The Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Plant Sterols on Total and LDL-Cholesterol in Plasma Is Affected by Adherence to Mediterranean Diet: Insights from the DESCO Randomized Clinical Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
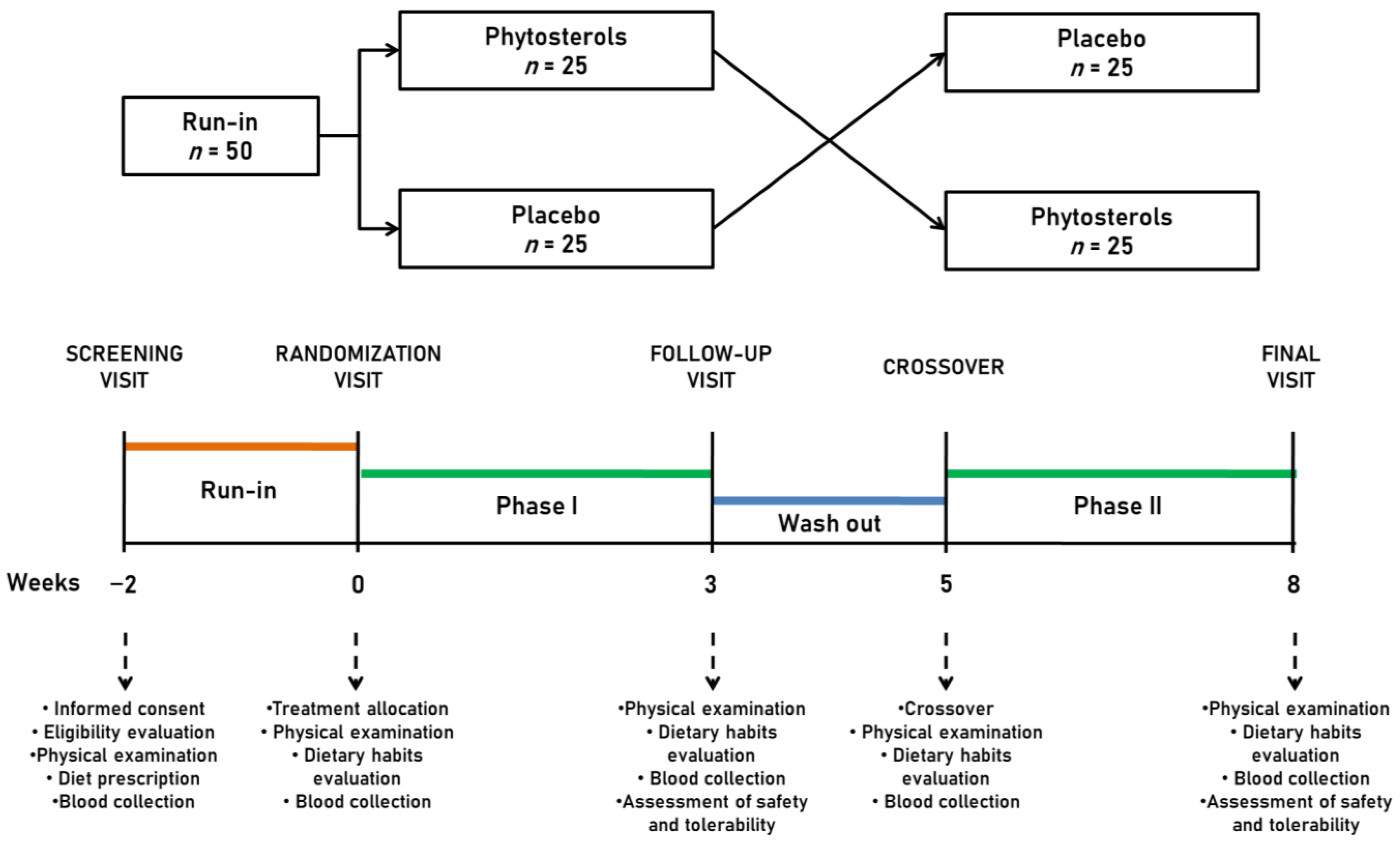
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Treatment
2.3. Assessments
2.3.1. Clinical Data and Anthropometric Measurements
2.3.2. Laboratory Analyses
2.3.3. Blood Pressure Measurements
2.3.4. Assessment of Safety and Tolerability
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Efficacy Analysis
3.2. Safety Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980-2017: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1736–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2019 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global burden of 87 risk factors in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1223–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Goff, D.; Aerts, N.; Odorico, M.; Guillou-Landreat, M.; Perraud, G.; Bastiaens, H.; Musinguzi, G.; Le Reste, J.Y.; Barais, M. Practical dietary interventions to prevent cardiovascular disease suitable for implementation in primary care: An ADAPTE-guided systematic review of international clinical guidelines. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2023, 20, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finicelli, M.; Di Salle, A.; Galderisi, U.; Peluso, G. The Mediterranean Diet: An Update of the Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Fogacci, F.; Borghi, C. An Evolving Definition of a “Healthy Diet”. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durai, V.; Redberg, R.F. Statin therapy for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease: Cons. Atherosclerosis 2022, 356, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turini, E.; Sarsale, M.; Petri, D.; Totaro, M.; Lucenteforte, E.; Tavoschi, L.; Baggiani, A. Efficacy of Plant Sterol-Enriched Food for Primary Prevention and Treatment of Hypercholesterolemia: A Systematic Literature Review. Foods 2022, 11, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission Regulation (EU) No. 1924/2006. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32006R1924&from=en (accessed on 1 October 2023).
- Authors/Task Force Members; ESC Committee for Practice Guidelines (CPG); ESC National Cardiac Societies. 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Atherosclerosis 2019, 290, 140–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gylling, H.; Plat, J.; Turley, S.; Ginsberg, H.N.; Ellegård, L.; Jessup, W.; Jones, P.J.; Lütjohann, D.; Maerz, W.; Masana, L.; et al. Plant sterols and plant stanols in the management of dyslipidaemia and prevention of cardiovascular disease. Atherosclerosis 2014, 232, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyriax, B.C.; Borof, K.; Walter, S.; Augustin, M.; Windler, E. Knowledge as to cholesterol reduction and use of phytosterol-enriched dietary foods in the general population: Insights from the Hamburg City Health Study. Atherosclerosis 2022, 341, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, K.; Gylling, H. Dose-dependent LDL-cholesterol lowering effect by plant stanol ester consumption: Clinical evidence. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowska, A.M.; Waśkiewicz, A.; Zujko, M.E.; Cicha-Mikołajczyk, A.; Mirończuk-Chodakowska, I.; Drygas, W. Dietary Plant Sterols and Phytosterol-Enriched Margarines and Their Relationship with Cardiovascular Disease among Polish Men and Women: The WOBASZ II Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doundoulakis, I.; Farmakis, I.T.; Theodoridis, X.; Konstantelos, A.; Christoglou, M.; Kotzakioulafi, E.; Chrysoula, L.; Siargkas, A.; Karligkiotis, A.; Kyprianou, G.; et al. Effects of dietary interventions on cardiovascular outcomes: A network meta-analysis. Nutr. Rev. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.heartscore.org/en_GB/ (accessed on 30 January 2023).
- Yanai, H.; Yoshida, H. Secondary dyslipidemia: Its treatments and association with atherosclerosis. Glob. Health Med. 2021, 3, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogacci, F.; Rizzoli, E.; Giovannini, M.; Bove, M.; D’Addato, S.; Borghi, C.; Cicero, A.F.G. Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Eufortyn® Colesterolo Plus on Serum Lipids, Endothelial Reactivity, Indexes of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Systemic Inflammation in Healthy Subjects with Polygenic Hypercholesterolemia: The ANEMONE Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnagnarella, P.; Dragà, D.; Misotti, A.M.; Sieri, S.; Spaggiari, L.; Cassano, E.; Baldini, F.; Soldati, L.; Maisonneuve, P. Validation of a short questionnaire to record adherence to the Mediterranean diet: An Italian experience. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bach-Faig, A.; Berry, E.M.; Lairon, D.; Reguant, J.; Trichopoulou, A.; Dernini, S.; Medina, F.X.; Battino, M.; Belahsen, R.; Miranda, G.; et al. Mediterranean diet pyramid today. Science and cultural updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, R.M.; Joshi, S.R.; Menon, P.S.; Shah, N.S. Index of central obesity—A novel parameter. Med. Hypotheses 2007, 68, 1272–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Fogacci, F.; Bove, M.; Giovannini, M.; Borghi, C. Impact of a short-term synbiotic supplementation on metabolic syndrome and systemic inflammation in elderly patients: A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedogni, G.; Kahn, H.S.; Bellentani, S.; Tiribelli, C. A simple index of lipid overaccumulation is a good marker of liver steatosis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2010, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amato, M.C.; Giordano, C.; Galia, M.; Criscimanna, A.; Vitabile, S.; Midiri, M.; Galluzzo, A.; AlkaMeSy Study Group. Visceral Adiposity Index: A reliable indicator of visceral fat function associated with cardiometabolic risk. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 920–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.; Mancia, G.; Spiering, W.; Agabiti Rosei, E.; Azizi, M.; Burnier, M.; Clement, D.L.; Coca, A.; de Simone, G.; Dominiczak, A.; et al. Authors/Task Force Members. 2018 ESC/ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2018, 36, 1953–2041. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Fogacci, F.; Veronesi, M.; Strocchi, E.; Grandi, E.; Rizzoli, E.; Poli, A.; Marangoni, F.; Borghi, C. A randomized Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Medium-Term Effects of Oat Fibers on Human Health: The Beta-Glucan Effects on Lipid Profile, Glycemia and inTestinal Health (BELT) Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Colletti, A.; Bajraktari, G.; Descamps, O.; Djuric, D.M.; Ezhov, M.; Fras, Z.; Katsiki, N.; Langlois, M.; Latkovskis, G.; et al. Lipid-lowering nutraceuticals in clinical practice: Position paper from an International Lipid Expert Panel. Nutr. Rev. 2017, 75, 731–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Fogacci, F.; Rosticci, M.; Parini, A.; Giovannini, M.; Veronesi, M.; D’Addato, S.; Borghi, C. Effect of a short-term dietary supplementation with phytosterols, red yeast rice or both on lipid pattern in moderately hypercholesterolemic subjects: A three-arm, double-blind, randomized clinical trial. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 14, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Fogacci, F.; Stoian, A.P.; Vrablik, M.; Al Rasadi, K.; Banach, M.; Toth, P.P.; Rizzo, M. Nutraceuticals in the Management of Dyslipidemia: Which, When, and for Whom? Could Nutraceuticals Help Low-Risk Individuals with Non-optimal Lipid Levels? Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2021, 23, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicero, A.F.G.; Morbini, M.; Bove, M.; D’Addato, S.; Fogacci, F.; Rosticci, M.; Borghi, C. Additional therapy for cholesterol lowering in ezetimibe-treated, statin-intolerant patients in clinical practice: Results from an internal audit of a university lipid clinic. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2016, 32, 1633–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedó, L.; Farràs, M.; Lee-Rueckert, M.; Escolà-Gil, J.C. Molecular Insights into the Mechanisms Underlying the Cholesterol- Lowering Effects of Phytosterols. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 6704–6723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, E.; Kord-Varkaneh, H.; Mohammadi, H.; Askarpour, M.; Miraghajani, M. Phytosterol Supplementation Could Improve Atherogenic and Anti-Atherogenic Apolipoproteins: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2020, 39, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruuth, M.; Äikäs, L.; Tigistu-Sahle, F.; Käkelä, R.; Lindholm, H.; Simonen, P.; Kovanen, P.T.; Gylling, H.; Öörni, K. Plant Stanol Esters Reduce LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein) Aggregation by Altering LDL Surface Lipids: The BLOOD FLOW Randomized Intervention Study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 2310–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira Godoy Ilha, A.; Sutti Nunes, V.; Silva Afonso, M.; Regina Nakandakare, E.; da Silva Ferreira, G.; de Paula Assis Bombo, R.; Rodrigues Giorgi, R.; Marcondes Machado, R.; Carlos Rocha Quintão, E.; Lottenberg, A.M. Phytosterols Supplementation Reduces Endothelin-1 Plasma Concentration in Moderately Hypercholesterolemic Individuals Independently of Their Cholesterol-Lowering Properties. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, M.; Jayaraman, S.; Eladl, M.A.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Abdelrahman, M.A.E.; Veeraraghavan, V.P.; Vengadassalapathy, S.; Umapathy, V.R.; Jaffer Hussain, S.F.; Krishnamoorthy, K.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on Therapeutic Perspectives of Phytosterols in Insulin Resistance: A Mechanistic Approach. Molecules 2022, 27, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasinariu, O.; Serban, R.; Trandafir, L.M.; Miron, I.; Starcea, M.; Vasiliu, I.; Alisi, A.; Temneanu, O.R. The Role of Phytosterols in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trautwein, E.A.; McKay, S. The Role of Specific Components of a Plant-Based Diet in Management of Dyslipidemia and the Impact on Cardiovascular Risk. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontané, L.; Pedro-Botet, J.; Garcia-Ribera, S.; Climent, E.; Muns, M.D.; Ballesta, S.; Satorra, P.; Flores-Le Roux, J.A.; Benaiges, D. Use of phytosterol-fortified foods to improve LDL cholesterol levels: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2023, 33, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lôbo, I.M.B.; Bordallo, C.O.S.; Sacramento, J.M.; Leite, L.O.; Santana, P.D.S. Phytosterol supplementation in capsules or tablets as adjunctive treatment for hypercholesterolemia: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2023, 57, 718–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, R.V.; Patti, A.M.; Cicero, A.F.G.; Lippi, G.; Rizzo, M.; Toth, P.P.; Banach, M. Polyphenols: Potential Use in the Prevention and Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 239–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ma, X.; Le Sayec, M.; Wu, H.; Dazzan, P.; Nosarti, C.; Heiss, C.; Gibson, R.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A. (Poly)phenol intake, plant-rich dietary patterns and cardiometabolic health: A cross-sectional study. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 4078–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajeri, M.; Cicero, A.F. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Association with Serum Levels of Nitric Oxide, Prostacyclin, and Thromboxane B2 among Prinzmetal Angina Patients and Healthy Persons. Nutrients 2023, 15, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karam, G.; Agarwal, A.; Sadeghirad, B.; Jalink, M.; Hitchcock, C.L.; Ge, L.; Kiflen, R.; Ahmed, W.; Zea, A.M.; Milenkovic, J.; et al. Comparison of seven popular structured dietary programmes and risk of mortality and major cardiovascular events in patients at increased cardiovascular risk: Systematic review and network meta-analysis. BMJ 2023, 380, e072003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ference, B.A.; Yoo, W.; Alesh, I.; Mahajan, N.; Mirowska, K.K.; Mewada, A.; Kahn, J.; Afonso, L.; Williams, K.A., Sr.; Flack, J.M. Effect of long-term exposure to lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol beginning early in life on the risk of coronary heart disease: A Mendelian randomization analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 2631–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibney, E.R.; Milenkovic, D.; Combet, E.; Ruskovska, T.; Greyling, A.; González-Sarrías, A.; de Roos, B.; Tomás-Barberán, F.; Morand, C.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A. Factors influencing the cardiometabolic response to (poly)phenols and phytosterols: A review of the COST Action POSITIVe activities. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58 (Suppl. 2), 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Ingredients | Quantity per Stick (15 mL) |
|---|---|
| Active Ingredients | |
| Non-GMO Natural Mixed Phytosterols | 2.50 g |
| Vitamin B1 (Thiamine hydrochloride) | 0.42 mg |
| Vitamin B1 content | 0.33 mg |
| Main excipients | |
| Fructose | 1.5 g |
| Natural flavors | 0.066 g |
| Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose | 0.00375 g |
| Demineralized water | e.q. to 15 mL |
| Parameters | Pre-Run-in | Post-Run-in |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 51.5 ± 13.7 | 51.6 ± 13.6 |
| Weight (kg) | 65.4 ± 10.5 | 65.2 ± 10.1 |
| Height (m) | 1.65 ± 0.08 | 1.65 ± 0.08 |
| Waist Circumference (cm) | 86.3 ± 11.6 | 86.0 ± 11.4 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 23.8 ± 3.2 | 23.7 ± 3.1 |
| Index of Central Obesity | 0.52 ± 0.06 | 0.52 ± 0.06 |
| Lipid Accumulation Product | 39.1 ± 39.5 | 39.2 ± 32.0 |
| Visceral Adiposity Index | 3.40 ± 2.44 | 3.58 ± 2.19 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 129.3 ± 9.7 | 128.9 ± 12.7 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 71.4 ± 7.0 | 71.3 ± 7.7 |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 240.9 ± 22.8 | 237.1 ± 22.8 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 126.4 ± 87.0 | 124.6 ± 69.1 |
| HDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 63.2 ± 15.3 | 63.6 ± 14.8 |
| LDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 151.1 ± 20.8 | 148.6 ± 21.5 |
| Non-HDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 177.7 ± 26.5 | 173.5 ± 25.3 |
| VLDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 25.3 ± 17.4 | 23.1 ± 10.2 |
| Apolipoprotein B-100 (mg/dL) | 122.9 ± 18.0 | 119.8 ± 17.0 |
| Parameters | Placebo (n. 50) | Phytosterols (n. 49) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Week 3 | Baseline | Week 3 | |
| Weight (Kg) | 64.9 ± 10.2 | 64.8 ± 10.2 | 65 ± 10.1 | 64.6 ± 10 |
| Body Mass Index (Kg/m2) | 23.7 ± 3.1 | 23.6 ± 3 | 23.7 ± 3 | 23.6 ± 3 |
| Waist Circumference (cm) | 86 ± 11.6 | 85.8 ± 11.6 | 85.8 ± 11.3 | 85.7 ± 11.3 |
| Index of Central Obesity | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 0.5 ± 0.1 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 129.8 ± 12.8 | 130.1 ± 11.9 | 127.6 ± 15.2 | 128 ± 10.6 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 72.1 ± 8.8 | 70.7 ± 8.2 | 70.4 ± 7.4 | 69.2 ± 9.7 |
| Lipid Accumulation Product | 38.6 ± 26.9 | 36.5 ± 25.8 | 37.3 ± 26.7 | 37.1 ± 29.3 |
| Visceral Adiposity Index | 3.6 ± 1.9 | 3.5 ± 2 | 3.6 ± 2.3 | 3.4 ± 2.2 |
| aMED score | 6.0 ± 0.9 | 6.2 ± 1.1 | 6.1 ± 0.8 | 6.4 ± 1.2 |
| Parameters | Placebo (n. 50) | Phytosterols (n. 49) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Week 3 | Mean Change from Baseline | Baseline | Week 3 | Mean Change from Baseline | |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 236.1 ± 23.5 | 233.9 ± 21 | −2.2 ± 4.0 | 234.4 ± 22.2 | 224.6 ± 24.6 * | −11.8 ± 4.0 § |
| LDL-C (mg/dL) | 146.9 ± 22.2 | 146.6 ± 21.1 | −0.3 ± 5.5 | 146.4 ± 21.3 | 138.6 ± 23.2 * | −7.8 ± 7.7 § |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 63.9 ± 14.6 | 63.4 ± 14 | −0.4 ± 3.3 | 63.7 ± 14.7 | 61.7 ± 13 | −2.1 ± 3.4 |
| Non-HDL-C (mg/dL) | 172.2 ± 26.5 | 170.3 ± 25.3 | −1.8 ± 5.5 | 170.7 ± 22.4 | 166.2 ± 25.3 | −4.5 ± 5.2 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 126.1 ± 60.1 | 119.5 ± 56 | −4.6 ± 8.4 | 121.3 ± 58 | 121.6 ± 68 | 0.3 ± 8.7 |
| VLDL-C (mg/dL) | 25.2 ± 12 | 23.9 ± 11.2 | −1.3 ± 2.3 | 23.9 ± 11.5 | 24.1 ± 13.8 | 0.2 ± 2.6 |
| Apolipoprotein B-100 (mg/dL) | 118.6 ± 17 | 117.2 ± 7.2 | −0.1 ± 4.4 | 118.0 ± 15.9 | 114.3 ± 16.8 * | −3.7 ± 4.1 |
| Model | Predictors | Non Standardized Coefficient | Standardized Coefficient | t | p | 95% Confidence Interval | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | Standard Error | Beta | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | ||||
| 1 | Active treatment | 2.149 | 0.124 | 0.801 | 7.221 | 0.008 | 1.324 | 2.576 |
| 2 | Active treatment | 2.177 | 0.121 | 0.828 | 7.326 | 0.009 | 1.346 | 2.619 |
| Pre-treatment LDL-C | 1.301 | 0.071 | 0.377 | 4.123 | 0.002 | 1.151 | 1.426 | |
| 3 | Active treatment | 2.201 | 0.128 | 0.854 | 7.422 | 0.011 | 1.354 | 2.744 |
| Pre-treatment LDL-C | 1.397 | 0.088 | 0.519 | 4.466 | 0.005 | 1.223 | 1.568 | |
| aMED score | 1.221 | 0.101 | 0.238 | 2.911 | 0.039 | 1.015 | 1.481 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cicero, A.F.G.; Fogacci, F.; Giovannini, M.; Rizzoli, E.; Grandi, E.; D’Addato, S.; Borghi, C. The Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Plant Sterols on Total and LDL-Cholesterol in Plasma Is Affected by Adherence to Mediterranean Diet: Insights from the DESCO Randomized Clinical Study. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4555. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214555
Cicero AFG, Fogacci F, Giovannini M, Rizzoli E, Grandi E, D’Addato S, Borghi C. The Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Plant Sterols on Total and LDL-Cholesterol in Plasma Is Affected by Adherence to Mediterranean Diet: Insights from the DESCO Randomized Clinical Study. Nutrients. 2023; 15(21):4555. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214555
Chicago/Turabian StyleCicero, Arrigo F. G., Federica Fogacci, Marina Giovannini, Elisabetta Rizzoli, Elisa Grandi, Sergio D’Addato, and Claudio Borghi. 2023. "The Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Plant Sterols on Total and LDL-Cholesterol in Plasma Is Affected by Adherence to Mediterranean Diet: Insights from the DESCO Randomized Clinical Study" Nutrients 15, no. 21: 4555. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214555
APA StyleCicero, A. F. G., Fogacci, F., Giovannini, M., Rizzoli, E., Grandi, E., D’Addato, S., & Borghi, C. (2023). The Effect of Dietary Supplementation with Plant Sterols on Total and LDL-Cholesterol in Plasma Is Affected by Adherence to Mediterranean Diet: Insights from the DESCO Randomized Clinical Study. Nutrients, 15(21), 4555. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15214555








