Exercise and Nutrition in the Mental Health of the Older Adult Population: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Participants
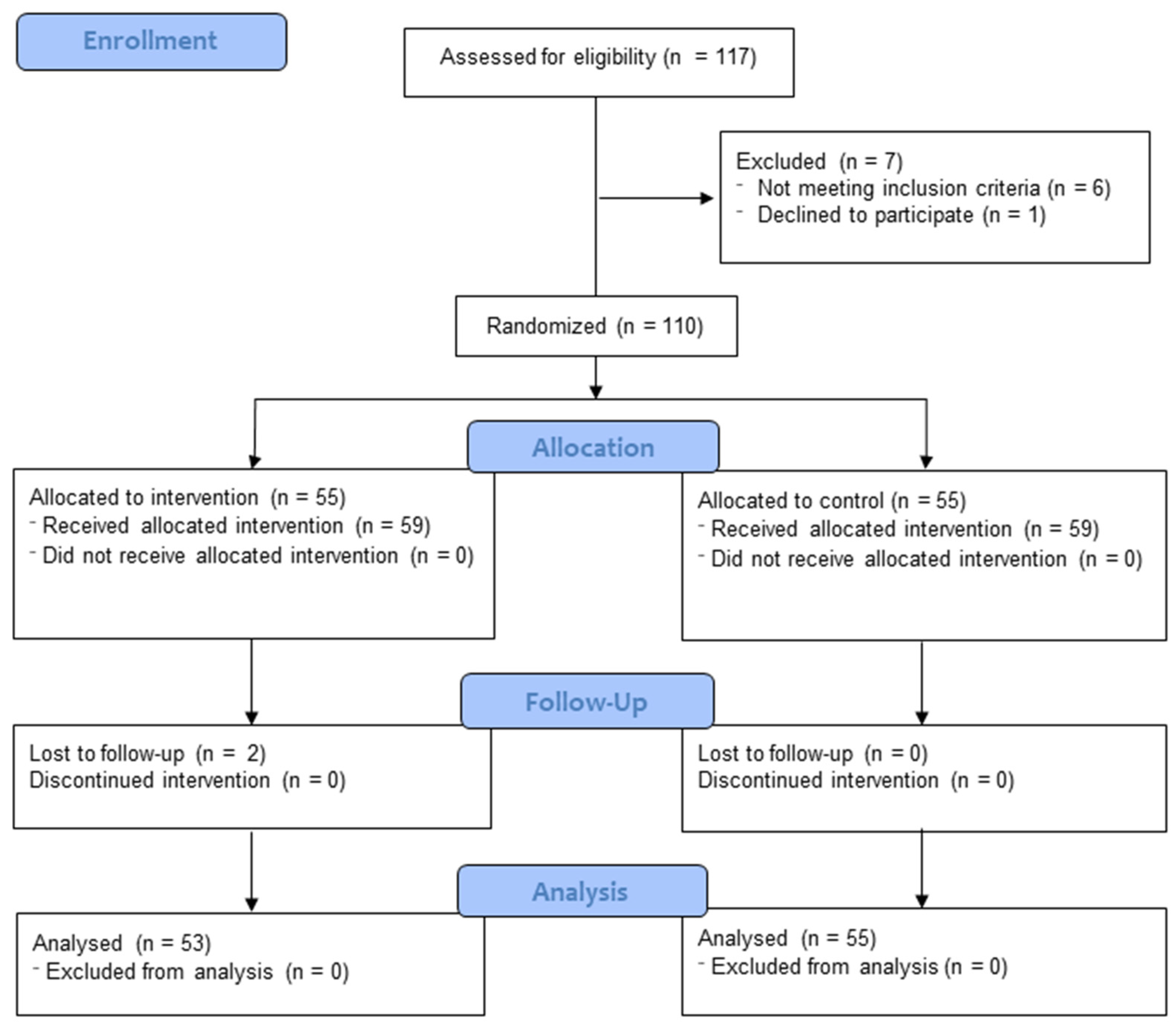
2.3. Randomization
2.4. Intervention
Resistance Training
2.5. Outcomes
2.5.1. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet
2.5.2. Anxiety and Depression
2.5.3. Sleep Quality
2.5.4. Perceived Stress
2.6. Sample Size Calculation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet
3.2. Anxiety and Depression
3.3. Perceived Stress
3.4. Sleep Quality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Christensen, K.; Doblhammer, G.; Rau, R.; Vaupel, J.W. Ageing populations: The challenges ahead. Lancet 2009, 374, 1196–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Population Prospects 2019: Highlights (ST/ESA/SER.A/423); United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Demography of Europe—An Ageing Population. (s.f.). Demography of Europe. Available online: https://www.ine.es/prodyser/demografia_UE/bloc-1c.html?lang=es (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Envejecimiento y salud. (s.f.). World Health Organization (WHO). Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ageing-and-health (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Dent, E.; Martin, F.C.; Bergman, H.; Woo, J.; Romero-Ortuno, R.; Walston, J.D. Management of frailty: Opportunities, challenges, and future directions. Lancet 2019, 394, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzo, R.R.; Khanal, P.; Shrestha, S.; Mohan, D.; Myint, P.K.; Su, T.T. Determinants of active aging and quality of life among older adults: Systematic review. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1193789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Qian, X.; Choi, E.P.H.; Chau, P.H. The Consequences of Unmet Needs for Assistance With Daily Life Activities Among Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Med. Care Res. Rev. 2024, 7, 10775587241233798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Yue, X.; Zhang, S. Prevalence of social frailty and risk factors among community-dwelling older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2024, 123, 105419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beekman, A.T.F.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Deeg, D.J.H.; de Beurs, E.; Geerling, S.W.; van Tilburg, W. The impact of depression on the well-being, disability and use of services in older adults: A longitudinal perspective. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 2002, 105, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization: WHO. (2023, 20 Octubre). Salud Mental de los Adultos Mayores. Available online: https://www.who.int/es/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-health-of-older-adults (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Üstün, T.N.; Ayuso-Mateos, J.L.; Chatterji, S.; Mathers, C.; Murray, C.J.L. Global burden of depressive disorders in the year 2000. Br. J. Psychiatry 2004, 184, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, A.; Scott, J.M.; Vos, T.; Whiteford, H. Global prevalence of anxiety disorders: A systematic review and meta-regression. Psychol. Med. 2013, 43, 897–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mental Health and Substance Use (MSD). (2017, 3 Enero). Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/depression-global-health-estimates (accessed on 1 February 2024).
- Kiefte-De Jong, J.C.; Mathers, J.C.; Franco, O.H. Nutrition and healthy ageing: The key ingredients. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2014, 73, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsner, R.J. Changes in eating behavior during the aging process. Eat. Behav. 2002, 3, 15–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, J.C. Food, nutrition and healthy ageing. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 27, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Evidence Analysis Library Division, Centre for Nutrition Policy and Promotion. A Series of Systematic Reviews on the Relationship between Dietary Patterns and Health Outcomes. 2014. Available online: https://www.cnpp.usda.gov/nutrition-evidence-library-dietary-patterns-systematic-review-project (accessed on 17 February 2024).
- Kant, A.K. Dietary patterns and health outcomes. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2004, 104, 615–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matison, A.P.; Mather, K.A.; Flood, V.M.; Reppermund, S. Associations between nutrition and the incidence of depression in middle-aged and older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational population-based studies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 70, 101403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, K.M.; McNaughton, S.A. Dietary patterns via reduced rank regression are associated with obesity and hypertension in Australian adults. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhber, N.; Majdi, M.R.; Ali-Abadi, M.; Shakeri, M.T.; Kimiagar, M.; Salek, R.; Moghaddam, P.A.; Sakhdari, A.; Azimi-Nezhad, M.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; et al. Association between malnutrition and depression in elderly people in Razavi Khorasan: A population study in Iran. Iran J. Public Health 2011, 40, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ford, D.W.; Jensen, G.L.; Still, C.; Wood, C.; Mitchell, D.C.; Erickson, P.; Bailey, R.; Smiciklas-Wright, H.; Coffman, D.L.; Hartman, T.J. The associations between diet quality and body mass index (BMI) and health and activity limitation index (halex) in the Geisinger Rural Aging Study (GRAS). J. Nutr. Health Aging 2014, 18, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza-Talarico, J.N.; Chesak, S.; Elizalde, N.; Liu, W.; Moon, C.; Oberfrank, N.D.C.F.; Rauer, A.J.; Takao, C.L.; Shaw, C.; Saravanan, A.; et al. Exploring the interplay of psychological and biological components of stress response and telomere length in the transition from middle age to late adulthood: A systematic review. Stress Health 2024, 5, e3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copeland, J.L.; Good, J.; Dogra, S. Strength training is associated with better functional fitness and perceived healthy aging among physically active older adults: A cross-sectional analysis of the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 31, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Labra, C.; Guimaraes-Pinheiro, C.; Maseda, A.; Lorenzo, T.; Millán-Calenti, J.C. Effects of physical exercise interventions in frail older adults: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. BMC Geriatr. 2015, 15, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.D.; Yeun, Y.R. Effects of Resistance Training on C-Reactive Protein and Inflammatory Cytokines in Elderly Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, E.; Hill, K.D.; Codde, J.; Jacques, A.; Ng, Y.L.; Hill, A.M. Encouraging Adults Aged 65 and over to Participate in Resistance Training by Linking Them with a Peer: A Pilot Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westcott, W.L. Resistance training is medicine: Effects of strength training on health. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2012, 11, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dionigi, R. Resistance Training and Older Adults’ Beliefs about Psychological Benefits: The Importance of Self-Efficacy and Social Interaction. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2008, 29, 723–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mcleod, J.C.; Stokes, T.; Phillips, S.M. Resistance Exercise Training as a Primary Countermeasure to Age-Related Chronic Disease. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, M.A.R.; Baptista, L.C.; Neves, R.S.; De França, E.; Loureiro, H.; Lira, F.S.; Caperuto, E.C.; Veríssimo, M.T.; Martins, R.A. The Effects of Concurrent Training Combining Both Resistance Exercise and High-Intensity Interval Training or Moderate-Intensity Continuous Training on Metabolic Syndrome. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, P.; Taaffe, D.R.; Galvão, D.A.; Newton, R.U.; Nonemacher, E.R.; Wendt, V.M.; Bassanesi, R.N.; Turella, D.J.P.; Rech, A. Resistance training effectiveness on body composition and body weight outcomes in individuals with overweight and obesity across the lifespan: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Obes. 2022, 23, e13428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, P.D.; Buck, D.J. The effect of resistance training on health-related quality of life in older adults: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Promot. Perspect. 2019, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Xiao, H. Exercise for Mental Well-Being: Exploring Neurobiological Advances and Intervention Effects in Depression. Life 2023, 13, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustin, N.; Bendau, A.; Heuer, S.; Kaminski, J.; Ströhle, A. Resistance Training in Depression. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2023, 120, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, B.R.; McDowell, C.P.; Hallgren, M.; Meyer, J.D.; Lyons, M.; Herring, M.P. Association of Efficacy of Resistance Exercise Training With Depressive Symptoms: Meta-analysis and Meta-regression Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. JAMA Psychiatry 2018, 75, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Pardo, P.J.; Espeso-García, A.; Vaquero-Cristóbal, R.; Abelleira-Lamela, T.; González-Gálvez, N. The Effect of Resistance Training with Outdoor Fitness Equipment on the Body Composition, Physical Fitness, and Physical Health of Middle-Aged and Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Healthcare 2024, 12, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, A.M.A.; El-Azeim, A.S.A.; Saif, H.F.A.E.A. Effect of aerobic exercise alone or combined with Mediterranean diet on dry eye in obese hypertensive elderly. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2023, 192, 3151–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ballart, J.D.; Piñol, J.L.; Zazpe, I.; Corella, D.; Carrasco, P.; Toledo, E.; Perez-Bauer, M.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Martín-Moreno, J.M. Relative validity of a semi-quantitative food-frequency questionnaire in an elderly Mediterranean population of Spain. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 103, 1808–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigmond, A.S.; Snaith, R.P. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1983, 67, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, M.J.; Blanch, J.; Peri, J.M.; De Pablo, J.; Pintor, L.; Bulbena, A. Validation study of the hospital anxiety and depression scale (HADS) in a Spanish population. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2003, 25, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagalaz-Anula, N.; Hita-Contreras, F.; Martínez-Amat, A.; Cruz-Díaz, D.; Aibar-Almazán, A.; Barranco-Zafra, R.J.; Lomas-Vega, R. The associations between menopausal symptoms and sleep quality in Spanish postmenopausal women. Climacteric 2019, 22, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hita-Contreras, F.; Martínez-López, E.; Latorre-Román, P.A.; Garrido, F.; Santos, M.A.; Martínez-Amat, A. Reliability and validity of the Spanish version of the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) in patients with fibromyalgia. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F.; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Kamarck, T.; Mermelstein, R. A global measure of perceived stress. J. Health Soc. Behav. 1983, 24, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remor, E. Psychometric Properties of a European Spanish Version of the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS). Span. J. Psychol. 2006, 9, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noradechanunt, C.; Worsley, A.; Groeller, H. Thai Yoga improves physical function and well-being in older adults: A randomised controlled trial. J. Sci. Med. Sport. 2017, 20, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. A power primer. Psychol. Bull. 1992, 112, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caprara, G. Mediterranean-Type Dietary Pattern and Physical Activity: The Winning Combination to Counteract the Rising Burden of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs). Nutrients 2021, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Key, M.N.; Szabo-Reed, A.N. Impact of Diet and Exercise Interventions on Cognition and Brain Health in Older Adults: A Narrative Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniela, M.; Catalina, L.; Ilie, O.; Paula, M.; Daniel-Andrei, I.; Ioana, B. Effects of Exercise Training on the Autonomic Nervous System with a Focus on Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidants Effects. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, K.M.B.; Ronca, D.B.; Michels, N.; Huybrechts, I.; Cuenca-Garcia, M.; Marcos, A.; Molnár, D.; Dallongeville, J.; Manios, Y.; Schaan, B.D.; et al. Does the Mediterranean Diet Protect against Stress-Induced Inflammatory Activation in European Adolescents? The HELENA Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, P.M.; Werneck, A.O.; dos Santos, L.; Oliveira, M.D.; Zou, L.; Schuch, F.B.; Cyrino, E.S. Can resistance training improve mental health outcomes in older adults? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Psychiatry Res. 2024, 333, 115746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calle, M.C.; Fernandez, M.L. Effects of resistance training on the inflammatory response. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2010, 4, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, A.; Babaei, M.; Rezaei, S.; Motallebnejad, Z.A.; Ganjalikhani, M.; Malekahmadi, M.; Esmaillzadeh, A. The effect of Mediterranean diet on nutritional status, muscle mass and strength, and inflammatory factors in patients with colorectal cancer-induced cachexia: Study protocol for a randomized clinical trial. Trials 2022, 23, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindaraju, T.; Sahle, B.W.; McCaffrey, T.A.; McNeil, J.J.; Owen, A.J. Dietary Patterns and Quality of Life in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2018, 10, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, N.; Stubbs, B.; Noale, M.; Solmi, M.; Luchini, C.; Maggi, S. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with better quality of life: Data from the osteoarthritis initiative. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlAufi, N.S.; Chan, Y.M.; Waly, M.I.; Chin, Y.S.; Mohd Yusof, B.N.; Ahmad, N. Application of Mediterranean Diet in Cardiovascular Diseases and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Motivations and Challenges. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allcock, L.; Mantzioris, E.; Villani, A. Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet is associated with physical and cognitive health: A cross-sectional analysis of community-dwelling older Australians. Front. Public Health. 2022, 10, 1017078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sousa-Fernandes, M.S.; Ordônio, T.F.; Santos, G.C.J.; Santos, L.E.R.; Calazans, C.T.; Gomes, D.A.; Santos, T.M. Effects of Physical Exercise on Neuroplasticity and Brain Function: A Systematic Review in Human and Animal Studies. Neural Plast. 2020, 2020, 8856621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, J.; Crockett, R.A.; Hsu, C.L.; Dao, E.; Tam, R.; Liu-Ambrose, T. Resistance Training Maintains White Matter and Physical Function in Older Women with Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: An Exploratory Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Alzheimers Dis. Rep. 2023, 7, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tryfonos, C.; Pavlidou, E.; Vorvolakos, T.; Alexatou, O.; Vadikolias, K.; Mentzelou, M.; Tsourouflis, G.; Serdari, A.; Antasouras, G.; Papadopoulou, S.K.; et al. Association of Higher Mediterranean Diet Adherence With Lower Prevalence of Disability and Symptom Severity, Depression, Anxiety, Stress, Sleep Quality, Cognitive Impairment, and Physical Inactivity in Older Adults With Multiple Sclerosis. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2023, 37, 318–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itsiopoulos, C.; Mayr, H.L.; Thomas, C.J. The anti-inflammatory effects of a Mediterranean diet: A review. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2022, 25, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehoe, L.; Walton, J.; Flynn, A. Nutritional challenges for older adults in Europe: Current status and future directions. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2019, 78, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincenza, G.; Monica, D.; Daniele, N.; Simone, J.P.M.; Andrea, A.; Miranda, T.S.; Nicolaas, S.; Anna, O. Association between dietary patterns and depression: An umbrella review of meta-analyses of observational studies and intervention trials. Nutr. Rev. 2023, 81, 346–359. [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln, A.K.; Shepherd, A.; Johnson, P.L.; Castaneda-Sceppa, C. The impact of resistance exercise training on the mental health of older Puerto Rican adults with type 2 diabetes. J. Gerontol. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2011, 66, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantzorou, M.; Vadikolias, K.; Pavlidou, E.; Serdari, A.; Vasios, G.; Tryfonos, C.; Giaginis, C. Nutritional status is associated with the degree of cognitive impairment and depressive symptoms in a Greek elderly population. Nutr. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moraes, W.; Piovezan, R.; Poyares, D.; Bittencourt, L.R.; Santos-Silva, R.; Tufik, S. Effects of aging on sleep structure throughout adulthood: A population-based study. Sleep. Med. 2014, 15, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Sá Souza, H.; de Melo, C.M.; Piovezan, R.D.; Miranda, R.E.E.P.C.; Carneiro-Junior, M.A.; Silva, B.M.; Thomatieli-Santos, R.V.; Tufik, S.; Poyares, D.; D’almeida, V. Resistance Training Improves Sleep and Anti-Inflammatory Parameters in Sarcopenic Older Adults: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa, H.L.; Moura, S.R.G.; Neves, R.V.P.; Tzanno-Martins, C.; Souza, M.K.; Haro, A.S.; Costa, F.; Silva, J.A.B.; Stone, W.; Honorato, F.S.; et al. Resistance training improves sleep quality, redox balance and inflammatory profile in maintenance hemodialysis patients: A randomized controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.M. Improving nutrition to support healthy ageing: What are the opportunities for intervention? Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2018, 77, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finicelli, M.; Di Salle, A.; Galderisi, U.; Peluso, G. The Mediterranean Diet: An Update of the Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulou, S.K.; Mantzorou, M.; Voulgaridou, G.; Pavlidou, E.; Vadikolias, K.; Antasouras, G.; Vorvolakos, T.; Psara, E.; Vasios, G.K.; Serdari, A.; et al. Nutritional Status Is Associated with Health-Related Quality of Life, Physical Activity, and Sleep Quality: A Cross-Sectional Study in an Elderly Greek Population. Nutrients 2023, 15, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantenbein, K.V.; Kanaka-Gantenbein, C. Mediterranean Diet as an Antioxidant: The Impact on Metabolic Health and Overall Wellbeing. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanini, M.Z.; Guallar-Castillón, P.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F.; Lopez-Garcia, E. Mediterranean Diet and Changes in Sleep Duration and Indicators of Sleep Quality in Older Adults. Sleep 2017, 40, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamalaki, E.; Anastasiou, C.A.; Ntanasi, E.; Tsapanou, A.; Kosmidis, M.H.; Dardiotis, E.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M.; Sakka, P.; Scarmeas, N.; Yannakoulia, M. Associations between the mediterranean diet and sleep in older adults: Results from the hellenic longitudinal investigation of aging and diet study. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2018, 18, 1543–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Total (n = 108) | Experimental (n = 53) | Control (n = 55) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age. Mean (SD). | 70.08 ± 2.63 | 69.73 ± 2.56 | 70.45 ± 2.68 | 0.460 | |
| Sex, n (%) | Male | 33 (30.6) | 15 (45.5) | 18 (54.5) | 0.324 |
| Female | 75 (69.4) | 38 (50.7) | 37 (49.3) | ||
| Occupational status | Retired | 71 (65.7) | 33 (46.5) | 38 (53.5) | 0.541 |
| Worker | 2 (1.9) | 2 (100.0) | 0 (0.00) | ||
| Unemployed | 35 (32.4) | 18 (51.4) | 17 (48.6) | ||
| Maritial status | Single | 29 (26.9) | 17 (58.6) | 12 (41.4) | 0.686 |
| Married | 49 (45.4) | 25 (51.0) | 24 (49.0) | ||
| Divorced/Widowed | 30 (27.8) | 11 (36.7) | 19 (63.3) | ||
| Educational status | Nothing | 23 (21.3) | 14 (60.9) | 9 (39.1) | 0.834 |
| Primary | 32 (29.6) | 17 (53.1) | 15 (46.9) | ||
| Secondary | 31 (28.7) | 13 (41.9) | 18 (58.1) | ||
| University | 22 (20.4) | 9 (40.9) | 13 (59.1) | ||
| Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet_MEDAS | 6.87 ± 1.02 | 6.98 ± 1.01 | 6.76 ± 1.02 | 0.728 | |
| Anxiety_HADS | 7.87 ± 3.31 | 7.49 ± 3.13 | 8.24 ± 3.46 | 0.666 | |
| Depression_HADS | 9.01 ± 2.55 | 9.25 ± 2.67 | 8.78 ± 2.42 | 0.437 | |
| Perceived stress (PSS) | 24.53 ± 13.86 | 23.60 ± 13.72 | 25.44 ± 14.06 | 0.751 | |
| Subjective quality_PSQI | 1.72 ± 0.92 | 1.93 ± 0.88 | 1.51 ± 0.92 | 0.197 | |
| Latency_PSQI | 1.30 ± 0.92 | 1.18 ± 0.89 | 1.42 ± 0.93 | 0.640 | |
| Duration_PSQI | 1.85 ± 0.95 | 2.07 ± 0.86 | 1.64 ± 0.10 | 0.083 | |
| Efficiency_PSQI | 1.53 ± 1.04 | 1.58 ± 1.051 | 1.47 ± 1.040 | 0.941 | |
| Discomfort_PSQI | 2.27 ± 0.69 | 2.35 ± 1.551 | 2.19 ± 0.798 | 0.057 | |
| Medication use_PSQI | 1.75 ± 0.86 | 1.67 ± 0.764 | 1.83 ± 0.950 | 0.076 | |
| Dysfunctions during the day_PSQI | 0.71 ± 0.73 | 0.72 ± 0.701 | 0.69 ± 0.771 | 0.488 | |
| Total score_PSQI | 10.41 ± 2.95 | 10.77 ± 2.982 | 10.07 ± 2.90 | 0.747 |
| Pre-Intervention | Post-Intervention | Group | Time | Group × Time | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EG | CG | EG | CG | F (1.06) | p Value | η2 | F (1.106) | p Value | η2 | F (1.106) | p Value | η2 | |
| Adherence to the Mediterranean diet_MEDAS | 6.98 ± 1.01 | 6.76 ± 1.02 | 9.16 ± 1.29 | 6.41 ± 1.23 | 72.710 | 0.000 | 0.389 | 107.084 | 0.000 | 0.484 | 55.325 | 0.000 | 0.327 |
| Anxiety_HADS | 7.49 ± 3.13 | 8.24 ± 3.46 | 6.26 ± 3.25 | 8.95 ± 3.60 | 11.842 | 0.001 | 0.094 | 0.466 | 0.496 | 0.004 | 6.580 | 0.012 | 0.055 |
| Depression_HADS | 7.81 ± 2.50 | 9.02 ± 2.45 | 9.25 ± 2.67 | 8.78 ± 2.42 | 0.797 | 0.374 | 0.007 | 8.213 | 0.005 | 0.067 | 15.985 | 0.000 | 0.123 |
| Perceived stress (PSS) | 23.60 ± 13.72 | 25.44 ± 14.06 | 21.47 ± 13.83 | 26.93 ± 14.19 | 2.059 | 0.154 | 0.018 | 0.417 | 0.520 | 0.004 | 13.668 | 0.000 | 0.107 |
| Subjective quality_PSQI | 1.93 ± 0.88 | 1.51 ± 0.92 | 1.14 ± 0.67 | 1.58 ± 0.97 | 0.002 | 0.962 | 0.000 | 43.908 | 0.000 | 0.278 | 61.958 | 0.000 | 0.352 |
| Latency_PSQI | 1.18 ± 0.89 | 1.42 ± 0.93 | 1.33 ± 1.02 | 1.58 ± 0.99 | 2.178 | 0.143 | 0.019 | 5.986 | 0.016 | 0.050 | 0.002 | 0.966 | 0.000 |
| Duration_PSQI | 2.07 ± 0.86 | 1.64 ± 0.10 | 1.12 ± 0.83 | 1.64 ± 1.10 | 0.087 | 0.769 | 0.001 | 37.844 | 0.000 | 0.289 | 43.088 | 0.000 | 0.274 |
| Efficiency_PSQI | 1.58 ± 1.05 | 1.47 ± 1.04 | 1.53 ± 0.97 | 1.54 ± 1.12 | 0.058 | 0.811 | 0.001 | 0.014 | 0.905 | 0.000 | 0.912 | 0.342 | 0.008 |
| Discomfort_PSQI | 2.35 ± 0.55 | 2.19 ± 0.78 | 1.16 ± 0.68 | 1.95 ± 0.96 | 6.865 | 0.010 | 0.0.57 | 89.484 | 0.000 | 0.440 | 39.953 | 0.000 | 0.260 |
| Medication use_PSQI | 1.67 ± 0.76 | 1.83 ± 0.95 | 1.95 ± 0.88 | 1.56 ± 1.06 | 0.666 | 0.416 | 0.006 | 0.002 | 0.963 | 0.000 | 7.447 | 0.007 | 0.061 |
| Dysfunctions during the day_PSQI | 0.72 ± 0.70 | 0.69 ± 0.77 | 0.65 ± 0.69 | 0.46 ± 0.54 | 0.901 | 0.344 | 0.008 | 7.734 | 0.006 | 0.064 | 2.285 | 0.133 | 0.020 |
| Total score_PSQI | 10.77 ± 2.98 | 10.07 ± 2.90 | 8.88 ± 2.53 | 10.31 ± 3.26 | 0.507 | 0.478 | 0.004 | 17.942 | 0.000 | 0.136 | 29.687 | 0.000 | 0.207 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carcelén-Fraile, M.d.C.; Déniz-Ramírez, N.d.P.; Sabina-Campos, J.; Aibar-Almazán, A.; Rivas-Campo, Y.; González-Martín, A.M.; Castellote-Caballero, Y. Exercise and Nutrition in the Mental Health of the Older Adult Population: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111741
Carcelén-Fraile MdC, Déniz-Ramírez NdP, Sabina-Campos J, Aibar-Almazán A, Rivas-Campo Y, González-Martín AM, Castellote-Caballero Y. Exercise and Nutrition in the Mental Health of the Older Adult Population: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients. 2024; 16(11):1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111741
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarcelén-Fraile, María del Carmen, Noelia del Pino Déniz-Ramírez, Jessica Sabina-Campos, Agustín Aibar-Almazán, Yulieth Rivas-Campo, Ana María González-Martín, and Yolanda Castellote-Caballero. 2024. "Exercise and Nutrition in the Mental Health of the Older Adult Population: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial" Nutrients 16, no. 11: 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111741
APA StyleCarcelén-Fraile, M. d. C., Déniz-Ramírez, N. d. P., Sabina-Campos, J., Aibar-Almazán, A., Rivas-Campo, Y., González-Martín, A. M., & Castellote-Caballero, Y. (2024). Exercise and Nutrition in the Mental Health of the Older Adult Population: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Nutrients, 16(11), 1741. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111741








