Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Ameliorates Silica-Induced Lung Injury through the Nrf2-Regulated Glutathione Metabolism Pathway in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. Animal and Experimental Design
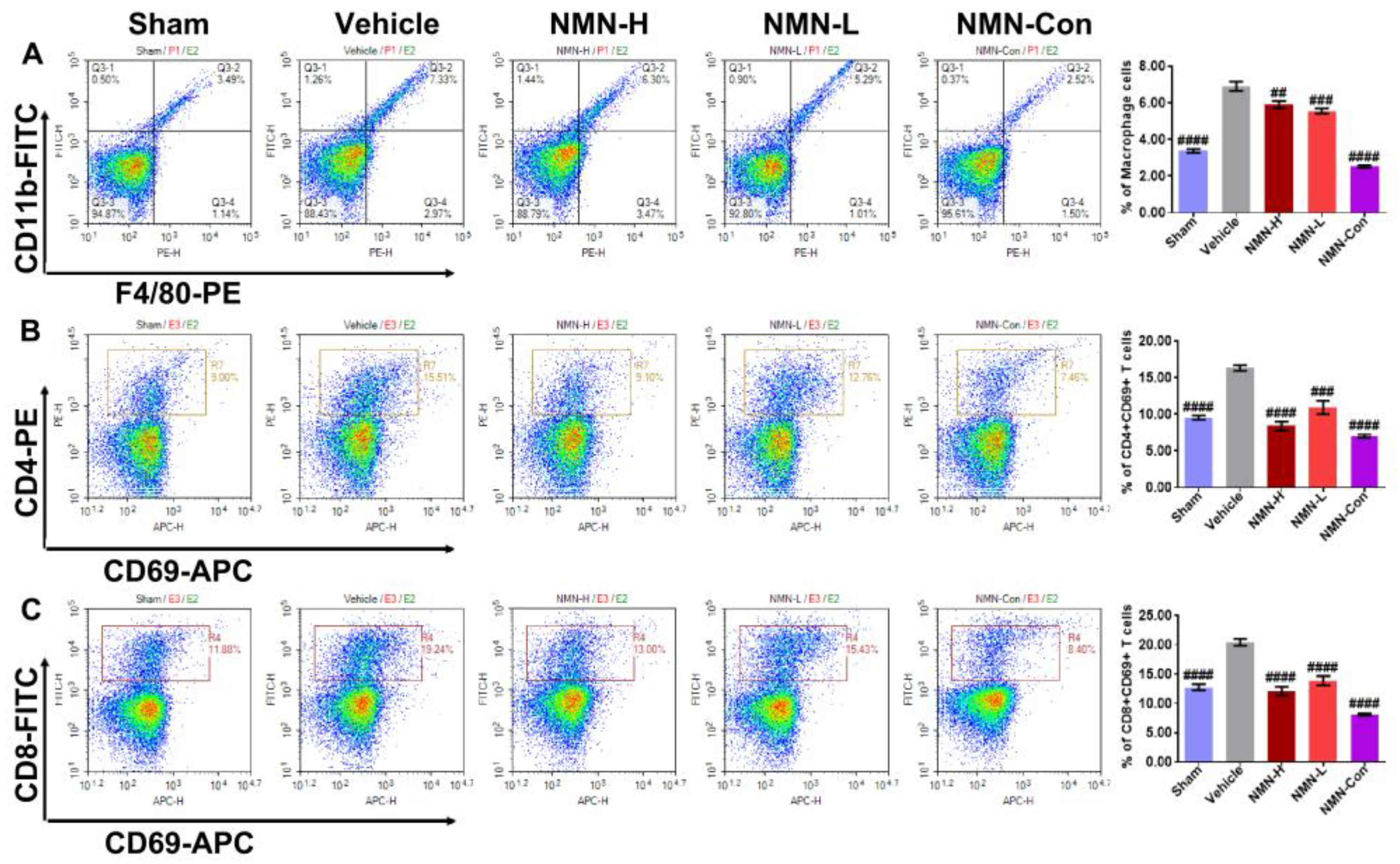
2.3. Flow Cytometry
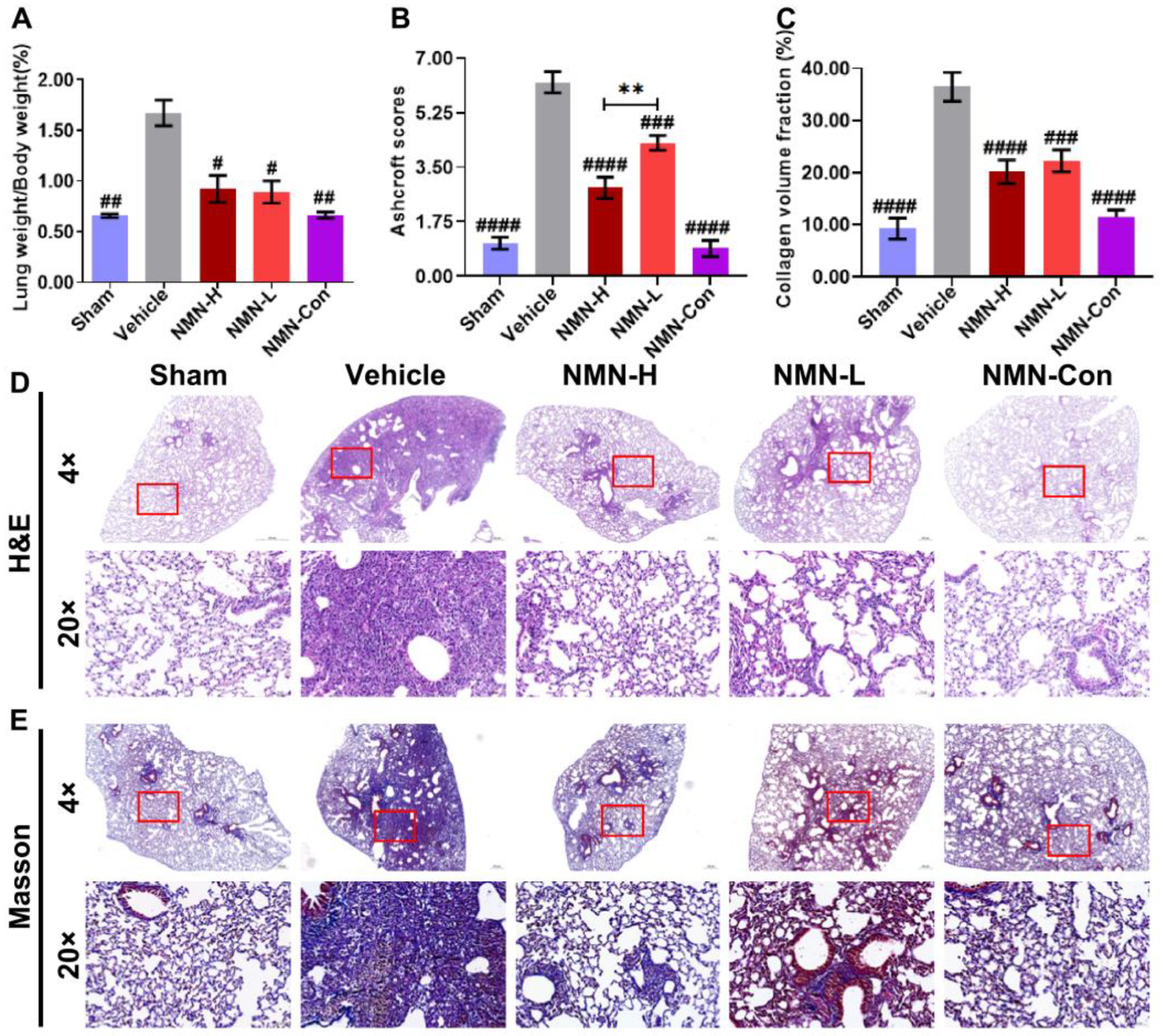
2.4. Histopathological Staining
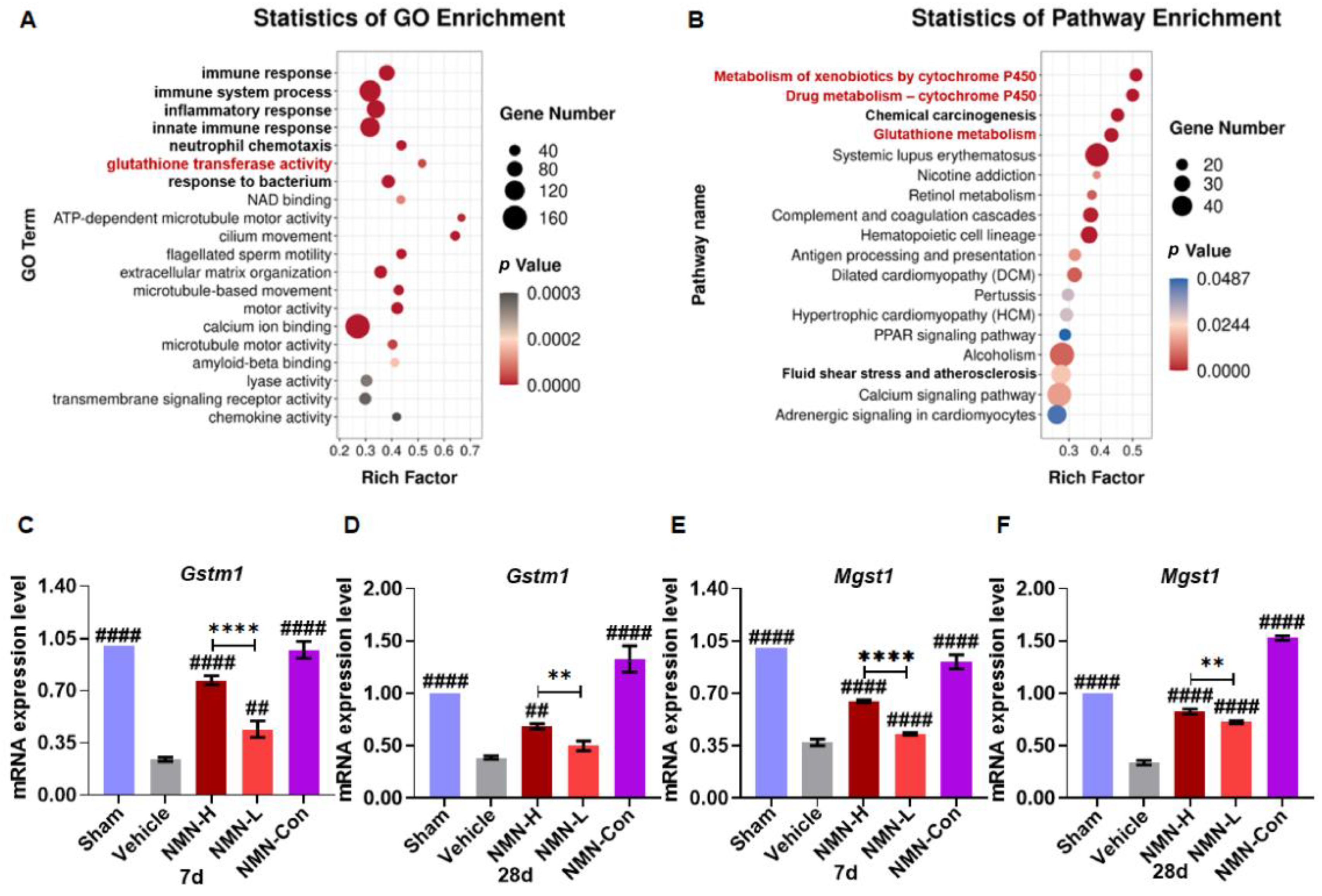
2.5. RNA Sequencing
2.6. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
2.8. GSH Detection
2.9. Western Blot
2.10. Data Statistics and Analysis
3. Results
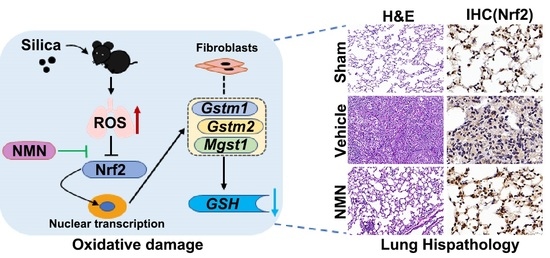
3.1. NMN Alleviates Silica-Induced Lung Injury
3.2. NMN Mitigates Silica-Induced Lung Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
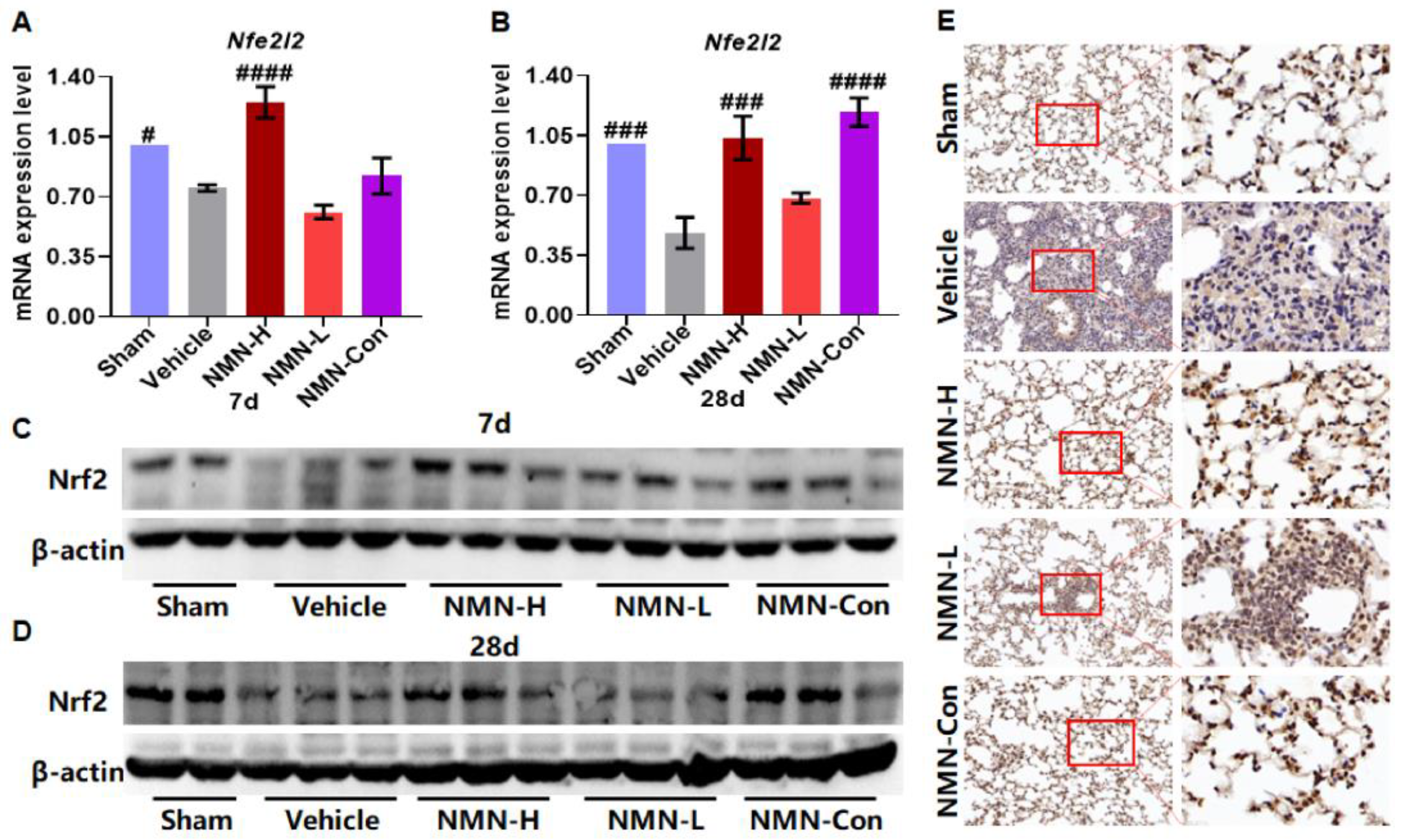
3.3. NMN Suppresses Silica-Induced Lung Injury through the Glutathione Metabolism Pathway
3.4. Silica Induces Glutathione Metabolism Disorder in Fibroblasts
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, P.; Xing, X.; Xi, S.; Jing, H.; Yuan, J.; Fu, Z.; Zhao, H. Trends in global, regional and national incidence of pneumoconiosis caused by different aetiologies: An analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Occup. Environ. Med. 2020, 77, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Brisson, C.; Clays, E.; Ferrario, M.M.; Ivanov, I.D.; Landsbergis, P.; Leppink, N.; Pega, F.; Pikhart, H.; Pruss-Ustun, A.; et al. WHO/ILO work-related burden of disease and injury: Protocol for systematic reviews of exposure to long working hours and of the effect of exposure to long working hours on ischaemic heart disease. Env. Int. 2018, 119, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoy, R.F.; Jeebhay, M.F.; Cavalin, C.; Chen, W.; Cohen, R.A.; Fireman, E.; Go, L.H.T.; León-Jiménez, A.; Menéndez-Navarro, A.; Ribeiro, M.; et al. Current global perspectives on silicosis-Convergence of old and newly emergent hazards. Respirology 2022, 27, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, H.; Goh, N.S.L.; Leong, T.L.; Hoy, R. Silica-associated lung disease: An old-world exposure in modern industries. Respirology 2019, 24, 1165–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, M.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Sun, Y.L.; Han, Z.F.; Zhou, Y.T.; Liu, Y.; Fan, T.H.; Li, Z.G.; Qi, X.M.; Luo, Y.; et al. Tetrandrine alleviates silicosis by inhibiting canonical and non-canonical NLRP3 inflammasome activation in lung macrophages. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2022, 43, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creutzenberg, O.; Pohlmann, G.; Schaudien, D.; Kock, H. Toxicokinetics of Nanoparticles Deposited in Lungs Using Occupational Exposure Scenarios. Front. Public Health 2022, 10, 909247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, C.; Fubini, B. Unveiling the Variability of "Quartz Hazard" in Light of Recent Toxicological Findings. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2017, 30, 469–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grytting, V.S.; Refsnes, M.; Låg, M.; Erichsen, E.; Røhr, T.S.; Snilsberg, B.; White, R.A.; Øvrevik, J. The importance of mineralogical composition for the cytotoxic and pro-inflammatory effects of mineral dust. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2022, 19, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, C.; Sydor, M.J.; Bellomo, C.; Leinardi, R.; Cananà, S.; Kendall, R.L.; Rebba, E.; Corno, M.; Ugliengo, P.; Mino, L.; et al. Molecular recognition between membrane epitopes and nearly free surface silanols explains silica membranolytic activity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 217, 112625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwinn, M.R.; Vallyathan, V. Respiratory burst: Role in signal transduction in alveolar macrophages. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part B Crit. Rev. 2006, 9, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Confalonieri, P.; Volpe, M.C.; Jacob, J.; Maiocchi, S.; Salton, F.; Ruaro, B.; Confalonieri, M.; Braga, L. Regeneration or Repair? The Role of Alveolar Epithelial Cells in the Pathogenesis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF). Cells 2022, 11, 2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimola, A.; Costa, D.; Sodupe, M.; Lambert, J.F.; Ugliengo, P. Silica surface features and their role in the adsorption of biomolecules: Computational modeling and experiments. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 4216–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benmerzoug, S.; Rose, S.; Bounab, B.; Gosset, D.; Duneau, L.; Chenuet, P.; Mollet, L.; Le Bert, M.; Lambers, C.; Geleff, S.; et al. STING-dependent sensing of self-DNA drives silica-induced lung inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissman, D.N. Progressive massive fibrosis: An overview of the recent literature. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 240, 108232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeeshani, H.; Li, J.; Ying, T.; Zhang, B.; Lu, J. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) as an anti-aging health product-Promises and safety concerns. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 37, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Seol, J.; Sato, T.; Fukamizu, Y.; Sakurai, T.; Okura, T. Effect of 12-Week Intake of Nicotinamide Mononucleotide on Sleep Quality, Fatigue, and Physical Performance in Older Japanese Adults: A Randomized, Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, M.; Yoshino, J.; Kayser, B.D.; Patti, G.J.; Franczyk, M.P.; Mills, K.F.; Sindelar, M.; Pietka, T.; Patterson, B.W.; Imai, S.I.; et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide increases muscle insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women. Science 2021, 372, 1224–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; He, B.; Zhu, D.; Wang, L.; Huang, R.; Zhu, J.; Wang, C.; Gao, F. Nicotinamide mononucleotide attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by reducing oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rats. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2021, 712, 109050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Qin, Y.; Huo, F.; Jian, Z.; Li, X.; Geng, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. NMN recruits GSH to enhance GPX4-mediated ferroptosis defense in UV irradiation induced skin injury. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Mol. Basis Dis. 2022, 1868, 166287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Pang, H.; Ma, T.; Ye, Q.; Chen, Q.; Chen, H.; Hu, Z.; Qin, C.F.; Xu, Z. Treatment of SARS-CoV-2-induced pneumonia with NAD(+) and NMN in two mouse models. Cell Discov. 2022, 8, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Bao, Q.; Qian, R.; Peng, L.; Fang, A.; Du, W.; Xie, L.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Alveolar macrophage-derived progranulin mediated pro-inflammatory Il-6 expression via regulating Creb1 in silicosis model. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 107, 108705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, H.; He, Q.; Gan, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, Y.; He, F.; Ye, T.; Yin, W. Galangin ameliorated pulmonary fibrosis in vivo and in vitro by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubner, R.H.; Gitter, W.; El Mokhtari, N.E.; Mathiak, M.; Both, M.; Bolte, H.; Freitag-Wolf, S.; Bewig, B. Standardized quantification of pulmonary fibrosis in histological samples. Biotechniques 2008, 44, 507–511, 514–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fubini, B.; Hubbard, A. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) generation by silica in inflammation and fibrosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 1507–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Takeno, M.; Honma, K.; Yamauchi, H.; Saito, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Morikubo, H.; Nagashima, Y.; Takagi, S.; Yamanaka, K.; et al. Heme oxygenase-1, a potential biomarker of chronic silicosis, attenuates silica-induced lung injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 174, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanka, K.S.; Shukla, S.; Gomez, H.M.; James, C.; Palanisami, T.; Williams, K.; Chambers, D.C.; Britton, W.J.; Ilic, D.; Hansbro, P.M.; et al. Understanding the pathogenesis of occupational coal and silica dust-associated lung disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. Off. J. Eur. Respir. Soc. 2022, 31, 210250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.F.; Pu, Q.; Dai, S.Y.; Ma, Q.; Li, X.; Zhu, W. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Alleviates Hyperosmolarity-Induced IL-17a Secretion and Macrophage Activation in Corneal Epithelial Cells/Macrophage Co-Culture System. J. Inflamm. Res. 2021, 14, 479–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.S.; Pfeiffer, L.M.; Hemenway, D.R.; Rincon, M. Interleukin-12 is not essential for silicosis in mice. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2006, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibrian, D.; Sanchez-Madrid, F. CD69: From activation marker to metabolic gatekeeper. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, T.; Hirahara, K.; Kokubo, K.; Kiuchi, M.; Aoki, A.; Morimoto, Y.; Kumagai, J.; Onodera, A.; Mato, N.; Tumes, D.J.; et al. CD103(hi) T(reg) cells constrain lung fibrosis induced by CD103(lo) tissue-resident pathogenic CD4 T cells. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1469–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.Y.; Hayashizaki, K.; Tokoyoda, K.; Takamura, S.; Motohashi, S.; Nakayama, T. Crucial role for CD69 in allergic inflammatory responses: CD69-Myl9 system in the pathogenesis of airway inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 278, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Hyodoh, F.; Hatayama, T.; Sakaguchi, H.; Hatada, S.; Miura, Y.; Takata-Tomokuni, A.; Katsuyama, H.; Otsuki, T. Induction of CD69 antigen expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells on exposure to silica, but not by asbestos/chrysotile-A. Immunol. Lett. 2005, 98, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2013, 53, 401–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Abulikemu, A.; Lv, S.; Qi, Y.; Duan, J.; Zhang, J.; Chen, R.; Guo, C.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z. Oxidative stress- and mitochondrial dysfunction-mediated cytotoxicity by silica nanoparticle in lung epithelial cells from metabolomic perspective. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 129969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Peden, D.B.; McConnell, R.; Fruin, S.; Diaz-Sanchez, D. Glutathione-S-transferase M1 regulation of diesel exhaust particle-induced pro-inflammatory mediator expression in normal human bronchial epithelial cells. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2012, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siritantikorn, A.; Johansson, K.; Ahlen, K.; Rinaldi, R.; Suthiphongchai, T.; Wilairat, P.; Morgenstern, R. Protection of cells from oxidative stress by microsomal glutathione transferase 1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 355, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, S.; D’Mello, V.; Caruso, D.; Abdul-Muneer, P.M. Traumatic brain injury-induced downregulation of Nrf2 activates inflammatory response and apoptotic cell death. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 97, 1627–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, F.; Liu, J.; Xie, Y.; Tang, D.; Kang, R. MGST1 is a redox-sensitive repressor of ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Chem. Biol. 2021, 28, 765–775.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, M.; Wang, W.; Zhai, Z.; Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Kothari, D.; Niu, K.; Wu, X. Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation protects the intestinal function in aging mice and D-galactose induced senescent cells. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 7507–7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuertes, E.; van der Plaat, D.A.; Minelli, C. Antioxidant genes and susceptibility to air pollution for respiratory and cardiovascular health. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 151, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukkonen, M.K.; Hämäläinen, S.; Kaleva, S.; Vehmas, T.; Huuskonen, M.S.; Oksa, P.; Vainio, H.; Piirilä, P.; Hirvonen, A. Genetic susceptibility to asbestos-related fibrotic pleuropulmonary changes. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fafián-Labora, J.A.; Rodríguez-Navarro, J.A.; O’Loghlen, A. Small Extracellular Vesicles Have GST Activity and Ameliorate Senescence-Related Tissue Damage. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 71–86.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, K.; Jarvliden, J.; Gogvadze, V.; Morgenstern, R. Multiple roles of microsomal glutathione transferase 1 in cellular protection: A mechanistic study. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1638–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Groups | Intratracheal Instillation (0 d) | i.g. * (Daily) | Number of Animals (7 d) | Number of Animals (28 d) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control group (Sham) | Normal saline (80 μL) | Normal saline | 3 | 5 |
| Model group (Vehicle) | Silica (50 mg/mL, 80 μL) | Normal saline | 5 | 6 |
| NMN high-dose group (NMN-H) | Silica (50 mg/mL, 80 μL) | NMN (1000 mg/kg) | 5 | 6 |
| NMN low-dose group (NMN-L) | Silica (50 mg/mL, 80 μL) | NMN (500 mg/kg) | 5 | 6 |
| NMN control group (NMN-Con) | Normal saline (80 μL) | NMN (1000 mg/kg) | 3 | 5 |
| Primer Name | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| Gstm1 | CCATTGCCAAACCCTTTGCT | TGACCTTGTCCCCTGCAAAC |
| Mgst1 | GCTCGGATCTACCACACCATTGC | CTCCTTAGCAGCCTGTAAGCCATTG |
| Gstm2 | GAGAGACAGAGGAGGAGAGGATTCG | TCTCAAAGTCAGGGCTGTAGCAAAC |
| Nfe2l2 | AAGCACAGCCAGCACATTCTCC | TGACCAGGACTCACGGGAACTTC |
| Gsto1 | GCCCGAGTGGTTCTTTGAGA | GTGCCTTCTTGTACGGGTCA |
| Gsta4 | TGTATGGGAAGGACCTGAAGGAGAG | ATGGAGCCACGGCAATCATCATC |
| β-actin | GAGGTATCCTGACCCTGAAGTA | CACACGCAGCTCATTGTAGA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Zhao, M.; Qian, R.; Wang, M.; Bao, Q.; Chen, X.; Du, W.; Zhang, L.; Ye, T.; Xie, Y.; et al. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Ameliorates Silica-Induced Lung Injury through the Nrf2-Regulated Glutathione Metabolism Pathway in Mice. Nutrients 2023, 15, 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010143
Wang L, Zhao M, Qian R, Wang M, Bao Q, Chen X, Du W, Zhang L, Ye T, Xie Y, et al. Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Ameliorates Silica-Induced Lung Injury through the Nrf2-Regulated Glutathione Metabolism Pathway in Mice. Nutrients. 2023; 15(1):143. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010143
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liqun, Manyu Zhao, Rui Qian, Mengzhu Wang, Qixue Bao, Xuxi Chen, Wen Du, Ling Zhang, Tinghong Ye, Yongmei Xie, and et al. 2023. "Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Ameliorates Silica-Induced Lung Injury through the Nrf2-Regulated Glutathione Metabolism Pathway in Mice" Nutrients 15, no. 1: 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010143
APA StyleWang, L., Zhao, M., Qian, R., Wang, M., Bao, Q., Chen, X., Du, W., Zhang, L., Ye, T., Xie, Y., Zhang, B., Peng, L., & Yao, Y. (2023). Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Ameliorates Silica-Induced Lung Injury through the Nrf2-Regulated Glutathione Metabolism Pathway in Mice. Nutrients, 15(1), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15010143