The Association between Diet–Exercise Patterns and Cirrhosis: A Cross-Sectional Study from NHANES 2017-March 2020
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Outcome Indexes
2.3. Assessing Diet and Exercise and Constructing Patterns
2.4. Other Laboratory Tests and Clinical Data
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
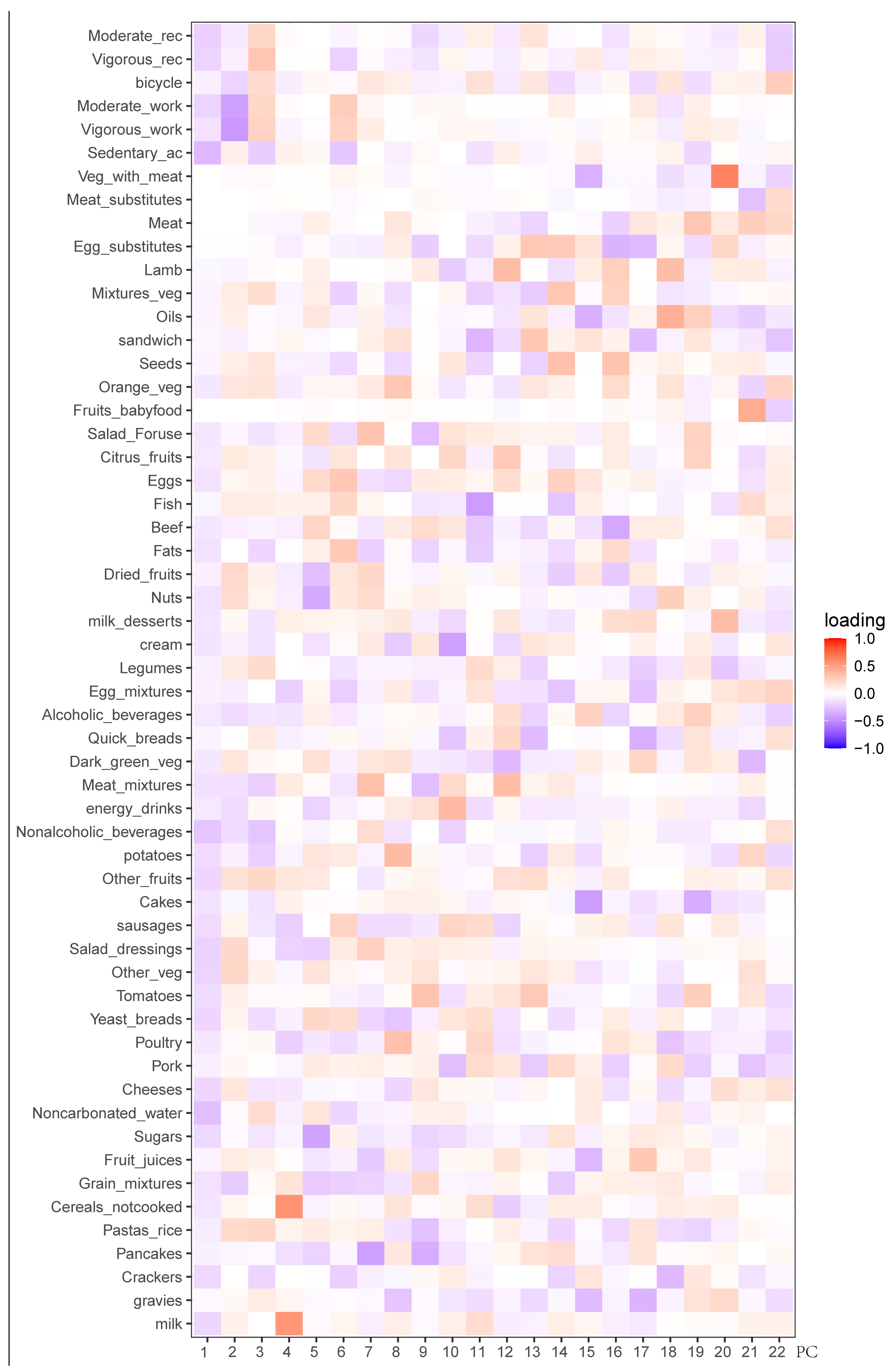
3.2. Clustering of Principal Components
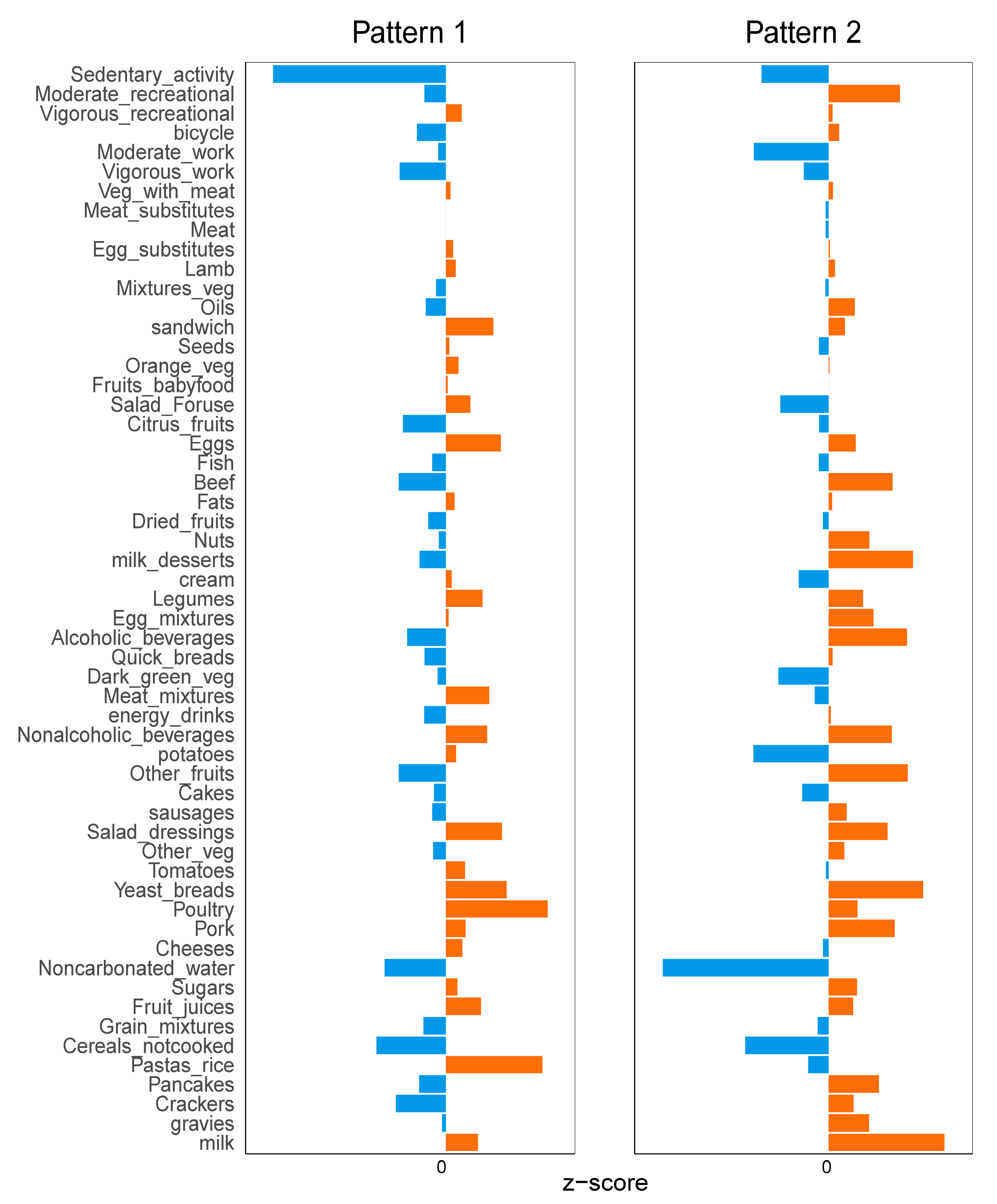
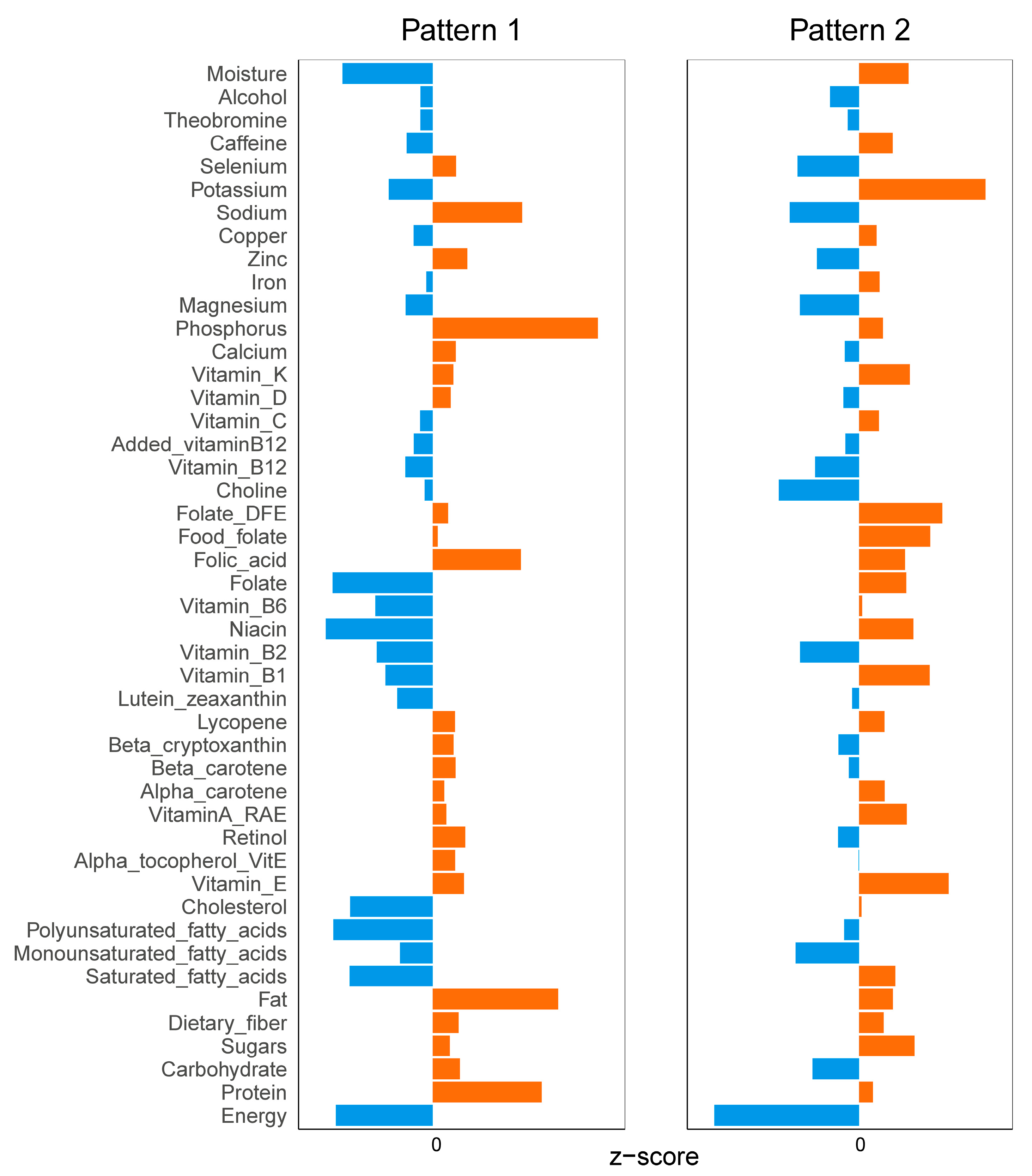
3.3. Diet and Exercise Characteristics between Two Different Patterns
3.4. Population Characteristics between Two Patterns
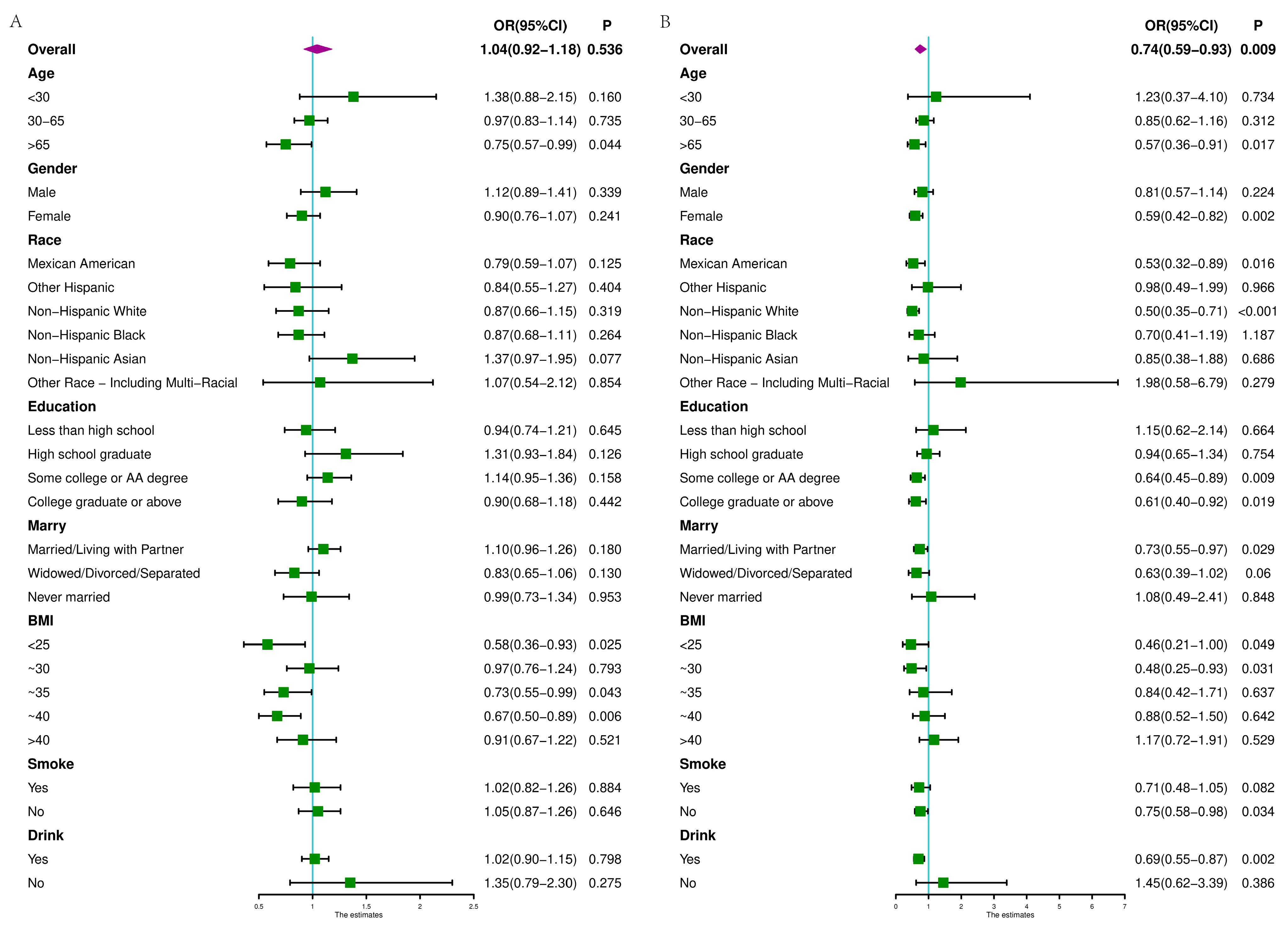
3.5. Risk Factors of CAPs
3.6. Risk Factors of LSMs
3.7. Other Diseases with Different Patterns
3.8. The Medication Effect of the Disease
4. Discussion
4.1. Selection of Pattern Factors
4.2. The Related Factors of Liver Cirrhosis
4.3. Other Discussions about Disease Prevention
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Topan, M.M.; Sporea, I.; Dănilă, M.; Popescu, A.; Ghiuchici, A.M.; Lupușoru, R.; Șirli, R. Association between Dietary Habits and Sarcopenia in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grüngreiff, K.; Reinhold, D.; Wedemeyer, H. The role of zinc in liver cirrhosis. Ann. Hepatol. 2016, 15, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daftari, G.; Tehrani, A.N.; Pashayee-Khamene, F.; Karimi, S.; Ahmadzadeh, S.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Salehpour, A.; Saber-Firoozi, M.; Hatami, B.; Yari, Z. Dietary protein intake and mortality among survivors of liver cirrhosis: A prospective cohort study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2023, 23, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.Q.; Terrault, N.A.; Tacke, F.; Gluud, L.L.; Arrese, M.; Bugianesi, E.; Loomba, R. Global epidemiology of cirrhosis—Aetiology, trends and predictions. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.K.; Fung, J.; Chu, N.H.S.; Tan, V.P.Y. Dietary Interventions in Liver Cirrhosis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 52, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, H.; Bando, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Nishiguchi, S.; Koga, M. Liver fibrosis markers of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 7427–7435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.; Baumgartner, K.; Bositis, C. Cirrhosis: Diagnosis and Management. Am. Fam. Physician 2019, 100, 759–770. [Google Scholar]
- Schuppan, D.; Surabattula, R.; Wang, X.Y. Determinants of fibrosis progression and regression in NASH. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Allen, A.M.; Wang, Z.; Prokop, L.J.; Murad, M.H.; Loomba, R. Fibrosis progression in nonalcoholic fatty liver vs nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of paired-biopsy studies. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 643–654.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Duan, Q.; Wu, R.; Harris, E.N.; Su, Q. Pathophysiological communication between hepatocytes and non-parenchymal cells in liver injury from NAFLD to liver fibrosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2021, 176, 113869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajja, K.C.; Mohan, D.P.; Rockey, D.C. Age and ethnicity in cirrhosis. J. Investig. Med. 2014, 62, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toshikuni, N.; Arisawa, T.; Tsutsumi, M. Nutrition and exercise in the management of liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7286–7297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Q.; Mathurin, P.; Cortez-Pinto, H.; Loomba, R. Global epidemiology of alcohol-associated cirrhosis and HCC: Trends, projections and risk factors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farchi, G.; Mariotti, S.; Menotti, A.; Seccareccia, F.; Torsello, S.; Fidanza, F. Diet and 20-y mortality in two rural population groups of middle-aged men in Italy. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1989, 50, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, M.J.Y.; Brownlee, I.; Murphy, A.M. Data-Driven Dietary Patterns, Nutrient Intake and Body Weight Status in a Cross-Section of Singaporean Children Aged 6–12 Years. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, P.; Gao, S.; Xiao, F.; He, M.; Fang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, Q. Association of macronutrients intake distribution with osteoarthritis risk among adults in NHANES, 2013–2016. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 976619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, K.; Tan, K.; Shen, J.; Gu, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, J.; Kang, L.; Sun, W.; Gao, L.; Gao, Y. Machine learning models including insulin resistance indexes for predicting liver stiffness in United States population: Data from NHANES. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 1008794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, M.; Lim, E.; Davis, J.; Chen, J.J. Dietary Quality Associated with Self-Reported Diabetes, Osteoarthritis, and Rheumatoid Arthritis among Younger and Older US Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study Using NHANES 2011–2016. Nutrients 2021, 13, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilar-Gomez, E.; Nephew, L.D.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Gawrieh, S.; Mladenovic, A.; Pike, F.; Samala, N.; Chalasani, N. High-quality diet, physical activity, and college education are associated with low risk of NAFLD among the US population. Hepatology 2022, 75, 1491–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrin, L.; Fourquet, B.; Hasquenoph, J.M.; Yon, S.; Fournier, C.; Mal, F.; Christidis, C.; Ziol, M.; Poulet, B.; Kazemi, F.; et al. Transient elastography: A new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2003, 29, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsochatzis, E.A.; Gurusamy, K.S.; Ntaoula, S.; Cholongitas, E.; Davidson, B.R.; Burroughs, A.K. Elastography for the diagnosis of severity of fibrosis in chronic liver disease: A meta-analysis of diagnostic accuracy. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasso, M.; Beaugrand, M.; de Ledinghen, V.; Douvin, C.; Marcellin, P.; Poupon, R.; Sandrin, L.; Miette, V. Controlled attenuation parameter (CAP): A novel VCTE™ guided ultrasonic attenuation measurement for the evaluation of hepatic steatosis: Preliminary study and validation in a cohort of patients with chronic liver disease from various causes. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 1825–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eddowes, P.J.; Sasso, M.; Allison, M.; Tsochatzis, E.; Anstee, Q.M.; Sheridan, D.; Guha, I.N.; Cobbold, J.F.; Deeks, J.J.; Paradis, V.; et al. Accuracy of FibroScan Controlled Attenuation Parameter and Liver Stiffness Measurement in Assessing Steatosis and Fibrosis in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 1717–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heredia, N.I.; Zhang, X.; Balakrishnan, M.; Daniel, C.R.; Hwang, J.P.; McNeill, L.H.; Thrift, A.P. Physical activity and diet quality in relation to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study in a representative sample of U.S. adults using NHANES 2017–2018. Prev. Med. 2022, 154, 106903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardullo, S.; Perseghin, G. Prevalence of NAFLD, MAFLD and associated advanced fibrosis in the contemporary United States population. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 1290–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.W.; Chen, C.; Kong, H.Y.; Huang, J.Q. Prevalence of Cirrhosis/Advanced Fibrosis Among HBsAg-Negative and HBcAb-Positive US Adults: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Infect. Dis. Ther. 2022, 11, 1901–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udompap, P.; Mannalithara, A.; Heo, N.Y.; Kim, D.; Kim, W.R. Increasing prevalence of cirrhosis among U.S. adults aware or unaware of their chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1027–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabbany, M.N.; Conjeevaram Selvakumar, P.K.; Watt, K.; Lopez, R.; Akras, Z.; Zein, N.; Carey, W.; Alkhouri, N. Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis-Associated Cirrhosis in the United States: An Analysis of National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 112, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazidi, M.; Pennathur, S.; Afshinnia, F. Link of dietary patterns with metabolic syndrome: Analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Nutr. Diabetes 2017, 7, e255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, Z.; Shi, Z. Dietary Patterns and Circadian Syndrome among Adults Attending NHANES 2005–2016. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.S.; Fulgoni, V.L., 3rd; Van Elswyk, M.E.; McNeill, S.H. Trends in Beef Intake in the United States: Analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2001–2018. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gherasim, A.; Arhire, L.I.; Niță, O.; Popa, A.D.; Graur, M.; Mihalache, L. The relationship between lifestyle components and dietary patterns. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maugeri, A.; Barchitta, M.; Favara, G.; La Mastra, C.; La Rosa, M.C.; Magnano San Lio, R.; Agodi, A. The Application of Clustering on Principal Components for Nutritional Epidemiology: A Workflow to Derive Dietary Patterns. Nutrients 2022, 15, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barchitta, M.; Magnano San Lio, R.; La Rosa, M.C.; La Mastra, C.; Favara, G.; Ferrante, G.; Galvani, F.; Pappalardo, E.; Ettore, C.; Ettore, G.; et al. The Effect of Maternal Dietary Patterns on Birth Weight for Gestational Age: Findings from the MAMI-MED Cohort. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaur, M.; Nigra, A.E.; Sanchez, T.R.; Navas-Acien, A.; Lazo, M.; Wu, H.C. Association of blood manganese, selenium with steatosis, fibrosis in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2017–2018. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, R.; Tang, X.Y.; Yang, C.; Gao, W.H.; Gao, S.J.; Xiang, H.J.; Yang, L. Marijuana use is inversely associated with liver steatosis detected by transient elastography in the general United States population in NHANES 2017–2018: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0284859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qarmiche, N.; El Kinany, K.; Otmani, N.; El Rhazi, K.; Chaoui, N.E.H. Cluster analysis of dietary patterns associated with colorectal cancer derived from a Moroccan case-control study. BMJ Health Care Inf. 2023, 30, e100710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrao, G.; Zambon, A.; Bagnardi, V.; Aricò, S.; Loguercio, C.; D’Amicis, A. Nutrient intakes, nutritional patterns and the risk of liver cirrhosis: An explorative case-control study. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2004, 19, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrao, G.; Ferrari, P.A.; Galatola, G. Exploring the role of diet in modifying the effect of known disease determinants: Application to risk factors of liver cirrhosis. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1995, 142, 1136–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ge, X.; Lu, J.; Xu, X.; Gao, J.; Wang, Q.; Song, C.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, C. Diet and Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Cirrhosis, and Liver Cancer: A Large Prospective Cohort Study in UK Biobank. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, H.E.; Takefala, T.G.; Kelly, J.T.; Keating, S.E.; Coombes, J.S.; Macdonald, G.A.; Hickman, I.J.; Mayr, H.L. The Effect of Diet and Exercise Interventions on Body Composition in Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, F.R.; Berzigotti, A.; Lord, J.M.; Lai, J.C.; Armstrong, M.J. Review article: Impact of exercise on physical frailty in patients with chronic liver disease. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 50, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, F.S. Relationship between dietary beef, fat, and pork and alcoholic cirrhosis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2009, 6, 2417–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.K.; Wilechansky, R.M.; Challa, P.K.; Zhang, X.; Giovannucci, E.; Stampfer, M.; Chan, A.T.; Simon, T.G. The empirical dietary inflammatory pattern score and the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and cirrhosis. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e0263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.K.; Dong, T.S.; Agopian, V.; Pisegna, J.R.; Durazo, F.A.; Enayati, P.; Sundaram, V.; Benhammou, J.N.; Noureddin, M.; Choi, G.; et al. Dietary Protein, Fiber and Coffee Are Associated with Small Intestine Microbiome Composition and Diversity in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kong, L.; Ye, C.; Dou, C.; Zheng, J.; Xu, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, Z.; Lu, J.; et al. Causal impacts of educational attainment on chronic liver diseases and the mediating pathways: Mendelian randomization study. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 2379–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroffolini, T.; Sagnelli, E.; Sagnelli, C.; Morisco, F.; Babudieri, S.; Furlan, C.; Pirisi, M.; Russello, M.; Smedile, A.; Pisaturo, M.; et al. The association between education level and chronic liver disease of any etiology. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 75, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juran, B.D.; Lazaridis, K.N. Environmental factors in primary biliary cirrhosis. Semin. Liver Dis. 2014, 34, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagström, H. Alcohol, smoking and the liver disease patient. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2017, 31, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam, M.K.; Flensborg-Madsen, T.; Eliasen, M.; Becker, U.; Tolstrup, J.S. Smoking and risk of liver cirrhosis: A population-based cohort study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzaro, D.; Becchetti, C.; Trapani, S.; Lavezzo, B.; Zanetto, A.; D’Arcangelo, F.; Merli, M.; Lapenna, L.; Invernizzi, F.; Taliani, G.; et al. Influence of sex in alcohol-related liver disease: Pre-clinical and clinical settings. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2023, 11, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, J.B.; Sundaram, V.; Lai, J.C. Gender Differences Among Patients Hospitalized With Cirrhosis in the United States. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2020, 54, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| CAP | LSM | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Degree of Steatosis | Grading Criteria (dB/m) | Degree of Fibrosis | Grading Criteria (kPa) |
| Absence of steatosis (S0) | <274 | No fibrosis | <8.2 |
| Mild steatosis (S1) | 274~289 | Significant fibrosis (F2) | 8.2~9.6 |
| Moderate steatosis (S2) | 290~301 | Severe fibrosis (F3) | 9.7~13.5 |
| Severe steatosis (S3) | ≥302 | Cirrhosis (F4) | ≥13.6 |
| Principal Component | Eigenvalue | % Variance | % Cumulative |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.940680 | 0.067254 | 0.067254 |
| 2 | 1.328780 | 0.031530 | 0.098784 |
| 3 | 1.237584 | 0.027350 | 0.126134 |
| 4 | 1.218778 | 0.026525 | 0.152659 |
| Characteristics | Pattern 1 (%) | Pattern 2 (%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.002 | ||
| <30 | 3,241,828 (14.76) | 35,007,500 (21.22) | |
| 30–65 | 13,536,842 (61.56) | 100,052,197 (60.63) | |
| >65 | 5,179,936 (23.59) | 29,948,397 (18.15) | |
| Gender | <0.001 | ||
| Male | 9,193,537 (41.87) | 83,202,734 (50.42) | |
| Female | 12,765,069 (58.13) | 81,805,359 (49.58) | |
| Race | <0.001 | ||
| Mexican American | 2,495,952 (11.37) | 12,688,146 (7.69) | |
| Other Hispanic | 2,499,944 (11.38) | 11,002,573 (6.67) | |
| Non-Hispanic White | 4,143,986 (18.87) | 115,321,210 (69.89) | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 8,385,491 (38.19) | 11,980,295 (7.26) | |
| Non-Hispanic Asian | 3,344,518 (15.23) | 7,116,489 (4.31) | |
| Other Race—Including Multi-Racial | 1,088,714 (4.96) | 6,899,379 (4.18) | |
| Education | <0.001 | ||
| Less than high school | 4,871,607 (22.19) | 13,064,312 (7.92) | |
| High school graduate | 5,370,959 (24.46) | 45,301,154 (27.45) | |
| Some college or AA degree | 7,028,360 (32.01) | 51,257,818 (31.06) | |
| College graduate or above | 4,687,680 (21.35) | 55,384,809 (33.56) | |
| Marital Status | <0.001 | ||
| Married/Living with partner | 11,905,527 (54.22) | 105,625,962 (64.01) | |
| Widowed/divorced/separated | 5,605,759 (25.53) | 27,685,874 (16.78) | |
| Never married | 4,447,320 (20.25) | 31,696,257 (19.21) | |
| BMI | 0.093 | ||
| <25 | 6,261,554 (28.52) | 43,502,609 (26.36) | |
| ~30 | 6,617,477 (30.14) | 53,427,479 (32.38) | |
| ~35 | 4,559,972 (20.77) | 37,975,128 (23.01) | |
| ~40 | 2,562,512 (11.67) | 17,343,029 (10.51) | |
| >40 | 1,957,091 (8.91) | 12,759,848 (7.73) | |
| Smoke | 0.036 | ||
| Yes | 8,577,129 (39.06) | 70,098,867 (42.48) | |
| No | 13,381,476 (60.94) | 94,909,226 (57.52) | |
| Drink | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 19,474,976 (88.69) | 155,278,680 (94.10) | |
| No | 2,483,630 (11.31) | 9,729,413 (5.90) |
| Characteristics | Simple OR (95%CI) | Stepwise (Part) OR (95%CI) | Stepwise (All) OR (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster characteristic | |||
| Prudent pattern (reference = dangerous pattern) | 1.04 (0.92–1.18) | 1.04 (0.89–1.21) | - |
| Sociodemographic characteristics | |||
| Age (continuous) | 1.02 (1.01–1.02) | 1.02 (1.02–1.03) | 1.02 (1.01–1.02) |
| Gender (reference = male) | 0.62 (0.51–0.93) | 0.47 (0.40–0.57) | 0.52 (0.44–0.62) |
| Race (reference = Mexican American) | |||
| Other Hispanic | 0.60 (0.47–0.76) | 0.57 (0.43–0.76) | 0.59 (0.45–0.76) |
| Non-Hispanic White | 0.60 (0.46–0.71) | 0.47 (0.37–0.59) | 0.48 (0.37–0.61) |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 0.39 (0.34–0.44) | 0.25 (0.20–0.31) | 0.23 (0.19–0.29) |
| Non-Hispanic Asian | 0.49 (0.40–0.61) | 0.99 (0.71–1.38) | 0.91 (0.64–1.30) |
| Other Race—Including Multi-Racial | 0.72 (0.50–1.04) | 0.62 (0.39–0.99) | 0.57 (0.34–0.95) |
| Education (reference = college graduate or above) | |||
| Less than high school | 1.44 (1.05–1.96) | 0.99 (0.69–1.43) | - |
| High school graduate | 1.68 (1.32–2.15) | 1.30 (1.00–1.69) | 1.23 (0.97–1.56) |
| Some college or AA degree | 1.53 (1.30–1.79) | 1.27 (1.04–1.57) | 1.19 (0.98–1.45) |
| Marital Status (reference = married/living with Partner) | |||
| Widowed/divorced/separated | 0.78 (0.64–0.95) | 0.72 (0.54–0.96) | 0.68 (0.51–0.92) |
| Never married | 0.54 (0.45–0.56) | 0.66 (0.52–0.85) | 0.67 (0.53–0.85) |
| BMI (continuous) | 1.20 (1.18–1.23) | 1.23 (1.20–1.25) | 1.22 (1.19–1.25) |
| Smoke (reference = no) | 1.21 (1.01–1.32) | 1.12 (0.88–1.43) | 1.13 (0.89–1.45) |
| Drink (reference = no) | 1.17 (0.80–1.73) | 1.62 (1.20–2.17) | 1.61 (1.19–2.67) |
| Relative diseases | |||
| Hypertension (reference = no) | 2.76 (2.35–3.26) | - | 1.49 (1.27–1.75) |
| Diabetes (reference = no) | |||
| Yes | 3.73 (2.86–4.86) | - | 1.78 (1.30–2.43) |
| Borderline | 2.59 (1.51–4.44) | - | 1.23 (0.79–1.93) |
| High cholesterol level (reference = no) | 1.63 (1.36–1.96) | - | 1.05 (0.91–1.21) |
| Weak/failing kidneys (reference = no) | 1.53 (0.93–2.50) | - | 0.96 (0.58–1.61) |
| Anemia (reference = no) | 0.81 (0.56–1.15) | - | 0.68 (0.41–1.12) |
| Cancer (reference = no) | 1.35 (1.02–1.77) | - | 1.09 (0.81–1.47) |
| Hepatitis B (reference = no) | 1.05 (0.52–2.14) | - | 1.69 (1.03–2.78) |
| Hepatitis C (reference = no) | 0.60 (0.27–1.34) | - | 0.85 (0.42–1.71) |
| Characteristics | Simple OR (95%CI) | Stepwise (Part) OR (95%CI) | Stepwise (All) OR (95%CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster characteristic | |||
| Prudent pattern (reference = dangerous pattern) | 0.73 (0.59–0.93) | 0.78 (0.56–0.99) | 0.83 (0.62–1.10) |
| Sociodemographic characteristics | |||
| Age (continuous) | 1.02 (1.01–1.03) | 1.02 (1.01–1.04) | 1.02 (1.00–1.03) |
| Gender (reference = male) | 0.5 (0.35–0.71) | 0.35 (0.24–0.50) | 0.42 (0.28–0.61) |
| Race (reference = Mexican American) | |||
| Other Hispanic | 0.89 (0.53–1.51) | 0.87 (0.52–1.48) | 0.89 (0.52–1.52) |
| Non-Hispanic White | 0.87 (0.58–1.32) | 0.89 (0.51–1.55) | 0.86 (0.49–1.49) |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 0.86 (0.60–1.24) | 0.65 (0.42–1.02) | 0.62 (0.39–1.00) |
| Non-Hispanic Asian | 0.58 (0.32–1.04) | 1.16 (0.60–2.25) | 1.17 (0.58–2.34) |
| Other Race—Including Multi-Racial | 0.95 (0.52–1.73) | 0.87 (0.44–1.73) | 0.87 (0.38–1.98) |
| Education (reference = college graduate or above) | |||
| Less than high school | 2.57 (1.72–3.82) | 1.81 (1.08–3.02) | 1.86 (1.06–3.11) |
| High school graduate | 2.74 (1.74–4.33) | 2.05 (1.17–3.58) | 2.11 (1.18–3.77) |
| Some college or AA degree | 1.74 (1.18–2.57) | 1.32 (0.82–2.11) | 1.45 (0.88–2.41) |
| Marital Status (reference = married/living with partner) | |||
| Widowed/divorced/separated | 1.02 (0.73–1.43) | 0.98 (0.69–1.39) | 0.95 (0.65–1.40) |
| Never married | 0.71 (0.48–1.06) | 0.88 (0.57–1.36) | 0.85 (0.54–1.34) |
| BMI (continuous) | 1.13 (1.11–1.15) | 1.15 (1.12–1.17) | 1.14 (1.12–1.17) |
| Smoke (reference = no) | 1.45 (1.08–10.64) | - | 1.10 (0.78–1.55) |
| Drink (reference = no) | 1.20 (0.75–1.92) | - | 1.32 (0.69–2.51) |
| Relative diseases | |||
| Hypertension (reference = no) | 2.79 (2.17–3.59) | - | 1.37 (1.00–1.86) |
| Diabetes (reference = no) | |||
| Yes | 5.06 (3.68–6.96) | - | 2.58 (1.81–3.68) |
| Borderline | 4.11 (1.76–9.57) | - | 2.00 (0.93–4.28) |
| High cholesterol level (reference = no) | 1.32 (1.05–1.66) | - | 1.42 (1.08–1.87) |
| Weak/failing kidneys (reference = no) | 1.66 (0.91–3.04) | - | 1.02 (0.51–2.02) |
| Anemia (reference = no) | 0.81 (0.37–1.76) | - | 0.68 (0.26–1.74) |
| Cancer (reference = no) | 1.44 (0.88–2.35) | - | 1.13 (0.75–1.69) |
| Hepatitis B (reference = no) | 1.20 (0.53–2.73) | - | 1.29 (0.41–4.04) |
| Hepatitis C (reference = no) | 3.61 (1.77–7.33) | - | 4.52 (2.19–9.36) |
| Items | Prudent Pattern | Dangerous Pattern | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| ALT | 21.490406 | 0.479526 | 23.106974 | 0.335490 | <0.001 |
| AST | 21.804752 | 0.413814 | 21.897648 | 0.285381 | 0.016 |
| GGT | 34.597871 | 1.189280 | 28.551904 | 0.634683 | 0.001 |
| ALP | 79.184514 | 0.873206 | 74.194045 | 0.595263 | <0.001 |
| platelets | 246.565500 | 2.190417 | 245.831812 | 2.075096 | 0.917 |
| FIB4 score | 0.552965 | 0.010495 | 0.459796 | 0.010593 | <0.001 |
| APRI score | 0.249157 | 0.006719 | 0.242441 | 0.004654 | 0.060 |
| Diseases | Prudent Pattern | Dangerous Pattern | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 8,376,303.32 | 49,404,887.08 | |
| No | 12,020,102.53 | 108,040,459.90 | |
| Unclear | 13,681.83 | 201,556.01 | |
| Diabetes | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 3,678,424.72 | 15,251,204.94 | |
| No | 16,044,882.26 | 138,976,678.90 | |
| Borderline | 686,780.70 | 3,373,390.36 | |
| Unclear | 0.00 | 45,628.83 | |
| High cholesterol level | 0.036 | ||
| Yes | 7,466,640.30 | 55,067,231.70 | |
| No | 12,799,540.30 | 102,234,088.60 | |
| Unclear | 143,907.10 | 345,582.70 | |
| Weak/failing kidneys | 0.066 | ||
| Yes | 845,002.44 | 4,406,153.99 | |
| No | 19,526,184.57 | 153,127,240.50 | |
| Unclear | 38,900.67 | 113,508.57 | |
| Anemia | <0.001 | ||
| Yes | 1,253,862.56 | 5,136,849.99 | |
| No | 19,117,978.38 | 152,449,807.40 | |
| Unclear | 38,246.74 | 60,245.60 | |
| Cancer | 0.443 | ||
| Yes | 1,966,659.00 | 16,701,760.00 | |
| No | 18,434,680.00 | 140,919,600.00 | |
| Unclear | 8752.74 | 25,543.26 | |
| Hepatitis B | 0.600 | ||
| Yes | 282,751.01 | 1,777,892.48 | |
| No | 20,056,424.13 | 155,561,266.90 | |
| Unclear | 70,912.55 | 307,743.62 | |
| Hepatitis C | 0.417 | ||
| Yes | 364,224.26 | 2,253,468.24 | |
| No | 19,976,243.68 | 155,098,150.60 | |
| Unclear | 69,619.74 | 295,284.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, J.; Han, X.; Chen, L.; Mai, L.; Su, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Q. The Association between Diet–Exercise Patterns and Cirrhosis: A Cross-Sectional Study from NHANES 2017-March 2020. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111617
Liu J, Han X, Chen L, Mai L, Su X, Dong Y, Wang B, Zhang Q. The Association between Diet–Exercise Patterns and Cirrhosis: A Cross-Sectional Study from NHANES 2017-March 2020. Nutrients. 2024; 16(11):1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111617
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Jialu, Xinhao Han, Lu Chen, Liudan Mai, Xiaoman Su, Yanlin Dong, Baolong Wang, and Qiuju Zhang. 2024. "The Association between Diet–Exercise Patterns and Cirrhosis: A Cross-Sectional Study from NHANES 2017-March 2020" Nutrients 16, no. 11: 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111617
APA StyleLiu, J., Han, X., Chen, L., Mai, L., Su, X., Dong, Y., Wang, B., & Zhang, Q. (2024). The Association between Diet–Exercise Patterns and Cirrhosis: A Cross-Sectional Study from NHANES 2017-March 2020. Nutrients, 16(11), 1617. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16111617





