The Effect of Watermelon Juice Supplementation on Heart Rate Variability and Metabolic Response during an Oral Glucose Challenge: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
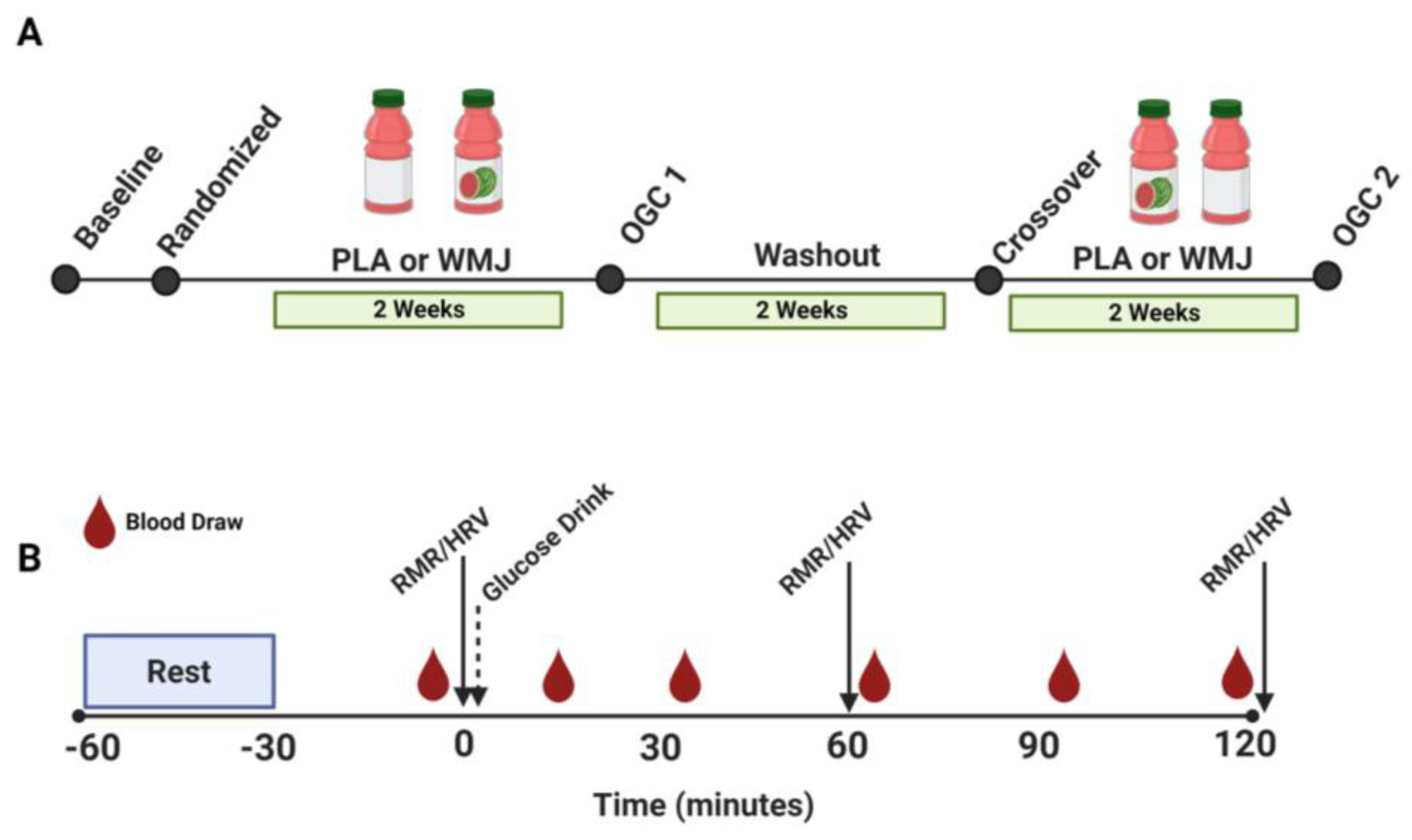
2.1. Participants and Study Design
2.2. Oral Glucose Challenge (OGC)
2.3. Heart Rate Variability (HRV)
2.4. Indirect Calorimetry
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. HRV
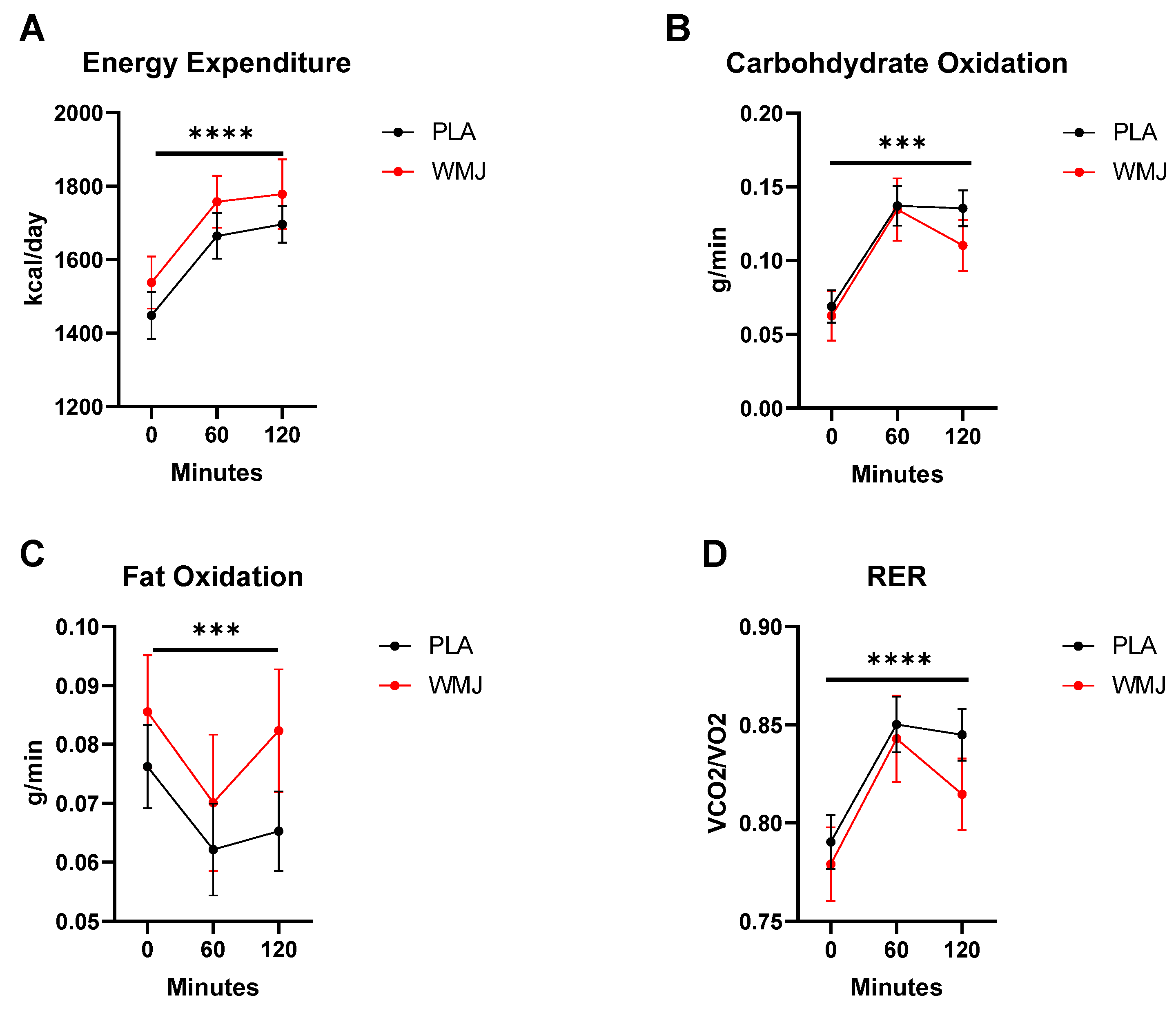
3.3. Metabolic Parameters
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, J.P.; Larson, M.G.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Wilson, P.F.; Tsuji, H.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Levy, D. Association of Hyperglycemia with Reduced Heart Rate Variability (The Framingham Heart Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2000, 86, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thayer, J.F.; Yamamoto, S.S.; Brosschot, J.F. The Relationship of Autonomic Imbalance, Heart Rate Variability and Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors. Int. J. Cardiol. 2010, 141, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poliakova, N.; Després, J.P.; Bergeron, J.; Alméras, N.; Tremblay, A.; Poirier, P. Influence of Obesity Indices, Metabolic Parameters and Age on Cardiac Autonomic Function in Abdominally Obese Men. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1270–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothberg, L.J.; Lees, T.; Clifton-Bligh, R.; Lal, S. Association Between Heart Rate Variability Measures and Blood Glucose Levels: Implications for Noninvasive Glucose Monitoring for Diabetes. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2016, 18, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, A.; Horvath, T.; Sarkozi, A.; Kollai, M. Relationship between Heart Rate Variability and Endothelial Function in Healthy Subjects. Auton. Neurosci. 2012, 169, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haensel, A.; Mills, P.J.; Nelesen, R.A.; Ziegler, M.G.; Dimsdale, J.E. The Relationship between Heart Rate Variability and Inflammatory Markers in Cardiovascular Diseases. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2008, 33, 1305–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millis, R.M.; Austin, R.E.; Hatcher, M.D.; Bond, V.; Goring, K.L. Metabolic Energy Correlates of Heart Rate Variability Spectral Power Associated with a 900-Calorie Challenge. J. Nutr. Metab. 2011, 2011, 715361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benichou, T.; Pereira, B.; Mermillod, M.; Tauveron, I.; Pfabigan, D.; Maqdasy, S.; Dutheil, F. Heart Rate Variability in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta–Analysis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolisso, G.; Manzella, D.; Tagliamonte, M.R.; Rizzo, M.R.; Gambardella, A.; Varricchio, M. Effects of Different Insulin Infusion Rates on Heart Rate Variability in Lean and Obese Subjects. Metabolism 1999, 48, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissman, A.; Lowenstein, L.; Peleg, A.; Thaler, I.; Zimmer, E.Z. Power Spectral Analysis of Heart Rate Variability During the 100-g Oral Glucose Tolerance Test in Pregnant Women. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eckstein, M.L.; Moser, O.; Tripolt, N.J.; Pferschy, P.N.; Obermayer, A.A.M.; Kojzar, H.; Mueller, A.; Abbas, F.; Sourij, C.; Sourij, H. Rapid Glucose Rise Reduces Heart Rate Variability in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: A Prospective Secondary Outcome Analysis. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 2021, 23, 1681–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mah, E.; Noh, S.K.; Ballard, K.D.; Park, H.J.; Volek, J.S.; Bruno, R.S. Supplementation of a γ-Tocopherol-Rich Mixture of Tocopherols in Healthy Men Protects against Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction Induced by Postprandial Hyperglycemia. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Title, L.M.; Cummings, P.M.; Giddens, K.; Nassar, B.A. Oral Glucose Loading Acutely Attenuates Endothelium-Dependent Vasodilation in Healthy Adults without Diabetes: An Effect Prevented by Vitamins C and E. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 2185–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, R.D.; Hu, D.; Greenaway, T.; Sharman, J.E.; Rattigan, S.; Richards, S.M.; Keske, M.A. Oral Glucose Challenge Impairs Skeletal Muscle Microvascular Blood Flow in Healthy People. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 315, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhary, S.; Nuttall, S.L.; Coote, J.H.; Townend, J.N. L-Arginine Augments Cardiac Vagal Control in Healthy Human Subjects. Hypertension 2002, 39, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsop, P.; Hauton, D. Oral Nitrate and Citrulline Decrease Blood Pressure and Increase Vascular Conductance in Young Adults: A Potential Therapy for Heart Failure. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 116, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamim, C.J.R.S.; Júnior, F.W.; de Figueirêdo, M.Í.L.S.; Benjamim, C.J.R.; Cavalcante, T.C.F.; da Silva, A.A.M.; Monteiro, L.R.L.; Santana, M.D.R.; Garner, D.M.; Valenti, V.E. Beetroot (Beta vulgaris L.) Extract Acutely Improves Heart Rate Variability Recovery Following Strength Exercise: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Trial-Pilot Study. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2021, 40, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allerton, T.D.; Proctor, D.N.; Stephens, J.M.; Dugas, T.R.; Spielmann, G.; Irving, B.A. L-Citrulline Supplementation: Impact on Cardiometabolic Health. Nutrients 2018, 10, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwedhelm, E.; Maas, R.; Freese, R.; Jung, D.; Lukacs, Z.; Jambrecina, A.; Spickler, W.; Schulze, F.; Böger, R.H. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Properties of Oral L-Citrulline and L-Arginine: Impact on Nitric Oxide Metabolism. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2008, 65, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, J.K.; Wu, G.; Perkins-Veazie, P.; Spears, K.; Claypool, P.L.; Baker, R.A.; Clevidence, B.A. Watermelon Consumption Increases Plasma Arginine Concentrations in Adults. Nutrition 2007, 23, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.J.; Blackwell, J.R.; Williams, E.; Vanhatalo, A.; Wylie, L.J.; Winyard, P.G.; Jones, A.M. Two Weeks of Watermelon Juice Supplementation Improves Nitric Oxide Bioavailability but Not Endurance Exercise Performance in Humans. Nitric Oxide Biol. Chem. 2016, 59, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincellette, C.M.; Losso, J.; Early, K.; Spielmann, G.; Irving, B.A.; Allerton, T.D. Supplemental Watermelon Juice Attenuates Acute Hyperglycemia-Induced Macro-and Microvascular Dysfunction in Healthy Adults. J. Nutr. 2021, 151, 3450–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heart Rate Variability: Standards of Measurement, Physiological Interpretation and Clinical Use. Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation 1996, 93, 1043–1065. [CrossRef]
- Shaffer, F.; Ginsberg, J.P. An Overview of Heart Rate Variability Metrics and Norms. Front. Public Health 2017, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleiger, R.E.; Stein, P.K.; Bigger, J.T.J. Heart Rate Variability: Measurement and Clinical Utility. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2005, 10, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billman, G. The LF/HF Ratio Does Not Accurately Measure Cardiac Sympatho-Vagal Balance. Front. Physiol. 2013, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frayn, K.N. Calculation of Substrate Oxidation Rates in Vivo from Gaseous Exchange. J. Appl. Physiol. 1983, 55, 628–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiviniemi, A.M.; Perkiömäki, N.; Auvinen, J.; Niemelä, M.; Tammelin, T.; Puukka, K.; Ruokonen, A.; Keinänen-Kiukaanniemi, S.; Tulppo, M.P.; Järvelin, M.R.; et al. Fitness, Fatness, Physical Activity, and Autonomic Function in Midlife. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 2459–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, S.; Marsh, A.M.; Coote, J.H.; Townend, J.N. Nitric Oxide and Cardiac Muscarinic Control in Humans. Hypertension 2004, 43, 1023–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travagli, R.A.; Gillis, R.A. Nitric Oxide-Mediated Excitatory Effect on Neurons of Dorsal Motor Nucleus of Vagus. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, G154–G160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musialek, P.; Lei, M.; Brown, H.F.; Paterson, D.J.; Casadei, B. Nitric Oxide Can Increase Heart Rate by Stimulating the Hyperpolarization-Activated Inward Current, If. Circ. Res. 1997, 81, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conlon, K.; Collins, T.; Kidd, C. The Role of Nitric Oxide in the Control by the Vagal Nerves of the Heart of the Ferret. Exp. Physiol. 1998, 83, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mah, E.; Noh, S.K.; Ballard, K.D.; Matos, M.E.; Volek, J.S.; Bruno, R.S. Postprandial Hyperglycemia Impairs Vascular Endothelial Function in Healthy Men by Inducing Lipid Peroxidation and Increasing Asymmetric Dimethylarginine:Arginine. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wascher, T.C.; Schmoelzer, I.; Wiegratz, A.; Stuehlinger, M.; Mueller-Wieland, D.; Kotzka, J.; Enderle, M. Reduction of Postchallenge Hyperglycaemia Prevents Acute Endothelial Dysfunction in Subjects with Impaired Glucose Tolerance. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 35, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawano, H.; Motoyama, T.; Hirashima, O.; Hirai, N.; Miyao, Y.; Sakamoto, T.; Kugiyama, K.; Ogawa, H.; Yasue, H. Hyperglycemia Rapidly Suppresses Flow-Mediated Endothelium-Dependent Vasodilation of Brachial Artery. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 1999, 34, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massa, N.M.L.; Silva, A.S.; Toscano, L.T.; Silva, J.D.; Gomes, R.; Persuhn, D.C.; Gonçalves, M.D.C.R. Watermelon Extract Reduces Blood Pressure but Does Not Change Sympathovagal Balance in Prehypertensive and Hypertensive Subjects. Blood Press. 2016, 25, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.; Chernykh, O.; Figueroa, A. Chronic L-Citrulline Supplementation Improves Cardiac Sympathovagal Balance in Obese Postmenopausal Women: A Preliminary Report. Auton. Neurosci. 2016, 198, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, F.; Pham, M.; Maloney, E.; Rizzo, N.O.; Morton, G.J.; Wisse, B.E.; Kirk, E.A.; Chait, A.; Schwartz, M.W. Vascular Inflammation, Insulin Resistance, and Reduced Nitric Oxide Production Precede the Onset of Peripheral Insulin Resistance. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1982–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, M.G. Impaired Microvascular Perfusion: A Consequence of Vascular Dysfunction and a Potential Cause of Insulin Resistance in Muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2008, 295, E732–E750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.-J.; Yang, Y.-C.; Lu, F.-H.; Lin, T.-S.; Chen, J.-J.; Yeh, T.-L.; Wu, C.-H.; Wu, J.-S. Altered Cardiac Autonomic Function May Precede Insulin Resistance in Metabolic Syndrome. Am. J. Med. 2010, 123, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, L.; Fedorchak, S.; Boychuk, C.R. Interplay Between Systemic Metabolic Cues and Autonomic Output: Connecting Cardiometabolic Function and Parasympathetic Circuits. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 624595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, A.C.; Dudenbostel, T.; Crowe-White, K. Watermelon Juice: A Novel Functional Food to Increase Circulating Lycopene in Older Adult Women. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2019, 74, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin-Jumah, M.N.; Nadeem, M.S.; Gilani, S.J.; Mubeen, B.; Ullah, I.; Alzarea, S.I.; Ghoneim, M.M.; Alshehri, S.; Al-Abbasi, F.A.; Kazmi, I. Lycopene: A Natural Arsenal in the War against Oxidative Stress and Cardiovascular Diseases. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Sex | Males (n = 6), Females (n = 12) |
| Age (years) | 23.6 ± 3.1 |
| Body weight (kg) | 66.8 ± 12.3 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.6 ± 3.1 |
| Time Points | 0 | 60 | 120 | p-Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | PLA | WMJ | PLA | WMJ | PLA | WMJ | Time | Treatment | Interaction |
| Plasma Glucose (mmol/L) | 5.19 ± 0.38 | 5.24 ± 0.36 | 7.05 ± 2.15 | 7.83 ± 1.95 | 5.22 ± 1.42 | 5.88 ± 1.67 | <0.0001 * | 0.0869 | 0.4063 |
| HR (bpm) | 64.3 ± 13.2 | 66.9 ± 15.4 | 68.5 ± 13.5 | 69.3 ± 17.9 | 70.7 ± 13.6 | 74.0 ± 21.6 | 0.0005 * | 0.6866 | 0.6570 |
| RR (ms) | 969.9 ± 195.5 | 933.6 ± 176.8 | 909.2 ± 188.2 | 908.1 ± 186.6 | 879.0 ± 177.6 | 858.6 ± 201.0 | 0.0002 * | 0.9153 | 0.5509 |
| SDNN (ms) | 67.7 ± 47.9 | 76.5 ± 37.5 | 50.1 ± 24.0 | 56.7 ± 28.2 | 58.6 ± 32.7 | 61.4 ± 35.3 | 0.0070 * | 0.7274 | 0.6777 |
| RMSSD (ms) | 73.9 ± 57.0 | 90.6 ± 54.0 | 52.8 ± 27.7 | 74.0 ± 46.8 | 54.0 ± 31.9 | 77.1 ± 56.0 | 0.0243 * | 0.1749 | 0.9207 |
| pNN50 (%) | 30.8 ± 26.7 | 43.4 ± 28.2 | 27.1 ± 23.4 | 42.2 ± 30.3 | 21.4 ± 22.6 | 35.5 ± 35.1 | 0.1379 | 0.0099* | 0.5850 |
| LF (ms2) | 2525 ± 2944 | 2234 ± 2478 | 985 ± 1006 | 1073 ± 802 | 1813 ± 1543 | 2222 ± 2052 | 0.0209 * | 0.8782 | 0.6531 |
| LF (nu) | 50.4 ± 14.1 | 44.7 ± 24.0 | 46.9 ± 18.0 | 45.5 ± 25.4 | 55.2 ± 18.4 | 54.1 ± 25.1 | 0.1480 | 0.7886 | 0.3320 |
| HF (ms2) | 2696 ± 3204 | 4205 ± 3636 | 1356 ± 1273 | 2560 ± 2755 | 1511 ± 1630 | 3212 ± 3378 | 0.0075 * | 0.0394 * | 0.6888 |
| HF (nu) | 49.5 ± 14.1 | 55.3 ± 24.0 | 53.1 ± 18.0 | 54.4 ± 25.4 | 44.8 ± 18.4 | 45.9 ± 25.1 | 0.1493 | 0.7892 | 0.3265 |
| TP (ms2) | 5404 ± 6141 | 6642 ± 5735 | 2412 ± 2009 | 3710 ± 3179 | 3572 ± 2720 | 5610 ± 5184 | 0.0132 * | 0.1190 | 0.9679 |
| LF/HF | 1.34 ± 1.36 | 1.50 ± 1.92 | 1.12 ± 0.81 | 1.50 ± 1.73 | 1.62 ± 1.11 | 2.06 ± 2.01 | 0.2383 | 0.1911 | 0.0516 * |
| REE | RER | CHO Ox | Fat Ox | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value | r | p-Value |
| RMSSD (ms) | −0.228 | 0.059 | −0.209 | 0.085 | −0.278 | 0.020 * | 0.115 | 0.347 |
| SDNN index (ms) | −0.184 | 0.130 | −0.241 | 0.046 | −0.290 | 0.015 * | 0.149 | 0.222 |
| pNN50 (%) | −0.246 | 0.042 | −0.089 | 0.468 | −0.157 | 0.199 | 0.003 | 0.983 |
| VLF (ms2) | −0.036 | 0.771 | −0.125 | 0.306 | −0.113 | 0.357 | 0.077 | 0.530 |
| LF (ms2) | −0.099 | 0.420 | −0.291 | 0.015 * | −0.291 | 0.015 * | 0.195 | 0.109 |
| HF (ms2) | −0.241 | 0.046 * | −0.176 | 0.148 | −0.247 | 0.040 * | 0.082 | 0.503 |
| LF/HF ratio | 0.269 | 0.025 * | −0.038 | 0.760 | 0.048 | 0.695 | 0.102 | 0.404 |
| Total power (ms2) | −0.194 | 0.110 | −0.247 | 0.041 | −0.289 | 0.016 * | 0.143 | 0.242 |
| PNS Index | −0.160 | 0.190 | −0.244 | 0.043 * | −0.296 | 0.013 * | 0.167 | 0.170 |
| SNS Index | 0.095 | 0.437 | 0.292 | 0.010 * | 0.326 | 0.006 * | −0.227 | 0.061 |
| Stress Index | 0.110 | 0.369 | 0.271 | 0.024 * | 0.303 | 0.011 * | −0.200 | 0.100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matthews, R.; Early, K.S.; Vincellette, C.M.; Losso, J.; Spielmann, G.; Irving, B.A.; Allerton, T.D. The Effect of Watermelon Juice Supplementation on Heart Rate Variability and Metabolic Response during an Oral Glucose Challenge: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2023, 15, 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040810
Matthews R, Early KS, Vincellette CM, Losso J, Spielmann G, Irving BA, Allerton TD. The Effect of Watermelon Juice Supplementation on Heart Rate Variability and Metabolic Response during an Oral Glucose Challenge: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Trial. Nutrients. 2023; 15(4):810. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040810
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatthews, Rachel, Kate S. Early, Cullen M. Vincellette, Jack Losso, Guillaume Spielmann, Brian A. Irving, and Timothy D. Allerton. 2023. "The Effect of Watermelon Juice Supplementation on Heart Rate Variability and Metabolic Response during an Oral Glucose Challenge: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Trial" Nutrients 15, no. 4: 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040810
APA StyleMatthews, R., Early, K. S., Vincellette, C. M., Losso, J., Spielmann, G., Irving, B. A., & Allerton, T. D. (2023). The Effect of Watermelon Juice Supplementation on Heart Rate Variability and Metabolic Response during an Oral Glucose Challenge: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Crossover Trial. Nutrients, 15(4), 810. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15040810






