The Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa among Greek Professional Dancers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedures
2.2. Sociodemographic, Medical, and Anthropometric Characteristics
2.2.1. Dietary Habits in Relation to Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet
2.2.2. Orthorexia
2.2.3. BIAAQ
2.2.4. Parental Bonding Instrument
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Risk of Orthorexia Nervosa
3.2. Association between Orthorexia Nervosa, Body Image Inflexibility, and Parental Bonding Profiles
3.3. Association between Parental Body Image Inflexibility and Parental Bonding Profiles
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bratman, S. Health Food Junkie. Yoga J. 1997, 136, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Cheshire, A.; Berry, M.; Fixsen, A. What Are the Key Features of Orthorexia Nervosa and Influences on Its Development? A Qualitative Investigation. Appetite 2020, 155, 104798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonidakis, F.; Poulopoulou, C.; Michopoulos, I.; Varsou, E. Validation of the Greek ORTO-15 Questionnaire for the Assessment of Orthorexia Nervosa and Its Relation to Eating Disorders Symptomatology. Eat. Weight Disord. 2021, 26, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratman, S. Orthorexia vs. Theories of Healthy Eating. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2017, 22, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambwani, S.; Shippe, M.; Gao, Z.; Austin, B. Is #cleaneating a Healthy or Harmful Dietary Strategy? Perceptions of Clean Eating and Associations with Disordered Eating among Young Adults. J. Eat. Disord. 2019, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cena, H.; Bathels, F.; Cuzzolaro, M.; Bratman, S.; Brytek-Matera, A.; Dunn, T.; Varga, M.; Missbach, B.; Donini, L.M. Definition and Diagnostic Criteria for Orthorexia Nervosa: A Narrative Review of the Literature. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2019, 24, 209–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, T.M.; Bratman, S. On Orthorexia Nervosa: A Review of the Literature and Proposed Diagnostic Criteria. Eat. Behav. 2016, 21, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroze, R.M.; Dunn, T.M.; Holland, J.C.; Yager, J.; Weintraub, P. Microthinking About Micronutrients: A Case of Transition From Obsessions About Healthy Eating to Near-Fatal “Orthorexia Nervosa” and Proposed Diagnostic Criteria. Psychosomatics 2015, 56, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaccari, G.; Cutino, A.; Luisi, F.; Giambalvo, N.; Daneshmand, S.; Pinelli, M.; Maina, G.; Galeazzi, G.; Kaleci, S.; Albert, U.; et al. Is Orthorexia Nervosa a Feature of Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder? A Multicentric, Controlled Study. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2021, 26, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobera, J.; Ríos, B.; Casals, G. Parenting Styles and Eating Disorders. J. Psychiatr. Ment. Health Nurs. 2011, 18, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulshreshtha, M.; Badu, N.; Goel, N.; Chandel, S. Disordered Eating Attitudes and Body Shape Concerns among North Indian Kathak Dancers. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2020, 54, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaquero-Cristóbal, R.; Kararez, M.; Esparza-Ros, F. Influence of the Dance Discipline on Body Image Distortion and Dissatisfaction in Preadolescents, Adolescents and Young Women Dancers. Nutr. Hosp. 2017, 34, 1442–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kararez, M.; Vaquero-Christóbal, R.; Esparza-Ros, F. Perception and Distortion of Body Image in Spanish Women Dancers Based on Academic Year and Age. Nutr. Hosp. 2018, 35, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Healthy Lifestyle—WHO Recommendations. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/news-room/fact-sheets/item/a-healthy-lifestyle---who-recommendations (accessed on 4 May 2020).
- Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Stefanadis, C. Dietary Patterns: A Mediterranean Diet Score and Its Relation to Clinical and Biological Markers of Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2006, 16, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrysohoou, C.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Das, U.N.; Stefanadis, C. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Attenuates Inflammation and Coagulation Process in Healthy Adults: The ATTICA Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabdoz, E.; Wilson, K.; Merwin, R.; Kellum, K. Assessment of Body Image Flexibility: The Body Image-Acceptance and Action Questionnaire. J. Context. Behav. Sci. 2013, 2, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basarkod, G.; Sahdra, B.; Ciarroch, J. Body Image—Acceptance and Action Questionnaire—5: An Abbreviation Using Genetic Algorithms. Behav. Ther. 2018, 49, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zachari, S.; Jillon, V.W. Measurement Invariance and Psychometric Properties of Three Positive Body Image Measures among Cisgender Sexual Minority and Heterosexual Women. Body Image 2022, 40, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosselli, M.; Sofi, F.; Rizzo, M.; Stefani, L. Body Composition and Eating Behavior in Non-Professional Adolescent Female Dancers. J. Sport. Med. Phys. Fit. 2022, 62, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepańska, E.; Janota, B.; Wlazlo, M.; Czapla, M. Eating Behaviours, the Frequency of Consumption of Selected Food Products, and Selected Elements of Lifestyle among Young Dancers. Rocz. Państwowego Zakładu Hig. 2021, 72, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.; Wyon, M. An International Study on Dietary Supplementation Use in Dancers. Med. Probl. Perform. Artist. 2014, 29, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva, C.L.; De Oliveira, E.P.; De Sousa, M.V.; Pimentel, G.D. Body Dissatisfaction and the Wish for Different Silhouette Is Associated with Higher Adiposity and Fat Intake in Female Ballet Dancers than Male. J. Sport. Med. Phys. Fit. 2015, 56, 141–148. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, K.L.; Mitchell, S.; Foskett, A.; Conlon, C.A.; von Hurst, P.R. Dietary Intake, Anthropometric Characteristics, and Iron and Vitamin D Status of Female Adolescent Ballet Dancers Living in New Zealand. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2014, 25, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stracciolini, A.; Quinn, B.J.; Geminiani, E.; Kinney, S.; McCrystal, T.; Owen, M.; Pepin, M.J.; Stein, C.J. Body Mass Index and Menstrual Patterns in Dancers. Clin. Pediatr. 2017, 56, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacchi, E.; Spiazzi, G.; Zendrini, G.; Bonin, C.; Moghetti, P. Low Body Weight and Menstrual Dysfunction Are Common Findings in Both Elite and Amateur Ballet Dancers. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2012, 36, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, Q.J.O.V.; Rodrigues, A.M. Risk Behavior for Orthorexia Nervosa in Nutrition Students. J. Bras. Psiquiatr. 2014, 63, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramacciotti, C.E.; Perrone, P.; Burgalassi, A.; Conversano, C.; Massimetti, G.; Dell’Osso, L. Orthorexia Nervosa in the General Population: A Preliminary Screening Using a Self-Administered Questionnaire (ORTO-15). Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2011, 16, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidan, T.; Ertekin, V.; Işikay, S.; Kirpinar, I. Prevalence of Orthorexia among Medical Students in Erzurum. Compr. Psychiatry 2010, 51, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camci, N.; Aksoydan, E. Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa among Turkish Performance Artists. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2009, 14, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikan, F.E. Self-Reported Distortion of Body Image among Classical Ballet Students in Brazil: Classification According to the Body Shape Questionnaire. Fisioter. Bras. 2019, 19, 821–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, C. XIII Annual Meeting of the European Association for Consultation-Liaison Psychiatry and Psychosomatics (EACLPP) XXVIII European Conference on Psychosomatic Research (ECPR). Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 2010, 68, 605–679. [Google Scholar]
- Brytek-Matera, A.; Magdalena, K.; Poggiogalle, E.; Donini, L.M. Adaptation of the ORTHO-15 Test to Polish Women and Men. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2014, 19, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Osso, L.; Carpita, B.; Muti, D.; Cremone, I.M.; Massimetti, G.; Diadema, E.; Gesi, C.; Carmassi, C. Prevalence and Characteristics of Orthorexia Nervosa in a Sample of University Students in Italy. Eat. Weight Disord. EWD 2018, 23, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas, A.G.; Alonso, D.A.; Sánchez-Miguel, P.A.; del Río Sánchez, C. Factors Dancers Associate with Their Body Dissatisfaction. Body Image 2018, 25, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mclnerney-Ernst, E.M. Orthorexia Nervosa: Real Construct or Newest Social Trend? Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Missouri-Kansas City, Kansas City, MO, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, S.M. Orthorexia Nervosa: Healthy Eating or Eating Disorder? Master’s Thesis, Eastern Illinois University, Charleston, IL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
| Variable | ON (n = 71) | Non ON (n = 25) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 68 (95.8%) F 3/2 (2.85) M 4/1 (1.4%) O 5 | 24 (96.0%) F 3/1 M 4 | 0.805 |
| Age (years) | 23.49 ± 5.45 | 23.16 ± 4.2 | 0.782 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.006 * | ||
| Underweight | 5 (7.0%) | 7 (28.0%) | |
| Normal weight | 66 (93.0%) | 18 (72.0%) | |
| Chronic disease | YES 7 (9.9%) | YES 3 (12.0%) | 0.763 |
| Medication | YES 10 (14.3%) | YES 4 (16.0%) | 0.836 |
| Dietary supplements | YES 29 (41.4%) | YES 10 (40.0%) | 0.901 |
| Dietary pattern | YES 10 (14.3%) | YES 4 (16.0%) | 0.836 |
| Educational level | 0.713 | ||
| Secondary education | 18 (25.7%) | 7 (28.0%) | |
| Tertiary education | 51 (72.9%) | 17 (68.0%) | |
| Postgraduate education | 1 (1.4%) | 1 (4.0%) | |
| MedDiet Score | 0.087 | ||
| Inadequate adherence | 11 (15.5%) | 8 (32.0%) | |
| Medium adherence | 58 (81.7%) | 15 (60.0%) | |
| High adherence | 2 (2.8%) | 2 (8.0%) | |
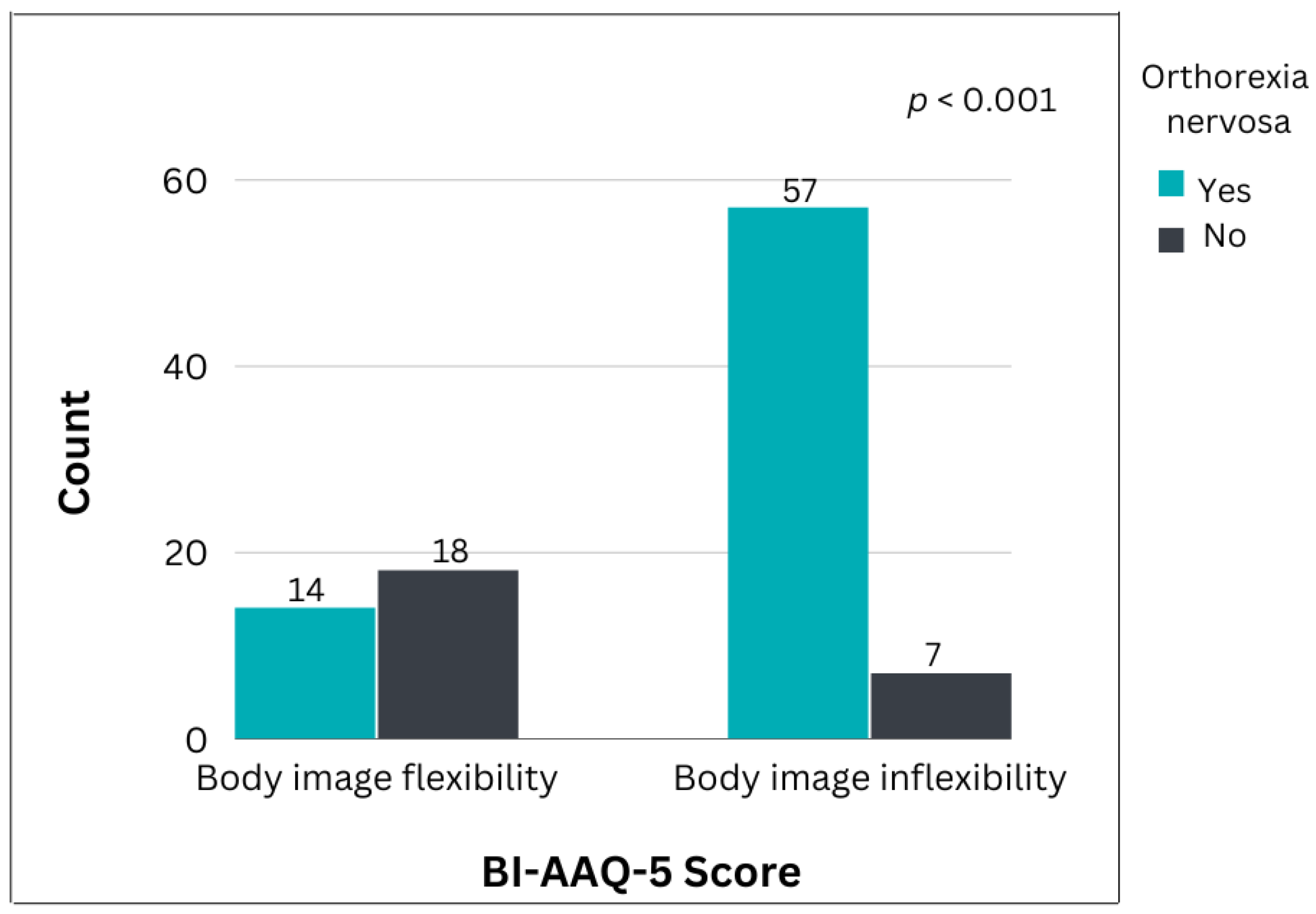
| Body image inflexibility (BIAAQ-5 1) | 57 (80.3%) | 7 (28.0%) | <0.001 * |
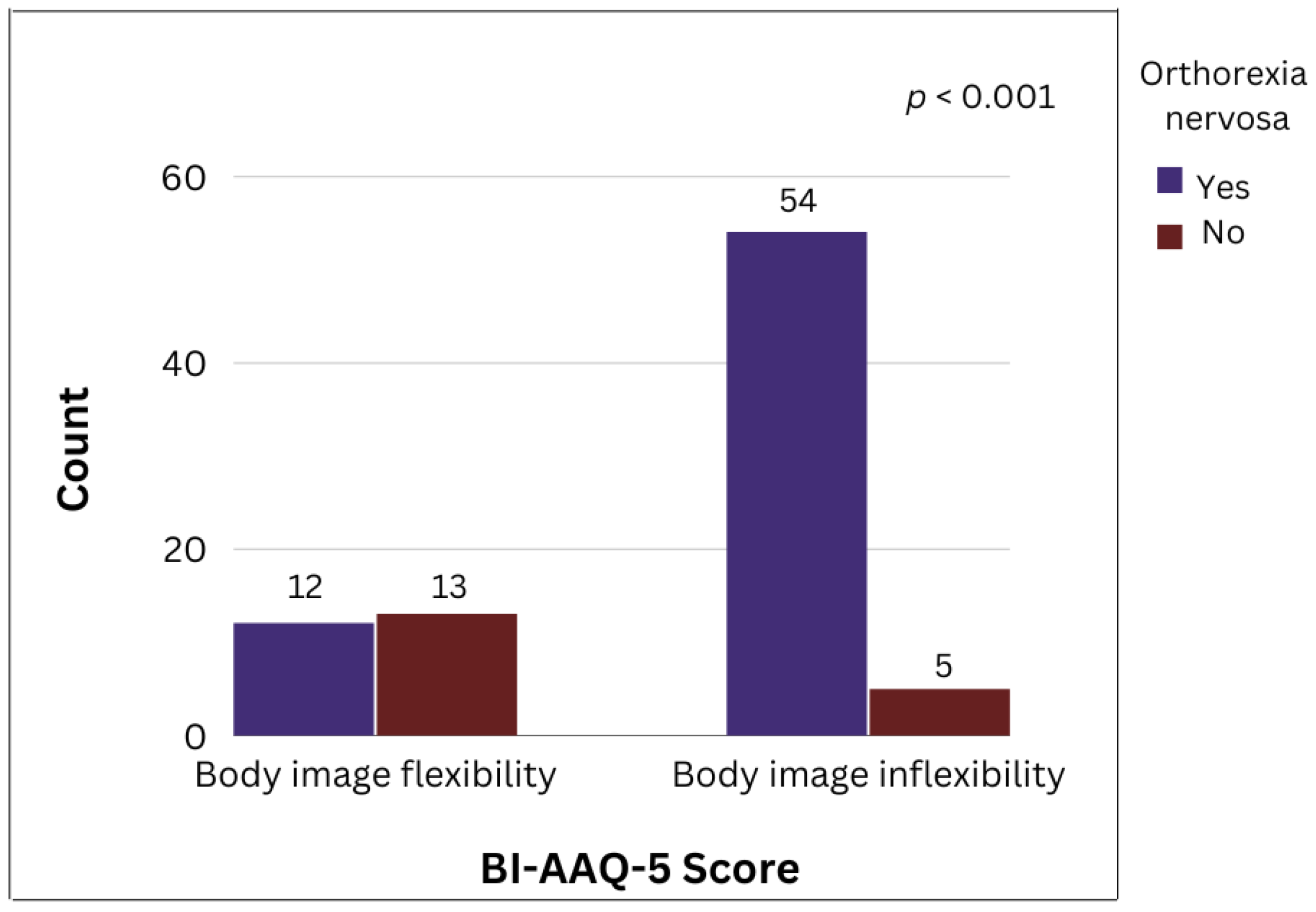
| Maternal body image inflexibility (BIAAQ-5 1) | 25 (35.2%) | 10 (40.0%) | 0.778 |
| Paternal body image inflexibility (BIAAQ-5 1) | 7 (9.9%) | 1 (4.2%) | 0.436 |
| Maternal bonding (PBI 2) | 0.973 | ||
| Neglectful parenting | 13 (18.3%) | 4 (16.0%) | |
| Affectionless control | 9 (12.7%) | 3 (12.0%) | |
| Optimal | 39 (54.9%) | 15 (60.0%) | |
| Affectionate constraint | 9 (12.7%) | 3 (12.0%) | |
| Paternal bonding (PBI 2) | 0.286 | ||
| Neglectful parenting | 16 (22.5%) | 5 (20.0%) | |
| Affectionless control | 16 (22.5%) | 2 (8.0%) | |
| Optimal | 29 (40.8%) | 16 (64.0%) | |
| Affectionate constraint | 3 (4.2%) | 1 (4.0%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Athanasaki, D.; Lakoumentas, J.; Feketea, G.; Vassilopoulou, E. The Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa among Greek Professional Dancers. Nutrients 2023, 15, 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020379
Athanasaki D, Lakoumentas J, Feketea G, Vassilopoulou E. The Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa among Greek Professional Dancers. Nutrients. 2023; 15(2):379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020379
Chicago/Turabian StyleAthanasaki, Dafni, John Lakoumentas, Gavriela Feketea, and Emilia Vassilopoulou. 2023. "The Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa among Greek Professional Dancers" Nutrients 15, no. 2: 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020379
APA StyleAthanasaki, D., Lakoumentas, J., Feketea, G., & Vassilopoulou, E. (2023). The Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa among Greek Professional Dancers. Nutrients, 15(2), 379. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15020379







