Abstract
Home parenteral support (HPS) is an essential but potentially burdensome treatment that can affect quality of life (QoL). The aims of this longitudinal study were to understand whether any changes in HPS over time were associated with QoL. The Parenteral Nutrition Impact Questionnaire (PNIQ) was used, and data were collected on HPS prescribed at three time points. Data were analysed using multi-level mixed regression models presented as effect size and were adjusted for confounders. Study recruited 572 participants from 15 sites. Of these, 201 and 145 completed surveys at second and third time-points, respectively. PNIQ score was out of 20 with a higher score indicating poorer QoL. Any reduction in HPS infusions per week was associated with an improved PNIQ score of −1.10 (95% CI −2.17, −0.02) unadjusted and −1.34 (95% CI −2.45, −0.24) adjusted. Per day change to the number of infusions per week was associated with a change in the PNIQ score of 0.32 (95% CI −0.15, 0.80) unadjusted and 0.34 (95% CI −0.17, 0.85) adjusted. This is the largest national study to demonstrate improvements in QoL associated with HPS reduction over time using an HPS-specific and patient-centric tool, adding unique data for use of therapies in intestinal failure.
1. Introduction
Patients with intestinal failure (IF) have a reduction in gut function to the point where sufficient macronutrients (carbohydrates, protein, and fat), micronutrients, and electrolytes or water can no longer be absorbed by the gut [1]. Home parenteral support (HPS) is a treatment offered to patients with IF in order to sustain life and maintain health [2,3,4].
IF can be classified as type 1 (acute and short term), type 2 (prolonged acute condition, often in metabolically unstable patients), or type 3/chronic (chronic condition, in metabolically stable patients) [5]. Chronic IF (CIF) requires long-term or sometimes life-long HPS, whereby patients receive intravenous infusions for several hours (usually 12–14) for a number of nights every week [6]. Although HPS represents a lifesaving therapy for those with CIF, it is considered a demanding treatment that can lead to serious complications, such as catheter-related bloodstream infections and thrombosis [7,8,9], whereas more long-term adverse complications of CIF include liver failure, osteoporosis, and loss of vascular access [10]. Given that HPS is a time-consuming and restrictive treatment, which often limits the ability to travel, work, and socialise [11,12,13,14,15], it is important to consider the impact this may have on the patient. Indeed, the focus of care for this group of patients should include quality of life (QoL) and consideration for the negative impacts HPS may cause [2,14,16,17]. It is well documented that patients who require HPS have a decreased QoL [2,7,18,19,20,21,22], suffer higher rates of depression and anxiety [11,18,23], and are less likely to ever return to full-time employment [18,24,25].
The most commonly used tools to measure QoL in CIF include Short Form-36 (SF-36) [24,26,27,28], EuroQol-5 Dimension (EQ5D) [27], and Home Parenteral Nutrition-Quality of Life (HPN-QOL) [29,30]. The SF-36 and EQ5D are generic measures of health status and were developed over 30 years ago [31,32,33]. As a result, these tools may now be considered too non-specific to adequately assess QoL in CIF [24]. The HPN-QOL, although specific to CIF, has 57 items and may be difficult to complete in a busy clinical setting in which health care professionals and patients are time poor. The ability to assess patient-reported outcomes for specific treatments is increasingly important to healthcare providers [34,35], such that specific and readily usable QoL measures are now essential for patients with CIF. Other specific QoL tools for HPS include the Short Bowel Syndrome-Quality of Life (SBS-QOL) tool [36]; the Home Parenteral Nutrition Patient-Reported Outcome Questionnaire (HPN-PROQ) [37]; and the Parenteral Nutrition Impact Questionnaire (PNIQ) [38,39]. Although the SBS-QOL and HPN-PROQ offer CIF-specific measurements, the PNIQ was the first HPS-specific tool that was patient centric and measured patient-reported QoL, solely evaluating the impact of parenteral support on an individual’s lived experience. A recent study involving the use of the PNIQ in multiple hospitals in the UK indicated that patients who required more HPS infusions per week reported poorer quality of life [19].
In an effort to gain a deeper understanding of the influence of HPS infusions on patients’ QoL, it is important to know the within-person variation over time. Evidence of the impact of HPS on QoL over time will be useful to inform the use of alternative medical or surgical therapies in this area. This is the first multicentre study to assess QoL longitudinally using a validated, HPS-specific, and patient-centric tool.
Our primary objective was to measure QoL and changes to HPS treatment longitudinally in people with CIF. We hypothesised that changes to a patient’s HPS treatment over time would affect QoL.
2. Materials and Methods
The study design was a prospective longitudinal cohort that collected patient survey data over three time-points between March 2020 and March 2022. Surveys were initially sent to participants in March 2020, September 2021, and January 2022. Survey data included patient demographics, clinical HPS characteristics, and QoL scores in patients receiving HPS treatment.
Patients were recruited between 2 March 2020 and 16 December 2021 from 14 NHS hospitals located throughout the UK and from a national patient-led charitable support group for people receiving artificial nutrition: Patients on Intravenous and Nasogastric Nutrition group (PINNT) (15 sites in total). The direct clinical care team at each NHS location and the point of contact at PINNT identified eligible patients and sent them an invitation pack along with the first survey for completion.
Eligible participants included patients aged 18 or over who were living with CIF and receiving HPS (parenteral nutrition or parenteral fluids and electrolytes) in the UK between March 2020 and March 2022. Patients were excluded if they could not give informed consent or could not read or write English.
Participants who consented to study recruitment by completion and return of survey 1 were also asked to consent to further contact by researchers. Those who consented to further contact and provided their contact details were sent two follow-up surveys in September 2021 and January 2022. At each time-point, participants were sent the survey by post or email, with a reminder letter or email being sent three weeks later. For cases in which emails failed or a participant was unable to complete the survey online, a paper version was sent instead if a postal address was available.
The primary outcome was to assess change in QoL over time using the PNIQ measured at three time-points. The PNIQ is made up of 20 questions. The questions are specifically related to HPS and aim to assess QoL and the overall impact of treatment in those who receive HPS. Each statement on PNIQ has a dichotomous response ‘True’ or ‘Not true’. Each response is allocated a score of 1 for ‘True’ and a score of 0 for ‘Not true’. All item scores are summed up to give a total score ranging from 0 (good QoL) to 20 (very poor QoL). Previous validation of the scoring scale of the PNIQ has identified high internal consistency (0.91) and test–retest reliability (0.92) [38].
Data were also collected on demographics (age, gender, ethnicity, etc.), socio-economic characteristics, and clinical HPS characteristics including length of time on HPS, number of infusions per week, changes in care or any surgeries, and the underlying aetiology leading to HPS.
Prior to data collection, we noted that response bias could have influenced the level of QoL reported, as people may be more likely to respond to a survey if they have a better QoL or a better sense of wellbeing on a given day. Equally, people may also be more likely to respond if they are having issues with the topic being asked about (in this case their HPS treatment) and so have a negative view of its impact and how it makes them feel day to day. There may have also been non-response bias if people had difficulty in responding due to ill health or access and ability to use electronic format response on a computer or similar device. To account for these factors, we posted surveys directly to people’s homes or sent the survey via email and allowed several months for responses to be returned. Detection bias could have influenced the association between the receipt of HPS and a reduced QoL if there was a difference in health care and support provided at different hospitals (clustering). A multi-level model was used during analysis to account for clustering within patients and recruitment sites. It was also considered that home support provided by community nurses or family caregivers may affect QoL; however, this has been reported in a cross-sectional study detailing carers’ roles in QoL in patients on HPS [40]. Caregiving was, therefore, not included here as a confounder but is an important factor to consider.
It is also important to note that data for this study were collected during and shortly after the lockdown periods that occurred due to the COVID-19 pandemic. As such, patients’ responses to questions relating to QoL and general well-being may have been negatively impacted [41,42,43]. To account for some of the impact of this, we paused the study during the height of the pandemic (April 2020–August 2020). However, it is of note that a recent cohort study stated that the COVID-19 pandemic had no influence on QoL in a large sample of patients involved in ongoing clinical research, implying that confidence could be placed in patient-reported outcome data collected during this period [44].
The study was approved by the National Research Ethics Committee North West (Ref: 19/LO/1971) and received Research and Development approval. Eligible participants receiving HPS were sent a study pack including an information sheet about the study and contact details of the research team. A receipt of a completed survey was taken as consent.
Patient responses were summarised and reported using standard descriptive statistics. The primary analysis looked to understand the ‘total association’ present as determined from a hypothetical causal relationship between HPS usage (HPS weekly frequency) and the participants’ QoL. The PNIQ scores were assessed for their distributional properties and a multi-level mixed regression model was applied. To account for the multi-level structure of the data and correlation associated within clusters (i.e., responses nested within patients nested within NHS recruitment sites), we used a multi-level mixed model with robust standard errors. The model included random intercept terms associated with patient ID and NHS site. Covariate data were assessed, and whenever possible, appropriate steps were taken to account for the missing values through imputation using the missing by indication method. Initially, a ‘baseline’ model was fitted that included the baseline QoL, time since baseline in months, and the HPS characteristic in instances for which HPS characteristic was a time-varying factor. This baseline model also included the change in the number of infusions per week, which was defined as a categorical change (no change, increase in infusions, and decrease in infusions compared to baseline). We also modelled change in number of infusions as a continuous measure (0 means no change, positive values mean an increase, negative values mean a decrease) to understand if a dose–response relationship was present. These two models were repeated firstly without adjustment, that is, ‘unadjusted’, and with adjustment for pre-defined confounders, that is, ‘adjusted’. The confounders were identified to be age, gender, ethnicity, income, aetiology, type of problem with bowel, if the patient was on antidepressants at any time point, and if the patient had had a recent operation.
3. Results
Between March 2020 and March 2022, there were 572 (35%) participants recruited from the 1643 surveys sent out from IF clinics in 14 NHS sites and from PINNT. A participant was considered recruited once they completed and returned a paper-based survey, which was sent to them by a member of their clinical team (survey 1). Of the 572 completed surveys, 382 included ‘signed consent to contact’ from the participant, whereby they agreed to be contacted again by university researchers. Survey 2 was sent in September 2021 (postal and online versions were available), with a reminder sent to those who had not responded after 3 weeks (n = 177). Of the 382 participants who completed survey 1, 201 completed survey 2, 128 failed to respond, and 53 were lost to follow up. Survey 3 was sent out in January 2022 by university researchers (postal and online versions were available), with a reminder sent to those who had not responded after 3 weeks (n = 45). Of the 201 participants who had completed surveys 1 and 2; 145 completed survey 3, 22 failed to respond, and 34 were lost to follow up. See Figure 1.
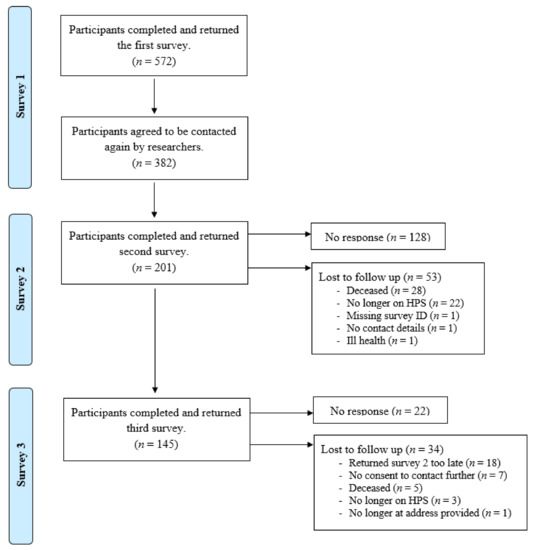
Figure 1.
Flow diagram for participant recruitment and retention over time.
3.1. Participant Characteristics
Sociodemographic characteristics of participants at baseline are reported in Table 1. Participants at baseline had a mean age of 59.5 (SD 15.9) years, with around two thirds of the participants being female (60.7%), and approximately half were married (52.1%). Despite the majority of participants stating that they had some kind of formal qualification (76.0%), over a quarter said that they were unable to work (29.4%). Approximately half of the participants were retired (49.0%), and so ability to work was not asked or recorded. See Table 1.

Table 1.
Sociodemographic characteristics of patients receiving home parenteral support at baseline.
3.2. Participant Characteristics within Recruitment Sites
Data were gathered on the mean age and percentage gender split for all patients receiving HPS across the different study sites in order to check that the characteristics of the study sample were representative of the total patient population of that site. For 11 of the 15 recruitment sites, the mean age and gender split appeared very similar when comparing the study sample population of the site to the total HPS-dependent population of the site. We could not compare characteristics at two of the sites, as they were unable to provide total population data and so were not included. One site did show a similar gender split between total and study populations; however, the mean age was much lower in the total population. (See Table S1). Overall, we concluded that the characteristics of the study sample at each site were representative of the total site population, although we cannot rule out selection bias due to other factors such as socio-economic status.
3.3. Participant PNIQ Scores and Characteristics of HPS Use, According to Time Point
Missing data meant that PNIQ scores could not be calculated for 20 patients at baseline, one patient at the first follow up, and four patients at the second follow up. For the remaining samples at each time point, the PNIQ score ranged from zero (very good QoL) to 20 (very poor QoL) with mean scores of 11.25 (SD 5.58), 10.68 (SD 5.64), and 11.07 (SD 5.50) at baseline, follow up one, and follow up two, respectively. The mean length of time receiving HPS was 74.02 (range: 1 to 444) months, 84.43 (range: 3 to 441) months, and 97.43 (range: 10 to 447) months at baseline, follow up one, and follow up two, respectively. The mean number of infusions per week (5.52 to 5.69) and number of hours per infusion (12.52 to 12.67) were very similar between time points. The number of patients reporting a change over time to their number of infusions per week was low, with the majority of patients (80–81%) reporting the same number of infusions over the three time points. See Table 2.

Table 2.
Parenteral Nutrition Impact Questionnaire scores and home parenteral support use at baseline, follow up 1, and follow up 2.
3.4. Multi-Level Mixed Modelling to Explore the Association between HPS and QoL
A series of multi-level regression models were fitted to better understand the within-person difference in PNIQ score at follow up due to the change, if any, in the amount of HPS infusions per week. As outlined in the Methods section, we fitted four models; models 1 and 2 had the number of HPS infusions set to be categorical and indicated that there was no evidence to suggest that ‘any increase’ in HPS infusions per week at follow up was associated with a change in PNIQ score. However, models 1 and 2 did indicate that for ‘any decrease’ in HPS infusions per week, the PNIQ score changes by −1.10 (95% CI −2.17 to −0.02) and −1.34 (95% CI −2.45 to −0.24) in the unadjusted and adjusted models, respectively. Models 3 and 4 had the number of HPS infusions per week set to be continuous and reported no evidence to suggest the presence of a significant ‘dose response’ change in PNIQ score based on the ‘per day’ change to frequency of infusions per week at follow up. However, these models did demonstrate that a ‘per day’ change in frequency of infusions per week resulted in a change in the PNIQ score by 0.32 (95% CI −0.15 to 0.80) in the unadjusted model and 0.34 (95% CI −0.17 to 0.85) in the adjusted model. This indicates that for each ‘per day’ reduction in infusions per week observed, compared to baseline, the PNIQ score improved by −0.32 (unadjusted) and −0.34 (adjusted). See Table 3.

Table 3.
Multi-level mixed regression analysis to show the impact of change over time in the number of home parenteral infusions per week on PNIQ score (Quality of life).
4. Discussion
This is the first study to evaluate QoL over multiple time points using an HPS-specific tool. The aim of this study was to measure PNIQ score longitudinally in patients who were receiving HPS, thus adding to the knowledge base by exploring within-person variation over time. Because previous research demonstrated that patients who required more infusions per week reported a poorer QoL (higher PNIQ score) [19], we hypothesised that within-person changes to HPS treatment over time would also be associated with changes to QoL over time. After adjusting for confounding factors related to the patient’s demographics, we observed that patients with any reduction over time in weekly HPS infusions also reported a decrease in PNIQ score (improved QoL) by as much as 1.34. The ‘per day’ change to the number of infusions per week (continuous change) was associated with an improvement to the PNIQ score of −0.34. This was not influenced by change in the site where the patient was receiving treatment, nor was it influenced by confounding factors such as age, gender, ethnicity, income, underlying disease, type of problem with bowel, if the patient was on antidepressants at any time point, and if the patient had had a recent operation.
A previous smaller study of 20 patients using the generic QoL tool, SF-36, showed that 8 of these patients had a non-statistically significant worse QoL score and an increase in the number of HPS infusions per week compared to baseline [26]. Likewise, a small prospective study that evaluated the effect of an educational booklet on improvement in HPS knowledge in 33 patients concluded that patients who reduced the frequency of HPS infusions had a significant increase in QoL as measured by EQ5D index and physical function domain of the SF-36 [27]. The ability to demonstrate change over time in the QoL in individuals receiving HPS treatment is, of course, relevant to the use of therapies that may reduce HPS requirements [45,46], such as surgical restoration of bowel continuity (bringing colon or distal bowel back into circuit) [47,48,49], intestinal lengthening [50], or treatment with entero-hormones such as glucagon-like peptide-2 analogues [51].
Limitations for this study include the number of participants who had a reduction to the frequency of HPS. Out of the total study population, only 12–13% reported a reduction of infusions over the study period. As the mean length of time receiving HPS at baseline was over 6 years, it is to be expected that this study population may be less likely to see any gut adaptation that would allow for HPS reduction [9,45,52]. However, this factor supports the need for further research in this area, ideally including longitudinal work in more patients following HPS initiation and perhaps specifically evaluating the benefits of the different therapeutic modalities that can help reduce HPS requirements. In addition, data presented were from the UK alone, and 94% of the patients were white. It would be interesting to determine variance between countries for QoL and to include more patients from varying ethnic backgrounds. Data may also be subject to bias due to the use of the missing-indicator method. Although this method is valid for handling missing baseline covariate data, it has been criticized for introducing bias in non-randomized studies [53].
5. Conclusions
This is the first and largest national study to evaluate changes in QoL over time using an HPS-specific and patient-centric tool. Patients with CIF who reported a reduction in weekly HPS infusions also reported a decrease in their PNIQ score, indicating improved QoL. The data further demonstrate that the PNIQ tool is sensitive enough to be used in patients receiving HPS and to identify within-person changes over time. Further work will be advantageous in the understanding of how to achieve a reduction in HPS over time and positively influence QoL.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/nu15030622/s1, Table S1: Age and gender characteristics within the total population and the study sample population at each recruitment site.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, D.J., S.L. and S.B.; data curation, D.J.; formal analysis, D.J. and M.G.; funding acquisition, S.L. and S.B.; investigation, D.J., C.F., S.G., D.B., A.C., C.C., B.T., S.C.C., J.F., C.D., A.F., C.L., S.R., C.G.M., D.R., R.M., L.S., P.N., C.W. and P.S.; methodology, D.J., S.L. and S.B.; project administration, D.J., A.M.S. and S.B.; supervision, S.L., A.M.S. and S.B.; visualisation, S.B.; writing—original draft, D.J.; writing—review and editing, S.L., C.F., A.M.S., M.G., S.G., D.B., A.C., C.C., B.T., S.C.C., J.F., C.D., A.F., C.L., S.R., C.G.M., D.R., R.M., L.S., P.N., C.W., P.S. and S.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Shire International GmbH, a member of the Takeda group of companies, grant number IIR-GB-002546.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Ethics Committee of National Research Ethics Committee North West (Ref: 19/LO/1971, date of approval: 23/12/2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Galen Research Limited (CRN 6282937) for the use of the Parenteral Nutrition Impact Questionnaire (PNIQ). We would also like to thank the people receiving HPS who completed the questionnaire and the teams at the NHS sites who helped with site management and patient recruitment, including named authors and Nicola Burch, Consultant Gastroenterologist; Jonathan Ogor, Senior Research Nurse; Anne Keen, Clinical Research Facility Team Manager; Jenny Crabtree, Clinical Trials Administrator; Helen Christensen, Research Nurse; Sandra Stringer, Gastroenterology Research Nurse; Suzie Marriott, Senior Research Nurse; Jane Fletcher, Lead Nutrition Nurse; Ashleigh Hogg, Clinical Trials Associate; Orlagh Skelton, Clinical Research Nurse; Hayley Leyland, Lead HPN Nurse; Mary Doona, Research Nurse; and Ben Booth, Nutrition Team Charge Nurse.
Conflicts of Interest
All authors declare no conflict of interest apart from the following: Debra Jones, Sorrel Burden, Simon Lal, Chloe French, and Anne Marie Sowerbutts declare funding for an Investigator Initiated Research grant from Shire International GmbH, a member of the Takeda group of companies IIR-GB-002546; payment was made to the institution. Simon Lal declares the following: grants to the institution from Baxter and Takeda; fees from Baxter, Takeda, NorthSea, VectivBio, Zealand (not linked to this work); payment was made from Fresenius, Takeda, B Braun (not linked to this work); support was provided for attending Takeda meetings (not linked to this work) and participation in data safety or advisory boards for Baxter, Takeda, NorthSea, VectivBio, Zealand (not linked to this work). Jane Fletcher declares an NIHR Clinical Doctoral Research Fellowship, grant provided to the institution, and Avanos, payment made to a charity trust fund. Clare Donnellan declares fees for talks from BMS and Takeda; payments were made to Clare. Daniel Rodgers declares a voluntary role of Honorary Secretary and Trustee of BAPEN. Sheldon Cooper declares a role of Honorary Treasurer and Trustee of BAPEN. Alastair Forbes declares events with B Braun, Nutricia, and Fresenius Kabi. Carolyn Wheatley declares a role of Chair of PINNT. In addition, there was personal reimbursement of consulting fees for Patient Leadership Council Meeting, VectivBio, and a relationship with Micrel for attendance at ESPEN 2022. Christopher Mountford declares a role of Honorary Treasurer BAPEN 2019–2022. Simon Gabe declares grants or contracts for research studies from Takeda, Zealand Pharma, and Napa Therapeutics. Furthermore, payment was made for lectures or presentations with Takeda and Fresenius, and support was provided for attending a conference with Calea.
References
- Jones, B.J.M. Home parenetral nutrition in the United Kingdom: A position paper. BAPEN 2003. Available online: https://www.bapen.org.uk/pdfs/hpn.pdf (accessed on 29 March 2022).
- Staun, M.; Pironi, L.; Bozzetti, F.; Baxter, J.; Forbes, A.; Joly, F.; Jeppesen, P.; Moreno, J.; Hebuterne, X.; Pertkiewicz, M.; et al. ESPEN Guidelines on Parenteral Nutrition: Home parenteral nutrition (HPN) in adult patients. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 28, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pironi, L.; Arends, J.; Bozzetti, F.; Cuerda, C.; Gillanders, L.; Jeppesen, P.B.; Joly, F.; Kelly, D.; Lal, S.; Staun, M.; et al. ESPEN guidelines on chronic intestinal failure in adults. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 247–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pironi, L.; Arends, J.; Baxter, J.; Bozzetti, F.; Pelaez, R.B.; Cuerda, C.; Forbes, A.; Gabe, S.; Gillanders, L.; Holst, M.; et al. ESPEN endorsed recommendations. Definition and classification of intestinal failure in adults. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 34, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pironi, L. Definitions of intestinal failure and the short bowel syndrome. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 30, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pironi, L.; Boeykens, K.; Bozzetti, F.; Joly, F.; Klek, S.; Lal, S.; Lichota, M.; Mühlebach, S.; Van Gossum, A.; Wanten, G.; et al. ESPEN guideline on home parenteral nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 39, 1645–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibb, M.; Teubner, A.; Theis, V.; Shaffer, J.; Lal, S. Review article: The management of long-term parenteral nutrition. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 37, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, L. Home Parenteral Nutrition: Survival, Cost, and Quality of Life. Gastroenterology 2006, 130, S52–S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messing, B.; Crenn, P.; Beau, P.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Rambaud, J.-C.; Matuchansky, C. Long-term survival and parenteral nutrition dependence in adult patients with the short bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 1999, 117, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibb, M.; Soop, M.; Teubner, A.; Shaffer, J.; Abraham, A.; Carlson, G.; Lal, S. Survival and nutritional dependence on home parenteral nutrition: Three decades of experience from a single referral centre. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman-de Waal, G.; Naber, T.; Schoonhoven, L.; Persoon, A.; Sauerwein, H.; van Achterberg, T. Problems Experienced by Patients Receiving Parenteral Nutrition at Home: Results of an Open Interview Study. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2006, 30, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman-de Waal, G.; Schoonhoven, L.; Jansen, J.; Wanten, G.; van Achterberg, T. The impact of home parenteral nutrition on daily life-a review. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 26, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persoon, A.; Huisman-de Waal, G.; Naber, T.A.; Schoonhoven, L.; Tas, T.; Sauerwein, H.; van Achterberg, T. Impact of long-term HPN on daily life in adults. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 24, 304–313. Available online: http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=med6&NEWS=N&AN=15784493 (accessed on 20 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Heaney, A.; McKenna, S.P.; Wilburn, J.; Rouse, M.; Taylor, M.; Burden, S.; Lal, S. The Impact of Home Parenteral Nutrition on the lives of adults with Type 3 Intestinal Failure. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 24, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowerbutts, A.M.; Panter, C.; Dickie, G.; Bennett, B.; Ablett, J.; Burden, S.; Lal, S. Short bowel syndrome and the impact on patients and their families: A qualitative study. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2020, 33, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, M.F.; Smith, C.E. Clinical, social, and economic impacts of home parenteral nutrition dependence in short bowel syndrome. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2014, 38, 32S–37S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumpf, V.J. Challenges and Obstacles of Long-Term Home Parenteral Nutrition. Nutr. Clin. Pr. 2019, 34, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, J.P.; Fayers, P.M.; McKinlay, A.W. A review of the quality of life of adult patients treated with long-term parenteral nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 25, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burden, S.T.; Jones, D.J.; Gittins, M.; Ablett, J.; Taylor, M.; Mountford, C.; Tyrrell-Price, J.; Donnellan, C.; Leslie, F.; Bowling, T.; et al. Needs-based quality of life in adults dependent on home parenteral nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1433–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowerbutts, A.M.; Jones, D.; Lal, S.; Burden, S. Quality of life in patients and in family members of those receiving home parenteral support with intestinal failure: A systematic review. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3210–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, M.F. Quality of life in adult home parenteral nutrition patients. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2005, 29, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, C.; Chapman, A.; Burden, S.; Lal, S.; MacCulloch, A. Systematic Literature Review of Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients Receiving Parenteral Nutrition. Value Health 2015, 18, A630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, B.S.; Levine, E.L. Permanent total parenteral nutrition: Psychological and social responses of the early stages. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1979, 3, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, G.L.; Maguire, G.; Williams, N.; Bradley, A.; Shaffer, J.L.; Irving, M.H. Quality of life on home parenteral nutrition: A single centre study of 37 patients. Clin. Nutr. 1995, 14, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, D.M.; Irving, M.H. Assessing the quality of life of patients with intestinal failure on home parenteral nutrition. Gut 1997, 40, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pironi, L.; Paganelli, F.; Mosconi, P.; Morselli-Labate, A.M.; Spinucci, G.; Merli, C.; Guidetti, M.; Miglioli, M. The SF-36 instrument for the follow-up of health-related quality-of-life assessment of patients undergoing home parenteral nutrition for benign disease. Transplant. Proc. 2004, 36, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culkin, A.; Gabe, S.M.; Madden, A.M. Improving clinical outcome in patients with intestinal failure using individualised nutritional advice. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2009, 22, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blüthner, E.; Bednarsch, J.; Stockmann, M.; Karber, M.; Pevny, S.; Maasberg, S.; Gerlach, U.A.; Pascher, A.; Wiedenmann, B.; Pratschke, J. Determinants of quality of life in patients with intestinal failure receiving long-term parenteral nutrition using the SF-36 questionnaire: A German single-center prospective observational study. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2020, 44, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, J.P.; Fayers, P.M.; Bozzetti, F.; Kelly, D.; Joly, F.; Wanten, G.; Jonkers, C.; Cuerda, C.; van Gossum, A.; Klek, S.; et al. An international study of the quality of life of adult patients treated with home parenteral nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 38, 1788–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, J.P.; Fayers, P.M.; McKinlay, A.W. The clinical and psychometric validation of a questionnaire to assess the quality of life of adult patients treated with long-term parenteral nutrition. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2010, 34, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J.E. SF-36 health survey update. Spine 2000, 25, 3130–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ware, J.E., Jr.; Sherbourne, C.D. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36). I. Conceptual framework and item selection. Med. Care 1992, 30, 473–483. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1593914 (accessed on 20 January 2023). [CrossRef]
- Devlin, N.J.; Brooks, R. EQ-5D and the EuroQol Group: Past, Present and Future. Appl. Health Econ. Health Policy 2017, 15, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, M.E.; Larsson, S.; Lee, T.H. Standardizing Patient Outcomes Measurement. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, S.P.; Wilburn, J. Patient Value: Its Nature, Measurement and Role in Real World Evidence Studies and Outcomes-Based Reimbursement. J. Med. Econ. 2018, 21, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghofer, P.; Fragkos, K.C.; Baxter, J.P.; Forbes, A.; Joly, F.; Heinze, H.; Loth, S.; Pertkiewicz, M.; Messing, B.; Jeppesen, P.B. Development and validation of the disease-specific Short Bowel Syndrome-Quality of Life (SBS-QoL) scale. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, M.F.; Machan, J.T.; Xue, Z.; Compher, C. Home Parenteral Nutrition Patient-Reported Outcome Questionnaire: Sensitive to Quality of Life Differences Among Chronic and Prolonged Acute Intestinal Failure Patients. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2021, 45, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilburn, J.; McKenna, S.P.; Heaney, A.; Rouse, M.; Taylor, M.; Culkin, A.; Gabe, S.; Burden, S.; Lal, S. Development and validation of the Parenteral Nutrition Impact Questionnaire (PNIQ), a patient-centric outcome measure for Home Parenteral Nutrition. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, S.P. Measuring patient-reported outcomes: Moving beyond misplaced common sense to hard science. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French, C.; Lal, S.; Jones, D.; Sowerbutts, A.M.; Brundrett, D.; Burch, N.; Calvert, C.; Cooper, S.C.; Donnellan, C.; Forbes, A.; et al. Impact of home parenteral nutrition on family members: A national multi-centre cross-sectional study. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 41, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsen, S.; El-Masry, R.; Ali, O.F.; Abdel-Hady, D. Quality of life during COVID-19 pandemic: A community-based study in Dakahlia governorate, Egypt. Glob. Heal. Res. Policy 2022, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouratidis, K. How COVID-19 reshaped quality of life in cities: A synthesis and implications for urban planning. Land Use Policy 2021, 111, 105772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansel, T.C.; Saltzman, L.Y.; Melton, P.A.; Clark, T.L.; Bordnick, P.S. COVID-19 behavioral health and quality of life. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.; Selles, R.W.; De Ridder, W.A.; Ter Stege, M.H.P.; Souer, J.S.; Wouters, R.M.; on behalf of the Hand-Wrist Study Group C. What Is the Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Quality of Life and Other Patient-reported Outcomes? An Analysis of the Hand-Wrist Study Cohort. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2021, 479, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, T.R.; Leader, L.M. Parenteral nutrition: Transient or permanent therapy in intestinal failure? Gastroenterology 2006, 130, S37–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopczynska, M.; Carlson, G.; Teubner, A.; Abraham, A.; Taylor, M.; Burden, S.T.; Hvas, C.L.; Jepsen, P.; Lal, S. Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with Intestinal Failure Due to Short Bowel Syndrome and Intestinal Fistula. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, S.; Teubner, A.; Shaffer, J.L. Review article: Intestinal failure. Aliment. Pharm. Ther. 2006, 24, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klek, S.; Forbes, A.; Gabe, S.; Hoist, M.; Wanten, G.; Irtun, O.; Damink, S.O.; Panisic-Sekeljic, M.; Pelaez, R.B.; Pironi, L.; et al. Management of acute intestinal failure: A position paper from the European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism (ESPEN) Special Interest Group. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 35, 1209–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, G.L. Surgical management of intestinal failure. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2003, 62, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rege, A. The Surgical Approach to Short Bowel Syndrome—Autologous Reconstruction versus Transplantation. Viszeralmedizin 2014, 30, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pape, U.F.; Iyer, K.R.; Jeppesen, P.B.; Kunecki, M.; Pironi, L.; Schneider, S.M.; Seidner, D.L.; Lee, H.M.; Caminis, J. Teduglutide for the treatment of adults with intestinal failure associated with short bowel syndrome: Pooled safety data from four clinical trials. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820905766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiot, A.; Messing, B.; Corcos, O.; Panis, Y.; Joly, F. Determinants of home parenteral nutrition dependence and survival of 268 patients with non-malignant short bowel syndrome. Clin. Nutr. 2013, 32, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groenwold, R.H.; White, I.R.; Donders, A.R.; Carpenter, J.R.; Altman, D.G.; Moons, K.G. Missing covariate data in clinical research: When and when not to use the missing-indicator method for analysis. CMAJ 2012, 184, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).