Biotransformation of American Ginseng Stems and Leaves by an Endophytic Fungus Umbelopsis sp. and Its Effect on Alzheimer’s Disease Control
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Chemicals
2.2. Identification of the Strain NSJG
2.3. Solid-State Fermentation of AGSL by Endophytic Fungus Strain NSJG
2.4. Extraction of Total Saponins
2.5. Determination of Total Saponins
2.6. Identification of Fermented Extracts
2.7. Culture and Cell Viability Assay of M146L
2.8. Measurement of Aβ42 Concentration and β-Secretase Activity by ELISA
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of the Strain NSJG
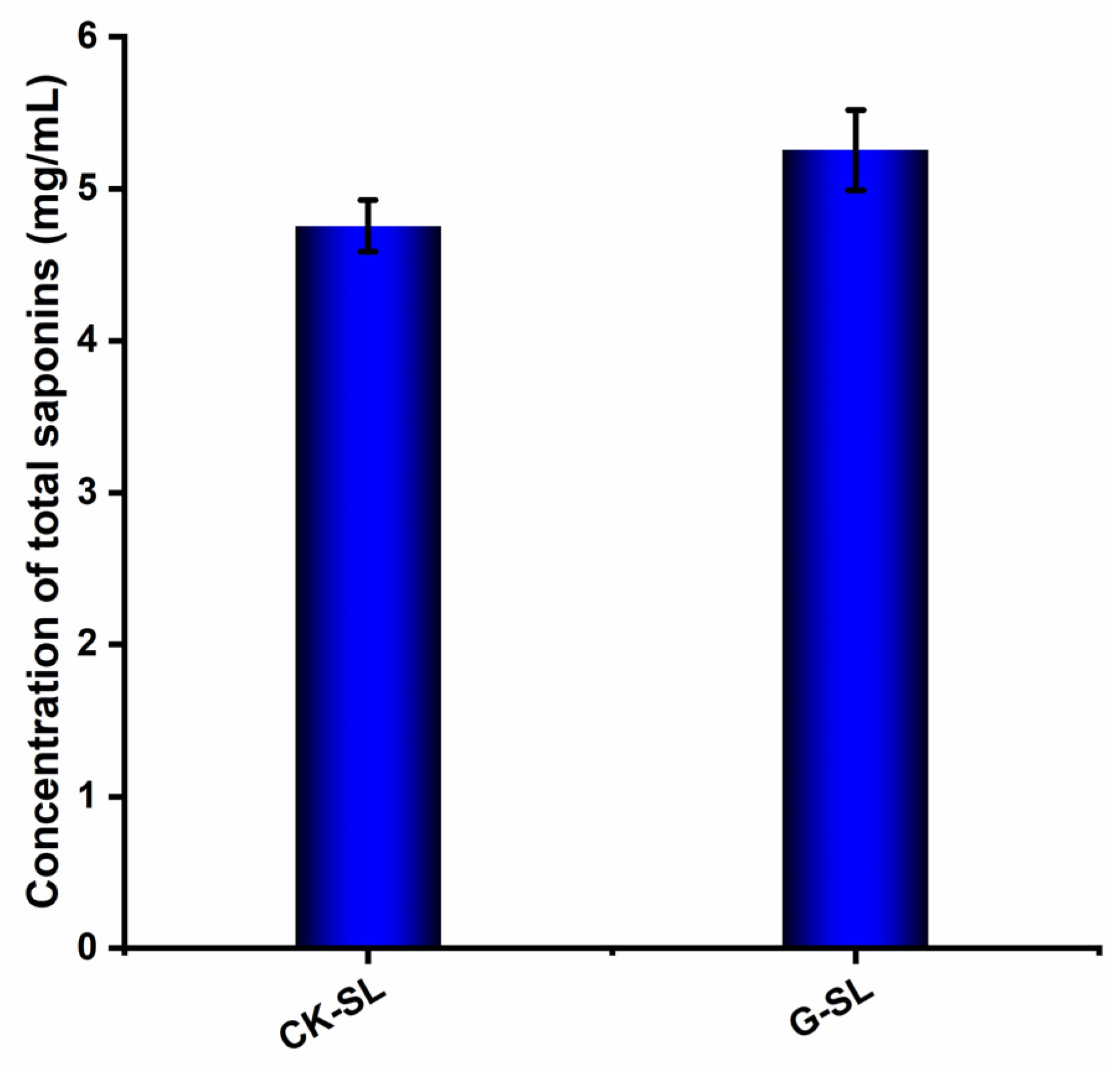
3.2. Determination of Total Saponin Concentration in Fermented Extracts of Biotransformed AGSL
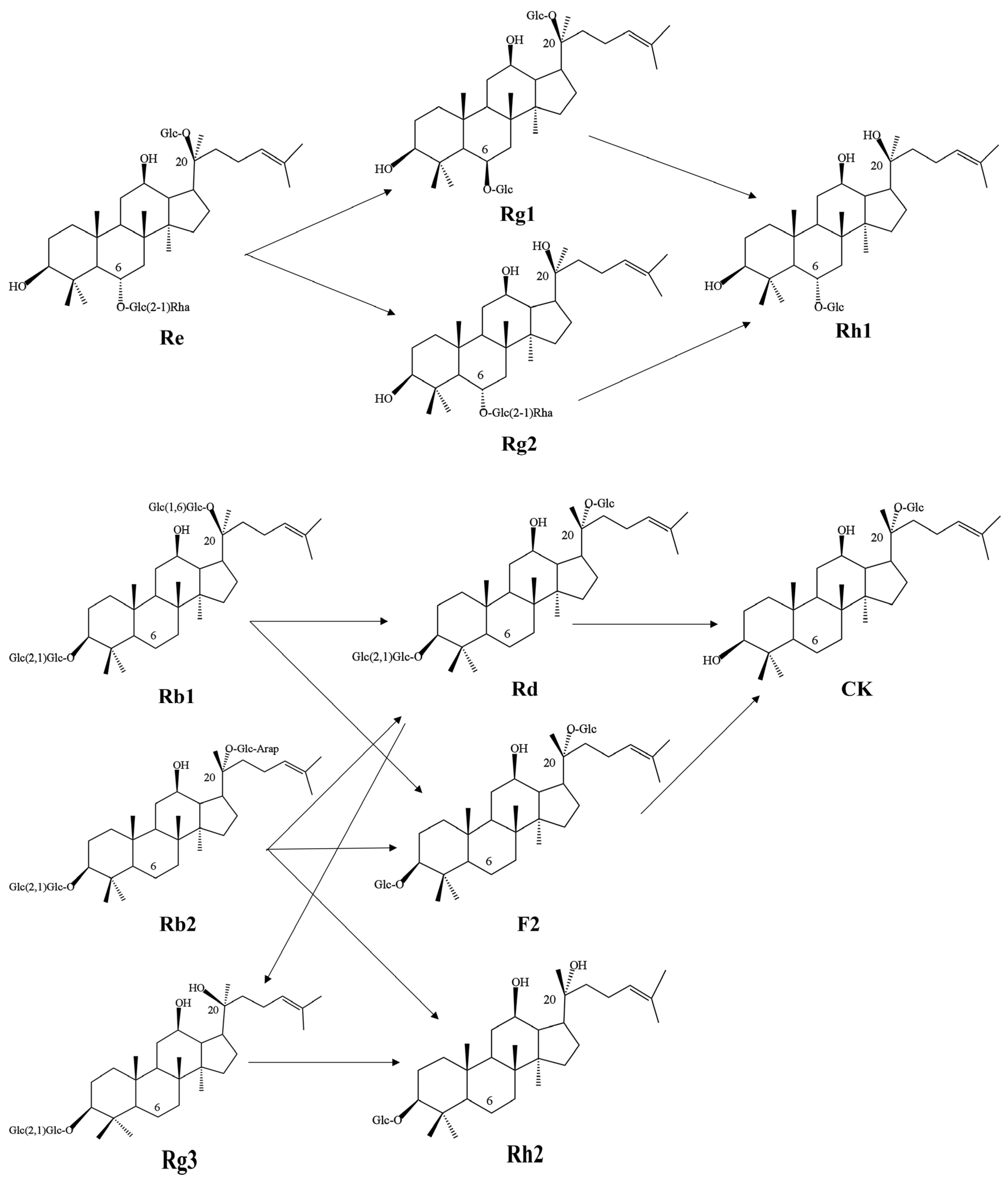
3.3. Identification and Analysis of Saponin Types in Fermented Extracts
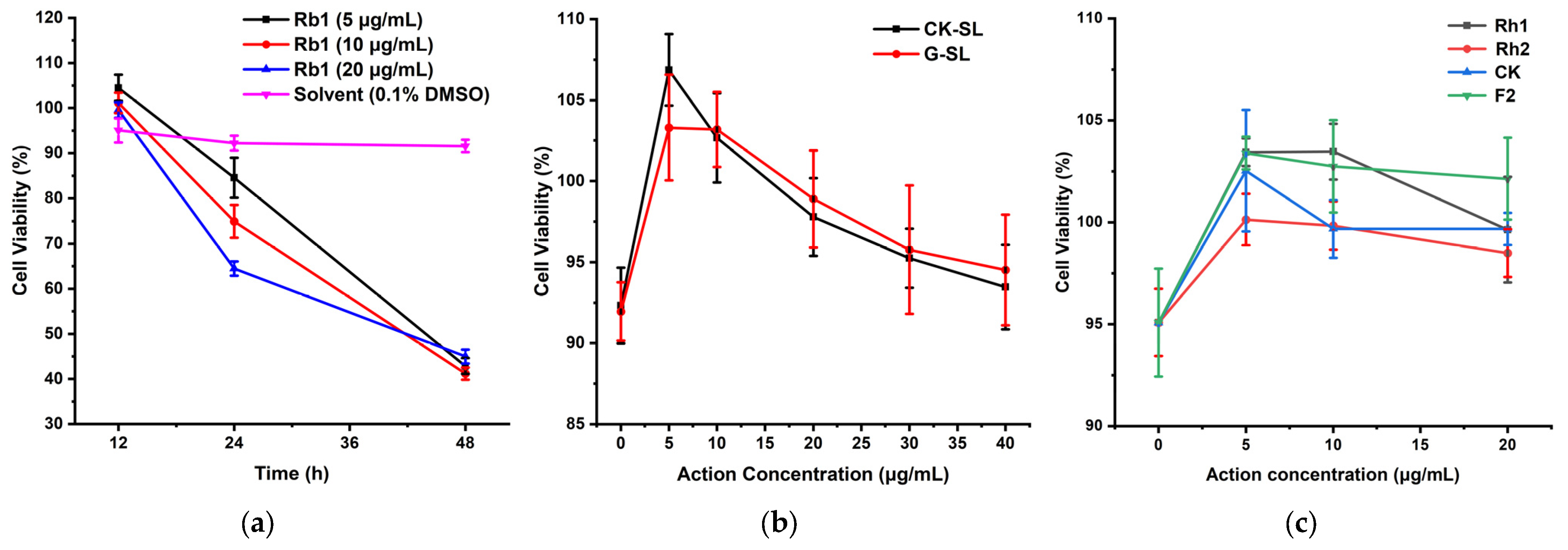
3.4. Cell Viability Assay of M146L
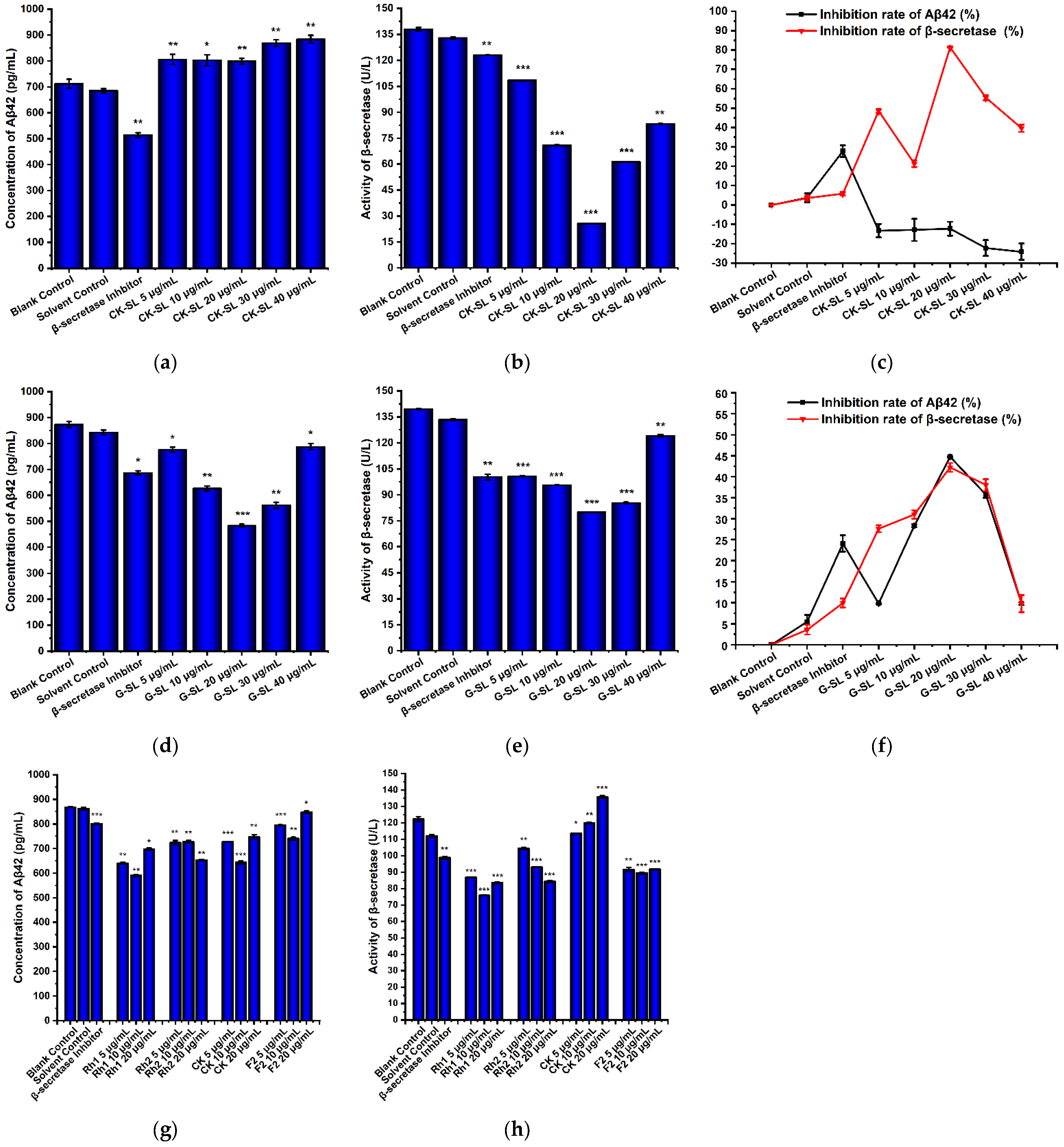
3.5. Evaluation of the Preventive Effect of Fermented Extracts on AD by the Changes in Aβ42 Concentration and β-Secretase Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shi, Z.Y.; Zeng, J.Z.; Wong, A.S.T. Chemical Structures and Pharmacological Profiles of Ginseng Saponins. Molecules 2019, 24, 2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, J.; Zuo, T.T.; Hu, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.D.; Xu, X.Y.; Yang, W.Z.; Guo, D.A. Advances and challenges in ginseng research from 2011 to 2020: The phytochemistry, quality control, metabolism, and biosynthesis. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2022, 39, 875–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.H.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, B.; Bae, B.S.; Kim, J.H. Red ginseng (Panax ginseng) decreases isoproterenol-induced cardiac injury via antioxidant properties in porcine. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.; Seo, J.Y.; Lee, S.K.; Oh, J.; Kim, J.S. Oral administration of hydrolyzed red ginseng extract improves learning and memory capability of scopolamine-treated C57BL/6J mice via upregulation of Nrf2-mediated antioxidant mechanism. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H. Cardiovascular Diseases and Panax ginseng: A Review on Molecular Mechanisms and Medical Applications. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qu, C.Y.; Li, J.X.; Wang, Y.F.; Li, W.; Wang, C.Z.; Wang, D.S.; Song, J.; Sun, G.Z.; Yuan, C.S. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Effects of Malonyl Ginsenosides from American Ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) on Type 2 Diabetic Mice. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 33652–33664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.D.; Kim, J.T.; Kim, S.H.; Chung, S.H. Ginseng and diabetes: The evidences from in vitro, animal and human studies. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucalo, I.; Jovanovski, E.; Rahelic, D.; Bozikov, V.; Romic, Z.; Vuksan, V. Effect of American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) on arterial stiffness in subjects with type-2 diabetes and concomitant hypertension. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2013, 150, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P.Y.; Mak, N.K.; Cheng, Y.K.; Leung, K.W.; Ng, T.B.; Fan, D.T.; Yeung, H.W.; Wong, R.N. Pharmacogenomics and the Yin/Yang actions of ginseng: Anti-tumor, angiomodulating and steroid-like activities of ginsenosides. Chin. Med. 2007, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, A.S.; Che, C.M.; Leung, K.W. Recent advances in ginseng as cancer therapeutics: A functional and mechanistic overview. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2015, 32, 256–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.I.; Kang, M.Y.; Lee, S.C. In Vitro and In Vivo Antioxidant Activity of Aged Ginseng (Panax ginseng). Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 21, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Piao, X.; Zhang, H.; Kang, J.P.; Yang, D.U.; Li, Y.; Pang, S.; Jin, Y.; Yang, D.C.; Wang, Y. Advances in Saponin Diversity of Panax ginseng. Molecules 2020, 25, 3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ma, M.; Wu, Z.; Liang, X.; Zheng, Q.; Li, D.; An, T.; Wang, G. Advances in the biosynthesis and metabolic engineering of rare ginsenosides. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 3391–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Hu, Z.; Li, A.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, N.; Ying, Z.; He, J.; Wang, C.; Yin, S.; Cheng, S. Recent Advances in Biotransformation of Saponins. Molecules 2019, 24, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Choi, B.R.; Kim, Y.C.; Choi, D.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, G.S.; Baek, N.I.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, D.Y. Comprehensive Profiling and Quantification of Ginsenosides in the Root, Stem, Leaf, and Berry of Panax ginseng by UPLC-QTOF/MS. Molecules 2017, 22, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini-Andreote, F. Endophytes: The Second Layer of Plant Defense. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, L.L.; Bae, H. Bacterial endophytes from ginseng and their biotechnological application. J. Ginseng Res. 2022, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Chen, L.; Xin, H.L.; Zheng, C.J.; Rahman, K.; Han, T.; Qin, L.P. A Friendly Relationship between Endophytic Fungi and Medicinal Plants: A Systematic Review. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Chen, Z.; Wang, B.; Wei, F.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Q.; He, M.; et al. Endophytes isolated from Panax notoginseng converted ginsenosides. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 14, 1730–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.E.; Kim, J.U.; Lee, J.W.; Lee, S.W.; Jo, I.H. Diversity of bacterial endophytes in Panax ginseng and their protective effects against pathogens. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisa, H.; Kamili, A.N.; Nawchoo, I.A.; Shafi, S.; Shameem, N.; Bandh, S.A. Fungal endophytes as prolific source of phytochemicals and other bioactive natural products: A review. Microb. Pathog. 2015, 82, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, H.Y.; You, X.L.; Li, Y.H. Diversity of endophytic fungi from roots of Panax ginseng and their saponin yield capacities. Springerplus 2013, 2, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Ma, S.; Shi, X.; Liu, C.; Ding, H.; Xue, W. Diversity and Ginsenoside Biotransformation Potential of Cultivable Endophytic Fungi Associated with Panax bipinnatifidus var. bipinnatifidus in Qinling Mountains, China. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 762862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Guo, X.; Lu, W. Efficient biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to Rd by isolated Aspergillus versicolor, excreting beta-glucosidase in the spore production phase of solid culture. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2015, 108, 1117–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Pi, Z.; Song, F.; Liu, Z. Ginsenosides attenuate d-galactose- and AlCl(3)-inducedspatial memory impairment by restoring the dysfunction of the neurotransmitter systems in the rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knopman, D.S.; Amieva, H.; Petersen, R.C.; Chetelat, G.; Holtzman, D.M.; Hyman, B.T.; Nixon, R.A.; Jones, D.T. Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karran, E.; De Strooper, B. The amyloid hypothesis in Alzheimer disease: New insights from new therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassar, R.; Kuhn, P.H.; Haass, C.; Kennedy, M.E.; Rajendran, L.; Wong, P.C.; Lichtenthaler, S.F. Function, therapeutic potential and cell biology of BACE proteases: Current status and future prospects. J. Neurochem. 2014, 130, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis across Computing Platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Q.; Yi, L.W.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Guo, F.; Huo, Y.S.; Zhao, D.Q.; Xu, F.; Wang, X.; Cai, S.Q. 177 Saponins, including 11 New Compounds in Wild Ginseng Tentatively Identified via HPLC-IT-TOF-MS(n), and Differences among Wild Ginseng, Ginseng under Forest, and Cultivated Ginseng. Molecules 2021, 26, 3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Nagarajan, A.; Uchil, P.D. Analysis of Cell Viability by the MTT Assay. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2018, 2018, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Gao, X.; Yan, P. Optimization of Fermentation Conditions and Product Identification of a Saponin-Producing Endophytic Fungus. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, W.; Fan, D. Biotransformation of Ginsenoside Rb1 to Ginsenoside CK by Strain XD101: A Safe Bioconversion Strategy. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2021, 193, 2110–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Yin, Z.H.; Wu, L.P.; Yin, C.R. Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to ginsenoside C-K by endophytic fungus Arthrinium sp. GE 17-18 isolated from Panax ginseng. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 63, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Dai, Y.; Han, H.; Yu, S.; Liu, S. Microbial conversion of ginsenoside Rd from Rb1 by the fungus mutant Aspergillus niger strain TH-10a. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2016, 46, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Shi, X.; Feng, M. Effects of external calcium on the biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to ginsenoside Rd by Paecilomyces bainier 229-7. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Zhou, C.Q.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, P.; Chen, D.F.; Liu, X.H.; Shi, X.L.; Feng, M.Q. Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to ginsenoside Rd by highly substrate-tolerant Paecilomyces bainier 229-7. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 7872–7876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Lu, X.; Hu, Y.; Fan, X. Chemical constituents of Panax ginseng and Panax notoginseng explain why they differ in therapeutic efficacy. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 161, 105263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yin, Z.H.; Yin, C.Y. Biotransformation of ginsenoside Rb1 to ginsenoside Rg3 by endophytic bacterium Burkholderia sp. GE 17-7 isolated from Panax ginseng. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 1579–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Ji, X.; Shi, Y.; Mu, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhong, M.; Han, Y.; Duan, C.; Li, X.; Li, D. Specific and efficient hydrolysis of all outer glucosyls in protopanaxadiol type and protopanaxatriol type ginsenosides by a beta-glucosidase from Thermoclostridium stercorarium. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2023, 162, 110152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, F.; Salihoglu, H.; Rodrigues, E.; Herzog, E.; Blume, T.; Filser, S.; Dorostkar, M.; Shimshek, D.R.; Brose, N.; Neumann, U.; et al. BACE1 inhibition more effectively suppresses initiation than progression of beta-amyloid pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 135, 695–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberds, S.L.; Anderson, J.; Basi, G.; Bienkowski, M.J.; Branstetter, D.G.; Chen, K.S.; Freedman, S.B.; Frigon, N.L.; Games, D.; Hu, K.; et al. BACE knockout mice are healthy despite lacking the primary beta-secretase activity in brain: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease therapeutics. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, K.L.C.; Dos Santos Alcantara, M.G.; Freire, N.M.L.; Brandao, E.M.; do Nascimento, V.L.; Dos Santos Viana, L.M.; de Aquino, T.M.; da Silva-Junior, E.F. BACE-1 Inhibitors Targeting Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2023, 20, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imbimbo, B.P.; Watling, M. Investigational BACE inhibitors for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2019, 28, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mycroft-West, C.J.; Devlin, A.J.; Cooper, L.C.; Procter, P.; Miller, G.J.; Fernig, D.G.; Guerrini, M.; Guimond, S.E.; Lima, M.A.; Yates, E.A.; et al. Inhibition of BACE1, the beta-secretase implicated in Alzheimer’s disease, by a chondroitin sulfate extract from Sardina pilchardus. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diling, C.; Tianqiao, Y.; Jian, Y.; Chaoqun, Z.; Ou, S.; Yizhen, X. Docking Studies and Biological Evaluation of a Potential beta-Secretase Inhibitor of 3-Hydroxyhericenone F from Hericium erinaceus. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, J.; Lu, C.; Jiang, N.; Wang, H.; Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, X. Protective effect of ginsenoside Rh2 on scopolamine-induced memory deficits through regulation of cholinergic transmission, oxidative stress and the ERK-CREB-BDNF signaling pathway. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liang, X.; Jin, P.; Li, N.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, W.; Zhang, H.; Sun, J. Screening and determination for potential acetylcholinesterase inhibitory constituents from ginseng stem-leaf saponins using ultrafiltration (UF)-LC-ESI-MS(2). Phytochem. Anal. 2019, 30, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Lin, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Kan, M.; Xiu, Z.; Chen, X.; Lan, X.; Li, X.; Shi, X.; et al. Ginsenoside Compound K Regulates Amyloid beta via the Nrf2/Keap1 Signaling Pathway in Mice with Scopolamine Hydrobromide-Induced Memory Impairments. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 67, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Ginsenoside Type | RT (min) | M/Z (M + Na) | Calculated Mass Errors (ppm) | Area | Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ginsenoside Rg1 | 4.64 | 823.4784 | 3.04 | 85,245,657 | 40.47 ± 1.22 |
| Ginsenoside Re | 4.84 | 969.5361 | 2.78 | 152,532,379 | 82.05 ± 1.11 |
| Pseudo-ginsenoside F11 | 8.88 | 823.4778 | 3.76 | 178,134,984 | 54.54 ± 1.50 |
| Ginsenoside Rb1 | 10.06 | 1131.5886 | −1.06 | 58,056,561 | 730.79 ± 4.20 |
| Ginsenoside Rg2 | 10.73 | 807.4833 | 3.22 | 41,858,831 | 106.53 ± 1.29 |
| Ginsenoside Rb2 | 11.01 | 1101.5778 | 2.90 | 49,691,314 | 22.26 ± 1.16 |
| Ginsenoside Rb3 | 11.13 | 1101.5776 | 3.09 | 60,010,017 | 31.61 ± 1.24 |
| Ginsenoside F1 | 11.55 | 661.4265 | 2.27 | 21,308,120 | 6.79 ± 0.91 |
| Ginsenoside Rd | 11.96 | 969.5357 | 0.41 | 119,144,652 | 75.29 ± 0.16 |
| Noto-ginsenoside Fe | 14.03 | 939.5225 | 6.07 | 91,980,256 | 57.52 ± 2.43 |
| Ginsenoside F2 | 15.54 | 807.4828 | 3.84 | 84,843,618 | 45.81 ± 1.54 |
| Ginsenoside Rg3 | 17.54 | 807.4832 | 3.34 | 76,407,798 | 40.90 ± 1.34 |
| Ginsenoside CK | 22.08 | 645.4313 | 2.79 | 61,108,452 | 13.09 ± 1.12 |
| Ginsenoside Rh2 | 23.80 | 645.4312 | 2.94 | 74,645,154 | 64.44 ± 1.18 |
| Ginsenoside Rk2 | 30.57 | 627.4207 | 3.03 | 15,798,842 | 24.21 ± 1.21 |
| Ginsenoside Type | RT (min) | M/Z (M + Na) | Calculated Mass Errors (ppm) | Area | Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ginsenoside Rg1 | 4.70 | 823.4783 | 3.16 | 27,951,782 | 13.27 ± 1.26 |
| Ginsenoside Re | 4.80 | 969.5358 | 3.09 | 125,128,845 | 67.31 ± 1.24 |
| Pseudo-ginsenoside F11 | 8.87 | 823.4782 | 3.28 | 147,836,511 | 45.27 ± 1.31 |
| Ginsenoside Rh1 | 10.95 | 661.4263 | 2.57 | 18,065,779 | 53.62 ± 1.03 |
| Ginsenoside Rb3 | 11.12 | 1101.5776 | 3.09 | 1,642,635 | 0.87 ± 0.12 |
| Ginsenoside F1 | 11.50 | 661.4262 | 2.72 | 16,295,188 | 5.20 ± 0.11 |
| Ginsenoside Rd | 12.02 | 969.5361 | 0.00 | 15,323,684 | 9.68 ± 1.00 |
| Noto-ginsenoside Fe | 13.47 | 939.5253 | 3.09 | 14,396,025 | 9.00 ± 1.24 |
| Ginsenoside F2 | 15.56 | 807.4832 | 3.34 | 119,537,757 | 64.54 ± 1.34 |
| Ginsenoside Rg3 | 17.59 | 807.4836 | 2.85 | 26,305,526 | 14.08 ± 1.14 |
| Ginsenoside CK | 22.05 | 645.4315 | 2.48 | 404,408,782 | 86.65 ± 0.99 |
| Ginsenoside Rh2 | 23.74 | 645.4315 | 2.48 | 132,476,841 | 114.37 ± 0.99 |
| Ginsenoside Rk2 | 30.53 | 627.4208 | 2.87 | 11,817,115 | 18.11 ± 1.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gao, X.; Yan, P. Biotransformation of American Ginseng Stems and Leaves by an Endophytic Fungus Umbelopsis sp. and Its Effect on Alzheimer’s Disease Control. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234878
Chen Q, Wang J, Gao Y, Wang Z, Gao X, Yan P. Biotransformation of American Ginseng Stems and Leaves by an Endophytic Fungus Umbelopsis sp. and Its Effect on Alzheimer’s Disease Control. Nutrients. 2023; 15(23):4878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234878
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qiqi, Jingying Wang, Yuhang Gao, Zixin Wang, Xiujun Gao, and Peisheng Yan. 2023. "Biotransformation of American Ginseng Stems and Leaves by an Endophytic Fungus Umbelopsis sp. and Its Effect on Alzheimer’s Disease Control" Nutrients 15, no. 23: 4878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234878
APA StyleChen, Q., Wang, J., Gao, Y., Wang, Z., Gao, X., & Yan, P. (2023). Biotransformation of American Ginseng Stems and Leaves by an Endophytic Fungus Umbelopsis sp. and Its Effect on Alzheimer’s Disease Control. Nutrients, 15(23), 4878. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234878








