Maternal Bonding as a Protective Factor for Orthorexia Nervosa Risk in Dietetics Students
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants and Procedures
2.2. Sociodemographic, Medical, and Anthropometric Characteristics
2.3. Study Instruments
2.3.1. Mediterranean Diet (MedDiet) Score
2.3.2. ORTO-15 Questionnaire
2.3.3. Eating Attitudes Test (EAT-26)
2.3.4. The Body Image-Acceptance and Action Questionnaire 5 (BI-AAQ-5)
2.3.5. STAI
2.3.6. The Parental Bonding Instrument (PBI)
2.3.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Risk of ON, ED, and Body Image Dissatisfaction, Stress Level, and Parental Bonding Relationship
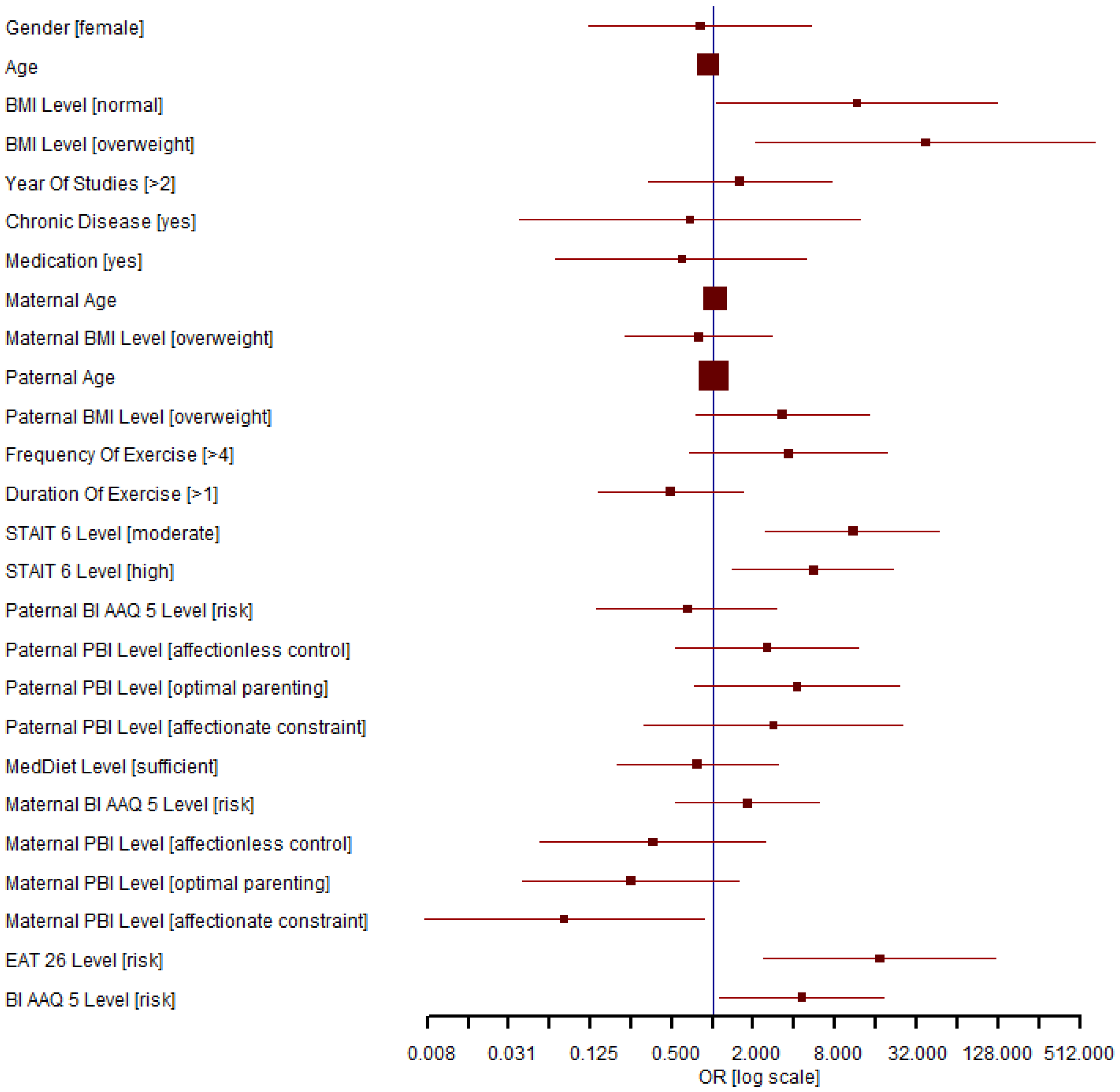
3.3. Factors That Influence the Presence of the Risk of ON
3.4. The Association of the Risk of ON with BMI, Body Image Inflexibility, Risk of ED, Anxiety Level, and Maternal Bonding Relationship
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bratman, S. Health Food Junkie. Yoga J. 1997, 136, 42–50. [Google Scholar]
- Cena, H.; Bathels, F.; Cuzzolaro, M.; Bratman, S.; Brytek-Matera, A.; Dunn, T.; Varga, M.; Missbach, B.; Donini, L.M. Definition and Diagnostic Criteria for Orthorexia Nervosa: A Narrative Review of the Literature. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2019, 24, 209–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, T.M.; Bratman, S. On Orthorexia Nervosa: A Review of the Literature and Proposed Diagnostic Criteria. Eat. Behav. 2016, 21, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedzielski, A.; Kaźmierczak-Wojtaś, N. Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa and Its Diagnostic Tools—A Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karla, S.; Kapoor, N.; Jacob, J. Orthorexia Nervosa. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2020, 70, 1282–1284. [Google Scholar]
- McComb, E.S.; Mills, J.S. Orthorexia Nervosa: A Review of Psychosocial Risk Factors. Appetite 2019, 140, 50–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasundaram, P.; Santhanam, P. Eating Disorders; StatPearls: Tampa, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Caferoglu, Z.; Toklu, H. Orthorexia Nervosa in Turkish Dietitians and Dietetic Students. L’Encéphale 2022, 48, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quick, M.V.; Byrd-Bredbenner, C. Disturbed Eating Behaviours and Associated Psychographic Characteristics of College Students. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 26, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Tan, M. Disordered Eating Behaviors and Food Addiction among Nutrition Major College Students. Nutrients 2016, 8, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caferoglu, Z.; Toklu, H. Intuitive Eating: Associations with Body Weight Status and Eating Attitudes in Dietetic Majors. Eat. Weight Disord. EWD 2022, 27, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Tarawah, R.; Bakr, E.-S. Prevalence of Eating Disorders Among Nutritional Sciences Students and Dietitians in Saudi Arabia. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, D.; Hare, M.S. Dietitians and Eating Disorders: An International Issue. Can. J. Diet. Pract. Res. 2012, 73, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassier, S.; Veldman, F. Eating Behaviour, Eating Attitude and Body Mass Index of Dietetic Students versus Non-Dietetic Majors: A South African Perspective. S. Afr. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 27, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mciver Mahn, H.; Lordly, D. A Review of Eating Disorders and Disordered Eating amongst Nutrition Students and Dietetic Professionals. Can. J. Diet. Pract. Res. 2015, 76, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sürücüoğlu, M.S.; Asil, E. Orthorexia Nervosa in Turkish Dietitians. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2015, 54, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremelling, K.; Sandon, L.; Vega, G.L.; McAdams, J.C. Orthorexia Nervosa and Eating Disorder Symptoms in Dietitians in the United States. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2017, 117, 1612–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poínhos, R.; Alves, D.; Vieira, E.; Pinhão, S.; Oliveira, B.M.P.M.; Correia, F. Eating Behaviour among Undergraduate Students. Comparing Nutrition Students with Other Courses. Appetite 2015, 84, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busatta, D.; Cassioli, E.; Rossi, E.; Campanino, C.; Ricca, V.; Rotella, F. Orthorexia among Patients with Eating Disorders, Student Dietitians and General Population: A Pilot Study. Eat. Weight Disord. EWD 2022, 27, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, Q.J.O.V.; Rodrigues, A.M. Risk Behavior for Orthorexia Nervosa in Nutrition Students. J. Bras. De Psiquiatr. 2014, 63, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccari, G.; Cutino, A.; Luisi, F.; Giambalvo, N.; Daneshmand, S.; Pinelli, M.; Maina, G.; Galeazzi, G.; Kaleci, S.; Albert, U.; et al. Is Orthorexia Nervosa a Feature of Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder? A Multicentric, Controlled Study. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2021, 26, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidan, T.; Ertekin, V.; Işikay, S.; Kirpinar, I. Prevalence of Orthorexia among Medical Students in Erzurum. Compr. Psychiatry 2010, 51, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mealha, V.; Ferreira, C.; Guerra, I.; Ravasco, P. Students of Dietetics & Nutrition—A High Risk Group for Eating Disorders? Nutr. Hosp. 2013, 28, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobera, J.; Ríos, B.; Casals, G. Parenting Styles and Eating Disorders. J. Psychiatr. Ment. Health Nurs. 2011, 18, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampshire, C.; Mahoney, B.; Davis, K.S. Parenting Styles and Disordered Eating Among Youths: A Rapid Scoping Review. Front. Psychol. 2022, 12, 802567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, P. Current Approach to Eating Disorders: A Clinical Update. Intern. Med. J. 2020, 50, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michou, M.; Costarelli, V. Disordered Eating Attitudes in Relation to Anxiety Levels, Self-Esteem and Body Image in Female Basketball Players. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2011, 9, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragkos, K.; Frangos, C. Assessing Eating Disorder Risk: The Pivotal Role of Achievement Anxiety, Depression and Female Gender in Non-Clinical Samples. Nutrients 2013, 5, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petisco-Rodríguez, C.; Sánchez-Sánchez, L.C.; Fernández-García, R.; Sánchez-Sánchez, J.; García-Montes, J.M. Disordered Eating Attitudes, Anxiety, Self-Esteem and Perfectionism in Young Athletes and Non-Athletes. Nutrients 2020, 17, 6754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Healthy Lifestyle—WHO Recommendations. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/news-room/fact-sheets/item/a-healthy-lifestyle---who-recommendations (accessed on 25 July 2023).
- Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Stefanadis, C. Dietary Patterns: A Mediterranean Diet Score and Its Relation to Clinical and Biological Markers of Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2006, 16, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoun, C.; Papazian, T.; Helou, K.; Osta, N.E.; Khabbaz, L.R. Comparison of Five International Indices of Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet among Healthy Adults: Similarities and Differences. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2019, 13, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysohoou, C.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Das, U.N.; Stefanadis, C. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Attenuates Inflammation and Coagulation Process in Healthy Adults: The ATTICA Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 44, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonidakis, F.; Poulopoulou, C.; Michopoulos, I.; Varsou, E. Validation of the Greek ORTO-15 Questionnaire for the Assessment of Orthorexia Nervosa and Its Relation to Eating Disorders Symptomatology. Eat. Weight Disord. 2021, 26, 2471–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donini, L.; Marsili, D.; Graziani, M.; Imbriale, M.; Cannella, C. Orthorexia Nervosa: Validation of a Diagnosis Questionnaire. Eat. Weight Disord. 2005, 10, e28–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrofanova, E.; Pummell, E.; Martinelli, L.; Petróczi, A. Does ORTO-15 Produce Valid Data for ‘Orthorexia Nervosa’? A Mixed-Method Examination of Participants’ Interpretations of the Fifteen Test Items. Eat. Weight Disord. 2021, 26, 897–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douka, A.; Grammatopoulou, E.; Skordilis, E.; Koutsouki, D. Factor Analysis and Cut-off Score of the 26-Item Eating Attitudes Test in a Greek Sample. J. Biol. Exerc. 2009, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papini, N.M.; Jung, M.; Cook, A.; Lopez, N.V.; Ptomey, L.T.; Herrmann, S.D.; Kang, M. Psychometric Properties of the 26-Item Eating Attitudes Test (EAT-26): An Application of Rasch Analysis. J. Eat. Disord. 2022, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karekla, M.; Mavraki, E.; Nikolaou, P.; Koushiou, M. Validation of the Greek Version of the Body Image-Acceptance and Action Questionnaire. Eur. J. Couns. Psychol. 2020, 8, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabdoz, E.; Wilson, K.; Merwin, R.; Kellum, K. Assessment of Body Image Flexibility: The Body Image-Acceptance and Action Questionnaire. J. Context. Behav. Sci. 2013, 2, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basarkod, G.; Sahdra, B.; Ciarroch, J. Body Image—Acceptance and Action Questionnaire—5: An Abbreviation Using Genetic Algorithms. Behav. Ther. 2018, 49, 388–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachari, S.; Jillon, V.W. Measurement Invariance and Psychometric Properties of Three Positive Body Image Measures among Cisgender Sexual Minority and Heterosexual Women. Body Image 2022, 40, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoulakis, K.; Papadopoulou, M.; Kleanthous, S.; Papadopoulou, A.; Bizeli, V.; Nimatoudis, I.; Iacovides, A.; Kaprinis, G. Reliability and Psychometric Properties of the Greek Translation of the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory Form Y: Preliminary Data. Ann. Gen Psychiatry 2006, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayikcioglu, O.; Bilgin, S.; Seymenoglu, G.; Devecib, A. State and Trait Anxiety Scores of Patients Receiving Intravitreal Injections. Biomed. Hub 2017, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emons, W.H.; Habibović, M.; Pedersen, S.S. Prevalence of Anxiety in Patients with an Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator: Measurement Equivalence of the HADS-A and the STAI-S. Qual. Life Res. 2019, 28, 3107–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tluczek, A.; Henriques, J.; Brown, R. Support for the Reliability and Validity of a Six-Item State Anxiety Scale Derived from the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory. J. Nurs. Meas. 2009, 17, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsaousis, I.; Mascha, K.; Giovazolias, T. Can Parental Bonding Be Assessed in Children? Factor Structure and Factorial Invariance of the Parental Bonding Instrument (PBI) between Adults and Children. Child Psychiatry Hum. Dev. 2012, 43, 238–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siomos, K.; Floros, G.; Fisoun, V.; Dafouli, E.; Farkonas, N.; Sergentani, E.; Lamprou, M.; Geroukalis, D. Evolution of Internet Addiction in Greek Adolescent Students over a Two-Year Period: The Impact of Parental Bonding. Eur. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2012, 21, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekhoven, D.J.; Bühlmann, P. MissForest—Non-Parametric Missing Value Imputation for Mixed-Type Data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meule, A.; von Rezori, V.; Blechert, J. Food Addiction and Bulimia Nervosa. Eur. Eat. Disord. Rev. 2014, 22, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Gkiouras, K.; Markaki, A.; Theodoridis, X.; Tsakiri, V.; Mavridis, P.; Dardavessis, T.; Chourdakis, M. Food Addiction, Orthorexia, and Food-Related Stress among Dietetics Students. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2018, 23, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinzl, J.; Hauer, K.; Traweger, C.; Kiefer, I. Orthorexia Nervosa in Dieticians. Psychother. Psychosom. 2006, 75, 395–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarenga, M.S.; Martins, M.C.T.; Sato, K.S.C.J.; Vargas, S.V.A.; Philippi, S.T.; Scagliusi, F.B. Orthorexia Nervosa Behavior in a Sample of Brazilian Dietitians Assessed by the Portuguese Version of ORTO-15. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2012, 17, e29–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, H.; do Carmo, A.; Dos Santos, L. The Brazilian Version of the DOS for the Detection of Orthorexia Nervosa: Transcultural Adaptation and Validation among Dietitians and Nutrition College Students. Eat Weight Disord. 2022, 26, 2713–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, M.A.; Al Hourani, H.M.; Alkhatib, B. Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa among Nutrition Students and Nutritionists: Pilot Study. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2020, 40, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matusik, A.; Grajek, M.; Szlacheta, P.; Korzonek-Szlacheta, I. Comparison of the Prevalence of Eating Disorders among Dietetics Students and Students of Other Fields of Study at Selected Universities (Silesia, Poland). Nutrients 2022, 14, 3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berryman, D.E.; Dubale, G.M.; Manchester, D.S.; Mittelstaedt, R. Dietetics Students Possess Negative Attitudes toward Obesity Similar to Nondietetics Students. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2006, 106, 1678–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syahirah Rusli, N.; Harith, S. Body Mass Index, Eating Habits and Physical Activity Among Dietetics Students in Universiti Sultan Zainal Abidin. J. Nutr. Sci. 2020, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, M.; Barna Konkolÿ, T.; Dukay-Szabó, S.; Túry, F.; van Furth, E.F. When Eating Healthy Is Not Healthy: Orthorexia Nervosa and Its Measurement with the ORTO-15 in Hungary. BMC Psychiatry 2014, 14, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezer, C.; Kabaran, S. The Risk of Orthorexia Nervosa for Female Students Studying Nutrition and Dietetics. SDU J. Health Sci. Inst. 2013, 4, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Dell’Osso, L.; Abelli, M.; Carpita, B.; Massimetti, G.; Pini, S.; Rivetti, L.; Gorrasi, F.; Tognetti, R.; Ricca, V.; Carmassi, C. Orthorexia Nervosa in a Sample of Italian University Population. Riv. Psichiatr. 2016, 51, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinosi, E.; Matarazzo, I.; Marini, S.; Acciavatti, T.; Lupi, M.; Corbo, M.; Santacroce, R.; Vellante, F.; Sarchione, F.; Berardis, D.D.; et al. Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa in a Population of Young Italian Adults. Eur. Psychiatry 2015, 30, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bağci Bosi, A.; Camur, D.; Güler, C. Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa in Resident Medical Doctors in the Faculty of Medicine (Ankara, Turkey). Appetite 2007, 49, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanlier, N.; Yassibas, E.; Bilici, S.; Sahin, G.; Celik, B. Does the Rise in Eating Disorders Lead to Increasing Risk of Orthorexia Nervosa? Correlations with Gender, Education, and Body Mass Index. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2016, 55, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberle, C.D.; Lipschuetz, S.L. Orthorexia Symptoms Correlate with Perceived Muscularity and Body Fat, Not BMI. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2018, 23, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakus, B.; Hidiroglu, S.; Keskin, N.; Karavus, M. Orthorexia Nervosa Tendency among Students of the Department of Nutrition and Dietetics at a University in Istanbul. North Clin. Istanb. 2017, 4, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donini, L.M.; Marsili, D.; Graziani, M.P.; Imbriale, M.; Cannella, C. Orthorexia Nervosa: A Preliminary Study with a Proposal for Diagnosis and an Attempt to Measure the Dimension of the Phenomenon. Eat. Weight Disord. 2004, 9, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camci, N.; Aksoydan, E. Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa among Turkish Performance Artists. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2009, 14, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brytek-Matera, A.; Pardini, S.; Szubert, J.; Novara, C. Orthorexia Nervosa and Disordered Eating Attitudes, Self-Esteem and Physical Activity among Young Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrandrea, P.; Gonidakis, F. Exercise Dependence and Orthorexia Nervosa in Crossfit: Exploring the Role of Perfectionism. Curr. Psychol. 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmborg, J.; Bremander, A.; Olsson, M.; Bergman, S. Health Status, Physical Activity, and Orthorexia Nervosa: A Comparison between Exercise Science Students and Business Students. Appetite 2017, 109, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, S.; Göring, A.; Jetzke, M.; Großarth, D.; Rudolph, H. The Prevalence of Orthorectic Eating Behavior of Student Athletes. Dtsch. Z. Sportmed. 2017, 68, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strahler, J.; Hermann, A.; Walter, B.; Stark, R. Orthorexia Nervosa: A Behavioral Complex or a Psychological Condition? J. Behav. Addict. 2018, 7, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, M.N.; Dundar, C. The Relationship between Orthorexia Nervosa, Anxiety, and Self-Esteem: A Cross-Sectional Study in Turkish Faculty Members. BMC Psychol. 2022, 10, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eker, E. Investigation of the Relationship Between Attachment Patterns and Depression, Self—Injury and Suicidal Behaviour of Eating Disorders Patients. Turk. Klin. J. Forensic Med. Forensic Sci. 2019, 16, 192–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farchakh, Y.; Hallit, S.; Soufia, M. Association between Orthorexia Nervosa, Eating Attitudes and Anxiety among Medical Students in Lebanese Universities: Results of a Cross-Sectional Study. Eat. Weight Disord. 2019, 24, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauzé, A.; Plouffe-Demers, M.; Fiset, D.; Saint-Amour, D.; Blais, C. The Relationship between Orthorexia Nervosa Symptomatology and Body Image Attitudes and Distortion. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R. Is the Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa in an Australian University Population 6.5%? Eat. Weight Disord. 2018, 23, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, M.A.; Caltabiano, M.L. The Interrelationship between Orthorexia Nervosa, Perfectionism, Body Image and Attachment Style. Eat. Weight Disord. Stud. Anorex. Bulim. Obes. 2017, 22, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra-Fernández, M.; Rodríguez-Cano, T.; Onieva-Zafra, M.; Perez-Haro, M.; Casero-Alonso, V.; Fernández-Martinez, E.; Notario-Pacheco, B. Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa in University Students and Its Relationship with Psychopathological Aspects of Eating Behaviour Disorders. BMC Psychiatry 2018, 18, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrada, J.; Roncero, M. Bidimensional Structure of the Orthorexia: Development and Initial Validation of a New Instrument. An. De Psicol. 2018, 34, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, C.; Vieira Borba, V.; Santos, L. Orthorexia Nervosa in a Sample of Portuguese Fitness Participants. Eat. Weight Disord. 2018, 23, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brytek-Matera, A.; Donini, L.M.; Krupa, M.; Poggiogalle, E.; Hay, P. Orthorexia Nervosa and Self-Attitudinal Aspects of Body Image in Female and Male University Students. J. Eat. Disord. 2015, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundros, J.; Clifford, D.; Silliman, K.; Morris, M. Prevalence of Orthorexia Nervosa among College Students Based on Bratman’s Test and Associated Tendencies. Appetite 2016, 101, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atencio-Osorio, M.; Carrillo-Arango, H.; Correa-Rodríguez, M.; Ochoa-Muñoz, A.; Ramírez-Vélez, R. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet in College Students: Evaluation of Psychometric Properties of the KIDMED Questionnaire. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karam, J.; Bibioni, M.; Serhan, M.; Tur, J. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet among Lebanese University Students. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theodoridis, X.; Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Gkiouras, K.; Papadopoulou, S.E.; Agorastou, T.; Gkika, I.; Maraki, M.I.; Dardavessis, T.; Chourdakis, M. Food Insecurity and Mediterranean Diet Adherence among Greek University Students. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjimbei, E.; Botsaris, G.; Gekas, V.; Panayiotou, A. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and Lifestyle Characteristics of University Students in Cyprus: A Cross-Sectional Survey. J. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 2016, 2742841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinovic, D.; Tokic, D.; Martinovic, L.; Vilovic, M.; Vrdoljak, J.; Kumric, M.; Bukic, J.; Ticinovic Kurir, T.; Tavra, M.; Bozic, J. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Tendency to Orthorexia Nervosa in Professional Athletes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gkiouras, K.; Mavridis, P.; Tsakiri, V.; Theodoridis, X.; Gerontidis, A.; Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Chourdakis, M. Evaluation of Orthorexia among Dietetics Students. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 24, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, J.D.; Paksarian, D.; He, J.; Merikangas, K.R. Parenting Style and Mental Disorders in a Nationally Representative Sample of US Adolescents. Soc. Psychiatry Psychiatr. Epidemiol. 2018, 53, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, C.; Yasmin, F. Impact of Parenting Style on Early Childhood Learning: Mediating Role of Parental Self-Efficacy. Front. Psychol. 2022, 13, 928629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheshire, A.; Berry, M.; Fixsen, A. What Are the Key Features of Orthorexia Nervosa and Influences on Its Development? A Qualitative Investigation. Appetite 2020, 155, 104798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkiouras, K.; Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Tsaliki, T.; Tsaliki, T.; Ntwali, L.; Nigdelis, M.P.; Gerontidis, A.; Taousani, E.; Tzimos, C.; Rogoza, R.; et al. Orthorexia nervosa: Replication and validation of the ORTO questionnaires translated into Greek in a survey of 848 Greek individuals. Hormones 2022, 21, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, P.; Lefevre, C. Instagram Use Is Linked to Increased Symptoms of Orthorexia Nervosa. Eat. Weight Disord. 2017, 22, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karniej, P.; Pérez, J.; Juárez-Vela, R.; Santolalla-Arnedo, I.; Gea-Caballero, V.; Pozo-Herce, P.; Dissen, A.; Czapla, M. Orthorexia Nervosa in Gay Men—The Result of a Spanish-Polish Eating Disorders Study. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Non-ON (N = 58) | ON (N = 74) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | 0.166 | ||
| Male | 3 (5.2%) | 9 (12.2%) | |
| Female | 55 (94.8%) | 65 (87.8%) | |
| Age (years) | 23.29 ± 4.13 | 22.66 ± 2.92 | 0.304 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.002 * | ||
| Underweight | 14 (24.1%) | 3 (4.1%) | |
| Normal weight | 38 (65.6%) | 55 (75.4%) | |
| Overweight | 6 (10.3%) | 15 (20.5%) | |
| Years of Study | 0.680 | ||
| ≤2 | 11 (19.0%) | 12 (16.2%) | |
| >2 | 47 (81.0%) | 62 (83.8%) | |
| Chronic Disease | 0.155 | ||
| No | 52 (89.7%) | 71 (95.9%) | |
| Yes | 6 (10.3%) | 3 (4.1%) | |
| Medication | 0.180 | ||
| No | 47 (83.9%) | 66 (91.7%) | |
| Yes | 9 (16.1%) | 6 (8.3%) | |
| Frequency of Exercise (sessions/week) | 0.023 * | ||
| ≤4 | 54 (93.1%) | 56 (78.9%) | |
| >4 | 4 (6.9%) | 15 (21.1%) | |
| Duration of Exercise (hours/session) | 0.474 | ||
| ≤1 | 18 (32.7%) | 28 (38.9%) | |
| >1 | 37 (67.3%) | 44 (61.1%) | |
| Anxiety Level (STAIT) | 0.019 * | ||
| None or low | 29 (50.0%) | 19 (26.7%) | |
| Moderate | 13 (22.4%) | 19 (26.7%) | |
| High | 16 (27.6%) | 33 (46.6%) | |
| MedDiet adherence | 0.131 | ||
| Insufficient | 8 (13.8%) | 18 (24.3%) | |
| Sufficient | 50 (86.2%) | 56 (75.7%) | |
| Eating Disorders concerns (EAT-26) | <0.001 * | ||
| No risk | 55 (94.8%) | 47 (63.5%) | |
| Risk | 3 (5.2%) | 27 (36.5%) | |
| Body image inflexibility (BI-AAQ-5) | <0.001 * | ||
| No risk | 51 (92.7%) | 41 (57.7%) | |
| Risk | 4 (7.3%) | 30 (42.3%) | |
| Maternal Age (years) | 51.72 ± 5.62 | 51.71 ± 5.17 | 0.991 |
| Maternal BMI (kg/m2) | 0.527 | ||
| Normal weight | 25 (49.0%) | 30 (46.9%) | |
| Overweight | 26 (51.0%) | 34 (53.1%) | |
| Maternal body image inflexibility (BI-AAQ-5) | 0.704 | ||
| No risk | 27 (46.6%) | 32 (43.2%) | |
| Risk | 31 (53.4%) | 42 (56.8%) | |
| Maternal bonding (PBI) | 0.887 | ||
| Neglectful parenting | 8 (14.3%) | 12 (16.9%) | |
| Affectionless control | 12 (21.4%) | 16 (22.5%) | |
| Optimal parenting | 30 (53.6%) | 38 (53.6%) | |
| Affectionate constraint | 6 (10.7%) | 5 (7.0%) | |
| Paternal Age (years) | 55.83 ± 6.99 | 56.18 ± 6.23 | 0.773 |
| Paternal BMI (kg/m2) | 0.099 | ||
| Normal weight | 14 (28.0%) | 10 (15.4%) | |
| Overweight | 36 (72.0%) | 55 (84.6%) | |
| Paternal body image inflexibility (BI-AAQ-5) | 0.285 | ||
| No risk | 9 (15.5%) | 17 (23.0%) | |
| Risk | 49 (84.5%) | 57 (77.0%) | |
| Paternal bonding (PBI) | 0.244 | ||
| Neglectful parenting | 12 (21.4%) | 12 (17.4%) | |
| Affectionless control | 11 (19.6%) | 22 (31.9%) | |
| Optimal parenting | 24 (42.9%) | 30 (43.5%) | |
| Affectionate constraint | 9 (16.1%) | 5 (7.2%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Athanasaki, D.; Lakoumentas, J.; Milani, G.P.; Agostoni, C.; Berghea, F.; Ionescu, M.D.; Vassilopoulou, E. Maternal Bonding as a Protective Factor for Orthorexia Nervosa Risk in Dietetics Students. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3577. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163577
Athanasaki D, Lakoumentas J, Milani GP, Agostoni C, Berghea F, Ionescu MD, Vassilopoulou E. Maternal Bonding as a Protective Factor for Orthorexia Nervosa Risk in Dietetics Students. Nutrients. 2023; 15(16):3577. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163577
Chicago/Turabian StyleAthanasaki, Dafni, John Lakoumentas, Gregorio Paolo Milani, Carlo Agostoni, Florian Berghea, Marcela Daniela Ionescu, and Emilia Vassilopoulou. 2023. "Maternal Bonding as a Protective Factor for Orthorexia Nervosa Risk in Dietetics Students" Nutrients 15, no. 16: 3577. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163577
APA StyleAthanasaki, D., Lakoumentas, J., Milani, G. P., Agostoni, C., Berghea, F., Ionescu, M. D., & Vassilopoulou, E. (2023). Maternal Bonding as a Protective Factor for Orthorexia Nervosa Risk in Dietetics Students. Nutrients, 15(16), 3577. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15163577









