cMIND Diet, Indoor Air Pollution, and Depression: A Cohort Study Based on the CLHLS from 2011 to 2018
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Dietary Assessment
2.3. Indoor Air Pollution Exposure Assessment
2.4. Depression Assessment
2.5. Covariates
2.6. Statistical Analysis
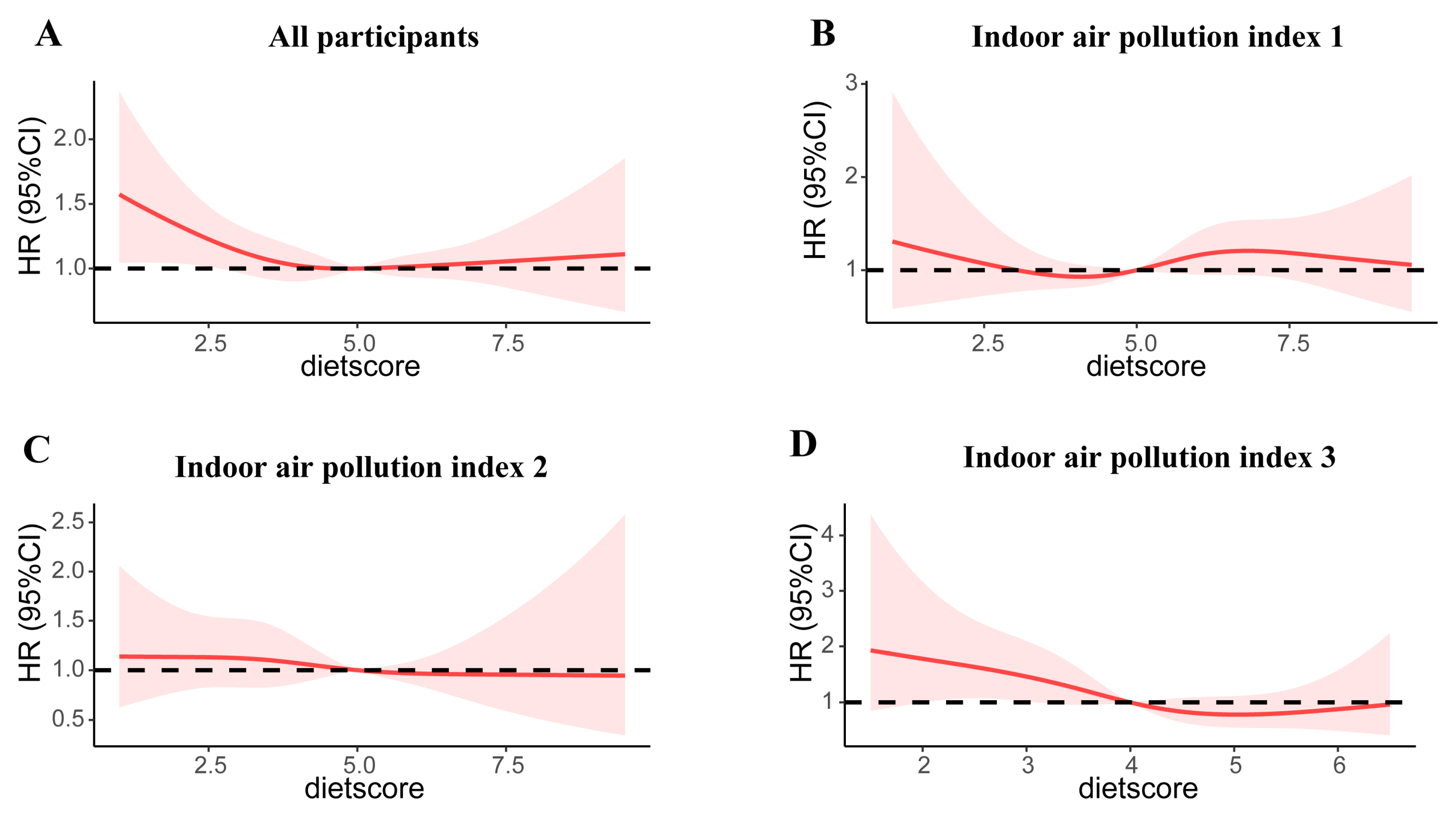
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN. World Population Ageing; UN: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Monahan, C.; Macdonald, J.; Lytle, A.; Apriceno, M.; Levy, S.R. COVID-19 and ageism: How positive and negative responses impact older adults and society. Am. Psychol. 2020, 75, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, R.M.; Reynolds, C.F., 3rd. Management of Depression in Older Adults. JAMA 2017, 317, 2114–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collaborators GMD. Global, regional, and national burden of 12 mental disorders in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Psychiatry 2022, 9, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- People’s Daily. The 2022 National Blue Book of Depression; People’s Daily: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, K.W.; Stein, M.B.; Nishimi, K.M.; Ge, T.; Coleman, J.R.; Chen, C.-Y.; Ratanatharathorn, A.; Zheutlin, A.B.; Dunn, E.C.; 23andMe Research Team; et al. An Exposure-Wide and Mendelian Randomization Approach to Identifying Modifiable Factors for the Prevention of Depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 2020, 177, 944–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- State of Global Air Report; Non-Profit NGO Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2019.
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Reed, W.; Maronpot, R.R.; Henríquez-Roldán, C.; Delgado-Chavez, R.; Calderón-Garcidueñas, A.; Dragustinovis, I.; Franco-Lira, M.; Aragón-Flores, M.; Solt, A.C.; et al. Brain Inflammation and Alzheimer’s-Like Pathology in Individuals Exposed to Severe Air Pollution. Toxicol. Pathol. 2004, 32, 650–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Torres-Jardón, R.; Avila-Ramírez, J.; Kulesza, R.J.; Angiulli, A.D. Air pollution and your brain: What do you need to know right now. Prim. Health Care Res. Dev. 2015, 16, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, P. The health toll of air pollution: Despite global efforts to clean up the air, outdoor and indoor air pollution still have a drastic negative effect on public health. EMBO Rep. 2020, 21, e51183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, G.; Mourad, M.; Leheste, J.R. Indoor Air Pollution and Decision-Making Behavior: An Interdisciplinary Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e26247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhou, T.; Song, Q.; Ma, H.; Hu, Y.; Heianza, Y.; Qi, L. Ambient air pollution, healthy diet and vegetable intakes, and mortality: A prospective UK Biobank study. Leuk. Res. 2022, 51, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Chen, H.; Shen, J.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, A.; Shi, X.; Yan, L.; Zeng, Y.; Yuan, C.; et al. Interaction between plant-based dietary pattern and air pollution on cognitive function: A prospective cohort analysis of Chinese older adults. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2022, 20, 100372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarris, J.; Logan, A.C.; Akbaraly, T.N.; Amminger, G.P.; Balanzá-Martínez, V.; Freeman, M.P.; Hibbeln, J.; Matsuoka, Y.; Mischoulon, D.; Mizoue, T.; et al. International Society for Nutritional Psychiatry Research consensus position statement: Nutritional medicine in modern psychiatry. World Psychiatry 2015, 14, 370–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, P.; Wang, Y.; Buchman, A.S.; Holland, T.M.; Bennett, D.A.; Morris, M.C. MIND Diet Associated with Reduced Incidence and Delayed Progression of Parkinsonism in Old Age. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 1211–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, L.; Wang, Y.; Holland, T.; Agarwal, P.; Aggarwal, N.; Morris, M.C. DASH and Mediterranean-Dash Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay (MIND) Diets Are Associated With Fewer Depressive Symptoms Over Time. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2020, 76, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Aihemaitijiang, S.; Ye, C.; Halimulati, M.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Z. Development of the cMIND Diet and Its Association with Cognitive Impairment in Older Chinese People. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2022, 26, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Dudley, L.; Poston, D.; Ashbaugh, V.; Gu, D. Healthy Longevity in China: Demographic, Socioeconomic, and Psychological Dimensions; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, J.E.; Parnell, W.R.; Black, K.E.; Skidmore, P.M. Reliability and relative validity of a food frequency questionnaire to assess food group intakes in New Zealand adolescents. Nutr. J. 2012, 11, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeedi, P.; Skeaff, S.A.; Wong, J.E.; Skidmore, P.M.L. Reproducibility and Relative Validity of a Short Food Frequency Questionnaire in 9–10 Year-Old Children. Nutrients 2016, 8, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfield-Watt, P.; Welch, A.; Day, N.; Bingham, S. Is ‘five-a-day’ an effective way of increasing fruit and vegetable intakes? Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Qiu, G.; Chan, K.-H.; Lam, K.-B.H.; Kurmi, O.P.; Bennett, D.A.; Yu, C.; Pan, A.; Lv, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. Association of Solid Fuel Use With Risk of Cardiovascular and All-Cause Mortality in Rural China. JAMA 2018, 319, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arku, R.E.; Brauer, M.; Duong, M.; Wei, L.; Hu, B.; Tse, L.A.; Mony, P.K.; Lakshmi, P.; Pillai, R.K.; Mohan, V.; et al. Adverse health impacts of cooking with kerosene: A multi-country analysis within the Prospective Urban and Rural Epidemiology Study. Environ. Res. 2020, 188, 109851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofuoglu, S.C.; Moschandreas, D.J. The link between symptoms of off ice building occupants and in-office air pollution: The Indoor Air Pollution Index. Indoor Air 2003, 13, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisinga, R.; Grotenhuis, M.T.; Pelzer, B. The reliability of a two-item scale: Pearson, Cronbach, or Spearman-Brown? Int. J. Public Health 2013, 58, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Ruggiano, N.; Li, Q.; Guo, Y.; Pan, X. Disparities in depression among Chinese older adults with neurodegenerative diseases. Aging Ment. Health 2022, 26, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, D.; Zhang, X.; He, K.; Chen, Y. Use of machine learning approach to predict depression in the elderly in China: A longitudinal study. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 282, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiske, A.; Wetherell, J.L.; Gatz, M. Depression in Older Adults. Annu. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2009, 5, 363–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, M.E.; Duff, H.; Kelly, S.; Power, J.E.M.; Brennan, S.; Lawlor, B.A.; Loughrey, D.G. The impact of social activities, social networks, social support and social relationships on the cognitive functioning of healthy older adults: A systematic review. Syst. Rev. 2017, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, K.R. Biological risk factors in late life depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2002, 52, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, K.; Zheng, M.; Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; Yu, Y.; et al. Analysis of Changes in Weight, Waist Circumference, or Both, and All-Cause Mortality in Chinese Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2225876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishtar, E.; Rogers, G.T.; Blumberg, J.B.; Au, R.; Jacques, P.F. Long-term dietary flavonoid intake and change in cognitive function in the Framingham Offspring cohort. Public Health Nutr. 2020, 23, 1576–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coletro, H.N.; Mendonça, R.D.D.; Meireles, A.L.; Machado-Coelho, G.L.L.; de Menezes, M.C. Ultra-processed and fresh food consumption and symptoms of anxiety and depression during the COVID—19 pandemic: COVID Inconfidentes. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 47, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundell, J. Reflections on the history of indoor air science, focusing on the last 50 years. Indoor Air 2017, 27, 708–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Song, Q.; Su, W.; Guo, X.; Wang, H.; Liang, Q.; Liang, M.; Qu, G.; Ding, X.; Zhou, X.; et al. Exposure to indoor air pollution from solid fuel and its effect on depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 49553–49567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; En, S.C.F.; Elkamel, A.; Ahmadi, L.; Yetilmezsoy, K. A review of standards and guidelines set by international bodies for the parameters of indoor air quality. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2015, 6, 751–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee TUFWDoCC. No. 1 Central Document Xinhua News Agency; Xinhua News Agency: Beijing, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kandola, A.; Ashdown-Franks, G.; Hendrikse, J.; Sabiston, C.M.; Stubbs, B. Physical activity and depression: Towards understanding the antidepressant mechanisms of physical activity. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 107, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyh, C.; Krüger, K.; Strasser, B. Physical Activity and Diet Shape the Immune System during Aging. Nutrients 2020, 12, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubert, C.; Kong, G.; Renoir, T.; Hannan, A.J. Exercise, diet and stress as modulators of gut microbiota: Implications for neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 134, 104621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lancet, T. Waking up to the importance of sleep. Lancet 2022, 400, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Rawtaer, I.; Fam, J.; Jiang, M.-J.; Feng, L.; Kua, E.H.; Mahendran, R. Sleep correlates of depression and anxiety in an elderly Asian population. Psychogeriatrics 2016, 16, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.; Ge, T.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Xia, Y. Longitudinal associations between household solid fuel use and depression in middle-aged and older Chinese population: A cohort study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 209, 111833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santomauro, D.F.; Herrera, A.M.M.; Shadid, J.; Zheng, P.; Ashbaugh, C.; Pigott, D.M.; Abbafati, C.; Adolph, C.; Amlag, J.O.; Aravkin, A.Y.; et al. Global prevalence and burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in 204 countries and territories in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2021, 398, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenham, C.; Smith, J.; Davies, S.E.; Feng, H.; Grépin, K.A.; Harman, S.; Herten-Crabb, A.; Morgan, R. Women are most affected by pandemics—Lessons from past outbreaks. Nature 2020, 583, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornicroft, G.; Chatterji, S.; Evans-Lacko, S.; Gruber, M.; Sampson, N.; Aguilar-Gaxiola, S.; Al-Hamzawi, A.; Alonso, J.; Andrade, L.; Borges, G.; et al. Undertreatment of people with major depressive disorder in 21 countries. Br. J. Psychiatry 2017, 210, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | Total | Quintile 1 | Quintile 2 | Quintile 3 | Quintile 4 | Quintile 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range of scores | 0–12.00 | 0–3.50 | 3.50–4.49 | 4.50–4.99 | 5.00–5.99 | 6.00–12.00 |
| N | 2724 | 504 | 549 | 301 | 604 | 766 |
| Indoor air pollution exposure * | 1.6 (0.6) | 1.9 (0.6) | 1.8 (0.6) | 1.6 (0.6) | 1.6 (0.6) | 1.4 (0.6) |
| Age, 65–79 years | 1475 (54.1) | 227 (45.0) | 261 (47.5) | 167 (55.5) | 347 (57.5) | 473 (61.7) |
| Sex, males | 1479 (54.3) | 253 (50.2) | 255 (46.4) | 170 (56.5) | 344 (57.0) | 457 (59.7) |
| Urban residence | 1296 (47.6) | 145 (28.8) | 223 (40.6) | 140 (46.5) | 311 (51.5) | 477 (62.3) |
| With formal education | 1515 (55.6) | 214 (42.5) | 250 (45.5) | 158 (52.5) | 363 (60.1) | 530 (69.2) |
| Financial independence | 1192 (43.8) | 154 (30.6) | 163 (29.7) | 141 (46.8) | 279 (46.2) | 455 (59.4) |
| Smoking status | ||||||
| Never smoked | 1661 (61.0) | 331 (65.7) | 369 (67.2) | 189 (62.8) | 344 (57.0) | 428 (55.9) |
| Former smoker | 442 (16.2) | 65 (12.9) | 78 (14.2) | 39 (13.0) | 98 (16.2) | 162 (21.1) |
| Current smoker | 621 (22.8) | 108 (21.4) | 102 (18.6) | 73 (24.3) | 162 (26.8) | 176 (23.0) |
| Alcohol consumption | ||||||
| Never drank | 1780 (65.3) | 359 (71.2) | 397 (72.3) | 196 (65.1) | 380 (62.9) | 448 (58.5) |
| Former drinker | 380 (14.0) | 61 (12.1) | 62 (11.3) | 41 (13.6) | 90 (14.9) | 126 (16.4) |
| Current drinker | 564 (20.7) | 84 (16.7) | 90 (16.4) | 64 (21.3) | 134 (22.2) | 192 (25.1) |
| With regular exercise | 1230 (45.2) | 149 (29.6) | 190 (34.6) | 111 (36.9) | 288 (47.7) | 492 (64.2) |
| Social relationships * | 5.7 (1.2) | 5.3 (1.2) | 5.5 (1.1) | 5.6 (1.1) | 5.8 (1.1) | 6.1 (1.1) |
| Body mass index | ||||||
| Underweight | 417 (15.3) | 128 (25.4) | 98 (17.9) | 48 (15.9) | 80 (13.2) | 63 (8.2) |
| Normal | 1764 (64.8) | 296 (58.7) | 367 (66.8) | 188 (62.5) | 400 (66.2) | 513 (67.0) |
| Overweight or obese | 543 (19.9) | 80 (15.9) | 84 (15.3) | 65 (21.6) | 124 (20.5) | 190 (24.8) |
| Waist circumference, normal | 1321 (48.5) | 303 (60.1) | 287 (52.3) | 139 (46.2) | 290 (48.0) | 302 (39.4) |
| MMSE score * | 27.0 (4.2) | 25.7 (5.4) | 26.6 (4.3) | 27.0 (4.2) | 27.6 (3.6) | 27.8 (3.4) |
| Sleep quality | ||||||
| Bad | 269 (9.9) | 69 (13.7) | 64 (11.7) | 35 (11.6) | 42 (7.0) | 59 (7.7) |
| So so | 604 (22.2) | 145 (28.8) | 131 (23.9) | 53 (17.6) | 126 (20.9) | 149 (19.5) |
| Good | 1851 (68.0) | 290 (57.5) | 354 (64.5) | 213 (70.8) | 436 (72.2) | 558 (72.8) |
| Hypertension | 974 (35.8) | 138 (27.4) | 179 (32.6) | 121 (40.2) | 211 (34.9) | 325 (42.4) |
| Diabetes | 354 (13.0) | 44 (8.7) | 64 (11.7) | 45 (15.0) | 64 (10.6) | 137 (17.9) |
| Heart diseases | 495 (18.2) | 73 (14.5) | 84 (15.3) | 54 (17.9) | 105 (17.4) | 179 (23.4) |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 344 (12.6) | 51 (10.1) | 71 (12.9) | 39 (13.0) | 68 (11.3) | 115 (15.0) |
| Dyslipidemia | 245 (9.0) | 36 (7.1) | 45 (8.2) | 21 (7.0) | 47 (7.8) | 96 (12.5) |
| Variables | All Participants | Lower cMIND Diet Score | Higher cMIND Diet Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | HR (95% CI) | |
| Indoor air pollution exposure | |||
| No pollution | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Moderate pollution | 0.94 (0.78, 1.13) | 0.93 (0.72, 1.12) | 0.95 (0.73, 1.24) |
| Severe pollution | 1.40 (1.07, 1.82) * | 1.50 (1.07, 2.08) * | 1.07 (0.65, 1.76) |
| Age, ≥80 years | 0.82 (0.68, 0.98) * | 0.68 (0.52, 0.90) ** | 0.94 (0.73, 1.20) |
| Sex, females | 1.46 (1.17, 1.81) ** | 1.48 (1.08, 2.03) * | 1.39 (1.03, 1.88) * |
| Urban residence | 0.82 (0.69, 0.98) * | 0.99 (0.76, 1.28) | 0.69 (0.54, 0.89) ** |
| With formal education | 1.14 (0.94, 1.38) | 1.18 (0.90, 1.56) | 1.10 (0.84, 1.43) |
| Financial independence | 0.89 (0.74, 1.07) | 0.82 (0.62, 1.09) | 0.86 (0.67, 1.12) |
| Smoking status | |||
| Never smoked | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Former smoker | 1.12 (0.86, 1.46) | 1.18 (0.82, 1.70) | 1.07 (0.72, 1.59) |
| Current smoker | 1.24 (0.97, 1.57) | 1.39 (1.00, 1.95) | 1.16 (0.82, 1.63) |
| Alcohol consumption | |||
| Never drank | Ref | Ref | Ref |
| Former drinker | 1.05 (0.81, 1.37) | 1.10 (0.76, 1.59) | 1.00 (0.69, 1.45) |
| Current drinker | 0.91 (0.72, 1.14) | 0.76 (0.54, 1.07) | 1.07 (0.78, 1.47) |
| Without regular exercise | 1.25 (1.05, 1.48) * | 0.94 (0.74, 1.20) | 1.58 (1.23, 2.02) *** |
| Social relationships | 0.96 (0.89, 1.03) | 0.97 (0.86, 1.09) | 0.95 (0.86, 1.05) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Ye, C.; Huang, X.; Halimulati, M.; Sun, M.; Ma, Y.; Fan, R.; Zhang, Z. cMIND Diet, Indoor Air Pollution, and Depression: A Cohort Study Based on the CLHLS from 2011 to 2018. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051203
Wang R, Ye C, Huang X, Halimulati M, Sun M, Ma Y, Fan R, Zhang Z. cMIND Diet, Indoor Air Pollution, and Depression: A Cohort Study Based on the CLHLS from 2011 to 2018. Nutrients. 2023; 15(5):1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051203
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ruoyu, Chen Ye, Xiaojie Huang, Mairepaiti Halimulati, Meng Sun, Yuxin Ma, Rui Fan, and Zhaofeng Zhang. 2023. "cMIND Diet, Indoor Air Pollution, and Depression: A Cohort Study Based on the CLHLS from 2011 to 2018" Nutrients 15, no. 5: 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051203
APA StyleWang, R., Ye, C., Huang, X., Halimulati, M., Sun, M., Ma, Y., Fan, R., & Zhang, Z. (2023). cMIND Diet, Indoor Air Pollution, and Depression: A Cohort Study Based on the CLHLS from 2011 to 2018. Nutrients, 15(5), 1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051203







