Neonatal Leptin Levels Predict the Early Childhood Developmental Assessment Scores of Preterm Infants
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bell, E.F.; Hintz, S.R.; Hansen, N.I.; Bann, C.M.; Wyckoff, M.H.; DeMauro, S.B.; Walsh, M.C.; Vohr, B.R.; Stoll, B.J.; Carlo, W.A.; et al. Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network. Mortality, in-hospital morbidity, care practices, and 2-year outcomes for extremely preterm infants in the US, 2013–2018. JAMA 2022, 327, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasini, A.; Monti, F.; Laguardia, M.C.; Stella, M.; Marvulli, L.; Neri, E. High protein intake in human/maternal milk fortification for 1250 gr infants: Intrahospital growth and neurodevelopmental outcome at two years. Acta Biomed. 2018, 88, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanys-Munoz, E.; Kennedy, K.; Castaneda-Gutierrez, E.; Forsyth, S.; Godfrey, K.M.; Koletzko, B.; Ozanne, S.E.; Rueda, R.; Schoemaker, M.; van der Beek, E.M.; et al. Systematic review indicates postnatal growth in term infants born small-for-gestational-age being associated with later neurocognitive and metabolic outcomes. Acta Paediatr. 2017, 106, 1230–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belfort, M.B.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Rich-Edwards, J.; Kleinman, K.P.; Gillman, M.W. Size at birth, infant growth, and blood pressure at 3 years of age. J. Pediatr. 2007, 151, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howe, L.D.; Chaturvedi, N.; Lawlor, D.A.; Ferreira, D.L.S.; Fraser, A.; Davey Smith, G.; Tilling, K.; Hughes, A.D. Rapid increases in infant adiposity and overweight/obesity in childhood are associated with higher central and brachial blood pressure in early adulthood. J. Hypertens. 2014, 32, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, C.M.; Shiell, A.W.; Newsome, C.A.; Syddall, H.E.; Shinebourne, E.A.; Fayers, P.M.; Martyn, C.N.; de Swiet, M. Fetal, infant, and childhood growth and adult blood pressure. Circulation 2002, 105, 1088–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermann, G.M.; Miller, R.L.; Erkonen, G.E.; Dallas, L.M.; Hsu, E.; Zhu, V.; Roghair, R.D. Neonatal catch up growth increases diabetes susceptibility but improves behavioral and cardiovascular outcomes of low birth weight male mice. Pediatr. Res. 2009, 66, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkonen, G.E.; Hermann, G.M.; Miller, R.L.; Thedens, D.L.; Nopoulos, P.C.; Wemmie, J.A.; Roghair, R.D. Neonatal leptin administration alters regional brain volumes and blocks neonatal growth restriction-induced behavioral and cardiovascular dysfunction in male mice. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 69, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, R.B. Direct and indirect effects of leptin on adipocyte metabolism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1842, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kratzsch, J.; Bae, Y.J.; Kiess, W. Adipokines in human breast milk. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 32, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schanton, M.; Maymó, J.L.; Pérez-Pérez, A.; Sánchez-Margalet, V.; Varone, C.L. Involvement of leptin in the molecular physiology of the placenta. Reproduction 2018, 155, R1–R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassink, S.G.; de Lancey, E.; Sheslow, D.V.; Smith-Kirwin, S.M.; O’Connor, D.M.; Considine, R.V.; Opentanova, I.; Dostal, K.; Spear, M.L.; Leef, K.; et al. Placental leptin: An important new growth factor in intrauterine and neonatal development? Pediatrics 1997, 100, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yura, S.; Sagawa, N.; Mise, H.; Mori, T.; Masuzaki, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Nakao, K. A positive umbilical venous-arterial difference of leptin level and its rapid decline after birth. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1998, 178, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valūniene, M.; Verkauskiene, R.; Boguszewski, M.; Dahlgren, J.; Lasiene, D.; Lasas, L.; Wikland, K.A. Leptin levels at birth and in early postnatal life in small- and appropriate-for-gestational-age infants. Medicina 2007, 43, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casabiell, X.; Piñeiro, V.; Tomé, M.A.; Peinó, R.; Diéguez, C.; Casanueva, F.F. Presence of leptin in colostrum and/or breast milk from lactating mothers: A potential role in the regulation of neonatal food intake. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 4270–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savino, F.; Liguori, S.A.; Benetti, S.; Sorrenti, M.; Fissore, M.F.; Cordero di Montezemolo, L. High serum leptin levels in infancy can potentially predict obesity in childhood, especially in formula-fed infants. Acta Paediatr. 2013, 102, e455–e459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matochik, J.A.; London, E.D.; Yildiz, B.O.; Ozata, M.; Caglayan, S.; DePaoli, A.M.; Wong, M.L.; Licinio, J. Effect of leptin replacement on brain structure in genetically leptin-deficient adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 2851–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Filho, G.J.; Babikian, T.; Asarnow, R.; Delibasi, T.; Esposito, K.; Erol, H.K.; Wong, M.L.; Licinio, J. Leptin replacement improves cognitive development. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatier, C.; Vantyghem, M.C.; Storey, C.; Jéru, I.; Christin-Maitre, S.; Fève, B.; Lascols, O.; Beltrand, J.; Carel, J.C.; Vigouroux, C.; et al. Monogenic forms of lipodystrophic syndromes: Diagnosis, detection, and practical management considerations from clinical cases. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2019, 35, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertl, T.; Funke, S.; Sárkány, I.; Szabó, I.; Rascher, W.; Blum, W.F.; Sulyok, E. Postnatal changes of leptin levels in full-term and preterm neonates: Their relation to intrauterine growth, gender and testosterone. Biol. Neonate. 1999, 75, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbrekera, B.; Colaizy, T.T.; Vasilakos, L.K.; Johnson, K.J.; Santillan, D.A.; Haskell, S.E.; Roghair, R.D. Origins of neonatal leptin deficiency in preterm infants. Pediatr. Res. 2019, 85, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vass, R.A.; Bell, E.F.; Colaizy, T.T.; Schmelzel, M.L.; Johnson, K.J.; Walker, J.R.; Ertl, T.; Roghair, R.D. Hormone levels in preterm and donor human milk before and after Holder pasteurization. Pediatr. Res. 2020, 88, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatmethakul, T.; Schmelzel, M.L.; Johnson, K.J.; Walker, J.R.; Santillan, D.A.; Colaizy, T.T.; Roghair, R.D. Postnatal leptin levels correlate with breast milk leptin content in infants born before 32 weeks gestation. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, S.; Iliadou, A.; Bergvall, N.; Tuvemo, T.; Norman, M.; Cnattingius, S. Risk of high blood pressure among young men increases with the degree of immaturity at birth. Circulation 2005, 112, 3430–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sucksdorff, M.; Lehtonen, L.; Chudal, R.; Suominen, A.; Joelsson, P.; Gissler, M.; Sourander, A. Preterm birth and poor fetal growth as risk factors of attention-deficit/ hyperactivity disorder. Pediatrics 2015, 136, e599–e608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerstjens, J.M.; Bos, A.F.; ten Vergert, E.M.; de Meer, G.; Butcher, P.R.; Reijneveld, S.A. Support for the global feasibility of the Ages and Stages Questionnaire as developmental screener. Early Hum. Dev. 2009, 85, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonhaut, L.; Armijo, I.; Schönstedt, M.; Alvarez, J.; Cordero, M. Validity of the ages and stages questionnaires in term and preterm infants. Pediatrics 2013, 131, e1468–e1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, J.T.; Kaelber, D.C.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Blowey, D.; Carroll, A.E.; Daniels, S.R.; de Ferranti, S.D.; Dionne, J.M.; Falkner, B.; Flinn, S.K.; et al. Clinical practice guideline for screening and management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20171904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montague, C.T.; Farooqi, I.S.; Whitehead, J.P.; Soos, M.A.; Rau, H.; Wareham, N.J.; Sewter, C.P.; Digby, J.E.; Mohammed, S.N.; Hurst, J.A.; et al. Congenital leptin deficiency is associated with severe early-onset obesity in humans. Nature 1997, 387, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, I.S.; Matarese, G.; Lord, G.M.; Keogh, J.M.; Lawrence, E.; Agwu, C.; Sanna, V.; Jebb, S.A.; Perna, F.; Fontana, S.; et al. Beneficial effects of leptin on obesity, T cell hyporesponsiveness, and neuroendocrine/metabolic dysfunction of human congenital leptin deficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1093–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Lobo, A.M.; Teixeira, P.D.; Furigo, I.C.; Melo, H.M.; de M Lyra e Silva, N.; De Felice, F.G.; Donato, J., Jr. Long-term consequences of the absence of leptin signaling in early life. eLife 2019, 8, e40970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.G.; Lee, B.J.; Jeong, J.K. Temporal leptin to determine cardiovascular and metabolic fate throughout the life. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouret, S.G.; Draper, S.J.; Simerly, R.B. Trophic action of leptin on hypothalamic neurons that regulate feeding. Science 2004, 304, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steppan, C.M.; Swick, A.G. A role for leptin in brain development. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 256, 600–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, S.A.; Altman, J.; Russo, R.J.; Zhang, X. Timetables of neurogenesis in the human brain based on experimentally determined patterns in the rat. Neurotoxicology 1993, 14, 83–144. [Google Scholar]
- Mela, V.; Diaz, F.; Borcel, E.; Argente, J.; Chowen, J.A.; Viveros, M.P. Long term hippocampal and cortical changes induced by maternal deprivation and neonatal leptin treatment in male and female rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, L.R.; Zhu, V.; Miller, A.; Roghair, R.D. Growth restriction, leptin, and the programming of adult behavior in mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2014, 275, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Z.H.; Liao, J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Liang, C.; Song, C.H.; Han, M.; Wang, L.H.; Xue, H.; Zhang, K.; Zabeau, L.; et al. Inhibition of the connexin 43 elevation may be involved in the neuroprotective activity of leptin against brain ischemic injury. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 34, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, G.; Deng, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, X. Neuroprotective effect of leptin on a primate model of cerebral ischemia. Anim. Biotechnol. 2022, 33, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, A.F.; Heyne, R.J.; Morgan, J.S.; Ahmad, N.; Rosenfeld, C.R. Elevated systolic blood pressure in preterm very-low-birth-weight infants ≤3 years of life. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2011, 26, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvi, P.; Revera, M.; Joly, L.; Reusz, G.; Iaia, M.; Benkhedda, S.; Chibane, A.; Parati, G.; Benetos, A.; Temmar, M. Role of birth weight and postnatal growth on pulse wave velocity in teenagers. J. Adolesc. Health 2012, 51, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabo, R.T.; Wang, A.; Deng, Y.; Sabo, C.S.; Sun, S.S. Relationships between childhood growth parameters and adult blood pressure: The Fels Longitudinal Study. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2017, 8, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, C.O.; Li, N.; Eaton, C.B.; Kelsey, K.T.; Cecil, K.M.; Kalkwarf, H.J.; Yolton, K.; Lanphear, B.P.; Chen, A.; Braun, J.M. Neonatal and adolescent adipocytokines as predictors of adiposity and cardiometabolic risk in adolescence. Obesity 2021, 29, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramiro-Cortijo, D.; Singh, P.; Herranz Carrillo, G.; Gila-Díaz, A.; Martín-Cabrejas, M.A.; Martin, C.R.; Arribas, S.M. Association of maternal body composition and diet on breast milk hormones and neonatal growth during the first month of lactation. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1090499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.J.; Rifas-Shiman, S.L.; Aris, I.M.; Mantzoros, C.; Hivert, M.F.; Oken, E. Leptin trajectories from birth to mid-childhood and cardio-metabolic health in early adolescence. Metabolism 2019, 91, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, N.S.; Costeloe, K.; Gibson, A.T.; Hennessy, E.M.; Marlow, N.; Wilkinson, A.R.; EPICure Study Group. The EPICure study: Associations and antecedents of neurological and developmental disability at 30 months of age following extremely preterm birth. Arch. Dis. Child Fetal Neonatal. Ed. 2005, 90, F134–F140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida-Takahashi, R.; Uotani, S.; Abe, T.; Degawa-Yamauchi, M.; Fukushima, T.; Fujita, N.; Sakamaki, H.; Yamasaki, H.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Eguchi, K. Rapid inhibition of leptin signaling by glucocorticoids in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 19658–19664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helland, I.B.; Reseland, J.E.; Saugstad, O.D.; Drevon, C.A. Leptin levels in pregnant women and newborn infants: Gender differences and reduction during the neonatal period. Pediatrics 1998, 101, E12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumgartner, R.N.; Waters, D.L.; Morley, J.E.; Patrick, P.; Montoya, G.D.; Garry, P.J. Age-related changes in sex hormones affect the sex difference in serum leptin independently of changes in body fat. Metabolism 1999, 48, 378–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, K.E.; Martin, C.R.; Cherkerzian, S.; Kellogg, M.; Belfort, M.B. Human milk hormone intake in the first month of life and physical growth outcomes in preterm infants. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, 1793–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Xiao, X.; Song, X.; Qi, Z.; Li, Y. Prediction of cord blood leptin on infant’s neurodevelopment: A birth cohort in rural Yunnan, China. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2023, 148, 105955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escuder-Vieco, D.; Espinosa-Martos, I.; Rodríguez, J.M.; Fernández, L.; Pallás-Alonso, C.R. Effect of HTST and Holder pasteurization on the concentration of immunoglobulins, growth factors, and hormones in donor human milk. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesolowska, A.; Sinkiewicz-Darol, E.; Barbarska, O.; Strom, K.; Rutkowska, M.; Karzel, K.; Rosiak, E.; Oledzka, G.; Orczyk-Pawiłowicz, M.; Rzoska, S.; et al. New achievements in high-pressure processing to preserve human milk bioactivity. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
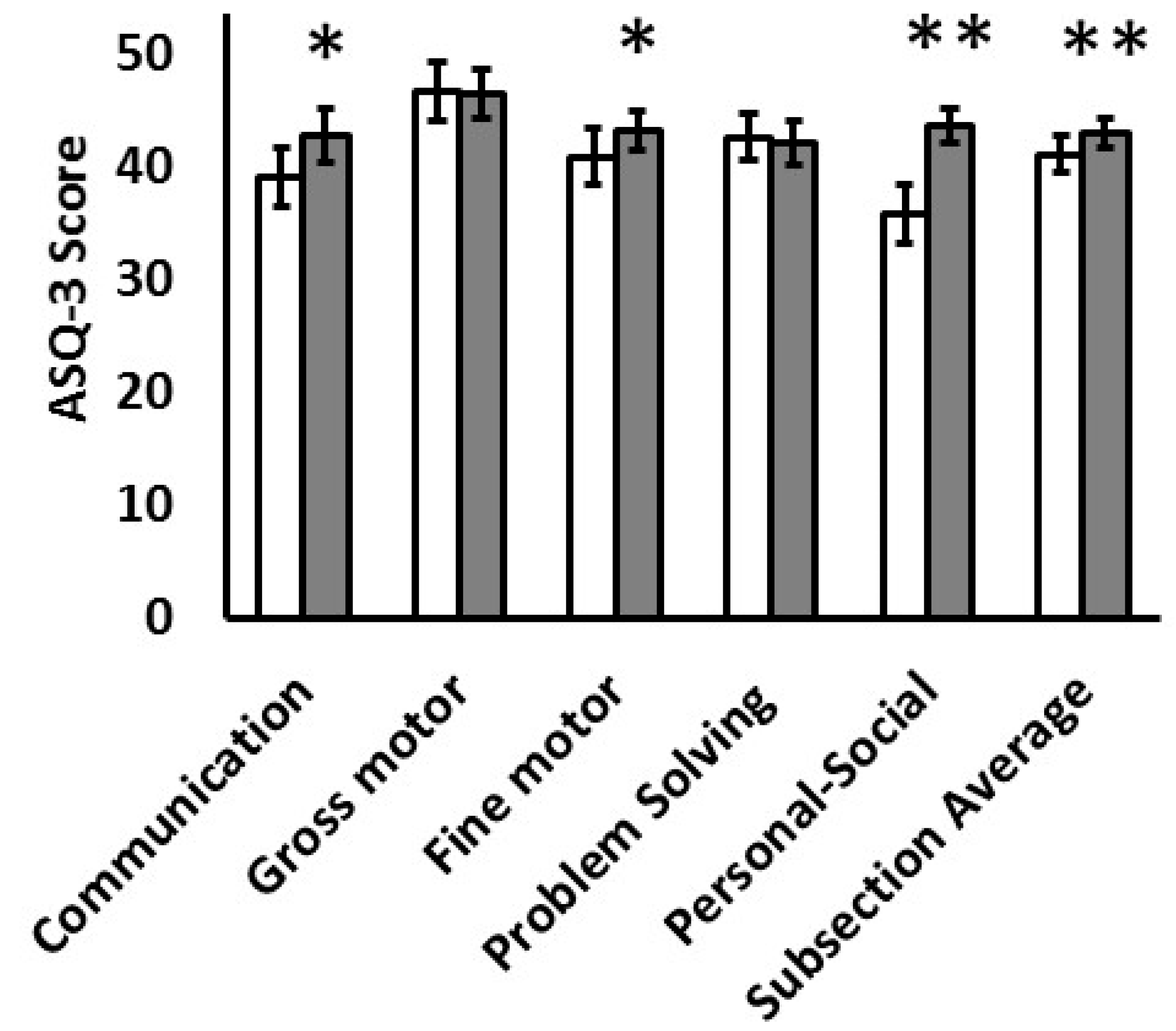
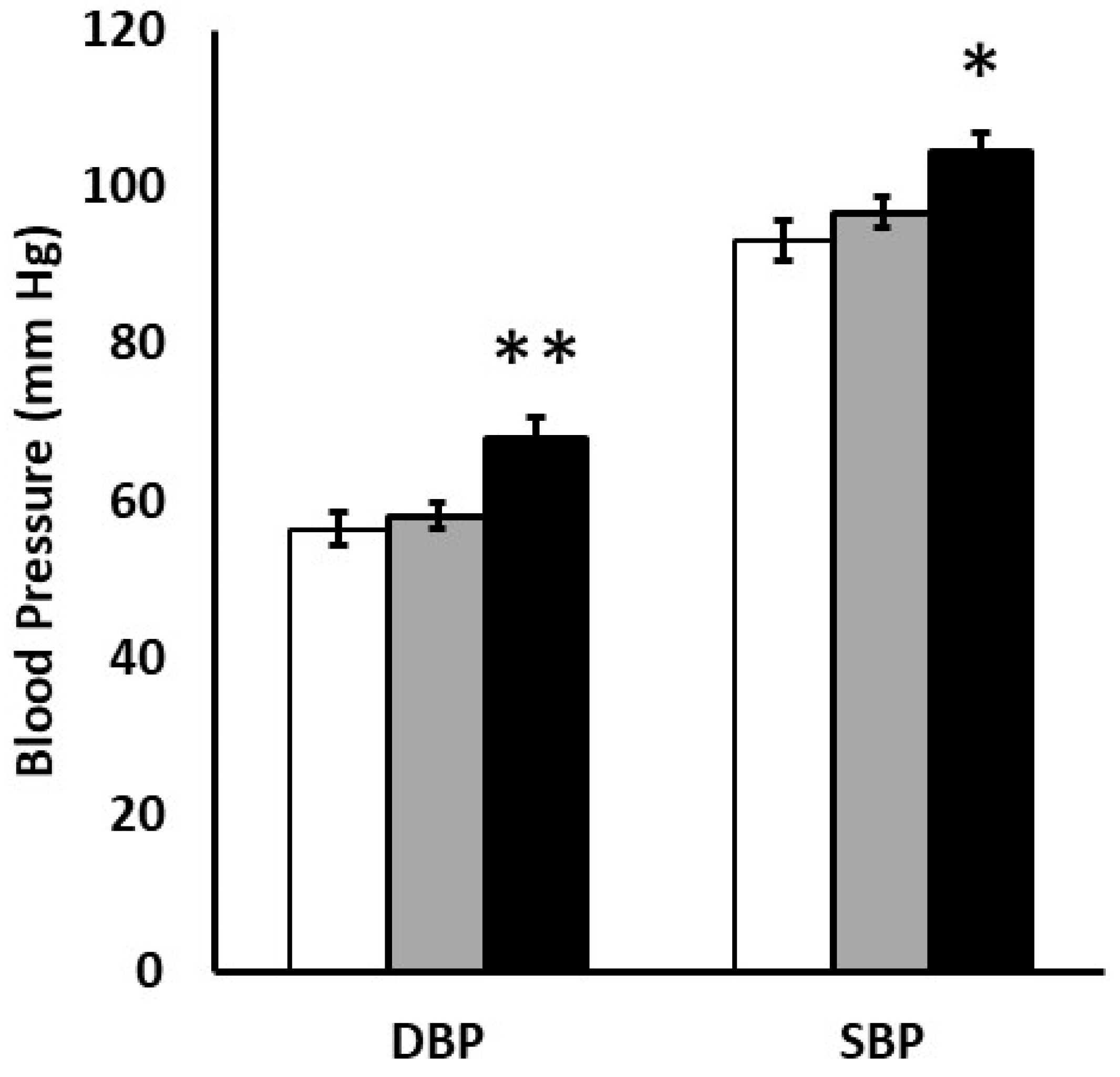

| Male | Female | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| SBP, mm Hg | 99 (92, 107) | 95 (90, 104) | 0.18 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 61 (53, 68) | 57 (53, 61) | 0.21 |
| ASQ-3, total score | 210 (178, 236) | 248 (210–265) * | 0.003 |
| SBP | DBP | ASQ-3 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Median (IQR) | R | p | R | p | R | p | |
| Gestational age (weeks) | 29.6 (27.3, 31.3) | 0.30 * | 0.02 | 0.24 | 0.07 | 0.24 | 0.06 |
| Birth weight (g) | 1195 (995, 1610) | 0.27 * | 0.04 | 0.31 * | 0.02 | 0.20 | 0.12 |
| Postnatal leptin (pg/mL) | 612 (300, 1735) | −0.06 | 0.68 | 0.10 | 0.50 | 0.19 | 0.17 |
| Follow-up weight (kg) | 11.1 (9.7, 12.7) | 0.23 | 0.09 | 0.27 * | 0.04 | −0.01 | 0.91 |
| Weight gain (g/d) | 11.3 (9.7, 13.4) | 0.35 * | 0.006 | 0.36 * | 0.005 | 0.10 | 0.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Roghair, R.D.; Colaizy, T.T.; Steinbrekera, B.; Vass, R.A.; Hsu, E.; Dagle, D.; Chatmethakul, T. Neonatal Leptin Levels Predict the Early Childhood Developmental Assessment Scores of Preterm Infants. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081967
Roghair RD, Colaizy TT, Steinbrekera B, Vass RA, Hsu E, Dagle D, Chatmethakul T. Neonatal Leptin Levels Predict the Early Childhood Developmental Assessment Scores of Preterm Infants. Nutrients. 2023; 15(8):1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081967
Chicago/Turabian StyleRoghair, Robert D., Tarah T. Colaizy, Baiba Steinbrekera, Réka A. Vass, Erica Hsu, Daniel Dagle, and Trassanee Chatmethakul. 2023. "Neonatal Leptin Levels Predict the Early Childhood Developmental Assessment Scores of Preterm Infants" Nutrients 15, no. 8: 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081967
APA StyleRoghair, R. D., Colaizy, T. T., Steinbrekera, B., Vass, R. A., Hsu, E., Dagle, D., & Chatmethakul, T. (2023). Neonatal Leptin Levels Predict the Early Childhood Developmental Assessment Scores of Preterm Infants. Nutrients, 15(8), 1967. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15081967









