Postnatal Overfeeding in Rodents Induces a Neurodevelopment Delay and Anxious-like Behaviour Accompanied by Sex- and Brain-Region-Specific Synaptic and Metabolic Changes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
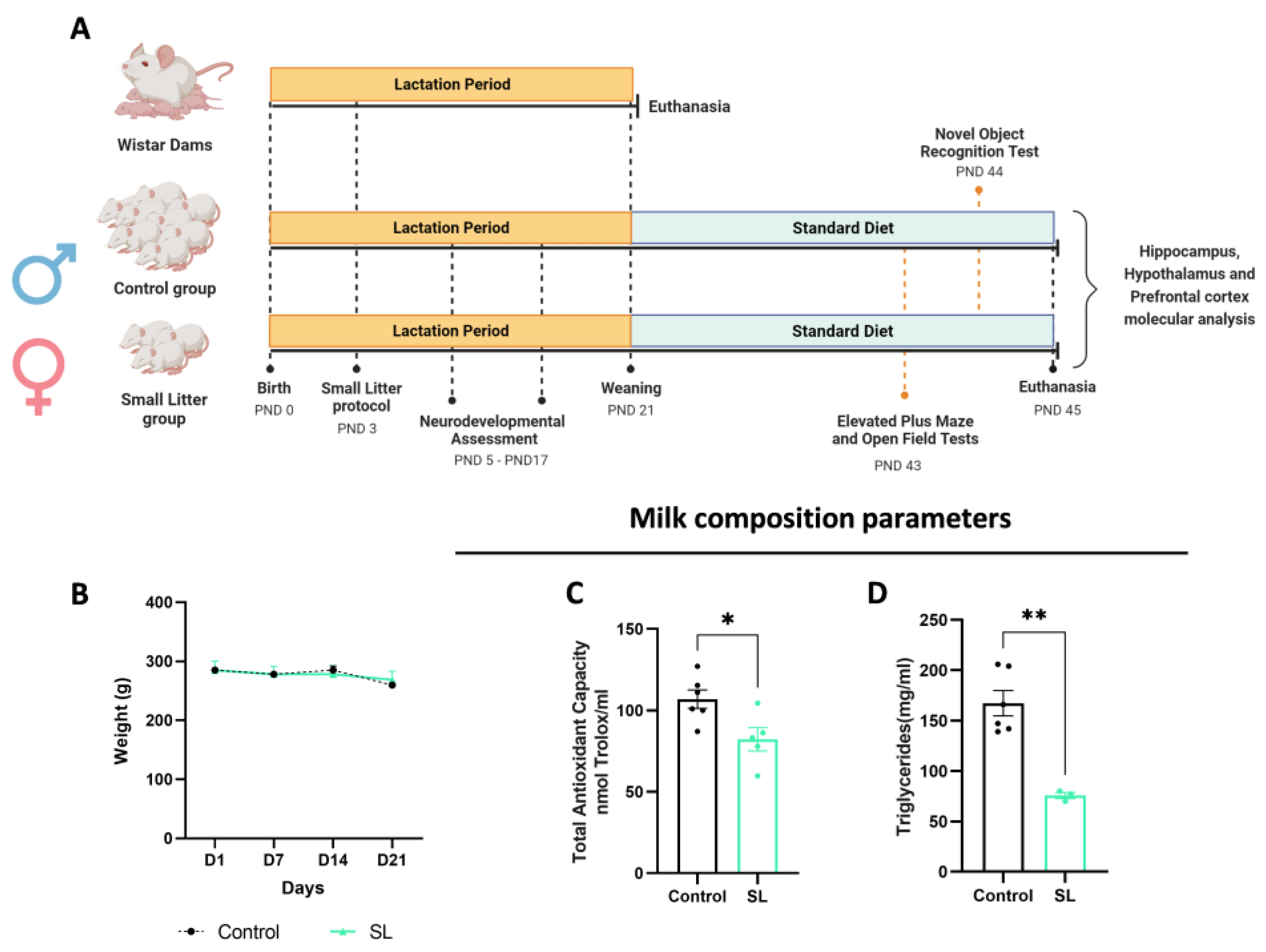
2.1. Animal Maintenance and Experimental Design
2.2. Maternal Milk Collection and Composition Analysis
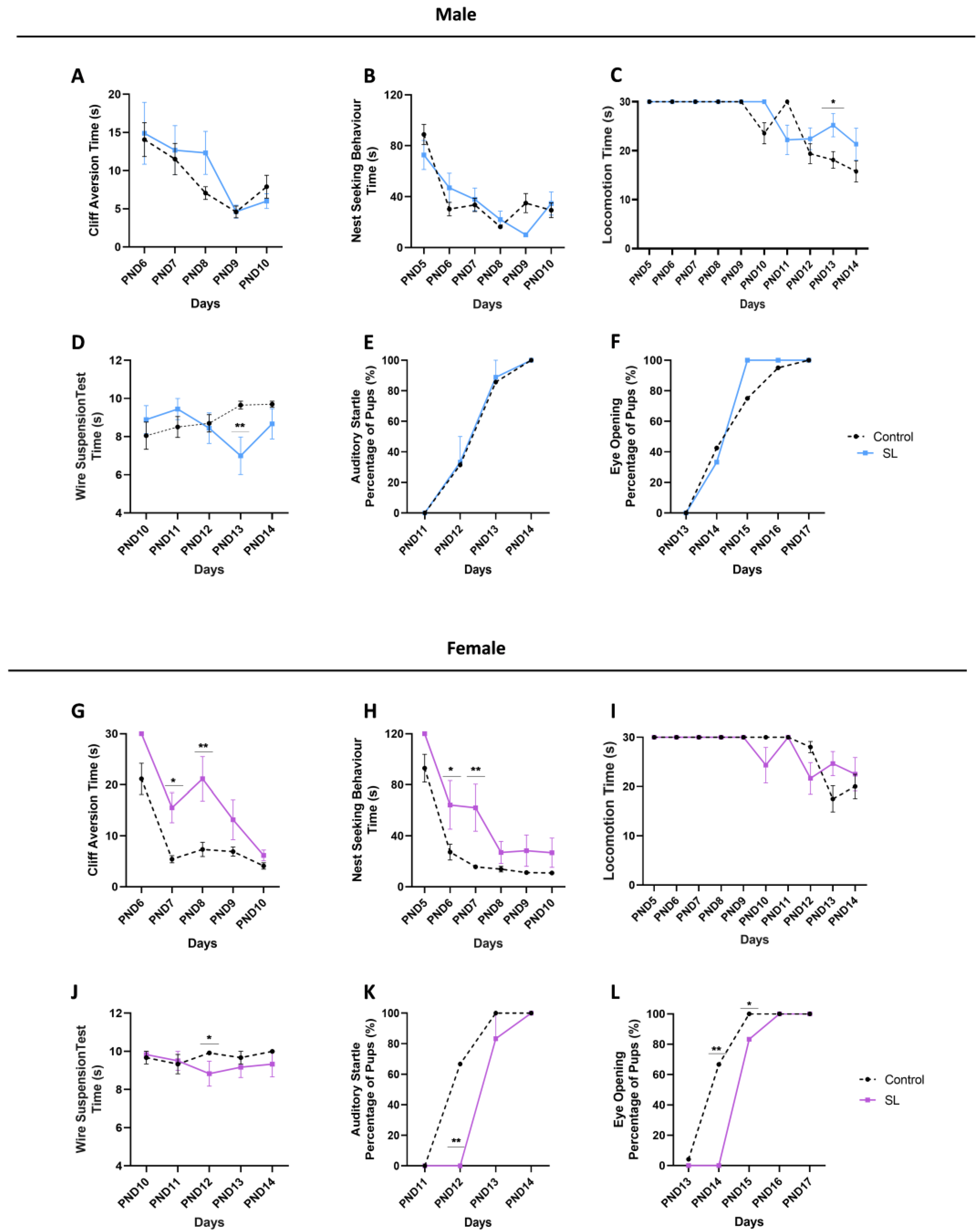
2.3. Infancy Neurodevelopmental Tests
2.3.1. Cliff Aversion
2.3.2. Nest Seeking Behaviour
2.3.3. Wire Suspension Test
2.3.4. Locomotion
2.3.5. Auditory Startle
2.3.6. Eye Opening
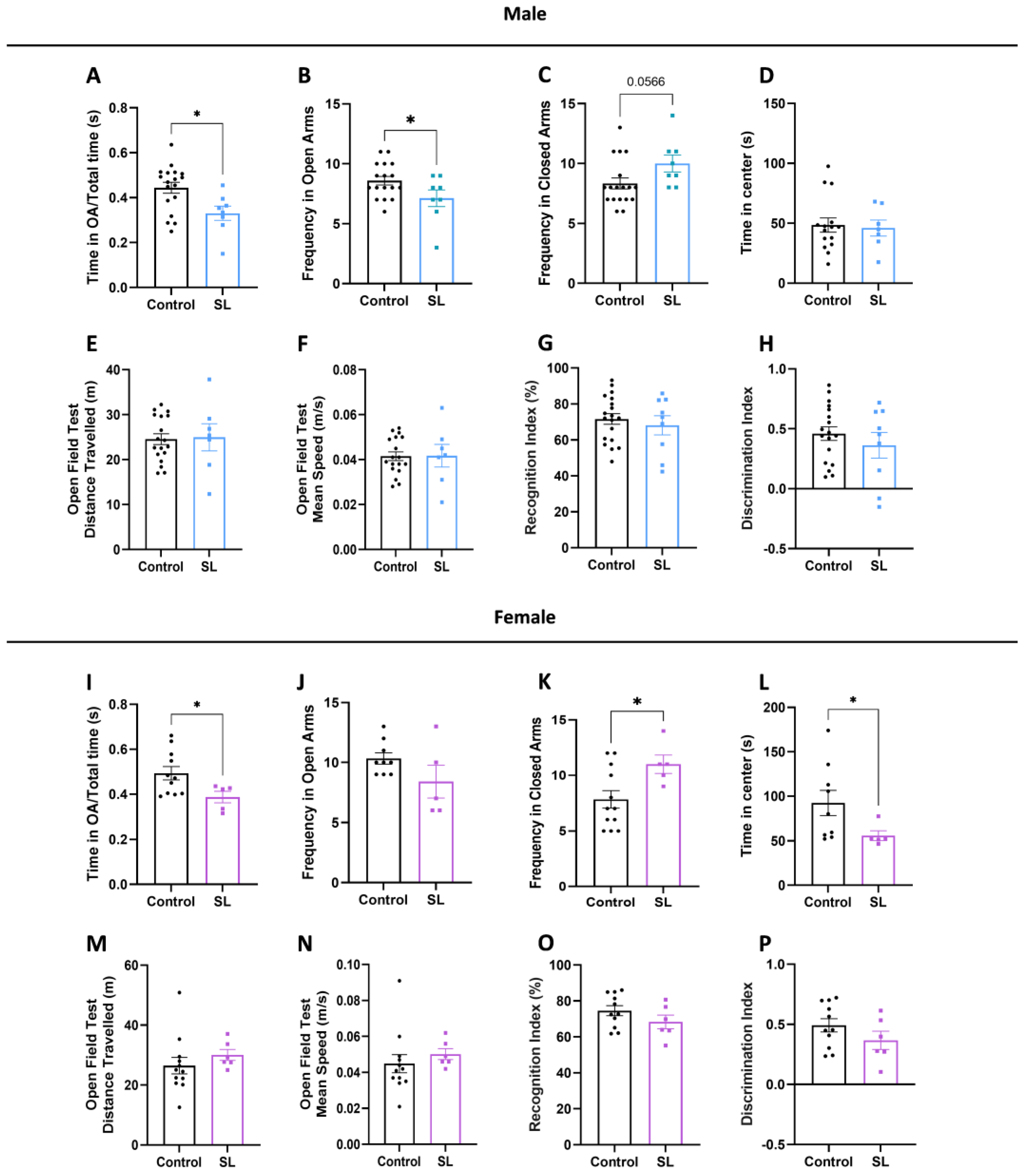
2.4. Middle Adolescence Behavioural Tests
2.4.1. Open Field Test (OPF)
2.4.2. Elevated plus Maze Test (EPM)
2.4.3. Novel Object Recognition Test (NOR)
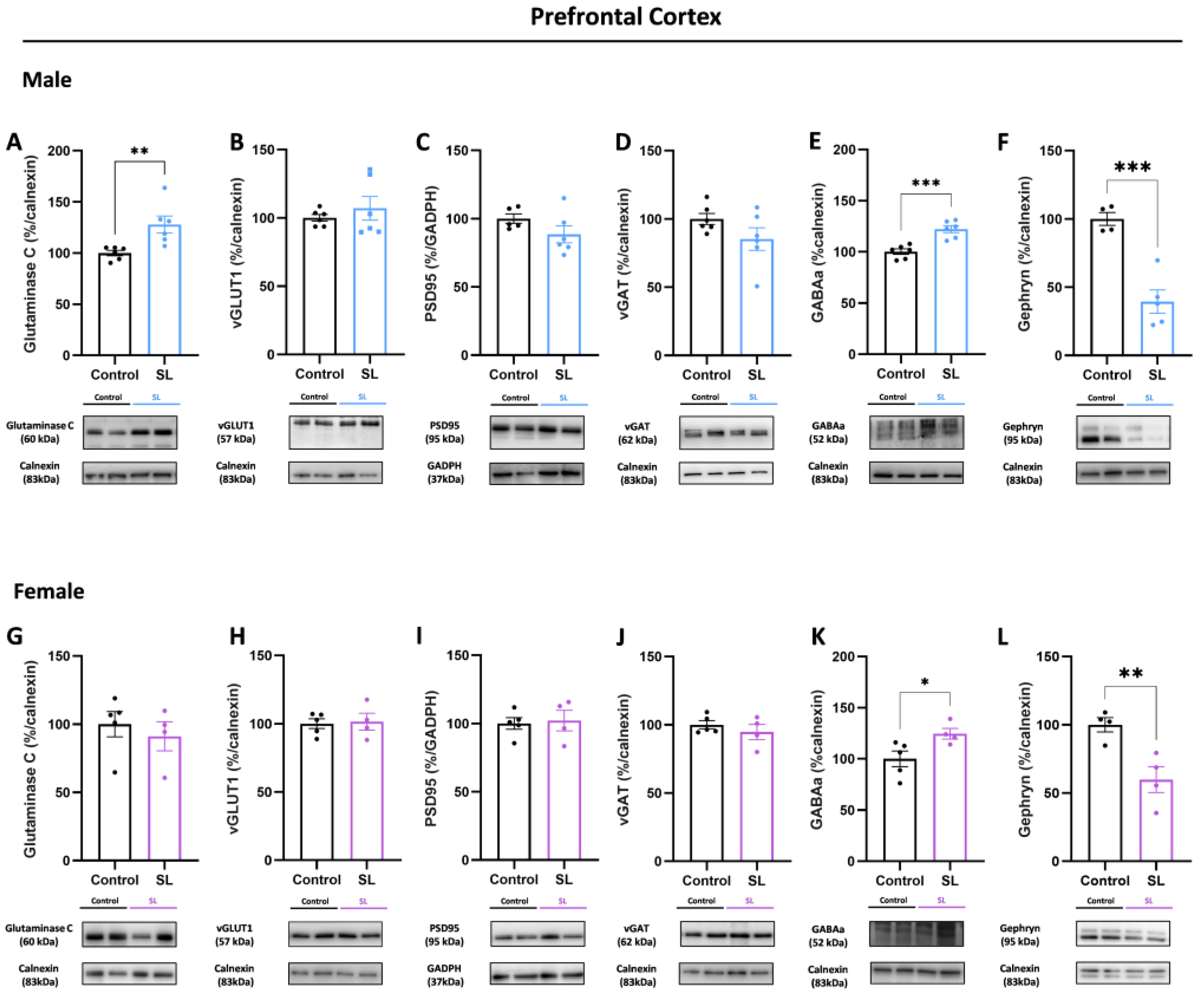
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Postnatal Overfeeding Modifies Milk Composition and Quality
3.2. Postnatal Overfeeding Induces a Sex-Dependent Neurodevelopmental Delay
3.3. Postnatal Overfeed Display an Anxious-like Behaviour in Both Males and Females
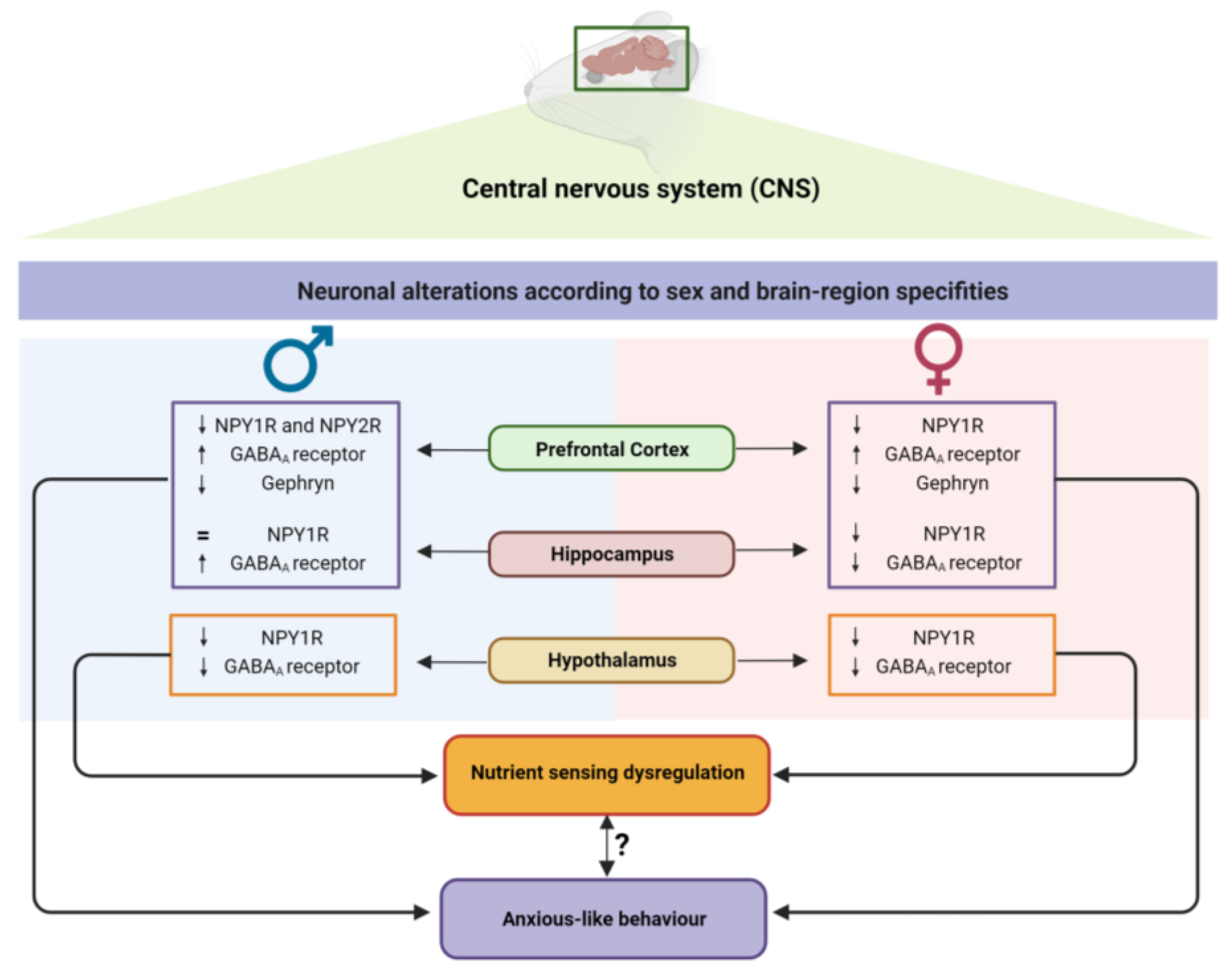
3.4. Sex-and Brain-Region-Specific Alterations in NPY System upon Overfeeding Conditions
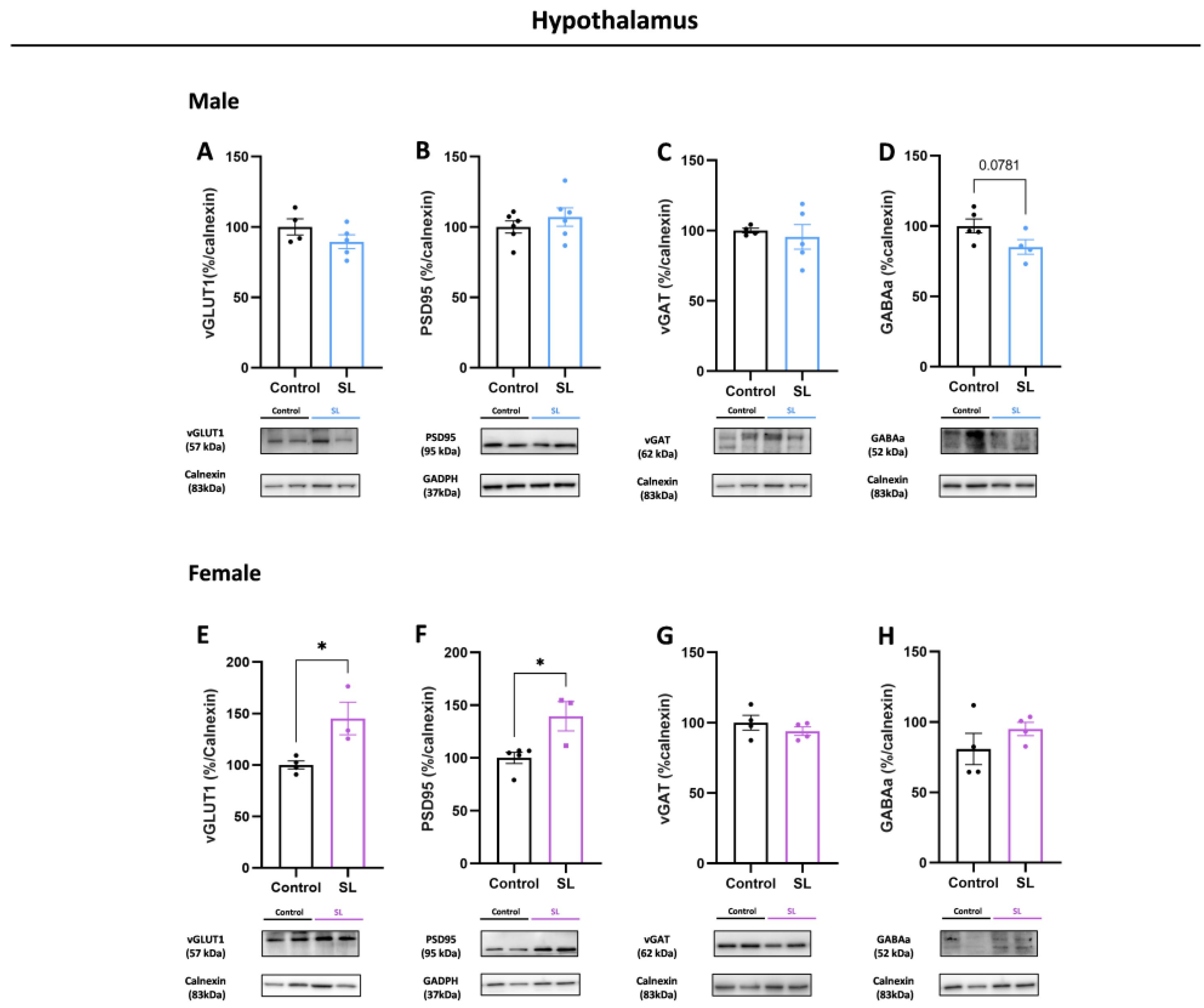
3.5. Early Overfeeding Induces a Sex- and Brain-Region-Specific Synaptic Imbalance
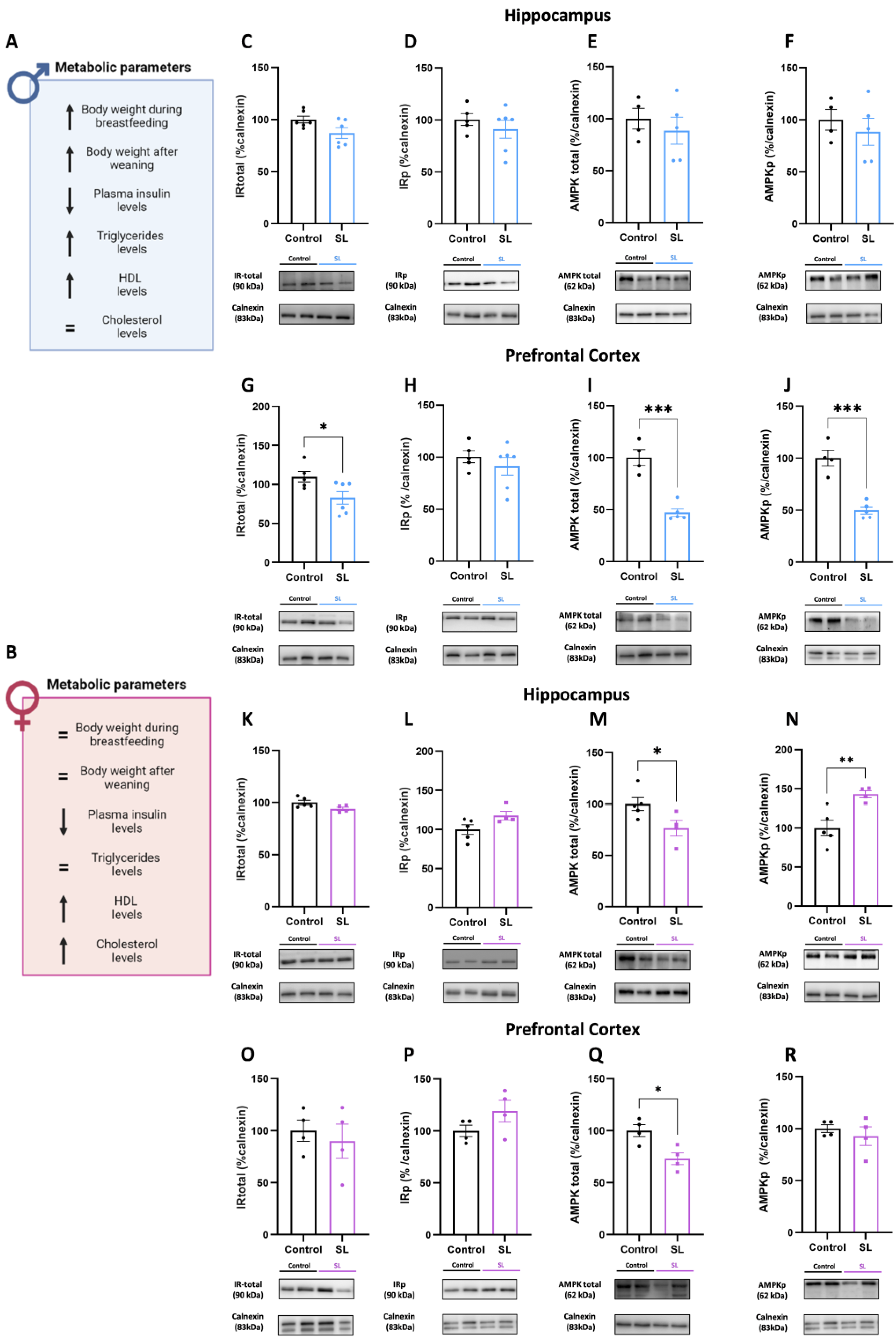
3.6. Postnatal Overfeeding Modulates AMPK Signalling in a Sex- and Brain-Region-Specific Manner
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amaro, A.; Baptista, F.I.; Matafome, P. Programming of future generations during breastfeeding: The intricate relation between metabolic and neurodevelopment disorders. Life Sci. 2022, 298, 120526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford-Smith, D.E.; Anthony, D.C. Mechanisms of Maternal Diet-Induced Obesity Affecting the Offspring Brain and Development of Affective Disorders. Metabolites 2023, 13, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, L.L.; Moura, E.G.; Lisboa, P.C. Litter Size Reduction as a Model of Overfeeding during Lactation and Its Consequences for the Development of Metabolic Diseases in the Offspring. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozeš, Š.; Šefčíková, Z.; Raček, L. Long-term effect of altered nutrition induced by litter size manipulation and cross-fostering in suckling male rats on development of obesity risk and health complications. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, 53, 1273–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habbout, A.; Li, N.; Rochette, L.; Vergely, C. Postnatal Overfeeding in Rodents by Litter Size Reduction Induces Major Short- and Long-Term Pathophysiological Consequences. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavas, M.M.; Kirigiti, M.A.; Xiao, X.Q.; Enriori, P.J.; Fisher, S.K.; Evans, A.E.; Grayson, B.E.; Cowley, M.A.; Smith, M.S.; Grove, K.L. Early Overnutrition Results in Early-Onset Arcuate Leptin Resistance and Increased Sensitivity to High-Fat Diet. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 1598–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junior, M.D.F.; Cavalcante, K.V.N.; Ferreira, L.A.; Lopes, P.R.; Pontes, C.N.R.; de Bessa, A.d.S.M.; Neves, Â.R.; Francisco, F.A.; Pedrino, G.R.; Xavier, C.H.; et al. Postnatal early overfeeding induces cardiovascular dysfunction by oxidative stress in adult male Wistar rats. Life Sci. 2019, 226, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salari, A.-A.; Samadi, H.; Homberg, J.R.; Kosari-Nasab, M. Small litter size impairs spatial memory and increases anxiety- like behavior in a strain-dependent manner in male mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enes-Marques, S.; Giusti-Paiva, A. Litter size reduction accentuates maternal care and alters behavioral and physiological phenotypes in rat adult offspring. J. Physiol. Sci. 2018, 68, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz-Guertin, J.M.; Jacob, T.C. GABA type a receptor trafficking and the architecture of synaptic inhibition. Dev. Neurobiol. 2018, 78, 238–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcher, C.; Medina, I.; Gaiarsa, J.-L. Mechanism of BDNF Modulation in GABAergic Synaptic Transmission in Healthy and Disease Brains. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naderipoor, P.; Amani, M.; Abedi, A.; Sakhaie, N.; Sadegzadeh, F.; Saadati, H. Alterations in the behavior, cognitive function, and BDNF level in adult male rats following neonatal blockade of GABA-A receptors. Brain Res. Bull. 2021, 169, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, L.O.; Carvalho, M.J.; Costa, J.; Ferreira, P.A.; Guedes, J.R.; Sousa, R.; Edfawy, M.; Seabra, C.M.; Cardoso, A.L.; Peça, J. Social subordination induced by early life adversity rewires inhibitory control of the prefrontal cortex via enhanced Npy1r signaling. Neuropsychopharmacology 2020, 45, 1438–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfrum, C.; Peleg-Raibstein, D. Maternal overnutrition leads to cognitive and neurochemical abnormalities in C57BL/6 mice. Nutr. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, J.; Boureau, P.; Moyon, T.; Nicklaus, S.; Parnet, P.; Paillé, V. Perinatal Western Diet Consumption Leads to Profound Plasticity and GABAergic Phenotype Changes within Hypothalamus and Reward Pathway from Birth to Sexual Maturity in Rat. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Luo, X.; Zhang, C. Emerging role of hypothalamus in the metabolic regulation in the offspring of maternal obesity. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1094616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timper, K.; Brüning, J.C. Hypothalamic circuits regulating appetite and energy homeostasis: Pathways to obesity. Dis. Model. Mech. 2017, 10, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrenho, D.; Santos, S.D.; Carvalho, A.L. The Role of Ghrelin in Regulating Synaptic Function and Plasticity of Feeding-Associated Circuits. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Kim, Y.J.; Chao, P.-T.; Bi, S. Overexpression of Neuropeptide Y in the Dorsomedial Hypothalamus Causes Hyperphagia and Obesity in Rats. Obesity 2013, 21, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumbs, M.; Eggels, L.; Kool, T.; Unmehopa, U.; Heuvel, J.V.D.; Lamuadni, K.; Mul, J.; la Fleur, S. Neuropeptide Y Signaling in the Lateral Hypothalamus Modulates Diet Component Selection and is Dysregulated in a Model of Diet-Induced Obesity. Neuroscience 2020, 447, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gøtzsche, C.; Woldbye, D. The role of NPY in learning and memory. Neuropeptides 2016, 55, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heilig, M. The NPY system in stress, anxiety and depression. Neuropeptides 2004, 38, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabban, E.L.; Alaluf, L.G.; Serova, L.I. Potential of neuropeptide Y for preventing or treating post-traumatic stress disorder. Neuropeptides 2016, 56, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tüfekci, K.K.; Bakirhan, E.G.; Terzi, F. A Maternal High-Fat Diet Causes Anxiety-Related Behaviors by Altering Neuropeptide Y1 Receptor and Hippocampal Volumes in Rat Offspring: The Potential Effect of N-Acetylcysteine. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 1499–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, D.; Rocha, M.; Amaro, A.; Ferreira-Junior, M.D.; Cavalcante, K.V.N.; Monteiro-Alfredo, T.; Barra, C.; Rosendo-Silva, D.; Saavedra, L.P.J.; Magalhães, J.; et al. Exposure to Obesogenic Environments during Perinatal Development Modulates Offspring Energy Balance Pathways in Adipose Tissue and Liver of Rodent Models. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiplakou, E.; Mitsiopoulou, C.; Mavrommatis, A.; Karaiskou, C.; Chronopoulou, E.G.; Mavridis, G.; Sotirakoglou, K.; Labrou, N.E.; Zervas, G. Effect of under- and overfeeding on sheep and goat milk and plasma enzymes activities related to oxidation. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2018, 102, e288–e298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-González, G.L.; Bautista, C.J.; Rojas-Torres, K.I.; Nathanielsz, P.W.; Zambrano, E. Importance of the lactation period in developmental programming in rodents. Nutr. Rev. 2020, 78, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisboa, P.C.; Pires, L.; Oliveira, E.D.; Lima, N.S.; Bonomo, I.T.; Reis, A.M.; Passos, M.C.F.; Moura, E.G. Prolactin Inhibition at Mid-lactation Influences Adiposity and Thyroid Function in Adult Rats. Horm. Metab. Res. 2010, 42, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Novais, C.O.; Batista, T.H.; Ribeiro, A.C.A.; Vitor-Vieira, F.; Rojas, V.C.; Ferri, B.G.; Vieira, J.S.; Giusti-Paiva, A.; Vilela, F.C. Maternal overweight induced by reduced litter size impairs the behavioral neurodevelopment of offspring. Life Sci. 2021, 277, 119611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, S.J.; Tilbrook, A. Neonatal overfeeding alters adult anxiety and stress responsiveness. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2009, 34, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- August, P.M.; Rodrigues, K.d.S.; Klein, C.P.; dos Santos, B.G.; Matté, C. Influence of gestational exercise practice and litter size reduction on maternal care. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 741, 135454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorantes-Barrios, C.J.; Domínguez-Salazar, E.; Gonzalez-Flores, O.; Cortés-Barberena, E.; Hurtado-Alvarado, G. Behavioral consequences of postnatal undernutrition and enriched environment during later life. Physiol. Behav. 2021, 241, 113566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira-Silva, J.; Lisboa, P.C.; Lotufo-Denucci, B.; Fraga, M.; de Moura, E.G.; Nunes, F.C.; Ribeiro-Carvalho, A.; Filgueiras, C.C.; Abreu-Villaça, Y.; Manhães, A.C. Maternal protein restriction during the lactation period disrupts the ontogenetic development of behavioral traits in male Wistar rat offspring. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2023, 14, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilbo, S.D.; Tsang, V. Enduring consequences of maternal obesity for brain inflammation and behavior of offspring. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 2104–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.R.; Valleau, J.C.; Barling, A.N.; Franco, J.G.; DeCapo, M.; Bagley, J.L.; Sullivan, E.L. Exposure to a High-Fat Diet during Early Development Programs Behavior and Impairs the Central Serotonergic System in Juvenile Non-Human Primates. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winther, G.; Eskelund, A.; Bay-Richter, C.; Elfving, B.; Müller, H.K.; Lund, S.; Wegener, G. Grandmaternal high-fat diet primed anxiety-like behaviour in the second-generation female offspring. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 359, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glendining, K.A.; Fisher, L.C.; Jasoni, C.L. Maternal high fat diet alters offspring epigenetic regulators, amygdala glutamatergic profile and anxiety. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 96, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boullu-Ciocca, S.; Dutour, A.; Guillaume, V.; Achard, V.; Oliver, C.; Grino, M. Postnatal Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats Upregulates Systemic and Adipose Tissue Glucocorticoid Metabolism during Development and in Adulthood. Diabetes 2005, 54, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, E.L.; DeJoseph, M.R.; Brownfield, M.S.; Urban, J.H. Involvement of Neuropeptide Y Y1 Receptors in the Regulation of Neuroendocrine Corticotropin-Releasing Hormone Neuronal Activity. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 3666–3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schumacher, R.; Rossetti, M.F.; Lazzarino, G.P.; Canesini, G.; García, A.P.; Stoker, C.; Andreoli, M.F.; Ramos, J.G. Temporary effects of neonatal overfeeding on homeostatic control of food intake involve alterations in POMC promoter methylation in male rats. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2021, 522, 111123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziko, I.; De Luca, S.; Dinan, T.; Barwood, J.M.; Sominsky, L.; Cai, G.; Kenny, R.; Stokes, L.; Jenkins, T.A.; Spencer, S.J. Neonatal overfeeding alters hypothalamic microglial profiles and central responses to immune challenge long-term. Brain Behav. Immun. 2014, 41, 32–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidel, E.; Plagemann, A.; Davidowa, H. Increased response to NPY of hypothalamic VMN neurons in postnatally overfed juvenile rats. Neuroreport 1999, 10, 1827–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, E.; Ciofi, P.; Prevot, V.; Bouret, S.G. Alteration in Neonatal Nutrition Causes Perturbations in Hypothalamic Neural Circuits Controlling Reproductive Function. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 11486–11494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.L.; de Moura, E.G.; Passos, M.C.F.; Trevenzoli, I.H.; da Conceição, E.P.S.; Bonono, I.T.; Neto, J.F.N.; Lisboa, P.C. Postnatal early overfeeding induces hypothalamic higher SOCS3 expression and lower STAT3 activity in adult rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampieri, T.T.; Bohlen, T.M.; Silveira, M.A.; Lana, L.C.; de Paula, D.G.; Donato, J.; Frazao, R. Postnatal Overnutrition Induces Changes in Synaptic Transmission to Leptin Receptor-Expressing Neurons in the Arcuate Nucleus of Female Mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eva, C.; Serra, M.; Mele, P.; Panzica, G.; Oberto, A. Physiology and gene regulation of the brain NPY Y1 receptor. Front. Neuroendocr. 2006, 27, 308–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichmann, F.; Holzer, P. Neuropeptide Y: A stressful review. Neuropeptides 2016, 55, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertocchi, I.; Oberto, A.; Longo, A.; Mele, P.; Sabetta, M.; Bartolomucci, A.; Palanza, P.; Sprengel, R.; Eva, C. Regulatory functions of limbic Y1 receptors in body weight and anxiety uncovered by conditional knockout and maternal care. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19395–19400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Kim, S.; Ko, J.; Um, J.W. Intracellular signaling mechanisms that shape postsynaptic GABAergic synapses. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2023, 81, 102728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landrigan, J.; Shawaf, F.; Dwyer, Z.; Abizaid, A.; Hayley, S. Interactive effects of ghrelin and ketamine on forced swim performance: Implications for novel antidepressant strategies. Neurosci. Lett. 2018, 669, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutter, M.; Krishnan, V.; Russo, S.J.; Jung, S.; McClung, C.A.; Nestler, E.J. Orexin Signaling Mediates the Antidepressant-Like Effect of Calorie Restriction. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3071–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Primary Antibody | Molecular Weight | Secondary Antibody | Company |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-IR-total | ~90 kDa | Anti-Rabbit | Cell Signaling |
| Anti-IR (phospho Y1361) | ~90 kDA | Anti-Rabbit | Abcam |
| Anti-AMPK-total | ~60 kDa | Anti-Rabbit | Cell Signaling |
| Anti-AMPK (phospho Y172) | ~60 kDa | Anti-Rabbit | Cell Signaling |
| Anti-Glutaminase C | ~66 kDa | Anti-Rabbit | Cell Signaling |
| Anti-vGLUT1 | ~57 kDa | Anti-Rabbit | Abcam |
| Anti-vGAT | ~62 kDa | Anti-Mouse | Abcam |
| Anti-GABAA | ~52 kDa | Anti-Rabbit | Abcam |
| Anti-PSD95 | ~95 kDa | Anti-Rabbit | Cell Signaling |
| Anti-NPY1R | ~52 kDa | Anti-Sheep | Bio-Rad |
| Anti-NPY2R | ~52 kDa | Anti-Goat | Abcam |
| Anti-GHSR1α | ~42 kDa | Anti-Rabbit | Abcam |
| Anti-Gephyrin | ~95 kDa | Anti-Mouse | ThermoFisher |
| Anti-Calnexin | ~83 kDa | Anti-Goat | Sicgen |
| Anti-GADPH | ~37 kDa | Anti-Goat | Sicgen |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amaro, A.; Sousa, D.; Sá-Rocha, M.; Ferreira-Junior, M.D.; Rosendo-Silva, D.; Saavedra, L.P.J.; Barra, C.; Monteiro-Alfredo, T.; Gomes, R.M.; de Freitas Mathias, P.C.; et al. Postnatal Overfeeding in Rodents Induces a Neurodevelopment Delay and Anxious-like Behaviour Accompanied by Sex- and Brain-Region-Specific Synaptic and Metabolic Changes. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163581
Amaro A, Sousa D, Sá-Rocha M, Ferreira-Junior MD, Rosendo-Silva D, Saavedra LPJ, Barra C, Monteiro-Alfredo T, Gomes RM, de Freitas Mathias PC, et al. Postnatal Overfeeding in Rodents Induces a Neurodevelopment Delay and Anxious-like Behaviour Accompanied by Sex- and Brain-Region-Specific Synaptic and Metabolic Changes. Nutrients. 2023; 15(16):3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163581
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmaro, Andreia, Diana Sousa, Mariana Sá-Rocha, Marcos Divino Ferreira-Junior, Daniela Rosendo-Silva, Lucas Paulo Jacinto Saavedra, Cátia Barra, Tamaeh Monteiro-Alfredo, Rodrigo Mello Gomes, Paulo Cezar de Freitas Mathias, and et al. 2023. "Postnatal Overfeeding in Rodents Induces a Neurodevelopment Delay and Anxious-like Behaviour Accompanied by Sex- and Brain-Region-Specific Synaptic and Metabolic Changes" Nutrients 15, no. 16: 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163581
APA StyleAmaro, A., Sousa, D., Sá-Rocha, M., Ferreira-Junior, M. D., Rosendo-Silva, D., Saavedra, L. P. J., Barra, C., Monteiro-Alfredo, T., Gomes, R. M., de Freitas Mathias, P. C., Baptista, F. I., & Matafome, P. (2023). Postnatal Overfeeding in Rodents Induces a Neurodevelopment Delay and Anxious-like Behaviour Accompanied by Sex- and Brain-Region-Specific Synaptic and Metabolic Changes. Nutrients, 15(16), 3581. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163581











