Changes in Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Body Weight among Lithuanian Students during and after the COVID-19 Pandemic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beaudry, K.M.; Ludwa, I.A.; Thomas, A.M.; Ward, W.E.; Falk, B.; Josse, A.R. First-year university is associated with greater body weight, body composition and adverse dietary changes in males than females. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilger, J.; Loerbroks, A.; Diehl, K. Eating behaviour of university students in Germany: Dietary intake, barriers to healthy eating and changes in eating behaviour since the time of matriculation. Appetite 2017, 109, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriaucioniene, V.; Raskiliene, A.; Petrauskas, D.; Petkeviciene, J. Trends in Eating Habits and Body Weight Status, Perception Patterns and Management Practices among First-Year Students of Kaunas (Lithuania) Universities, 2000–2017. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Government of the Republic of Lithuania: Quarantine Announced throughout the Territory of the Republic of Lithuania (Attached Resolution). 2020. Available online: https://lrv.lt/en/news/quarantine-announcedthroughout-the-territory-of-the-republic-of-lithuania-attached-resolution (accessed on 17 May 2023).
- Altena, E.; Baglioni, C.; Espie, C.A.; Ellis, J.; Gavriloff, D.; Holzinger, B.; Schlarb, A.; Frase, L.; Jernelöv, S.; Riemann, D. Dealing with sleep problems during home confinement due to the COVID-19 outbreak: Practical recommendations from a task force of the European CBT-I Academy. J. Sleep Res. 2020, 29, e13052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehi, T.; Khan, R.; Halawani, R.; Dos Santos, H. Effect of COVID-19 outbreak on the diet, body weight and food security status of students of higher education: A systematic review. Br. J. Nutr. 2023, 129, 1916–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoro, M.; Wakimoto, K.; Otaki, N.; Fukuo, K. Increased Prevalence of Breakfast Skipping in Female College Students in COVID-19. Asia Pac. J. Public Health 2021, 33, 438–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, B.C.; Steffen, J.; Schlichtiger, J.; Brunner, S. Altered nutrition behavior during COVID-19 pandemic lockdown in young adults. Eur. J. Nutr. 2021, 60, 2593–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fila-Witecka, K.; Senczyszyn, A.; Kołodziejczyk, A.; Ciułkowicz, M.; Maciaszek, J.; Misiak, B.; Szcześniak, D.; Rymaszewska, J. Lifestyle Changes among Polish University Students during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celorio-Sardà, R.; Comas-Basté, O.; Latorre-Moratalla, M.L.; Zerón-Rugerio, M.F.; Urpi-Sarda, M.; Illán-Villanueva, M.; Farran-Codina, A.; Izquierdo-Pulido, M.; Vidal-Carou, M.D.C. Effect of COVID-19 Lockdown on Dietary Habits and Lifestyle of Food Science Students and Professionals from Spain. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, K.; Bschaden, A.; Stroebele-Benschop, N. Changes in lifestyle, diet, and body weight during the first COVID 19 ‘lockdown’ in a student sample. Appetite 2021, 167, 105638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprake, E.F.; Russell, J.M.; Cecil, J.E.; Cooper, R.J.; Grabowski, P.; Pourshahidi, L.K.; Barker, M.E. Dietary patterns of university students in the UK: A cross-sectional study. Nutr. J. 2018, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munt, A.E.; Partridge, S.R.; Allman-Farinelli, M. The barriers and enablers of healthy eating among young adults: A missing piece of the obesity puzzle: A scoping review. Obes. Rev. 2017, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Lacoba, R.; Pardo-Garcia, I.; Amo-Saus, E.; Escribano-Sotos, F. Social determinants of food group consumption based on Mediterranean diet pyramid: A cross-sectional study of university students. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227620. [Google Scholar]
- Mello Rodrigues, V.; Bray, J.; Fernandes, A.C.; Luci Bernardo, G.; Hartwell, H.; Secchi Martinelli, S.; Lazzarin Uggioni, P.; Barletto Cavalli, S.; Proença, R.P.D.C. Vegetable consumption and factors associated with increased intake among college students: A scoping review of the last 10 years. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brancaccio, M.; Mennitti, C.; Gentile, A.; Correale, L.; Buzzachera, C.F.; Ferraris, C.; Montomoli, C.; Frisso, G.; Borrelli, P.; Scudiero, O. Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Job Activity, Dietary Behaviours and Physical Activity Habits of University Population of Naples, Federico II-Italy. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragun, R.; Veček, N.N.; Marendić, M.; Pribisalić, A.; Đivić, G.; Cena, H.; Polašek, O.; Kolčić, I. Have Lifestyle Habits and Psychological Well-Being Changed among Adolescents and Medical Students Due to COVID-19 Lockdown in Croatia? Nutrients 2020, 13, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, A.; Singh, G.; Patwardhan, K. Patterns of Physical Activity Among University Students and Their Perceptions About the Curricular Content Concerned with Health: Cross-sectional Study. JMIRx Med. 2022, 3, e3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winpenny, E.M.; Smith, M.; Penney, T.; Foubister, C.; Guagliano, J.M.; Love, R.; Clifford Astbury, C.; van Sluijs, E.M.F.; Corder, K. Changes in physical activity, diet, and body weight across the education and employment transitions of early adulthood: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2020, 21, e12962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallè, F.; Sabella, E.A.; Da Molin, G.; De Giglio, O.; Caggiano, G.; Di Onofrio, V.; Ferracuti, S.; Montagna, M.T.; Liguori, G.; Orsi, G.B.; et al. Understanding Knowledge and Behaviors Related to CoViD-19 Epidemic in Italian Undergraduate Students: The EPICO Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.F.; Liao, M.Q.; Cai, W.L.; Yu, X.X.; Li, S.N.; Ke, X.Y.; Tan, S.X.; Luo, Z.Y.; Cui, Y.F.; Wang, Q.; et al. Physical activity, screen exposure and sleep among students during the pandemic of COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Larrad, A.; Mañas, A.; Labayen, I.; González-Gross, M.; Espin, A.; Aznar, S.; Serrano-Sánchez, J.A.; Vera-Garcia, F.J.; González-Lamuño, D.; Ara, I.; et al. Impact of COVID-19 Confinement on Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour in Spanish University Students: Role of Gender. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavolacci, M.P.; Wouters, E.; Van de Velde, S.; Buffel, V.; Déchelotte, P.; Van Hal, G.; Ladner, J. The Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Health Behaviors among Students of a French University. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbieri, P.N.; Giuntella, O.; Saccardo, S.; Sadoff, S. Lifestyle and mental health 1 year into COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrand, L.; Shaw, K.A.; Ko, J.; Deprez, D.; Chilibeck, P.D.; Zello, G.A. The impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on university students’ dietary intake, physical activity, and sedentary behaviour. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 46, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalal, S.M.; Beth, M.R.M.; Al-Hassan, H.J.M.; Alshealah, N.M.J. Body Mass Index, Practice of Physical Activity and Lifestyle of Students During COVID-19 Lockdown. J. Multidiscip. Healthc. 2021, 14, 1901–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Blanco, C.; Rodríguez-Almagro, J.; Onieva-Zafra, M.D.; Parra-Fernández, M.L.; Prado-Laguna, M.D.C.; Hernández-Martínez, A. Physical Activity and Sedentary Lifestyle in University Students: Changes during Confinement Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, D.; Rešetar, J.; Šteković, M.; Czlapka-Matyasik, M.; Verbanac, D.; Gajdoš Kljusurić, J. Diet Quality and Its Association with Lifestyle and Dietary Behaviors among Croatian Students during Two COVID-19 Lockdowns. Foods 2023, 12, 2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, M.; Duncan, M.J.; Patte, K.A.; Roy, B.D.; Ditor, D.S.; Klentrou, P. Changes in Body Mass, Physical Activity, and Dietary Intake during the COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdowns in Canadian University Students. Biology 2023, 12, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabauskas, V.; Klumbiene, J.; Petkeviciene, J.; Sakyte, E.; Kriaucioniene, V.; Veryga, A. Health Behaviour among Lithuanian Adult Population, 2014; Lithuanian University of Health Sciences Press: Kaunas, Lithuania, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bhawra, J.; Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Hall, M.G.; Vanderlee, L.; White, C.M.; Hammond, D. Patterns and correlates of nutrition knowledge across five countries in the 2018 international food policy study. Nutr. J. 2023, 22, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Dalamitros, A.A.; Beltran-Velasco, A.I.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Social and psychophysiological consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic: An extensive literature review. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irazusta-Garmendia, A.; Orpí, E.; Bach-Faig, A.; González Svatetz, C.A. Food Sustainability Knowledge, Attitudes, and Dietary Habits among Students and Professionals of the Health Sciences. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, G.; Young, E.; Butler, I.; Coe, S. The Impact of Lockdown During the COVID-19 Outbreak on Dietary Habits in Various Population Groups: A Scoping Review. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 626432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intiful, F.D.; Steele-Dadzie, R.; Mawusi Amos, P.; Pobee, R.; Ainuson-Quampah, J.; Ammah, C.; Antwi, T.; Wilson, K.N.; Asante, M. The Impact of Interpersonal Relationships on Dietary Habits. Interpersonal Relationships; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, K.; Onell, C.; Edlund, K.; Källberg, H.; Holm, L.W.; Sundberg, T.; Skillgate, E. Lifestyle behaviors in Swedish university students before and during the first six months of the COVID-19 pandemic: A cohort study. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moynihan, A.B.; van Tilburg, W.A.; Igou, E.R.; Wisman, A.; Donnelly, A.E.; Mulcaire, J.B. Eaten up by boredom: Consuming food to escape awareness of the bored self. Front. Psychol. 2015, 6, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, M.; Ponzo, V.; Rosato, R.; Scumaci, E.; Goitre, I.; Benso, A.; Belcastro, S.; Crespi, C.; De Michieli, F.; Ghigo, E.; et al. Changes in Weight and Nutritional Habits in Adults with Obesity during the “Lockdown” Period Caused by the COVID-19 Virus Emergency. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petitte, T.; Mallow, J.; Barnes, E.; Petrone, A.; Barr, T.; Theeke, L. A systematic review of loneliness and common chronic physical conditions in adults. Open Psychol. J. 2015, 8, 113e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaudias, V.; Iceta, S.; Zerhouni, O.; Rodgers, R.F.; Billieux, J.; Llorca, P.M.; Boudesseul, J.; de Chazeron, I.; Romo, L.; Maurage, P.; et al. COVID-19 pandemic lockdown and problematic eating behaviors in a student population. J. Behav. Addict. 2020, 9, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, M.; Langiano, E.; Falese, L.; Diotaiuti, P.; Cortis, C.; De Vito, E. Changes in Physical Activity Levels and Eating Behaviours during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Sociodemographic Analysis in University Students. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 5550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandell, C.; Saltychev, M. Change in alcohol consumption and physical activity during the COVID-19 pandemic amongst 76 medical students. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.T.; Kannan, T.M. Comparison of eating behaviour by relative weight change status of young adults throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. Dialogues Health 2023, 2, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baceviciene, M.; Jankauskiene, R. Changes in sociocultural attitudes towards appearance, body image, eating attitudes and behaviours, physical activity, and quality of life in students before and during COVID-19 lockdown. Appetite 2021, 166, 105452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosendiak, A.A.; Wysocki, M.P.; Krysiński, P.P. Lifestyle, Physical Activity and Dietary Habits of Medical Students of Wroclaw Medical University during the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stănilă, A.M.; Oraviţan, M.; Matichescu, M.L.; Stănilă, C.V.; Avram, C.A.; Almăjan-Guţă, B.; Avram, C. Factors predisposing to weight gain in young adults during COVID-19 home confinement. Timisoara Phys. Educ. Rehabil. J. 2021, 14, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urhan, M.; Okut Aysin, E. Nutritional and health behaviour predictors of the weight gain during the COVID-19 pandemic. Eur. J. Nutr. 2022, 61, 2993–3002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidor, A.; Rzymski, P. Dietary choices and habits during COVID-19 lockdown: Experience from Poland. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drieskens, S.; Berger, N.; Vandevijvere, S.; Gisle, L.; Braekman, E.; Charafeddine, R.; De Ridder, K.; Demarest, S. Short-term impact of the COVID-19 confinement measures on health behaviours and weight gain among adults in Belgium. Arch. Public Health 2021, 79, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowring, A.L.; Peeters, A.; Freak-Poli, R.; Lim, M.S.; Gouillou, M.; Hellard, M. Measuring the accuracy of self-reported height and weight in a community-based sample of young people. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2012, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoong, S.L.; Carey, M.L.; D’Este, C.; Sanson-Fisher, R.W. Agreement between self-reported and measured weight and height collected in general practice patients: A prospective study. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2013, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
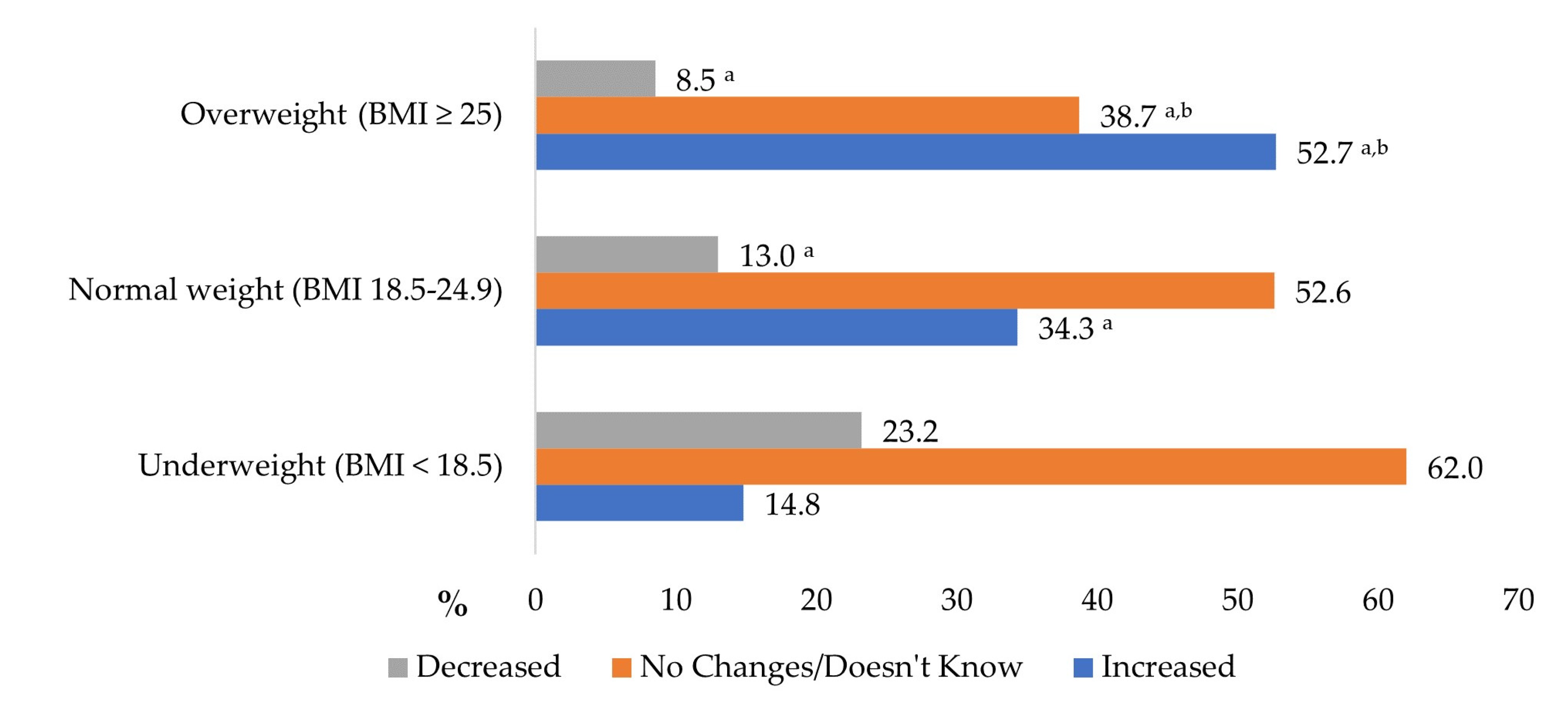
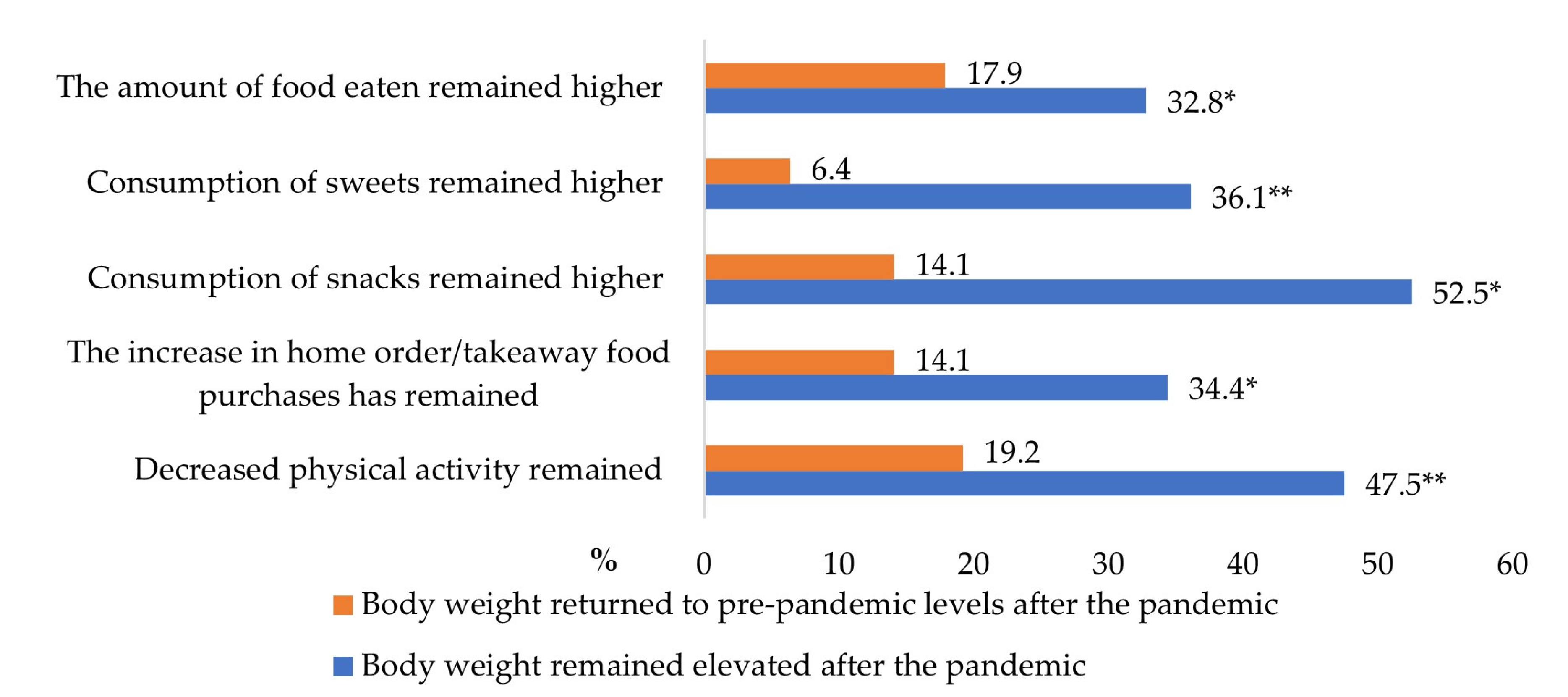
| Characteristics | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Male | 325 | 22.7 |
| Female | 1105 | 77.3 |
| Age groups | ||
| 18–19 years | 640 | 44.8 |
| 20 years and older | 790 | 55.2 |
| Place of study | ||
| Vilnius University of Applied Sciences | 508 | 35.6 |
| Kaunas University of Applied Sciences | 579 | 40.5 |
| Klaipeda State University of Applied Sciences | 176 | 12.3 |
| Siauliai State University of Applied Sciences | 167 | 11.7 |
| Body mass index | ||
| <18.5 kg/m2 | 142 | 9.9 |
| 18.5–24.9 kg/m2 | 936 | 65.4 |
| ≥25 kg/m2 | 262 | 24.7 |
| Variables | Changes | p-Value (χ2 Test) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increased | Remained as Usual | Decreased | |||||
| M | F | M | F | M | F | ||
| Consumption of red meat | 6.9 | 6.5 | 82.9 * | 91.7 | 10.2 * | 1.8 | 0.001 |
| Consumption of porridge, flakes | 14.6 | 11.7 | 77.3 * | 85.2 | 8.1 * | 3.1 | 0.002 |
| Consumption of fresh vegetables | 21.4 * | 15.7 | 72.7 * | 83.1 | 5.9 * | 1.2 | <0.001 |
| Consumption of boiled, pickled vegetables | 11.8 * | 5.2 | 82.9 * | 92.3 | 5.3 * | 2.5 | <0.001 |
| Consumption of fresh fruits or berries | 21.4 | 17.2 | 72.6 * | 80.9 | 6.0 * | 1.8 | 0.002 |
| Consumption of nuts, seeds | 12.9 | 11.7 | 79.7 * | 86.5 | 7.4 * | 1.8 | 0.001 |
| Consumption of home-made confectionery | 21.1 * | 14.5 | 70.2 * | 82.8 | 8.7 * | 2.8 | <0.001 |
| Consumption of sweets | 20.8 | 16.0 | 71.1 * | 80.0 | 8.1 * | 4.0 | 0.003 |
| Consumption of sweetened beverages | 13.2 * | 7.1 | 69.9 * | 80.3 | 16.9 * | 12.6 | 0.001 |
| Consumption of fast food | 23.2 * | 14.8 | 62.4 * | 74.8 | 14.4 | 10.5 | <0.001 |
| Consumption of snacks | 33.7 * | 24.1 | 60.9 * | 73.5 | 5.3 * | 2.5 | <0.001 |
| Amount of food ordered for home delivery/takeaway | 21.9 | 21.2 | 66.0 | 68.2 | 12.1 | 10.6 | 0.88 |
| Physical activity | 15.1 * | 7.7 | 50.0 * | 59.1 | 34.9 | 33.2 | 0.001 |
| Body weight | 31.1 * | 38.7 | 61.2 * | 46.8 | 7.7 * | 14.5 | <0.001 |
| Food Products | Frequency of Consumption of the Food Product after the COVID-19 Pandemic | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1–4 Times a Month or Less (Ref) | At Least Several Times a Week | Daily | |||||
| OR ** | 95% CI | p-Value | OR ** | 95% CI | p-Value | ||
| Red meat | 1 | 4.0 | 2.0–8.2 | <0.001 | 7.4 | 3.4–16.1 | <0.001 |
| Poultry | 1 | 4.8 | 2.4–9.7 | <0.001 | 3.4 | 1.8–6.7 | <0.001 |
| Meat products | 1 | 2.1 | 1.4–3.3 | 0.001 | 3.3 | 1.8–5.6 | <0.001 |
| Fish and seafood | 1 | 3.3 | 2.3–4.9 | <0.001 | 2.9 | 1.3–6.5 | 0.009 |
| Fermented cheese | 1 | 2.2 | 1.3–3.8 | 0.003 | 3.3 | 1.0–6.3 | <0.001 |
| Milk and milk products | 1 | 2.0 | 1.1–3.4 | 0.02 | 3.1 | 1.8–5.4 | <0.001 |
| Porridge | 1 | 0.3 | 0.2–0.4 | <0.001 | 0.2 | 0.1–0.3 | <0.001 |
| Legumes | 1 | 4.7 | 2.9–7.5 | <0.001 | 9.0 | 4.6–17.7 | <0.001 |
| Nuts | 1 | 4.0 | 2.6–6.1 | <0.001 | 6.0 | 3.8–9.4 | <0.001 |
| Fresh vegetables | 1 | 1.6 | 0.9–2.8 | 0.08 | 3.5 | 2.0–5.9 | <0.001 |
| Fresh fruits and berries | 1 | 2.3 | 1.5–3.5 | <0.001 | 4.5 | 3.0–6.8 | <0.001 |
| Confectionery | 1 | 2.2 | 1.6–3.0 | <0.001 | 4.3 | 2.8–6.7 | <0.001 |
| Sweets | 1 | 2.8 | 2.0–3.9 | <0.001 | 4.7 | 3.2–7.0 | <0.001 |
| Soft drinks | 1 | 3.5 | 2.4–5.0 | <0.001 | 6.7 | 4.3–1.5 | <0.001 |
| Energy drinks | 1 | 7.6 | 5.1–11.1 | <0.001 | 13.5 | 7.8–23.4 | 0.001 |
| Fast food | 1 | 3.9 | 3.0–5.2 | <0.001 | 2.5 | 1.3–4.7 | <0.001 |
| Unhealthy snacks | 1 | 1.5 | 1.1–1.9 | 0.004 | 1.5 | 0.9–2.6 | 0.09 |
| Food Products | Sex | Frequency of Consumption of the Food Product | p-Value (χ2 Test) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | At Least Several Times a Week | 1–4 Times a Month or Less Frequently | |||
| Red meat (pork, beef) | M | 28.3 * | 55.7 | 16.0 * | <0.001 |
| F | 12.9 | 53.7 | 33.4 | ||
| Poultry (chicken, turkey) | M | 31.9 * | 54.2 * | 13.9 * | <0.001 |
| F | 17.6 | 63.6 | 18.8 | ||
| Meat products | M | 15.8 * | 45.8 * | 38.4 * | <0.001 |
| F | 7.9 | 38.7 | 53.4 | ||
| Fish and seafood | M | 5.8 * | 5.8 * | 58.8 * | <0.001 |
| F | 3.3 | 3.3 | 71.2 | ||
| Fermented cheese | M | 18.3 * | 46.9 | 34.8 * | 0.01 |
| F | 12.4 | 46.7 | 40.9 | ||
| Milk and milk products | M | 33.0 | 44.4 | 22.5 | 0.66 |
| F | 35.1 | 41.7 | 23.2 | ||
| Porridge | M | 20.3 | 40.9 | 38.8 | 0.29 |
| F | 17.8 | 38.7 | 43.5 | ||
| Legumes | M | 6.8 | 36.4 * | 56.8 * | 0.008 |
| F | 4.9 | 29.0 | 66.1 | ||
| Nuts | M | 22.2 | 40.6 * | 37.2 * | 0.006 |
| F | 19.9 | 33.0 | 47.1 | ||
| Fresh vegetables | M | 36.9 * | 46.8 * | 16.3 * | <0.001 |
| F | 50.3 | 39.4 | 10.3 | ||
| Fresh fruits and berries | M | 28.9 * | 42.5 | 28.6 | 0.02 |
| F | 36.7 | 39.9 | 23.4 | ||
| Confectionery | M | 12.3 | 34.5 | 53.2 | 0.15 |
| F | 8.7 | 36.4 | 54.9 | ||
| Sweets | M | 18.2 | 39.1 | 42.8 | 0.25 |
| F | 14.6 | 42.6 | 42.8 | ||
| Soft drinks | M | 15.8 * | 15.8 * | 48.3 * | <0.001 |
| F | 9.9 | 9.9 | 63.6 | ||
| Energy drinks | M | 7.1 | 29.1 * | 63.8 * | <0.001 |
| F | 5.3 | 19.1 | 75.6 | ||
| Fast food | M | 5.8 * | 33.8 * | 60.3 * | <0.001 |
| F | 2.9 | 21.8 | 75.3 | ||
| Unhealthy snacks | M | 8.0 * | 36.6 * | 55.4 * | <0.001 |
| F | 4.0 | 25.5 | 70.5 | ||
| Variables | Changes in Health Behavior | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increased | Remained as Usual | Decreased | p-Value (χ2 Test) | |
| Consumption of red meat | 70.1 | 34.2 * | 37.8 * | <0.001 |
| Consumption of meat products | 63.4 | 34.2 * | 38.4 * | <0.001 |
| Consumption of porridge, flakes | 48.7 | 33.3 * | 54.5 | <0.001 |
| Consumption of fresh vegetables | 55.4 | 30.9 * | 55.1 | <0.001 |
| Consumption of fresh fruits or berries | 53.8 | 31.4 * | 51.4 | <0.001 |
| Consumption of nuts, seeds | 57.2 | 32.5 * | 53.4 | <0.001 |
| Consumption of purchased confectionery | 63.5 | 31.6 * | 36.1 * | <0.001 |
| Consumption of home-made confectionery | 58.6 | 31.2 * | 36.2 * | <0.001 |
| Consumption of sweets | 59.9 | 30.8 * | 36.3 * | <0.001 |
| Consumption of sweetened beverages | 64.7 | 30.9 * | 43.5 * | <0.001 |
| Consumption of fast food | 61.2 | 27.7 * | 43.5 * | <0.001 |
| Consumption of snacks | 60.4 | 26.2 * | 25.4 * | <0.001 |
| Amount of food ordered for home delivery/takeaway | 65.3 | 20.5 * | 51.0 | <0.001 |
| Physical activity | 35.4 | 20.8 * | 61.9 * | <0.001 |
| Variables | OR | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Females vs. males | 1.5 | 1.1–2.1 | 0.007 |
| Increased consumption of red meat * | 2.6 | 1.6–4.4 | <0.001 |
| Increased consumption of homemade confectionery * | 1.5 | 1.1–2.1 | 0.01 |
| Increased consumption of fast food * | 1.7 | 1.2–2.4 | 0.003 |
| Increased consumption of snacks * | 1.9 | 1.3–2.6 | <0.001 |
| Decreased physical activity ** | 3.8 | 2.9–5.0 | <0.001 |
| BMI after COVID 19 pandemic # | 1.2 | 1.1–1.2 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kriaučionienė, V.; Grincaitė, M.; Raskilienė, A.; Petkevičienė, J. Changes in Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Body Weight among Lithuanian Students during and after the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4091. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184091
Kriaučionienė V, Grincaitė M, Raskilienė A, Petkevičienė J. Changes in Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Body Weight among Lithuanian Students during and after the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nutrients. 2023; 15(18):4091. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184091
Chicago/Turabian StyleKriaučionienė, Vilma, Monika Grincaitė, Asta Raskilienė, and Janina Petkevičienė. 2023. "Changes in Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Body Weight among Lithuanian Students during and after the COVID-19 Pandemic" Nutrients 15, no. 18: 4091. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184091
APA StyleKriaučionienė, V., Grincaitė, M., Raskilienė, A., & Petkevičienė, J. (2023). Changes in Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Body Weight among Lithuanian Students during and after the COVID-19 Pandemic. Nutrients, 15(18), 4091. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15184091










