A Genome-Wide Association Study of Metabolic Syndrome in the Taiwanese Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Taiwan Biobank and Study Population
2.2. Phenotypic Data
2.3. Genotyping
2.4. Quality Control
2.5. Imputation
2.6. Association Analysis
2.7. Functional Annotation and Pathway-Enrichment Analyses
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Study Participants
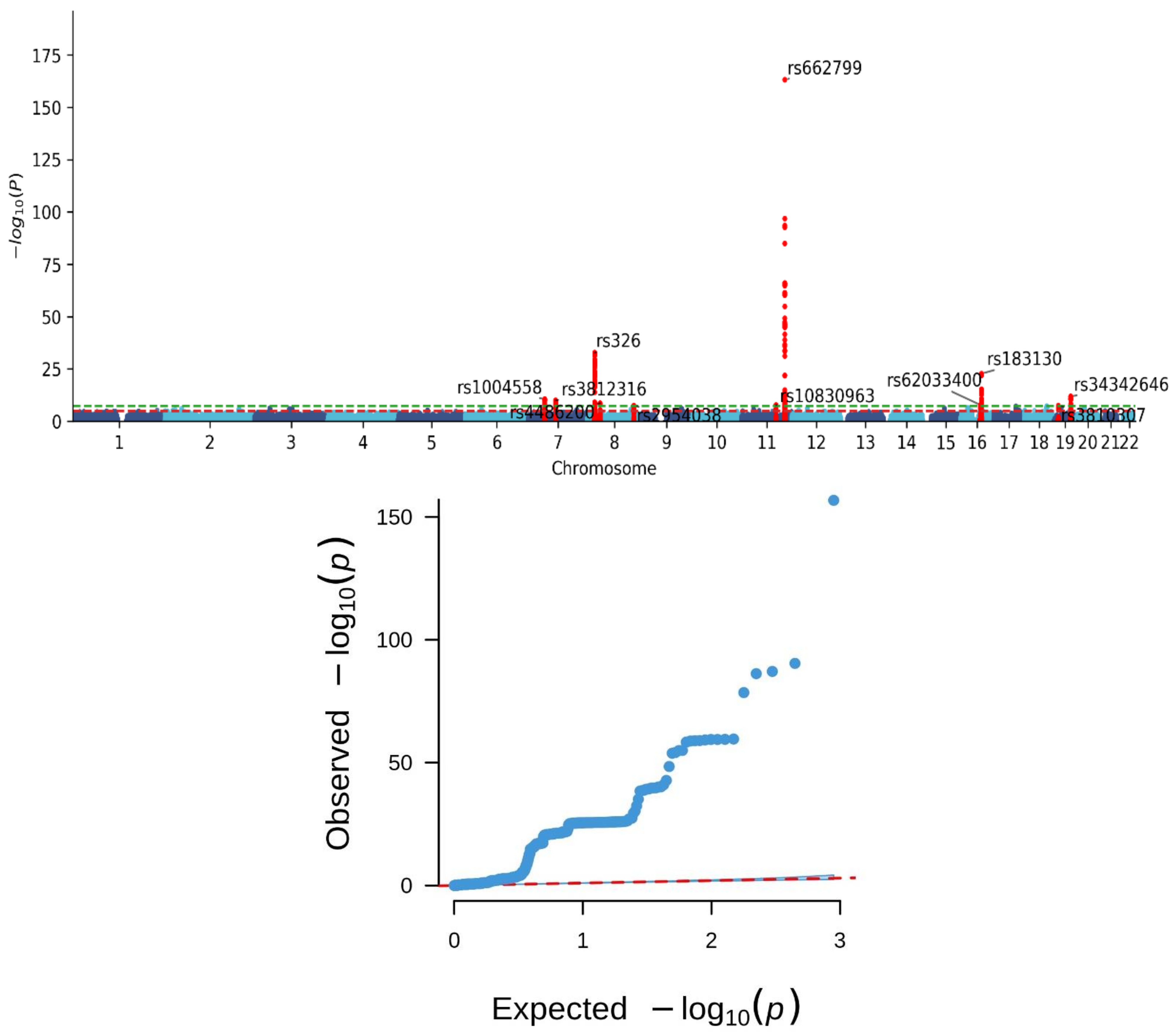
3.2. Genomic Risk Loci for MetS
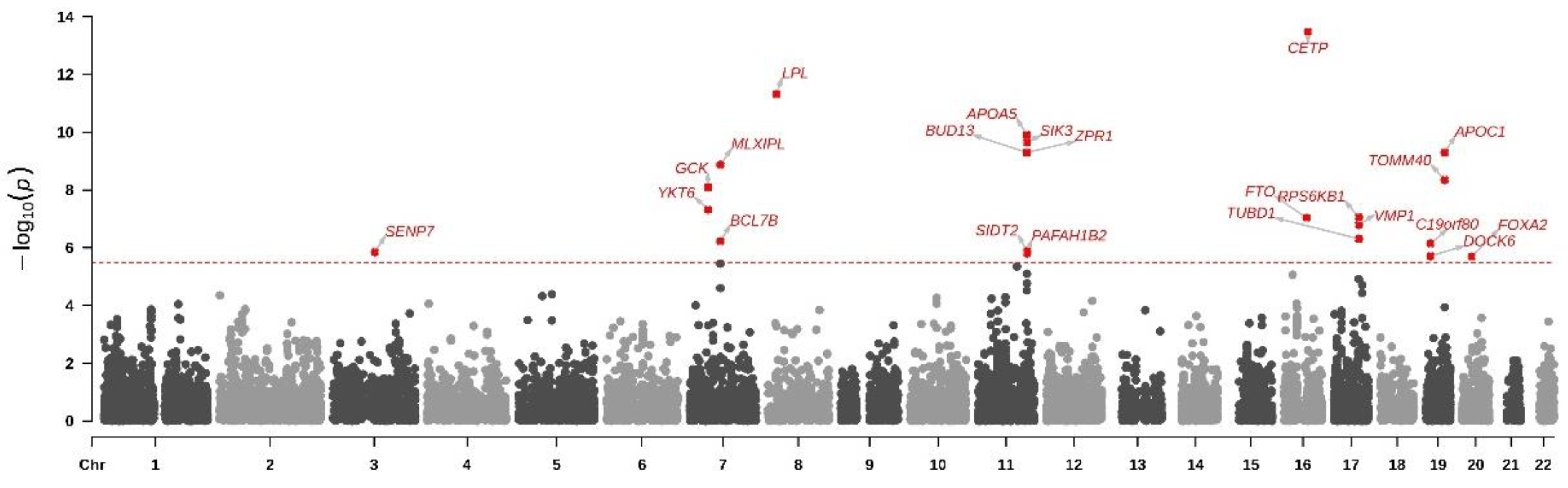
3.3. Gene-Based Analysis for Mets
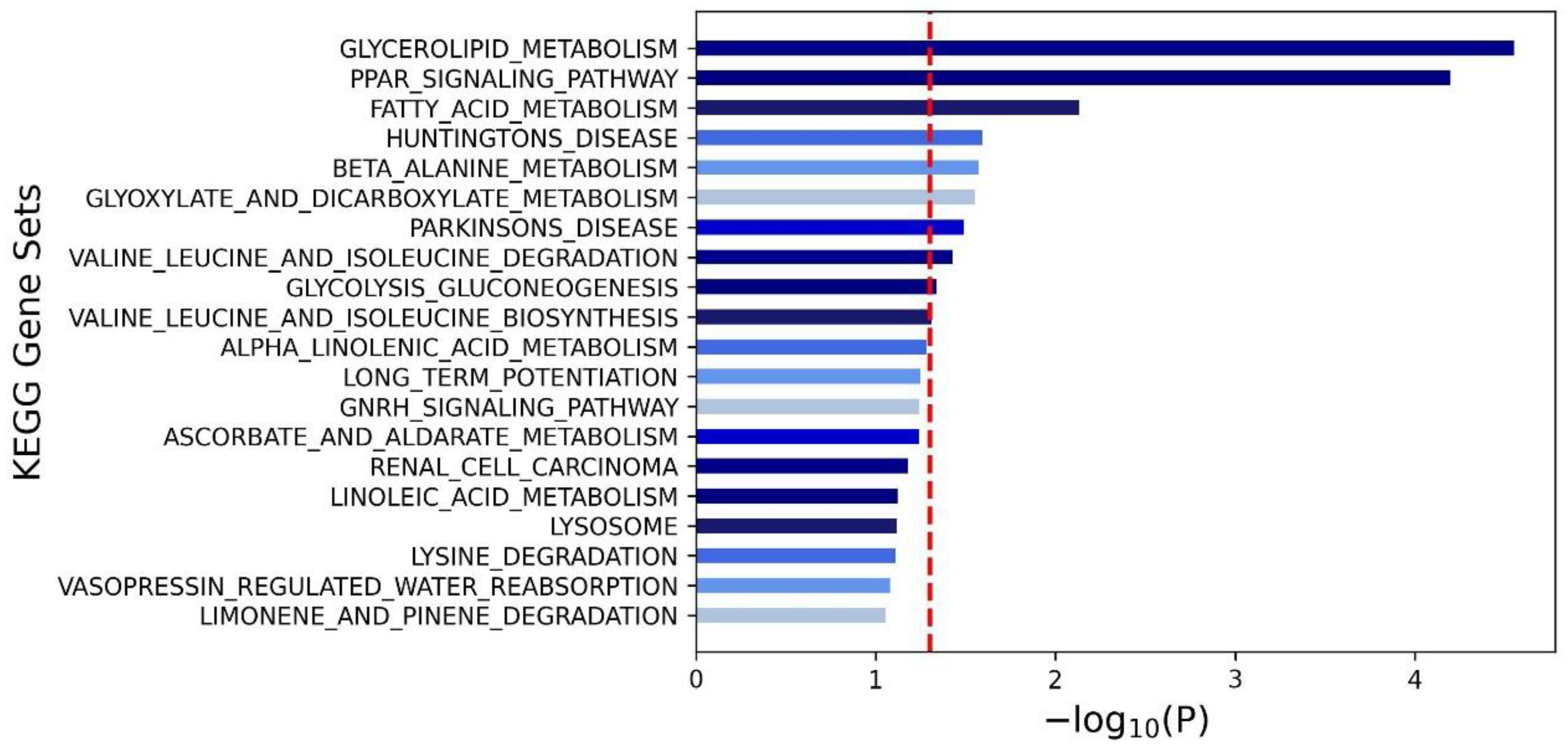
3.4. Pathway Analysis for Mets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ahmed, M.; Kumari, N.; Mirgani, Z.; Saeed, A.; Ramadan, A.; Ahmed, M.H.; Almobarak, A.O. Metabolic syndrome; Definition, Pathogenesis, Elements, and the Effects of medicinal plants on it’s elements. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2022, 21, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Tan, W.; Pan, X.; Tian, E.; Wu, Z.; Yang, J. Metabolic Syndrome-Related Kidney Injury: A Review and Update. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 904001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, C.H.; Huang, D.Q.; Nguyen, M.H. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease versus metabolic-associated fatty liver disease: Prevalence, outcomes and implications of a change in name. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2022, 28, 790–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belladelli, F.; Montorsi, F.; Martini, A. Metabolic syndrome, obesity and cancer risk. Curr. Opin. Urol. 2022, 32, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranasinghe, P.; Mathangasinghe, Y.; Jayawardena, R.; Hills, A.P.; Misra, A. Prevalence and trends of metabolic syndrome among adults in the asia-pacific region: A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2017, 17, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saklayen, M.G. The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2018, 20, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, S.Y.; Chen, C.H.; Chou, P. Prevalence of metabolic syndrome in a large health check-up population in Taiwan. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2004, 12, 611–620. [Google Scholar]
- Ordovas, J.M.; Shen, J. Gene-environment interactions and susceptibility to metabolic syndrome and other chronic diseases. J. Periodontol. 2008, 79 (Suppl. S8), 1508–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitsavos, C.; Panagiotakos, D.; Weinem, M.; Stefanadis, C. Diet, exercise and the metabolic syndrome. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2006, 3, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stancáková, A.; Baldaufová, L.; Javorský, M.; Kozárová, M.; Salagovic, J.; Tkác, I. Effect of gene polymorphisms on lipoprotein levels in patients with dyslipidemia of metabolic syndrome. Physiol. Res. 2006, 55, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rios, A.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Gomez-Delgado, F.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Marin, C.; Leon-Acuña, A.; Camargo, A.; Rodriguez-Cantalejo, F.; Blanco-Rojo, R.; Quintana-Navarro, G.; et al. Beneficial effect of CETP gene polymorphism in combination with a Mediterranean diet influencing lipid metabolism in metabolic syndrome patients: CORDIOPREV study. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grallert, H.; Sedlmeier, E.M.; Huth, C.; Kolz, M.; Heid, I.M.; Meisinger, C.; Herder, C.; Strassburger, K.; Gehringer, A.; Haak, M.; et al. APOA5 variants and metabolic syndrome in Caucasians. J. Lipid Res. 2007, 48, 2614–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.F.; Boden-Albala, B.; Juo, S.H.; Park, N.; Rundek, T.; Sacco, R.L. Heritabilities of the metabolic syndrome and its components in the Northern Manhattan Family Study. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 2006–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, V.; Patel, N.; Turcotte, M.; Bossé, Y.; Paré, G.; Meyre, D. Benefits and limitations of genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiyama, A.; Nakanishi, M. Navigating the DNA methylation landscape of cancer. Trends Genet. 2021, 37, 1012–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howles, S.A.; Thakker, R.V. Genetics of kidney stone disease. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2020, 17, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Schunkert, H. Genetics of coronary artery disease in the post-GWAS era. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 290, 980–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranavchand, R.; Reddy, B.M. Genomics era and complex disorders: Implications of GWAS with special reference to coronary artery disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and cancers. J. Postgrad. Med. 2016, 62, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.Y.; Yang, J.H.; Yeh, E.C.; Tsai, M.F.; Kao, H.J.; Lo, C.Z.; Chang, L.P.; Lin, W.J.; Hsieh, F.J.; Belsare, S.; et al. Genetic profiles of 103,106 individuals in the Taiwan Biobank provide insights into the health and history of Han Chinese. NPJ Genom. Med. 2021, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Lee, J.I.; Jhan, J.H.; Lee, Y.C.; Geng, J.H.; Chen, S.C.; Hung, C.H.; Kuo, C.H. Secondhand smoke increases the risk of developing kidney stone disease. Sci Rep. 2021, 11, 17694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Lee, J.I.; Lu, C.C.; Su, Y.D.; Chiu, C.T.; Chen, S.C.; Geng, J.H.; Chen, C.H. Hyperuricemia and Its Association with Osteoporosis in a Large Asian Cohort. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.Y.; Lee, J.I.; Shen, J.T.; Lee, Y.C.; Wang, H.S.; Tsao, Y.H.; Wu, Y.H.; Huang, S.P.; Chen, S.C.; Jhan, J.H.; et al. The association between menopause, postmenopausal hormone therapy, and kidney stone disease in Taiwanese women. Ann. Epidemiol. 2023, 78, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.F.; Lee, J.I.; Huang, S.P.; Geng, J.H.; Chen, S.C. Regular Exercise Decreases the Risk of Osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 897363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.W.; Lee, J.I.; Huang, C.Y.; Lu, C.C.; Liu, Y.H.; Huang, S.P.; Chen, S.C.; Geng, J.H. Habitual Tea Consumption and Risk of Cataracts: A Longitudinal Study. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 19, 1596–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Administration, H.P. Definition of the Metabolic Syndrome. Available online: https://www.hpa.gov.tw/Pages/Detail.aspx?nodeid=639&pid=1219 (accessed on 7 November 2023).
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, H.S.; Tsai, S.Y.; Chu, H.W.; Lin, M.R.; Lin, G.H.; Tai, Y.T.; Shen, C.Y.; Chang, W.C. Genome-wide association study identifies genetic risk loci for adiposity in a Taiwanese population. PLoS Genet. 2022, 18, e1009952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delaneau, O.; Marchini, J.; Zagury, J.F. A linear complexity phasing method for thousands of genomes. Nat. Methods 2011, 9, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchini, J.; Howie, B.; Myers, S.; McVean, G.; Donnelly, P. A new multipoint method for genome-wide association studies by imputation of genotypes. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 906–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Taskesen, E.; van Bochoven, A.; Posthuma, D. Functional mapping and annotation of genetic associations with FUMA. Nat Commun. 2017, 8, 1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Umićević Mirkov, M.; de Leeuw, C.A.; van den Heuvel, M.P.; Posthuma, D. Genetic mapping of cell type specificity for complex traits. Nat Commun. 2019, 10, 3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Leeuw, C.A.; Mooij, J.M.; Heskes, T.; Posthuma, D. MAGMA: Generalized gene-set analysis of GWAS data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Human Genome Sequencing Consortium. Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome. Nature 2004, 431, 931–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberzon, A.; Birger, C.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Ghandi, M.; Mesirov, J.P.; Tamayo, P. The Molecular Signatures Database (MSigDB) hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 2015, 1, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, G.; Bandesh, K.; Giri, A.K.; Kauser, Y.; Chanda, P.; Parekatt, V.; Mathur, S.; Madhu, S.V.; Venkatesh, P.; Bhansali, A.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Metabolic Syndrome Reveals Primary Genetic Variants at CETP Locus in Indians. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahua-Pablo, J.Á.; Cruz, M.; Méndez-Palacios, A.; Antúnez-Ortiz, D.L.; Vences-Velázquez, A.; del Carmen Alarcón-Romero, L.; Parra, E.J.; Tello-Flores, V.A.; Leyva-Vázquez, M.A.; Valladares-Salgado, A.; et al. Polymorphisms in the LPL and CETP Genes and Haplotype in the ESR1 Gene Are Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Women from Southwestern Mexico. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21539–21554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.; Ma, R.; Guo, H.; He, J.; Hu, Y.; Mu, L.; Yan, Y.; Ma, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; et al. Association between Six CETP Polymorphisms and Metabolic Syndrome in Uyghur Adults 527 from Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hechmi, M.; Dallali, H.; Gharbi, M.; Jmel, H.; Fassatoui, M.; Ben Halima, Y.; Bahri, S.; Bahlous, A.; Abid, A.; Jamoussi, H.; et al. Association of rs662799 variant and APOA5 gene haplotypes with metabolic syndrome and its components: A meta-analysis in North Africa. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40, BSR2020070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiaz, M.; Shaiq, P.A.; Raj, G.K.; Saqlain, M.; Mehmood, A.; Naqvi, S.M.S.; Cheung, B.K. Association study of Apolipoprotein A5 gene (APOA5 gene) variant with the metabolic syndrome in local Pakistani population. J. Pak. Med.Assoc. 2019, 69, 301–305. [Google Scholar]
- Hanh, N.T.H.; Nhung, B.T.; Hop, L.T.; Tuyet, L.T.; Dao, D.T.A.; Thu, N.T.T.; Binh, T.Q. The APOA5-rs662799 Polymorphism Is a Determinant of Dyslipidemia in Vietnamese Primary School Children. Lipids 2020, 55, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; You, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Song, Y.; Liu, X.; Kou, C. Association of BUD13 polymorphisms with metabolic syndrome in Chinese population: A case-control study. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Masjoudi, S.; Sedaghati-Khayat, B.; Givi, N.J.; Bonab, L.N.H.; Azizi, F.; Daneshpour, M.S. Kernel machine SNP set analysis finds the association of BUD13, ZPR1, and APOA5 variants with metabolic syndrome in Tehran Cardio-metabolic Genetics Study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Santana, L.S.; Caetano, L.A.; Costa-Riquetto, A.D.; Franco, P.C.; Dotto, R.P.; Reis, A.F.; Weinert, L.S.; Silveiro, S.P.; Vendramini, M.F.; do Prado, F.A.; et al. Targeted sequencing identifies novel variants in common and rare MODY genes. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleem, S.; Iqbal, R.; Shar, T.; Noreen, S.; Rafiq, N.; Javed, I.; Kosar, S.; Majeed, H.N.; Sattar, N.A.; Abid, M.K. Complications of Diabetes: An Insight into Genetic Polymorphism and Role of Insulin. Recent Pat. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Discov. 2018, 12, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timsit, J.; Ciangura, C.; Dubois-Laforgue, D.; Saint-Martin, C.; Bellanne-Chantelot, C. Pregnancy in Women With Monogenic Diabetes due to Pathogenic Variants of the Glucokinase Gene: Lessons and Challenges. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 802423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dron, J.S.; Hegele, R.A. Genetics of Hypertriglyceridemia. Front Endocrinol 2020, 11, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, S.; Cho, Y.S. Identification of female-specific genetic variants for metabolic syndrome and its component traits to 608 improve the prediction of metabolic syndrome in females. BMC Med. Genet. 2019, 20, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Hotta-Hirashima, N.; Asano, F.; Kitazono, T.; Iwasaki, K.; Nakata, S.; Komiya, H.; Asama, N.; Matsuoka, T.; Fujiyama, T.; et al. Kinase signalling in excitatory neurons regulates sleep quantity and depth. Nature 2022, 612, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yan, G.; Zheng, L.; Gu, W.; Liu, F.; Chen, W.; Cui, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. YKT6, as a potential predictor of prognosis and immunotherapy response for oral squamous cell carcinoma, is related to cell invasion, metastasis, and CD8+ T cell infiltration. Oncoimmunology. 2021, 10, 1938890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Z.; Jiang, J.J.; Xu, H.J.; Sun, X.D.; Liu, Z.C.; Hu, Z.M. High expression of YKT6 associated with progression and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 56, 1349–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dapar, M.L.G.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y. A pan-cancer analysis of the oncogenic role of YKT6 in human tumors. Medicine 2023, 102, e33546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwintkiewicz, J.; Spaczynski, R.Z.; Foyouzi, N.; Pehlivan, T.; Duleba, A.J. Insulin and oxidative stress modulate proliferation of rat ovarian theca-interstitial cells through diverse signal transduction pathways. Biol. Reprod. 2006, 74, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Xie, W.; Xie, W.; Wei, W.; Guo, J. Beyond controlling cell size: Functional analyses of S6K in tumorigenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Huang, H.; Han, Q.; Hu, Z.; Teng, X.L.; Ding, R.; Ye, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Z.; et al. SENP7 senses oxidative stress to sustain metabolic fitness and antitumor functions of CD8+ T cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amrute-Nayak, M.; Gand, L.V.; Khan, B.; Holler, T.; Kefalakes, E.; Kosanke, M.; Kraft, T.; Nayak, A. SENP7 deSUMOylase-governed transcriptional program coordinates sarcomere assembly and is targeted in muscle atrophy. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lind, L. Genome-Wide Association Study of the Metabolic Syndrome in UK Biobank. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2019, 17, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coltell, O.; Sorlí, J.V.; Asensio, E.M.; Barragán, R.; González, J.I.; Giménez-Alba, I.M.; Zanón-Moreno, V.; Estruch, R.; Ramírez-Sabio, J.B.; Pascual, E.C.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study for Serum Omega-3 and Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Exploratory Analysis of the Sex-Specific Effects and Dietary Modulation in Mediterranean Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2020, 12, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.Y.; Goodman, D.L.; Willems, E.L.; Freedland, A.R.; Norden-Krichmar, T.M.; Santorico, S.A.; Edwards, K.L.; American Diabetes GENNID Study Group. Genome-wide association analysis of metabolic syndrome quantitative traits in the GENNID multiethnic family study. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 13, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.W.; Lee, J.E.; Shin, E.; Kwon, H.; Choe, E.K.; Choi, S.Y.; Rhee, H.; Choi, S.H. Genome-wide association study of metabolic syndrome in Korean populations. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, K.H.; Wan, H.L.; Teng, M.S.; Chou, H.H.; Hsu, L.A.; Ko, Y.L. Genetic Variants at the APOE Locus Predict Cardiometabolic Traits and Metabolic Syndrome: A Taiwan Biobank Study. Genes 2022, 13, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.; Kuo, P.H.; Liu, Y.L.; Yang, A.C.; Kao, C.F.; Tsai, S.J. Association and interaction of APOA5, BUD13, CETP, LIPA and health-related behavior with metabolic syndrome in a Taiwanese population. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.J.; Tuan, W.L.; Hsu, L.A.; Er, L.K.; Teng, M.S.; Wu, S.; Ko, Y.L. Pleiotropic Effects of APOB Variants on Lipid Profiles, Metabolic Syndrome, and the Risk of Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, E.; Kuo, P.H.; Liu, Y.L.; Yang, A.C.; Tsai, S.J. Transforming growth factor-β signaling pathway-associated genes SMAD2 and TGFBR2 are implicated in metabolic syndrome in a Taiwanese population. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, N.W.; Chou, K.C.; Wang, Y.T.; Hung, C.L.; Kuo, C.F.; Tsai, S.Y. Building a model for predicting metabolic syndrome using artificial intelligence based on an investigation of whole-genome sequencing. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Possik, E.; Madiraju, S.R.M.; Prentki, M. Glycerol-3-phosphate phosphatase/PGP: Role in intermediary metabolism and target for cardiometabolic diseases. Biochimie 2017, 143, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Deswal, A.; Dunbar, S.B.; Francis, G.S.; Horwich, T.; Jessup, M.; Kosiborod, M.; Pritchett, A.M.; Ramasubbu, K.; et al. Contributory Risk and Management of Comorbidities of Hypertension, Obesity, Diabetes Mellitus, Hyperlipidemia, and Metabolic Syndrome in Chronic Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 134, e535–e578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougarne, N.; Weyers, B.; Desmet, S.J.; Deckers, J.; Ray, D.W.; Staels, B.; De Bosscher, K. Molecular Actions of PPARα in Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 760–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, N.; Wagner, K.D. The Role of PPARs in Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janani, C.; Ranjitha Kumari, B.D. PPAR gamma gene—A review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2015, 9, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, A.Z.; Althagafi, I.I.; Shamshad, H. Role of PPAR receptor in different diseases and their ligands: Physiological importance and clinical implications. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 166, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, M.; Audano, M.; Sahebkar, A.; Sirtori, C.R.; Mitro, N.; Ruscica, M. PPAR Agonists and Metabolic Syndrome: An Established Role? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, I.; Ichimura, A.; Ohue-Kitano, R.; Igarashi, M. Free Fatty Acid Receptors in Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 171–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marc Prentki, S.R. Murthy Madiraju, Glycerolipid Metabolism and Signaling in Health and Disease. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 647–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, J.; Li, L.; Fattah, F.J.; Dong, Y.; Bey, E.A.; Patel, M.; Gao, J.; Boothman, D.A. Review of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) mechanisms of action and rationale for targeting in cancer and other diseases. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2014, 24, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, P.; Leray, V.; Diez, M.; Serisier, S.; Le Bloc’h, J.; Siliart, B.; Dumon, H. Liver lipid metabolism. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2008, 92, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elouej, S.; Rejeb, I.; Attaoua, R.; Nagara, M.; Sallem, O.K.; Kamoun, I.; Chargui, M.; Jamoussi, H.; Turki, Z.; Abid, A.; et al. Gender-specific associations of genetic variants with metabolic syndrome components in the Tunisian population. Endocr. Res. 2016, 41, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, P.; Azizi, Z.; Raparelli, V.; Norris, C.M.; Kautzky-Willer, A.; Kublickiene, K.; Herrero, M.T.; Emam, K.E.; Vollenweider, P.; Preisig, M.; et al. Role of sex and gender-related variables in development of metabolic syndrome: A prospective cohort study. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | All | Metabolic Syndrome | No Metabolic Syndrome |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 107,230 | 24,171 | 83,059 |
| Demographic data | |||
| Age, yrs | 49.91 ± 10.92 | 53.99 ± 10.1 | 48.83 ± 10.92 |
| Women, n (%) | 68,641 (64) | 13,567 (56) | 55,074 (66) |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 24.22 ± 3.77 | 27.27 ± 3.76 | 23.33 ± 3.28 |
| Systolic BP, mm Hg | 120.28 ± 18.6 | 133.03 ± 17.9 | 116.57 ± 17.1 |
| Diastolic BP, mm Hg | 73.74 ± 11.35 | 80.63 ± 11.27 | 71.74 ± 10.57 |
| Metabolic syndrome and its components | |||
| Metabolic syndrome, n (%) | 24,171 (23) | 24,171 (100) | 0 (0) |
| Hypertension *, n (%) | 37,603 (35) | 18,060 (75) | 19,543 (24) |
| Impaired glucose tolerance †, n (%) | 22,131 (21) | 13,522 (56) | 8609 (10) |
| Increased waist circumference ‡, n (%) | 49,870 (47) | 21,178 (88) | 28,692 (35) |
| Hypertriglyceridemia §, n (%) | 22,397 (21) | 15,463 (64) | 6934 (8) |
| Low high-density lipoprotein ǁ, n (%) | 27,677 (26) | 15,911 (66) | 11,766 (14) |
| SNP | Chr | Position | Effect Allele | Other Allele | EAF | Beta Coefficient | SE | p | Nearest Gene(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1004558 | 7 | 44240407 | C | T | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 2.78 × 10−11 | YKT6 |
| rs3812316 | 7 | 73020337 | C | G | 0.08 | −0.12 | 0.02 | 1.06 × 10−10 | MLXIPL |
| rs326 | 8 | 19819439 | A | G | 0.19 | −0.16 | 0.01 | 1.71 × 10−33 | LPL |
| rs4486200 | 8 | 34293752 | C | T | 0.50 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 2.31 × 10−9 | RPL10AP3, LINC01288 |
| rs2954038 | 8 | 126507389 | A | C | 0.29 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 3.33 × 10−8 | TRIB1, LINC00861 |
| rs10830963 | 11 | 92708710 | C | G | 0.44 | 0.06 | 0.01 | 1.80 × 10−8 | MTNR1B |
| rs662799 | 11 | 116663707 | A | G | 0.32 | 0.31 | 0.01 | 7.32 × 10−164 | APOA5 |
| rs62033400 | 16 | 53811788 | A | G | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.02 | 1.52 × 10−8 | FTO |
| rs183130 | 16 | 56991363 | C | T | 0.15 | −0.15 | 0.01 | 1.86 × 10−23 | CETP, HERPUD1 |
| rs34342646 | 19 | 45388130 | G | A | 0.09 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 1.41 × 10−12 | NECTIN2 |
| Gene | Chr | NSNPS | Z | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CETP | 16 | 42 | 7.50 | 3.25 × 10−14 |
| LPL | 8 | 31 | 6.81 | 4.77 × 10−12 |
| APOA5 | 11 | 4 | 6.33 | 1.22 × 10−10 |
| SIK3 | 11 | 473 | 6.24 | 2.21 × 10−10 |
| ZPR1 | 11 | 14 | 6.11 | 5.00 × 10−10 |
| APOC1 | 19 | 2 | 6.11 | 5.00 × 10−10 |
| BUD13 | 11 | 15 | 6.11 | 5.00 × 10−10 |
| MLXIPL | 7 | 19 | 5.95 | 1.36 × 10−9 |
| TOMM40 | 19 | 10 | 5.75 | 4.45 × 10−9 |
| GCK | 7 | 49 | 5.65 | 7.99 × 10−9 |
| YKT6 | 7 | 24 | 5.34 | 4.71 × 10−8 |
| RPS6KB1 | 17 | 60 | 5.22 | 8.74 × 10−8 |
| FTO | 16 | 339 | 5.21 | 9.26 × 10−8 |
| VMP1 | 17 | 104 | 5.11 | 1.62 × 10−7 |
| TUBD1 | 17 | 37 | 4.90 | 4.88 × 10−7 |
| BCL7B | 7 | 2 | 4.86 | 6.00 × 10−7 |
| C19orf80 (ANGPTL8) | 19 | 1 | 4.82 | 7.14 × 10−7 |
| SIDT2 | 11 | 24 | 4.69 | 1.34 × 10−6 |
| SENP7 | 3 | 378 | 4.68 | 1.42 × 10−6 |
| PAFAH1B2 | 11 | 60 | 4.66 | 1.57 × 10−6 |
| DOCK6 | 19 | 36 | 4.62 | 1.95 × 10−6 |
| FOXA2 | 20 | 4 | 4.61 | 2.04 × 10−6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ho, C.-Y.; Lee, J.-I.; Huang, S.-P.; Chen, S.-C.; Geng, J.-H. A Genome-Wide Association Study of Metabolic Syndrome in the Taiwanese Population. Nutrients 2024, 16, 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010077
Ho C-Y, Lee J-I, Huang S-P, Chen S-C, Geng J-H. A Genome-Wide Association Study of Metabolic Syndrome in the Taiwanese Population. Nutrients. 2024; 16(1):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010077
Chicago/Turabian StyleHo, Chih-Yi, Jia-In Lee, Shu-Pin Huang, Szu-Chia Chen, and Jiun-Hung Geng. 2024. "A Genome-Wide Association Study of Metabolic Syndrome in the Taiwanese Population" Nutrients 16, no. 1: 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010077
APA StyleHo, C.-Y., Lee, J.-I., Huang, S.-P., Chen, S.-C., & Geng, J.-H. (2024). A Genome-Wide Association Study of Metabolic Syndrome in the Taiwanese Population. Nutrients, 16(1), 77. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010077






