; Tripathi, A.; Nanal, S. Randomized clinical trial: The effect of probiotic Bacillus coagulans Unique IS2 vs. placebo on the symptoms management of irritable bowel syndrome in adults. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruis, W.; Chrubasik, S.; Boehm, S.; Stange, C.; Schulze, J. A double-blind placebo-controlled trial to study therapeutic effects of probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 in subgroups of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2012, 27, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Jung, K.; Kim, A.; Lee, J.H.; Cho, D.; Seo, J.; Jung, E.S.; Kang, H.J.; Roh, J.; Kim, W. Effect of Oral Intake of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum APsulloc 331261 (GTB1(TM)) on Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrzydlo-Radomanska, B.; Prozorow-Krol, B.; Cichoz-Lach, H.; Majsiak, E.; Bierla, J.B.; Kanarek, E.; Sowinska, A.; Cukrowska, B. The Effectiveness and Safety of Multi-Strain Probiotic Preparation in Patients with Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niedzielin, K.; Kordecki, H.; Birkenfeld, B. A controlled, double-blind, randomized study on the efficacy of Lactobacillus plantarum 299V in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2001, 13, 1143–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barraza-Ortiz, D.A.; Perez-Lopez, N.; Medina-Lopez, V.M.; Minero-Alfaro, J.I.; Zamarripa-Dorsey, F.; Fernandez-Martinez, N.D.C.; Llorente-Ramon, A.; Ramos-Aguilar, G.A. Combination of a Probiotic and an Antispasmodic Increases Quality of Life and Reduces Symptoms in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Pilot Study. Dig. Dis. 2021, 39, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Zuniga, V.; Llop, E.; Suarez, C.; Alvarez, B.; Abreu, L.; Espadaler, J.; Serra, J. I.31, a new combination of probiotics, improves irritable bowel syndrome-related quality of life. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8709–8716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineton de Chambrun, G.; Neut, C.; Chau, A.; Cazaubiel, M.; Pelerin, F.; Justen, P.; Desreumaux, P. A randomized clinical trial of Saccharomyces cerevisiae versus placebo in the irritable bowel syndrome. Dig. Liver Dis. 2015, 47, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simrén, M.; Ohman, L.; Olsson, J.; Svensson, U.; Ohlson, K.; Posserud, I.; Strid, H. Clinical trial: The effects of a fermented milk containing three probiotic bacteria in patients with irritable bowel syndrome—A randomized, double-blind, controlled study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 31, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dapoigny, M.; Piche, T.; Ducrotte, P.; Lunaud, B.; Cardot, J.M.; Bernalier-Donadille, A. Efficacy and safety profile of LCR35 complete freeze-dried culture in irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized, double-blind study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 2067–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ki Cha, B.; Mun Jung, S.; Hwan Choi, C.; Song, I.D.; Woong Lee, H.; Joon Kim, H.; Hyuk, J.; Kyung Chang, S.; Kim, K.; Chung, W.S.; et al. The effect of a multispecies probiotic mixture on the symptoms and fecal microbiota in diarrhea-dominant irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 46, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Li, M.; Li, Y.Y.; Li, L.X.; Zhai, W.Z.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.X.; Gu, X.; Song, L.J.; Li, Z.; et al. The effect of Clostridium butyricum on symptoms and fecal microbiota in diarrhea-dominant irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, E.; Vahedi, H.; Merat, S.; Momtahen, S.; Riahi, A. Therapeutic effects, tolerability and safety of a multi-strain probiotic in Iranian adults with irritable bowel syndrome and bloating. Arch. Iran. Med. 2014, 17, 466–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gayathri, R.; Aruna, T.; Malar, S.; Shilpa, B.; Dhanasekar, K.R. Efficacy of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CNCM I-3856 as an add-on therapy for irritable bowel syndrome. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2020, 35, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.; Yakoob, J.; Jafri, W.; Ahmad, Z.; Azam, Z.; Usman, M.W.; Shamim, S.; Islam, M. Cytokine and clinical response to Saccharomyces boulardii therapy in diarrhea-dominant irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized trial. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 26, 630–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Chang, L. Diagnosis and management of IBS. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, K.; Krumian, R.; Hattner, J.; de Montigny, D.; Stewart, M.; Gaddam, S. Lactobacillus acidophilus CL1285, Lactobacillus casei LBC80R and Lactobacillus rhamnosus CLR2 improve quality-of-life and IBS symptoms: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled study. Benef. Microbes 2018, 9, 697–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarren, C.; Tornblom, H.; Aziz, I.; Magnusson, M.K.; Sundin, J.; Vigsnaes, L.K.; Amundsen, I.D.; McConnell, B.; Seitzberg, D.; Ohman, L.; et al. Human milk oligosaccharide supplementation in irritable bowel syndrome patients: A parallel, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2020, 32, e13920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, M.; Gudmand-Hoyer, E. Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of fructooligosaccharides in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 1570–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niv, E.; Halak, A.; Tiommny, E.; Yanai, H.; Strul, H.; Naftali, T.; Vaisman, N. Randomized clinical study: Partially hydrolyzed guar gum (PHGG) versus placebo in the treatment of patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 13, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexea, O.; Bacarea, V.; Pique, N. The combination of oligo- and polysaccharides and reticulated protein for the control of symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: Results of a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel group, multicentre clinical trial. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2016, 4, 455–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.; Rossi, M.; Kanno, T.; Parkes, G.C.; Anderson, S.; Mason, A.J.; Irving, P.M.; Lomer, M.C.; Whelan, K. beta-Galactooligosaccharide in Conjunction with Low FODMAP Diet Improves Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptoms but Reduces Fecal Bifidobacteria. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 115, 906–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Yu, W.; Jiang, J.; Feng, X.; Li, N. Efficacy of pectin in the treatment of diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi 2015, 18, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azpiroz, F.; Dubray, C.; Bernalier-Donadille, A.; Cardot, J.M.; Accarino, A.; Serra, J.; Wagner, A.; Respondek, F.; Dapoigny, M. Effects of scFOS on the composition of fecal microbiota and anxiety in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized, double blind, placebo controlled study. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2017, 29, e12911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogha, M.; Esfahani, M.Z.; Zargarzadeh, A.H. The efficacy of a synbiotic containing Bacillus Coagulans in treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized placebo-controlled trial. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2014, 7, 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Cho, D.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Han, K.S.; Yang, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, K.N. A Randomized Clinical Trial of Synbiotics in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: Dose-Dependent Effects on Gastrointestinal Symptoms and Fatigue. Korean J. Fam. Med. 2019, 40, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, C.; Tremolaterra, F.; Pascariello, A.; Ciacci, C.; Iovino, P. A randomised clinical trial (RCT) of a symbiotic mixture in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): Effects on symptoms, colonic transit and quality of life. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2013, 28, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Skrzydlo-Radomanska, B.; Prozorow-Krol, B.; Cichoz-Lach, H.; Majsiak, E.; Bierla, J.B.; Kosikowski, W.; Szczerbinski, M.; Gantzel, J.; Cukrowska, B. The Effectiveness of Synbiotic Preparation Containing Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium Probiotic Strains and Short Chain Fructooligosaccharides in Patients with Diarrhea Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome-A Randomized Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.H.; Jang, Y.S.; Kang, D.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, E.J.; Park, S.Y.; Kim, C.H.; Min, Y.W.; Chang, D.K. Efficacy of a Synbiotic Containing Lactobacillus paracasei DKGF1 and Opuntia humifusa in Elderly Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Gut Liver 2023, 17, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andriulli, A.; Neri, M.; Loguercio, C.; Terreni, N.; Merla, A.; Cardarella, M.P.; Federico, A.; Chilovi, F.; Milandri, G.L.; De Bona, M.; et al. Clinical trial on the efficacy of a new symbiotic formulation, Flortec, in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A multicenter, randomized study. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 42 Pt 2 (Suppl. S3), S218–S223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NCT02431533, I. The Efficacy of PX0612 in the Treatment of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Available online: https://classic.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02431533 (accessed on 22 March 2024).
- El-Salhy, M.; Mazzawi, T.; Hausken, T.; Hatlebakk, J.G. The fecal microbiota transplantation response differs between patients with severe and moderate irritable bowel symptoms. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 57, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holvoet, T.; Joossens, M.; Vazquez-Castellanos, J.F.; Christiaens, E.; Heyerick, L.; Boelens, J.; Verhasselt, B.; van Vlierberghe, H.; De Vos, M.; Raes, J.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Reduces Symptoms in Some Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome with Predominant Abdominal Bloating: Short- and Long-term Results From a Placebo-Controlled Randomized Trial. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 145–157 e148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Lin, H.; Chen, P.; Tan, S.; Wen, Z.; Lin, L.; He, J.; Wen, J.; Lu, S. Dynamic changes of intestinal flora in patients with irritable bowel syndrome combined with anxiety and depression after oral administration of enterobacteria capsules. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 11885–11897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsen, P.H.; Hilpüsch, F.; Cavanagh, J.P.; Leikanger, I.S.; Kolstad, C.; Valle, P.C.; Goll, R. Faecal microbiota transplantation versus placebo for moderate-to-severe irritable bowel syndrome: A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, single-centre trial. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, A.M.A.; Halkjaer, S.I.; Christensen, A.H.; Gunther, S.; Browne, P.D.; Kallemose, T.; Hansen, L.H.; Petersen, A.M. The effect of faecal microbiota transplantation on abdominal pain, stool frequency, and stool form in patients with moderate-to-severe irritable bowel syndrome: Results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holster, S.; Lindqvist, C.M.; Repsilber, D.; Salonen, A.; de Vos, W.M.; Konig, J.; Brummer, R.J. The Effect of Allogenic Versus Autologous Fecal Microbiota Transfer on Symptoms, Visceral Perception and Fecal and Mucosal Microbiota in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized Controlled Study. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2019, 10, e00034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, P.P.; Chin, V.K.; Looi, C.Y.; Wong, W.F.; Madhavan, P.; Yong, V.C. The Microbiome and Irritable Bowel Syndrome—A Review on the Pathophysiology, Current Research and Future Therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, E.; Călinoiu, L.F.; Mitrea, L.; Vodnar, D.C. Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics: Implications and Beneficial Effects against Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halkjær, S.I.; Christensen, A.H.; Lo, B.Z.S.; Browne, P.D.; Günther, S.; Hansen, L.H.; Petersen, A.M. Faecal microbiota transplantation alters gut microbiota in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: Results from a randomised, double-blind placebo-controlled study. Gut 2018, 67, 2107–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Salhy, M.; Hatlebakk, J.G.; Gilja, O.H.; Bråthen Kristoffersen, A.; Hausken, T. Efficacy of faecal microbiota transplantation for patients with irritable bowel syndrome in a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Gut 2020, 69, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, A.C.; Quigley, E.M.; Lacy, B.E.; Lembo, A.J.; Saito, Y.A.; Schiller, L.R.; Soffer, E.E.; Spiegel, B.M.; Moayyedi, P. Efficacy of prebiotics, probiotics, and synbiotics in irritable bowel syndrome and chronic idiopathic constipation: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 109, 1547–1561, quiz 1546, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Sun, F.; Duan, L. Efficacy of Probiotics for Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 859967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Tun, H.M.; Liu, Q.; Yeoh, Y.K.; Mak, J.W.Y.; Chan, F.K.; Ng, S.C. Gut microbiome signatures reflect different subtypes of irritable bowel syndrome. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2157697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Schoot, A.; Helander, C.; Whelan, K.; Dimidi, E. Probiotics and synbiotics in chronic constipation in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 2759–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Gong, J.; Wang, W.; Long, Y.; Fu, X.; Fu, Y.; Qian, W.; Hou, X. Are there any different effects of Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus and Streptococcus on intestinal sensation, barrier function and intestinal immunity in PI-IBS mouse model? PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constante, M.; De Palma, G.; Lu, J.; Jury, J.; Rondeau, L.; Caminero, A.; Collins, S.M.; Verdu, E.F.; Bercik, P. Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 modulates the microbiota-gut-brain axis in a humanized mouse model of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2021, 33, e13985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Lv, L.; Wang, C. Efficacy of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 827395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Salhy, M.; Mazzawi, T. Fecal microbiota transplantation for managing irritable bowel syndrome. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 12, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holvoet, T.; Joossens, M.; Wang, J.; Boelens, J.; Verhasselt, B.; Laukens, D.; van Vlierberghe, H.; Hindryckx, P.; De Vos, M.; De Looze, D.; et al. Assessment of faecal microbial transfer in irritable bowel syndrome with severe bloating. Gut 2017, 66, 980–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Sterne, J.A.C. Chapter 8: Assessing risk of bias in a randomized trial. In Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions; Higgins, J.P.T., Thomas, J., Chandler, J., Cumpston, M., Li, T., Page, M.J., Welch, V.A., Eds.; Cochrane: London, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar]

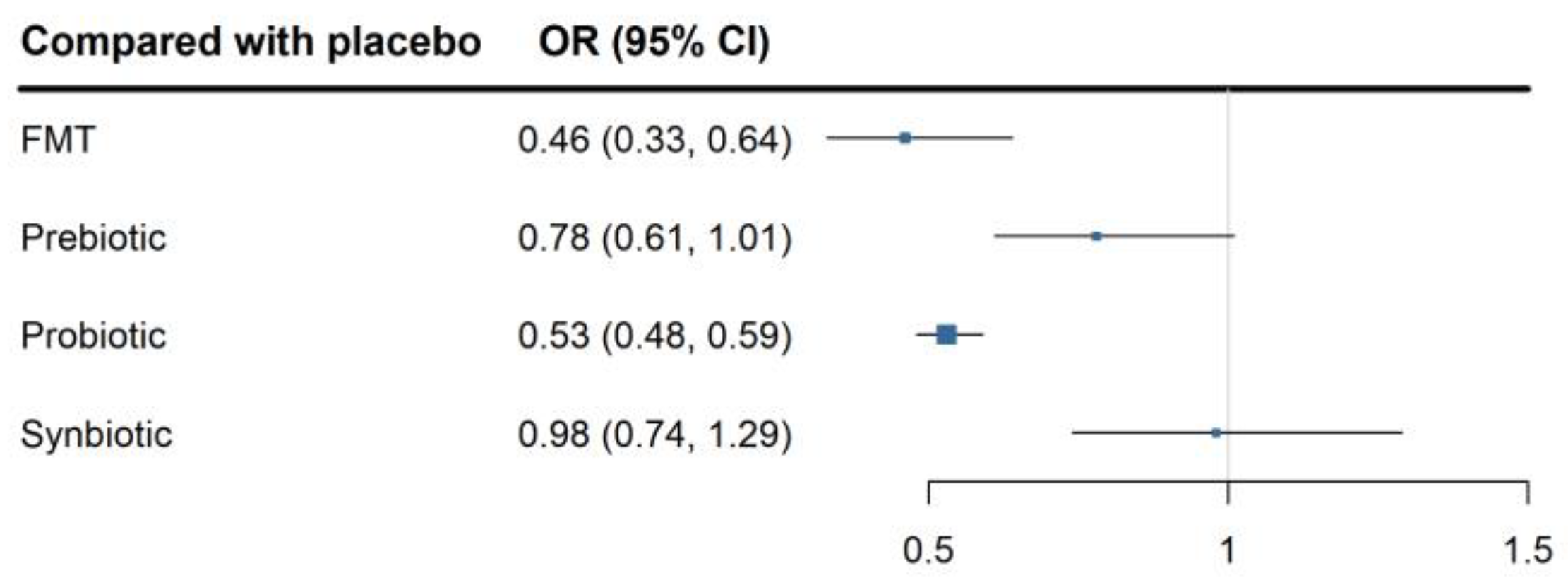
| Probiotic | ||||
| 0.88 (0.64, 1.19) | FMT | |||
| 0.68 (0.51, 0.89) * | 0.77 (0.52, 1.14) | Prebiotic | ||
| 0.54 (0.40, 0.72) * | 0.62 (0.41, 0.92) * | 0.80 (0.55, 1.16) | Synbiotic | |
| 0.53 (0.48, 0.59) * | 0.60 (0.45, 0.81) * | 0.78 (0.61, 1.01) | 0.98 (0.74, 1.29) | Placebo |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Li, L. The Efficacy of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132114
Wu Y, Li Y, Zheng Q, Li L. The Efficacy of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Nutrients. 2024; 16(13):2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132114
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Youhe, Yuetong Li, Qi Zheng, and Lanjuan Li. 2024. "The Efficacy of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis" Nutrients 16, no. 13: 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132114
APA StyleWu, Y., Li, Y., Zheng, Q., & Li, L. (2024). The Efficacy of Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, and Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 16(13), 2114. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16132114






