New Aspect of Composition and Biological Properties of Glechoma hederacea L. Herb: Detailed Phytochemical Analysis and Evaluation of Antioxidant, Anticoagulant Activity and Toxicity in Selected Human Cells and Plasma In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Plant Material
2.3. Preparation of the Extract and Fractions from Aerial Parts of G. hederacea
2.4. The Qualitative Analysis Using Ultra-High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry UHPLC-QTOF-MS
2.5. Ultra-High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC-MS) Conditions
2.6. Stock Solution of Extract and Fractions from Aerial Parts of G. hederacea
2.7. Plasma Isolation
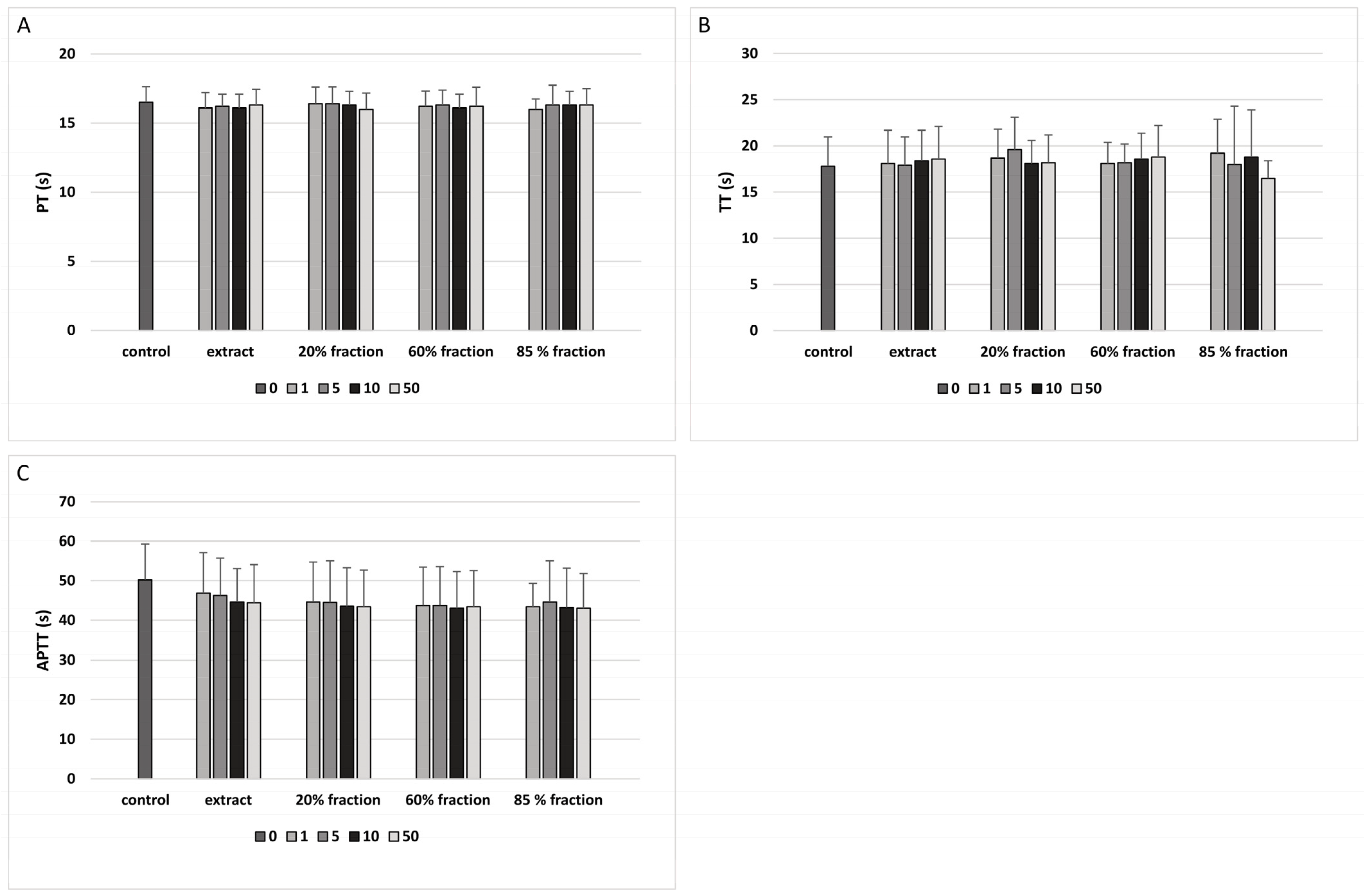
2.8. Coagulation Times of Human Plasma
2.9. Lipid Peroxidation Measurement in Human Plasma
2.10. Carbonyl Group Measurement in Human Plasma
2.11. PBM Cells Isolation
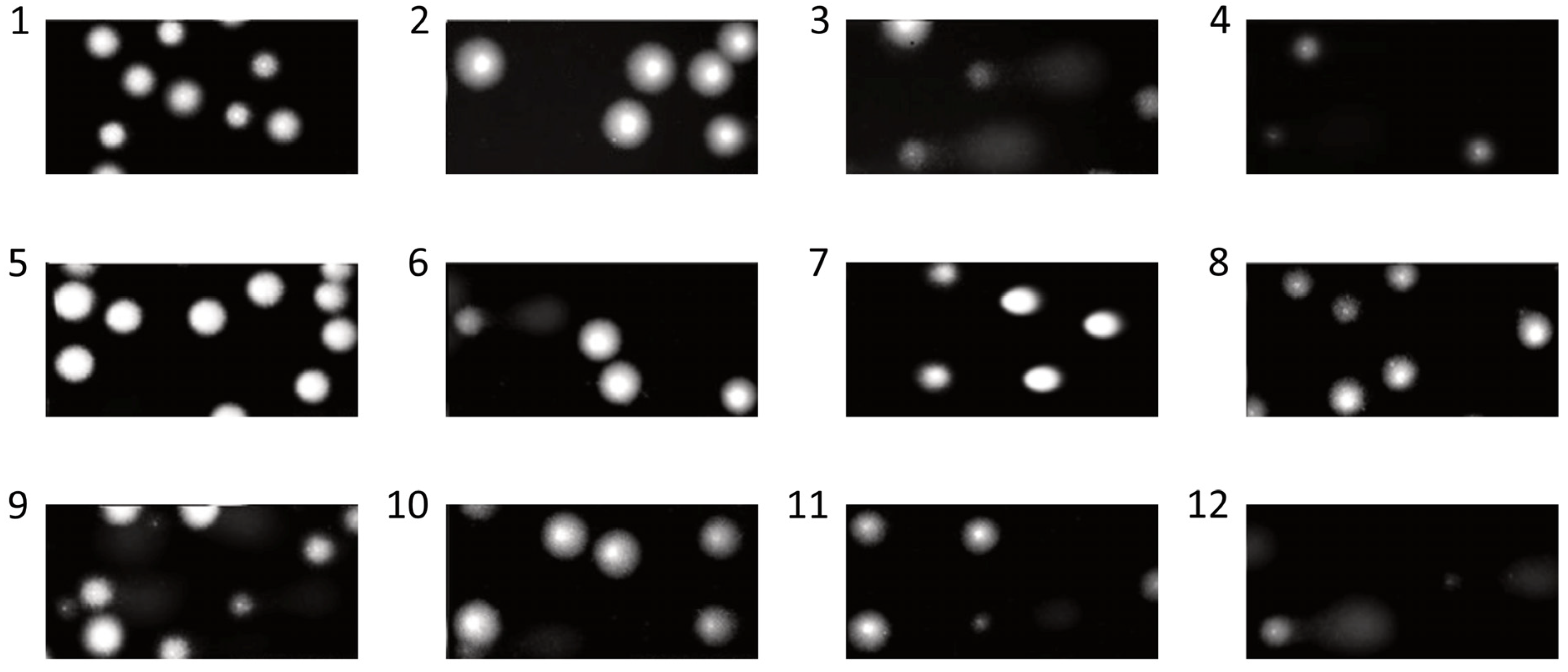
2.12. DNA Damage
2.13. PBM Cells Viability
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.Y.; Lin, S.Y.; Chen, W.Y.; Liao, S.L.; Wu, C.C.; Pan, P.H.; Chou, S.T.; Chen, C.J. Glechoma hederacea Extracts Attenuate Cholestatic Liver Injury in a Bile Duct-Ligated Rat Model. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 204, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, S.-T.; Lin, T.-H.; Peng, H.-Y.; Chao, W.-W. Phytochemical Profile of Hot Water Extract of Glechoma hederacea and Its Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Activities. Life Sci. 2019, 231, 116519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, W.W.; Liou, Y.J.; Ma, H.T.; Chen, Y.H.; Chou, S.-T. Phytochemical Composition and Bioactive Effects of Ethyl Acetate Fraction Extract (EAFE) of Glechoma hederacea L. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45, e13815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, W.-W.; Chan, W.-C.; Ma, H.-T.; Chou, S.-T. Phenolic Acids and Flavonoids-Rich Glechoma hederacea L. (Lamiaceae) Water Extract against H2O2-Induced Apoptosis in PC12 Cells. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, K.; Amanowicz, K.; Paśko, P.; Podolak, I.; Galanty, A. Optimization of the Extraction Procedure for the Phenolic-Rich Glechoma hederacea L. Herb and Evaluation of Its Cytotoxic and Antioxidant Potential. Plants 2022, 11, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, P.; Olas, B.; Wachowicz, B. Stres Oksydacyjny w Przebiegu Hemostazy. Postepy Biochem. 2010, 56, 329–347. [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal, O. Different Classes of Anticoagulant Drugs in Clinical Use. Is There a Class Effect? J. Hematol. Thromboembolic Dis. 2015, 3, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olas, B. The Multifunctionality of Berries toward Blood Platelets and the Role of Berry Phenolics in Cardiovascular Disorders. Platelets 2017, 28, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milovanovic, M.; Zivkovic, D.; Vucelic-Radovic, B. Antioxidant Effects of Glechoma hederacea as a Food Additive. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2010, 5, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manach, C.; Scalbert, A.; Morand, C.; Rémésy, C.; Jiménez, L. Polyphenols: Food Sources and Bioavailability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolnik, A.; Soluch, A.; Kowalska, I.; Olas, B. Antioxidant and Hemostatic Properties of Preparations from Asteraceae Family and Their Chemical Composition—Comparative Studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 111982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malinowska, J.; Kołodziejczyk-Czepas, J.; Moniuszko-Szajwaj, B.; Kowalska, I.; Oleszek, W.; Stochmal, A.; Olas, B. Phenolic Fractions from Trifolium Pallidum and Trifolium Scabrum Aerial Parts in Human Plasma Protect against Changes Induced by Hyperhomocysteinemia in Vitro. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 4023–4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sławińska, N.; Żuchowski, J.; Stochmal, A.; Olas, B. Extract from Sea Buckthorn Seeds—A Phytochemical, Antioxidant, and Hemostasis Study; Effect of Thermal Processing on Its Chemical Content and Biological Activity In Vitro. Nutrients 2023, 15, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluska, M.; Juszczak, M.; Wysokiński, D.; Żuchowski, J.; Stochmal, A.; Woźniak, K. Kaempferol Derivatives Isolated from Lens Culinaris Medik. Reduce DNA Damage Induced by Etoposide in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 8, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.P.; McCoy, M.T.; Tice, R.R.; Schneider, E.L. A Simple Technique for Quantitation of Low Levels of DNA Damage in Individual Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1988, 175, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokarz, P.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.; Kaarniranta, K.; Blasiak, J. All-Trans Retinoic Acid Modulates DNA Damage Response and the Expression of the VEGF-A and MKI67 Genes in ARPE-19 Cells Subjected to Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, J.; Wilson, I.; Orton, T.; Pognan, F. Investigation of the Alamar Blue (Resazurin) Fluorescent Dye for the Assessment of Mammalian Cell Cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5421–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garran, T.A.; Ji, R.; Chen, J.L.; Xie, D.; Guo, L.; Huang, L.Q.; Lai, C.J.S. Elucidation of Metabolite Isomers of Leonurus Japonicus and Leonurus Cardiaca Using Discriminating Metabolite Isomerism Strategy Based on Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. 2019, 1598, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moloto, M.R.; Phan, A.D.T.; Shai, J.L.; Sultanbawa, Y.; Sivakumar, D. Comparison of Phenolic Compounds, Carotenoids, Amino Acid Composition, In Vitro Antioxidant and Anti-Diabetic Activities in the Leaves of Seven Cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) Cultivars. Foods 2020, 9, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyżanowska-Kowalczyk, J.; Pecio, Ł.; Mołdoch, J.; Ludwiczuk, A.; Kowalczyk, M. Novel Phenolic Constituents of Pulmonaria officinalis L. LC-MS/MS Comparison of Spring and Autumn Metabolite Profiles. Molecules 2018, 23, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammerer, D.; Claus, A.; Carle, R.; Schieber, A. Polyphenol Screening of Pomace from Red and White Grape Varieties (Vitis vinifera L.) by HPLC-DAD-MS/MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 4360–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Rabaneda, F.; Jáuregui, O.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Viladomat, F.; Bastida, J.; Codina, C. Qualitative Analysis of Phenolic Compounds in Apple Pomace Using Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Mass Spectrometry in Tandem Mode. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 18, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirantes-Piné, R.; Arráez-Román, D.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. Characterization of Phenolic and Other Polar Compounds in a Lemon Verbena Extract by Capillary Electrophoresis-Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 2818–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Nakabayashi, R.; Mori, T.; Yamada, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Rai, A.; Sugiyama, R.; Yamamoto, H.; Nakaya, T.; Yamazaki, M.; et al. A Cheminformatics Approach to Characterize Metabolomes in Stable-Isotope-Labeled Organisms. Nat. Methods 2019, 16, 295–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluchoff-Fiasson, K.; Fiasson, J.L.; Waton, H. Quercetin Glycosides from European Aquatic Ranunculus Species of Subgenus Batrachium. Phytochemistry 1997, 45, 1063–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baggett, N.; Case, M.A.; Darby, P.R.; Gray, C.J. 7-β-d-Galactopyranosyloxycoumarin-4-Acetic Acid and Its Methyl Ester as Substrates for the β-d-Galactosidase of Escherichia Coli. Carbohydr. Res. 1990, 197, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raal, A.; Jaama, M.; Utt, M.; Püssa, T.; Žvikas, V.; Jakštas, V.; Koshovyi, O.; Nguyen, K.V.; Thi Nguyen, H. The Phytochemical Profile and Anticancer Activity of Anthemis Tinctoria and Angelica Sylvestris Used in Estonian Ethnomedicine. Plants 2022, 11, 994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astiti, M.A.; Jittmittraphap, A.; Leaungwutiwong, P.; Chutiwitoonchai, N.; Pripdeevech, P.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, S.; Kittakoop, P. LC-QTOF-MS/MS Based Molecular Networking Approach for the Isolation of α-Glucosidase Inhibitors and Virucidal Agents from Coccinia grandis (L.) Voigt. Foods 2021, 10, 3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simirgiotis, M.J.; Caligari, P.D.S.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G. Identification of Phenolic Compounds from the Fruits of the Mountain Papaya Vasconcellea Pubescens A. DC. Grown in Chile by Liquid Chromatography–UV Detection–Mass Spectrometry. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rached, W.; Barros, L.; Ziani, B.E.C.; Bennaceur, M.; Calhelha, R.C.; Heleno, S.A.; Alves, M.J.; Marouf, A.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS/MS Screening of Phytochemical Compounds and the Bioactive Properties of Different Plant Parts of Zizyphus lotus (L.) Desf. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 5898–5909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karar, M.; Kuhnert, N. UPLC-ESI-Q-TOF-MS/MS Characterization of Phenolics from Crataegus Monogyna and Crataegus Laevigata (Hawthorn) Leaves, Fruits and Their Herbal Derived Drops (Crataegutt Tropfen). J. Chem. Biol. Ther. 2015, 1, 1000102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zang, C.; Nie, Q.; Yang, B.; Zhang, B.; Duan, S. Simultaneous Determination of Seven Flavonoids, Two Phenolic Acids and Two Cholesterines in Tanreqing Injection by UHPLC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 163, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, C.M.S.; Habermann, G.; Marchi, M.R.R.; Zocolo, G.J. The Role of Matrix Effects on the Quantification of Abscisic Acid and Its Metabolites in the Leaves of Bauhinia variegata L. Using Liquid Chromatography Combined with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 24, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, K.; Seo, S.; Nakajima, J. Constituents from Leaves of Apocynum venetum L. J. Nat. Med. 2008, 62, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreca, D.; Gattuso, G.; Laganà, G.; Leuzzi, U.; Bellocco, E. C- and O-Glycosyl Flavonoids in Sanguinello and Tarocco Blood Orange (Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck) Juice: Identification and Influence on Antioxidant Properties and Acetylcholinesterase Activity. Food Chem. 2016, 196, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, E.A.; van den Bos, A.A.; Kite, G.C.; Veitch, N.C.; Simmonds, M.S.J. Flavonol Glycosides Acylated with 3-Hydroxy-3-Methylglutaric Acid as Systematic Characters in Rosa. Phytochemistry 2012, 81, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazuma, K.; Noda, N.; Suzuki, M. Malonylated Flavonol Glycosides from the Petals of Clitoria Ternatea. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheleva-Dimitrova, D.; Simeonova, R.; Gevrenova, R.; Savov, Y.; Balabanova, V.; Nasar-Eddin, G.; Bardarov, K.; Danchev, N. In Vivo Toxicity Assessment of Clinopodium vulgare L. Water Extract Characterized by UHPLC-HRMS. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 134, 110841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Liu, X.; Xu, H.; Gong, Y.; Yuan, F.; Gao, Y. On-Line HPLC-ABTS Screening and HPLC-DAD-MS/MS Identification of Free Radical Scavengers in Gardenia (Gardenia jasminoides Ellis) Fruit Extracts. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuengchamnong, N.; Krittasilp, K.; Ingkaninan, K. Characterisation of Phenolic Antioxidants in Aqueous Extract of Orthosiphon Grandiflorus Tea by LC-ESI-MS/MS Coupled to DPPH Assay. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 1287–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velamuri, R.; Sharma, Y.; Fagan, J.; Schaefer, J. Application of UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS in Phytochemical Profiling of Sage (Salvia officinalis) and Rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis). Planta Med. Int. Open 2020, 07, e133–e144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Li, B.; Han, Y.; Liu, A.; Zhang, J.; Peng, J.; Jiang, M.; Hou, Y.; Bai, G. A Rapid Integrated Bioactivity Evaluation System Based on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Quality Control of Flos Chrysanthemi. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 131, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Xu, Q.; Li, R.; Shi, L.; Han, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, G.; Qin, M. Chemical Profiles and Quality Evaluation of Buddleja Officinalis Flowers by HPLC-DAD and HPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 164, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Song, S.; Lee, I.; Kim, Y.; Yoo, I.; Ryoo, I.; Bae, K. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Constituents from Glechoma hederacea Var. Longituba. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2011, 21, 3483–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, G.; Xiao, H.; Liu, J.; Liang, X. Identification of Phenolic Constituents in Radix Salvia Miltiorrhizae by Liquid Chromatography/Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 20, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhu, S.K.; Okuyama, E.; Fujimoto, H.; Ishibashi, M. Diterpenes from Leucas Aspera Inhibiting Prostaglandin-Induced Contractions. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aihaiti, K.; Li, J.; Yaermaimaiti, S.; Liu, L.; Xin, X.; Aisa, H.A. Non-Volatile Compounds of Hyssopus Cuspidatus Boriss and Their Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venuprasad, M.P.; Kumar Kandikattu, H.; Razack, S.; Khanum, F. Phytochemical Analysis of Ocimum Gratissimum by LC-ESI–MS/MS and Its Antioxidant and Anxiolytic Effects. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2014, 92, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.U.; Mumtaz, M.W.; Mukhtar, H.; Rashid, U.; Akhtar, M.T.; Raza, S.A.; Nadeem, M. UHPLC-QTOF-MS/MS Based Phytochemical Characterization and Anti-Hyperglycemic Prospective of Hydro-Ethanolic Leaf Extract of Butea Monosperma. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Yang, M.; Ji, X.; Li, D.; Xie, Y.; Lyu, Y.; Zuo, Z. Protective Effect of Glechoma hederacea Extract against Gallstone Formation in Rodent Models. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Ham, S.L.; Khan, Z.; Kim, S.Y.; Choi, S.U.; Kim, C.S.; Lee, K.R. Terpenoids from Glechoma hederacea Var. Longituba and Their Biological Activities. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.Y.; Sung, B.; Kim, N.D. Role of Induced Programmed Cell Death in the Chemopreventive Potential of Apigenin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Amarat, W.; Abukhalil, M.H.; Alruhaimi, R.S.; Alqhtani, H.A.; Aldawood, N.; Alfwuaires, M.A.; Althunibat, O.Y.; Aladaileh, S.H.; Algefare, A.I.; Alanezi, A.A.; et al. Upregulation of Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling and Attenuation of Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Cell Death Mediate the Protective Effect of Apigenin against Cyclophosphamide Hepatotoxicity. Metabolites 2022, 12, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, P.; Shikha, D.; Thakur, M.; Aneja, A. Functionality of Apigenin as a Potent Antioxidant with Emphasis on Bioavailability, Metabolism, Action Mechanism and in Vitro and in Vivo Studies: A Review. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e13950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Khan, F.; Qari, H.A.; Oves, M. Rutin (Bioflavonoid) as Cell Signaling Pathway Modulator: Prospects in Treatment and Chemoprevention. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, Q.; Sui, Y.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, X. Rutin Protects Endothelial Dysfunction by Disturbing Nox4 and ROS-Sensitive NLRP3 Inflammasome. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 86, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, D.K.; Meena, A.; Dubey, V.; Masood, N.; Luqman, S. Rutin Protects T-butyl Hydroperoxide-Induced Oxidative Impairment via Modulating the Nrf2 and INOS Activity. Phytomedicine 2019, 55, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, B. Rutin Ameliorates Gout via Reducing XOD Activity, Inhibiting ROS Production and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Quail. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 158, 114175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M. Rosmarinic Acid. Phytochemistry 2003, 62, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, A.A.; Hassanen, E.I.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Tohamy, A.F.; Aboseada, M.A.; Hassan, H.M.; Zaki, A.R. Rosmarinic Acid Attenuates Chromium-Induced Hepatic and Renal Oxidative Damage and DNA Damage in Rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2020, 34, e22579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerogianni, P.S.; Chatziathanasiadou, M.V.; Diamantis, D.A.; Tzakos, A.G.; Galaris, D. Lipophilic Ester and Amide Derivatives of Rosmarinic Acid Protect Cells against H2O2-Induced DNA Damage and Apoptosis: The Potential Role of Intracellular Accumulation and Labile Iron Chelation. Redox Biol. 2018, 15, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vostálová, J.; Zdarilová, A.; Svobodová, A. Prunella Vulgaris Extract and Rosmarinic Acid Prevent UVB-Induced DNA Damage and Oxidative Stress in HaCaT Keratinocytes. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2010, 302, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Peak | RT (min) | Max. m/z (−/+) | Ion Formula | mSigma (−) | HRMS-MS/MS Fragment (ESI−), m/z/Fragment (ESI+), m/z | Class | Tentative ID | References: | Area Frac. % of Extract | Area Frac. % of 20% | Area Frac. % of 60% | Area Frac. % of 85% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.70 | 371.0632 | C15H15O11 | 0.7 | 209.0303 (100), 191.0207 (35) | phenolic acids | 4-caffeoylglucaric acid | [18] | 0.46 | 7.61 | nd | nd |
| 2 | 4.81 | 315.0734 | C13H15O9 | 5.6 | 315.0731 (100), 153.0185 (10.9), 109.0282 (1.4) | phenolic acids | gentisic acid 5-O-glucoside | [19] | 0.23 | nd | nd | |
| 3 | 5.21 | 371.0627 | C15H15O11 | 4.6 | 209.0309 (100), 191.0201 (40.5) | phenolic acids | 2-caffeoylglucaric acid | [18] | 0.59 | 7.20 | nd | nd |
| 4 | 5.56 | 353.0889 | C16H17O9 | 8.2 | 353.0888 (8,6), 191.0566 (100), 179.0355 (54.4), 135.0436 (7.2) | phenolic acids | 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid (neochlorogenic acid) | identified by comparison to reference compound | 2.75 | 27.34 | ta | nd |
| 5 | 6.11 | 297.0624 | C13H13O8 | 3.6 | 179.0360 (40), 135.0289 (100) | phenolic acids | 3-O-caffeoylthreonic acid | [20] | 0.8 | 9.09 | ta | nd |
| 6 | 6.75 | 297.0622 | C13H13O8 | 9.6 | 179.0350 (17.3), 135.0281 (100) | phenolic acids | 2-O-caffeoylthreonic acid | [20] | 2.77 | 23.98 | ta | nd |
| 7 | 7.24 | 337.0933 | C16H17O8 | 11.1 | 191.0891 (24.6), 163.0392 (100) | phenolic acids | p-coumaroylquinic acid | [20] | 0.99 | 9.27 | ta | nd |
| 8 | 7.91 | 353.0884 | C16H17O9 | 3.4 | 353 (0,4, 191 (100), 179 (0,8), 173 (0,4), 161 (0,6) | phenolic acids | 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid (chlorogenic acid) | identified by comparison to reference compound | 4.94 | 20.84 | 5.00 | nd |
| 9 | 8.38 | 353.0887 | C16H17O9 | 5.8 | 353.0888 (9.6), 191.0566 (100), 179.0356 (77.7), 173.0454 (72.3), 161.0246 (2.6), 135.0437 (17.3) | phenolic acids | 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid (cryptochlorogenic acid) | identified by comparison to reference compound | 0.99 | ta | ta | nd |
| 10 | 8.53 | 325.0572 | C14H13O9 | 13.8 | 193.0510 (100) | phenolic acids | fertaric acid | [21] | 0.38 | ta | ta | nd |
| 11 | 8.96 | 625.1414 | C27H29O17 | 7.1 | 625.1420 (11.6), 463.0870 (100), 301.0354 (66.5) | flavonoid | quercetin-3-gentiobioside (quercetin 3-O-diglucoside) | [22] | 0.79 | nd | ta | nd |
| 12 | 9.52 | 297.0620 | C13H13O8 | 10.5 | 179.0360 (33.3), 135.0276 (100) | phenolic acids | 4-O-caffeoylthreonic acid | [20] | 0.98 | nd | ta | nd |
| 13 | 9.72 | 353.0885 | C16H17O9 | 1.7 | 191.0563 (100) | phenolic acids | 1-O-caffeoylquinic acid | identified by comparison to reference compound | 0.48 | nd | ta | nd |
| 14 | 9.96 | 387.1662 | C18H27O9 | 3.3 | 387.1662 (100), 207.1032 (14.3) | oxylipins | tuberonic acid glucoside | [23] | 1.24 | nd | ta | nd |
| 711.1416 | C30H31O20 | 9.4 | 667.1517 (9.1), 505.0999 (24.1) 463.0859 (100), 301.0360 (53.6) | flavonoids | quercetin 3-O-(6″-malonylglucoside)-7-glucoside | [24,25] | nd | ta | nd | |||
| 15 | 10.25 | 395.099 | C18H19O10 | 5.5 | 335.0780 (3.5), 233.0674 (100) | phenolic glycosides | 7-β-galactopyranosyl-oxycoumarin-4-acetic acid methyl ester | [26] | 1.1 | nd | ta | nd |
| 16 | 11.98 | 741.1870 | C32H37O20 | 14.2 | 741.1904 (13.7), 591.1338 (2.4), 475.0886 (1.8), 3010.0282 (100) | flavonoids | quercetin rutinoside pentoside | [27,28] | 2.25 | nd | 3.07 | nd |
| 755.2050 | C33H39O20 | 7.2 | 755.2046 (12.7), 300.0279(100) | flavonoids | quercetin-3-O-(2″rhamnosyl)-7-O-rutinoside (manghaslin) | [29] | nd | nd | ||||
| 17 | 13.43 | 609.1460 | C27H29O16 | 5.1 | 609.1463 (27.9), 301.0343 (100) | flavonoids | rutin (quercetin rutinoside, quercetin-3-O-α-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-D-glucopyranose) | identified by comparison to reference compound | 8.31 | nd | 11.29 | nd |
| 18 | 13.69 | 389.1822 | C18H29O9 | 10.6 | 389.1823 (100), 227.1298 (7.6) 209.1187 (9.6) | fatty acyls | (−)-11-hydroxy-9,10-dihydrojasmonic acid 11-β-D-glucoside | [30,31] | 1.74 | nd | 2.3 | nd |
| 19 | 13.82 | 753.1892 | C33H37O20 | 21.9/12.4 | 609.1473 (16.1), 301.0279 (100) | flavonoids | quercetin deoxyhexsoside hexsoside 3-hydroxyl-3-methyloglutaryl | not found | 3.11 | nd | 3.74 | nd |
| 463.0885 | C21H19O12 | 30.5/7.9 | 463.0899 (9.3), 301.0348 (100) | flavonoids | hyperoside (quercetin 3-galactoside) | identified by comparison to reference compound | nd | nd | ||||
| 20 | 14.05 | 447.0936 | C21H19O11 | 4.4 | 447.0932 (53.1), 285.0405 (100) | flavonoids | luteolin 7-O-glucoside | identified by comparison to reference compound [32] | 0.88 | nd | ta | nd |
| 21 | 14.24 | 279.1238 | C15H19O5 | 5.8 | 279.1229 (73.8), 217.1230 (100), 165.0898 (53.7) | sesquiterpenes | phaseic acid | [33] | 1.2 | nd | ta | nd |
| 22 | 14.59 | 549.0889 | C24H21O15 | 7.4 | 505.0995 (9.5), 301.0277 (100) | flavonoids | quercetin 3-O-(6″-malonylglucoside)/quercetin 3-O-(6′′-malonylgalactoside | [34] | 1.45 | nd | 1.75 | nd |
| 23 | 14.69 | 607.1306 | C27H27O16 | 4.5 | 463.0887 (27.1), 301.0277 (100) | flavonoids | quercetin 3-[6″-(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl)-galactoside] | [29,35,36] | 3.42 | nd | 2.51 | nd |
| 593.1508 | C27H29O15 | 15.8 | 593.1509 (26.5), 285.0399 (100) | flavonoids | kaempferol 3-robinobioside | [37] | nd | 2.37 | nd | |||
| 24 | 14.81 | 717.1457/719.1591 | C36H29O16 | 7.4 | (+) 521.1081 (2), 295.0599 (100), 181.0493 (8.3) | phenolic acids | yunnaneic acid G/salvianolic acid E/salvianolic acid L/isosalvianolic acid B/lithospermic acid B/clinopodic acid I | [38] | 3.76 | nd | 4.92 | nd |
| 25 | 15.04 | 515.1199 | C25H23O12 | 16.3 | 353.0880 (50.9), 191.0563 (100), 179.0348 (58.5) | phenolic acids | 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid | identified by comparison to reference compound and [39] | 2.08 | nd | nd | |
| 26 | 15.11 | 719.1622 | C36H31O16 | 3.2 | 359.0779 (53.2), 243.0299 (36.7), 229.0142 (49.3), 197.0459 (82.7), 179.0351 (25.2), 161.0237 (100), 135.0433 (6.1) | cyclobutane lignans | sagerinic acid | [40,41,44] | 1.80 | nd | 4.83 | nd |
| 27 | 15.55 | 431.0985 | C21H19O10 | 2.2 | 431.0985 (100), 269.0447 (50) | flavonoids | apigenin 7-O-glucoside | identified by comparison to reference compound and [41] | 1.81 | nd | nd | |
| 28 | 15.90 | 533.0946 | C24H21O14 | 14.8 | 489.1047 (100), 285.0407 (87.9) | flavonoids | luteolin 7-O-(6″-malonylglucoside) | [42] | 3.06 | nd | 1.63 | nd |
| 29 | 16.02 | 359.0777 | C18H15O8 | 8.0 | 197.0459 (100), 179.0352 (32.1), 161.0238 (88.9), 135.0435 (5.0), 133.0275 (6.3) | phenolic acids | rosmarinic acid | identified by comparison to reference compound | 15.94 | nd | 22.00 | nd |
| 591.1367 | C27H27O15 | 14.3 | 489.1041 (77.3), 447.0948 (34.3), 285.0404 (100) | flavonoids | kaempferol 3-[6″-(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl)-glucoside] | [35] | nd | 2.15 | nd | |||
| 30 | 17.19 | 717.1467 | C36H29O16 | 6.7 | 519.0942 (3.4), 339.0515 (47.9), 321.0408 (100) | phenolic acids | yunnaneic acid G/salvianolic acid E/salvianolic acid L/isosalvianolic acid B/lithospermic acid B/clinopodic acid I | [38] | 5.87 | nd | 8.37 | nd |
| 31 | 17.42 | 517.0991/519.1129 | C24H21O13 | 14.5 | 473.1103 (5.5), 269.0457 (100)/519.1130 (89.9), 433.1128 (8.6), 271.0599 (100) | flavonoids | apigenin 7-(6″-malonylglucoside) | [43] | 2.79 | nd | 4.82 | nd |
| 32 | 18.21 | 773.3969 | C38H61O16 | 10.4 | 773.3969 (56.2), 627.3386 (100), 465.2845 (17.7) | diterpenes | diterpene dHex-Hex-HMG | not found | 4.87 | nd | 5.82 | 40.37 |
| 33 | 18.32 | 367.1405 | C18H23O8 | 10.8 | 163.0761 (100), 148.0511 (78.3) | lactones | unknown lactone | not found | 1.26 | nd | 1.43 | ta |
| 34 | 18.44 | 373.0932 | C19H17O8 | 8.9 | 197.0453 (95.4), 175.0404 (73.6), 135.0435 (100) | phenolic acids | 3-O-methyl-rosmarinic acid | [44] | 1.29 | nd | ta | |
| 35 | 18.65 | 373.0934 | C19H17O8 | 1.2 | 179.0350 (17.6), 135.0434 (100) | phenolic acids | rosmarinic acid methyl ester | [44,47] | 8.58 | nd | 12.01 | ta |
| 717.1469 | C36H29O16 | 16.4 | 519.0920 (10.5), 339.0515 (100), 321.0424 (10.6), 295.0621 (5.6) | phenolic acids | yunnaneic acid G/salvianolic acid E/salvianolic acid L/isosalvianolic acid B/lithospermic acid B/clinopodic acid I | [38] | nd | nd | ta | |||
| 745.1782 | C38H33O16 | 17.6 | 489.1197 (57.8), 445.1294 (68.1), 379.0825 (42.5), 339.0513 (100), 295.0617 (38.9), 229.0142 (22.6) | phenolic acids | dimethyl lithospermate B | [45] | nd | nd | ta | |||
| 36 | 18.92 | 717.1458 | C36H29O16 | 6.4 | 519.0925 (8.1), 339.0510 (100), 321.0430 (12.5), 295.0626 (6.4) | phenolic acids | yunnaneic acid G/salvianolic acid E/salvianolic acid L/isosalvianolic acid B/lithospermic acid B/clinopodic acid I | [38] | 1.32 | nd | nd | ta |
| 37 | 20.43 | 771.3812 | C38H59O16 | 6.4 | 591.3215 (10.6), 547.3276 (100), 465.2870 (8.3), 465.2870 (8.2), 161.0447 (46.8) | diterpens | leucasperoside C | [46] | 1.67 | nd | nd | 26.32 |
| 38 | 21.59 | 269.0456 | C15H9O16 | 4.6 | 269.0458 (100), 225.0562 (1.6) | flavonoids | apigenin | identified by comparison to reference compound and [49] | 0.88 | nd | nd | 17.55 |
| 39 | 22.01 | 313.072 | C17H13O6 | 5.3 | 161.0238 (100) | flavon | unknown flavon | not found | 0.88 | nd | nd | 8.38 |
| 40 | 24.78 | 327.0876 | C18H15O6 | 9.8 | 327,0875 (100), 312.0622 (32.5), 284.0656 (14.2), 242.0557 (16.6), 150.0317 (37.3) | flavon | salvigenin | [48] | 0.27 | nd | nd | 7.37 |
| Compound | Phenolic Acids (mg/g ± SD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extract | 20% Fraction | 60% of Fraction | 85% of Fraction | |
| 4-caffeoylglucaric acid | traces | 3.2 ± 0.19 | ND | ND |
| gentisic acid 5-O-glucoside | 0.82 ± 0.17 | 2.58 ± 0.1 | ND | ND |
| 2-caffeoylglucaric acid | 1.15 ± 0.29 | 5.35 ± 0.71 | ND | ND |
| 3-O-caffeoylquinic acid (neochlorogenic acid) | 16.6 ± 1.07 | 45.07 ± 1.43 | 1.44 ± 0.16 | ND |
| 3-O-caffeoylthreonic acid | 2.69 ± 0.63 | 8.09 ± 0.25 | ND | |
| 2-O-caffeoylthreonic acid | 13.55 ± 0.06 | 35.35 ± 1.39 | 2.83 ± 0.31 | Traces |
| p-coumaroylquinic acid | 1.1 ± 0.23 | 3.67 ± 0.6 | ND | |
| 5-O-caffeoylquinic acid (chlorogenic acid) | 27.44 ± 0.54 | 18.58 ± 0.95 | 31.77 ± 4.03 | ND |
| 4-O-caffeoylquinic acid (cryptochlorogenic acid) | 2.61 ± 0.64 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | 3.76 ± 0.45 | ND |
| fertaric acid | 3.32 ± 0.78 | 2.53 ± 0.32 | 4.78 ± 0.61 | 1.36 ± 0.08 |
| 4-O-caffeoylthreonic acid | 1.87 ± 0.42 | ND | 2.6 ± 0.32 | ND |
| 1-O-caffeoylquinic acid | 1.12 ± 0.22 | ND | 1.62 ± 0.22 | ND |
| 7-β-galactopyranosyl-oxycoumarin-4-acetic acid methyl ester | 2.93 ± 0.60 | ND | 4.34 ± 0.52 | ND |
| yunnaneic acid G/salvianolic acid E/salvianolic acid L/isosalvianolic acid B/lithospermic acid B/clinopodic acid I | 5.71 ± 0.95 | ND | 9.14 ± 1.38 | ND |
| rosmarinic acid | 63.72 ± 1.27 | ND | 101.52 ± 5.76 | Traces |
| yunnaneic acid G/salvianolic acid E/salvianolic acid L/isosalvianolic acid B/lithospermic acid B/clinopodic acid I | 0.91 ± 0.55 | ND | 1.29 ± 0.18 | ND |
| yunnaneic acid G/salvianolic acid E/salvianolic acid L/isosalvianolic acid B/lithospermic acid B/clinopodic acid I | 7.59 ± 0.80 | ND | 12.3 ± 1.65 | ND |
| 3′-O-methyl-rosmarinic acid | 1.46 ± 0.13 | Traces | 2.16 ± 0.32 | ND |
| rosmarinic acid methyl ester | 23.08 ± 0.94 | Traces | 36.83 ± 1.47 | Traces |
| total phenolic acids | 177.64 | 126.13 | 216.38 | 1.36 |
| Compound | Flavonoids (mg/g ± SD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extract | 20% Fraction | 60% Fraction | 85% Fraction | |
| quercetin 3-O-(6″-malonylglucoside)-7-glucoside | 2.16 ± 0.58 | ND | 3.85 ± 0.53 | ND |
| quercetin-3-O-(2″rhamnosyl)-7-O-rutinoside | 4.52 ± 1.19 | ND | 7.56 ± 0.34 | ND |
| rutin | 38.65 ± 4.92 | ND | 62.31 ± 0.98 | Traces |
| hyperoside | 9.03 ± 2.24 | ND | 14.79 ± 2.01 | 1.25 ± 0.1 |
| quercetin deoxyhexsoside hexsoside 3-hydroxyl-3-methyloglutaryl; luteolin 7-O-glucoside | 8.68 ± 2.28 | ND | 14.22 ± 2.04 | ND |
| quercetin 3-[6′′-(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl)-galactoside] | 14.75 ± 4.14 | ND | 23.94 ± 2.89 | Traces |
| apigenin 7-O-glucoside | 6.32 ± 1.74 | ND | 10.14 ± 0.6 | Traces |
| luteolin 7-O-(6″-malonylglucoside) | 5.94 ± 1.99 | ND | 9.75 ± 0.81 | ND |
| kaempferol 3-[6″-(3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl)-glucoside] | 8.04 ± 2.11 | ND | 12.75 ± 1.8 | ND |
| apigenin 7-(6″-malonylglucoside) | 10.51 ± 2.6 | ND | 17.41 ± 1.65 | ND |
| luteolin | 2.05 ± 0.6 | ND | 3.07 ± 0.5 | 2.1 ± 0.19 |
| apigenin | 3.49 ± 1.03 | ND | 2.33 ± 0.38 | 26.17 ± 1.44 |
| unknown flavon | 1.66 ± 0.7 | ND | 1.98 ± 0.12 | 2.5 ± 0.24 |
| total flavonoids | 115.8 | 184.1 | 32.02 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sławińska, N.; Kluska, M.; Moniuszko-Szajwaj, B.; Stochmal, A.; Woźniak, K.; Olas, B. New Aspect of Composition and Biological Properties of Glechoma hederacea L. Herb: Detailed Phytochemical Analysis and Evaluation of Antioxidant, Anticoagulant Activity and Toxicity in Selected Human Cells and Plasma In Vitro. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071671
Sławińska N, Kluska M, Moniuszko-Szajwaj B, Stochmal A, Woźniak K, Olas B. New Aspect of Composition and Biological Properties of Glechoma hederacea L. Herb: Detailed Phytochemical Analysis and Evaluation of Antioxidant, Anticoagulant Activity and Toxicity in Selected Human Cells and Plasma In Vitro. Nutrients. 2023; 15(7):1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071671
Chicago/Turabian StyleSławińska, Natalia, Magdalena Kluska, Barbara Moniuszko-Szajwaj, Anna Stochmal, Katarzyna Woźniak, and Beata Olas. 2023. "New Aspect of Composition and Biological Properties of Glechoma hederacea L. Herb: Detailed Phytochemical Analysis and Evaluation of Antioxidant, Anticoagulant Activity and Toxicity in Selected Human Cells and Plasma In Vitro" Nutrients 15, no. 7: 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071671
APA StyleSławińska, N., Kluska, M., Moniuszko-Szajwaj, B., Stochmal, A., Woźniak, K., & Olas, B. (2023). New Aspect of Composition and Biological Properties of Glechoma hederacea L. Herb: Detailed Phytochemical Analysis and Evaluation of Antioxidant, Anticoagulant Activity and Toxicity in Selected Human Cells and Plasma In Vitro. Nutrients, 15(7), 1671. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15071671







