Exogenous Ketone Supplementation and Ketogenic Diets for Exercise: Considering the Effect on Skeletal Muscle Metabolism
Abstract
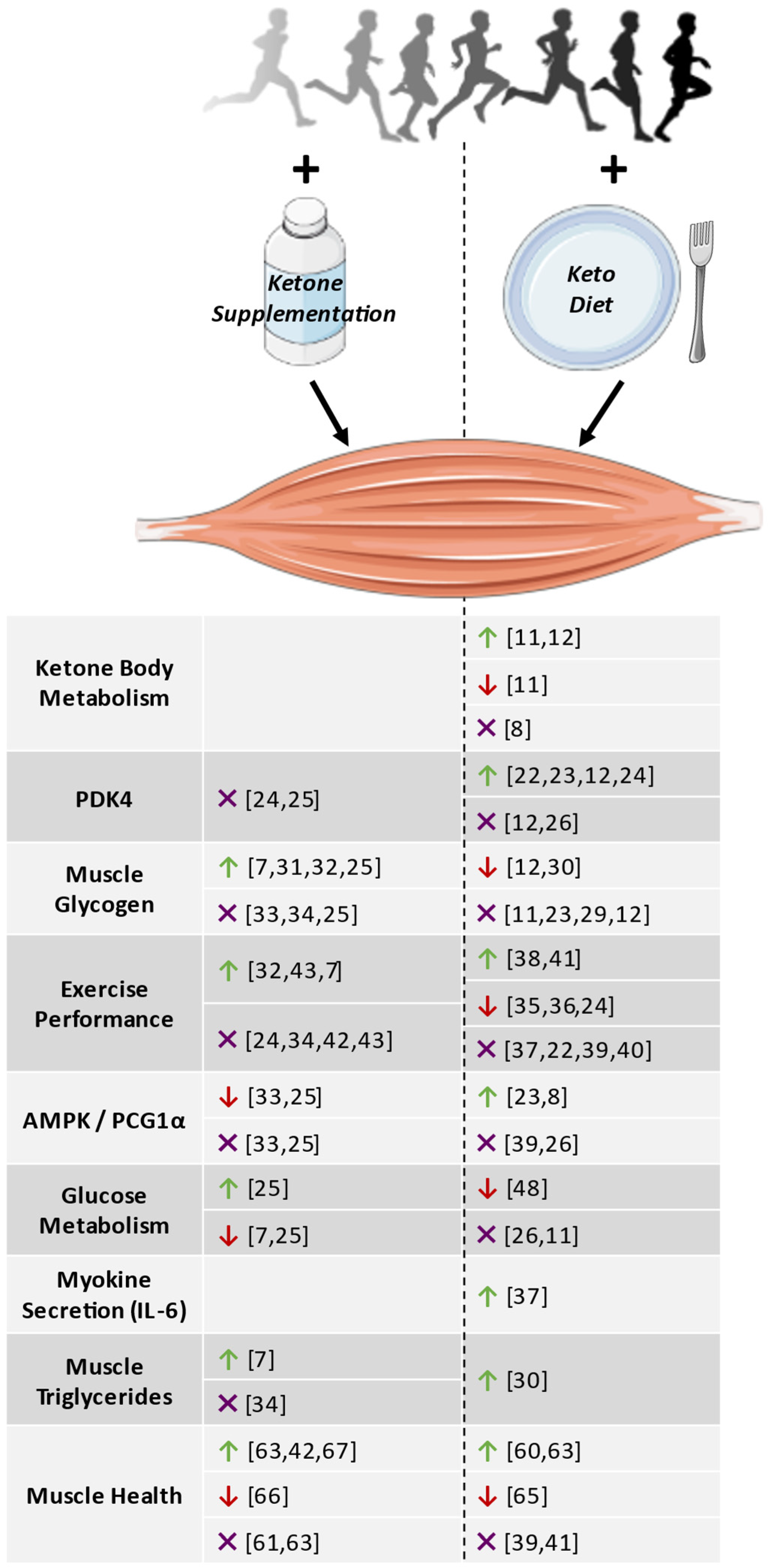
:1. Introduction
2. Effect of Exercise on Muscle Ketone Body Metabolism
3. Muscle PDK4 Activation Following a Keto Diet and Exercise
4. Muscle Glycogen Stores Following Exercise and Exogenous or Endogenous Ketone Supplementation
5. Increased Ketolysis as a Potential Mechanism to Alter Exercise Performance
6. Alterations in AMPK and PCG1α Activation Following an Exercise and Keto Regimen
7. Influence of Increased Exposure to Ketones on Glucose Metabolism
8. Secretion of IL-6 Following a Keto Diet and Exercise Regimen
9. Muscle TAG Levels Following Exercise and a Keto Diet or Ketone Supplementation
10. Impact of Ketones on Muscle Health Following Exercise
11. Summary
12. Limitations and Future Direction
13. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Puchalska, P.; Crawford, P.A. Multi-Dimensional Roles of Ketone Bodies in Fuel Metabolism, Signaling, and Therapeutics. Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 262–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, A.M.; Williamson, D.H. Physiological Roles of Ketone Bodies as Substrates and Signals in Mammalian Tissues. Physiol. Rev. 1980, 60, 143–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchalska, P.; Nelson, A.B.; Stagg, D.B.; Crawford, P.A. Determination of Ketone Bodies in Biological Samples via Rapid UPLC-MS/MS. Talanta 2021, 225, 122048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, R.J.; Edmond, J. Utilization of L(+)-3-Hydroxybutyrate, D(-)-3-Hydroxybutyrate, Acetoacetate, and Glucose for Respiration and Lipid Synthesis in the 18-Day-Old Rat. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 5222–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batch, J.T.; Lamsal, S.P.; Adkins, M.; Sultan, S.; Ramirez, M.N. Advantages and Disadvantages of the Ketogenic Diet: A Review Article. Cureus 2020, 12, e9639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, B.J.; Cox, P.J.; Evans, R.D.; Santer, P.; Miller, J.J.; Faull, O.K.; Magor-Elliott, S.; Hiyama, S.; Stirling, M.; Clarke, K. On the Metabolism of Exogenous Ketones in Humans. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, P.J.; Kirk, T.; Ashmore, T.; Willerton, K.; Evans, R.; Smith, A.; Murray, A.J.; Stubbs, B.; West, J.; McLure, S.W.; et al. Nutritional Ketosis Alters Fuel Preference and Thereby Endurance Performance in Athletes. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Huang, Q.; Tominaga, T.; Liu, C.; Suzuki, K. An 8-Week Ketogenic Diet Alternated Interleukin-6, Ketolytic and Lipolytic Gene Expression, and Enhanced Exercise Capacity in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Tripathy, D. Skeletal Muscle Insulin Resistance Is the Primary Defect in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32 (Suppl. 2), S157–S163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, W.R.; Ochala, J. Skeletal Muscle: A Brief Review of Structure and Function. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 96, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Saito, H.; Sumi, K.; Sakamoto, Y.; Tachi, Y.; Iida, K. Short-Term and Long-Term Ketogenic Diet Therapy and the Addition of Exercise Have Differential Impacts on Metabolic Gene Expression in the Mouse Energy-Consuming Organs Heart and Skeletal Muscle. Nutr. Res. 2018, 60, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukazawa, A.; Koike, A.; Karasawa, T.; Tsutsui, M.; Kondo, S.; Terada, S. Effects of a Ketogenic Diet Containing Medium-Chain Triglycerides and Endurance Training on Metabolic Enzyme Adaptations in Rat Skeletal Muscle. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holcomb, L.E.; Rowe, P.; O’Neill, C.C.; DeWitt, E.A.; Kolwicz, S.C. Sex Differences in Endurance Exercise Capacity and Skeletal Muscle Lipid Metabolism in Mice. Physiol. Rep. 2022, 10, e15174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Midaoui, A.; Chiasson, J.L.; Tancrède, G.; Nadeau, A. Physical Training Reverses Defect in 3-Ketoacid CoA-Transferase Activity in Skeletal Muscle of Diabetic Rats. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 288, E748–E752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winder, W.W.; Baldwin, K.M.; Holloszy, J.O. Exercise-Induced Increase in the Capacity of Rat Skeletal Muscle to Oxidize Ketones. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1975, 53, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, H.J.; Reichmann, H. Differential Response of Enzyme Activities in Rat Diaphragm and Intercostal Muscles to Exercise Training. J. Neurol. Sci. 1988, 84, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmori, H.; Kawai, K.; Yamashita, K. Enhanced Ketone Body Uptake by Perfused Skeletal Muscle in Trained Rats. Endocrinol. Jpn. 1990, 37, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrick, H.L.; Brunetta, H.S.; Pignanelli, C.; Nunes, E.A.; van Loon, L.J.C.; Burr, J.F.; Holloway, G.P. In Vitro Ketone-Supported Mitochondrial Respiration Is Minimal When Other Substrates Are Readily Available in Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle. J. Physiol. 2020, 598, 4869–4885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.E.; Bae, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, H.E.; Zhang, D.; Cho, S.C.; Song, W. Effects of Exercise-Induced Beta-Hydroxybutyrate on Muscle Function and Cognitive Function. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilegaard, H.; Neufer, P.D. Transcriptional Regulation of Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase 4 in Skeletal Muscle during and after Exercise. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2004, 63, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyle, K.E.; Canham, J.P.; Consitt, L.A.; Zheng, D.; Koves, T.R.; Gavin, T.P.; Holbert, D.; Neufer, P.D.; Ilkayeva, O.; Muoio, D.M.; et al. A High-Fat Diet Elicits Differential Responses in Genes Coordinating Oxidative Metabolism in Skeletal Muscle of Lean and Obese Individuals. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, B.; Zou, K. Effect of Ketogenic Diet on Exercise Tolerance and Transcriptome of Gastrocnemius in Mice. Open Life Sci. 2023, 18, 20220570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.-Y.; Linden, M.A.; Fuller, S.E.; Goldsmith, F.R.; Simon, J.; Batdorf, H.M.; Scott, M.C.; Essajee, N.M.; Brown, J.M.; Noland, R.C. Combined Effects of a Ketogenic Diet and Exercise Training Alter Mitochondrial and Peroxisomal Substrate Oxidative Capacity in Skeletal Muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 320, E1053–E1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dearlove, D.J.; Soto Mota, A.; Hauton, D.; Pinnick, K.; Evans, R.; Miller, J.; Fischer, R.; Mccullagh, J.S.O.; Hodson, L.; Clarke, K.; et al. The Effects of Endogenously- and Exogenously-Induced Hyperketonemia on Exercise Performance and Adaptation. Physiol. Rep. 2022, 10, e15309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Terada, S.; Banjo, M.; Seike, K.; Nakano, S.; Hatta, H. Effects of β-Hydroxybutyrate Treatment on Glycogen Repletion and Its Related Signaling Cascades in Epitrochlearis Muscle during 120 Min of Postexercise Recovery. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 44, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyatt, H.W.; Kephart, W.C.; Holland, A.M.; Mumford, P.; Mobley, C.B.; Lowery, R.P.; Roberts, M.D.; Wilson, J.M.; Kavazis, A.N. A Ketogenic Diet in Rodents Elicits Improved Mitochondrial Adaptations in Response to Resistance Exercise Training Compared to an Isocaloric Western Diet. Front. Physiol. 2016, 7, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigh-Larsen, J.F.; Ørtenblad, N.; Spriet, L.L.; Overgaard, K.; Mohr, M. Muscle Glycogen Metabolism and High-Intensity Exercise Performance: A Narrative Review. Sports Med. 2021, 51, 1855–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, J.D.; Baxter, J.; Satapati, S.; Burgess, S.C. The Effect of Short-Term Fasting on Liver and Skeletal Muscle Lipid, Glucose, and Energy Metabolism in Healthy Women and Men. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 577–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volek, J.S.; Freidenreich, D.J.; Saenz, C.; Kunces, L.J.; Creighton, B.C.; Bartley, J.M.; Davitt, P.M.; Munoz, C.X.; Anderson, J.M.; Maresh, C.M.; et al. Metabolic Characteristics of Keto-Adapted Ultra-Endurance Runners. Metabolism 2016, 65, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, V.J.; LaFountain, R.A.; Barnhart, E.; Sapper, T.S.; Short, J.; Arnold, W.D.; Hyde, P.N.; Crabtree, C.D.; Kackley, M.L.; Kraemer, W.J.; et al. A Ketogenic Diet Combined with Exercise Alters Mitochondrial Function in Human Skeletal Muscle While Improving Metabolic Health. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 319, E995–E1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdsworth, D.A.; Cox, P.J.; Kirk, T.; Stradling, H.; Impey, S.G.; Clarke, K. A Ketone Ester Drink Increases Postexercise Muscle Glycogen Synthesis in Humans. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 1789–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poffé, C.; Ramaekers, M.; Van Thienen, R.; Hespel, P. Ketone Ester Supplementation Blunts Overreaching Symptoms during Endurance Training Overload. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 3009–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandoorne, T.; De Smet, S.; Ramaekers, M.; Van Thienen, R.; De Bock, K.; Clarke, K.; Hespel, P. Intake of a Ketone Ester Drink during Recovery from Exercise Promotes MTORC1 Signaling but Not Glycogen Resynthesis in Human Muscle. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poffé, C.; Ramaekers, M.; Bogaerts, S.; Hespel, P. Exogenous Ketosis Impacts Neither Performance nor Muscle Glycogen Breakdown in Prolonged Endurance Exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 128, 1643–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfort, J.; Zarzeczny, R.; Pilis, W.; Nazar, K.; Kaciuba-Uścitko, H. The Effect of a Low-Carbohydrate Diet on Performance, Hormonal and Metabolic Responses to a 30-s Bout of Supramaximal Exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1997, 76, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjödin, A.; Hellström, F.; Sehlstedt, E.; Svensson, M.; Burén, J. Effects of a Ketogenic Diet on Muscle Fatigue in Healthy, Young, Normal-Weight Women: A Randomized Controlled Feeding Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, A.; Cenci, L.; Pompei, P.; Sahin, N.; Bianco, A.; Neri, M.; Caprio, M.; Moro, T. Effects of Two Months of Very Low Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet on Body Composition, Muscle Strength, Muscle Area, and Blood Parameters in Competitive Natural Body Builders. Nutrients 2021, 13, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kysel, P.; Haluzíková, D.; Doležalová, R.P.; Laňková, I.; Lacinová, Z.; Kasperová, B.J.; Trnovská, J.; Hrádková, V.; Mráz, M.; Vilikus, Z.; et al. The Influence of Cyclical Ketogenic Reduction Diet vs. Nutritionally Balanced Reduction Diet on Body Composition, Strength, and Endurance Performance in Healthy Young Males: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, M.D.; Holland, A.M.; Kephart, W.C.; Mobley, C.B.; Mumford, P.W.; Lowery, R.P.; Fox, C.D.; McCloskey, A.E.; Shake, J.J.; Mesquita, P.; et al. A Putative Low-Carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet Elicits Mild Nutritional Ketosis but Does Not Impair the Acute or Chronic Hypertrophic Responses to Resistance Exercise in Rodents. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 120, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcomb, L.E.; O’Neill, C.C.; DeWitt, E.A.; Kolwicz, S.C. The Effects of Fasting or Ketogenic Diet on Endurance Exercise Performance and Metabolism in Female Mice. Metabolites 2021, 11, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Huang, Q.; Yada, K.; Liu, C.; Suzuki, K. An 8-Week Ketogenic Low Carbohydrate, High Fat Diet Enhanced Exhaustive Exercise Capacity in Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poffé, C.; Robberechts, R.; Podlogar, T.; Kusters, M.; Debevec, T.; Hespel, P. Exogenous Ketosis Increases Blood and Muscle Oxygenation but Not Performance during Exercise in Hypoxia. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2021, 321, R844–R857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monsalves-Alvarez, M.; Morales, P.E.; Castro-Sepulveda, M.; Sepulveda, C.; Rodriguez, J.M.; Chiong, M.; Eisner, V.; Lavandero, S.; Troncoso, R. β-Hydroxybutyrate Increases Exercise Capacity Associated with Changes in Mitochondrial Function in Skeletal Muscle. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechchate, H.; Abdualkader, A.M.; Bernacchi, J.B.; Gopal, K.; Tabatabaei Dakhili, S.A.; Yang, K.; Greenwell, A.A.; Kong, X.; Crawford, P.A.; Al Batran, R. Defective Muscle Ketone Body Oxidation Disrupts BCAA Catabolism by Altering Mitochondrial Branched-Chain Aminotransferase. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 324, E425–E436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhang, D.; Chung, D.; Tang, Z.; Huang, H.; Dai, L.; Qi, S.; Li, J.; Colak, G.; Chen, Y.; et al. Metabolic Regulation of Gene Expression by Histone Lysine β-Hydroxybutyrylation. Mol. Cell 2016, 62, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, E.A.; Ruderman, N.B. AMPK and the Biochemistry of Exercise: Implications for Human Health and Disease. Biochem. J. 2009, 418, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Ward, W.F. PGC-1alpha: A Key Regulator of Energy Metabolism. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2006, 30, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, C.C.; van Boom, K.M.; Armino, N.; Larmuth, K.; Noakes, T.D.; Smith, J.A.; Kohn, T.A. Reduced Glucose Tolerance and Skeletal Muscle GLUT4 and IRS1 Content in Cyclists Habituated to a Long-Term Low-Carbohydrate, High-Fat Diet. Int. J. Sport. Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2020, 30, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, F.; Lavigne, C.; Jacques, H.; Marette, A. Defective Insulin-Induced GLUT4 Translocation in Skeletal Muscle of High Fat-Fed Rats Is Associated with Alterations in both Akt/Protein Kinase B and Atypical Protein Kinase C (Zeta/Lambda) Activities. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1901–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, B.B.; Pedersen, O. Suppression of GLUT4 Expression in Skeletal Muscle of Rats That Are Obese from High Fat Feeding but Not from High Carbohydrate Feeding or Genetic Obesity. Endocrinology 1993, 132, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasawa, T.; Kondo, S.; Fukazawa, A.; Koike, A.; Tsutsui, M.; Terada, S. Effects of Dietary Fat Restriction on Endurance Training-Induced Metabolic Adaptations in Rat Skeletal Muscle. J. Oleo Sci. 2021, 70, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaei Dakhili, S.A.; Yang, K.; Locatelli, C.A.A.; Saed, C.T.; Greenwell, A.A.; Chan, J.S.F.; Chahade, J.J.; Scharff, J.; Al Imarah, S.; Eaton, F.; et al. Ketone Ester Administration Improves Glycemia in Obese Mice. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2023, 325, C750–C757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greaves, G.; Xiang, R.; Rafiei, H.; Malas, A.; Little, J.P. Prior Ingestion of a Ketone Monoester Supplement Reduces Postprandial Glycemic Responses in Young Healthy-Weight Individuals. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 46, 309–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garneau, L.; Aguer, C. Role of Myokines in the Development of Skeletal Muscle Insulin Resistance and Related Metabolic Defects in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2019, 45, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, S.; Harley, R.; McAuley, J.J.; Crowe, L.A.N.; Pedret, C.; Kirwan, P.D.; Siebert, S.; Millar, N.L. The Effect of Exercise on Cytokines: Implications for Musculoskeletal Health: A Narrative Review. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2022, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, C.; Steensberg, A.; Pilegaard, H.; Osada, T.; Saltin, B.; Pedersen, B.K.; Neufer, P.D. Transcriptional Activation of the IL-6 Gene in Human Contracting Skeletal Muscle: Influence of Muscle Glycogen Content. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 2748–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, M.J.; Cheng, Y. Triglyceride Metabolism in Exercising Muscle. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, D.E.; Goodpaster, B.H. Skeletal Muscle Triglyceride. An Aspect of Regional Adiposity and Insulin Resistance. Diabetes Care 2001, 24, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodpaster, B.H.; He, J.; Watkins, S.; Kelley, D.E. Skeletal Muscle Lipid Content and Insulin Resistance: Evidence for a Paradox in Endurance-Trained Athletes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 5755–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Ma, S.; Tominaga, T.; Suzuki, K.; Liu, C. An 8-Week, Low Carbohydrate, High Fat, Ketogenic Diet Enhanced Exhaustive Exercise Capacity in Mice Part 2: Effect on Fatigue Recovery, Post-Exercise Biomarkers and Anti-Oxidation Capacity. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jameson, T.S.O.; Islam, H.; Wall, B.T.; Little, J.P.; Stephens, F.B. Oral Ketone Monoester Supplementation Does Not Accelerate Recovery of Muscle Force or Modulate Circulating Cytokine Concentrations after Muscle-Damaging Eccentric Exercise in Healthy Males and Females. Exp. Physiol. 2022, 107, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunan, D.; Howatson, G.; van Someren, K.A. Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage Is Not Attenuated by Beta-Hydroxy-Beta-Methylbutyrate and Alpha-Ketoisocaproic Acid Supplementation. J. Strength. Cond. Res. 2010, 24, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, R.C.P.; Camerino, S.R.A.S.; França, T.C.L.; Rodrigues, D.S.A.; Gouveia, M.G.S.; Ximenes-da-Silva, A.; Bassini, A.; Prado, E.S.; Cameron, L.C. Keto Analogues and Amino Acids Supplementation Induces a Decrease of White Blood Cell Counts and a Reduction of Muscle Damage during Intense Exercise under Thermoneutral Conditions. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-S.; Lee, M.-G. Effects of Unaccustomed Downhill Running on Muscle Damage, Oxidative Stress, and Leukocyte Apoptosis. J. Exerc. Nutrition Biochem. 2015, 19, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissiou, M.; Borkoles, E.; Kobayashi, K.; Polman, R. The Effect of an 8 Week Prescribed Exercise and Low-Carbohydrate Diet on Cardiorespiratory Fitness, Body Composition and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Obese Individuals: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prins, P.J.; Buxton, J.D.; McClure, T.S.; D’Agostino, D.P.; Ault, D.L.; Welton, G.L.; Jones, D.W.; Atwell, A.D.; Slack, M.A.; Slack, M.L.; et al. Ketone Bodies Impact on Hypoxic CO2 Retention Protocol During Exercise. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 780755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poffé, C.; Robberechts, R.; Van Thienen, R.; Hespel, P. Exogenous Ketosis Elevates Circulating Erythropoietin and Stimulates Muscular Angiogenesis During Endurance Training Overload. J. Physiol. 2023, 601, 2345–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reference | Study Population | Study Design | Key Finding(s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| [7] | Male endurance athletes |
|
|
| [8] | Male mice |
|
|
| [11] | Male mice |
|
|
| [12] | Male rats |
|
|
| [13] | Male and female mice |
|
|
| [14] | Male rats |
|
|
| [15] | Male rats |
|
|
| [16] | Male rats |
|
|
| [17] | Male rats |
|
|
| [18] | Male rats |
|
|
| [19] | C2C12 cells |
|
|
| [22] | Male mice |
|
|
| [23] | Male mice |
|
|
| [24] | Participants performing >6 weekly hours of endurance exercise |
|
|
| [25] | Epitrochlearis from male mice |
|
|
| [26] | Gastrocnemius from male mice |
|
|
| [29] | Male endurance runners |
|
|
| [30] | Military personnel |
|
|
| [31] | Male athletes |
|
|
| [32] | Physically active males |
|
|
| [33] | Physically active males |
|
|
| [34] | Male cyclists |
|
|
| [35] | Male participants |
|
|
| [36] | Female participants |
|
|
| [37] | Male bodybuilders |
|
|
| [38] | Male and female participants |
|
|
| [39] | Male rats |
|
|
| [40] | Female mice |
|
|
| [41] | Male rats |
|
|
| [42] | Male cyclists |
|
|
| [43] | Male mice |
|
|
| [44] | Male SCOT knockout mice |
|
|
| [48] | Male cyclists |
|
|
| [51] | Male rats |
|
|
| [60] | Male mice |
|
|
| [61] | Recreational athletes |
|
|
| [62] | Male participants |
|
|
| [63] | Male cyclists |
|
|
| [65] | Participants with obesity |
|
|
| [66] | Male distance runners |
|
|
| [67] | Physically active males |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khouri, H.; Ussher, J.R.; Aguer, C. Exogenous Ketone Supplementation and Ketogenic Diets for Exercise: Considering the Effect on Skeletal Muscle Metabolism. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194228
Khouri H, Ussher JR, Aguer C. Exogenous Ketone Supplementation and Ketogenic Diets for Exercise: Considering the Effect on Skeletal Muscle Metabolism. Nutrients. 2023; 15(19):4228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194228
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhouri, Hannah, John R. Ussher, and Céline Aguer. 2023. "Exogenous Ketone Supplementation and Ketogenic Diets for Exercise: Considering the Effect on Skeletal Muscle Metabolism" Nutrients 15, no. 19: 4228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194228
APA StyleKhouri, H., Ussher, J. R., & Aguer, C. (2023). Exogenous Ketone Supplementation and Ketogenic Diets for Exercise: Considering the Effect on Skeletal Muscle Metabolism. Nutrients, 15(19), 4228. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15194228







