Prevalence and Prognostic Significance of Malnutrition in Patients with Abnormal Glycemic Status and Coronary Artery Disease: A Multicenter Cohort Study in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Setting, and Participants
2.2. Blood Sampling and Laboratory Testing
2.3. Endpoints and Covariables
2.4. Assessment of Nutritional Status
2.5. Statistical Analysis
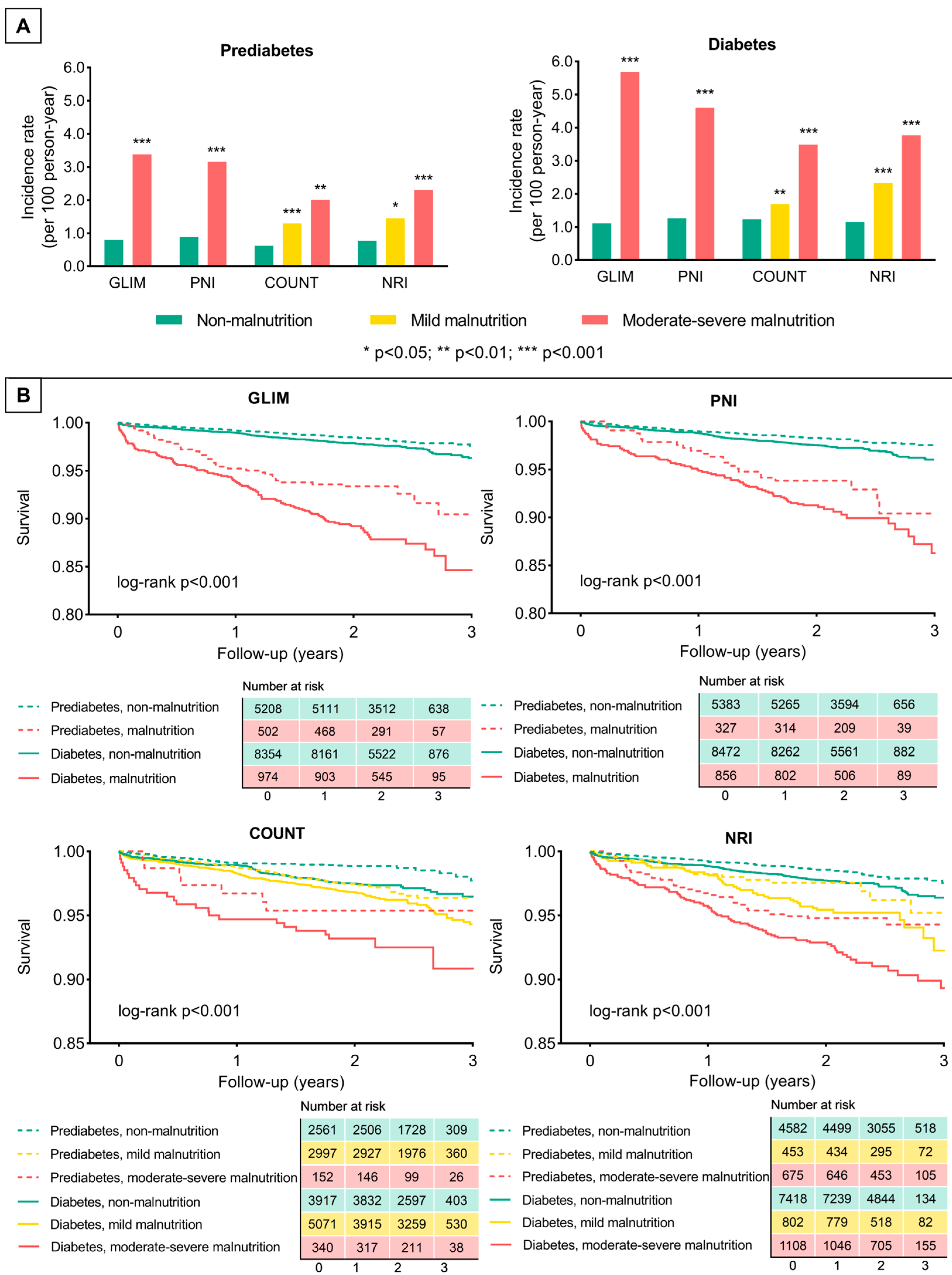
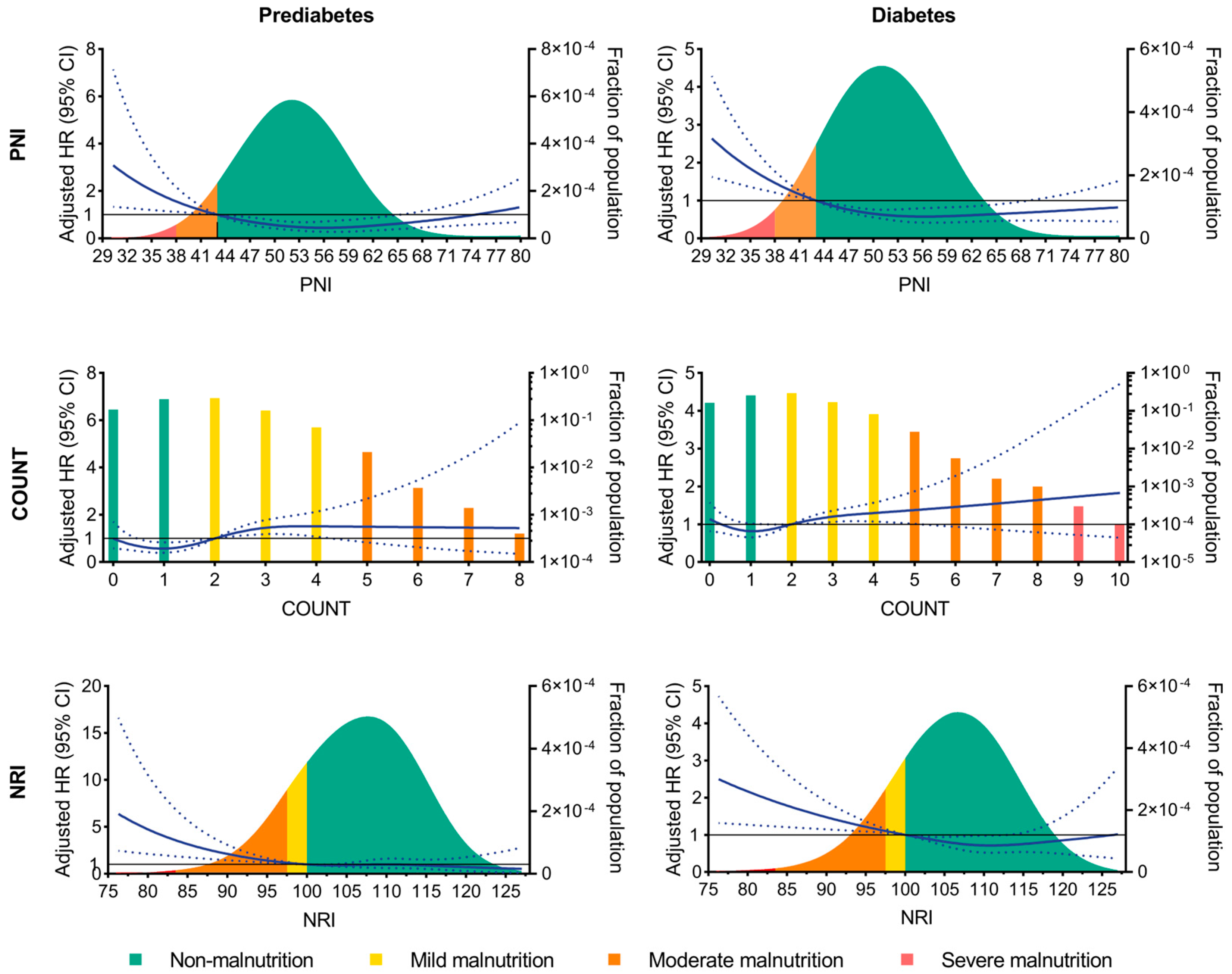
3. Results
3.1. Study Population and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Prevalence of Malnutrition
3.3. Association of Malnutrition and Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blaak, E.E. Current metabolic perspective on malnutrition in obesity: Towards more subgroup-based nutritional approaches? Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2020, 79, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zupo, R.; Castellana, F.; Bortone, I.; Griseta, C.; Sardone, R.; Lampignano, L.; Lozupone, M.; Solfrizzi, V.; Castellana, M.; Giannelli, G.; et al. Nutritional domains in frailty tools: Working towards an operational definition of nutritional frailty. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 64, 101148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zupo, R.; Castellana, F.; Guerra, V.; Donghia, R.; Bortone, I.; Griseta, C.; Lampignano, L.; Dibello, V.; Lozupone, M.; Coelho-Junior, H.J.; et al. Associations between nutritional frailty and 8-year all-cause mortality in older adults: The Salus in Apulia Study. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 290, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, J.; Baracos, V.; Bertz, H.; Bozzetti, F.; Calder, P.C.; Deutz, N.E.P.; Erickson, N.; Laviano, A.; Lisanti, M.P.; Lobo, D.N.; et al. ESPEN expert group recommendations for action against cancer-related malnutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czapla, M.; Karniej, P.; Juarez-Vela, R.; Lokiec, K. The Association between Nutritional Status and In-Hospital Mortality among Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome-A Result of the Retrospective Nutritional Status Heart Study (NSHS). Nutrients 2020, 12, 3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czapla, M.; Juarez-Vela, R.; Lokiec, K.; Wleklik, M.; Karniej, P.; Smereka, J. The Association between Nutritional Status and Length of Hospital Stay among Patients with Hypertension. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaluzna-Oleksy, M.; Krysztofiak, H.; Migaj, J.; Wleklik, M.; Dudek, M.; Uchmanowicz, I.; Lesiak, M.; Straburzynska-Migaj, E. Relationship between Nutritional Status and Clinical and Biochemical Parameters in Hospitalized Patients with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction, with 1-year Follow-Up. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposeiras Roubin, S.; Abu Assi, E.; Cespon Fernandez, M.; Barreiro Pardal, C.; Lizancos Castro, A.; Parada, J.A.; Perez, D.D.; Blanco Prieto, S.; Rossello, X.; Ibanez, B.; et al. Prevalence and Prognostic Significance of Malnutrition in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 828–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, L.; He, S. Prognostic nutritional index and the risk of mortality in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 331, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Wei, X.B.; Huang, J.L.; Ke, Z.H.; Tan, N.; Chen, J.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Yu, D.Q. The prognostic nutritional index might predict clinical outcomes in patients with idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2020, 30, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einarson, T.R.; Acs, A.; Ludwig, C.; Panton, U.H. Prevalence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: A systematic literature review of scientific evidence from across the world in 2007–2017. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, R.C.W. Epidemiology of diabetes and diabetic complications in China. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, G.; Huang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; et al. Prevalence and prognostic significance of malnutrition in diabetic patients with coronary artery disease: A cohort study. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 18, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.T.; Shao, Q.Y.; Li, Q.X.; Yang, Z.Q.; Han, K.N.; Liang, J.; Shen, H.; Liu, X.L.; Zhou, Y.J.; Wang, Z.J. Nutritional Risk Index Improves the GRACE Score Prediction of Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 8, 773200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, M.; Hayiroglu, M.I.; Keskin, T.; Kaya, A.; Tatlisu, M.A.; Altay, S.; Uzun, A.O.; Borklu, E.B.; Guvenc, T.S.; Avci, I.I.; et al. A novel and useful predictive indicator of prognosis in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, the prognostic nutritional index. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 27, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Paris, A.; Martin-Palmero, A.; Gomez-Candela, C.; Garcia-Almeida, J.M.; Burgos-Pelaez, R.; Sanz-Arque, A.; Espina, S.; Arbones-Mainar, J.M.; Study, V.g. GLIM Criteria at Hospital Admission Predict 8-Year All-Cause Mortality in Elderly Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results From VIDA Study. JPEN J. Parenter. Enteral. Nutr. 2020, 44, 1492–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saintrain, M.V.L.; Sandrin, R.; Bezerra, C.B.; Lima, A.O.P.; Nobre, M.A.; Braga, D.R.A. Nutritional assessment of older adults with diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 155, 107819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Choe, Y.; Mustad, V.A.; Chakraborty, S.; Goates, S.; Luo, M.; Mechanick, J.I. Impact of malnutrition on survival and healthcare utilization in Medicare beneficiaries with diabetes: A retrospective cohort analysis. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2018, 6, e000471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y.X.; Yang, K.; Liang, J.; Wang, S.; Gan, H.T. Pilot study of the Mini Nutritional Assessment on predicting outcomes in older adults with type 2 diabetes. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2017, 17, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cederholm, T.; Jensen, G.L.; Correia, M.; Gonzalez, M.C.; Fukushima, R.; Higashiguchi, T.; Baptista, G.; Barazzoni, R.; Blaauw, R.; Coats, A.J.S.; et al. GLIM criteria for the diagnosis of malnutrition—A consensus report from the global clinical nutrition community. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, S.C.; Chandramouli, C.; Lo, C.I.; Lin, C.F.; Sung, K.T.; Huang, W.H.; Lai, Y.H.; Yun, C.H.; Su, C.H.; Yeh, H.I.; et al. Associations of obesity and malnutrition with cardiac remodeling and cardiovascular outcomes in Asian adults: A cohort study. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, T.; Goseki, N.; Kosaki, G. Prognostic nutritional index in gastrointestinal surgery of malnourished cancer patients. Nihon Geka Gakkai Zasshi 1984, 85, 1001–1005. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Wang, D.; He, L.; Zhang, G.; Yu, J.; Chen, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, T.; Lin, Y.; Luo, H. Normal reference intervals of prognostic nutritional index in healthy adults: A large multi-center observational study from Western China. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignacio de Ulibarri, J.; Gonzalez-Madrono, A.; de Villar, N.G.; Gonzalez, P.; Gonzalez, B.; Mancha, A.; Rodriguez, F.; Fernandez, G. CONUT: A tool for controlling nutritional status. First validation in a hospital population. Nutr. Hosp. 2005, 20, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bouillanne, O.; Morineau, G.; Dupont, C.; Coulombel, I.; Vincent, J.P.; Nicolis, I.; Benazeth, S.; Cynober, L.; Aussel, C. Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index: A new index for evaluating at-risk elderly medical patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausmuller, S.; Heitzinger, G.; Pavo, N.; Spinka, G.; Goliasch, G.; Arfsten, H.; Gabler, C.; Strunk, G.; Hengstenberg, C.; Hulsmann, M.; et al. Malnutrition outweighs the effect of the obesity paradox. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2022, 13, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, W.L.; Collins, P.F.; Hickling, D.F.; Bell, J.J. Evaluating the concurrent validity of body mass index (BMI) in the identification of malnutrition in older hospital inpatients. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 2417–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campillo, B.; Paillaud, E.; Uzan, I.; Merlier, I.; Abdellaoui, M.; Perennec, J.; Louarn, F.; Bories, P.N.; Comite de Liaison, A.-N. Value of body mass index in the detection of severe malnutrition: Influence of the pathology and changes in anthropometric parameters. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, N.K.; Pawar, H.S.; Mitra, A.; Mitra, A. Rising trend of diabetes mellitus amongst the undernourished: State -of- the -art review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2017, 11 (Suppl 1), S169–S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, G.; Hu, B.; Astor, B.C.; Greene, T.; Erlinger, T.; Kusek, J.W.; Lipkowitz, M.; Lewis, J.A.; Randall, O.S.; Hebert, L.; et al. Malnutrition-inflammation modifies the relationship of cholesterol with cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 2131–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matia Martin, P.; Robles Agudo, F.; Lopez Medina, J.A.; Sanz Paris, A.; Tarazona Santabalbina, F.; Domenech Pascual, J.R.; Lopez Penabad, L.; Sanz Barriuso, R.; GluceNut Study, G. Effectiveness of an oral diabetes-specific supplement on nutritional status, metabolic control, quality or life, and functional status in elderly patients. A multicentre study. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laksir, H.; Lansink, M.; Regueme, S.C.; de Vogel-van den Bosch, J.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H.; Bourdel-Marchasson, I. Glycaemic response after intake of a high energy, high protein, diabetes-specific formula in older malnourished or at risk of malnutrition type 2 diabetes patients. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2084–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Paris, A.; Boj-Carceller, D.; Lardies-Sanchez, B.; Perez-Fernandez, L.; Cruz-Jentoft, A.J. Health-Care Costs, Glycemic Control and Nutritional Status in Malnourished Older Diabetics Treated with a Hypercaloric Diabetes-Specific Enteral Nutritional Formula. Nutrients 2016, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuetz, P.; Fehr, R.; Baechli, V.; Geiser, M.; Deiss, M.; Gomes, F.; Kutz, A.; Tribolet, P.; Bregenzer, T.; Braun, N.; et al. Individualised nutritional support in medical inpatients at nutritional risk: A randomised clinical trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 2312–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evert, A.B.; Dennison, M.; Gardner, C.D.; Garvey, W.T.; Lau, K.H.K.; MacLeod, J.; Mitri, J.; Pereira, R.F.; Rawlings, K.; Robinson, S.; et al. Nutrition Therapy for Adults With Diabetes or Prediabetes: A Consensus Report. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 731–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| All Participants (n = 15,038) | |
|---|---|
| Demographic characteristics | |
| Age, years | 62 (54–68) |
| Female | 3904 (25.96) |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 25.71 (23.67–27.78) |
| Smoking status | |
| Current smoker | 3674 (24.43) |
| Former smoker | 4928 (32.77) |
| Never smoker | 6436 (42.80) |
| Clinical characteristics | |
| CAD presentation | |
| ACS | 7283 (48.43) |
| CCS | 7755 (51.57) |
| Length of stay, day | 5 (3–8) |
| Glycemic status | |
| Prediabetes | 5710 (37.97) |
| Diabetes | 9328 (62.03) |
| Hypertension | 10,843 (72.10) |
| Dyslipidemia | 13,903 (92.45) |
| Peripheral artery disease | 816 (5.43) |
| COPD | 242 (1.61) |
| Prior myocardial infarction | 2642 (17.57) |
| Prior stroke | 2319 (15.42) |
| Laboratory tests | |
| FBG, mmol/L | 6.29 (5.37–8.04) |
| HbA1c, % | 6.1 (5.8–7.1) |
| Lymphocyte count, ×109/L | 1.84 (1.37–2.56) |
| Serum albumin, g/L | 42.5 (38.9–46.1) |
| hs-CRP, mg/L | 1.92 (1.03–4.73) |
| Total cholesterol, mmol/L | 3.99 (3.37–4.76) |
| eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 438 (2.91) |
| LVEF <40% | 431 (2.87) |
| Angiographic characteristics | |
| Coronary angiography | 14,816 (98.52) |
| LMCA/three-vessel disease | 7071 (47.02) |
| SYNTAX score | |
| ≤22 | 12,254 (82.75) |
| 23–32 | 1958 (13.22) |
| ≥33 | 596 (4.02) |
| PCI | 10,970 (72.95) |
| Medication | |
| Aspirin | 14,829 (98.61) |
| P2Y12 inhibitors | 13,530 (89.97) |
| Statins | 14,700 (97.75) |
| β-blockers | 12,183 (81.01) |
| ACEIs/ARBs | 9417 (62.62) |
| Malnutrition | |
| GLIM | 1476 (9.82) |
| PNI | 1183 (7.87) |
| COUNT | 8560 (56.92) |
| Mild | 8068 (53.65) |
| Moderate–severe | 492 (3.27) |
| NRI | 3038 (20.21) |
| Mild | 1255 (8.35) |
| Moderate–severe | 1783 (11.86) |
| GLIM | PNI | COUNT | NRI | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Malnutrition (n = 1476) | Non-Malnutrition (n = 13,562) | p | Malnutrition (n = 1183) | Non-Malnutrition (n = 13,855) | p | Moderate–Severe Malnutrition (n = 492) | Mild Malnutrition (n = 8068) | Non-Malnutrition (n = 6478) | p | Moderate–Severe Malnutrition (n = 1783) | Mild Malnutrition (n = 1255) | Non-Malnutrition (n = 12,000) | p | |
| Demographic characteristics | ||||||||||||||
| Age, years | 72 (65–78) | 61 (54–67) | <0.001 | 67 (61–75) | 61 (54–68) | <0.001 | 66 (59–74) | 62 (55–69) | 61 (53–67) | <0.001 | 67 (60–74) | 64 (58–70) | 61 (54–67) | <0.001 |
| Female | 744 (50.41) | 31 (23.30) | <0.001 | 352 (29.75) | 3552 (25.64) | 0.002 | 112 (22.76) | 1830 (22.68) | 1962 (30.29) | <0.001 | 524 (29.39) | 388 (30.92) | 2992 (24.93) | <0.001 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 22.49 (21.10–23.83) | 26.03 (24.22–28.09) | <0.001 | 24.77 (22.59–26.85) | 25.83 (23.81–27.99) | <0.001 | 24.73 (22.57–27.02) | 25.63 (23.62–27.73) | 25.95 (23.88–28.08) | <0.001 | 24.22 (21.61–26.59) | 25.34 (23.26–27.68) | 25.95 (24.02–28.06) | <0.001 |
| Smoking status | ||||||||||||||
| Current smoker | 254 (17.21) | 3420 (25.22) | <0.001 | 267 (22.57) | 3407 (24.59) | 0.036 | 104 (21.14) | 1766 (21.89) | 1804 (27.85) | <0.001 | 484 (27.15) | 309 (24.62) | 2881 (24.01) | <0.001 |
| Former smoker | 435 (29.47) | 4493 (33.13) | 368 (31.11) | 4560 (32.91) | 173 (35.16) | 2889 (35.81) | 1866 (28.81) | 440 (24.68) | 364 (29.00) | 4124 (34.37) | ||||
| Never smoker | 787 (53.32) | 5649 (41.65) | 548 (46.32) | 5888 (42.50) | 215 (43.70) | 3413 (42.30) | 2808 (43.35) | 859 (48.18) | 582 (46.37) | 4995 (41.62) | ||||
| Clinical characteristics | ||||||||||||||
| CAD presentation | ||||||||||||||
| ACS | 986 (66.80) | 6297 (46.43) | <0.001 | 996 (84.19) | 6287 (45.38) | <0.001 | 307 (62.40) | 3740 (46.36) | 3236 (49.95) | <0.001 | 1271 (71.28) | 750 (59.76) | 5262 (43.85) | <0.001 |
| CCS | 490 (33.20) | 7265 (53.57) | 187 (15.81) | 7568 (54.62) | 185 (37.60) | 4328 (53.64) | 3242 (50.05) | 512 (28.72) | 505 (40.24) | 6738 (5.15) | ||||
| Length of stay, day | 7 (4–10) | 5 (3–7) | <0.001 | 7 (5–11) | 5 (3–7) | <0.001 | 6 (4–10) | 5 (3–8) | 5 (3–8) | <0.001 | 6 (4–10) | 5 (3–9) | 5 (3–7) | <0.001 |
| Glycemic status | ||||||||||||||
| Prediabetes | 502 (34.01) | 5208 (38.40) | <0.001 | 327 (27.64) | 5383 (38.85) | <0.001 | 152 (30.89) | 2997 (37.15) | 2561 (39.53) | <0.001 | 675 (37.86) | 453 (36.10) | 4582 (38.18) | 0.348 |
| Diabetes | 974 (65.99) | 8354 (61.60) | 856 (72.36) | 8472 (61.15) | 340 (69.11) | 5071 (62.85) | 3917 (60.47) | 1108 (62.14) | 802 (63.90) | 7418 (61.82) | ||||
| Hypertension | 1096 (74.25) | 9747 (71.87) | 0.052 | 853 (72.10) | 330 (27.90) | 0.999 | 334 (67.89) | 5918 (73.35) | 4592 (70.89) | <0.001 | 1167 (65.45) | 887 (70.68) | 8789 (73.24) | <0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia | 1364 (92.41) | 12,539 (92.46) | 0.951 | 1096 (92.65) | 12,807 (92.44) | 0.793 | 464 (94.31) | 7500 (92.96) | 5939 (91.68) | 0.004 | 1511 (84.74) | 1121 (89.32) | 11,271 (93.92) | <0.001 |
| Peripheral artery disease | 99 (6.71) | 717 (5.29) | 0.022 | 52 (4.40) | 764 (5.51) | 0.103 | 26 (5.28) | 481 (5.96) | 309 (4.77) | 0.007 | 84 (4.71) | 61 (4.86) | 671 (5.59) | 0.202 |
| COPD | 84 (5.69) | 158 (1.17) | <0.001 | 47 (3.97) | 195 (1.41) | <0.001 | 20 (4.07) | 134 (1.66) | 88 (1.36) | <0.001 | 42 (2.36) | 25 (1.99) | 175 (1.46) | 0.010 |
| Prior myocardial infarction | 252 (17.07) | 2390 (17.62) | 0.598 | 205 (17.33) | 2437 (17.59) | 0.821 | 106 (21.54) | 1584 (19.63) | 952 (14.70) | <0.001 | 287 (16.10) | 209 (16.65) | 2146 (17.88) | 0.122 |
| Prior stroke | 288 (19.51) | 2031 (14.98) | <0.001 | 208 (17.58) | 2111 (15.24) | 0.032 | 79 (16.06) | 1324 (16.41) | 916 (14.14) | <0.001 | 324 (18.17) | 172 (13.71) | 1823 (15.19) | 0.001 |
| Laboratory tests | ||||||||||||||
| FBG, mmol/L | 6.88 (5.60–8.80) | 6.24 (5.35–7.95) | <0.001 | 7.37 (5.98–9.59) | 6.21 (5.33–7.91) | <0.001 | 6.60 (5.42–8.48) | 6.24 (5.30–7.95) | 6.33 (5.43–8.11) | <0.001 | 6.33 (5.17–8.38) | 6.19 (5.03–8.02) | 6.30 (5.42–8.00) | <0.001 |
| HbA1c, % | 6.15 (5.80–7.10) | 6.10 (5.80–7.10) | 0.520 | 6.0 (5.7–7.0) | 6.2 (5.8–7.1) | <0.001 | 6.0 (5.7–6.9) | 6.1 (5.8–7.0) | 6.2 (5.8–7.2) | <0.001 | 6.1 (5.8–7.1) | 6.1 (5.8–7.2) | 6.2 (5.8–7.1) | 0.347 |
| Lymphocyte count, ×109/L | 1.66 (1.21–2.27) | 1.86 (1.39–2.58) | <0.001 | 1.15 (0.87–1.60) | 1.89 (1.44–2.60) | <0.001 | 0.96 (0.69–1.44) | 1.53 (1.18–2.21) | 2.13 (1.77–2.92) | <0.001 | 2.12 (1.41–15.20) | 1.97 (1.41–11.50) | 1.80 (1.36–2.41) | <0.001 |
| Serum albumin, g/L | 39.0 (35.9–43.2) | 42.8 (39.3–46.4) | <0.001 | 35.0 (33.1–36.4) | 43.0 (39.8–46.5) | <0.001 | 35.5 (32.5–41.6) | 42.2 (38.6–45.9) | 43.1 (39.8–46.7) | <0.001 | 35.8 (34.0–36.9) | 38.4 (37.8–38.9) | 44 (41.0–47.0) | <0.001 |
| hs-CRP, mg/L | 6.73 (3.68–11.45) | 1.92 (0.94, 3.71) | <0.001 | 6.02 (1.92–11.56) | 1.92 (0.97–4.15) | <0.001 | 2.82 (1.55–10.71) | 1.92 (0.86–4.35) | 1.93 (1.23–4.88) | <0.001 | 2.36 (1.85–10.30) | 1.92 (1.25–6.29) | 1.92 (0.95–4.17) | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol, mmol/L | 4.10 (3.41–4.86) | 3.98 (3.36–4.74) | 0.011 | 3.86 (3.26–4.50) | 4.00 (3.38–4.78) | 0.001 | 3.08 (2.54–3.50) | 3.48 (3.09–4.08) | 4.70 (4.13–5.32) | <0.001 | 3.88 (3.25–4.58) | 3.80 (3.23–4.63) | 4.04 (3.40–4.79) | <0.001 |
| eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 199 (13.48) | 239 (1.76) | <0.001 | 108 (9.13) | 330 (2.38) | <0.001 | 33 (6.71) | 237 (2.94) | 169 (2.61) | <0.001 | 139 (7.80) | 55 (4.38) | 244 (2.03) | <0.001 |
| LVEF < 40% | 129 (8.74) | 302 (2.23) | <0.001 | 77 (6.51) | 354 (2.56) | <0.001 | 29 (5.89) | 232 (2.88) | 171 (2.64) | <0.001 | 103 (5.78) | 34 (2.71) | 294 (2.45) | <0.001 |
| Angiographic characteristics | ||||||||||||||
| Coronary angiography | 1441 (97.63) | 13,375 (98.62) | 0.003 | 1153 (97.46) | 13,663 (98.61) | <0.001 | 471 (95.73) | 7959 (98.65) | 6386 (98.58) | <0.001 | 1716 (96.24) | 1223 (97.45) | 11,877 (98.98) | <0.001 |
| LMCA/three-vessel disease | 825 (55.89) | 6246 (46.06) | <0.001 | 656 (55.45) | 6415 (46.30) | <0.001 | 248 (50.41) | 3778 (46.83) | 3046 (47.02) | 0.346 | 953 (53.45) | 643 (51.24) | 5475 (45.62) | <0.001 |
| SYNTAX score | ||||||||||||||
| ≤22 | 1091 (75.82) | 11,163 (83.50) | <0.001 | 889 (77.17) | 11,365 (83.22) | <0.001 | 373 (79.19) | 6643 (83.52) | 5237 (82.05) | 0.004 | 1284 (74.91) | 952 (77.91) | 10,018 (84.38) | <0.001 |
| 23–32 | 235 (16.33) | 1723 (12.89) | 188 (16.32) | 1770 (12.96) | 65 (13.80) | 1010 (12.70) | 883 (13.83) | 286 (16.69) | 196 (16.04) | 1476 (12.43) | ||||
| ≥33 | 113 (7.85) | 483 (3.61) | 75 (6.51) | 521 (3.82) | 33 (7.01) | 301 (3.78) | 263 (4.12) | 144 (8.40) | 74 (6.06) | 378 (3.18) | ||||
| PCI | 1105 (74.86) | 9865 (72.74) | 0.081 | 950 (80.30) | 10,020 (72.32) | <0.001 | 356 (72.36) | 5823 (72.17) | 4791 (73.96) | 0.053 | 1313 (73.64) | 939 (74.82) | 8718 (72.65) | 0.202 |
| Medication | ||||||||||||||
| Aspirin | 1445 (97.90) | 13,384 (98.69) | 0.014 | 1154 (97.55) | 13,675 (98.70) | 0.001 | 475 (96.54) | 7967 (98.75) | 6388 (98.61) | <0.001 | 1748 (98.04) | 1233 (98.25) | 11,848 (98.73) | 0.033 |
| P2Y12 inhibitors | 1357 (91.94) | 12,173 (89.76) | 0.008 | 1088 (91.97) | 12,442 (89.80) | 0.017 | 451 (91.67) | 7271 (90.12) | 5809 (89.67) | 0.358 | 1631 (91.48) | 1139 (90.76) | 10,760 (89.67) | 0.038 |
| Statins | 1430 (96.88) | 13,270 (97.85) | 0.018 | 1144 (96.70) | 13,556 (97.84) | 0.011 | 482 (97.97) | 7897 (97.88) | 6321 (97.58) | 0.445 | 1726 (96.80) | 1215 (96.81) | 11,759 (97.99) | <0.001 |
| β-blockers | 1178 (79.81) | 11,005 (81.15) | 0.214 | 934 (78.95) | 11,249 (81.19) | 0.059 | 385 (78.25) | 6629 (82.16) | 5169 (79.79) | <0.001 | 1186 (66.52) | 915 (72.91) | 10,082 (84.02) | <0.001 |
| ACEIs/ARBs | 907 (61.45) | 8510 (62.75) | 0.327 | 790 (66.78) | 8627 (62.27) | 0.002 | 302 (61.38) | 5038 (62.44) | 4077 (62.94) | 0.703 | 1099 (61.64) | 838 (66.77) | 7480 (62.33) | 0.006 |
| All-Cause Death | MACCE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prediabetes | Diabetes | Prediabetes | Diabetes | |
| GLIM (non-malnutrition as reference) | ||||
| Crude HR (95% CI) | 3.49 (2.28, 5.33) * | 4.39 (3.45, 5.57) * | 1.91 (1.34, 2.70) * | 2.50 (2.05, 3.04) * |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.65 (1.00, 2.71) † | 2.41 (1.78, 3.27) * | 1.01 (0.69, 1.48) | 1.62 (1.29, 2.05) * |
| PSM HR (95% CI) | 2.58 (0.86, 7.73) | 2.72 (1.43, 5.20) ‡ | 0.74 (0.33, 1.66) | 1.99 (1.21, 3.25) ‡ |
| PNI, categorical (non-malnutrition as reference) | ||||
| Crude HR (95% CI) | 3.59 (2.29, 5.63) * | 3.62 (2.82, 4.63) * | 2.59 (1.84, 3.64) * | 2.27 (1.86, 2.77) * |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.84 (1.14, 2.96) † | 1.83 (1.41, 2.39) * | 1.70 (1.19, 2.44) ‡ | 1.46 (1.18, 1.81) * |
| PSM HR (95% CI) | 1.78 (1.10, 2.90) † | 1.77 (1.34, 2.33) ‡ | 1.55 (1.04, 2.33) † | 1.40 (1.09, 1.80) ‡ |
| COUNT, categorical (non-malnutrition as reference) | ||||
| Mild malnutrition | ||||
| Crude HR (95% CI) | 2.09 (1.42, 3.08) * | 1.38 (1.09, 1.75) ‡ | 1.52 (1.19, 1.94) * | 1.25 (1.06, 1.47) ‡ |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.86 (1.25, 2.75) ‡ | 1.21 (0.95, 1.54) | 1.43 (1.11, 1.83) † | 1.13 (0.96, 1.33) |
| PSM HR (95% CI) | 1.01 (0.32, 2.49) | 1.82 (1.01, 3.50) † | 1.34 (0.66, 2.75) | 1.63 (1.04, 2.55) † |
| Moderate–severe malnutrition | ||||
| Crude HR (95% CI) | 3.23 (1.44, 7.26) ‡ | 2.94 (1.93, 4.48) * | 2.03 (1.12, 3.70) † | 1.91 (1.36, 2.69) * |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | 2.08 (0.92, 4.73) | 1.51 (1.00, 2.34) † | 1.56 (0.85, 2.86) | 1.26 (0.89, 1.80) |
| PSM HR (95% CI) | 1.92 (1.01, 3.85) † | 1.44 (1.05, 3.23) † | 1.85 (1.00, 4.19) † | 1.46 (0.88, 2.41) |
| NRI, categorical (non-malnutrition as reference) | ||||
| Mild malnutrition | ||||
| Crude HR (95% CI) | 1.88 (1.03, 3.27) † | 2.03 (1.45, 2.83) * | 1.45 (0.98, 2.14) | 1.41 (1.09, 1.82) * |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.39 (0.79, 2.44) | 1.43 (1.02, 2.01) † | 1.20 (0.81, 1.79) | 1.17 (0.90, 1.51) |
| PSM HR (95% CI) | 1.35 (0.69, 2.62) | 1.35 (0.90, 2.03) | 1.01 (0.36, 2.87) | 1.32 (0.74, 2.35) |
| Moderate–severe malnutrition | ||||
| Crude HR (95% CI) | 2.98 (2.01, 4.41) * | 3.26 (2.55, 4.18) * | 1.84 (1.37, 2.48) * | 2.20 (1.82, 2.66) * |
| Adjusted HR (95% CI) | 1.59 (1.03, 2.46) † | 1.62 (1.24, 2.14) * | 1.22 (0.88, 1.68) | 1.49 (1.22, 1.83) * |
| PSM HR (95% CI) | 1.67 (1.07, 2.62) † | 1.80 (1.36, 2.38) * | 1.14 (0.60, 2.16) | 1.56 (1.04, 2.32) * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, T.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Q.; Guo, X.; Tang, X.; et al. Prevalence and Prognostic Significance of Malnutrition in Patients with Abnormal Glycemic Status and Coronary Artery Disease: A Multicenter Cohort Study in China. Nutrients 2023, 15, 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030732
Li T, Wang X, Liu Z, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Feng Y, Wang Q, Guo X, Tang X, et al. Prevalence and Prognostic Significance of Malnutrition in Patients with Abnormal Glycemic Status and Coronary Artery Disease: A Multicenter Cohort Study in China. Nutrients. 2023; 15(3):732. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030732
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Tianyu, Xiaozeng Wang, Zhenyu Liu, Zheng Zhang, Yongzhen Zhang, Zhifang Wang, Yingqing Feng, Qingsheng Wang, Xiaogang Guo, Xiaofang Tang, and et al. 2023. "Prevalence and Prognostic Significance of Malnutrition in Patients with Abnormal Glycemic Status and Coronary Artery Disease: A Multicenter Cohort Study in China" Nutrients 15, no. 3: 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030732
APA StyleLi, T., Wang, X., Liu, Z., Zhang, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, Z., Feng, Y., Wang, Q., Guo, X., Tang, X., Xu, J., Song, Y., Chen, Y., Xu, N., Yao, Y., Liu, R., Zhu, P., Han, Y., & Yuan, J. (2023). Prevalence and Prognostic Significance of Malnutrition in Patients with Abnormal Glycemic Status and Coronary Artery Disease: A Multicenter Cohort Study in China. Nutrients, 15(3), 732. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030732







