Evaluation of Anti-Oxinflammatory and ACE-Inhibitory Properties of Protein Hydrolysates Obtained from Edible Non-Mulberry Silkworm Pupae (Antheraea assama and Philosomia ricinii)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Chemicals
2.2. Extraction of Whole Protein and Preparation of Protein Hydrolysates
2.3. ACE-Inhibition Activity Determination
2.4. Determination of Antioxidant Activities
2.4.1. DPPH Radical Scavenging Assay
2.4.2. ABTS Radical Scavenging Assay
2.5. Peptide Fractionation Using Ultrafiltration
2.6. Peptide Fractionation Using RP-HPLC
2.7. Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cell Line (HUVECs) Culture
2.8. Cell Viability Assay
2.9. Immunocytochemistry
2.10. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
2.11. COX-2 and IL-1β Detection Using ELISA
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
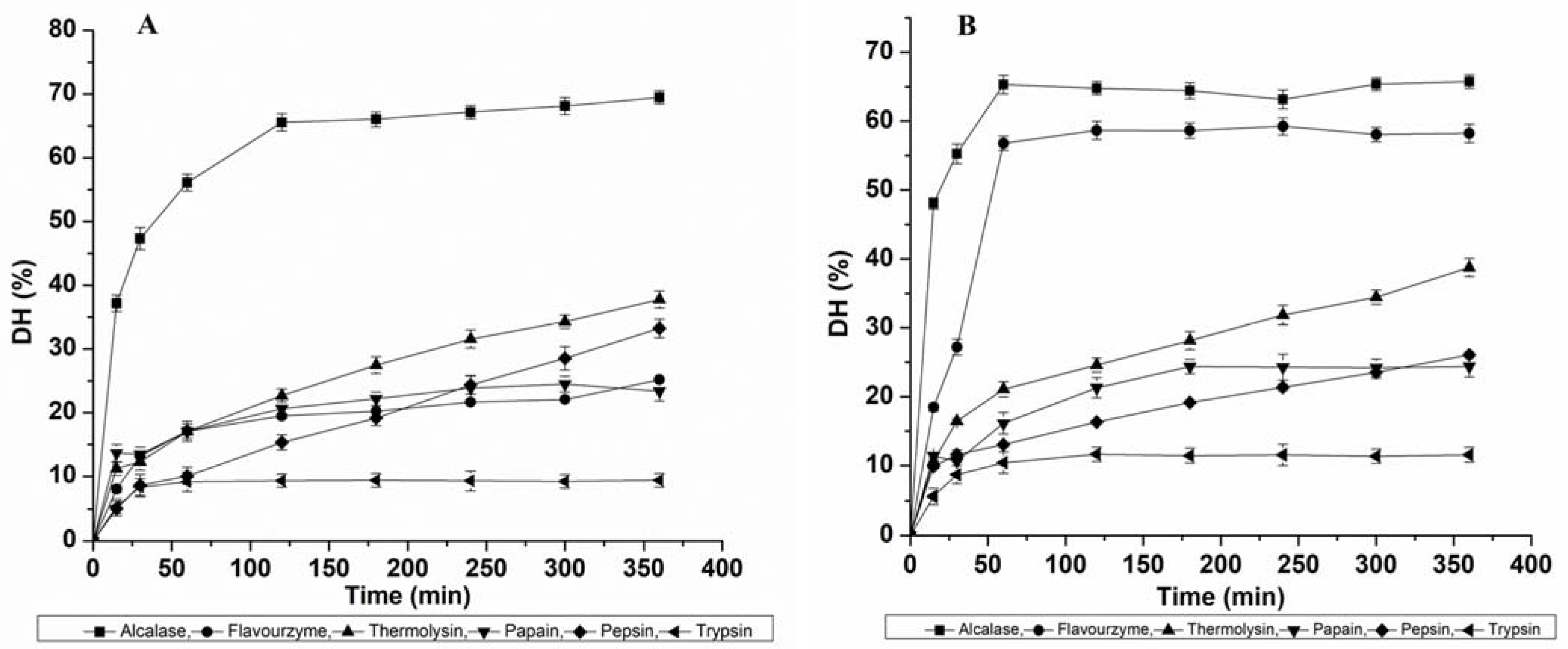
3.1. Effects of Different Proteases on the Degree of Hydrolysis
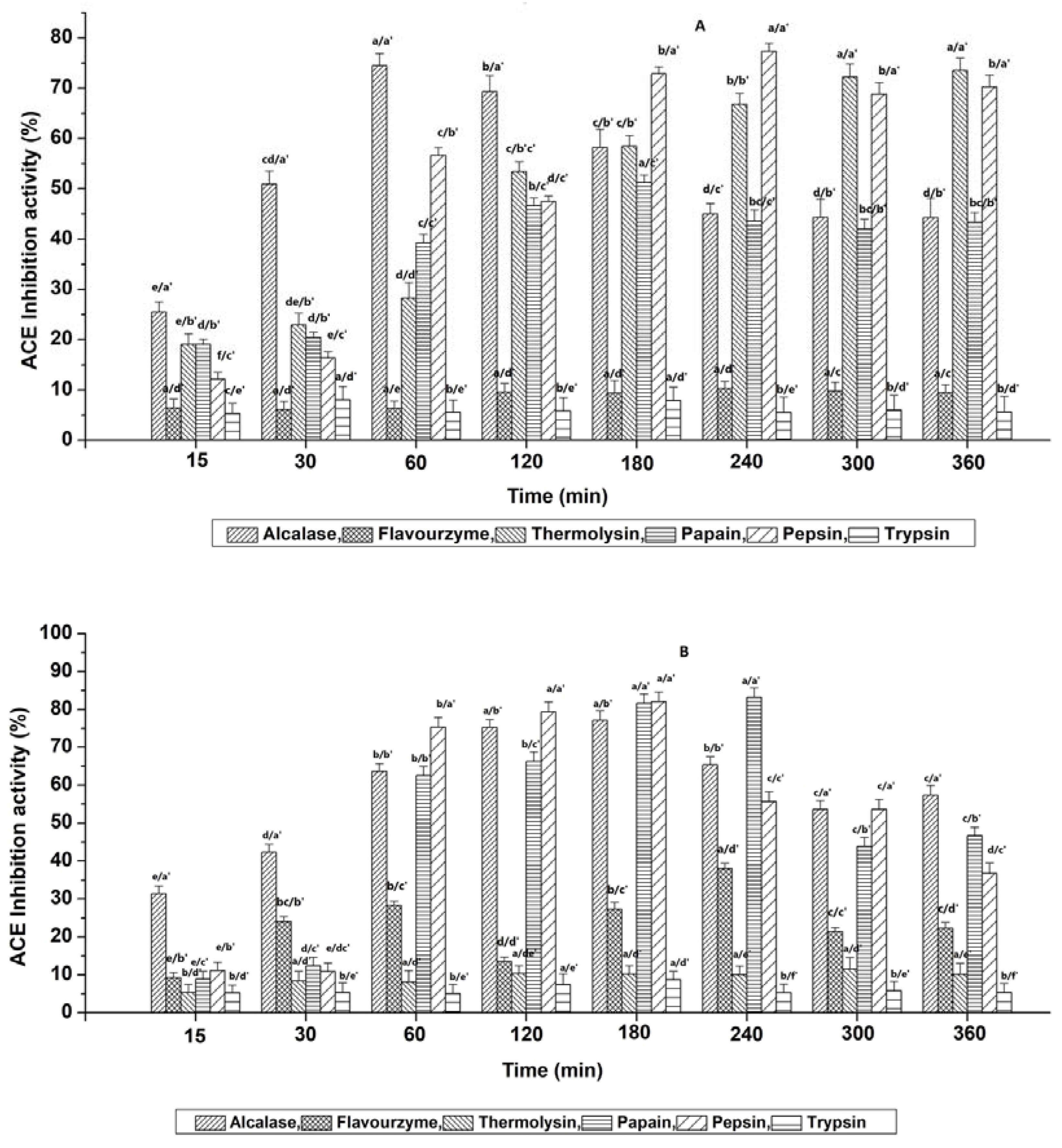
3.2. ACE-Inhibitory Potential of Hydrolysates
3.3. Antioxidative Potential of Selected Hydrolysates
3.4. Antioxidative and ACE-Inhibition Potential of Ultrafiltrates
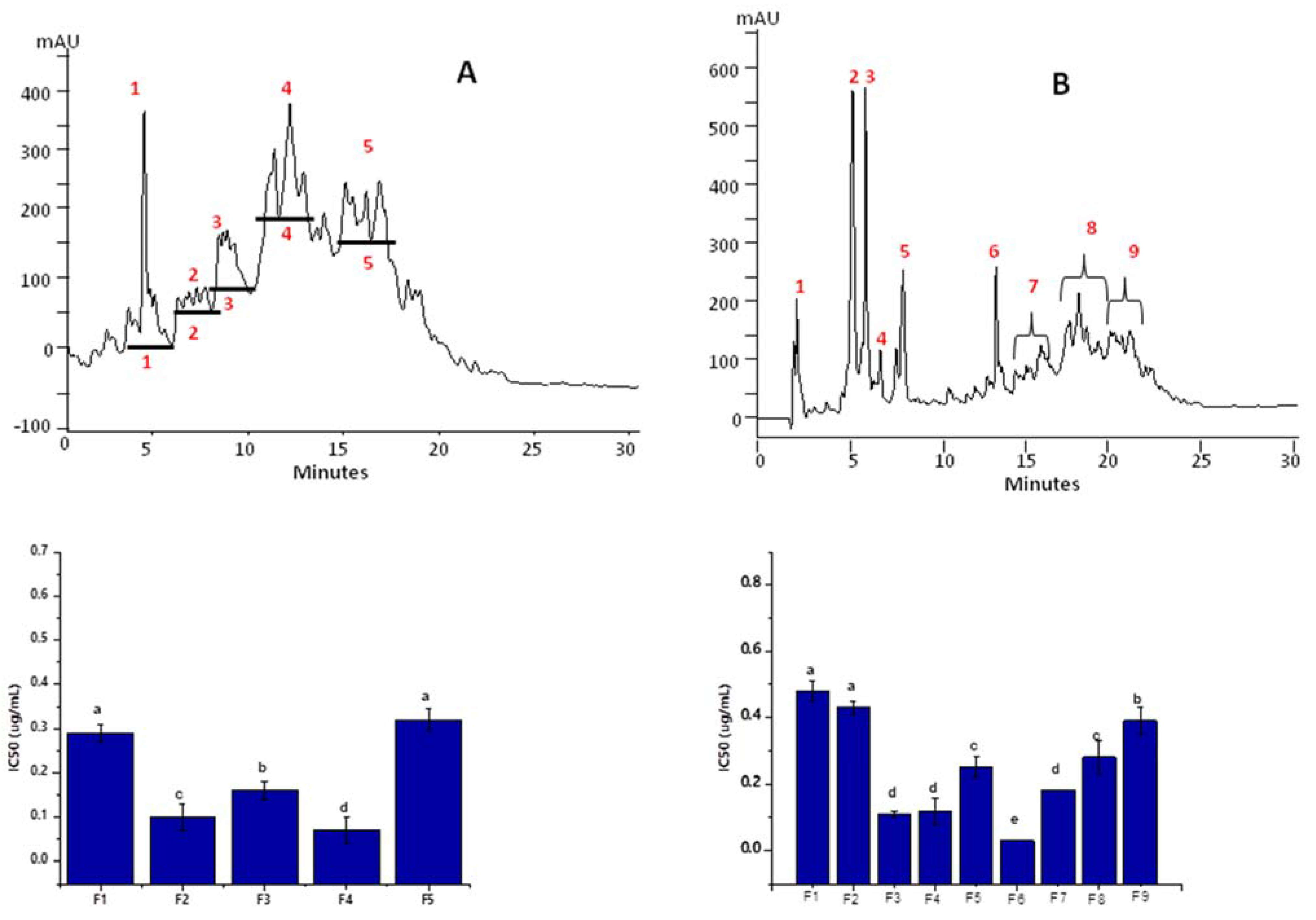
3.5. Fractionation of Peptides in Alc_M60min_F3 and Pap_E240min_F3
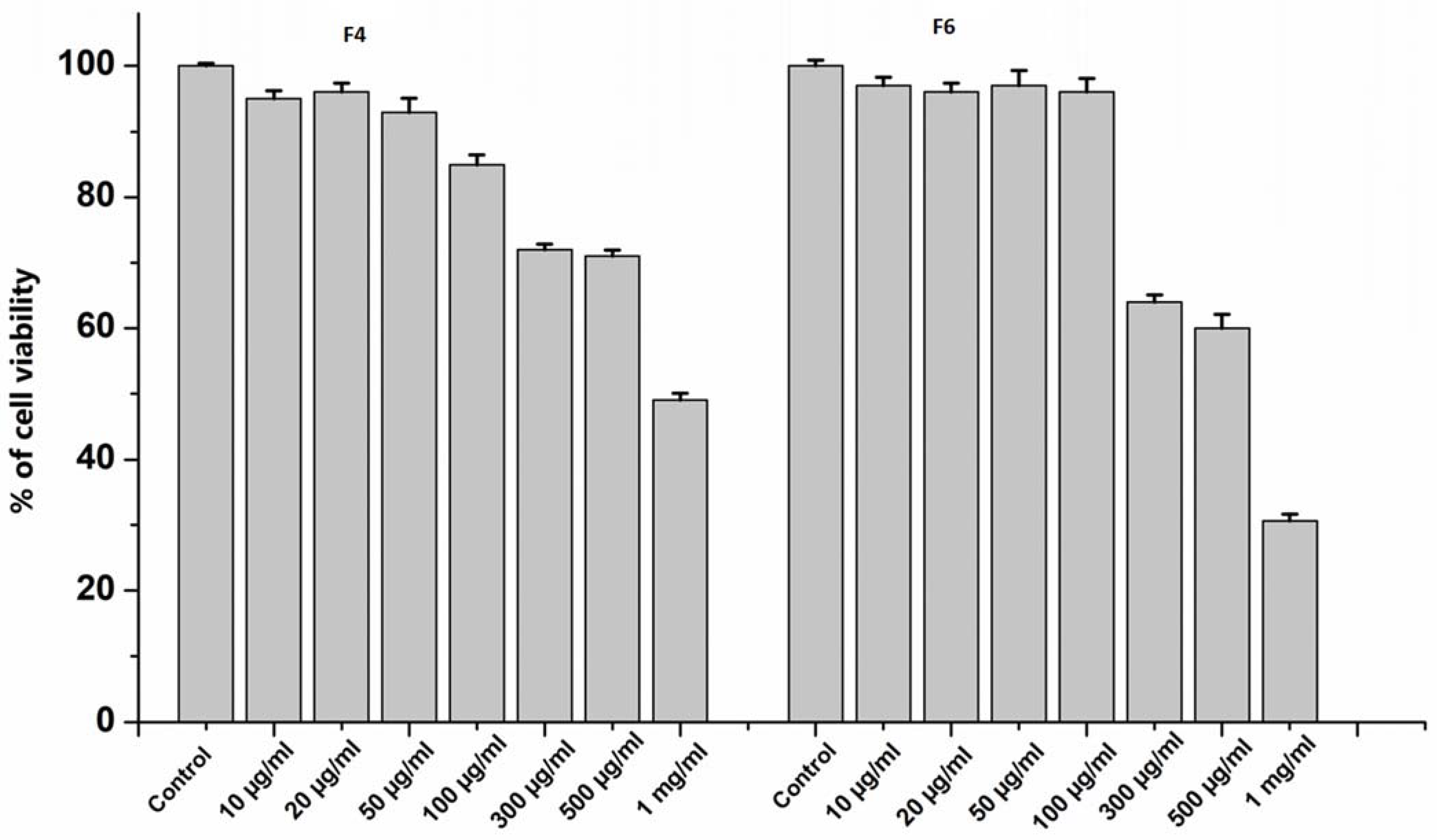
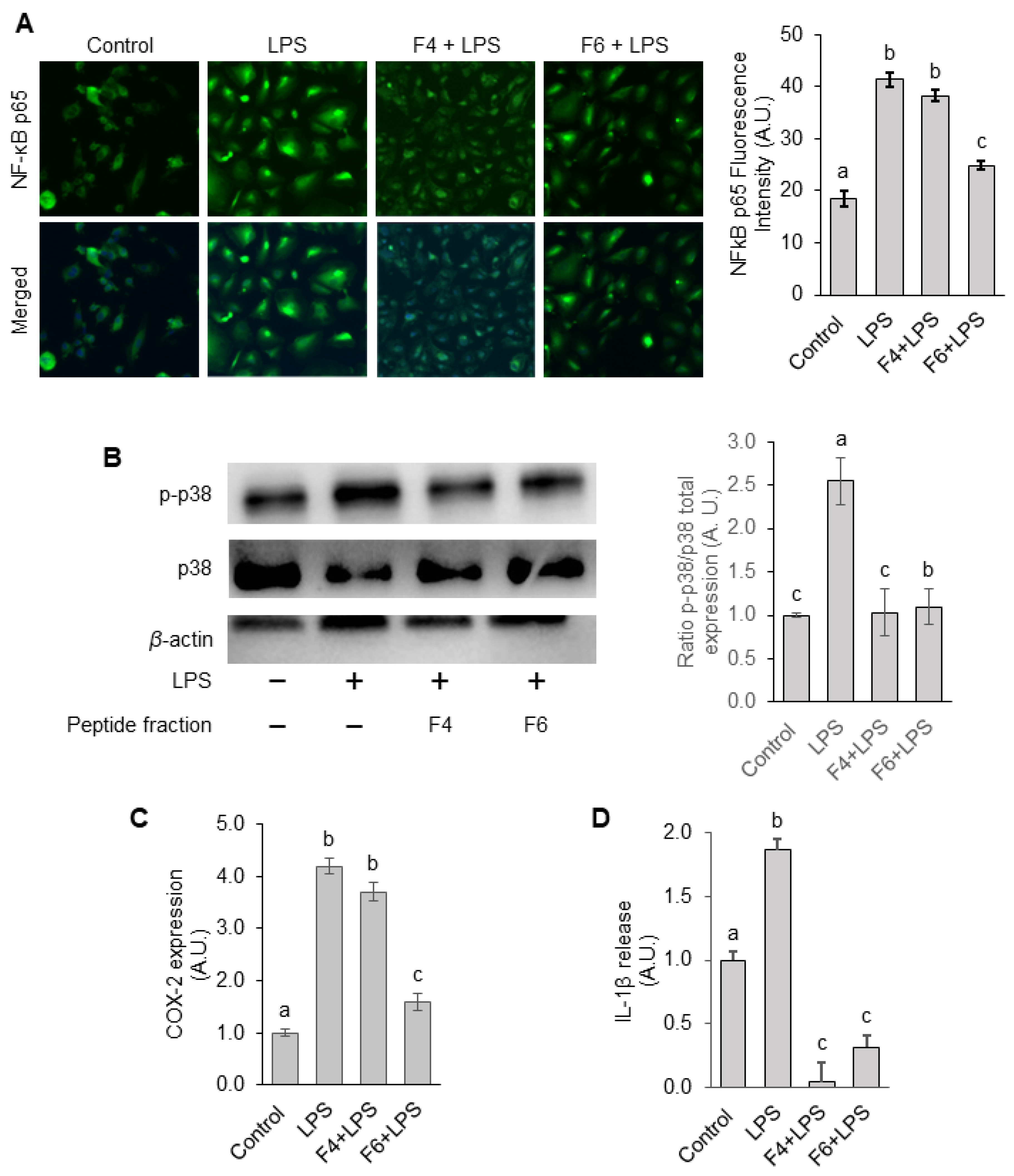
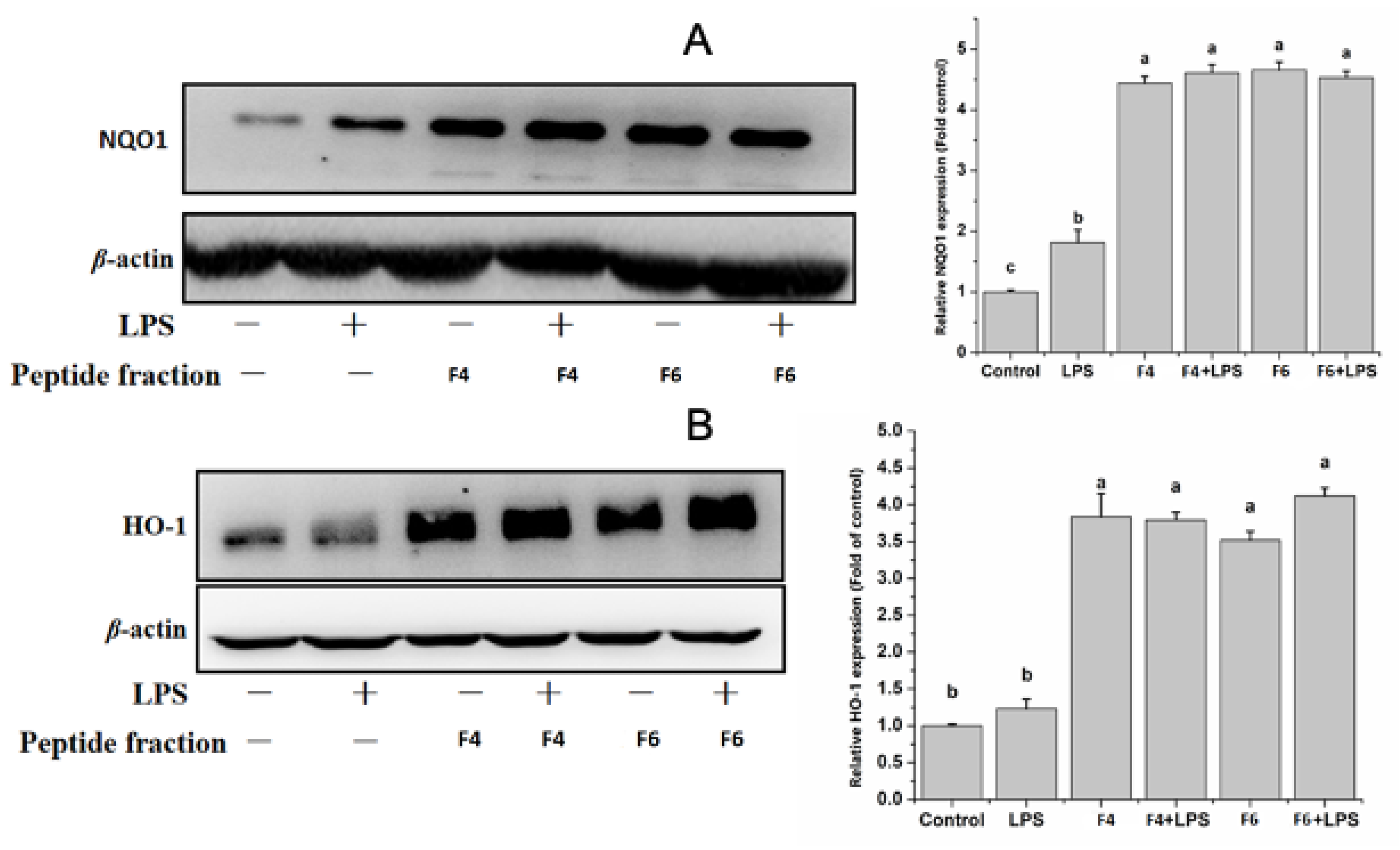
3.6. Anti-Oxinflammatory Activity of Purified Peptide Fractions F4 and F6 in Human Endothelial Cells
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kvietys:, P.R.; Granger, D.N. Role of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species in the Vascular Responses to Inflammation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 52, 556–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, K.; Shoemaker, R.; Yiannikouris, F.; Cassis, L.A. The Renin-Angiotensin System: A Target of and Contributor to Dyslipidemias, Altered Glucose Homeostasis, and Hypertension of the Metabolic Syndrome. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H1219–H1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valacchi, G.; Virgili, F.; Cervellati, C.; Pecorelli, A. OxInflammation: From Subclinical Condition to Pathological Biomarker. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haybar, H.; Shahrabi, S.; Rezaeeyan, H.; Shirzad, R.; Saki, N. Endothelial Cells: From Dysfunction Mechanism to Pharmacological Effect in Cardiovascular Disease. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2019, 19, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combination Therapy with ACE Inhibitors/Angiotensin II Receptor Antagonists and Diuretics in Hypertension. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2003, 1, 43–50. [CrossRef]
- Lammi, C.; Aiello, G.; Boschin, G.; Arnoldi, A. Multifunctional Peptides for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A New Concept in the Area of Bioactive Food-Derived Peptides. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 55, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, B.; Raj, S.J. Therapeutic Applications and Properties of Silk Proteins from Bombyx Mori. Front. Life Sci. 2012, 6, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomotake, H.; Katagiri, M.; Yamato, M. Silkworm Pupae (Bombyx Mori) Are New Sources of High Quality Protein and Lipid. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. (Tokyo) 2010, 56, 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, N.; Hazarika, N.C.; Narain, K.; Mahanta, J. Nutritive Value of Non-Mulberry and Mulberry Silkworm Pupae and Consumption Pattern in Assam, India. Nutr. Res. 2003, 23, 1303–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.wur.nl/upload_mm/7/4/1/ca8baa25-b035-4bd2-9fdc-a7df1405519a_WORLD%20LIST%20EDIBLE%20INSECTS%202015.pdf (accessed on 12 April 2020).
- Jia, J.; Wu, Q.; Yan, H.; Gui, Z. Purification and Molecular Docking Study of a Novel Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptide from Alcalase Hydrolysate of Ultrasonic-Pretreated Silkworm Pupa (Bombyx Mori) Protein. Process Biochem. 2015, 50, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, F.G.; Jones, O.G.; O’Haire, M.E.; Liceaga, A.M. Functional Properties of Tropical Banded Cricket (Gryllodes Sigillatus) Protein Hydrolysates. Food Chem. 2017, 224, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, F.; Johnson, P.E.; Liceaga, A. Effect of Enzymatic Hydrolysis on Bioactive Properties and Allergenicity of Cricket (Gryllodes Sigillatus) Protein. Food Chem. 2018, 262, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, S.-J.; Wu, J. Angiotensin-I Converting Enzyme Inhibitory and Antioxidant Activities of Egg Protein Hydrolysates Produced with Gastrointestinal and Nongastrointestinal Enzymes. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C801–C807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, F.; Pambianchi, E.; Pecorelli, A.; Woodby, B.; Messano, N.; Therrien, J.-P.; Lila, M.A.; Valacchi, G. Redox Regulation of Cutaneous Inflammasome by Ozone Exposure. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 152, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpi, N.; Pecorelli, A.; Lorenzoni, P.; Di Lazzaro, F.; Belmonte, G.; Aglianò, M.; Cantarini, L.; Giannini, F.; Grasso, G.; Valacchi, G. Antiangiogenic VEGF Isoform in Inflammatory Myopathies. Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 2013, e219313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Ma, H.; Luo, L.; Yin, X. Angiotensin I-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Inhibitory Peptide Derived from Tenebrio Molitor (L.) Larva Protein Hydrolysate. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2013, 236, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dion-Poulin, A.; Laroche, M.; Doyen, A.; Turgeon, S.L. Functionality of cricket and mealworm hydrolysates generated after pretreatment of meals with high hydrostatic pressures. Molecules 2020, 25, 5366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purschke, B.; Meinlschmidt, P.; Horn, C.; Rieder, O.; Jäger, H. Improvement of techno-functional properties of edible insect protein from migratory locust by enzymatic hydrolysis. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2018, 244, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, P.; Borges, S.; Pintado, M. Enzymatic hydrolysis of insect Alphitobius diaperinus towards the development of bioactive peptide hydrolysates. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 3539–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, K.K.; Merz, M.; Appel, D.; De Araujo, M.M.; Fischer, L. New insights into the flavoring potential of cricket (Acheta domesticus) and mealworm (Tenebrio molitor) protein hydrolysates and their Maillard products. Food Chem. 2021, 364, 130336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salampessy, J.; Reddy, N.; Kailasapathy, K.; Phillips, M. Functional and Potential Therapeutic ACE-Inhibitory Peptides Derived from Bromelain Hydrolysis of Trevally Proteins. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 14, 716–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, L.; Smagghe, G.; Herregods, G.; Van Camp, J. ACE Inhibitory Activity in Enzymatic Hydrolysates of Insect Protein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5207–5211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vercruysse, L.; Smagghe, G.; Beckers, T.; Camp, J.V. Antioxidative and ACE Inhibitory Activities in Enzymatic Hydrolysates of the Cotton Leafworm, Spodoptera Littoralis. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, E.; Baraniak, B.; Karaś, M. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of hydrolysates and peptide fractions obtained by enzymatic hydrolysis of selected heat-treated edible insects. Nutrients 2017, 9, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska, E.; Karaś, M.; Jakubczyk, A. Antioxidant activity of predigested protein obtained from a range of farmed edible insects. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.Y.; Jia, J.Q.; Tan, G.X.; Xu, J.L.; Gui, Z.Z. Physicochemical properties of silkworm larvae protein isolate and gastrointestinal hydrolysate bioactivities. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 6145–6153. [Google Scholar]
- Gleeson, J.P.; Ryan, S.M.; Brayden, D.J. Oral Delivery Strategies for Nutraceuticals: Delivery Vehicles and Absorption Enhancers. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, D.L.; Botting, R.M.; Hla, T. Cyclooxygenase Isozymes: The Biology of Prostaglandin Synthesis and Inhibition. Pharmacol. Rev. 2004, 56, 387–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.M.; Sobey, C.G.; Latz, E.; Mansell, A.; Drummond, G.R. IL–1β and IL–18: Inflammatory Markers or Mediators of Hypertension? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 5589–5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Xu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Mintah, B.K.; Dabbour, M.; Yang, F.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Z.; Dai, C.; He, R.; et al. Recent Insight on Edible Insect Protein: Extraction, Functional Properties, Allergenicity, Bioactivity, and Applications. Foods 2022, 11, 2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.-J.; Lv, C.-H.; Chen, Z.; Shi, M.; Zeng, C.-X.; Hou, D.-X.; Qin, S. The Regulatory Effect of Phytochemicals on Chronic Diseases by Targeting Nrf2-ARE Signaling Pathway. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonolo, F.; Folda, A.; Scalcon, V.; Marin, O.; Bindoli, A.; Rigobello, M.P. Nrf2-Activating Bioactive Peptides Exert Anti-Inflammatory Activity through Inhibition of the NF-ΚB Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| S. No. | Hydrolysates | ACE Inhibition (%) | ACE Inhibition (IC50 mg mL−1) | DPPH (EC50 mg mL−1) | ABTS (EC50 mg mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Alc_M60min | 74.46 ± 2.44 | 0.17 ± 0.02 f | 1.01 ± 0.05 c | 2.45 ± 0.48 c |
| 2. | Ther_M360min | 73.59 ± 2.39 | 1.52 ± 0.14 a | 2.58 ± 0.14 ab | 2.34 ± 0.19 c |
| 3. | Pep_M180min | 72.89 ± 1.36 | 1.29 ± 0.21 ab | 0.9 ± 0.13 c | 4.02 ± 1.04 a |
| 4. | Pep_M240min | 77.35 ± 1.57 | 0.12 ± 0.01 f | 2.08 ± 0.38 b | 3.47 ± 1.05 b |
| 5. | Alc_E180min | 77.05 ± 2.12 | 0.65 ± 0.21 d | 0.75 ± 0.21 c | 3.52 ± 1.11 b |
| 6. | Pap_E240min | 83.21 ± 2.51 | 0.33 ± 0.11 e | 0.48 ± 0.27 d | 2.08 ± 0.64 cd |
| 7. | Pep_E60min | 75.31 ± 2.57 | 1.71 ± 0.29 a | 3.88 ± 0.91 a | 1.26 ± 0.27 d |
| 8. | Pep_E180min | 82.07 ± 2.56 | 0.87 ± 0.18 bc | 2.11 ± 0.57 b | 3.41 ± 0.28 b |
| Fraction | Molecular Weight | ACE Inhibition (IC50 µg mL−1) | DPPH (EC50 µg mL−1) | ABTS (EC50 µg mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alc_M60min_F1 | MW > 10 kDa | 16.57 ± 1.79 a | 144.13 ± 4.66 a | 70.73 ± 2.38 b |
| Alc_M60min_F2 | 3 < MW < 10 KDa | 2.34 ± 1.08 b | 129.58 ± 4.05 b | 56.35 ± 3.11 c |
| Alc_M60min_F3 | MW < 3 kDa | 0.49 ± 0.25 c | 90.21 ± 3.27 c | 85.14 ± 4.63 a |
| Pap_E240min_F1 | MW > 10 kDa | 56.45 ± 1.38 a | 66.41 ± 3.05 a | 88.76 ± 4.80 a |
| Pap_E240min_F2 | 3 < MW < 10 KDa | 10.6 ± 2.77 b | 58.21 ± 2.56 b | 23.71 ± 3.57 b |
| Pap_E240min_F3 | MW < 3 kDa | 0.67 ± 0.16 c | 49.32 ± 4.09 c | 19.21 ± 3.64 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarkar, P.; Pecorelli, A.; Woodby, B.; Pambianchi, E.; Ferrara, F.; Duary, R.K.; Valacchi, G. Evaluation of Anti-Oxinflammatory and ACE-Inhibitory Properties of Protein Hydrolysates Obtained from Edible Non-Mulberry Silkworm Pupae (Antheraea assama and Philosomia ricinii). Nutrients 2023, 15, 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15041035
Sarkar P, Pecorelli A, Woodby B, Pambianchi E, Ferrara F, Duary RK, Valacchi G. Evaluation of Anti-Oxinflammatory and ACE-Inhibitory Properties of Protein Hydrolysates Obtained from Edible Non-Mulberry Silkworm Pupae (Antheraea assama and Philosomia ricinii). Nutrients. 2023; 15(4):1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15041035
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarkar, Preeti, Alessandra Pecorelli, Brittany Woodby, Erika Pambianchi, Francesca Ferrara, Raj Kumar Duary, and Giuseppe Valacchi. 2023. "Evaluation of Anti-Oxinflammatory and ACE-Inhibitory Properties of Protein Hydrolysates Obtained from Edible Non-Mulberry Silkworm Pupae (Antheraea assama and Philosomia ricinii)" Nutrients 15, no. 4: 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15041035
APA StyleSarkar, P., Pecorelli, A., Woodby, B., Pambianchi, E., Ferrara, F., Duary, R. K., & Valacchi, G. (2023). Evaluation of Anti-Oxinflammatory and ACE-Inhibitory Properties of Protein Hydrolysates Obtained from Edible Non-Mulberry Silkworm Pupae (Antheraea assama and Philosomia ricinii). Nutrients, 15(4), 1035. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15041035






