A Mediterranean Eating Pattern Combining Energy and Time-Restricted Eating Improves Vaspin and Omentin Concentrations Compared to Intermittent Fasting in Overweight Individuals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Diets
2.3. Anthropometric Measurements
2.4. Biochemical Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Ethical Aspects
3. Results
3.1. Demographic, Anthropometric and Dietary Data
3.2. Adipokine Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trepanowski, J.F.; Bloomer, R.J. The impact of religious fasting on human health. Nutr. J. 2010, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarri, K.O.; Linardakis, M.K.; Bervanaki, F.N.; Tzanakis, N.E.; Kafatos, A.G. Greek Orthodox fasting rituals: A hidden characteristic of the Mediterranean diet of Crete. Br. J. Nutr. 2004, 92, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarri, K.O.; Tzanakis, N.E.; Linardakis, M.K.; Mamalakis, G.D.; Kafatos, A.G. Effects of Greek Orthodox Christian Church fasting on serum lipids and obesity. BMC Public Health 2003, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarri, K.; Linardakis, M.; Codrington, C.; Kafatos, A. Does the periodic vegetarianism of Greek Orthodox Christians benefit blood pressure? Prev. Med. 2007, 44, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karras, S.N.; Koufakis, T.; Adamidou, L.; Antonopoulou, V.; Karalazou, P.; Thisiadou, K.; Mitrofanova, E.; Mulrooney, H.; Petróczi, A.; Zebekakis, P.; et al. Effects of orthodox religious fasting versus combined energy and time restricted eating on body weight, lipid concentrations and glycaemic profile. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 72, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karras, S.N.; Koufakis, T.; Adamidou, L.; Polyzos, S.A.; Karalazou, P.; Thisiadou, K.; Zebekakis, P.; Makedou, K.; Kotsa, K. Similar late effects of a 7-week orthodox religious fasting and a time restricted eating pattern on anthropometric and metabolic profiles of overweight adults. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 72, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karras, S.N.; Koufakis, T.; Adamidou, L.; Dimakopoulos, G.; Karalazou, P.; Thisiadou, K.; Makedou, K.; Kotsa, K. Effects of Christian Orthodox Fasting Versus Time-Restricted Eating on Plasma Irisin Concentrations among Overweight Metabolically Healthy Individuals. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, S.N.; Koufakis, T.; Adamidou, L.; Dimakopoulos, G.; Karalazou, P.; Thisiadou, K.; Makedou, K.; Zebekakis, P.; Kotsa, K. Implementation of Christian Orthodox fasting improves plasma adiponectin concentrations compared with time-restricted eating in overweight premenopausal women. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 73, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzeh, F.S.; Hasanain, D.M.; Qadhi, A.H.; Ghafouri, K.J.; Azhar, W.F.; Ghaith, M.M.; Aldairi, A.F.; Almasmoum, H.A.; Assaggaf, H.M.; Alhussain, M.H.; et al. Consumption of Food Components of the Mediterranean Diet Decreases the Risk of Breast Cancer in the Makkah Region, Saudi Arabia: A Case-Control Study. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 863029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Vasilopoulou, E.; Georga, K. Macro- and micronutrients in a traditional Greek menu. Forum. Nutr. 2005, 57, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, S.N.; Koufakis, T.; Petróczi, A.; Folkerts, D.; Kypraiou, M.; Mulrooney, H.; Naughton, D.P.; Persynaki, A.; Zebekakis, P.; Skoutas, D.; et al. Christian Orthodox fasting in practice: A comparative evaluation between Greek Orthodox general population fasters and Athonian monks. Nutrition 2019, 59, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karras, S.N.; Persynaki, A.; Petróczi, A.; Barkans, E.; Mulrooney, H.; Kypraiou, M.; Tzotzas, T.; Tziomalos, K.; Kotsa, K.; Tsioudas, A.; et al. Health benefits and consequences of the Eastern Orthodox fasting in monks of Mount Athos: A cross-sectional study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radzik-Zając, J.; Wytrychowski, K.; Wiśniewski, A.; Barg, W. The role of the novel adipokines vaspin and omentin in chronic inflammatory diseases. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2023, 29, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavileci, B.; Koldaş, Z.L. The relationship between Vaspin, Nesfatin-1 plasma levels and presence of fragmented QRS with the severity of coronary atherosclerosis. Adv. Med. Sci. 2022, 67, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klöting, N.; Kovacs, P.; Kern, M.; Heiker, J.T.; Fasshauer, M.; Schön, M.R.; Stumvoll, M.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G.; Blüher, M. Central vaspin administration acutely reduces food intake and has sustained blood glucose-lowering effects. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 1819–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Tian, T.; Wang, L.; Lee, P.; Hua, Q. Serum vaspin concentration in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and macrovascular complications. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2017, 17, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Huang, Y.; Gai, C.; Chai, G.; Lee, S. Serum vaspin levels are positively associated with diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Investig. 2021, 12, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.Z.; Lee, M.J.; Hu, H.; Pray, J.; Wu, H.-B.; Hansen, B.C.; Shuldiner, A.R.; Fried, S.K.; McLenithan, J.C.; Gong, D.-W. Identification of omentin as a novel depot-specific adipokine in human adipose tissue: Possible role in modulating insulin action. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 290, E1253–E1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.K.; Adya, R.; Randeva, H.S. Omentin: A novel link between inflammation, diabesity, and cardiovascular disease. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2010, 20, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Kaminga, A.C.; Wen, S.W.; Acheampong, K.; Liu, A. Omentin-1 in diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0226292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperling, M.; Grzelak, T.; Pelczyńska, M.; Bogdański, P.; Formanowicz, D.; Czyżewska, K. Association of Serum Omentin-1 Concentration with the Content of Adipose Tissue and Glucose Tolerance in Subjects with Central Obesity. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dore, R.; Krotenko, R.; Reising, J.P.; Murru, L.; Sundaram, S.M.; Di Spiezio, A.; Müller-Fielitz, H.; Schwaninger, M.; Jöhren, O.; Mittag, J.; et al. Nesfatin-1 decreases the motivational and rewarding value of food. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 1645–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Li, S.Z.; Fan, X.T.; Tian, Z.; Lu, X.-Q.; Dong, J. Circulating Nesfatin-1 Levels and Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Diabetes Res. 2017, 2017, 7687098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeghate, E. Visfatin: Structure, function and relation to diabetes mellitus and other dysfunctions. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1851–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saddi-Rosa, P.; Oliveira, C.S.; Giuffrida, F.M.; Reis, A.F. Visfatin, glucose metabolism and vascular disease: A review of evidence. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2010, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoogian, E.N.C.; Chow, L.S.; Taub, P.R.; Laferrère, B.; Panda, S. Time-restricted Eating for the Prevention and Management of Metabolic Diseases. Endocr. Rev. 2022, 43, 405–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domaszewski, P.; Konieczny, M.; Pakosz, P.; Łukaniszyn-Domaszewska, K.; Mikuláková, W.; Sadowska-Krępa, E.; Anton, S. Effect of a six-week times restricted eating intervention on the body composition in early elderly men with overweight. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Sun, Y.; Ye, Y.; Hu, D.; Zhang, H.; He, Z.; Zhao, H.; Yang, H.; Mao, Y. Randomized controlled trial for time-restricted eating in healthy volunteers without obesity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.F.O.; Sena-Evangelista, K.C.M.; Lyra, C.O.; Pedrosa, L.F.C.; Arrais, R.F.; Lima, S.C.V.C. Motivations for weight loss in adolescents with overweight and obesity: A systematic review. BMC Pediatr. 2018, 18, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karras, S.N.; Koufakis, T.; Adamidou, L.; Dimakopoulos, G.; Karalazou, P.; Thisiadou, K.; Zebekakis, P.; Makedou, K.; Kotsa, K. Different patterns of changes in free 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations during intermittent fasting among meat eaters and non-meat eaters and correlations with amino acid intake. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 74, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.D.; Ryan, D.H.; Apovian, C.M.; Ard, J.D.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Donato, K.A.; Hu, F.B.; Hubbard, V.S.; Jakicic, J.M.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS guideline for the management of overweight and obesity in adults: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. Circulation 2014, 129, S102–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greek National Dietary Guidelines for Adults. 2014. Available online: http://www.fao.org/nutrition/education/food-dietary-guidelines/regions/countries/greece/en/ (accessed on 25 March 2023).
- Mansour, S.W.; Tawfiq, M.S.; Khalefa, A.A.; Hadhoud, S.E.; El-Shorbgy, E.A.A. Effect of Diet Regimen on Serum Vaspin Level in Obese Diabetic Female Patients. ZUMJ 2019, 25, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.M.; Lee, H.J.; Park, H.S.; Kang, J.H.; Kim, K.S.; Song, Y.S.; Jang, Y.J. Effects of weight reduction on serum vaspin concentrations in obese subjects: Modification by insulin resistance. Obesity 2010, 18, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handisurya, A.; Riedl, M.; Vila, G.; Maier, C.; Clodi, M.; Prikoszovich, T.; Ludvik, B.; Prager, G.; Luger, A.; Kautzky-Willer, A. Serum vaspin concentrations in relation to insulin sensitivity following RYGB-induced weight loss. Obes. Surg. 2010, 20, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Luis, D.A.; Izaola, O.; Primo, D.; Aller, R. Modifications of serum levels of omentin-1 and other cardiovascular risk factors following weight loss secondary to a Mediterranean hypocaloric diet. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 2280–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanová, M.; Dostálová, I.; Trachta, P.; Drápalová, J.; Kaválková, P.; Haluzíková, D.; Matoulek, M.; Lacinová, Z.; Mráz, M.; Kasalický, M.; et al. Serum concentrations and subcutaneous adipose tissue mRNA expression of omentin in morbid obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: The effect of very-low-calorie diet, physical activity and laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. Physiol. Res. 2014, 63, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan, A.; Bechtold, D.A.; Pot, G.K.; Johnston, J.D. Chrono-nutrition: From molecular and neuronal mechanisms to human epidemiology and timed feeding patterns. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 53–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.; Youn, B.-S.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, E.H.; Park, J.W.; Namkoong, C.; Jeong, J.Y.; Yoon, S.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, K.-U.; et al. Circadian rhythm of serum vaspin in healthy male volunteers: Relation to meals. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 1869–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, S.; Gargari, B.P.; Izadi, A.; Imani, B.; Asjodi, F. The effects of Ramadan fasting on serum concentrations of vaspin and omentin-1 in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 2018, 19, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, E.F.; Beyl, R.; Early, K.S.; Cefalu, W.T.; Ravussin, E.; Peterson, C.M. Early Time-Restricted Feeding Improves Insulin Sensitivity, Blood Pressure, and Oxidative Stress Even without Weight Loss in Men with Prediabetes. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1212–1221.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michielsen, C.C.J.R.; Hangelbroek, R.W.; Feskens, E.J.M.; Afman, L.A. Disentangling the Effects of Monounsaturated Fatty Acids from Other Components of a Mediterranean Diet on Serum Metabolite Profiles: A Randomized Fully Controlled Dietary Intervention in Healthy Subjects at Risk of the Metabolic Syndrome. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2019, 63, e1801095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua, J.; de la Sacristana, A.G.; Romero, I.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Latre, J.; Sanchez, E.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Lopez-Miranda, J.; Perez-Jimenez, F. Monounsaturated fat-rich diet prevents central body fat distribution and decreases postprandial adiponectin expression induced by a carbohydrate-rich diet in insulin-resistant subjects. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1717–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, Y.; Farzollahpour, F.; Mirzababaei, A.; Maghbooli, Z.; Mirzaei, K. Associations of dietary fats intake and adipokines levels in obese women. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 43, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangeneh, F.; Yazdi, R.S.; Naghizadeh, M.M.; Abedinia, N. Effect of Ramadan Fasting on Stress Neurohormones in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. J. Family Reprod. Health 2015, 9, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spanaki, C.; Rodopaios, N.E.; Koulouri, A.; Pliakas, T.; Papadopoulou, S.K.; Vasara, E.; Skepastianos, P.; Serafeim, T.; Boura, I.; Dermitzakis, E.; et al. The Christian Orthodox Church Fasting Diet Is Associated with Lower Levels of Depression and Anxiety and a Better Cognitive Performance in Middle Life. Nutrients 2021, 13, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; Kuang, H.; Yu, Q.; Bai, M.; Mu, J. Association between vaspin level and coronary artery disease in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2016, 113, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klöting, N.; Berndt, J.; Kralisch, S.; Kovacs, P.; Fasshauer, M.; Schön, M.R.; Stumvoll, M.; Blüher, M. Vaspin gene expression in human adipose tissue: Association with obesity and type 2 diabetes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 339, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askin, L.; Duman, H.; Ozyıldız, A.; Tanriverdi, O.; Turkmen, S. Association between Omentin-1 and Coronary Artery Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Research. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2020, 16, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Watanabe, R.; Konii, H.; Shirai, R.; Sato, K.; Matsuyama, T.-A.; Ishibashi-Ueda, H.; Koba, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Hirano, T.; et al. Counteractive effects of omentin-1 against atherogenesis†. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 110, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobellis, G.; Corradi, D.; Sharma, A.M. Epicardial adipose tissue: Anatomic, biomolecular and clinical relationships with the heart. Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med. 2005, 2, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
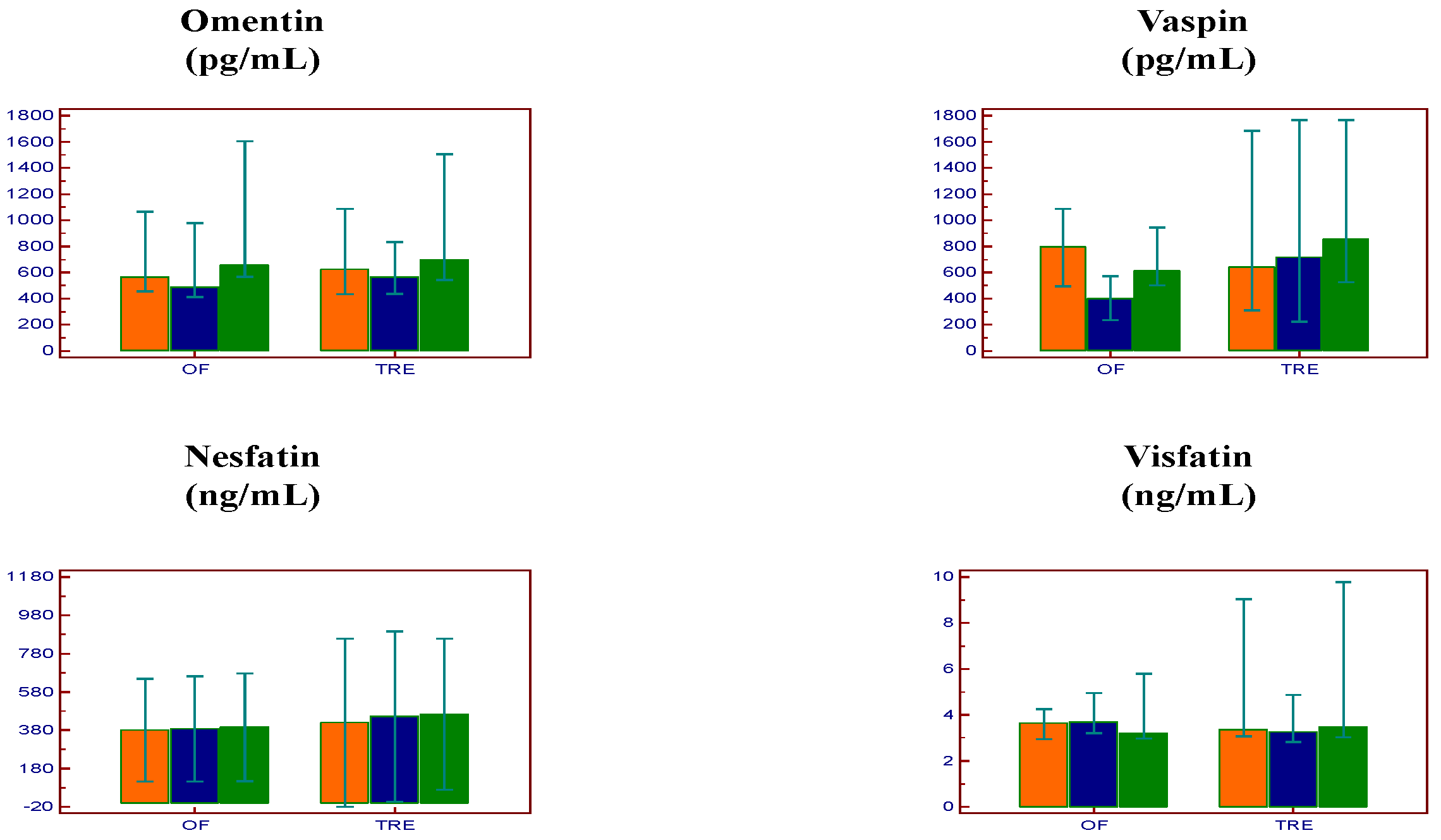
| Parameter | Baseline | Week 7 | Week 12 | p (Baseline-Week 7) | p (Week 7-Week 12) | p (Baseline-Week 12) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orthodox Fasters/Time-Restricted Eating | ||||||
| Age (years) | 50.3 */47.7 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Male gender (%) | 24.0/33.3 | - | - | - | - | - |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 29.3/29.1 | 28.5/28.3 | 28.3/28.0 | <0.001 †/0.02 | 0.97/0.19 | 0.004/<0.001 |
| Body fat (%) | 36.3/32.8 | 35.5/31.8 | 32.9/30.5 | 1.00/0.29 | 0.001/0.01 | 0.01/0.02 |
| Lean body mass (kg) | 47.8/53.2 | 47.3/53.1 | 48.8/53.5 | 1.00/1.00 | 0.001/1.00 | 0.74/1.00 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 93.4/94.9 | 92.6/91.5 | 92.0/90.5 | 0.33/0.01 | 0.18/0.60 | 0.10/0.007 |
| Omentin (pg/mL) | 568.5/622.1 | 489.4/567.5 | 659.0/698.2 | 0.28/0.77 | 0.001/0.41 | 0.001/0.94 |
| Vaspin (pg/mL) | 795.8/641.6 | 402.7/715.4 | 612.5/855.3 | 0.002/1.00 | 0.004/0.60 | 1.00/0.90 |
| Nesfatin (ng/mL) | 380.9/419.5 | 387.9/452.1 | 395.1/464.0 | 0.10/0.95 | 1.00/1.00 | 1.00/1.00 |
| Visfatin (ng/mL) | 3.6/3.4 | 3.7/3.2 | 3.2/3.5 | 1.00/0.19 | 0.87/0.94 | 0.39/1.00 |
| Daily fat intake (g) | 86.9/84.6 | 70.2/57.0 | 87.5/78.2 | <0.001/<0.001 | 0.01/0.01 | 1.00/0.11 |
| Daily saturated fat intake (g) | 24.5/25.6 | 9.5/13.4 | 27.0/21.7 | <0.001/<0.001 | <0.001/0.004 | 1.00/0.43 |
| Daily monounsaturated fat intake (g) | 32.9/35.4 | 45.6/32.5 | 32.0/26.0 | <0.001/1.00 | <0.001/0.18 | 1.00/0.23 |
| Total dietary fiber intake (g) | 30.7/34.0 | 30.6/28.3 | 22.7/24.4 | 1.00/1.00 | 0.22/0.42 | 0.40/0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karras, S.N.; Koufakis, T.; Popovic, D.S.; Adamidou, L.; Karalazou, P.; Thisiadou, K.; Zebekakis, P.; Makedou, K.; Kotsa, K. A Mediterranean Eating Pattern Combining Energy and Time-Restricted Eating Improves Vaspin and Omentin Concentrations Compared to Intermittent Fasting in Overweight Individuals. Nutrients 2023, 15, 5058. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245058
Karras SN, Koufakis T, Popovic DS, Adamidou L, Karalazou P, Thisiadou K, Zebekakis P, Makedou K, Kotsa K. A Mediterranean Eating Pattern Combining Energy and Time-Restricted Eating Improves Vaspin and Omentin Concentrations Compared to Intermittent Fasting in Overweight Individuals. Nutrients. 2023; 15(24):5058. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245058
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarras, Spyridon N., Theocharis Koufakis, Djordje S. Popovic, Lilian Adamidou, Paraskevi Karalazou, Katerina Thisiadou, Pantelis Zebekakis, Kali Makedou, and Kalliopi Kotsa. 2023. "A Mediterranean Eating Pattern Combining Energy and Time-Restricted Eating Improves Vaspin and Omentin Concentrations Compared to Intermittent Fasting in Overweight Individuals" Nutrients 15, no. 24: 5058. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245058
APA StyleKarras, S. N., Koufakis, T., Popovic, D. S., Adamidou, L., Karalazou, P., Thisiadou, K., Zebekakis, P., Makedou, K., & Kotsa, K. (2023). A Mediterranean Eating Pattern Combining Energy and Time-Restricted Eating Improves Vaspin and Omentin Concentrations Compared to Intermittent Fasting in Overweight Individuals. Nutrients, 15(24), 5058. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15245058









