Effects of Acute Guarana (Paullinia cupana) Ingestion on Mental Performance and Vagal Modulation Compared to a Low Dose of Caffeine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
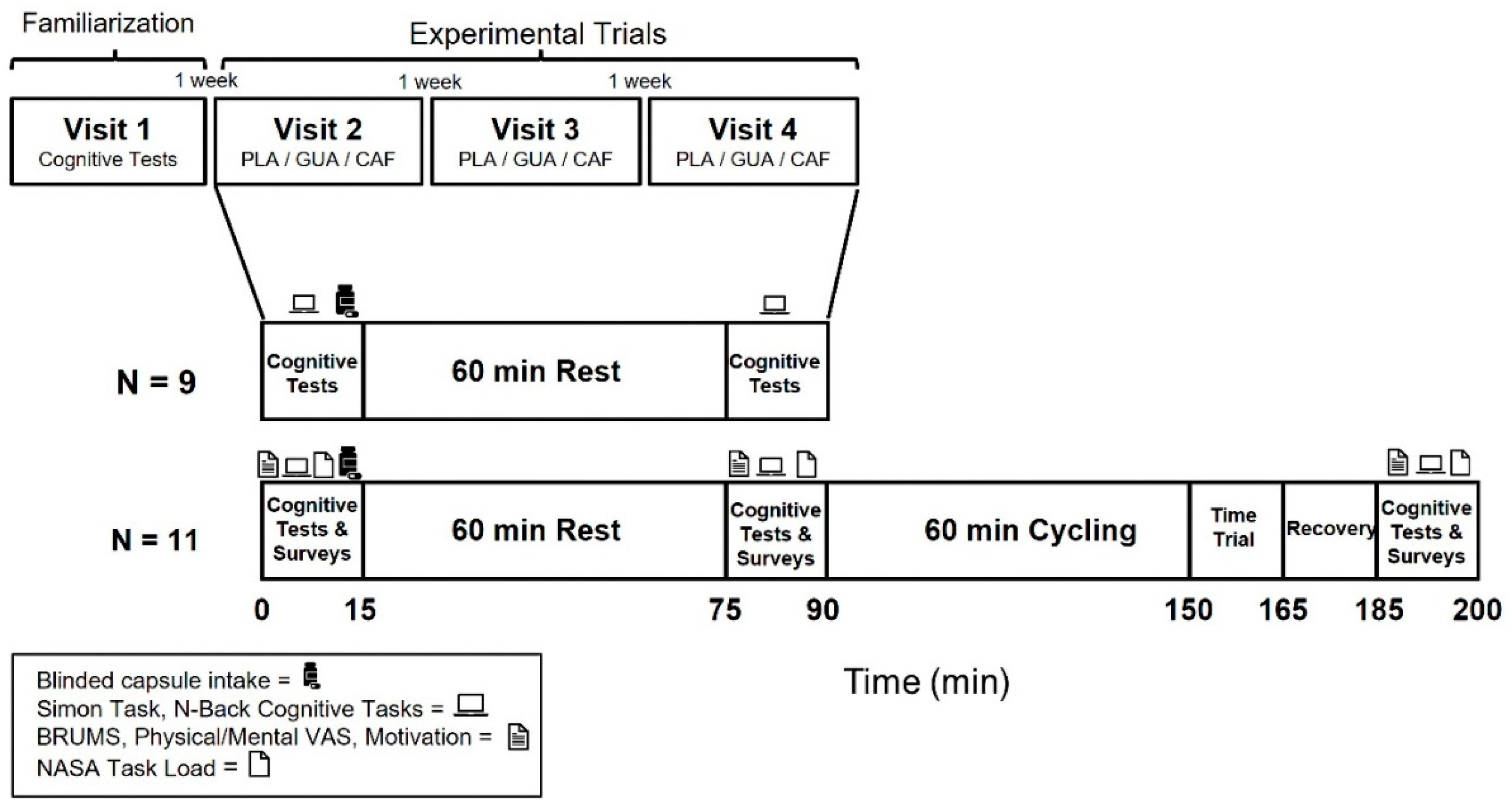
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Participants
2.3. Interventions
2.3.1. Preliminary Testing and Familiarization
2.3.2. Supplement Administration
2.3.3. Cognitive and Mood Assessments Administration
2.4. Experimental Cognitive and Mood Assessments
2.4.1. Simon Task
2.4.2. 2N-Back Task
2.4.3. The Brunel Mood Scale
2.4.4. The NASA Task Load Index
2.4.5. Motivation and Energy Visual Analog Scales
2.5. Experimental Physiological Assessments
Heart Rate Variability
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
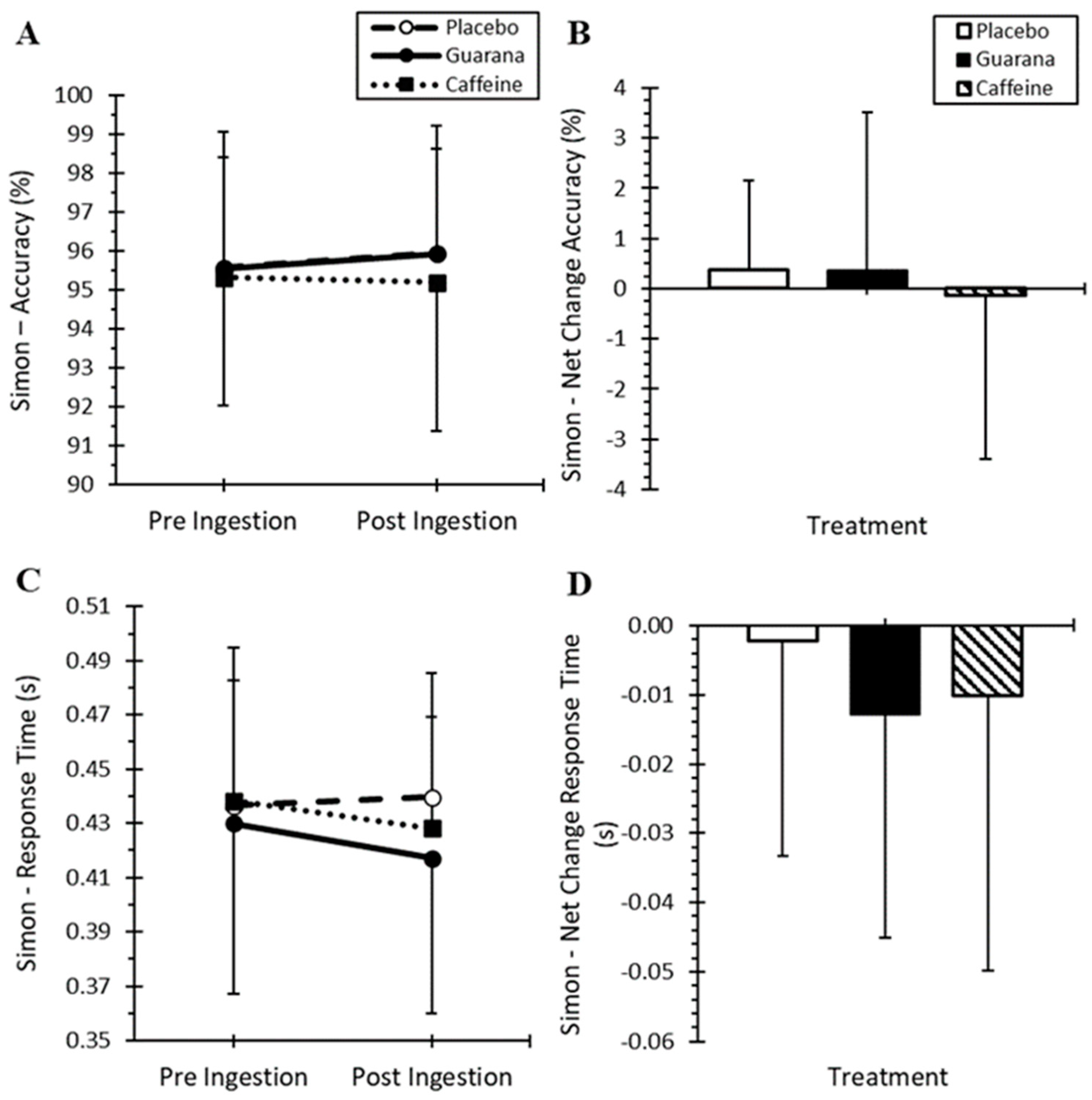
3.1. Simon Task Performance
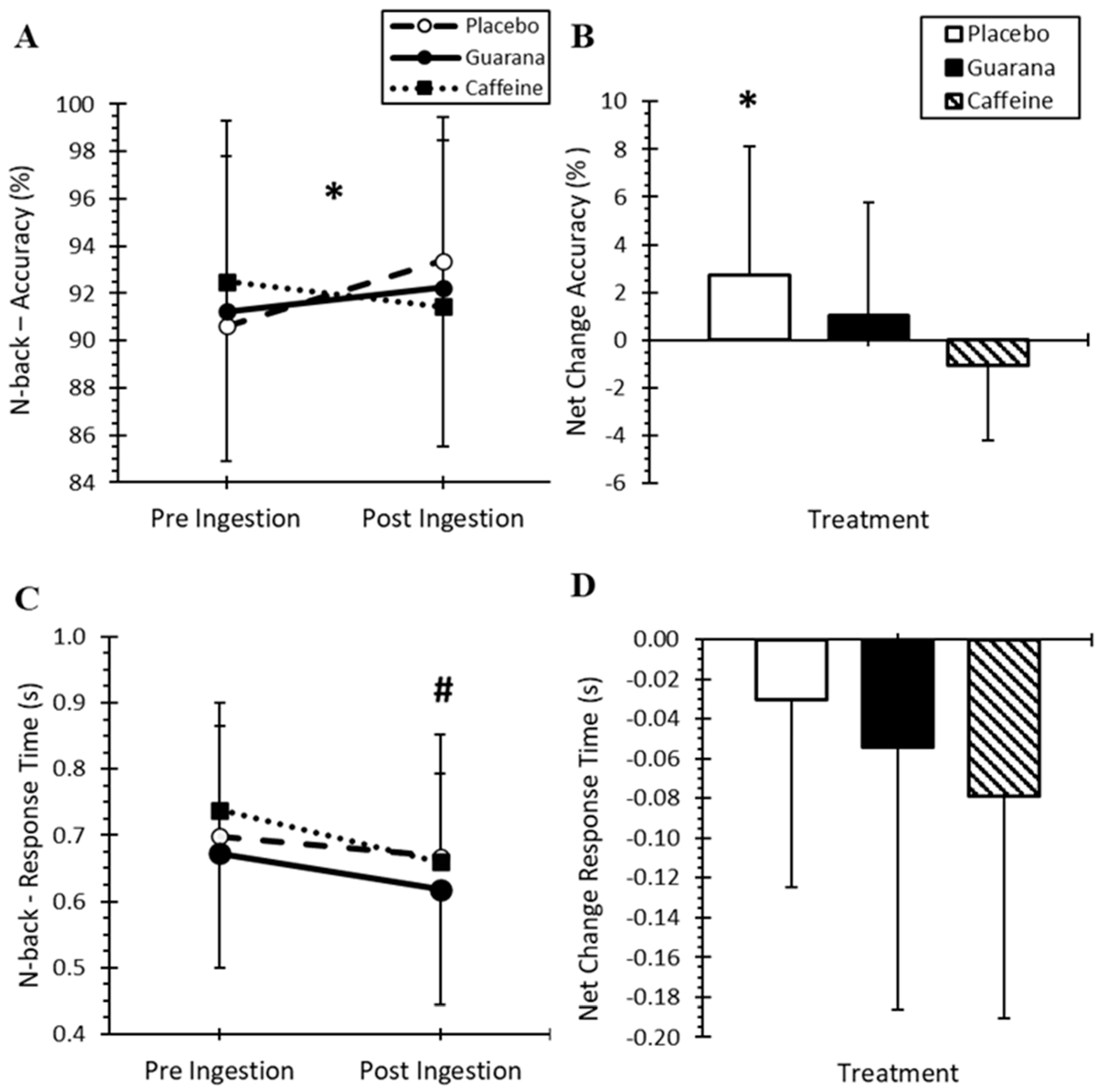
3.2. 2N-Back Task Performance
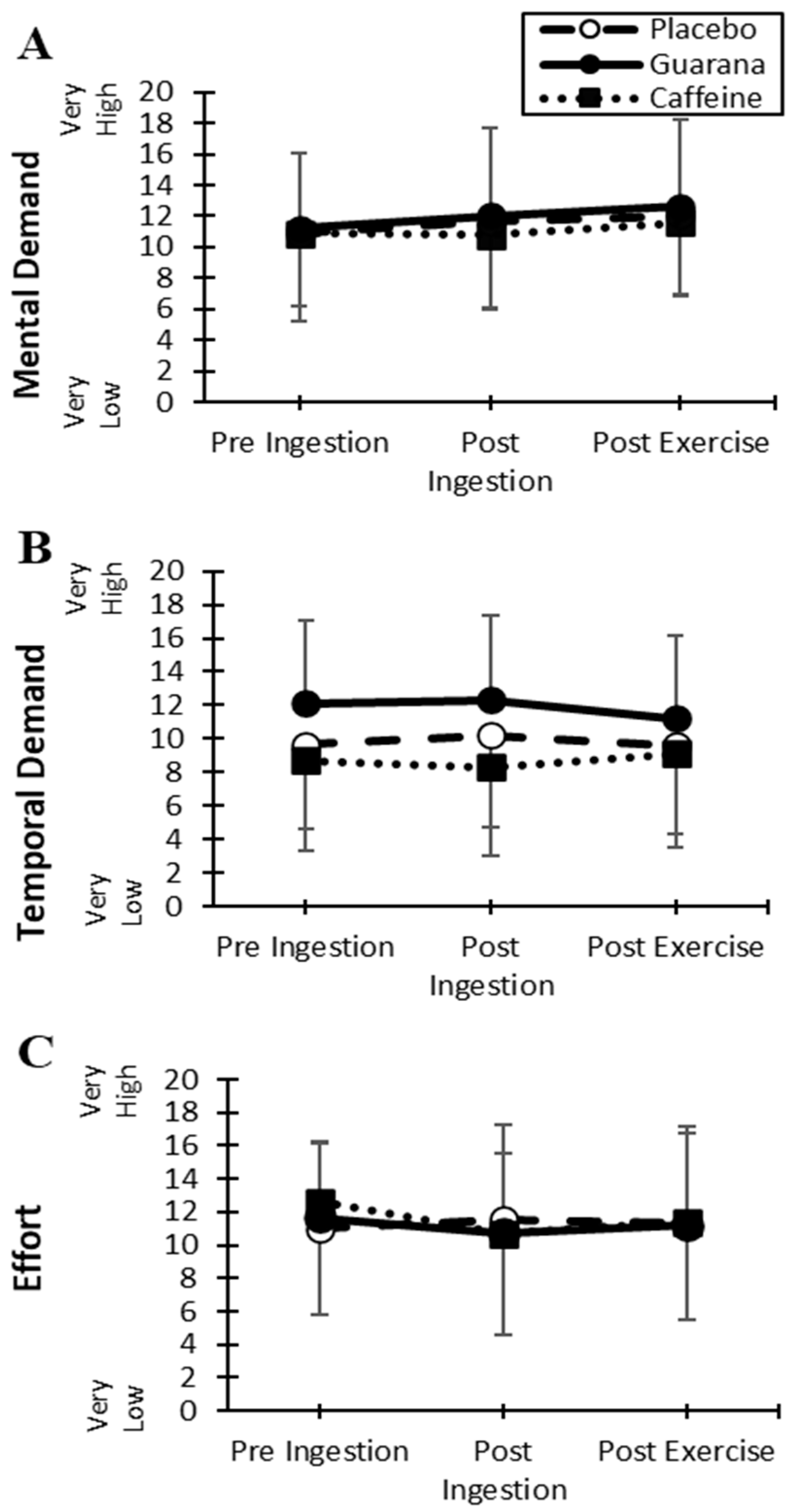
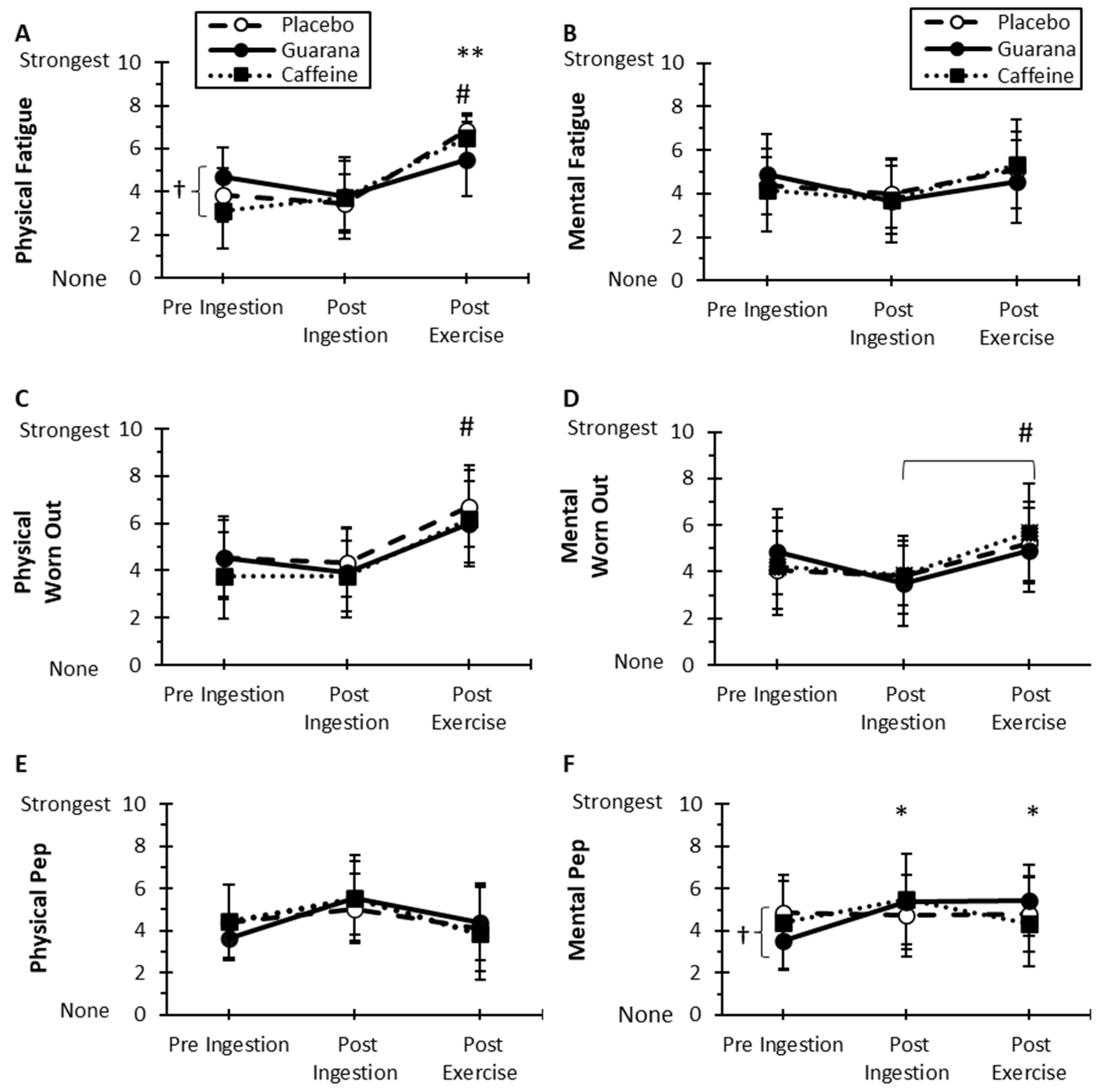
3.3. NASA Task Load Index Fatigue Scores
3.4. Brunel Mood Scale Scores
3.5. Motivation and Energy Visual Analog Ratings
3.6. Heart Rate Variability Recordings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harvey, P.D. Domains of cognition and their assessment. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 21, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyng, C.M.; Amin, H.U.; Saad, M.N.M.; Malik, A.S. The influences of emotion on learning and memory. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, Y.; Craig, A.; Craig, R.; Chai, R.; Nguyen, H.T. The influence of mental fatigue on brain activity: Evidence from a systematic review with meta-analyses. Psychophysiology 2020, 57, e13554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakim, H.; Khemiri, A.; Chortane, O.G.; Boukari, S.; Chortane, S.G.; Bianco, A.; Marsigliante, S.; Patti, A.; Muscella, A. Mental fatigue effects on the produced perception of effort and its impact on subsequent physical performances. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 10973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madireddy, S. Most effective combination of nutraceuticals for improved memory and cognitive performance in the house cricket, Acheta domesticus. Nutrients 2021, 13, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs, E. Influence of energy drink ingredients on mood and cognitive performance. Nutr. Rev. 2014, 72, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frary, C.D.; Johnson, R.K.; Wang, M.Q. Food sources and intakes of caffeine in the diets of persons in the United States. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2005, 105, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaeth, A.M.; Goel, N.; Dinges, D.F. Cumulative neurobehavioral and physiological effects of chronic caffeine intake: Individual differences and implications for the use of caffeinated energy products. Nutr. Rev. 2014, 72, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, N.; Akhter, S.; Miao, Y. Pathways and mechanism of caffeine binding to human adenosine A2A receptor. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 673170. [Google Scholar]
- Fiani, B.; Zhu, L.; Musch, B.; Briceno, S.; Andel, R.; Sadeq, N.; Ansari, A.Z. The neurophysiology of caffeine as a central nervous system stimulant and the resultant effects on cognitive function. Cureus 2021, 13, 15032. [Google Scholar]
- Voskoboinik, A.; Koh, Y.; Kistler, P.M. Cardiovascular effects of caffeinated beverages. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2019, 29, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grgić, J.; Del Coso, J. Ergogenic effects of acute caffeine intake on muscular endurance and muscular strength in women: A meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehlig, A. Interindividual differences in caffeine metabolism and factors driving caffeine consumption. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 384–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.H.; Palmer, A.A.; de Wit, H. Genetics of caffeine consumption and responses to caffeine. Psychopharmacology 2010, 211, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskell, C.F.; Kennedy, D.O.; Wesnes, K.; Scholey, A.B. Cognitive and mood improvements of caffeine in habitual consumers and habitual non-consumers of caffeine. Psychopharmacology 2005, 179, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Madan, C.R. How does caffeine influence memory? Drug, experimental, and demographic factors. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 131, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryant, C.; Farmer, A.; Tiplady, B.; Keating, J.; Sherwood, R.; Swift, C.G.; Jackson, S.H.D. Psychomotor performance: Investigating the dose-response relationship for caffeine and theophylline in elderly volunteers. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1998, 54, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, E.B.; Pinaffi-Langley, A.C.C.; De Souza Figueira, M.; Cordeiro, K.S.; Negrão, L.D.; Soares, M.J.; da Silva, C.P.; Alfino, M.C.Z.; Sampaio, G.R.; de Camargo, A.C. Effects of the consumption of guarana on human health: A narrative review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 21, 272–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schimpl, F.C.; Da Silva, J.A.G.; De Carvalho Gonçalves, J.F.; Mazzafera, P. Guarana: Revisiting a highly caffeinated plant from the Amazon. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olechno, E.; Puścion-Jakubik, A.; Zujko, M.E.; Socha, K. Influence of various factors on caffeine content in coffee brews. Foods 2021, 10, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borota, D.; Murray, E.; Keceli, G.; Chang, A.; Watabe, J.M.; Ly, M.; Toscano, J.P.; Yassa, M.A. Post-study caffeine administration enhances memory consolidation in humans. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.; Sutherland, D.E.; Christopher, G. Effects of repeated doses of caffeine on mood and performance of alert and fatigued volunteers. J. Psychopharmacol. 2005, 19, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, G.S.; Canuto, K.M.; Ribeiro, P.R.V.; de Brito, E.S.; Nascimento, M.M.; Zocolo, G.J.; de Jesus, R.M. Chemical profiling of guarana seeds (Paullinia cupana) from different geographical origins using UPLC-QTOF-MS combined with chemometrics. Food Res. Int. 2017, 102, 700–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.A.; Sampaio, G.R.; Freitas, R.A.M.S.; Da Silva Torres, E.A.F. Polyphenols from guaraná after in vitro digestion: Evaluation of bioaccessibility and inhibition of activity of carbohydrate-hydrolyzing enzymes. Food Chem. 2018, 267, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomportes, L.; Davranche, K.; Brisswalter, I.; Hays, A.; Brisswalter, J. Heart rate variability and cognitive function following a multi-vitamin and mineral supplementation with added guarana (Paullinia cupana). Nutrients 2014, 7, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomportes, L.; Brisswalter, J.; Hays, A.; Davranche, K. Effects of carbohydrate, caffeine, and guarana on cognitive performance, perceived exertion, and shooting performance in high-level athletes. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2019, 14, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hack, B.; Penna, E.M.; Talik, T.; Chandrashekhar, R.; Millard-Stafford, M.L. Effect of guarana (Paullinia cupana) on cognitive performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients 2023, 15, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haskell, C.F.; Kennedy, D.O.; Wesnes, K.; Milne, A.; Scholey, A.B. A double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-dose evaluation of the acute behavioural effects of guaraná in humans. J. Psychopharmacol. 2006, 21, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Haskell, C.F.; Wesnes, K.; Scholey, A.B. Improved cognitive performance in human volunteers following administration of guarana (Paullinia cupana) extract: Comparison and interaction with Panax ginseng. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2004, 79, 401–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staiano, W.; Bonet, L.R.S.; Romagnoli, M.; Ring, C. Mental fatigue impairs repeated sprint and jump performance in team sport athletes. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2023, 26, 1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, J.; Marcora, S.M.; De Pauw, K.; Bailey, S.; Meeusen, R.; Roelands, B. The effects of mental fatigue on physical performance: A systematic review. Sports Med. 2017, 47, 1569–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgić, J.; Grgic, I.; Pickering, C.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Bishop, D.J.; Pedisic, Z. Wake up and smell the coffee: Caffeine supplementation and exercise performance—An umbrella review of 21 published meta-analyses. Br. J. Sports Med. 2019, 54, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurney, T.; Bradley, N.; Izquierdo, D.; Ronca, F. Cognitive effects of guarana supplementation with maximal intensity cycling. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 130, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veasey, R.C.; Haskell-Ramsay, C.F.; Kennedy, D.N.; Wishart, K.; Maggini, S.; Fuchs, C.J.; Stevenson, E.J. The effects of supplementation with a vitamin and mineral complex with guaraná prior to fasted exercise on affect, exertion, cognitive performance, and substrate metabolism: A randomized controlled trial. Nutrients 2015, 7, 6109–6127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penna, E.M.; Harp, A.; Hack, B.; Talik, T.N.; Millard-Stafford, M. Guarana (Paullinia cupana) but not low-dose caffeine improves cycling time-trial performance versus placebo. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2024, 34, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, J.; Rudell, A.P. Auditory S-R compatibility: The effect of an irrelevant cue on information processing. J. Appl. Psychol. 1967, 51, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, W.K. Age differences in short-term retention of rapidly changing information. J. Exp. Psychol. 1958, 55, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, P.C.; Lane, A.M. User Guide to Brunel Mood Scale; University of Southern Queensland: Toowoomba, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, S.G.; Staveland, L.E. Development of NASA-TLX (Task Load Index): Results of empirical and theoretical research. Adv. Psychol. 1988, 52, 139–183. [Google Scholar]
- Maridakis, V.; O’Connor, P.J.; Tomporowski, P.D. Sensitivity to change in cognitive performance and mood measures of energy and fatigue in response to morning caffeine alone or in combination with carbohydrate. Int. J. Neurosci. 2009, 119, 1239–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himariotis, A.T.; Coffey, K.F.; Noël, S.; Cornell, D.J. Validity of a smartphone application in calculating measures of heart rate variability. Sensors 2022, 22, 9883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, F.; Ginsberg, J.P. An overview of heart rate variability metrics and norms. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.N.; Wightman, E.L. Mental performance and sport: Caffeine and co-consumed bioactive ingredients. Sports Med. 2022, 52, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, D.O.; Haskell, C.F.; Robertson, B.; Reay, J.; Brewster-Maund, C.; Luedemann, J.; Scholey, A.B. Improved cognitive performance and mental fatigue following a multi-vitamin and mineral supplement with added guaraná (Paullinia cupana). Appetite 2008, 50, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.; Ball, P. Psychological and cardiovascular effects of guarana and yerba mate: A comparison with coffee. Interam. J. Psychol. 2004, 38, 87–94. [Google Scholar]
- Michael, S.; Graham, K.; Davis, G.M. Cardiac autonomic responses during exercise and post-exercise recovery using heart rate variability and systolic time intervals—A review. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mongin, D.; Chabert, C.; Extremera, M.G.; Hue, O.; Courvoisier, D.S.; Carpena, P.; Galvan, P.A.B. Decrease of heart rate variability during exercise: An index of cardiorespiratory fitness. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0273981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, J.P.E. Flavonoids and brain health: Multiple effects underpinned by common mechanisms. Genes Nutr. 2009, 4, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macready, A.L.; Kennedy, O.B.; Ellis, J.A.; Williams, C.M.; Spencer, J.P.E.; Butler, L.T. Flavonoids and cognitive function: A review of human randomized controlled trial studies and recommendations for future studies. Genes Nutr. 2009, 4, 227–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Xian, D.; Xiong, X.; Lai, R.; Song, J.; Zhong, J. Proanthocyanidins against oxidative stress: From molecular mechanisms to clinical applications. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8584136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conger, S.A.; Tuthill, L.M.; Millard-Stafford, M. Does caffeine increase fat metabolism? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2023, 33, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Placebo | Guarana | Caffeine | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simon ACC (%) | −0.57 ± 1.71 | −0.23 ± 2.61 | −0.57 ± 3.46 |
| Simon RT (s) | −0.02 ± 0.03 | −0.03 ± 0.02 | −0.04 ± 0.06 |
| 2N-Back ACC (%) | 1.93 ± 2.12 | 1.82 ± 3.18 | −0.68 ± 3.89 |
| 2N-Back RT (s) | −0.10 ± 0.10 | −0.10 ± 0.10 | −0.09 ± 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Talik, T.N.; Penna, E.M.; Hack, B.P.; Harp, A.; Millard-Stafford, M. Effects of Acute Guarana (Paullinia cupana) Ingestion on Mental Performance and Vagal Modulation Compared to a Low Dose of Caffeine. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16121892
Talik TN, Penna EM, Hack BP, Harp A, Millard-Stafford M. Effects of Acute Guarana (Paullinia cupana) Ingestion on Mental Performance and Vagal Modulation Compared to a Low Dose of Caffeine. Nutrients. 2024; 16(12):1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16121892
Chicago/Turabian StyleTalik, Tyler N., Eduardo Macedo Penna, Brian P. Hack, Alec Harp, and Mindy Millard-Stafford. 2024. "Effects of Acute Guarana (Paullinia cupana) Ingestion on Mental Performance and Vagal Modulation Compared to a Low Dose of Caffeine" Nutrients 16, no. 12: 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16121892
APA StyleTalik, T. N., Penna, E. M., Hack, B. P., Harp, A., & Millard-Stafford, M. (2024). Effects of Acute Guarana (Paullinia cupana) Ingestion on Mental Performance and Vagal Modulation Compared to a Low Dose of Caffeine. Nutrients, 16(12), 1892. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16121892







