Agaricus blazei Polysaccharide Alleviates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice by Modulating Intestinal Barrier and Remodeling Metabolism
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animal Experiments
2.3. Disease Activity Index (DAI) Scoring
2.4. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent (ELISA) Assay
2.5. Tissue Section and Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Staining
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. 16S rRNA Sequencing
2.8. Nontargeted Metabolomics Analysis
2.9. Correlation Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. ABP Attenuates DSS-Induced UC in Mice
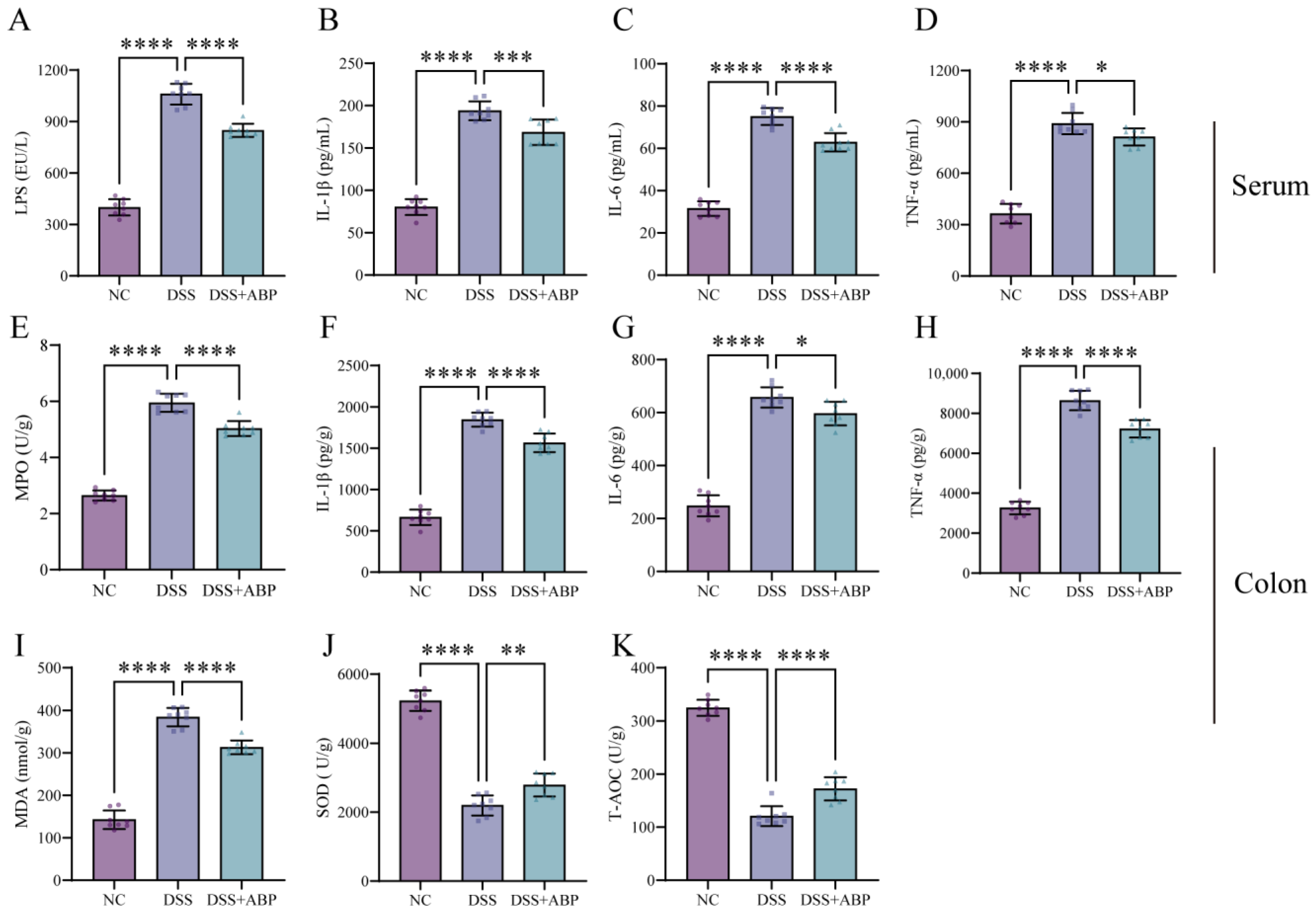
3.2. ABP Reduces Inflammation and Oxidative Damage
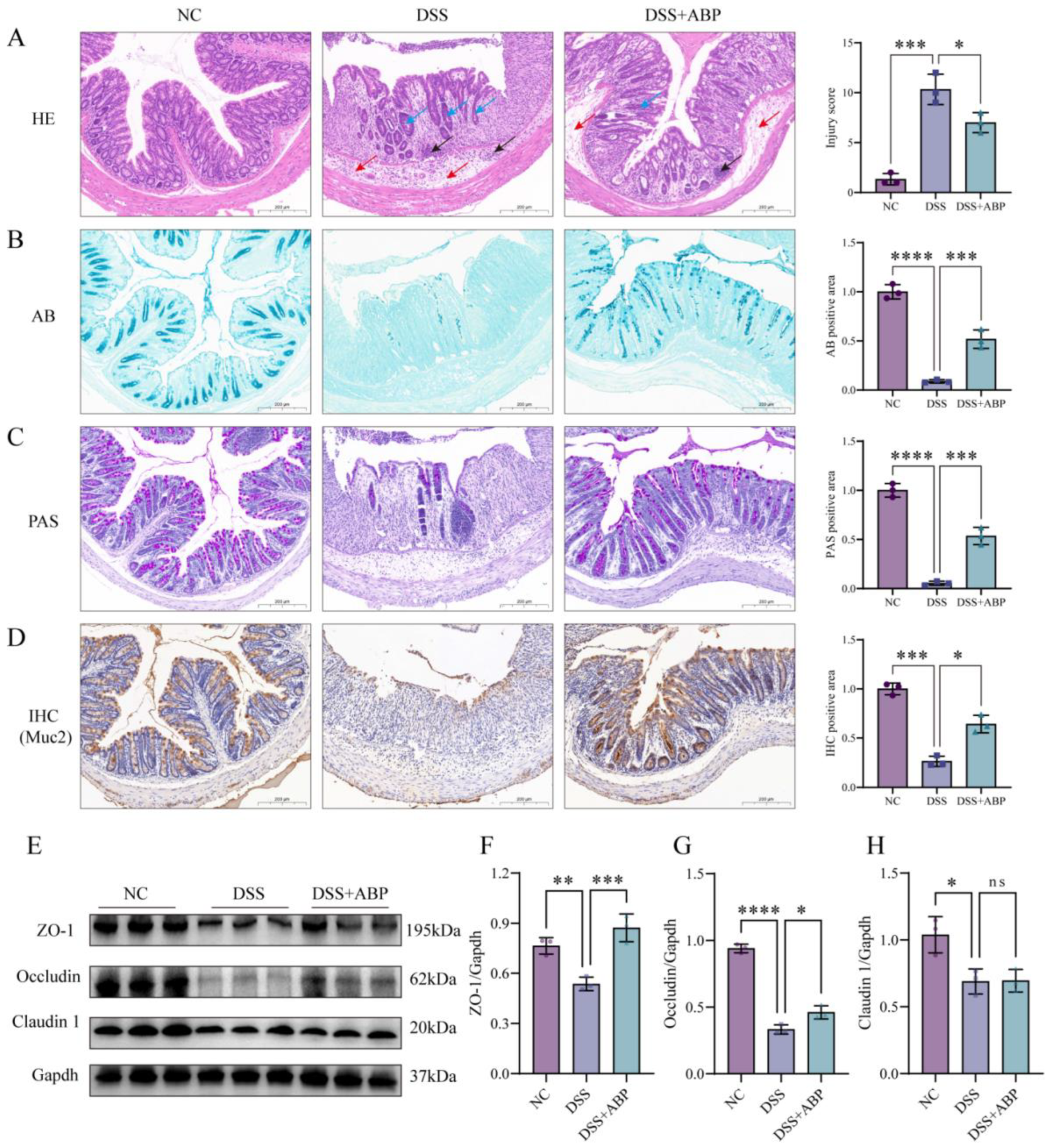
3.3. ABP Enhanced Intestinal Physical and Chemical Barrier Protection
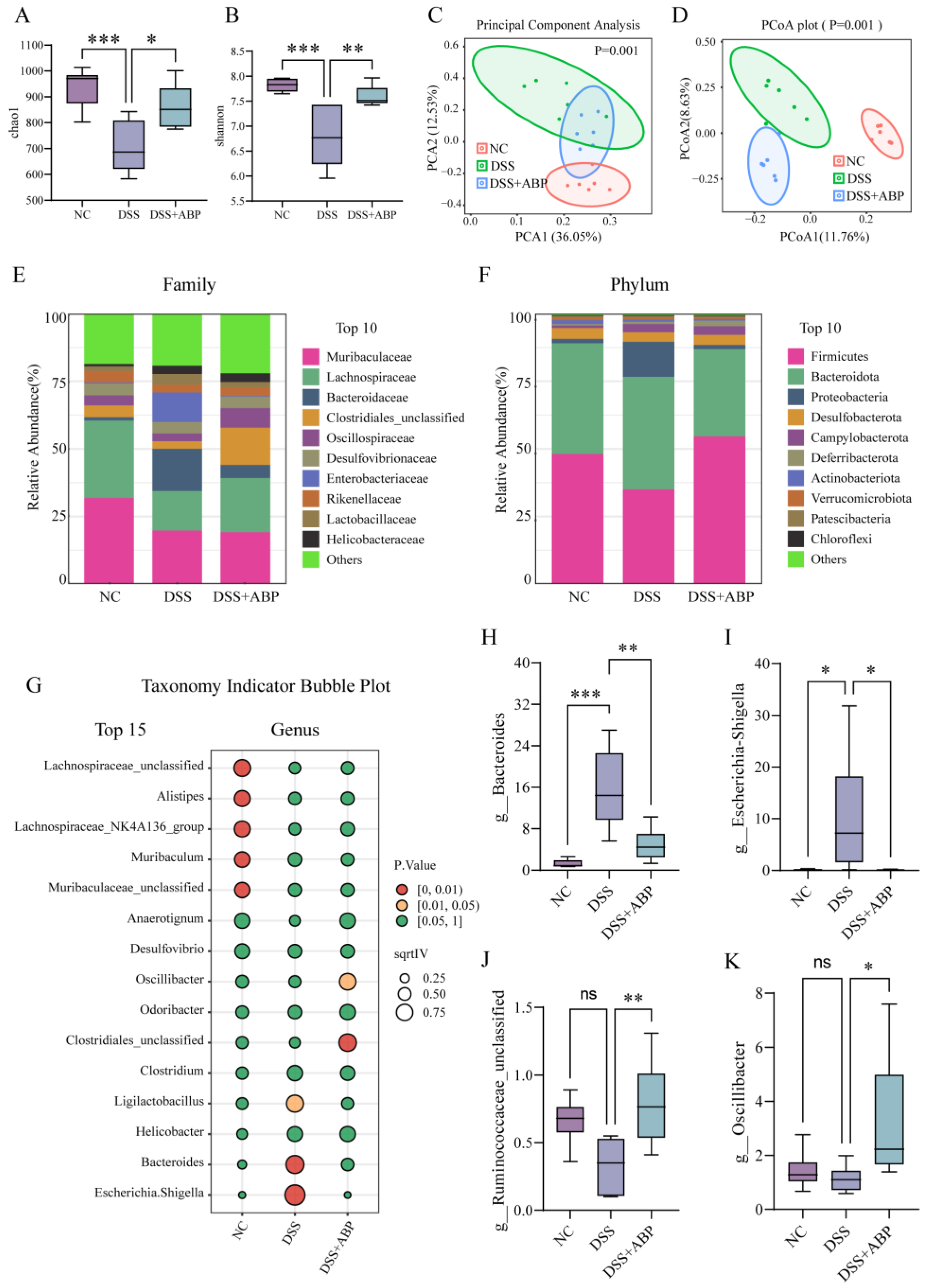
3.4. 16S rRNA Analysis of the Effect of ABP on Gut Microbiota
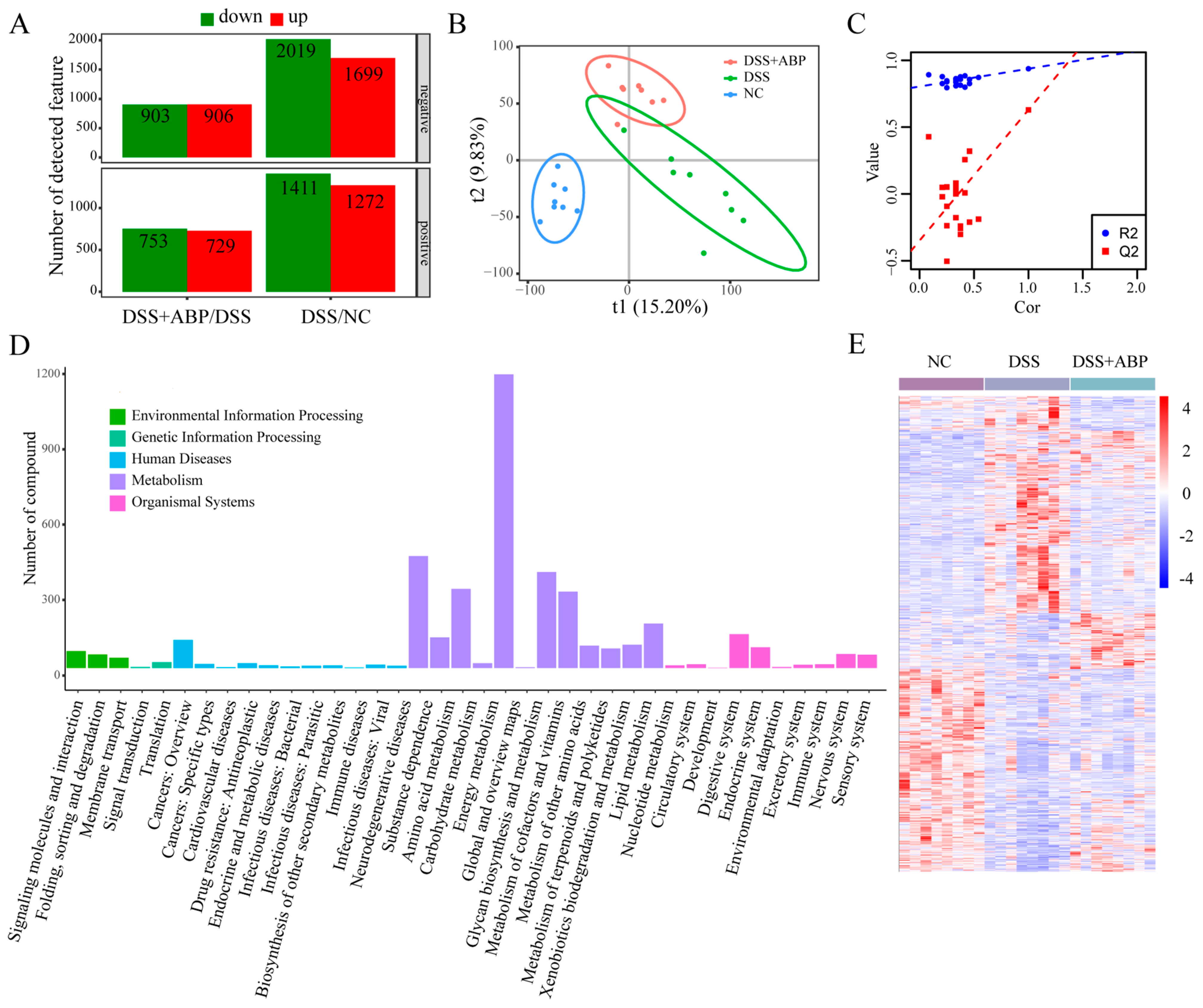
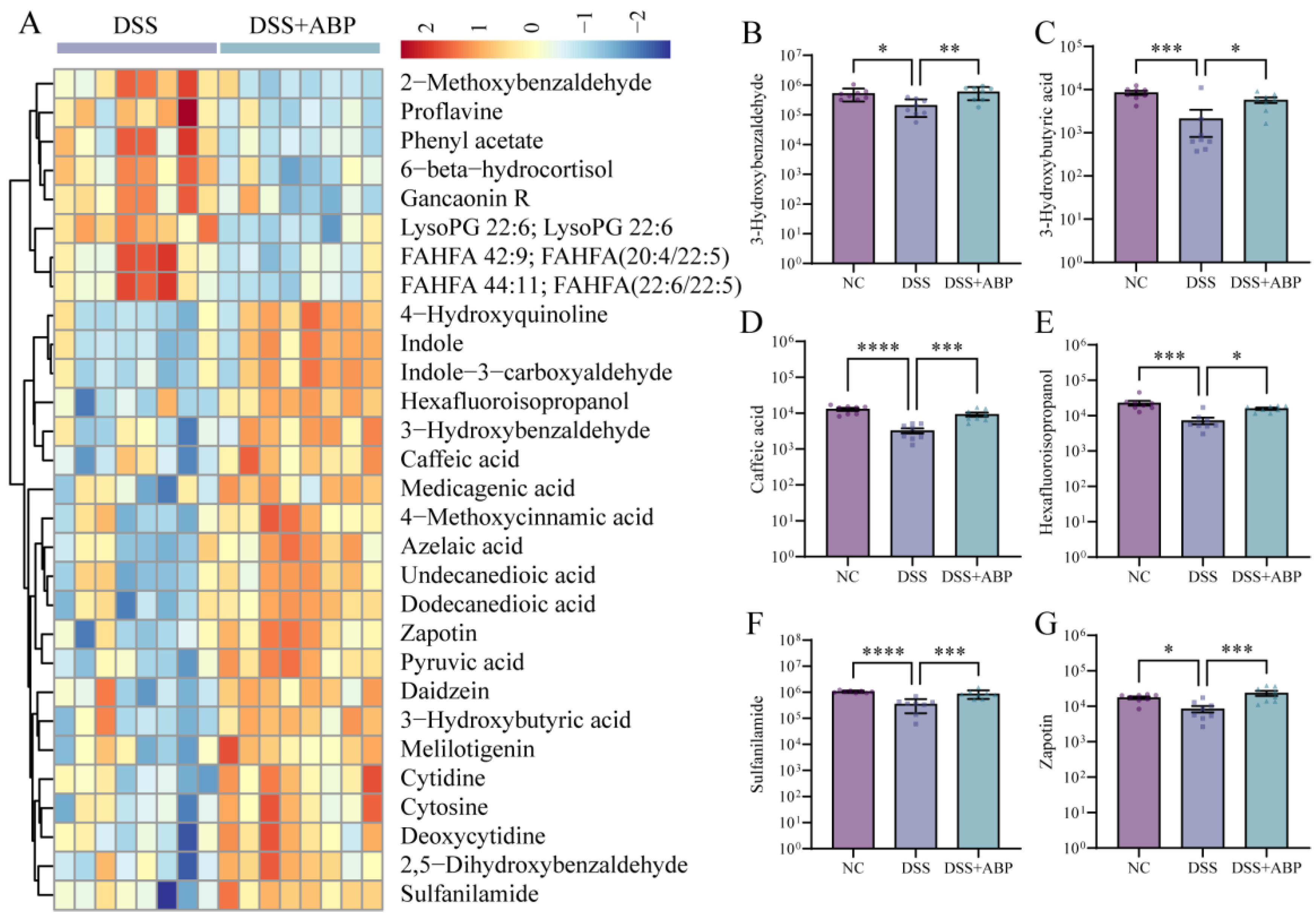
3.5. Untargeted Metabolomics Analysis of the Effects of ABP on Metabolites
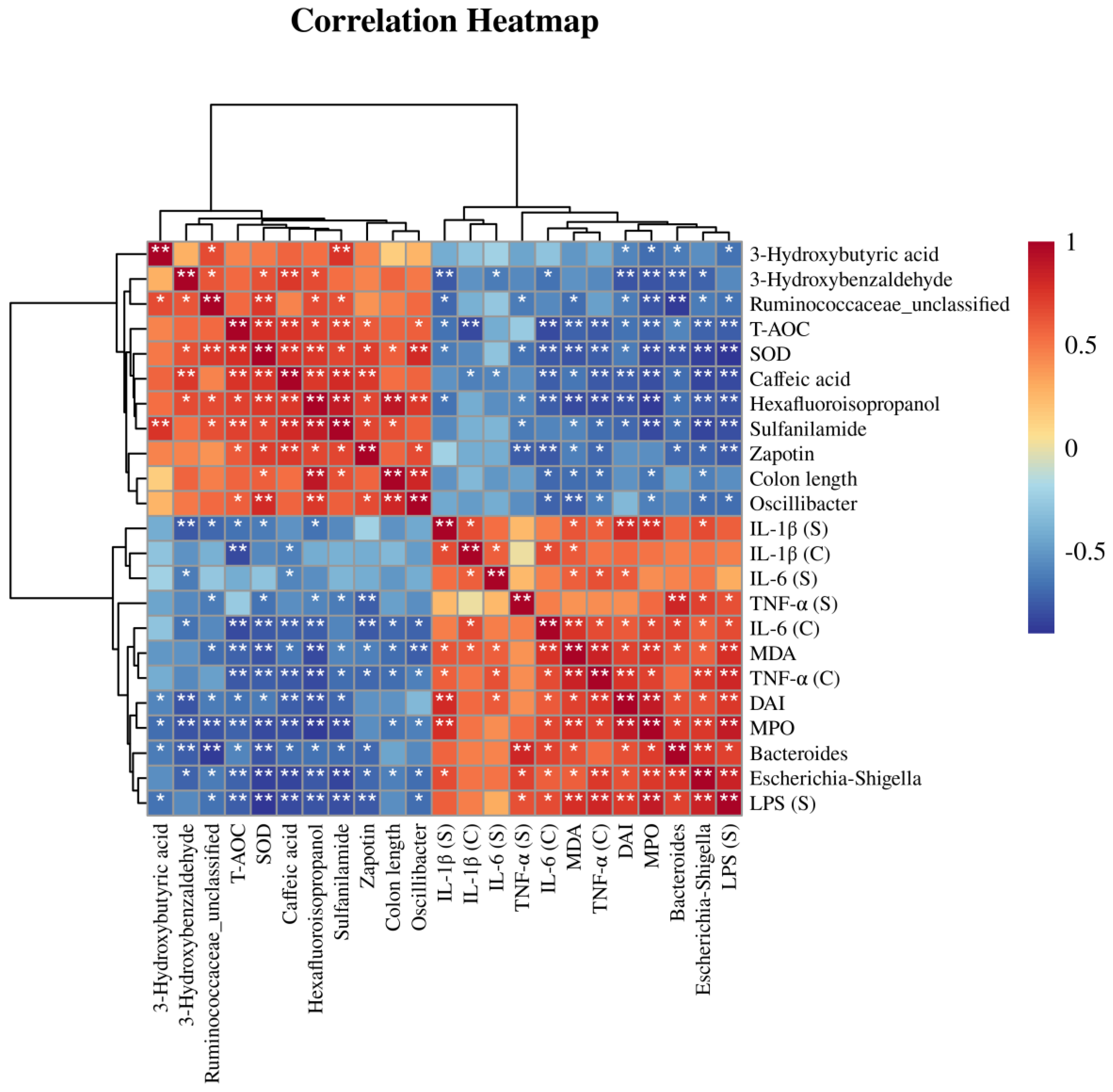
3.6. Correlation Analysis of Differential Bacteria, Differentially Abundant Metabolites, and Physiological and Biochemical Indicators
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bisgaard, T.H.; Allin, K.H.; Keefer, L.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Jess, T. Depression and anxiety in inflammatory bowel disease: Epidemiology, mechanisms and treatment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruner, L.P.; White, A.M.; Proksell, S. Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Prim. Care 2023, 50, 411–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massironi, S.; Viganò, C.; Palermo, A.; Pirola, L.; Mulinacci, G.; Allocca, M.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L.; Danese, S. Inflammation and malnutrition in inflammatory bowel disease. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 8, 579–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Collen, L.V.; Mowat, C.; Isaacs, K.L.; Singh, S.; Kane, S.V.; Farraye, F.A.; Snapper, S.; Jneid, H.; Lavie, C.J.; et al. Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Cardiovascular Diseases. Am. J. Med. 2022, 135, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, X.; Du, H. Inflammatory bowel disease: A potential pathogenic factor of Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 119, 110610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, J.W.Y.; Sun, Y.; Limsrivilai, J.; Abdullah, M.; Kaibullayeva, J.; Balderramo, D.; Vergara, B.I.; Paudel, M.S.; Banerjee, R.; Hilmi, I.; et al. Development of the global inflammatory bowel disease visualization of epidemiology studies in the 21(st) century (GIVES-21). BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2023, 23, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.; Biancone, L.; Fiorino, G.; Katsanos, K.H.; Kopylov, U.; Al Sulais, E.; Axelrad, J.E.; Balendran, K.; Burisch, J.; de Ridder, L.; et al. ECCO Guidelines on Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Malignancies. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2023, 17, 827–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, Q.; Song, H. The Influence of Polysaccharides on Lipid Metabolism: Insights from Gut Microbiota. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, e2300522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Huang, G. Preparation and antioxidant activities of cuaurbit polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Perera, C.; Hemar, Y. Antitumor activity of mushroom polysaccharides: A review. Food Funct. 2012, 3, 1118–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roszczyk, A.; Turło, J.; Zagożdżon, R.; Kaleta, B. Immunomodulatory Properties of Polysaccharides from Lentinula edodes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 2, 8980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Guo, D.; Fang, L.; Sang, T.; Wu, J.; Guo, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.; et al. Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide modulates gut microbiota and immune cell function to inhibit inflammation and tumorigenesis in colon. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 267, 118231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, M.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, S.Q.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.H. Huangshan Floral Mushroom Polysaccharide Ameliorates Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Mice by Modulating Th17/Treg Balance in a Gut Microbiota-Dependent Manner. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, e2200408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Cong, Y. Gut microbiota-derived metabolites in the regulation of host immune responses and immune-related inflammatory diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 866–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yntema, T.; Koonen, D.P.Y.; Kuipers, F. Emerging Roles of Gut Microbial Modulation of Bile Acid Composition in the Etiology of Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wu, Q.; Liu, W.; Hu, G.; Meng, H.; Wang, J. Therapeutic efficacy and underlying mechanisms of Gastrodia elata polysaccharides on dextran sulfate sodium-induced inflammatory bowel disease in mice: Modulation of the gut microbiota and improvement of metabolic disorders. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 248, 125919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Song, J.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Xu, H.; Wu, K.; Gao, J.; Zhao, M.; Zheng, Y. Bergamot polysaccharides relieve DSS-induced ulcerative colitis via regulating the gut microbiota and metabolites. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhang, B.; Yin, J.; Liuqi, S.; Wang, J.; Peng, B.; Wang, S. Fucoidan Ameliorated Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Ulcerative Colitis by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Bile Acid Metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 14864–14876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firenzuoli, F.; Gori, L.; Lombardo, G. The Medicinal Mushroom Agaricus blazei Murrill: Review of Literature and Pharmaco-Toxicological Problems. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. ECAM 2008, 5, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Li, X.; Guo, X.; Sheng, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, G.; Han, X.; An, L.; Du, P. Effects of Agaricus blazei Murrill polysaccharides on hyperlipidemic rats by regulation of intestinal microflora. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 2758–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Campelo, M.; Neto, J.F.C.; Lima, A.B.N.; das Chagas Neto, F.C.; da Costa Gonzaga, M.L.; de Aguiar Soares, S.; Leal, L.; Ribeiro, M.; Ricardo, N. Polysaccharides and extracts from Agaricus brasiliensis Murill—A comprehensive review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 1697–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, M.; Minato, K.; Ito, H.; Kawade, M.; Terai, H.; Tsuchida, H. Anti-tumor polysaccharide from the mycelium of liquid-cultured Agaricus blazei mill. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1999, 47, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Cui, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z. A polysaccharide from Agaricus blazei inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2012, 50, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeli, J.P.; Ribeiro, L.R.; Gonzaga, M.L.; Soares Sde, A.; Ricardo, M.P.; Tsuboy, M.S.; Stidl, R.; Knasmueller, S.; Linhares, R.E.; Mantovani, M.S. Protective effects of beta-glucan extracted from Agaricus brasiliensis against chemically induced DNA damage in human lymphocytes. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2006, 22, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Tian, N.; Wang, H.; Yan, H. Chemically Sulfated Polysaccharides from Agaricus blazei Murill: Synthesis, Characterization and Anti-HIV Activity. Chem. Biodivers. 2021, 18, e2100338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cui, L.; Yao, S.; Lv, L.; Liu, J. Low-molecular-weight polysaccharides from Agaricus blazei Murrill modulate the Th1 response in cancer immunity. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3429–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Huang, M.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Liu, J. Agaricus blazei Murrill Polysaccharide Attenuates Periodontitis via H(2) S/NRF2 Axis-Boosted Appropriate Level of Autophagy in PDLCs. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, e2300112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.M.; Campelo, M.D.S.; Câmara Neto, J.F.; Gonzaga, M.; Bastos, M.; Soares, S.A.; Ricardo, N.; Cerqueira, G.S.; Leitão, R.F.C.; Ribeiro, M. Agaricus blazei Murill polysaccharides/alginate/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend as dressings for wound healing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.W.; Kim, K.H.; Choi, H.J.; Lee, D.S. Anti-diabetic activity of beta-glucans and their enzymatically hydrolyzed oligosaccharides from Agaricus blazei. Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Lu, X.; Guo, X.; Xu, G.; Han, X.; An, L.; Du, P. Isolation and purification of acidic polysaccharides from Agaricus blazei Murill and evaluation of their lipid-lowering mechanism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 157, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, H.; Wen, Y.; Jiang, D.; Zhu, S.; He, X.; Xiong, Q.; Gao, J.; Hou, S.; Huang, S.; et al. Tremella fuciformis polysaccharides ameliorated ulcerative colitis via inhibiting inflammation and enhancing intestinal epithelial barrier function. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 180, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ren, D.; Shao, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, P.; Yang, X. Theabrownin from Fu Brick Tea Improves Ulcerative Colitis by Shaping the Gut Microbiota and Modulating the Tryptophan Metabolism. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 2898–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, B.; Bajaj-Elliott, M.; MacDonald, T.T.; Inglin, R.; Eysselein, V.E.; Büchler, M.W. Characterisation of acute murine dextran sodium sulphate colitis: Cytokine profile and dose dependency. Digestion 2000, 62, 240–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.C.; Yu, H.C.; Martin, R.; Cirulli, E.T.; Schenker-Ahmed, N.M.; Hicks, M.; Cohen, I.V.; Jönsson, T.J.; Heister, R.; Napier, L.; et al. Precision medicine integrating whole-genome sequencing, comprehensive metabolomics, and advanced imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3053–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruchon, S.; Poupot, R. The ABP Dendrimer, a Drug-Candidate against Inflammatory Diseases That Triggers the Activation of Interleukin-10 Producing Immune Cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Sugamori, K.S.; Tung, A.; McPherson, J.P.; Grant, D.M. N-hydroxylation of 4-aminobiphenyl by CYP2E1 produces oxidative stress in a mouse model of chemically induced liver cancer. Toxicol. Sci. Off. J. Soc. Toxicol. 2015, 144, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Han, J.; Liu, L. A polysaccharide from the fruiting bodies of Agaricus blazei Murill induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in human leukemia HL-60 cells. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2014, 35, 8963–8968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimiya, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Oshiman, K.; Kobori, H.; Moriguchi, K.; Nakashima, H.; Matumoto, Y.; Takahara, S.; Ebina, T.; Katakura, R. Selective tumoricidal effect of soluble proteoglucan extracted from the basidiomycete, Agaricus blazei Murill, mediated via natural killer cell activation and apoptosis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. CII 1998, 46, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.C.; Liu, J.C.; Zhao, X.M.; Cao, J. A low molecular weight polysaccharide isolated from Agaricus blazei Murill (LMPAB) exhibits its anti-metastatic effect by down-regulating metalloproteinase-9 and up-regulating Nm23-H1. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2009, 37, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Lv, A.; Li, R.; Tang, Z.; Ma, D.; Huang, X.; Zhang, R.; Ge, M. Agaricus blazei Murill Polysaccharides Protect Against Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Damage in Chicken Spleens. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 184, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, R.; Wang, H.; Yan, Y.; Ming, G. Protective Effect of Agaricus blazei Polysaccharide Against Cadmium-Induced Damage on the Testis of Chicken. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 184, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, W.; Gong, W. Polysaccharide Agaricus blazei Murill stimulates myeloid derived suppressor cell differentiation from M2 to M1 type, which mediates inhibition of tumour immune-evasion via the Toll-like receptor 2 pathway. Immunology 2015, 146, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teshima, C.W.; Dieleman, L.A.; Meddings, J.B. Abnormal intestinal permeability in Crohn’s disease pathogenesis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1258, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, F.; Florian, P.; Bojarski, C.; Richter, J.; Christ, M.; Hillenbrand, B.; Mankertz, J.; Gitter, A.H.; Bürgel, N.; Fromm, M.; et al. Interleukin-13 is the key effector Th2 cytokine in ulcerative colitis that affects epithelial tight junctions, apoptosis, and cell restitution. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 550–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H. Intestinal permeability regulation by tight junction: Implication on inflammatory bowel diseases. Intest. Res. 2015, 13, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Li, Y.; Zhou, B.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, Y. Early-life supplementation of grape polyphenol extract promotes polyphenol absorption and modulates the intestinal microbiota in association with the increase in mRNA expression of the key intestinal barrier genes. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, M.C.; Madsen, K.; Doyle, J.; Meddings, J. Reducing small intestinal permeability attenuates colitis in the IL10 gene-deficient mouse. Gut 2009, 58, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landy, J.; Ronde, E.; English, N.; Clark, S.K.; Hart, A.L.; Knight, S.C.; Ciclitira, P.J.; Al-Hassi, H.O. Tight junctions in inflammatory bowel diseases and inflammatory bowel disease associated colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 3117–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetland, G.; Johnson, E.; Lyberg, T.; Kvalheim, G. The Mushroom Agaricus blazei Murill Elicits Medicinal Effects on Tumor, Infection, Allergy, and Inflammation through Its Modulation of Innate Immunity and Amelioration of Th1/Th2 Imbalance and Inflammation. Adv. Pharmacol. Sci. 2011, 2011, 157015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, M.; Zhang, M.; Sun, W.; Zhang, J.; Jia, L. Agaricus blazei Murill polysaccharides alleviate oxidative stress and inflammatory responses against liver and lung injury. Food Biosci. 2022, 47, 101645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, F.; Zhang, H.; Ye, Y.; Liu, P.; Lin, D.; Zhou, H.; Li, M.; Yang, B. Polysaccharides from Agaricus blazei Murrill ameliorate dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis via attenuating intestinal barrier dysfunction. J. Funct. Food. 2022, 92, 105072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hold, G.L.; Smith, M.; Grange, C.; Watt, E.R.; El-Omar, E.M.; Mukhopadhya, I. Role of the gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease pathogenesis: What have we learnt in the past 10 years? World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 1192–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juste, C.; Kreil, D.P.; Beauvallet, C.; Guillot, A.; Vaca, S.; Carapito, C.; Mondot, S.; Sykacek, P.; Sokol, H.; Blon, F.; et al. Bacterial protein signals are associated with Crohn’s disease. Gut 2014, 63, 1566–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarris, G.; de Rougemont, A.; Charkaoui, M.; Michiels, C.; Martin, L.; Belliot, G. Enteric Viruses and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Viruses 2021, 13, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, E.M.; Ke, X.; Hitchcock, D.; Jeanfavre, S.; Avila-Pacheco, J.; Nakata, T.; Arthur, T.D.; Fornelos, N.; Heim, C.; Franzosa, E.A.; et al. Bacteroides-Derived Sphingolipids Are Critical for Maintaining Intestinal Homeostasis and Symbiosis. Cell Host Microbe 2019, 25, 668–680.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Lee, Y.K.; Zhai, Q.; Chen, W. Roles of intestinal bacteroides in human health and diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3518–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, M.; Li, Z.; You, H.; Rodrigues, R.; Jump, D.B.; Morgun, A.; Shulzhenko, N. Role of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes pathophysiology. EBioMedicine 2020, 51, 102590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, N.; Yamashita, T.; Osone, T.; Hosooka, T.; Shinohara, M.; Kitahama, S.; Sasaki, K.; Sasaki, D.; Yoneshiro, T.; Suzuki, T.; et al. Bacteroides spp. promotes branched-chain amino acid catabolism in brown fat and inhibits obesity. iScience 2021, 24, 103342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Garrido, J.; Ruano-Gallego, D.; Choudhary, J.S.; Frankel, G. The type III secretion system effector network hypothesis. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.Q.; Quiñones, B.; Laniohan, N.; Carychao, D.; Pham, A.; He, X.; Cooley, M. Pathogenicity assessment of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains isolated from wild birds in a major agricultural region in California. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1214081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.; The, H.C. Recent insights into Shigella. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2018, 31, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, Y.Y.; Ha, C.W.; Hoffmann, J.M.; Oscarsson, J.; Dinudom, A.; Mather, T.J.; Cook, D.I.; Hunt, N.H.; Caterson, I.D.; Holmes, A.J.; et al. Effects of dietary fat profile on gut permeability and microbiota and their relationships with metabolic changes in mice. Obesity 2015, 23, 1429–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, J.K.; Seo, S.H.; Park, S.E.; Kim, H.W.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, J.S.; Pyo, J.Y.; Cho, K.M.; Kwon, S.J.; Park, D.H.; et al. Gut Microbiome and Metabolome Profiles Associated with High-Fat Diet in Mice. Metabolites 2021, 11, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Jiang, A.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, W.; Ren, C.; Qian, X.; Zhou, Z.; Gong, A. NMN Maintains Intestinal Homeostasis by Regulating the Gut Microbiota. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 714604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xiong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; Zhang, B. Genetically proxied intestinal microbiota and risk of erectile dysfunction. Andrology 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirmer, M.; Garner, A.; Vlamakis, H.; Xavier, R.J. Microbial genes and pathways in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 497–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, X.; Sun, L.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, W. Role of the Gut Microbiota and Its Metabolites in Tumorigenesis or Development of Colorectal Cancer. Adv. Sci. (Weinh. Baden-Wurtt. Ger.) 2023, 10, e2205563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rooks, M.G.; Garrett, W.S. Gut microbiota, metabolites and host immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieërs, G.; Belkhir, L.; Enaud, R.; Leclercq, S.; Philippart de Foy, J.M.; Dequenne, I.; de Timary, P.; Cani, P.D. How Probiotics Affect the Microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Luo, A.; Lu, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, H.; Song, H.; Wei, C.; Wang, Y.; Duan, X. p-Hydroxybenzoic acid alleviates inflammatory responses and intestinal mucosal damage in DSS-induced colitis by activating ERβ signaling. J. Funct. Food. 2021, 87, 104835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Mishima, M.; Nagane, M.; Mizugaki, H.; Suzuki, T.; Komuro, M.; Shimizu, T.; Fukuyama, T.; Takeda, S.; Ogata, M.; et al. The novel sustained 3-hydroxybutyrate donor poly-D-3-hydroxybutyric acid prevents inflammatory bowel disease through upregulation of regulatory T-cells. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e22708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, T.; Xue, J.; He, W.; Luo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Bai, X.; Wang, Q.; et al. FA-97, a New Synthetic Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester Derivative, Ameliorates DSS-Induced Colitis Against Oxidative Stress by Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strawa, J.W.; Jakimiuk, K.; Tomczyk, M. Zapotin, a Polymethoxyflavone, with Potential Therapeutic Attributes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, Z.-H.; He, S.; Xie, W.-Y.; Zhao, P.-S.; Ren, W.-Z.; Gao, W.; Yuan, B. Agaricus blazei Polysaccharide Alleviates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice by Modulating Intestinal Barrier and Remodeling Metabolism. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4877. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234877
Ji Z-H, He S, Xie W-Y, Zhao P-S, Ren W-Z, Gao W, Yuan B. Agaricus blazei Polysaccharide Alleviates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice by Modulating Intestinal Barrier and Remodeling Metabolism. Nutrients. 2023; 15(23):4877. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234877
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Zhong-Hao, Song He, Wen-Yin Xie, Pei-Sen Zhao, Wen-Zhi Ren, Wei Gao, and Bao Yuan. 2023. "Agaricus blazei Polysaccharide Alleviates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice by Modulating Intestinal Barrier and Remodeling Metabolism" Nutrients 15, no. 23: 4877. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234877
APA StyleJi, Z.-H., He, S., Xie, W.-Y., Zhao, P.-S., Ren, W.-Z., Gao, W., & Yuan, B. (2023). Agaricus blazei Polysaccharide Alleviates DSS-Induced Colitis in Mice by Modulating Intestinal Barrier and Remodeling Metabolism. Nutrients, 15(23), 4877. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15234877





