Lipidomic Assessment of the Inhibitory Effect of Standardized Water Extract of Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser. Leaves during Adipogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Water Extract of Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser. Leaves (WHS)
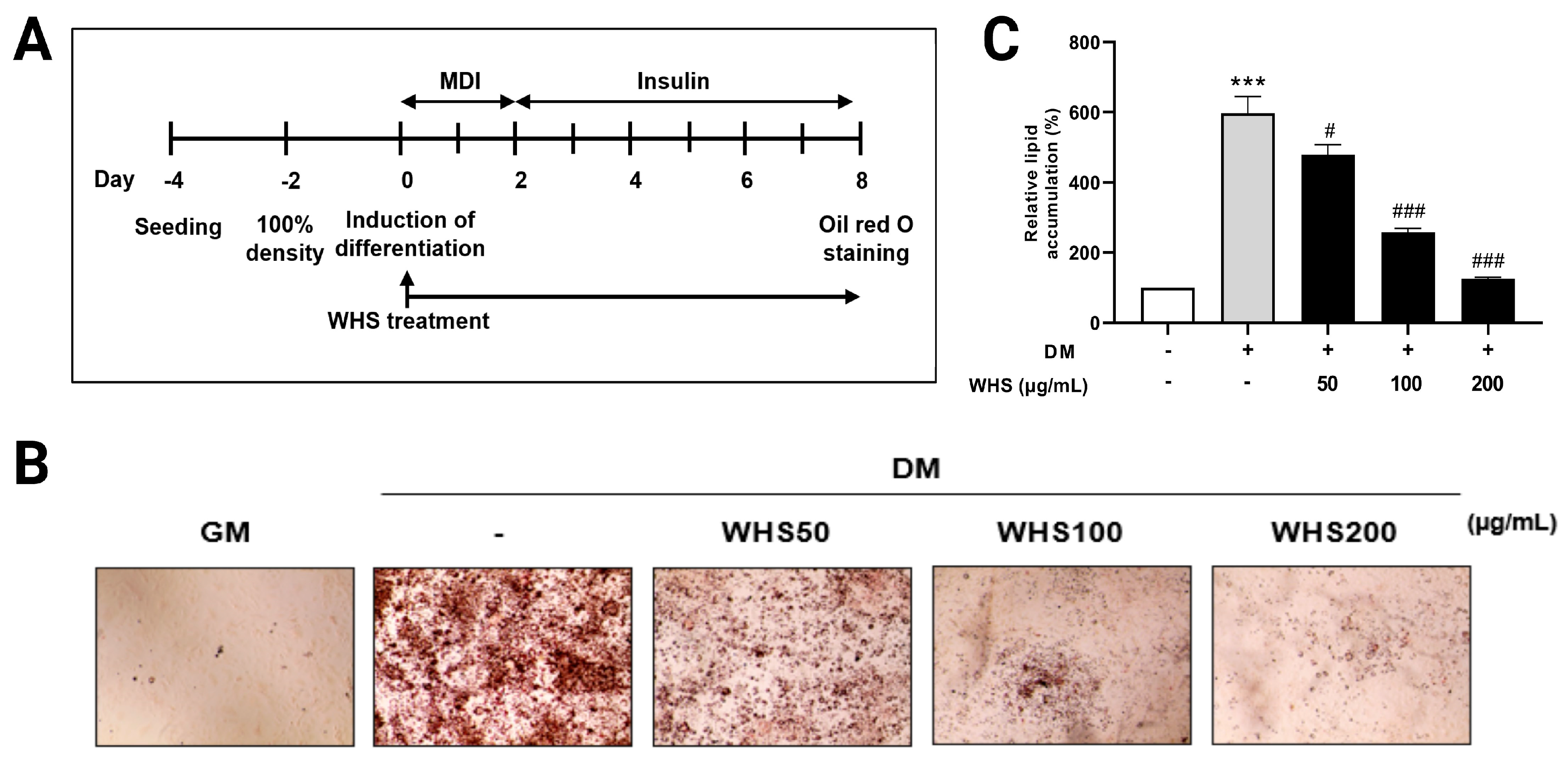
2.2. 3T3-L1 Cell Culture and Differentiation
2.3. Oil-Red O Staining
2.4. Lipid Extraction
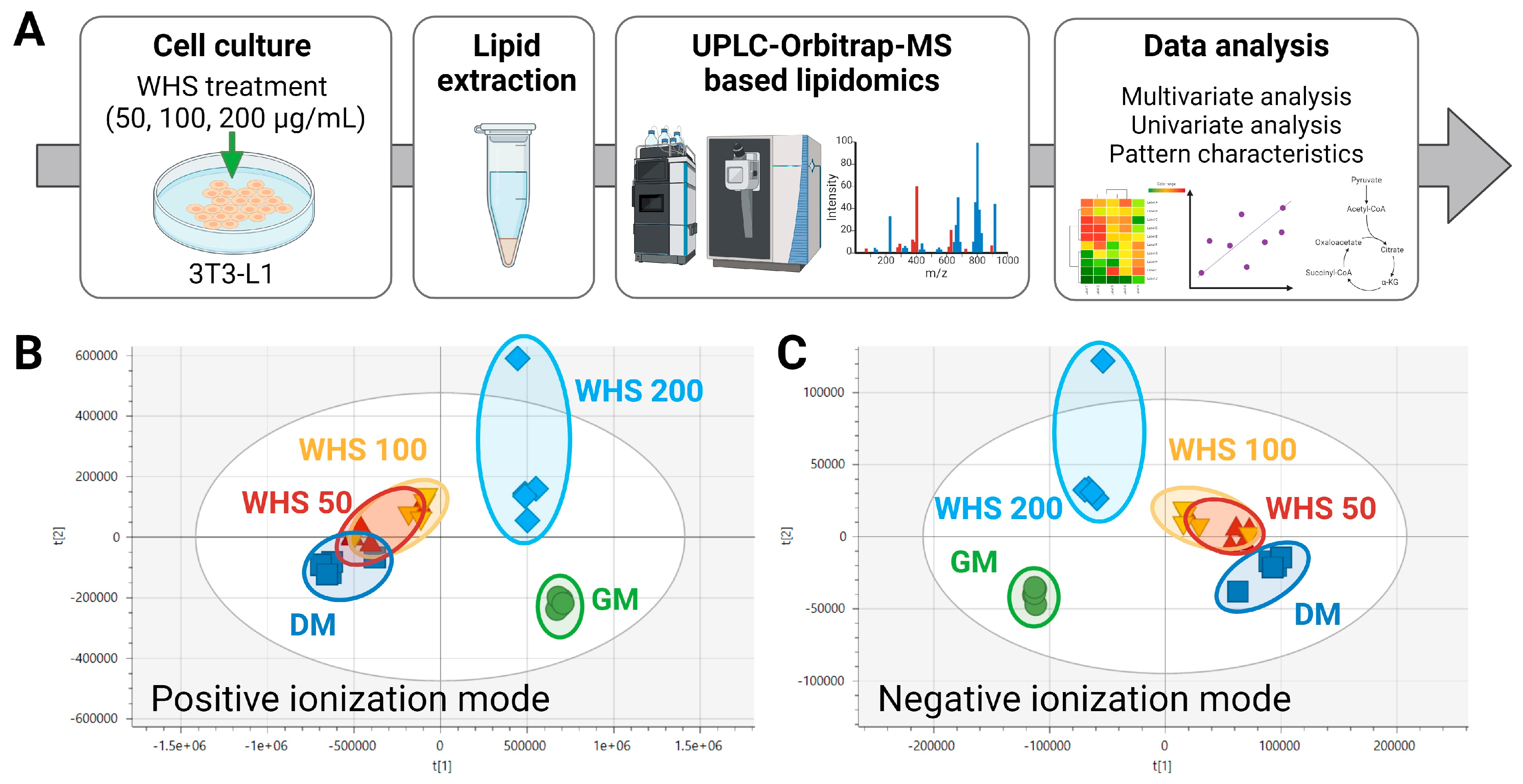
2.5. Lipidomic Analysis and Data Processing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. WHS Inhibits the Lipid Accumulation during Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes
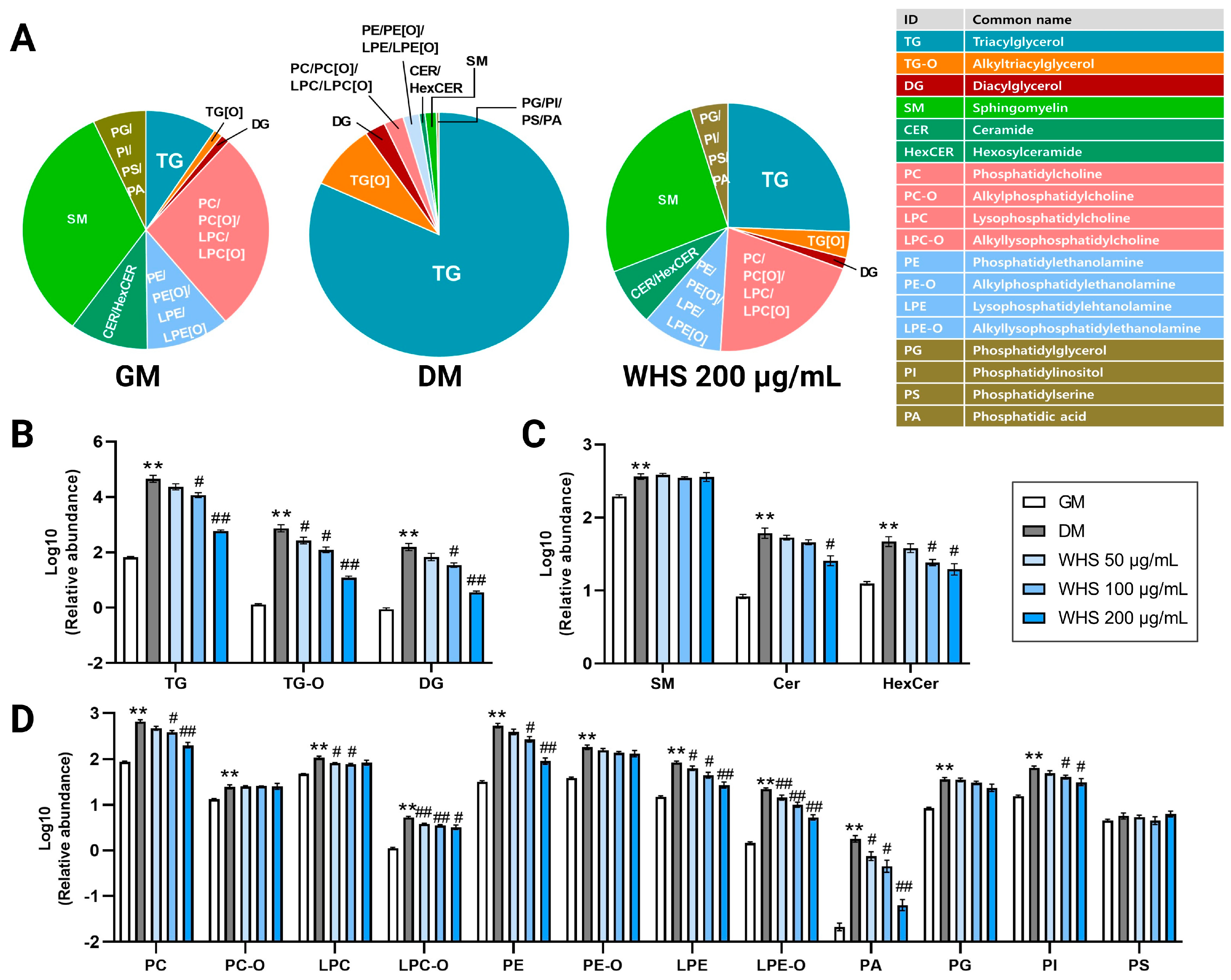
3.2. Difference in Lipid Profile of Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocytes Cell and WHS Treatment
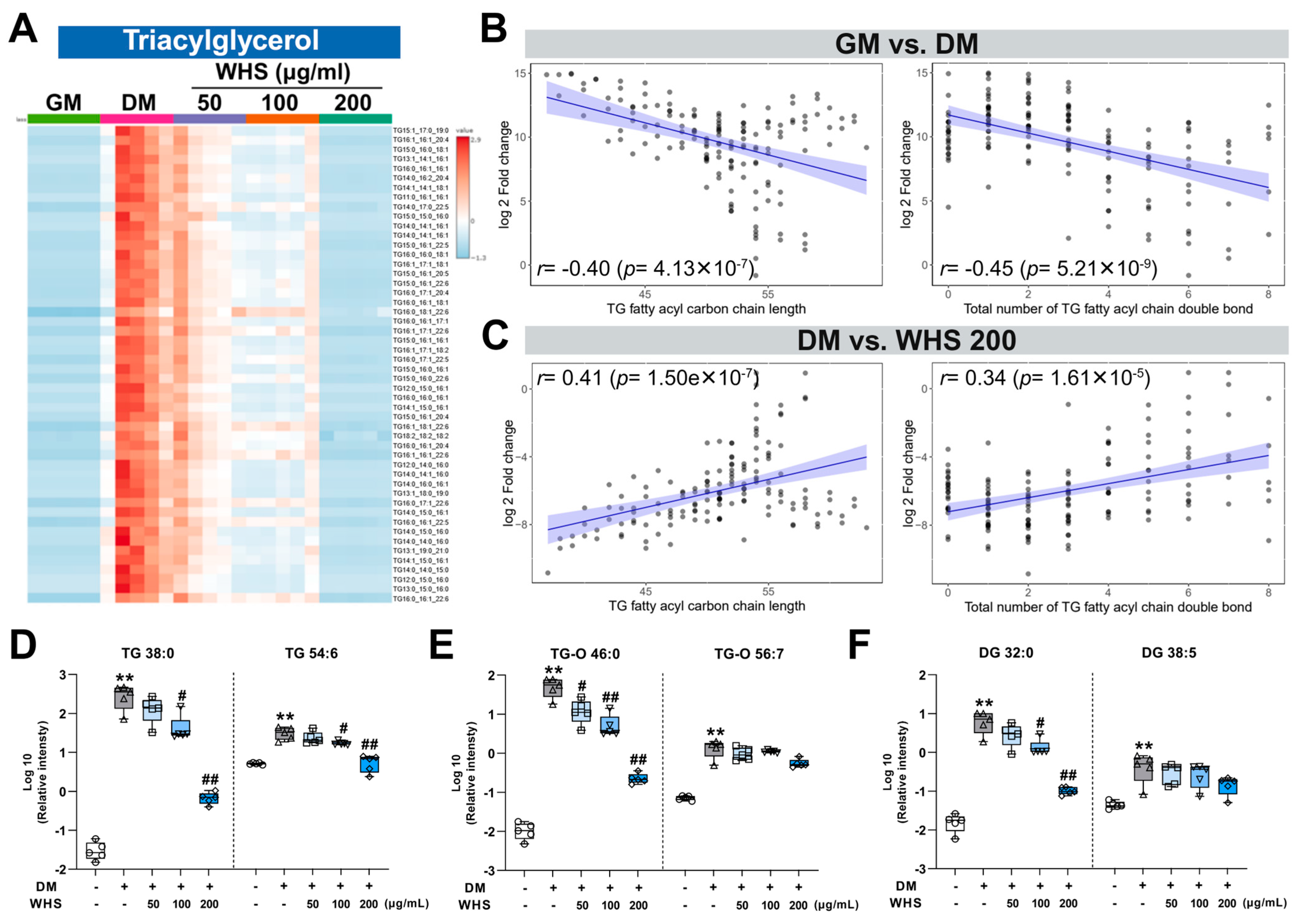
3.3. Effect of WHS on Glycerolipid Metabolism during Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocyte
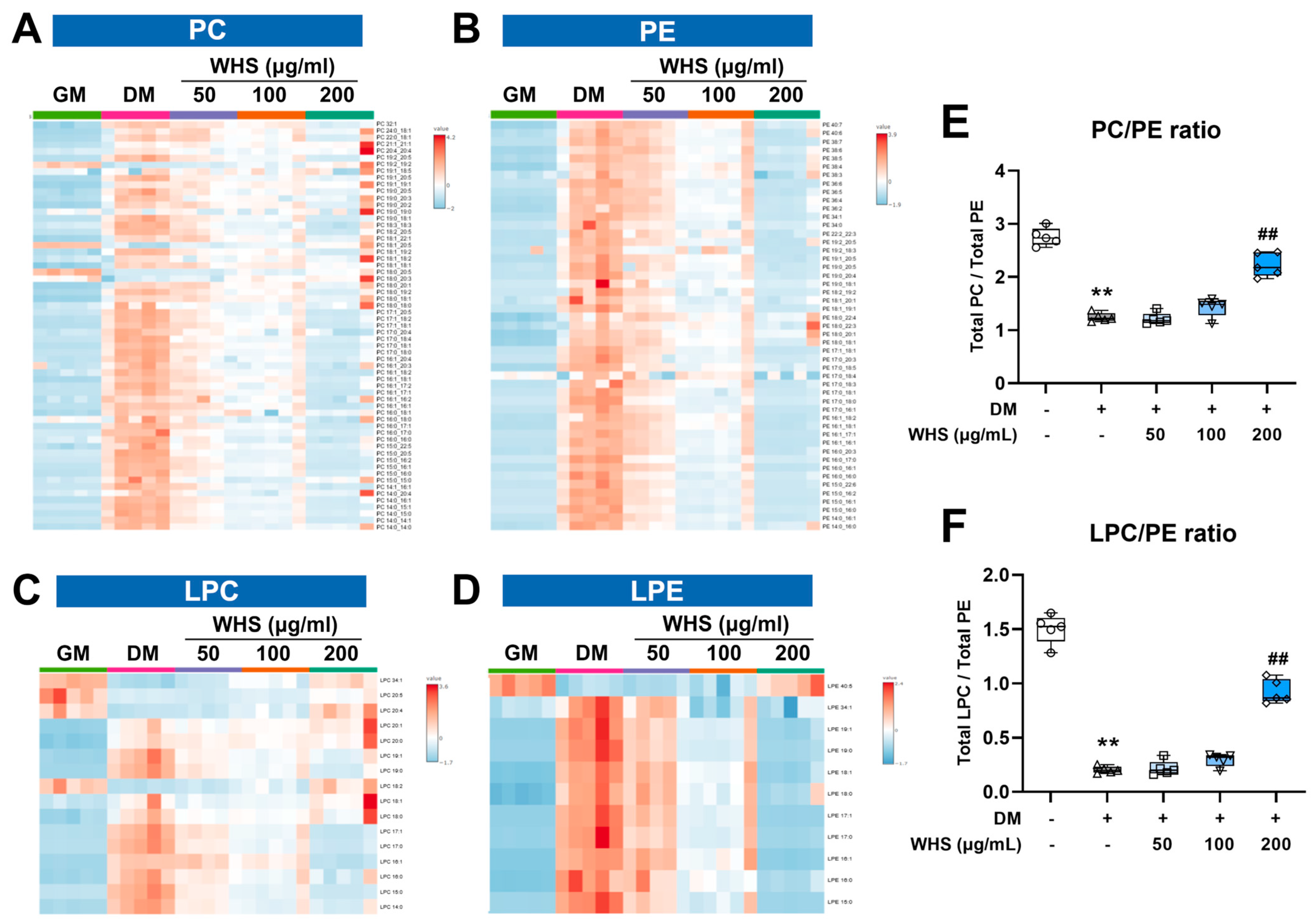
3.4. Effect of WHS on Glycerophospholipid Metabolism during Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocyte
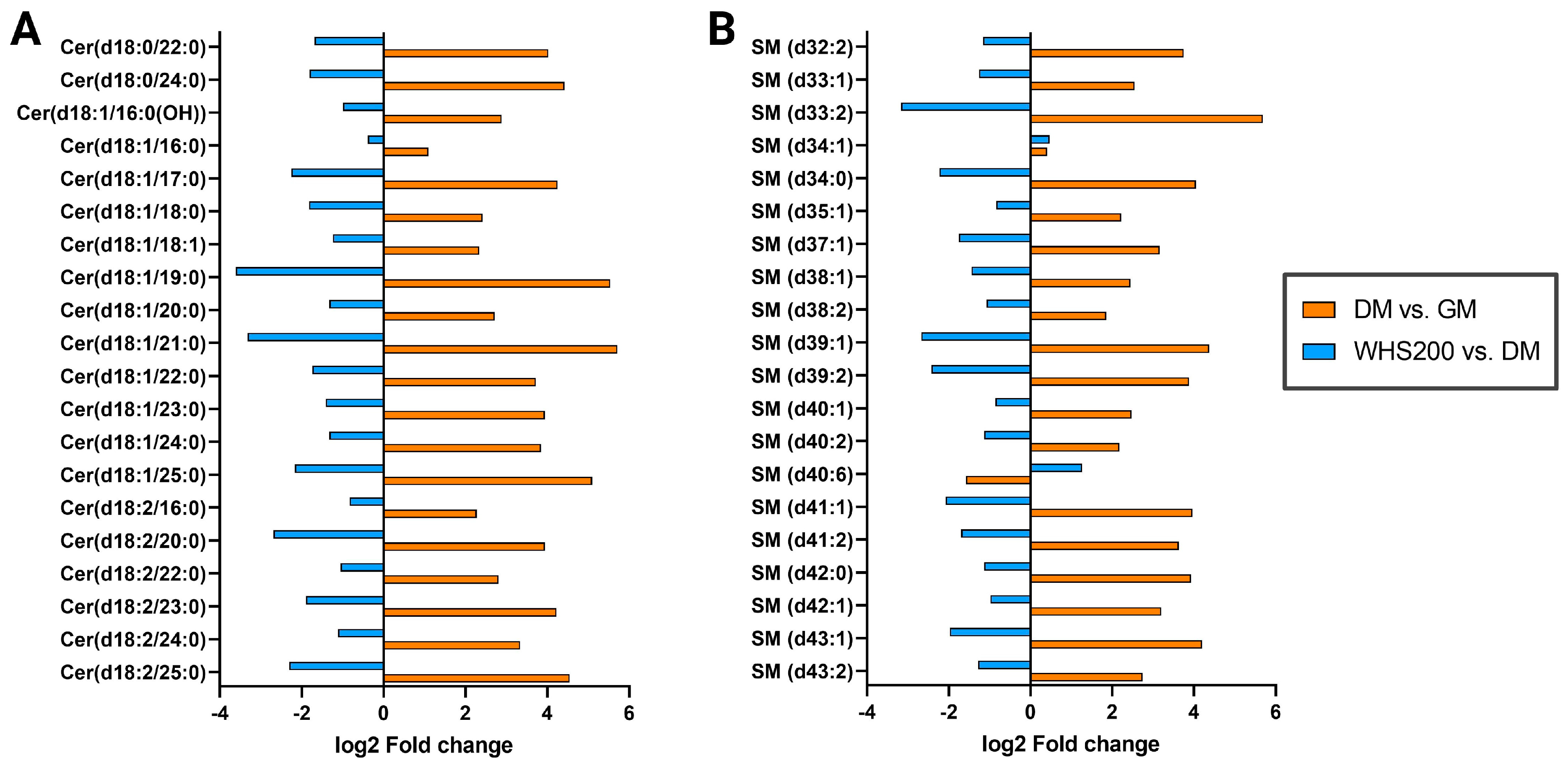
3.5. Effect of WHS on Sphingolipid Metabolism during Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Preadipocyte
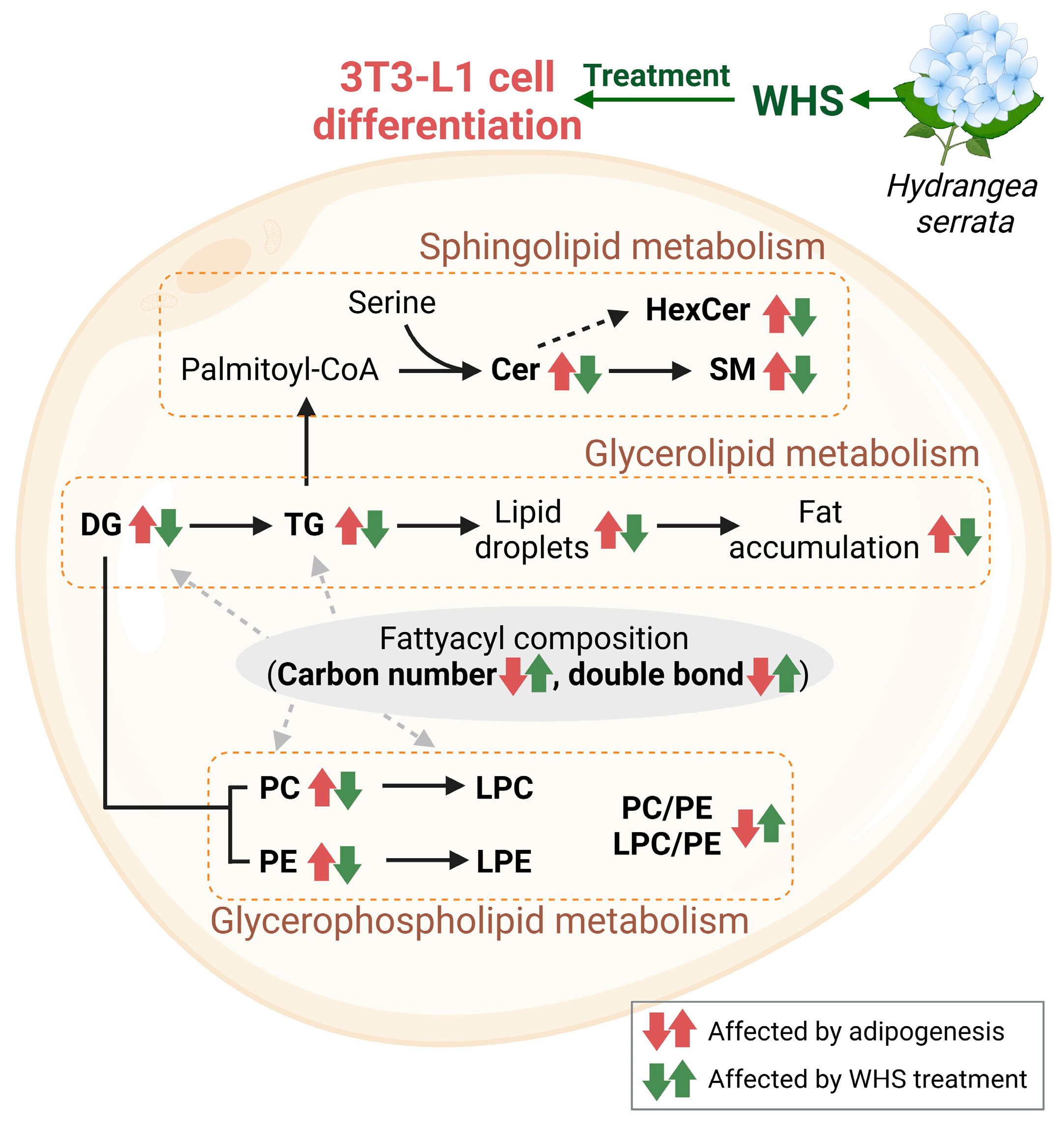
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Austin, M.A.; Breslow, J.L.; Hennekens, C.H.; Buring, J.E.; Willett, W.C.; Krauss, R.M. Low-density lipoprotein subclass patterns and risk of myocardial infarction. JAMA 1988, 260, 1917–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chooi, Y.C.; Ding, C.; Magkos, F. The epidemiology of obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsberg, H.N.; Zhang, Y.L.; Hernandez-Ono, A. Regulation of plasma triglycerides in insulin resistance and diabetes. Arch. Med. Res. 2005, 36, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.A.; Tao, C.; Gupta, R.K.; Scherer, P.E. Tracking adipogenesis during white adipose tissue development, expansion and regeneration. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haeusler, R.A.; McGraw, T.E.; Accili, D. Biochemical and cellular properties of insulin receptor signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Farese, R.V., Jr. Inhibition of triglyceride synthesis as a treatment strategy for obesity: Lessons from DGAT1-deficient mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambino, R.; Bugianesi, E.; Rosso, C.; Mezzabotta, L.; Pinach, S.; Alemanno, N.; Saba, F.; Cassader, M. Different Serum Free Fatty Acid Profiles in NAFLD Subjects and Healthy Controls after Oral Fat Load. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, U.; Seppänen-Laakso, T.; Yetukuri, L.; Ågren, J.; Kolehmainen, M.; Laaksonen, D.E.; Ruskeepää, A.L.; Gylling, H.; Uusitupa, M.; Orešič, M.; et al. Triacylglycerol fatty acid composition in diet-induced weight loss in subjects with abnormal glucose metabolism--the GENOBIN study. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.; Song, Y.; Wang, B.; Lin, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Feng, Z. Integrated lipidomics and RNA sequencing analysis reveal novel changes during 3T3-L1 cell adipogenesis. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wentworth, J.M.; Naselli, G.; Ngui, K.; Smyth, G.K.; Liu, R.; O’brien, P.E.; Bruce, C.; Weir, J.; Cinel, M.; Meikle, P.J.; et al. GM3 ganglioside and phosphatidylethanolamine-containing lipids are adipose tissue markers of insulin resistance in obese women. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.S.; Han, H.S.; Lee, S.B.; Myung, D.B.; Lee, K.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, K.T. Chemical Constituents from Leaves of Hydrangea serrata and Their Anti-photoaging Effects on UVB-Irradiated Human Fibroblasts. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 42, 424–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, M.S.; Lee, S.; Yoo, S.H. The establishment of efficient bioconversion, extraction, and isolation processes for the production of phyllodulcin, a potential high intensity sweetener, from sweet hydrangea leaves (Hydrangea macrophylla Thunbergii). Phytochem. Anal. 2016, 27, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilshara, M.G.; Jayasooriya, R.G.P.T.; Lee, S.; Jeong, J.B.; Seo, Y.T.; Choi, Y.H.; Jeong, J.W.; Jang, Y.P.; Jeong, Y.K.; Kim, G.Y. Water extract of processed Hydrangea macrophylla (Thunb.) Ser. leaf attenuates the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators by suppressing Akt-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 35, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.S.; Shin, J.S.; Myung, D.B.; Ahn, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, K.T. Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser. Extract Attenuate UVB-Induced Photoaging through MAPK/AP-1 Inactivation in Human Skin Fibroblasts and Hairless Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akanda, M.R.; Tae, H.J.; Kim, I.S.; Ahn, D.; Tian, W.; Islam, A.; Nam, H.H.; Choo, B.K.; Park, B.Y. Hepatoprotective Role of Hydrangea macrophylla against Sodium Arsenite-Induced Mitochondrial-Dependent Oxidative Stress via the Inhibition of MAPK/Caspase-3 Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.S.; Chung, K.S.; Shin, Y.K.; Yu, J.S.; Kang, S.H.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, K.T. Effect of Standardized Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser. Leaves Extract on Body Weight and Body Fat Reduction in Overweight or Obese Humans: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.S.; Lee, H.H.; Gil, H.S.; Chung, K.S.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, D.H.; Yoon, J.; Chung, E.K.; Lee, J.K.; Yang, W.M.; et al. Standardized hot water extract from the leaves of Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser. alleviates obesity via the AMPK pathway and modulation of the gut microbiota composition in high fat diet-induced obese mice. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 2672–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.S.; Chung, K.S.; Shin, Y.K.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, K.T. Standardized Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser. Extract Ameliorates Obesity in db/db Mice. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X. Lipidomics for studying metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 668–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Han, X. Lipidomics: Techniques, Applications, and Outcomes Related to Biomedical Sciences. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 954–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popkova, Y.; Dannenberger, D.; Schiller, J.; Engel, K.M. Differences in the lipid patterns during maturation of 3T3-L1 adipocytes investigated by thin-layer chromatography, gas chromatography, and mass spectrometric approaches. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2237–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Li, J.L.; Li, D.; Tobin, J.F.; Gimeno, R.E. Molecular identification of microsomal acyl-CoA:glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase, a key enzyme in de novo triacylglycerol synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 19695–19700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.A.; Haas, J.T.; Streeper, R.S.; Stone, S.J.; Kumari, M.; Yang, K.; Han, X.; Brownell, N.; Gross, R.W.; Zechner, R.; et al. DGAT enzymes are required for triacylglycerol synthesis and lipid droplets in adipocytes. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vessby, B. Dietary fat, fatty acid composition in plasma and the metabolic syndrome. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2003, 14, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warensjo, E.; Riserus, U.; Vessby, B. Fatty acid composition of serum lipids predicts the development of the metabolic syndrome in men. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 1999–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laaksonen, D.E.; Lakka, T.A.; Lakka, H.M.; Nyyssönen, K.; Rissanen, T.; Niskanen, L.K.; Salonen, J.T. Serum fatty acid composition predicts development of impaired fasting glycaemia and diabetes in middle-aged men. Diabet. Med. 2002, 19, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, L.K.; Fielding, B.A.; Bradshaw, H.A.; Ilic, V.; Beysen, C.; Clark, M.L.; Moore, N.R.; Frayn, K.N. Substituting dietary saturated fat with polyunsaturated fat changes abdominal fat distribution and improves insulin sensitivity. Diabetologia 2002, 45, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaurio, R.A.; Janko, C.; Muñoz, L.E.; Frey, B.; Herrmann, M.; Gaipl, U.S. Phospholipids: Key players in apoptosis and immune regulation. Molecules 2009, 14, 4892–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanshaw, R.G.; Smith, B.D. New reagents for phosphatidylserine recognition and detection of apoptosis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 5035–5042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, T.; Zhou, X.; Wang, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Kang, A.; Deng, H.; Xu, J.; Shen, C.; Di, L.; et al. Development and application of a comprehensive lipidomic analysis to investigate Tripterygium wilfordii-induced liver injury. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 4341–4355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, P.F. Static and dynamic lipid asymmetry in cell membranes. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Sui, X.L.; Xu, Y.P.; Gu, F.J.; Zhang, A.S.; Chen, J.H. NLRP3 inflammasome and lipid metabolism analysis based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS in gouty nephropathy. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Kamata, K. Role of lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) in atherosclerosis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 3209–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Li, J.; Zou, X.; Greggain, J.; Færgeman, N.J.; Liang, B.; Watts, J.L. Regulation of lipid droplet size and phospholipid composition by stearoyl-CoA desaturase. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2504–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Veen, J.N.; Kennelly, J.P.; Wan, S.; Vance, J.E.; Vance, D.E.; Jacobs, R.L. The critical role of phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859 Pt B, 1558–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, J.E.; Vance, D.E. Phospholipid biosynthesis in mammalian cells. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 82, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Agellon, L.B.; Allen, T.M.; Umeda, M.; Jewell, L.; Mason, A.; Vance, D.E. The ratio of phosphatidylcholine to phosphatidylethanolamine influences membrane integrity and steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shama, S.; Jang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shahin, N.N.; Motawi, T.K.; Kim, S.; Gawrieh, S.; Liu, W. Phosphatidylethanolamines Are Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in Obese Adults and Induce Liver Cell Metabolic Perturbations and Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, J.; Walsh, M.T.; Hammad, S.M.; Hussain, M.M. Sphingolipids and Lipoproteins in Health and Metabolic Disorders. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramstedt, B.; Slotte, J.P. Membrane properties of sphingomyelins. FEBS Lett. 2002, 531, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samad, F.; Hester, K.D.; Yang, G.; Hannun, Y.A.; Bielawski, J. Altered adipose and plasma sphingolipid metabolism in obesity: A potential mechanism for cardiovascular and metabolic risk. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2579–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Badeanlou, L.; Bielawski, J.; Roberts, A.J.; Hannun, Y.A.; Samad, F. Central role of ceramide biosynthesis in body weight regulation, energy metabolism, and the metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E211–E224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longato, L.; Tong, M.; Wands, J.R.; de la Monte, S.M. High fat diet induced hepatic steatosis and insulin resistance: Role of dysregulated ceramide metabolism. Hepatol. Res. 2012, 42, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raichur, S.; Brunner, B.; Bielohuby, M.; Hansen, G.; Pfenninger, A.; Wang, B.; Bruning, J.C.; Larsen, P.J.; Tennagels, N. The role of C16:0 ceramide in the development of obesity and type 2 diabetes: CerS6 inhibition as a novel therapeutic approach. Mol. Metab. 2019, 21, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Fan, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Huan, C.; Bui, H.H.; Kuo, M.S.; Park, T.S.; Cao, G.; Jiang, X.C. Impact of sphingomyelin synthase 1 deficiency on sphingolipid metabolism and atherosclerosis in mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Dong, J.; Ding, T.; Kuo, M.S.; Cao, G.; Jiang, X.C.; Li, Z. Sphingomyelin synthase 2 activity and liver steatosis: An effect of ceramide-mediated peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma2 suppression. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.E.; Yang, H.O.; Shin, Y.-K.; Kim, H.; Park, S.; Lee, G. Lipidomic Assessment of the Inhibitory Effect of Standardized Water Extract of Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser. Leaves during Adipogenesis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16101508
Yu JS, Kim HJ, Kim YE, Yang HO, Shin Y-K, Kim H, Park S, Lee G. Lipidomic Assessment of the Inhibitory Effect of Standardized Water Extract of Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser. Leaves during Adipogenesis. Nutrients. 2024; 16(10):1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16101508
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Jae Sik, Hee Ju Kim, Yeo Eun Kim, Hyun Ok Yang, Yu-Kyong Shin, Hyunjae Kim, Soyoon Park, and Gakyung Lee. 2024. "Lipidomic Assessment of the Inhibitory Effect of Standardized Water Extract of Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser. Leaves during Adipogenesis" Nutrients 16, no. 10: 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16101508
APA StyleYu, J. S., Kim, H. J., Kim, Y. E., Yang, H. O., Shin, Y.-K., Kim, H., Park, S., & Lee, G. (2024). Lipidomic Assessment of the Inhibitory Effect of Standardized Water Extract of Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser. Leaves during Adipogenesis. Nutrients, 16(10), 1508. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16101508








