Home Parenteral Nutrition for Children: What Are the Factors Indicating Dependence and Mortality?
Abstract
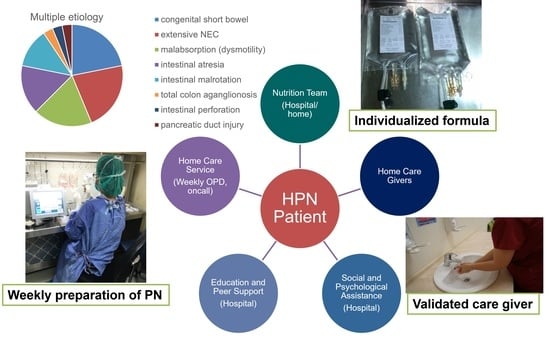
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Data
3.2. Clinical Outcomes
3.3. SBS and IF
3.4. Central-Catheter-Related Complications
3.5. Liver Function and Cholestasis
3.6. Risk Factor Analysis
3.7. Survival and Mortality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wiskin, A.E.; Russell, R.; Barclay, A.R.; Thomas, J.; Batra, A.; BANS Committee of BAPEN. Prevalence of home parenteral nutrition in children. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 42, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afolabi, T.M.; Fairman, K.A. Pediatric Home Parenteral Nutrition: Indications and Short-Term Outcomes in a Large National Sample of Commercially Insured Children and Adolescents. Nutr. Clin. Pract. 2019, 34, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivic, I.; Mišak, Z.; Kerman, V.; Prlic, H.; Kolacek, S.; Hojsak, I. Central catheter-related bloodstream infection rates in children on home parenteral nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2020, 70, e59–e62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, A.; Chadwick, P.; Smith, T.R.; Nightingale, J.M.; Lal, S. Diagnosis and management of catheter-related bloodstream infections in patients on home parenteral nutrition. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2020, 11, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanko, R.T.; Nathan, G.; Mendelow, H.; Adibi, S.A. Development of hepatic cholestasis and fibrosis in patients with massive loss of intestine supported by prolonged parenteral nutrition. Gastroenterology 1987, 92, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beath, S.V.; Kelly, D.A. Total parenteral nutrition–induced cholestasis: Prevention and management. Clin. Liver Dis. 2016, 20, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischoff, S.C.; Bernal, W.; Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M.; Plank, L.D.; Schütz, T.; Plauth, M. ESPEN practical guideline: Clinical nutrition in liver disease. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 3533–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plauth, M.; Bernal, W.; Dasarathy, S.; Merli, M.; Plank, L.D.; Schütz, T.; Bischoff, S.C. ESPEN guideline on clinical nutrition in liver disease. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 485–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihatsch, W.; Shamir, R.; Van Goudoever, J.B.; Fewtrell, M.; Lapillonne, A.; Lohner, S.; Mihalyi, K.; Decsi, T.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.B.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guidelines on pediatric parenteral nutrition: Guideline development process for the updated guidelines. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2306–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wales, P.W.; Allen, N.; Worthington, P.; Compher, C.; American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition; Teitelbaum, D. ASPEN clinical guidelines: Support of pediatric patients with intestinal failure at risk of parenteral nutrition–associated liver disease. JPEN J. Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2014, 38, 538–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.; Ksiazyk, J.; Prell, C.; Tabbers, M.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guidelines on pediatric parenteral nutrition: Home parenteral nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2401–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riskin, A.; Picaud, J.-C.; Shamir, R.; Braegger, C.; Bronsky, J.; Cai, W.; Campoy, C.; Carnielli, V.; Darmaun, D.; Decsi, T.; et al. ESPGHAN/ESPEN/ESPR/CSPEN guidelines on pediatric parenteral nutrition: Standard versus individualized parenteral nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2409–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargasz, A. Neonatal and pediatric parenteral nutrition. AACN Adv. Crit. Care 2012, 23, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirtallo, J.; Johnson, D.; Kumpf, V. Safe practices for parenteral nutrition. JPEN J. Parenter Enteral Nutr. 2004, 28, S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, B.; Carlson, G.; Khalil, B.A.; Morabito, A. Intestinal bowel lengthening in children with short bowel syndrome: Systematic review of the Bianchi and STEP procedures. World J. Surg. 2013, 37, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares, Y.Z.; Bunster, M.I.H.; Bayón, M.L.C.; Osiac, L.R.; Lorca, J.C.; Reus, G.A.; Antilef, R.M.; Balboa, P.; Cors, C.; De la Fuente, G.; et al. Home parenteral nutrition in pediatric patients with intestinal insufficiency. Rev. Chil. Pediatr. 2019, 90, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi Nader, E.; Lambe, C.; Talbotec, C.; Pigneur, B.; Lacaille, F.; Garnier-Lengliné, H.; Petit, L.M.; Poisson, C.; Rocha, A.; Corriol, O.; et al. Outcome of home parenteral nutrition in 251 children over a 14-y period: Report of a single center. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 1327–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piedra, P.; Dryja, D.; LaScolea, L., Jr. Incidence of catheter-associated gram-negative bacteremia in children with short bowel syndrome. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1989, 27, 1317–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, R.M.; Plopper, C.; Waitzberg, D.L.; Cukier, C.; Santoro, S.; Martins, J.R.; Song, R.J.; Gama-Rodrigues, J. Remaining small bowel length: Association with catheter sepsis in patients receiving home total parenteral nutrition: Evidence of bacterial translocation. World J. Surg. 2000, 24, 1537–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bines, J.E. Intestinal failure: A new era in clinical management. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, S86–S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touloukian, R.J.; Smith, G.W. Normal intestinal length in preterm infants. J. Pediatr. Surg. 1983, 18, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, L.; Austin, S.; Cole, T. Small intestinal length: A factor essential for gut adaptation. Gut 1991, 32, 1321–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colomb, V.; Dabbas-Tyan, M.; Taupin, P.; Talbotec, C.; Révillon, Y.; Jan, D.; De Potter, S.; Gorski-Colin, A.M.; Lamor, M.; Herreman, K.; et al. Long-term outcome of children receiving home parenteral nutrition: A 20-year single-center experience in 302 patients. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2007, 44, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.S.; Sokol, R.J. Intestinal Microbiota, Lipids, and the Pathogenesis of Intestinal Failure–Associated Liver Disease. J. Pediatr. 2015, 167, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, D.; Zabron, A.; Gabe, S. Chronic biochemical cholestasis in patients receiving home parenteral nutrition: Prevalence and predisposing factors. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2008, 27, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wales, P.W.; de Silva, N.; Kim, J.H.; Lecce, L.; Sandhu, A.; Moore, A.M. Neonatal short bowel syndrome: A cohort study. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2005, 40, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamond, I.R.; de Silva, N.; Pencharz, P.B.; Kim, J.H.; Wales, P.W. Neonatal short bowel syndrome outcomes after the establishment of the first Canadian multidisciplinary intestinal rehabilitation program: Preliminary experience. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2007, 42, 806–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouw, E.; Chessman, K.; Lesher, A.; Tagge, E. Use of an ethanol lock to prevent catheter-related infections in children with short bowel syndrome. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2008, 43, 1025–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raad, I.I.; Luna, M.; Khalil, S.-A.M.; Costerton, J.W.; Lam, C.; Bodey, G.P. The relationship between the thrombotic and infectious complications of central venous catheters. JAMA 1994, 271, 1014–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- So, S.; Patterson, C.; Gold, A.; Rogers, A.; Belza, C.; de Silva, N.; Avitzur, Y.; Wales, P.W. Neurodevelopmental outcomes of infants with intestinal failure at 12 and 26 months corrected age. Early Hum. Dev. 2019, 130, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| HPN Free | HPN Dependent | Mortality | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient number | 13 | 6 | 5 | |
| Female | 4 (30.7%) | 3 (50.0%) | 3 (60.0%) | 0.472 |
| Age of disease onset (days, mean) | 1–90 (34.2) | 6–5340 (905.0) | 1–2520 (529.8) | 0.316 |
| Prematurity | 6 (46.1%) | 6 (100.0%) | 4 (80.0%) | 0.053 |
| Low BBW (<2500 g) | 8 (61.5%) | 4 (66.7%) | 3 (60.0%) | 0.969 |
| BW of disease onset (kg, mean) | 0.8–4.3 (2.64) | 2.5–4.5 (9.94) | 2.0–19.0 (5.95) | 0.275 |
| BW percentile | ||||
| 50–75 25–50 10–25 3–10 <3 | 1 0 1 0 11 | 0 0 0 1 5 | 0 0 1 0 4 | 0.643 - 0.485 0.209 0.972 |
| HPN Free (13) | HPN Dependent (6) | Mortality (5) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HPN period (month, mean) | 5–115 (29.0) | 19–207 (91.3) | 7–89 (46.0) | 0.045 |
| Hospitalization times (mean) | 1–24 (6.5) | 4–39 (14.2) | 4–55 (20.2) | 0.006 |
| Interval of hospitalization (month, mean) | 2.1–9.0 (4.60) | 3.2–12.8 (7.12) | 1.5–4.1 (2.57) | 0.021 |
| Follow-up period (month, mean) | 26–232 (115.8) | 24–193 (99.3) | 7–90 (46.3) | 0.097 |
| Commercial admixture usage | 0 | 1 (16.6%) * | 1 (20%) ** | 0.270 |
| BW gain by month in 3 months after HPN (%, mean) | 25.6% | 19.6% | 24.7% | 0.715 |
| BW gain by month in 6 months after HPN (%, mean) | 25.4% | 17.3% | 17.7% | 0.448 |
| BW gain after HPN (%, mean) | 347.9% | 493.5% | 356.1% | 0.666 |
| BW gain after HPN by month (%, mean) | 15.2% | 9.7% | 14.1% | 0.691 |
| HPN Free (13) | HPN Dependent (6) | Mortality (5) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Congenital short bowel | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0.758 |
| Multiple intestinal atresia | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0.545 |
| Extended intestinal resection | 1 | 4 | 3 | 0.014 |
| Intestinal malabsorption | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0.131 |
| Pancreatic leak | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.643 |
| Small intestines length (cm, mean) | 30–150 (75.7) | 3–150 (58.0) | 20–75 (35.0) | 0.236 |
| <30 cm (<10% predicted) | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0.033 |
| 30–90 cm (10–30%) | 8 | 3 | 1 | 0.287 |
| >90 cm (>30%) | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0.500 |
| Absence of IC valve | 2 | 4 | 3 | 0.050 |
| Majority of colon (>50%) loss | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0.033 |
| HPN Free (13) | HPN Dependent (6) | Mortality (5) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central line placement (mean) | 1–4 (2.3) 11.3 catheter-month | 3–23 (7.0) 15.7 catheter-month | 1–9 (4.0) 10.9 catheter-month | 0.098 |
| 1 time | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0.307 |
| 2 times | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0.131 |
| 3 times | 2 | 3 | 2 | 0.254 |
| >3 times | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0.636 |
| Infection (mean) | 0–4 (1.5) 19.8 catheter-month | 0–12 (3.8) 23.8 catheter-month | 1–5 (2.6) 17.7 catheter-month | 0.175 |
| Occlusion (mean) | 0–1 (0.1) | 0–3 (0.8) | 0–1 (0.2) | 0.116 |
| Dislodgement (mean) | 0–1 (0.2) | 0–3 (0.7) | 0–5 (1.0) | 0.363 |
| Rupture (mean) | 0–1 (0.5) | 0–7 (1.7) | 0–1 (0.2) | 0.056 |
| HPN Free (13) | HPN Dependent (6) | Mortality (5) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cholestasis * | 2 | 3 | 5 | 0.004 |
| Duration (m) | 0–17 (1.4) | 0–4 (1.4) | 2–41 (19.3) | 0.001 |
| Elevated AST/ALT ** | 8 | 4 | 5 | 0.370 |
| Duration (m) | 0–36 (4.2) | 0–166 (46.3) | 6–41 (26.5) | 0.057 |
| Child-Turcotte-Pugh classification | <0.0001 | |||
| A | 13 | 6 | 0 | |
| B | 0 | 0 | 3 | |
| C | 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| PELD score *** (mean) | −16.6–0.0 (−10.18) | −5.0–15.0 (−1.60) | 8.4–24.6 (18.72) | <0.0001 |
| Positive PELD score *** | 1 | 5 | 5 | <0.0001 |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
| Variables | OR (95% CI) | p | Coefficient | SE | p |
| Male | 0.37 (0.06–1.97) | 0.244 | |||
| BW < 3 percentile | 0.48 (0.06–3.61) | 0.479 | |||
| Neonatal onset | 3.11 (0.55–17.33) | 0.195 | |||
| Prematurity | 1.22 (0.14–10.48) | 0.854 | |||
| Short admission internal (<3 m) | 2.06 (0.27–5.35) | 0.479 | |||
| Extended resection | 14.40 (1.35–152.53) | 0.026 | 0.4760 | 0.2044 | 0.032 |
| Small intestine < 10% predicted | 16.20 (0.76–343.81) | 0.074 | |||
| No IC valve | 9.62 (1.37–67.24) | 0.022 | −0.1420 | 0.2283 | 0.542 |
| Colon loss (>50%) | 6.60 (0.96–44.92) | 0.053 | |||
| Central line > 2 times | 16.00 (1.54–166.05) | 0.005 | 0.4298 | 0.1633 | 0.017 |
| Cholestasis | 32.00 (2.80–364.79) | 0.020 | 0.1066 | 0.2749 | 0.703 |
| Child B or C | 22.84 (1.09–478.83) | 0.043 | 0.3148 | 0.3805 | 0.419 |
| Positive PELD | 31.90 (1.52–668.78) | 0.025 | 0.1747 | 0.3881 | 0.658 |
| GI bleeding or chronic anemia | 5.83 (0.98–34.64) | 0.052 | |||
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | OR (95% CI) | p | Coefficient | SE | p |
| Male | 0.38 (0.05–2.92) | 0.358 | |||
| BW < 3 percentile | 1.06 (0.09–12.40) | 0.958 | |||
| Neonatal onset | 1.09 (0.14–8.12) | 0.932 | |||
| Prematurity | 1.33 (0.10–16.48) | 0.822 | |||
| Short admission internal (<3 m) | 12.75 (1.26–128.78) | 0.031 | 0.0873 | 0.1269 | 0.5002 |
| Extended resection | 1.86 (0.23–14.64) | 0.552 | |||
| Small intestine < 10% predicted | 5.66 (0.56–57.23) | 0.141 | |||
| No IC valve | 3.25 (0.42–24.84) | 0.256 | |||
| Colon loss (>50%) | 15.00 (1.29–174.39) | 0.030 | 0.1278 | 0.1128 | 0.2720 |
| Central line > 2 times | 2.90 (0.27–31.21) | 0.377 | |||
| Cholestasis | 37.88 (1.74–823.97) | 0.020 | −0.0009 | 0.1278 | 0.9939 |
| Child B or C * | 429.00 (7.60–24198.81) | 0.003 | 1.0000 ** | 0 | - |
| Positive PELD | 135.66 (4.81–3825.41) | 0.004 | 0.7691 | 0.1735 | 0.0003 |
| GI bleeding or chronic anemia | 29.00 (1.36–616.62) | 0.030 | −0.0330 | 0.1233 | 0.7917 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-C.; Chou, C.-M.; Huang, S.-Y.; Chen, H.-C. Home Parenteral Nutrition for Children: What Are the Factors Indicating Dependence and Mortality? Nutrients 2023, 15, 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030706
Chen Y-C, Chou C-M, Huang S-Y, Chen H-C. Home Parenteral Nutrition for Children: What Are the Factors Indicating Dependence and Mortality? Nutrients. 2023; 15(3):706. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030706
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Ying-Cing, Chia-Man Chou, Sheng-Yang Huang, and Hou-Chuan Chen. 2023. "Home Parenteral Nutrition for Children: What Are the Factors Indicating Dependence and Mortality?" Nutrients 15, no. 3: 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030706
APA StyleChen, Y.-C., Chou, C.-M., Huang, S.-Y., & Chen, H.-C. (2023). Home Parenteral Nutrition for Children: What Are the Factors Indicating Dependence and Mortality? Nutrients, 15(3), 706. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15030706