Intergenerational Inheritance of Hepatic Steatosis in a Mouse Model of Childhood Obesity: Potential Involvement of Germ-Line microRNAs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
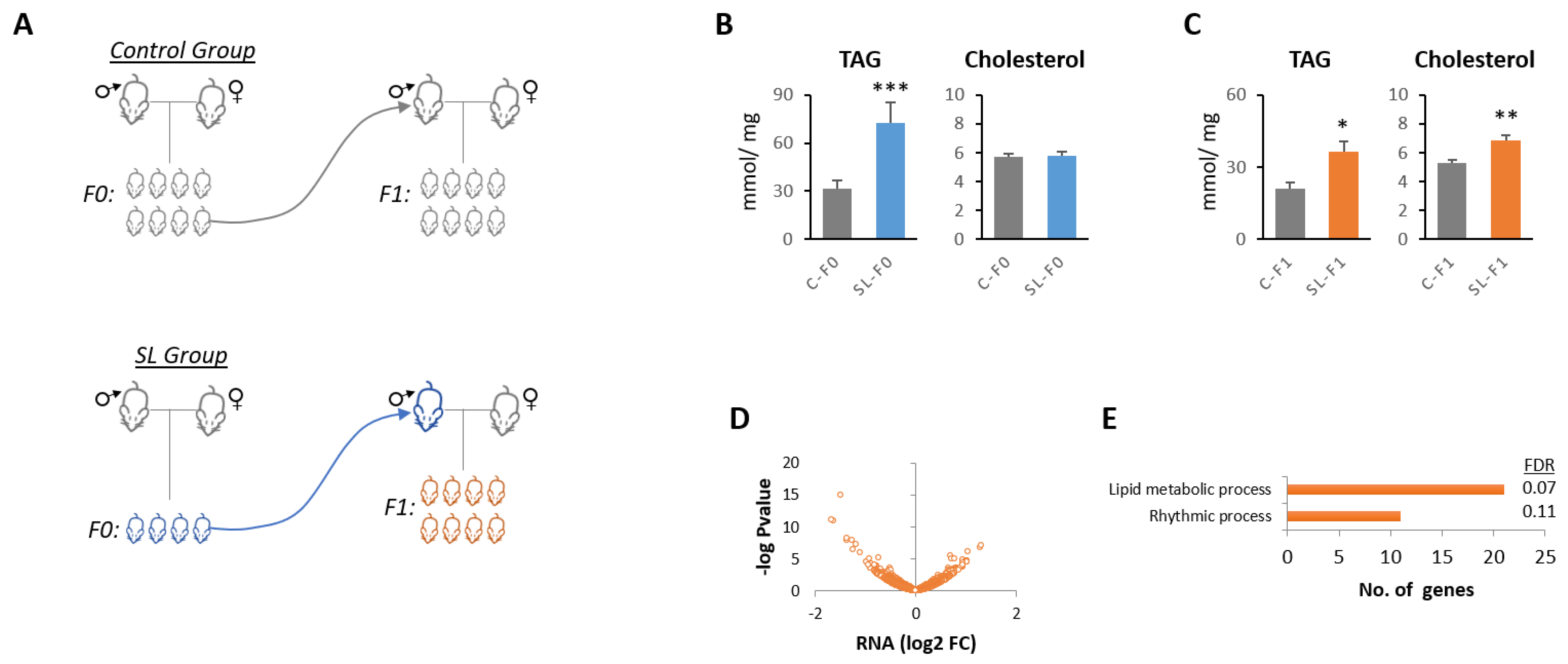
2.1. Animal Care and Experimental Design
2.2. TAG and Cholesterol Determination
2.3. Tissue Culture and Incubations with AZA
2.4. Sperm Isolation
2.5. DNA and RNA Extraction
2.6. Affymetrix Microarrays
2.7. Agilent DNA Methylation Microarrays
2.8. Small RNA Sequencing and Analysis
2.9. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
2.10. Statistical Analysis
2.11. Data and Resource Availability
3. Results
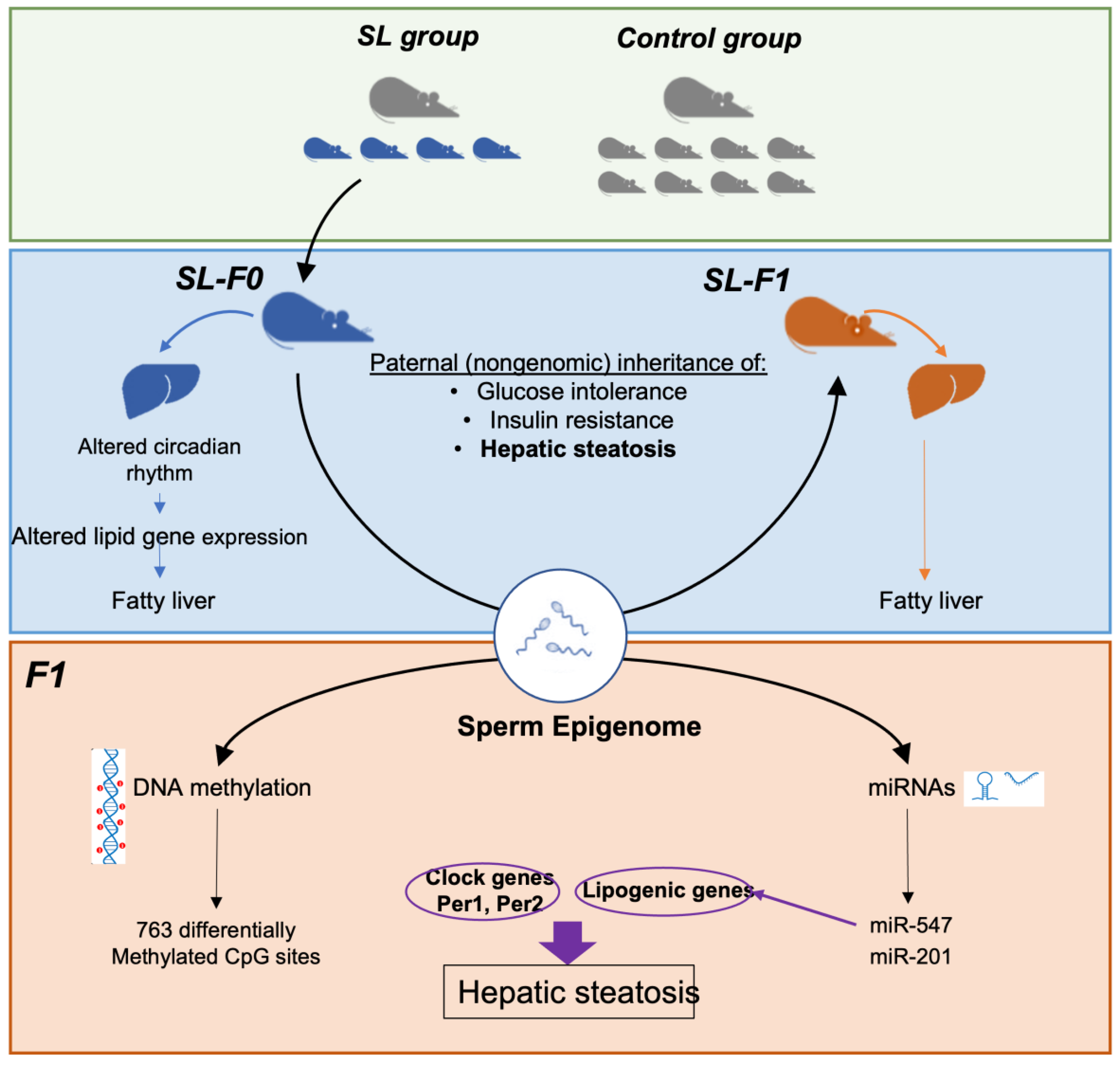
3.1. Paternal Overnutrition Induced Hepatic Steatosis in the First-Generation Offspring
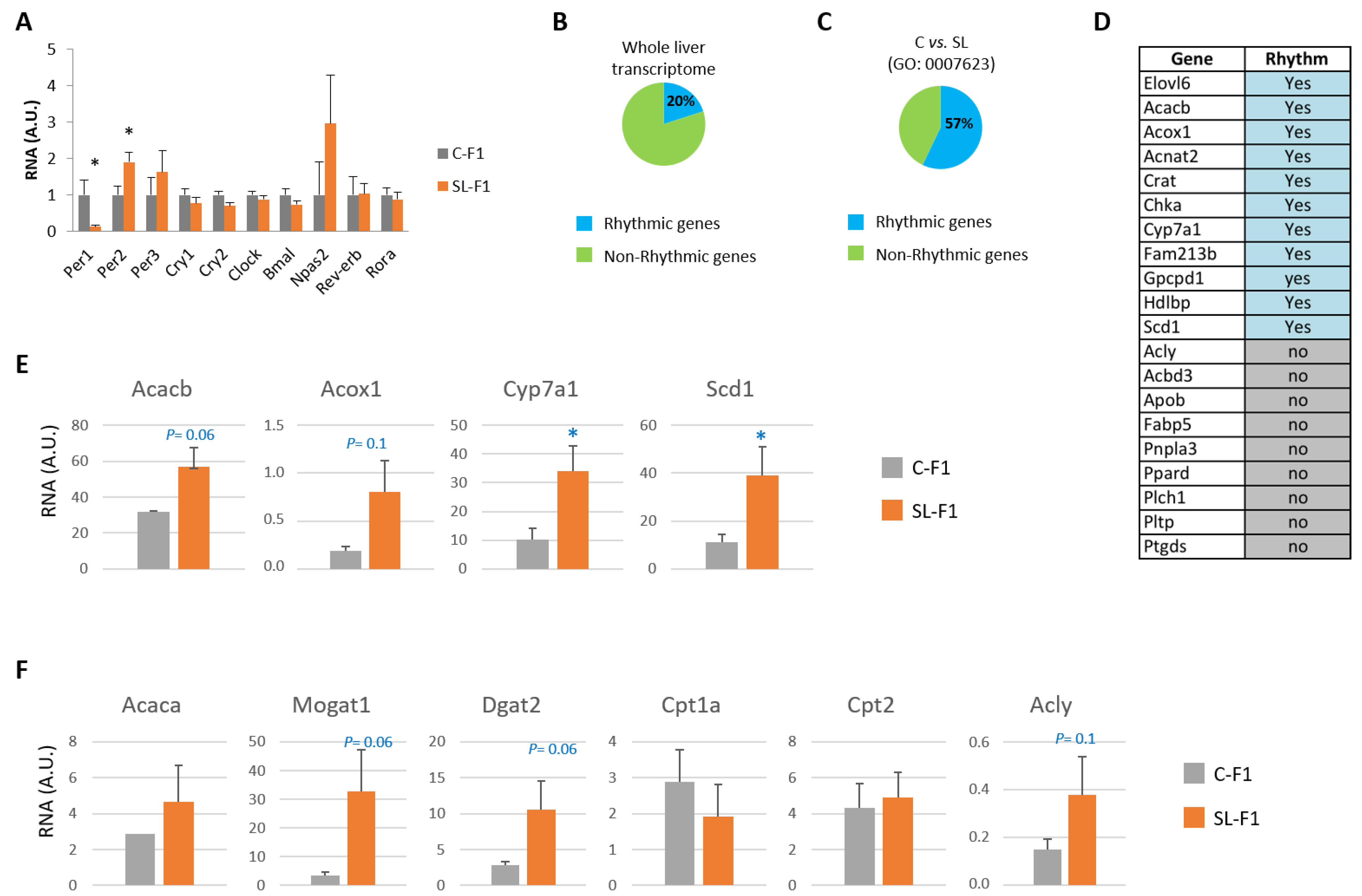
3.2. Litter Size Reduction Altered the Expression of Genes Involved in the Circadian Rhythm and Lipid Metabolism
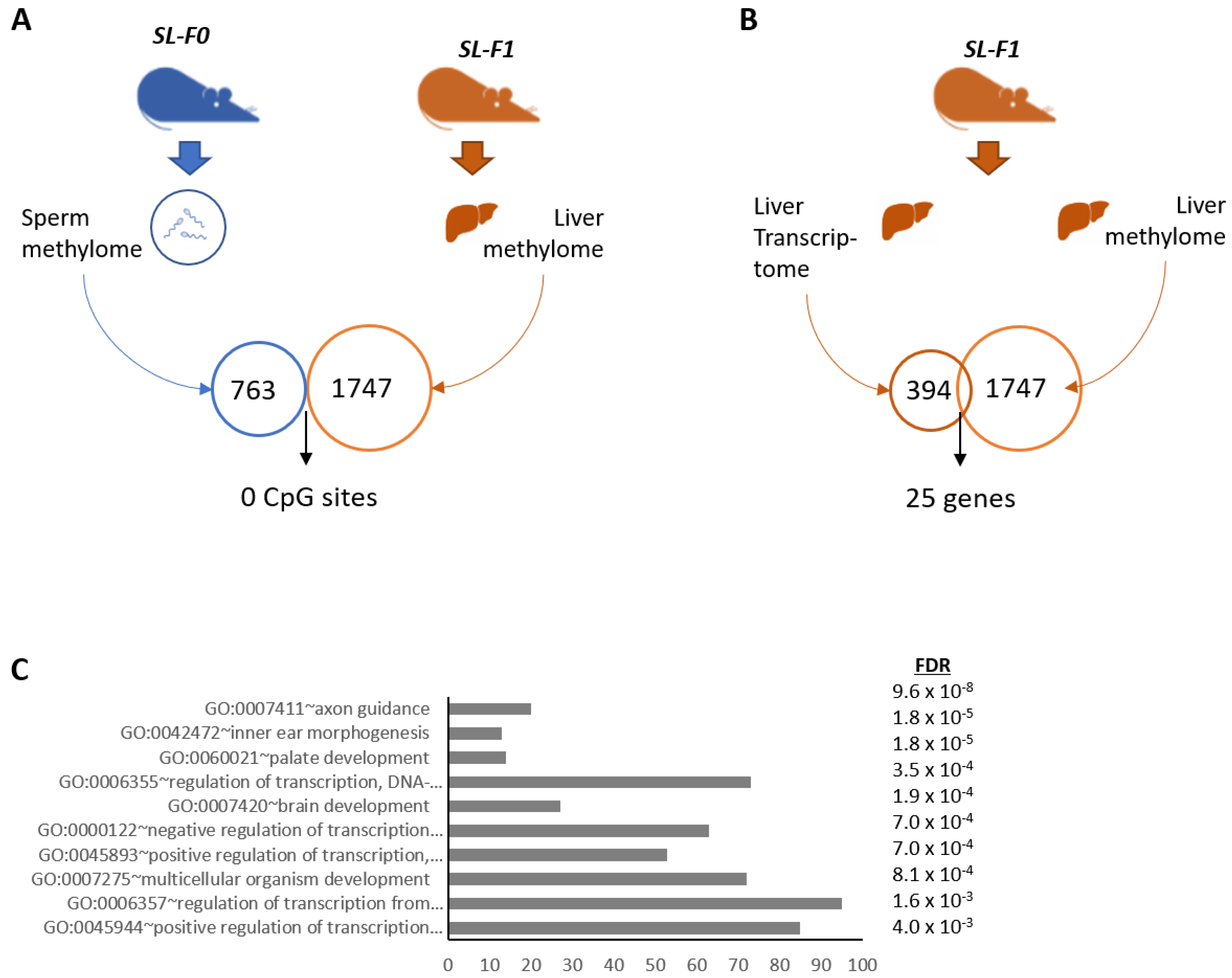
3.3. DNA Methylation Did Not Correlate with the Expression of Clock and Lipid-Related Genes
3.4. Two miRNAs Were Differentially Expressed in the Testes of SL-F0 Mice and Might Be Linked to the Hepatic Lipid Metabolism in the Offspring
4. Discussion
- -
- First, both miRNAs are expressed in Sertoli cells during postnatal development [53]. Together, they are involved in the maturation of spermatocytes and are prominently expressed in mature spermatozoa but not in oocytes [54]. Hence, they are strong candidates for being carriers of paternal information onto the offspring.
- -
- Second, the hepatic miRNA-targetome has been recently reported [55]. It provides evidence that miR-201 and mir-547 may regulate the expression of lipid-related target genes, including Acox1, Cpt2, Apob, or Scd1. Considering that these genes were identified in our hepatic transcriptome, here, we make the case that both microRNAs might be inherited–transmitted from SL-F0 male mice and influence the hepatic lipid transcriptome.
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The, N.S.; Suchindran, C.; North, K.E.; Popkin, B.M.; Gordon-Larsen, P. Association of Adolescent Obesity with Risk of Severe Obesity in Adulthood. JAMA 2010, 304, 2042–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, L.J.; Langley-Evans, S.C.; McMullen, S. Childhood Obesity and Risk of the Adult Metabolic Syndrome: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Obes. 2012, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logue, J.; Sattar, N. Childhood Obesity: A Ticking Time Bomb for Cardiovascular Disease? Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 90, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, J.J.; Kelly, J. Long-Term Impact of Overweight and Obesity in Childhood and Adolescence on Morbidity and Premature Mortality in Adulthood: Systematic Review. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Chillarón, J.C.; Díaz, R.; Martínez, D.; Pentinat, T.; Ramón-Krauel, M.; Ribó, S.; Plösch, T. The Role of Nutrition on Epigenetic Modifications and Their Implications on Health. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2242–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pembrey, M.; Saffery, R.; Bygren, L.O. Human Transgenerational Responses to Early-Life Experience: Potential Impact on Development, Health and Biomedical Research. J. Med. Genet. 2014, 51, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaati, G.; Bygren, L.O.; Pembrey, M.; Sjöström, M. Transgenerational Response to Nutrition, Early Life Circumstances and Longevity. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 15, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaati, G.; Bygren, L.O.; Edvinsson, S. Cardiovascular and Diabetes Mortality Determined by Nutrition during Parents’ and Grandparents’ Slow Growth Period. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 10, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pembrey, M.E.; Bygren, L.O.; Kaati, G.; Edvinsson, S.; Northstone, K.; Sjöström, M.; Golding, J. ALSPAC Study Team Sex-Specific, Male-Line Transgenerational Responses in Humans. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 14, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bygren, L.O. Intergenerational Health Responses to Adverse and Enriched Environments. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2013, 34, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billah, M.M.; Khatiwada, S.; Morris, M.J.; Maloney, C.A. Effects of Paternal Overnutrition and Interventions on Future Generations. Int. J. Obes. 2022, 46, 901–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soubry, A. Epigenetics as a Driver of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease: Did We Forget the Fathers? Bioessays 2018, 40, 1700113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soubry, A. POHaD: Why We Should Study Future Fathers. Environ. Epigenetics 2018, 4, dvy007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra-Vargas, M.; Ramon-Krauel, M.; Lerin, C.; Jimenez-Chillaron, J.C. Size Does Matter: Litter Size Strongly Determines Adult Metabolism in Rodents. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramon-Krauel, M.; Pentinat, T.; Bloks, V.W.; Cebrià, J.; Ribo, S.; Pérez-Wienese, R.; Vilà, M.; Palacios-Marin, I.; Fernández-Pérez, A.; Vallejo, M.; et al. Epigenetic Programming at the Mogat1 Locus May Link Neonatal Overnutrition with Long-Term Hepatic Steatosis and Insulin Resistance. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 6025–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribas-Aulinas, F.; Ribo, S.; Parra-Vargas, M.; Fernández-Pérez, A.; Cebrià, J.; Guardiola-Perello, M.; Ramon-Krauel, M.; Lerin, C.; Diaz, R.; Kalko, S.G.; et al. Neonatal Overfeeding during Lactation Rapidly and Permanently Misaligns the Hepatic Circadian Rhythm and Programmes Adult NAFLD. Mol. Metab. 2021, 45, 101162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribas-Aulinas, F.; Parra-Vargas, M.; Ramon-Krauel, M.; Diaz, R.; Lerin, C.; Cambras, T.; Jimenez-Chillaron, J.C. Time-Restricted Feeding during Puberty Ameliorates Adiposity and Prevents Hepatic Steatosis in a Mouse Model of Childhood Obesity. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentinat, T.; Ramon-Krauel, M.; Cebria, J.; Diaz, R.; Jimenez-Chillaron, J.C. Transgenerational Inheritance of Glucose Intolerance in a Mouse Model of Neonatal Overnutrition. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 5617–5623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daxinger, L.; Whitelaw, E. Understanding Transgenerational Epigenetic Inheritance via the Gametes in Mammals. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkin, I.; Barrès, R. Sperm Epigenetics and Influence of Environmental Factors. Mol. Metab. 2018, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soubry, A.; Guo, L.; Huang, Z.; Hoyo, C.; Romanus, S.; Price, T.; Murphy, S.K. Obesity-Related DNA Methylation at Imprinted Genes in Human Sperm: Results from the TIEGER Study. Clin. Epigenetics 2016, 8, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nätt, D.; Kugelberg, U.; Casas, E.; Nedstrand, E.; Zalavary, S.; Henriksson, P.; Nijm, C.; Jäderquist, J.; Sandborg, J.; Flinke, E.; et al. Human Sperm Displays Rapid Responses to Diet. PLoS Biol. 2019, 17, e3000559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houfflyn, S.; Matthys, C.; Soubry, A. Male Obesity: Epigenetic Origin and Effects in Sperm and Offspring. Curr. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2017, 3, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keyhan, S.; Burke, E.; Schrott, R.; Huang, Z.; Grenier, C.; Price, T.; Raburn, D.; Corcoran, D.L.; Soubry, A.; Hoyo, C.; et al. Male Obesity Impacts DNA Methylation Reprogramming in Sperm. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soubry, A.; Murphy, S.K.; Vansant, G.; He, Y.; Price, T.M.; Hoyo, C. Opposing Epigenetic Signatures in Human Sperm by Intake of Fast Food Versus Healthy Food. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 625204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donkin, I.; Versteyhe, S.; Ingerslev, L.R.; Qian, K.; Mechta, M.; Nordkap, L.; Mortensen, B.; Appel, E.V.R.; Jørgensen, N.; Kristiansen, V.B.; et al. Obesity and Bariatric Surgery Drive Epigenetic Variation of Spermatozoa in Humans. Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Chillaron, J.C.; Ramon-Krauel, M.; Ribo, S.; DIaz, R. Transgenerational Epigenetic Inheritance of Diabetes Risk as a Consequence of Early Nutritional Imbalances. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2016, 75, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero-Bosagna, C.; Skinner, M.K. Environmentally Induced Epigenetic Transgenerational Inheritance of Phenotype and Disease. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2012, 354, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champagne, F.A. Epigenetic Legacy of Parental Experiences: Dynamic and Interactive Pathways to Inheritance. Dev. Psychopathol. 2016, 28, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gapp, K.; von Ziegler, L.; Tweedie-Cullen, R.Y.; Mansuy, I.M. Early Life Epigenetic Programming and Transmission of Stress-Induced Traits in Mammals: How and When Can Environmental Factors Influence Traits and Their Transgenerational Inheritance? Bioessays 2014, 36, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro Barbosa, T.; Ingerslev, L.R.; Alm, P.S.; Versteyhe, S.; Massart, J.; Rasmussen, M.; Donkin, I.; Sjögren, R.; Mudry, J.M.; Vetterli, L.; et al. High-Fat Diet Reprograms the Epigenome of Rat Spermatozoa and Transgenerationally Affects Metabolism of the Offspring. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.F.; Lin, R.C.Y.; Laybutt, D.R.; Barres, R.; Owens, J.A.; Morris, M.J. Chronic High-Fat Diet in Fathers Programs β 2-Cell Dysfunction in Female Rat Offspring. Nature 2010, 467, 963–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carone, B.R.; Fauquier, L.; Habib, N.; Shea, J.M.; Hart, C.E.; Li, R.; Bock, C.; Li, C.; Gu, H.; Zamore, P.D.; et al. Paternally Induced Transgenerational Environmental Reprogramming of Metabolic Gene Expression in Mammals. Cell 2010, 143, 1084–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, D.; Pentinat, T.; Ribó, S.; Daviaud, C.; Bloks, V.W.; Cebria, J.; Villalmanzo, N.; Kalko, S.G.; Ramon-Krauel, M.; Díaz, R.; et al. In Utero Undernutrition in Male Mice Programs Liver Lipid Metabolism in the Second-Generation Offspring Involving Altered Lxra DNA Methylation. Cell Metab. 2014, 19, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, U.; Conine, C.C.; Shea, J.M.; Boskovic, A.; Derr, A.G.; Bing, X.Y.; Belleannee, C.; Kucukural, A.; Serra, R.W.; Sun, F.; et al. Biogenesis and Function of TRNA Fragments during Sperm Maturation and Fertilization in Mammals. Science 2016, 351, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Yan, M.; Cao, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Feng, G.H.; Peng, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Sperm TsRNAs Contribute to Intergenerational Inheritance of an Acquired Metabolic Disorder. Science 2016, 351, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, V.; Fourré, S.; de Abreu, D.A.F.; Derieppe, M.-A.; Remy, J.-J.; Rassoulzadegan, M. RNA-Mediated Paternal Heredity of Diet-Induced Obesity and Metabolic Disorders. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irizarry, R.A.; Hobbs, B.; Collin, F.; Beazer-Barclay, Y.D.; Antonellis, K.J.; Scherf, U.; Speed, T.P. Exploration, Normalization, and Summaries of High Density Oligonucleotide Array Probe Level Data. Biostatistics 2003, 4, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breitling, R.; Armengaud, P.; Amtmann, A.; Herzyk, P. Rank Products: A Simple, yet Powerful, New Method to Detect Differentially Regulated Genes in Replicated Microarray Experiments. FEBS Lett. 2004, 573, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and Integrative Analysis of Large Gene Lists Using DAVID Bioinformatics Resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabatake, M.; Blyth, B.J.; Daino, K.; Imaoka, T.; Nishimura, M.; Fukushi, M.; Shimada, Y. DNA Methylation Patterns in Rat Mammary Carcinomas Induced by Pre- and Post-Pubertal Irradiation. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and Memory-Efficient Alignment of Short DNA Sequences to the Human Genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An Efficient General Purpose Program for Assigning Sequence Reads to Genomic Features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, T.M.; Eddy, S.R. TRNAscan-SE: A Program for Improved Detection of Transfer RNA Genes in Genomic Sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Z.; Roy, C.K.; Dong, X.; Bolcun-Filas, E.; Wang, J.; Han, B.W.; Xu, J.; Moore, M.J.; Schimenti, J.C.; Weng, Z.; et al. An Ancient Transcription Factor Initiates the Burst of PiRNA Production during Early Meiosis in Mouse Testes. Mol. Cell 2013, 50, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, S.; Antoch, M.P.; Miller, B.H.; Su, A.I.; Schook, A.B.; Straume, M.; Schultz, P.G.; Kay, S.A.; Takahashi, J.S.; Hogenesch, J.B. Coordinated Transcription of Key Pathways in the Mouse by the Circadian Clock. Cell 2002, 109, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, E.J. Exploring the Extent and Scope of Epigenetic Inheritance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, J.; Rassoulzadegan, M.; Tuorto, F.; Chen, Q. Sperm RNA Code Programmes the Metabolic Health of Offspring. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, C.; Kappeler, L.; Saget, S.; Grandjean, V.; Lévy, R. Role of MiRNA in the Transmission of Metabolic Diseases Associated With Paternal Diet-Induced Obesity. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, E.; Vavouri, T. Mechanisms of Epigenetic Inheritance of Variable Traits through the Germline. Reproduction 2020, 159, R251–R263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panneerdoss, S.; Chang, Y.-F.; Buddavarapu, K.C.; Chen, H.-I.H.; Shetty, G.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Kumar, T.R.; Rao, M.K. Androgen-Responsive MicroRNAs in Mouse Sertoli Cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammoud, S.S.; Low, D.H.P.; Yi, C.; Carrell, D.T.; Guccione, E.; Cairns, B.R. Chromatin and Transcription Transitions of Mammalian Adult Germline Stem Cells and Spermatogenesis. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 15, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y.-Y.; Chen, P.-P.; Xu, H.; Xie, S.-J.; Xu, S.-J.; Li, B.; Li, J.-H.; Liu, S.; Yang, J.-H.; et al. Genome-Wide Identification of MicroRNA Targets Reveals Positive Regulation of the Hippo Pathway by MiR-122 during Liver Development. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinke, H.; Asher, G. Circadian Clock Control of Liver Metabolic Functions. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Yao, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Bao, Z. Circadian Clock Genes in the Metabolism of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Bosagna, C.; Weeks, S.; Skinner, M.K. Identification of Genomic Features in Environmentally Induced Epigenetic Transgenerational Inherited Sperm Epimutations. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaspar, D.; Hastreiter, S.; Irmler, M.; Hrabé de Angelis, M.; Beckers, J. Nutrition and Its Role in Epigenetic Inheritance of Obesity and Diabetes across Generations. Mamm. Genome 2020, 31, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, A.J.; Dias, I.; Tsuro, H.; Allen, D.; Emes, R.D.; Moreton, J.; Wilson, R.; Ingram, R.J.M.; Sinclair, K.D. Paternal Diet Programs Offspring Health through Sperm- and Seminal Plasma-Specific Pathways in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 10064–10069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, Y.; Williams, L.; Vuguin, P.M.; Charron, M.J. Minireview: Epigenetic Programming of Diabetes and Obesity: Animal Models. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, S.E.; Skinner, M.K. Epigenetic Transgenerational Inheritance of Obesity Susceptibility. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, X.H.; Zhu, C.C.; Sun, S.C. Effects of Obesity and Diabetes on the Epigenetic Modification of Mammalian Gametes. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 7847–7855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rando, O.J. Daddy Issues: Paternal Effects on Phenotype. Cell 2012, 151, 702–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Block, T.; El-Osta, A. Epigenetic Programming, Early Life Nutrition and the Risk of Metabolic Disease. Atherosclerosis 2017, 266, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radford, E.J.; Ito, M.; Shi, H.; Corish, J.A.; Yamazawa, K.; Isganaitis, E.; Seisenberger, S.; Hore, T.A.; Reik, W.; Erkek, S.; et al. In Utero Undernourishment Perturbs the Adult Sperm Methylome and Intergenerational Metabolism. Science 2014, 345, 1255903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shea, J.M.; Serra, R.W.; Carone, B.R.; Shulha, H.P.; Kucukural, A.; Ziller, M.J.; Vallaster, M.P.; Gu, H.; Tapper, A.R.; Gardner, P.D.; et al. Genetic and Epigenetic Variation, but Not Diet, Shape the Sperm Methylome. Dev. Cell 2015, 35, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitelaw, E. Sperm DNA Methylation: Not a Vehicle for Dietary Reprogramming of Offspring? Dev. Cell 2015, 35, 668–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitelaw, E. Disputing Lamarckian Epigenetic Inheritance in Mammals. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, V.; Rassoulzadegan, M. Epigenetic Inheritance of the Sperm: An Unexpected Role of RNA. Gynecol. Obstet. Fertil. 2009, 37, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawano, M.; Kawaji, H.; Grandjean, V.; Kiani, J.; Rassoulzadegan, M. Novel Small Noncoding RNAs in Mouse Spermatozoa, Zygotes and Early Embryos. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raad, G.; Serra, F.; Martin, L.; Derieppe, M.-A.; Gilleron, J.; Costa, V.L.; Pisani, D.F.; Amri, E.-Z.; Trabucchi, M.; Grandjean, V. Paternal Multigenerational Exposure to an Obesogenic Diet Drives Epigenetic Predisposition to Metabolic Diseases in Mice. Elife 2021, 10, e61736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, P.; Bailbé, D.; Bianchi, L.; Pommier, G.; Liu, J.; Tolu, S.; Stathopoulou, M.G.; Portha, B.; Grandjean, V.; Movassat, J. Paternal High-Protein Diet Programs Offspring Insulin Sensitivity in a Sex-Specific Manner. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, E.I.; Stafford, J.M.; Reinberg, D. Epigenetic Inheritance: Histone Bookmarks across Generations. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 664–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donohoe, D.R.; Bultman, S.J. Metaboloepigenetics: Interrelationships between Energy Metabolism and Epigenetic Control of Gene Expression. J. Cell Physiol. 2012, 227, 3169–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.; Fiorino, E.; Giudici, M.; Gilardi, F.; Galmozzi, A.; Mitro, N.; Cermenati, G.; Godio, C.; Caruso, D.; de Fabiani, E.; et al. Linking Epigenetics to Lipid Metabolism: Focus on Histone Deacetylases. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2012, 29, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribas-Aulinas, F.; Ribo, S.; Casas, E.; Mourin-Fernandez, M.; Ramon-Krauel, M.; Diaz, R.; Lerin, C.; Kalko, S.G.; Vavouri, T.; Jimenez-Chillaron, J.C. Intergenerational Inheritance of Hepatic Steatosis in a Mouse Model of Childhood Obesity: Potential Involvement of Germ-Line microRNAs. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051241
Ribas-Aulinas F, Ribo S, Casas E, Mourin-Fernandez M, Ramon-Krauel M, Diaz R, Lerin C, Kalko SG, Vavouri T, Jimenez-Chillaron JC. Intergenerational Inheritance of Hepatic Steatosis in a Mouse Model of Childhood Obesity: Potential Involvement of Germ-Line microRNAs. Nutrients. 2023; 15(5):1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051241
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibas-Aulinas, Francesc, Sílvia Ribo, Eduard Casas, Marta Mourin-Fernandez, Marta Ramon-Krauel, Ruben Diaz, Carles Lerin, Susana G. Kalko, Tanya Vavouri, and Josep C. Jimenez-Chillaron. 2023. "Intergenerational Inheritance of Hepatic Steatosis in a Mouse Model of Childhood Obesity: Potential Involvement of Germ-Line microRNAs" Nutrients 15, no. 5: 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051241
APA StyleRibas-Aulinas, F., Ribo, S., Casas, E., Mourin-Fernandez, M., Ramon-Krauel, M., Diaz, R., Lerin, C., Kalko, S. G., Vavouri, T., & Jimenez-Chillaron, J. C. (2023). Intergenerational Inheritance of Hepatic Steatosis in a Mouse Model of Childhood Obesity: Potential Involvement of Germ-Line microRNAs. Nutrients, 15(5), 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051241




